Narrative Writing
Adding Details to Your Writing
What is Narrative Writing?
- “So, what happened?” When someone asks you that, what do you say? You respond by telling a story- when it happened, where it happened, how and why it happened. This is what we call narration.
- Narrative writing tells a story about an event that happened.
What should a good narrative story include?
- Good narrative stories use details to describe all the important elements of an event (Who, what, when, where, and why.)
- The story should be focused and stick to one main idea.
- Unimportant details should be left out of the story.
- Narrative stories should be organized in a logical way (Beginning, Middle, and End)
- Transitions should be used to move from part of the story to the next.
- The story should make a point or lead to a conclusion.
5-sentence Narrative Stories
- So far this year we have been working on writing five sentence narrative stories.
- Here is how these stories were organized:
Sentence 1- Topic Sentence introducing the main idea
Sentence 2- Beginning
Sentence 3- Middle
Sentence 4 -End
Sentence 5- Concluding Sentence
- Transition words like first, next, and last help the story flow smoothly from beginning, to middle, to end.
Let’s look at an example
My Bicycle Accident
When I was in third grade I got hurt in a bicycle accident. My brother and I were riding our bikes down the steep hill at the end of our street. I was going so fast that I hit a bump in the road and flipped over my handlebars. I hit my head hard on the pavement and had to be taken to the hospital by my mother. I am lucky that only fractured my skull and got a concussion that day, it could have been much worse.
Here are all the parts:
Topic Sentence
Concluding Sentence
So, how does my story measure up?
- This narrative story tells about a true event that happened in my life.
- It uses details to describe all the important elements of my event:
- Who- my brother and myself
- What- had a bike accident
- When- in third grade
- Where- on the hill at the end of my street
- Why- I was going very fast and hit a bump
- The story is focused and sticks to one main idea.
- Main idea: A time when I was hurt in a bike accident.
- The story ends by making a point. This is called a conclusion.
- Conclusion: Even though I got hurt, I feel lucky to be alive because things could have been much worse.
How can I make my story better?
- Even though my story has all the major parts a narrative story needs to have, it could be even better.
- Adding more details and descriptions would make my story more interesting for my audience.
Let’s Give it a Try!
When I was in third grade I got hurt in a bicycle accident. My brother and I were riding our bikes down the steep hill at the end of our street. We were racing as fast as we could down the hill, trying to see who could get to the bottom first. I was going so fast that I hit a bump in the road and flipped over my handlebars. I hit my head hard on the pavement and had to be taken to the hospital by my mother. I am lucky that only fractured my skull and got a concussion that day, it could have been much worse.
Add a new detail sentence
When I was in third grade I got hurt in a bicycle accident. My brother and I were riding our bikes down the steep hill at the end of our street. We were racing as fast as we could down the hill, trying to see who could get to the bottom first. I was going so fast that I hit a bump in the road and flipped over my handlebars. Before I knew it I was sailing through the air, headfirst, without a helmet on. I hit my head hard on the pavement and had to be taken to the hospital by my mother. I am lucky that only fractured my skull and got a concussion that day, it could have been much worse.
When I was in third grade I got hurt in a bicycle accident. My brother and I were riding our bikes down the steep hill at the end of our street. We were racing as fast as we could down the hill, trying to see who could get to the bottom first. I was going so fast that I hit a bump in the road and flipped over my handlebars. Before I knew it I was sailing through the air, headfirst, without a helmet on. I hit my head hard on the pavement and had to be taken to the hospital by my mother. She raced me to the Emergency Room where the doctors took x-rays of my head and body. I am lucky that only fractured my skull and got a concussion that day, it could have been much worse.

A Step-by-Step Plan for Teaching Narrative Writing
July 29, 2018
Can't find what you are looking for? Contact Us

Listen to this post as a podcast:
Sponsored by Peergrade and Microsoft Class Notebook
This post contains Amazon Affiliate links. When you make a purchase through these links, Cult of Pedagogy gets a small percentage of the sale at no extra cost to you.
“Those who tell the stories rule the world.” This proverb, attributed to the Hopi Indians, is one I wish I’d known a long time ago, because I would have used it when teaching my students the craft of storytelling. With a well-told story we can help a person see things in an entirely new way. We can forge new relationships and strengthen the ones we already have. We can change a law, inspire a movement, make people care fiercely about things they’d never given a passing thought.
But when we study storytelling with our students, we forget all that. Or at least I did. When my students asked why we read novels and stories, and why we wrote personal narratives and fiction, my defense was pretty lame: I probably said something about the importance of having a shared body of knowledge, or about the enjoyment of losing yourself in a book, or about the benefits of having writing skills in general.
I forgot to talk about the power of story. I didn’t bother to tell them that the ability to tell a captivating story is one of the things that makes human beings extraordinary. It’s how we connect to each other. It’s something to celebrate, to study, to perfect. If we’re going to talk about how to teach students to write stories, we should start by thinking about why we tell stories at all . If we can pass that on to our students, then we will be going beyond a school assignment; we will be doing something transcendent.
Now. How do we get them to write those stories? I’m going to share the process I used for teaching narrative writing. I used this process with middle school students, but it would work with most age groups.
A Note About Form: Personal Narrative or Short Story?
When teaching narrative writing, many teachers separate personal narratives from short stories. In my own classroom, I tended to avoid having my students write short stories because personal narratives were more accessible. I could usually get students to write about something that really happened, while it was more challenging to get them to make something up from scratch.
In the “real” world of writers, though, the main thing that separates memoir from fiction is labeling: A writer might base a novel heavily on personal experiences, but write it all in third person and change the names of characters to protect the identities of people in real life. Another writer might create a short story in first person that reads like a personal narrative, but is entirely fictional. Just last weekend my husband and I watched the movie Lion and were glued to the screen the whole time, knowing it was based on a true story. James Frey’s book A Million Little Pieces sold millions of copies as a memoir but was later found to contain more than a little bit of fiction. Then there are unique books like Curtis Sittenfeld’s brilliant novel American Wife , based heavily on the early life of Laura Bush but written in first person, with fictional names and settings, and labeled as a work of fiction. The line between fact and fiction has always been really, really blurry, but the common thread running through all of it is good storytelling.
With that in mind, the process for teaching narrative writing can be exactly the same for writing personal narratives or short stories; it’s the same skill set. So if you think your students can handle the freedom, you might decide to let them choose personal narrative or fiction for a narrative writing assignment, or simply tell them that whether the story is true doesn’t matter, as long as they are telling a good story and they are not trying to pass off a fictional story as fact.
Here are some examples of what that kind of flexibility could allow:
- A student might tell a true story from their own experience, but write it as if it were a fiction piece, with fictional characters, in third person.
- A student might create a completely fictional story, but tell it in first person, which would give it the same feel as a personal narrative.
- A student might tell a true story that happened to someone else, but write it in first person, as if they were that person. For example, I could write about my grandmother’s experience of getting lost as a child, but I might write it in her voice.
If we aren’t too restrictive about what we call these pieces, and we talk about different possibilities with our students, we can end up with lots of interesting outcomes. Meanwhile, we’re still teaching students the craft of narrative writing.
A Note About Process: Write With Your Students
One of the most powerful techniques I used as a writing teacher was to do my students’ writing assignments with them. I would start my own draft at the same time as they did, composing “live” on the classroom projector, and doing a lot of thinking out loud so they could see all the decisions a writer has to make.
The most helpful parts for them to observe were the early drafting stage, where I just scratched out whatever came to me in messy, run-on sentences, and the revision stage, where I crossed things out, rearranged, and made tons of notes on my writing. I have seen over and over again how witnessing that process can really help to unlock a student’s understanding of how writing actually gets made.
A Narrative Writing Unit Plan
Before I get into these steps, I should note that there is no one right way to teach narrative writing, and plenty of accomplished teachers are doing it differently and getting great results. This just happens to be a process that has worked for me.
Step 1: Show Students That Stories Are Everywhere
Getting our students to tell stories should be easy. They hear and tell stories all the time. But when they actually have to put words on paper, they forget their storytelling abilities: They can’t think of a topic. They omit relevant details, but go on and on about irrelevant ones. Their dialogue is bland. They can’t figure out how to start. They can’t figure out how to end.
So the first step in getting good narrative writing from students is to help them see that they are already telling stories every day . They gather at lockers to talk about that thing that happened over the weekend. They sit at lunch and describe an argument they had with a sibling. Without even thinking about it, they begin sentences with “This one time…” and launch into stories about their earlier childhood experiences. Students are natural storytellers; learning how to do it well on paper is simply a matter of studying good models, then imitating what those writers do.
So start off the unit by getting students to tell their stories. In journal quick-writes, think-pair-shares, or by playing a game like Concentric Circles , prompt them to tell some of their own brief stories: A time they were embarrassed. A time they lost something. A time they didn’t get to do something they really wanted to do. By telling their own short anecdotes, they will grow more comfortable and confident in their storytelling abilities. They will also be generating a list of topic ideas. And by listening to the stories of their classmates, they will be adding onto that list and remembering more of their own stories.
And remember to tell some of your own. Besides being a good way to bond with students, sharing your stories will help them see more possibilities for the ones they can tell.
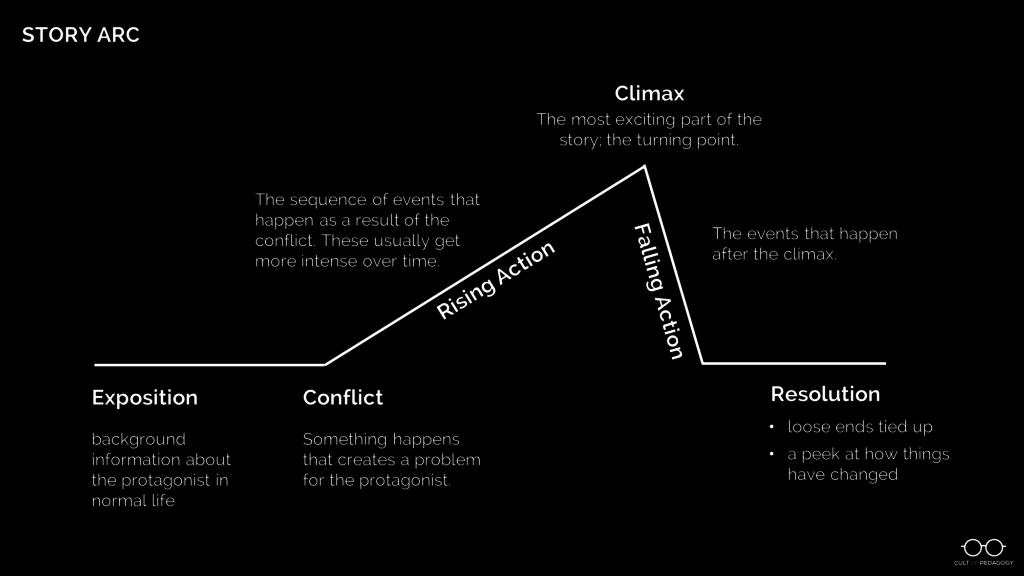
Step 2: Study the Structure of a Story
Now that students have a good library of their own personal stories pulled into short-term memory, shift your focus to a more formal study of what a story looks like.
Use a diagram to show students a typical story arc like the one below. Then, using a simple story (try a video like The Present or Room ), fill out the story arc with the components from that story. Once students have seen this story mapped out, have them try it with another one, like a story you’ve read in class, a whole novel, or another short video.
Step 3: Introduce the Assignment
Up to this point, students have been immersed in storytelling. Now give them specific instructions for what they are going to do. Share your assignment rubric so they understand the criteria that will be used to evaluate them; it should be ready and transparent right from the beginning of the unit. As always, I recommend using a single point rubric for this.
Step 4: Read Models
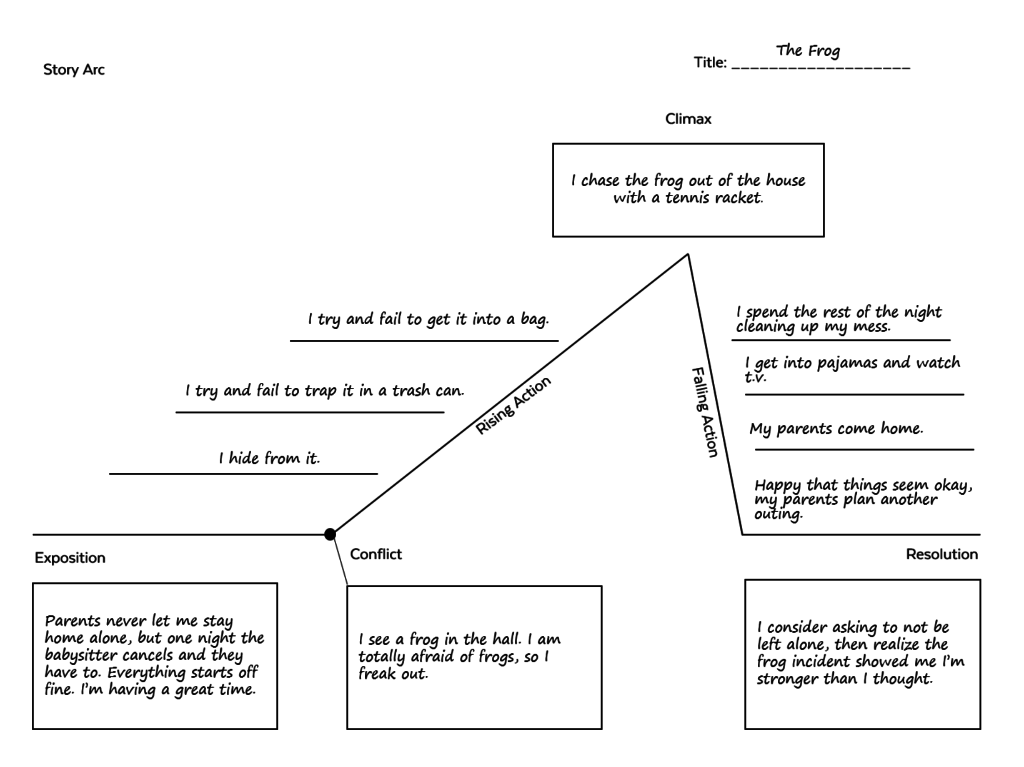
Once the parameters of the assignment have been explained, have students read at least one model story, a mentor text that exemplifies the qualities you’re looking for. This should be a story on a topic your students can kind of relate to, something they could see themselves writing. For my narrative writing unit (see the end of this post), I wrote a story called “Frog” about a 13-year-old girl who finally gets to stay home alone, then finds a frog in her house and gets completely freaked out, which basically ruins the fun she was planning for the night.
They will be reading this model as writers, looking at how the author shaped the text for a purpose, so that they can use those same strategies in their own writing. Have them look at your rubric and find places in the model that illustrate the qualities listed in the rubric. Then have them complete a story arc for the model so they can see the underlying structure.
Ideally, your students will have already read lots of different stories to look to as models. If that isn’t the case, this list of narrative texts recommended by Cult of Pedagogy followers on Twitter would be a good place to browse for titles that might be right for your students. Keep in mind that we have not read most of these stories, so be sure to read them first before adopting them for classroom use.
Step 5: Story Mapping
At this point, students will need to decide what they are going to write about. If they are stuck for a topic, have them just pick something they can write about, even if it’s not the most captivating story in the world. A skilled writer could tell a great story about deciding what to have for lunch. If they are using the skills of narrative writing, the topic isn’t as important as the execution.
Have students complete a basic story arc for their chosen topic using a diagram like the one below. This will help them make sure that they actually have a story to tell, with an identifiable problem, a sequence of events that build to a climax, and some kind of resolution, where something is different by the end. Again, if you are writing with your students, this would be an important step to model for them with your own story-in-progress.
Step 6: Quick Drafts
Now, have students get their chosen story down on paper as quickly as possible: This could be basically a long paragraph that would read almost like a summary, but it would contain all the major parts of the story. Model this step with your own story, so they can see that you are not shooting for perfection in any way. What you want is a working draft, a starting point, something to build on for later, rather than a blank page (or screen) to stare at.
Step 7: Plan the Pacing
Now that the story has been born in raw form, students can begin to shape it. This would be a good time for a lesson on pacing, where students look at how writers expand some moments to create drama and shrink other moments so that the story doesn’t drag. Creating a diagram like the one below forces a writer to decide how much space to devote to all of the events in the story.

Step 8: Long Drafts
With a good plan in hand, students can now slow down and write a proper draft, expanding the sections of their story that they plan to really draw out and adding in more of the details that they left out in the quick draft.
Step 9: Workshop
Once students have a decent rough draft—something that has a basic beginning, middle, and end, with some discernible rising action, a climax of some kind, and a resolution, you’re ready to shift into full-on workshop mode. I would do this for at least a week: Start class with a short mini-lesson on some aspect of narrative writing craft, then give students the rest of the period to write, conference with you, and collaborate with their peers. During that time, they should focus some of their attention on applying the skill they learned in the mini-lesson to their drafts, so they will improve a little bit every day.
Topics for mini-lessons can include:
- How to weave exposition into your story so you don’t give readers an “information dump”
- How to carefully select dialogue to create good scenes, rather than quoting everything in a conversation
- How to punctuate and format dialogue so that it imitates the natural flow of a conversation
- How to describe things using sensory details and figurative language; also, what to describe…students too often give lots of irrelevant detail
- How to choose precise nouns and vivid verbs, use a variety of sentence lengths and structures, and add transitional words, phrases, and features to help the reader follow along
- How to start, end, and title a story

Step 10: Final Revisions and Edits
As the unit nears its end, students should be shifting away from revision , in which they alter the content of a piece, toward editing , where they make smaller changes to the mechanics of the writing. Make sure students understand the difference between the two: They should not be correcting each other’s spelling and punctuation in the early stages of this process, when the focus should be on shaping a better story.
One of the most effective strategies for revision and editing is to have students read their stories out loud. In the early stages, this will reveal places where information is missing or things get confusing. Later, more read-alouds will help them immediately find missing words, unintentional repetitions, and sentences that just “sound weird.” So get your students to read their work out loud frequently. It also helps to print stories on paper: For some reason, seeing the words in print helps us notice things we didn’t see on the screen.
To get the most from peer review, where students read and comment on each other’s work, more modeling from you is essential: Pull up a sample piece of writing and show students how to give specific feedback that helps, rather than simply writing “good detail” or “needs more detail,” the two comments I saw exchanged most often on students’ peer-reviewed papers.
Step 11: Final Copies and Publication
Once revision and peer review are done, students will hand in their final copies. If you don’t want to get stuck with 100-plus papers to grade, consider using Catlin Tucker’s station rotation model , which keeps all the grading in class. And when you do return stories with your own feedback, try using Kristy Louden’s delayed grade strategy , where students don’t see their final grade until they have read your written feedback.
Beyond the standard hand-in-for-a-grade, consider other ways to have students publish their stories. Here are some options:
- Stories could be published as individual pages on a collaborative website or blog.
- Students could create illustrated e-books out of their stories.
- Students could create a slideshow to accompany their stories and record them as digital storytelling videos. This could be done with a tool like Screencastify or Screencast-O-Matic .
So this is what worked for me. If you’ve struggled to get good stories from your students, try some or all of these techniques next time. I think you’ll find that all of your students have some pretty interesting stories to tell. Helping them tell their stories well is a gift that will serve them for many years after they leave your classroom. ♦
Want this unit ready-made?
If you’re a writing teacher in grades 7-12 and you’d like a classroom-ready unit like the one described above, including slideshow mini-lessons on 14 areas of narrative craft, a sample narrative piece, editable rubrics, and other supplemental materials to guide students through every stage of the process, take a look at my Narrative Writing unit . Just click on the image below and you’ll be taken to a page where you can read more and see a detailed preview of what’s included.

What to Read Next

Categories: Instruction , Podcast
Tags: English language arts , Grades 6-8 , Grades 9-12 , teaching strategies
52 Comments
Wow, this is a wonderful guide! If my English teachers had taught this way, I’m sure I would have enjoyed narrative writing instead of dreading it. I’ll be able to use many of these suggestions when writing my blog! BrP
Lst year I was so discouraged because the short stories looked like the quick drafts described in this article. I thought I had totally failed until I read this and realized I did not fai,l I just needed to complete the process. Thank you!
I feel like you jumped in my head and connected my thoughts. I appreciate the time you took to stop and look closely at form. I really believe that student-writers should see all dimensions of narrative writing and be able to live in whichever style and voice they want for their work.
Can’t thank you enough for this. So well curated that one can just follow it blindly and ace at teaching it. Thanks again!
Great post! I especially liked your comments about reminding kids about the power of storytelling. My favourite podcasts and posts from you are always about how to do things in the classroom and I appreciate the research you do.
On a side note, the ice breakers are really handy. My kids know each other really well (rural community), and can tune out pretty quickly if there is nothing new to learn about their peers, but they like the games (and can remember where we stopped last time weeks later). I’ve started changing them up with ‘life questions’, so the editable version is great!
I love writing with my students and loved this podcast! A fun extension to this narrative is to challenge students to write another story about the same event, but use the perspective of another “character” from the story. Books like Wonder (R.J. Palacio) and Wanderer (Sharon Creech) can model the concept for students.
Thank you for your great efforts to reveal the practical writing strategies in layered details. As English is not my first language, I need listen to your podcast and read the text repeatedly so to fully understand. It’s worthy of the time for some great post like yours. I love sharing so I send the link to my English practice group that it can benefit more. I hope I could be able to give you some feedback later on.
Thank you for helping me get to know better especially the techniques in writing narrative text. Im an English teacher for 5years but have little knowledge on writing. I hope you could feature techniques in writing news and fearute story. God bless and more power!
Thank you for this! I am very interested in teaching a unit on personal narrative and this was an extremely helpful breakdown. As a current student teacher I am still unsure how to approach breaking down the structures of different genres of writing in a way that is helpful for me students but not too restrictive. The story mapping tools you provided really allowed me to think about this in a new way. Writing is such a powerful way to experience the world and more than anything I want my students to realize its power. Stories are how we make sense of the world and as an English teacher I feel obligated to give my students access to this particular skill.
The power of story is unfathomable. There’s this NGO in India doing some great work in harnessing the power of storytelling and plots to brighten children’s lives and enlighten them with true knowledge. Check out Katha India here: http://bit.ly/KathaIndia
Thank you so much for this. I did not go to college to become a writing professor, but due to restructuring in my department, I indeed am! This is a wonderful guide that I will use when teaching the narrative essay. I wonder if you have a similar guide for other modes such as descriptive, process, argument, etc.?
Hey Melanie, Jenn does have another guide on writing! Check out A Step-by-Step Plan for Teaching Argumentative Writing .
Hi, I am also wondering if there is a similar guide for descriptive writing in particular?
Hey Melanie, unfortunately Jenn doesn’t currently have a guide for descriptive writing. She’s always working on projects though, so she may get around to writing a unit like this in the future. You can always check her Teachers Pay Teachers page for an up-to-date list of materials she has available. Thanks!
I want to write about the new character in my area
That’s great! Let us know if you need any supports during your writing process!
I absolutely adore this unit plan. I teach freshmen English at a low-income high school and wanted to find something to help my students find their voice. It is not often that I borrow material, but I borrowed and adapted all of it in the order that it is presented! It is cohesive, understandable, and fun. Thank you!!
So glad to hear this, Nicole!
Thanks sharing this post. My students often get confused between personal narratives and short stories. Whenever I ask them to write a short story, she share their own experiences and add a bit of fiction in it to make it interesting.
Thank you! My students have loved this so far. I do have a question as to where the “Frog” story mentioned in Step 4 is. I could really use it! Thanks again.
This is great to hear, Emily! In Step 4, Jenn mentions that she wrote the “Frog” story for her narrative writing unit . Just scroll down the bottom of the post and you’ll see a link to the unit.
I also cannot find the link to the short story “Frog”– any chance someone can send it or we can repost it?
This story was written for Jenn’s narrative writing unit. You can find a link to this unit in Step 4 or at the bottom of the article. Hope this helps.
I cannot find the frog story mentioned. Could you please send the link.? Thank you
Hi Michelle,
The Frog story was written for Jenn’s narrative writing unit. There’s a link to this unit in Step 4 and at the bottom of the article.
Debbie- thanks for you reply… but there is no link to the story in step 4 or at the bottom of the page….
Hey Shawn, the frog story is part of Jenn’s narrative writing unit, which is available on her Teachers Pay Teachers site. The link Debbie is referring to at the bottom of this post will take you to her narrative writing unit and you would have to purchase that to gain access to the frog story. I hope this clears things up.
Thank you so much for this resource! I’m a high school English teacher, and am currently teaching creative writing for the first time. I really do value your blog, podcast, and other resources, so I’m excited to use this unit. I’m a cyber school teacher, so clear, organized layout is important; and I spend a lot of time making sure my content is visually accessible for my students to process. Thanks for creating resources that are easy for us teachers to process and use.
Do you have a lesson for Informative writing?
Hey Cari, Jenn has another unit on argumentative writing , but doesn’t have one yet on informative writing. She may develop one in the future so check back in sometime.
I had the same question. Informational writing is so difficult to have a good strong unit in when you have so many different text structures to meet and need text-dependent writing tasks.
Creating an informational writing unit is still on Jenn’s long list of projects to get to, but in the meantime, if you haven’t already, check out When We All Teach Text Structures, Everyone Wins . It might help you out!
This is a great lesson! It would be helpful to see a finished draft of the frog narrative arc. Students’ greatest challenge is transferring their ideas from the planner to a full draft. To see a full sample of how this arc was transformed into a complete narrative draft would be a powerful learning tool.
Hi Stacey! Jenn goes into more depth with the “Frog” lesson in her narrative writing unit – this is where you can find a sample of what a completed story arc might look. Also included is a draft of the narrative. If interested in checking out the unit and seeing a preview, just scroll down to the bottom of the post and click on the image. Hope this helps!
Helped me learn for an entrance exam thanks very much
Is the narrative writing lesson you talk about in https://www.cultofpedagogy.com/narrative-writing/
Also doable for elementary students you think, and if to what levels?
Love your work, Sincerely, Zanyar
Hey Zanyar,
It’s possible the unit would work with 4th and 5th graders, but Jenn definitely wouldn’t recommend going any younger. The main reason for this is that some of the mini-lessons in the unit could be challenging for students who are still concrete thinkers. You’d likely need to do some adjusting and scaffolding which could extend the unit beyond the 3 weeks. Having said that, I taught 1st grade and found the steps of the writing process, as described in the post, to be very similar. Of course learning targets/standards were different, but the process itself can be applied to any grade level (modeling writing, using mentor texts to study how stories work, planning the structure of the story, drafting, elaborating, etc.) Hope this helps!
This has made my life so much easier. After teaching in different schools systems, from the American, to British to IB, one needs to identify the anchor standards and concepts, that are common between all these systems, to build well balanced thematic units. Just reading these steps gave me the guidance I needed to satisfy both the conceptual framework the schools ask for and the standards-based practice. Thank you Thank you.
Would this work for teaching a first grader about narrative writing? I am also looking for a great book to use as a model for narrative writing. Veggie Monster is being used by his teacher and he isn’t connecting with this book in the least bit, so it isn’t having a positive impact. My fear is he will associate this with writing and I don’t want a negative association connected to such a beautiful process and experience. Any suggestions would be helpful.
Thank you for any information you can provide!
Although I think the materials in the actual narrative writing unit are really too advanced for a first grader, the general process that’s described in the blog post can still work really well.
I’m sorry your child isn’t connecting with The Night of the Veggie Monster. Try to keep in mind that the main reason this is used as a mentor text is because it models how a small moment story can be told in a big way. It’s filled with all kinds of wonderful text features that impact the meaning of the story – dialogue, description, bold text, speech bubbles, changes in text size, ellipses, zoomed in images, text placement, text shape, etc. All of these things will become mini-lessons throughout the unit. But there are lots of other wonderful mentor texts that your child might enjoy. My suggestion for an early writer, is to look for a small moment text, similar in structure, that zooms in on a problem that a first grader can relate to. In addition to the mentor texts that I found in this article , you might also want to check out Knuffle Bunny, Kitten’s First Full Moon, When Sophie Gets Angry Really Really Angry, and Whistle for Willie. Hope this helps!
I saw this on Pinterest the other day while searching for examples of narritives units/lessons. I clicked on it because I always click on C.o.P stuff 🙂 And I wasn’t disapointed. I was intrigued by the connection of narratives to humanity–even if a student doesn’t identify as a writer, he/she certainly is human, right? I really liked this. THIS clicked with me.
A few days after I read the P.o.C post, I ventured on to YouTube for more ideas to help guide me with my 8th graders’ narrative writing this coming spring. And there was a TEDx video titled, “The Power of Personal Narrative” by J. Christan Jensen. I immediately remembered the line from the article above that associated storytelling with “power” and how it sets humans apart and if introduced and taught as such, it can be “extraordinary.”
I watched the video and to the suprise of my expectations, it was FANTASTIC. Between Jennifer’s post and the TEDx video ignited within me some major motivation and excitement to begin this unit.
Thanks for sharing this with us! So glad that Jenn’s post paired with another text gave you some motivation and excitement. I’ll be sure to pass this on to Jenn!
Thank you very much for this really helpful post! I really love the idea of helping our students understand that storytelling is powerful and then go on to teach them how to harness that power. That is the essence of teaching literature or writing at any level. However, I’m a little worried about telling students that whether a piece of writing is fact or fiction does not matter. It in fact matters a lot precisely because storytelling is powerful. Narratives can shape people’s views and get their emotions involved which would, in turn, motivate them to act on a certain matter, whether for good or for bad. A fictional narrative that is passed as factual could cause a lot of damage in the real world. I believe we should. I can see how helping students focus on writing the story rather than the truth of it all could help refine the needed skills without distractions. Nevertheless, would it not be prudent to teach our students to not just harness the power of storytelling but refrain from misusing it by pushing false narratives as factual? It is true that in reality, memoirs pass as factual while novels do as fictional while the opposite may be true for both cases. I am not too worried about novels passing as fictional. On the other hand, fictional narratives masquerading as factual are disconcerting and part of a phenomenon that needs to be fought against, not enhanced or condoned in education. This is especially true because memoirs are often used by powerful people to write/re-write history. I would really like to hear your opinion on this. Thanks a lot for a great post and a lot of helpful resources!
Thank you so much for this. Jenn and I had a chance to chat and we can see where you’re coming from. Jenn never meant to suggest that a person should pass off a piece of fictional writing as a true story. Good stories can be true, completely fictional, or based on a true story that’s mixed with some fiction – that part doesn’t really matter. However, what does matter is how a student labels their story. We think that could have been stated more clearly in the post , so Jenn decided to add a bit about this at the end of the 3rd paragraph in the section “A Note About Form: Personal Narrative or Short Story?” Thanks again for bringing this to our attention!
You have no idea how much your page has helped me in so many ways. I am currently in my teaching credential program and there are times that I feel lost due to a lack of experience in the classroom. I’m so glad I came across your page! Thank you for sharing!
Thanks so much for letting us know-this means a whole lot!
No, we’re sorry. Jenn actually gets this question fairly often. It’s something she considered doing at one point, but because she has so many other projects she’s working on, she’s just not gotten to it.
I couldn’t find the story
Hi, Duraiya. The “Frog” story is part of Jenn’s narrative writing unit, which is available on her Teachers Pay Teachers site. The link at the bottom of this post will take you to her narrative writing unit, which you can purchase to gain access to the story. I hope this helps!
I am using this step-by-step plan to help me teach personal narrative story writing. I wanted to show the Coca-Cola story, but the link says the video is not available. Do you have a new link or can you tell me the name of the story so I can find it?
Thank you for putting this together.
Hi Corri, sorry about that. The Coca-Cola commercial disappeared, so Jenn just updated the post with links to two videos with good stories. Hope this helps!
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.
Bell Ringers
Middle school narrative writing made simple.
For the first few years that I taught, I hated teaching narrative writing to my middle schoolers. Writing days meant endless stress. Students were constantly calling my name. There were nonstop problems. Students hardly made progress with their narrative essays because they didn’t know what to do or were waiting on me to help them. It was terrible!
Fast forward to the present day, I look forward to narrative writing in my classroom. Writing days often mean a lot of productivity and a rather calm classroom. So, what has changed to transform my opinion on writing days?
I began using reference sheets! Throughout this blog, I’ll share how reference sheets for narrative writing are the way to a simple, productive middle school writing unit.

What is narrative writing?
Before I dive too deep into reference sheets, I want to make sure we are on the same page with narrative essays. A narrative essay can be fiction or nonfiction . Sometimes narratives are called short stories or personal narratives. Essentially, narratives are stories.
What makes narrative writing so exciting for students is the opportunity to create a detailed story. Whether the story is fiction or nonfiction, the space to add imagery, details, and imagination are huge perks for more creative students.
The downside is that many students can get lost in narratives. For some, the ability for your creativity to run wild can leave them with option paralysis. For others, they are so excited to tell their story that they leave every grammar and language rule behind.
What are reference sheets?
As I spoke about, writing used to be a chaotic experience for me (and my students). I decided I either had to clone myself to help more kids or find a way for the kids to help themselves (and since cloning wasn’t an option…). Enter the reference sheets.
A reference sheet is probably what it sounds like. They are pages of notes that students can reference for information . You can actually snag ALL my narrative writing reference pages in a cute booklet FOR FREE by clicking HERE .

The goal is that students use these reference pages when they are stuck or have questions during writing. Instead of you being the first person they get information from, the reference sheet becomes their guide. Kinda like that three before me rule.
These reference guides can have anything you want in them, but you want to stick to key, need-to-know information. For narrative essays, this might look like dialogue, writing an introduction / body / conclusion, editing, and so forth. The reference page should be easy to find and read through. It can even contain examples for students to reference and model their essay after.
How Reference Sheets Saved my Writing Unit
Before reference sheets, I could easily earn 10,000 steps walking circles around my classroom. I never actually sat down with a student for long to dig deep into their writing. Instead, I was just trying to keep students motivated to write or answer questions like, “Do I put a comma here?”
With reference sheets, my writing routine changed. Here’s what my class now looks like during narrative writing.
- Mini-lesson : I introduce the skill I want students to work on today with their writing. For example, if I want students to add dialogue or edit dialogue in their narrative today, I will provide a mini-lesson on punctuation and placement of dialogue. During the mini-lesson, students will have a reference sheet I made, and we will use it to move through the mini-lesson.
- Example : Next, I will provide some sort of example to my students to model the skill. This example may also be on the reference page I gave them, or it might not. I’ll engage students in the example, and ask them to apply the skill.
- Independent Work : Students are now familiar with their specific skill and task of the day, and they have a go-to guide if they need it. Students are then challenged with working diligently to apply the new skill to their own writing. If they get stuck, they will consult the reference sheet before me.
- Conferences : While independent workers use their reference sheets to edit their writing, certain students will meet with me. Having the majority of the class work independently and not depend on me to answer so many questions frees up time to reteach, clarify, or simply talk to students about their writing. Often I do these in small groups to make use of time.
- Exit Ticket: Lastly, I try to engage students in some type of sharing. They can share something they are proud of, something they wrote, or a question they have.
This type of structure on a writing day would not be possible without my students being able to help themselves and have quick access to information. It’s all thanks to a reference page. Wanna learn more about how I plan my narrative writing units? Check out my other blog post!
If you want to try out reference pages in your own classroom, I have a narrative writing reference booklet ready with all the essential information your students will need. . It will save you time and sanity on your writing days. You can check out that resource here. It includes skills such as plot, details, transitions, dialogue, and much more.

I hope you try out reference pages of your own to see the magic happen in your classroom! If you aren’t sure where to start, try the writing day schedule I wrote about above. You can tweak it for your own students.
- Read more about: Middle School Writing
You might also like...

Improve Student Writing with Quick Writes

Using Writing Conferences for Effective Literary Analysis

Teach Students How to Effectively Conduct Research
Get your free middle school ela pacing guides with completed scopes and sequences for the school year..

My ELA scope and sequence guides break down every single middle school ELA standard and concept for reading, writing, and language in 6th, 7th, and 8th grade. Use the guides and resources exactly as is or as inspiration for you own!
Meet Martina

I’m a Middle School ELA teacher committed to helping you improve your teaching & implement systems that help you get everything done during the school day!
Let's Connect
Member login.
PRIVACY POLICY
TERMS OF USE
WEBSITE DISCLAIMERS
MEMBERSHIP AGREEEMENT
© The Hungry Teacher • Website by KristenDoyle.co • Contact Martina

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Narrative writing tells a story about an event that happened. What should a good narrative story include? Good narrative stories use details to describe all the important elements of an...
This document provides an overview of the key elements of narrative writing, including characters, setting, plot, beginning, middle, and end. It discusses common story features like problems and resolutions. It also gives examples of different types of characters, settings, and potential story hooks or openings.
If you’re a writing teacher in grades 7-12 and you’d like a classroom-ready unit like the one described above, including slideshow mini-lessons on 14 areas of narrative craft, a sample narrative piece, editable rubrics, and other supplemental materials to guide students through every stage of the process, take a look at my Narrative Writing ...
Throughout this blog, I’ll share how reference sheets for narrative writing are the way to a simple, productive middle school writing unit. What is narrative writing? Before I dive too deep into reference sheets, I want to make sure we are on the same page with narrative essays.
Narrative writing. This document provides an overview of the key elements of narrative writing, including plot structure, characters, setting, style, conflict, theme, and point of view. It discusses the basic components of a narrative, such as the introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution of a story's plot.
This document discusses the elements and structure of a narrative essay. A narrative essay tells a story using elements like setting, characters, plot, theme, and mood. It should include an introduction with a hook and thesis to set up the story, a body organized chronologically with transitional sentences connecting events, and a conclusion ...
Below are several sources of expository writing samples for middle school students. The Write Source Expository Writing Samples; Holt, Rinehart, Winston Expository Essay Models; Finally, here is an article in the New York Times that will help you teach your students real-world expository writing skills. Descriptive writing examples for middle ...
Zip. Teach your upper middle and high school students to write engaging narrative and personal narrative essays with these handouts, graphic organizers, and writing prompts.Full-color Anchor Charts help students learn the elements of narrative and personal narrative writing.
Introduce or reinforce Personal Narrative Writing as this PowerPoint Presentation guides your students through the process step by step. ️ Graphic Organizers and Student Resources are included and demonstrated! This 37 slide presentation complete with custom animations actually results in almost 100 different views as it progresses. ️ ...
ELA Teacher Toolbox. Teach your upper middle and high school students to write engaging narrative and personal narrative essays with these handouts, graphic organizers, and writing prompts.Full-color Anchor Charts help students learn the elements of narrative and personal narrative writing.