

83 Qualitative Research Questions & Examples

Free Website Traffic Checker
Discover your competitors' strengths and leverage them to achieve your own success
Qualitative research questions help you understand consumer sentiment. They’re strategically designed to show organizations how and why people feel the way they do about a brand, product, or service. It looks beyond the numbers and is one of the most telling types of market research a company can do.
The UK Data Service describes this perfectly, saying, “The value of qualitative research is that it gives a voice to the lived experience .”
Read on to see seven use cases and 83 qualitative research questions, with the added bonus of examples that show how to get similar insights faster with Similarweb Research Intelligence.

What is a qualitative research question?
A qualitative research question explores a topic in-depth, aiming to better understand the subject through interviews, observations, and other non-numerical data. Qualitative research questions are open-ended, helping to uncover a target audience’s opinions, beliefs, and motivations.
How to choose qualitative research questions?
Choosing the right qualitative research questions can be incremental to the success of your research and the findings you uncover. Here’s my six-step process for choosing the best qualitative research questions.
- Start by understanding the purpose of your research. What do you want to learn? What outcome are you hoping to achieve?
- Consider who you are researching. What are their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs? How can you best capture these in your research questions ?
- Keep your questions open-ended . Qualitative research questions should not be too narrow or too broad. Aim to ask specific questions to provide meaningful answers but broad enough to allow for exploration.
- Balance your research questions. You don’t want all of your questions to be the same type. Aim to mix up your questions to get a variety of answers.
- Ensure your research questions are ethical and free from bias. Always have a second (and third) person check for unconscious bias.
- Consider the language you use. Your questions should be written in a way that is clear and easy to understand. Avoid using jargon , acronyms, or overly technical language.

Types of qualitative research questions
For a question to be considered qualitative, it usually needs to be open-ended. However, as I’ll explain, there can sometimes be a slight cross-over between quantitative and qualitative research questions.
Open-ended questions
These allow for a wide range of responses and can be formatted with multiple-choice answers or a free-text box to collect additional details. The next two types of qualitative questions are considered open questions, but each has its own style and purpose.
- Probing questions are used to delve deeper into a respondent’s thoughts, such as “Can you tell me more about why you feel that way?”
- Comparative questions ask people to compare two or more items, such as “Which product do you prefer and why?” These qualitative questions are highly useful for understanding brand awareness , competitive analysis , and more.
Closed-ended questions
These ask respondents to choose from a predetermined set of responses, such as “On a scale of 1-5, how satisfied are you with the new product?” While they’re traditionally quantitative, adding a free text box that asks for extra comments into why a specific rating was chosen will provide qualitative insights alongside their respective quantitative research question responses.
- Ranking questions get people to rank items in order of preference, such as “Please rank these products in terms of quality.” They’re advantageous in many scenarios, like product development, competitive analysis, and brand awareness.
- Likert scale questions ask people to rate items on a scale, such as “On a scale of 1-5, how satisfied are you with the new product?” Ideal for placement on websites and emails to gather quick, snappy feedback.
Qualitative research question examples
There are many applications of qualitative research and lots of ways you can put your findings to work for the success of your business. Here’s a summary of the most common use cases for qualitative questions and examples to ask.
Qualitative questions for identifying customer needs and motivations
These types of questions help you find out why customers choose products or services and what they are looking for when making a purchase.
- What factors do you consider when deciding to buy a product?
- What would make you choose one product or service over another?
- What are the most important elements of a product that you would buy?
- What features do you look for when purchasing a product?
- What qualities do you look for in a company’s products?
- Do you prefer localized or global brands when making a purchase?
- How do you determine the value of a product?
- What do you think is the most important factor when choosing a product?
- How do you decide if a product or service is worth the money?
- Do you have any specific expectations when purchasing a product?
- Do you prefer to purchase products or services online or in person?
- What kind of customer service do you expect when buying a product?
- How do you decide when it is time to switch to a different product?
- Where do you research products before you decide to buy?
- What do you think is the most important customer value when making a purchase?
Qualitative research questions to enhance customer experience
Use these questions to reveal insights into how customers interact with a company’s products or services and how those experiences can be improved.
- What aspects of our product or service do customers find most valuable?
- How do customers perceive our customer service?
- What factors are most important to customers when purchasing?
- What do customers think of our brand?
- What do customers think of our current marketing efforts?
- How do customers feel about the features and benefits of our product?
- How do customers feel about the price of our product or service?
- How could we improve the customer experience?
- What do customers think of our website or app?
- What do customers think of our customer support?
- What could we do to make our product or service easier to use?
- What do customers think of our competitors?
- What is your preferred way to access our site?
- How do customers feel about our delivery/shipping times?
- What do customers think of our loyalty programs?
Qualitative research question example for customer experience
- ♀️ Question: What is your preferred way to access our site?
- Insight sought: How mobile-dominant are consumers? Should you invest more in mobile optimization or mobile marketing?
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: While using this type of question is ideal if you have a large database to survey when placed on a site or sent to a limited customer list, it only gives you a point-in-time perspective from a limited group of people.
- A new approach: You can get better, broader insights quicker with Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence. To fully inform your research, you need to know preferences at the industry or market level.
- ⏰ Time to insight: 30 seconds
- ✅ How it’s done: Similarweb offers multiple ways to answer this question without going through a lengthy qualitative research process.
First, I’m going to do a website market analysis of the banking credit and lending market in the finance sector to get a clearer picture of industry benchmarks.
Here, I can view device preferences across any industry or market instantly. It shows me the device distribution for any country across any period. This clearly answers the question of how mobile dominate my target audience is , with 59.79% opting to access site via a desktop vs. 40.21% via mobile
I then use the trends section to show me the exact split between mobile and web traffic for each key player in my space. Let’s say I’m about to embark on a competitive campaign that targets customers of Chase and Bank of America ; I can see both their audiences are highly desktop dominant compared with others in their space .
Qualitative question examples for developing new products or services
Research questions like this can help you understand customer pain points and give you insights to develop products that meet those needs.
- What is the primary reason you would choose to purchase a product from our company?
- How do you currently use products or services that are similar to ours?
- Is there anything that could be improved with products currently on the market?
- What features would you like to see added to our products?
- How do you prefer to contact a customer service team?
- What do you think sets our company apart from our competitors?
- What other product or service offerings would like to see us offer?
- What type of information would help you make decisions about buying a product?
- What type of advertising methods are most effective in getting your attention?
- What is the biggest deterrent to purchasing products from us?
Qualitative research question example for service development
- ♀️ Question: What type of advertising methods are most effective in getting your attention?
- Insight sought: The marketing channels and/or content that performs best with a target audience .
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: When using qualitative research surveys to answer questions like this, the sample size is limited, and bias could be at play.
- A better approach: The most authentic insights come from viewing real actions and results that take place in the digital world. No questions or answers are needed to uncover this intel, and the information you seek is readily available in less than a minute.
- ⏰ Time to insight: 5 minutes
- ✅ How it’s done: There are a few ways to approach this. You can either take an industry-wide perspective or hone in on specific competitors to unpack their individual successes. Here, I’ll quickly show a snapshot with a whole market perspective.

Using the market analysis element of Similarweb Digital Intelligence, I select my industry or market, which I’ve kept as banking and credit. A quick click into marketing channels shows me which channels drive the highest traffic in my market. Taking direct traffic out of the equation, for now, I can see that referrals and organic traffic are the two highest-performing channels in this market.
Similarweb allows me to view the specific referral partners and pages across these channels.

Looking closely at referrals in this market, I’ve chosen chase.com and its five closest rivals . I select referrals in the channel traffic element of marketing channels. I see that Capital One is a clear winner, gaining almost 25 million visits due to referral partnerships.

Next, I get to see exactly who is referring traffic to Capital One and the total traffic share for each referrer. I can see the growth as a percentage and how that has changed, along with an engagement score that rates the average engagement level of that audience segment. This is particularly useful when deciding on which new referral partnerships to pursue.
Once I’ve identified the channels and campaigns that yield the best results, I can then use Similarweb to dive into the various ad creatives and content that have the greatest impact.

These ads are just a few of those listed in the creatives section from my competitive website analysis of Capital One. You can filter this list by the specific campaign, publishers, and ad networks to view those that matter to you most. You can also discover video ad creatives in the same place too.
In just five minutes ⏰
- I’ve captured audience loyalty statistics across my market
- Spotted the most competitive players
- Identified the marketing channels my audience is most responsive to
- I know which content and campaigns are driving the highest traffic volume
- I’ve created a target list for new referral partners and have been able to prioritize this based on results and engagement figures from my rivals
- I can see the types of creatives that my target audience is responding to, giving me ideas for ways to generate effective copy for future campaigns
Qualitative questions to determine pricing strategies
Companies need to make sure pricing stays relevant and competitive. Use these questions to determine customer perceptions on pricing and develop pricing strategies to maximize profits and reduce churn.
- How do you feel about our pricing structure?
- How does our pricing compare to other similar products?
- What value do you feel you get from our pricing?
- How could we make our pricing more attractive?
- What would be an ideal price for our product?
- Which features of our product that you would like to see priced differently?
- What discounts or deals would you like to see us offer?
- How do you feel about the amount you have to pay for our product?
Get Faster Answers to Qualitative Research Questions with Similarweb Today
Qualitative research question example for determining pricing strategies
- ♀️ Question: What discounts or deals would you like to see us offer?
- Insight sought: The promotions or campaigns that resonate with your target audience.
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: Consumers don’t always recall the types of ads or campaigns they respond to. Over time, their needs and habits change. Your sample size is limited to those you ask, leaving a huge pool of unknowns at play.
- A better approach: While qualitative insights are good to know, you get the most accurate picture of the highest-performing promotion and campaigns by looking at data collected directly from the web. These analytics are real-world, real-time, and based on the collective actions of many, instead of the limited survey group you approach. By getting a complete picture across an entire market, your decisions are better informed and more aligned with current market trends and behaviors.
- ✅ How it’s done: Similarweb’s Popular Pages feature shows the content, products, campaigns, and pages with the highest growth for any website. So, if you’re trying to unpack the successes of others in your space and find out what content resonates with a target audience, there’s a far quicker way to get answers to these questions with Similarweb.

Here, I’m using Capital One as an example site. I can see trending pages on their site showing the largest increase in page views. Other filters include campaign, best-performing, and new–each of which shows you page URLs, share of traffic, and growth as a percentage. This page is particularly useful for staying on top of trending topics , campaigns, and new content being pushed out in a market by key competitors.
Qualitative research questions for product development teams
It’s vital to stay in touch with changing consumer needs. These questions can also be used for new product or service development, but this time, it’s from the perspective of a product manager or development team.
- What are customers’ primary needs and wants for this product?
- What do customers think of our current product offerings?
- What is the most important feature or benefit of our product?
- How can we improve our product to meet customers’ needs better?
- What do customers like or dislike about our competitors’ products?
- What do customers look for when deciding between our product and a competitor’s?
- How have customer needs and wants for this product changed over time?
- What motivates customers to purchase this product?
- What is the most important thing customers want from this product?
- What features or benefits are most important when selecting a product?
- What do customers perceive to be our product’s pros and cons?
- What would make customers switch from a competitor’s product to ours?
- How do customers perceive our product in comparison to similar products?
- What do customers think of our pricing and value proposition?
- What do customers think of our product’s design, usability, and aesthetics?
Qualitative questions examples to understand customer segments
Market segmentation seeks to create groups of consumers with shared characteristics. Use these questions to learn more about different customer segments and how to target them with tailored messaging.
- What motivates customers to make a purchase?
- How do customers perceive our brand in comparison to our competitors?
- How do customers feel about our product quality?
- How do customers define quality in our products?
- What factors influence customers’ purchasing decisions ?
- What are the most important aspects of customer service?
- What do customers think of our customer service?
- What do customers think of our pricing?
- How do customers rate our product offerings?
- How do customers prefer to make purchases (online, in-store, etc.)?
Qualitative research question example for understanding customer segments
- ♀️ Question: Which social media channels are you most active on?
- Insight sought: Formulate a social media strategy . Specifically, the social media channels most likely to succeed with a target audience.
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: Qualitative research question responses are limited to those you ask, giving you a limited sample size. Questions like this are usually at risk of some bias, and this may not be reflective of real-world actions.
- A better approach: Get a complete picture of social media preferences for an entire market or specific audience belonging to rival firms. Insights are available in real-time, and are based on the actions of many, not a select group of participants. Data is readily available, easy to understand, and expandable at a moment’s notice.
- ✅ How it’s done: Using Similarweb’s website analysis feature, you can get a clear breakdown of social media stats for your audience using the marketing channels element. It shows the percentage of visits from each channel to your site, respective growth, and specific referral pages by each platform. All data is expandable, meaning you can select any platform, period, and region to drill down and get more accurate intel, instantly.

This example shows me Bank of America’s social media distribution, with YouTube , Linkedin , and Facebook taking the top three spots, and accounting for almost 80% of traffic being driven from social media.
When doing any type of market research, it’s important to benchmark performance against industry averages and perform a social media competitive analysis to verify rival performance across the same channels.
Qualitative questions to inform competitive analysis
Organizations must assess market sentiment toward other players to compete and beat rival firms. Whether you want to increase market share , challenge industry leaders , or reduce churn, understanding how people view you vs. the competition is key.
- What is the overall perception of our competitors’ product offerings in the market?
- What attributes do our competitors prioritize in their customer experience?
- What strategies do our competitors use to differentiate their products from ours?
- How do our competitors position their products in relation to ours?
- How do our competitors’ pricing models compare to ours?
- What do consumers think of our competitors’ product quality?
- What do consumers think of our competitors’ customer service?
- What are the key drivers of purchase decisions in our market?
- What is the impact of our competitors’ marketing campaigns on our market share ? 10. How do our competitors leverage social media to promote their products?
Qualitative research question example for competitive analysis
- ♀️ Question: What other companies do you shop with for x?
- Insight sought: W ho are your competitors? Which of your rival’s sites do your customers visit? How loyal are consumers in your market?
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: Sample size is limited, and customers could be unwilling to reveal which competitors they shop with, or how often they around. Where finances are involved, people can act with reluctance or bias, and be unwilling to reveal other suppliers they do business with.
- A better approach: Get a complete picture of your audience’s loyalty, see who else they shop with, and how many other sites they visit in your competitive group. Find out the size of the untapped opportunity and which players are doing a better job at attracting unique visitors – without having to ask people to reveal their preferences.
- ✅ How it’s done: Similarweb website analysis shows you the competitive sites your audience visits, giving you access to data that shows cross-visitation habits, audience loyalty, and untapped potential in a matter of minutes.

Using the audience interests element of Similarweb website analysis, you can view the cross-browsing behaviors of a website’s audience instantly. You can see a matrix that shows the percentage of visitors on a target site and any rival site they may have visited.

With the Similarweb audience overlap feature, view the cross-visitation habits of an audience across specific websites. In this example, I chose chase.com and its four closest competitors to review. For each intersection, you see the number of unique visitors and the overall proportion of each site’s audience it represents. It also shows the volume of unreached potential visitors.

Here, you can see a direct comparison of the audience loyalty represented in a bar graph. It shows a breakdown of each site’s audience based on how many other sites they have visited. Those sites with the highest loyalty show fewer additional sites visited.
From the perspective of chase.com, I can see 47% of their visitors do not visit rival sites. 33% of their audience visited 1 or more sites in this group, 14% visited 2 or more sites, 4% visited 3 or more sites, and just 0.8% viewed all sites in this comparison.
How to answer qualitative research questions with Similarweb
Similarweb Research Intelligence drastically improves market research efficiency and time to insight. Both of these can impact the bottom line and the pace at which organizations can adapt and flex when markets shift, and rivals change tactics.
Outdated practices, while still useful, take time . And with a quicker, more efficient way to garner similar insights, opting for the fast lane puts you at a competitive advantage.
With a birds-eye view of the actions and behaviors of companies and consumers across a market , you can answer certain research questions without the need to plan, do, and review extensive qualitative market research .
Wrapping up
Qualitative research methods have been around for centuries. From designing the questions to finding the best distribution channels, collecting and analyzing findings takes time to get the insights you need. Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence drastically improves efficiency and time to insight. Both of which impact the bottom line and the pace at which organizations can adapt and flex when markets shift.
Similarweb’s suite of digital intelligence solutions offers unbiased, accurate, honest insights you can trust for analyzing any industry, market, or audience.
- Methodologies used for data collection are robust, transparent, and trustworthy.
- Clear presentation of data via an easy-to-use, intuitive platform.
- It updates dynamically–giving you the freshest data about an industry or market.
- Data is available via an API – so you can plug into platforms like Tableau or PowerBI to streamline your analyses.
- Filter and refine results according to your needs.
Are quantitative or qualitative research questions best?
Both have their place and purpose in market research. Qualitative research questions seek to provide details, whereas quantitative market research gives you numerical statistics that are easier and quicker to analyze. You get more flexibility with qualitative questions, and they’re non-directional.
What are the advantages of qualitative research?
Qualitative research is advantageous because it allows researchers to better understand their subject matter by exploring people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations in a particular context. It also allows researchers to uncover new insights that may not have been discovered with quantitative research methods.
What are some of the challenges of qualitative research?
Qualitative research can be time-consuming and costly, typically involving in-depth interviews and focus groups. Additionally, there are challenges associated with the reliability and validity of the collected data, as there is no universal standard for interpreting the results.

by Liz March
Digital Research Specialist
Liz March has 15 years of experience in content creation. She enjoys the outdoors, F1, and reading, and is pursuing a BSc in Environmental Science.
Related Posts

Importance of Market Research: 9 Reasons Why It’s Crucial for Your Business

Audience Segmentation: Definition, Importance & Types

Geographic Segmentation: Definition, Pros & Cons, Examples, and More

Demographic Segmentation: The Key To Transforming Your Marketing Strategy

Unlocking Consumer Behavior: What Makes Your Customers Tick?
Customer Segmentation: Expert Tips on Understanding Your Audience
Wondering what similarweb can do for your business.
Give it a try or talk to our insights team — don’t worry, it’s free!
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Qualitative Research Questions
Try Qualtrics for free
How to write qualitative research questions.
11 min read Here’s how to write effective qualitative research questions for your projects, and why getting it right matters so much.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a blanket term covering a wide range of research methods and theoretical framing approaches. The unifying factor in all these types of qualitative study is that they deal with data that cannot be counted. Typically this means things like people’s stories, feelings, opinions and emotions , and the meanings they ascribe to their experiences.
Qualitative study is one of two main categories of research, the other being quantitative research. Quantitative research deals with numerical data – that which can be counted and quantified, and which is mostly concerned with trends and patterns in large-scale datasets.
What are research questions?
Research questions are questions you are trying to answer with your research. To put it another way, your research question is the reason for your study, and the beginning point for your research design. There is normally only one research question per study, although if your project is very complex, you may have multiple research questions that are closely linked to one central question.
A good qualitative research question sums up your research objective. It’s a way of expressing the central question of your research, identifying your particular topic and the central issue you are examining.
Research questions are quite different from survey questions, questions used in focus groups or interview questions. A long list of questions is used in these types of study, as opposed to one central question. Additionally, interview or survey questions are asked of participants, whereas research questions are only for the researcher to maintain a clear understanding of the research design.
Research questions are used in both qualitative and quantitative research , although what makes a good research question might vary between the two.
In fact, the type of research questions you are asking can help you decide whether you need to take a quantitative or qualitative approach to your research project.
Discover the fundamentals of qualitative research
Quantitative vs. qualitative research questions
Writing research questions is very important in both qualitative and quantitative research, but the research questions that perform best in the two types of studies are quite different.
Quantitative research questions
Quantitative research questions usually relate to quantities, similarities and differences.
It might reflect the researchers’ interest in determining whether relationships between variables exist, and if so whether they are statistically significant. Or it may focus on establishing differences between things through comparison, and using statistical analysis to determine whether those differences are meaningful or due to chance.
- How much? This kind of research question is one of the simplest. It focuses on quantifying something. For example:
How many Yoruba speakers are there in the state of Maine?
- What is the connection?
This type of quantitative research question examines how one variable affects another.
For example:
How does a low level of sunlight affect the mood scores (1-10) of Antarctic explorers during winter?
- What is the difference? Quantitative research questions in this category identify two categories and measure the difference between them using numerical data.
Do white cats stay cooler than tabby cats in hot weather?
If your research question fits into one of the above categories, you’re probably going to be doing a quantitative study.
Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions focus on exploring phenomena, meanings and experiences.
Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research isn’t about finding causal relationships between variables. So although qualitative research questions might touch on topics that involve one variable influencing another, or looking at the difference between things, finding and quantifying those relationships isn’t the primary objective.
In fact, you as a qualitative researcher might end up studying a very similar topic to your colleague who is doing a quantitative study, but your areas of focus will be quite different. Your research methods will also be different – they might include focus groups, ethnography studies, and other kinds of qualitative study.
A few example qualitative research questions:
- What is it like being an Antarctic explorer during winter?
- What are the experiences of Yoruba speakers in the USA?
- How do white cat owners describe their pets?
Qualitative research question types
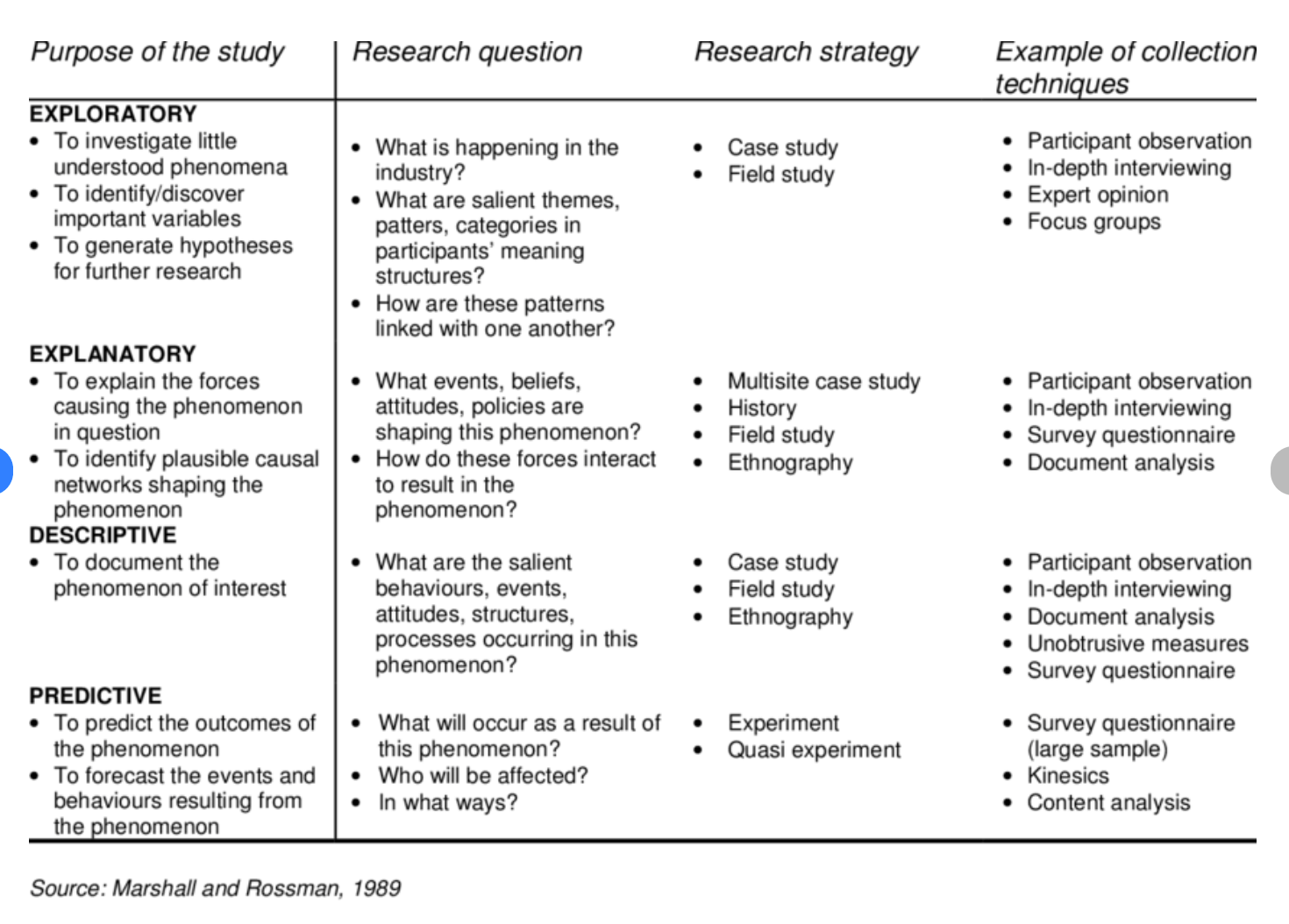
Marshall and Rossman (1989) identified 4 qualitative research question types, each with its own typical research strategy and methods.
- Exploratory questions
Exploratory questions are used when relatively little is known about the research topic. The process researchers follow when pursuing exploratory questions might involve interviewing participants, holding focus groups, or diving deep with a case study.
- Explanatory questions
With explanatory questions, the research topic is approached with a view to understanding the causes that lie behind phenomena. However, unlike a quantitative project, the focus of explanatory questions is on qualitative analysis of multiple interconnected factors that have influenced a particular group or area, rather than a provable causal link between dependent and independent variables.
- Descriptive questions
As the name suggests, descriptive questions aim to document and record what is happening. In answering descriptive questions , researchers might interact directly with participants with surveys or interviews, as well as using observational studies and ethnography studies that collect data on how participants interact with their wider environment.
- Predictive questions
Predictive questions start from the phenomena of interest and investigate what ramifications it might have in the future. Answering predictive questions may involve looking back as well as forward, with content analysis, questionnaires and studies of non-verbal communication (kinesics).
Why are good qualitative research questions important?
We know research questions are very important. But what makes them so essential? (And is that question a qualitative or quantitative one?)
Getting your qualitative research questions right has a number of benefits.
- It defines your qualitative research project Qualitative research questions definitively nail down the research population, the thing you’re examining, and what the nature of your answer will be.This means you can explain your research project to other people both inside and outside your business or organization. That could be critical when it comes to securing funding for your project, recruiting participants and members of your research team, and ultimately for publishing your results. It can also help you assess right the ethical considerations for your population of study.
- It maintains focus Good qualitative research questions help researchers to stick to the area of focus as they carry out their research. Keeping the research question in mind will help them steer away from tangents during their research or while they are carrying out qualitative research interviews. This holds true whatever the qualitative methods are, whether it’s a focus group, survey, thematic analysis or other type of inquiry.That doesn’t mean the research project can’t morph and change during its execution – sometimes this is acceptable and even welcome – but having a research question helps demarcate the starting point for the research. It can be referred back to if the scope and focus of the project does change.
- It helps make sure your outcomes are achievable
Because qualitative research questions help determine the kind of results you’re going to get, it helps make sure those results are achievable. By formulating good qualitative research questions in advance, you can make sure the things you want to know and the way you’re going to investigate them are grounded in practical reality. Otherwise, you may be at risk of taking on a research project that can’t be satisfactorily completed.
Developing good qualitative research questions
All researchers use research questions to define their parameters, keep their study on track and maintain focus on the research topic. This is especially important with qualitative questions, where there may be exploratory or inductive methods in use that introduce researchers to new and interesting areas of inquiry. Here are some tips for writing good qualitative research questions.
1. Keep it specific
Broader research questions are difficult to act on. They may also be open to interpretation, or leave some parameters undefined.
Strong example: How do Baby Boomers in the USA feel about their gender identity?
Weak example: Do people feel different about gender now?
2. Be original
Look for research questions that haven’t been widely addressed by others already.
Strong example: What are the effects of video calling on women’s experiences of work?
Weak example: Are women given less respect than men at work?
3. Make it research-worthy
Don’t ask a question that can be answered with a ‘yes’ or ‘no’, or with a quick Google search.
Strong example: What do people like and dislike about living in a highly multi-lingual country?
Weak example: What languages are spoken in India?
4. Focus your question
Don’t roll multiple topics or questions into one. Qualitative data may involve multiple topics, but your qualitative questions should be focused.
Strong example: What is the experience of disabled children and their families when using social services?
Weak example: How can we improve social services for children affected by poverty and disability?
4. Focus on your own discipline, not someone else’s
Avoid asking questions that are for the politicians, police or others to address.
Strong example: What does it feel like to be the victim of a hate crime?
Weak example: How can hate crimes be prevented?
5. Ask something researchable
Big questions, questions about hypothetical events or questions that would require vastly more resources than you have access to are not useful starting points for qualitative studies. Qualitative words or subjective ideas that lack definition are also not helpful.
Strong example: How do perceptions of physical beauty vary between today’s youth and their parents’ generation?
Weak example: Which country has the most beautiful people in it?
Related resources
Qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, business research methods 12 min read, qualitative research interviews 11 min read, market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Qualitative Research Questions: Gain Powerful Insights + 25 Examples
We review the basics of qualitative research questions, including their key components, how to craft them effectively, & 25 example questions.
Einstein was many things—a physicist, a philosopher, and, undoubtedly, a mastermind. He also had an incredible way with words. His quote, "Everything that can be counted does not necessarily count; everything that counts cannot necessarily be counted," is particularly poignant when it comes to research.
Some inquiries call for a quantitative approach, for counting and measuring data in order to arrive at general conclusions. Other investigations, like qualitative research, rely on deep exploration and understanding of individual cases in order to develop a greater understanding of the whole. That’s what we’re going to focus on today.
Qualitative research questions focus on the "how" and "why" of things, rather than the "what". They ask about people's experiences and perceptions , and can be used to explore a wide range of topics.
The following article will discuss the basics of qualitative research questions, including their key components, and how to craft them effectively. You'll also find 25 examples of effective qualitative research questions you can use as inspiration for your own studies.
Let’s get started!
What are qualitative research questions, and when are they used?
When researchers set out to conduct a study on a certain topic, their research is chiefly directed by an overarching question . This question provides focus for the study and helps determine what kind of data will be collected.
By starting with a question, we gain parameters and objectives for our line of research. What are we studying? For what purpose? How will we know when we’ve achieved our goals?
Of course, some of these questions can be described as quantitative in nature. When a research question is quantitative, it usually seeks to measure or calculate something in a systematic way.
For example:
- How many people in our town use the library?
- What is the average income of families in our city?
- How much does the average person weigh?
Other research questions, however—and the ones we will be focusing on in this article—are qualitative in nature. Qualitative research questions are open-ended and seek to explore a given topic in-depth.
According to the Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry , “Qualitative research aims to address questions concerned with developing an understanding of the meaning and experience dimensions of humans’ lives and social worlds.”
This type of research can be used to gain a better understanding of people’s thoughts, feelings and experiences by “addressing questions beyond ‘what works’, towards ‘what works for whom when, how and why, and focusing on intervention improvement rather than accreditation,” states one paper in Neurological Research and Practice .
Qualitative questions often produce rich data that can help researchers develop hypotheses for further quantitative study.
- What are people’s thoughts on the new library?
- How does it feel to be a first-generation student at our school?
- How do people feel about the changes taking place in our town?
As stated by a paper in Human Reproduction , “...‘qualitative’ methods are used to answer questions about experience, meaning, and perspective, most often from the standpoint of the participant. These data are usually not amenable to counting or measuring.”
Both quantitative and qualitative questions have their uses; in fact, they often complement each other. A well-designed research study will include a mix of both types of questions in order to gain a fuller understanding of the topic at hand.
If you would like to recruit unlimited participants for qualitative research for free and only pay for the interview you conduct, try using Respondent today.
Crafting qualitative research questions for powerful insights
Now that we have a basic understanding of what qualitative research questions are and when they are used, let’s take a look at how you can begin crafting your own.
According to a study in the International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education, there is a certain process researchers should follow when crafting their questions, which we’ll explore in more depth.
1. Beginning the process
Start with a point of interest or curiosity, and pose a draft question or ‘self-question’. What do you want to know about the topic at hand? What is your specific curiosity? You may find it helpful to begin by writing several questions.
For example, if you’re interested in understanding how your customer base feels about a recent change to your product, you might ask:
- What made you decide to try the new product?
- How do you feel about the change?
- What do you think of the new design/functionality?
- What benefits do you see in the change?
2. Create one overarching, guiding question
At this point, narrow down the draft questions into one specific question. “Sometimes, these broader research questions are not stated as questions, but rather as goals for the study.”
As an example of this, you might narrow down these three questions:
into the following question:
- What are our customers’ thoughts on the recent change to our product?
3. Theoretical framing
As you read the relevant literature and apply theory to your research, the question should be altered to achieve better outcomes. Experts agree that pursuing a qualitative line of inquiry should open up the possibility for questioning your original theories and altering the conceptual framework with which the research began.
If we continue with the current example, it’s possible you may uncover new data that informs your research and changes your question. For instance, you may discover that customers’ feelings about the change are not just a reaction to the change itself, but also to how it was implemented. In this case, your question would need to reflect this new information:
- How did customers react to the process of the change, as well as the change itself?
4. Ethical considerations
A study in the International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education stresses that ethics are “a central issue when a researcher proposes to study the lives of others, especially marginalized populations.” Consider how your question or inquiry will affect the people it relates to—their lives and their safety. Shape your question to avoid physical, emotional, or mental upset for the focus group.
In analyzing your question from this perspective, if you feel that it may cause harm, you should consider changing the question or ending your research project. Perhaps you’ve discovered that your question encourages harmful or invasive questioning, in which case you should reformulate it.
5. Writing the question
The actual process of writing the question comes only after considering the above points. The purpose of crafting your research questions is to delve into what your study is specifically about” Remember that qualitative research questions are not trying to find the cause of an effect, but rather to explore the effect itself.
Your questions should be clear, concise, and understandable to those outside of your field. In addition, they should generate rich data. The questions you choose will also depend on the type of research you are conducting:
- If you’re doing a phenomenological study, your questions might be open-ended, in order to allow participants to share their experiences in their own words.
- If you’re doing a grounded-theory study, your questions might be focused on generating a list of categories or themes.
- If you’re doing ethnography, your questions might be about understanding the culture you’re studying.
Whenyou have well-written questions, it is much easier to develop your research design and collect data that accurately reflects your inquiry.
In writing your questions, it may help you to refer to this simple flowchart process for constructing questions:
Download Free E-Book
25 examples of expertly crafted qualitative research questions
It's easy enough to cover the theory of writing a qualitative research question, but sometimes it's best if you can see the process in practice. In this section, we'll list 25 examples of B2B and B2C-related qualitative questions.
Let's begin with five questions. We'll show you the question, explain why it's considered qualitative, and then give you an example of how it can be used in research.
1. What is the customer's perception of our company's brand?
Qualitative research questions are often open-ended and invite respondents to share their thoughts and feelings on a subject. This question is qualitative because it seeks customer feedback on the company's brand.
This question can be used in research to understand how customers feel about the company's branding, what they like and don't like about it, and whether they would recommend it to others.
2. Why do customers buy our product?
This question is also qualitative because it seeks to understand the customer's motivations for purchasing a product. It can be used in research to identify the reasons customers buy a certain product, what needs or desires the product fulfills for them, and how they feel about the purchase after using the product.
3. How do our customers interact with our products?
Again, this question is qualitative because it seeks to understand customer behavior. In this case, it can be used in research to see how customers use the product, how they interact with it, and what emotions or thoughts the product evokes in them.
4. What are our customers' biggest frustrations with our products?
By seeking to understand customer frustrations, this question is qualitative and can provide valuable insights. It can be used in research to help identify areas in which the company needs to make improvements with its products.
5. How do our customers feel about our customer service?
Rather than asking why customers like or dislike something, this question asks how they feel. This qualitative question can provide insights into customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction with a company.
This type of question can be used in research to understand what customers think of the company's customer service and whether they feel it meets their needs.
20 more examples to refer to when writing your question
Now that you’re aware of what makes certain questions qualitative, let's move into 20 more examples of qualitative research questions:
- How do your customers react when updates are made to your app interface?
- How do customers feel when they complete their purchase through your ecommerce site?
- What are your customers' main frustrations with your service?
- How do people feel about the quality of your products compared to those of your competitors?
- What motivates customers to refer their friends and family members to your product or service?
- What are the main benefits your customers receive from using your product or service?
- How do people feel when they finish a purchase on your website?
- What are the main motivations behind customer loyalty to your brand?
- How does your app make people feel emotionally?
- For younger generations using your app, how does it make them feel about themselves?
- What reputation do people associate with your brand?
- How inclusive do people find your app?
- In what ways are your customers' experiences unique to them?
- What are the main areas of improvement your customers would like to see in your product or service?
- How do people feel about their interactions with your tech team?
- What are the top five reasons people use your online marketplace?
- How does using your app make people feel in terms of connectedness?
- What emotions do people experience when they're using your product or service?
- Aside from the features of your product, what else about it attracts customers?
- How does your company culture make people feel?
As you can see, these kinds of questions are completely open-ended. In a way, they allow the research and discoveries made along the way to direct the research. The questions are merely a starting point from which to explore.
This video offers tips on how to write good qualitative research questions, produced by Qualitative Research Expert, Kimberly Baker.
Wrap-up: crafting your own qualitative research questions.
Over the course of this article, we've explored what qualitative research questions are, why they matter, and how they should be written. Hopefully you now have a clear understanding of how to craft your own.
Remember, qualitative research questions should always be designed to explore a certain experience or phenomena in-depth, in order to generate powerful insights. As you write your questions, be sure to keep the following in mind:
- Are you being inclusive of all relevant perspectives?
- Are your questions specific enough to generate clear answers?
- Will your questions allow for an in-depth exploration of the topic at hand?
- Do the questions reflect your research goals and objectives?
If you can answer "yes" to all of the questions above, and you've followed the tips for writing qualitative research questions we shared in this article, then you're well on your way to crafting powerful queries that will yield valuable insights.
Download Free E-Book
.png?width=2500&name=Respondent_100+Questions_Banners_1200x644%20(1).png)
Asking the right questions in the right way is the key to research success. That’s true for not just the discussion guide but for every step of a research project. Following are 100+ questions that will take you from defining your research objective through screening and participant discussions.
Fill out the form below to access free e-book!
Recommend Resources:
- How to Recruit Participants for Qualitative Research
- The Best UX Research Tools of 2022
- 10 Smart Tips for Conducting Better User Interviews
- 50 Powerful Questions You Should Ask In Your Next User Interview
- How To Find Participants For User Research: 13 Ways To Make It Happen
- UX Diary Study: 5 Essential Tips For Conducing Better Studies
- User Testing Recruitment: 10 Smart Tips To Find Participants Fast
- Qualitative Research Questions: Gain Powerful Insights + 25
- How To Successfully Recruit Participants for A Study (2022 Edition)
- How To Properly Recruit Focus Group Participants (2022 Edition)
- The Best Unmoderated Usability Testing Tools of 2022
50 Powerful User Interview Questions You Should Consider Asking
We researched the best user interview questions you can use for your qualitative research studies. Use these 50 sample questions for your next...
A Guide to Usability Testing Questions (Including 100 Examples)
Asking the right questions in the right way is the key to the success of your UX research project. With tips and 100+ question examples, Respondent...
How To Unleash Your Extra Income Potential With Respondent
The number one question we get from new participants is “how can I get invited to participate in more projects.” In this article, we’ll discuss a few...
- (855) 776-7763
Training Maker
All Products
Qualaroo Insights
ProProfs.com
- Get Started Free
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!
How to Write Qualitative Research Questions: Types & Examples

Market Research Specialist
Emma David, a seasoned market research professional, specializes in employee engagement, survey administration, and data management. Her expertise in leveraging data for informed decisions has positively impacted several brands, enhancing their market position.
Qualitative research questions focus on depth and quality, exploring the “why and how” behind decisions, without relying on statistical tools.
Unlike quantitative research, which aims to collect tangible, measurable data from a broader demographic, qualitative analysis involves smaller, focused datasets, identifying patterns for insights.
The information collected by qualitative surveys can vary from text to images, demanding a deep understanding of the subject, and therefore, crafting precise qualitative research questions is crucial for success.
In this guide, we’ll discuss how to write effective qualitative research questions, explore various types, and highlight characteristics of good qualitative research questions.
Let’s dive in!
What Are Qualitative Research Questions?
Qualitative questions aim to understand the depth and nuances of a phenomenon, focusing on “why” and “how” rather than quantifiable measures.
They explore subjective experiences, perspectives, and behaviors, often using open-ended inquiries to gather rich, descriptive data.
Unlike quantitative questions, which seek numerical data, qualitative questions try to find out meanings, patterns, and underlying processes within a specific context.
These questions are essential for exploring complex issues, generating hypotheses, and gaining deeper insights into human behavior and phenomena.
Here’s an example of a qualitative research question:
“How do you perceive and navigate organizational culture within a tech startup environment?”
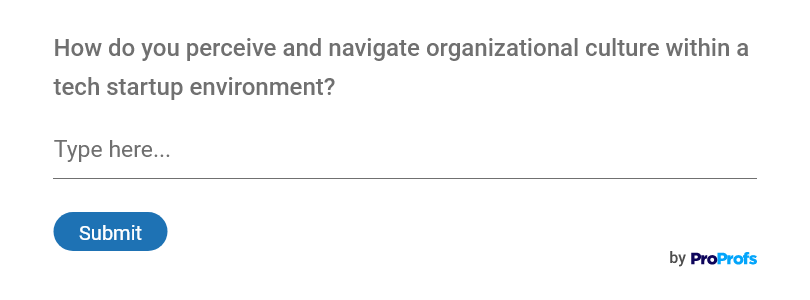
This question asks about the respondent’s subjective interpretations and experiences of organizational culture within a specific context, such as a tech startup.
It seeks to uncover insights into the values, norms, and practices that shape workplace dynamics and employee behaviors, providing qualitative data for analysis and understanding.
When Should We Use Qualitative Research Questions?
Qualitative research questions typically aim to open up conversations, encourage detailed narratives, and foster a deep understanding of the subject matter. Here are some scenarios they are best suited for:
- Exploring Complex Phenomena : When the research topic involves understanding complex processes, behaviors, or interactions that cannot be quantified easily, qualitative questions help delve into these intricate details.
- Understanding Contexts and Cultures : To grasp the nuances of different social contexts, cultures, or subcultures, qualitative research questions allow for an in-depth exploration of these environments and how they influence individuals and groups.
- Exploring Perceptions and Experiences : When the aim is to understand people’s perceptions, experiences, or feelings about a particular subject, qualitative questions facilitate capturing the depth and variety of these perspectives.
- Developing Concepts or Theories : In the early stages of research, where concepts or theories are not yet well-developed, qualitative questions can help generate hypotheses, identify variables, and develop theoretical frameworks based on observations and interpretations.
- Investigating Processes : To understand how processes unfold over time and the factors that influence these processes, qualitative questions are useful for capturing the dynamics and complexities involved.
- Seeking to Understand Change : When researching how individuals or groups experience change, adapt to new circumstances, or make decisions, qualitative research questions can provide insights into the motivations, challenges, and strategies involved.
- Studying Phenomena Not Easily Quantified : For phenomena that are not easily captured through quantitative measures, such as emotions, beliefs, or motivations, qualitative questions can probe these abstract concepts more effectively.
- Addressing Sensitive or Taboo Topics : In studies where topics may be sensitive, controversial, or taboo, qualitative research questions allow for a respectful and empathetic exploration of these subjects, providing space for participants to share their experiences in their own words.
How to Write Qualitative Research Questions?
Read this guide to learn how you can craft well-thought-out qualitative research questions:
1. Begin with Your Research Goals
The first step in formulating qualitative research questions is to have a clear understanding of what you aim to discover or understand through your research. There are two types of qualitative questionnaires or research – Ontological and Epistemological.
Finding out the nature of your research influences all aspects of your research design, including the formulation of research questions.
Subsequently:
- Identify your main objective : Consider the broader context of your study. Are you trying to explore a phenomenon, understand a process, or interpret the meanings behind behaviors? Your main objective should guide the formulation of your questions, ensuring they are aligned with what you seek to achieve.
- Focus on the ‘how’ and ‘why’ : Qualitative research is inherently exploratory and aims to understand the nuances of human behavior and experience. Starting your questions with “how” or “why” encourages a deeper investigation into the motivations, processes, and contexts underlying the subject matter. This approach facilitates an open-ended exploration, allowing participants to provide rich, detailed responses that illuminate their perspectives and experiences.
Take a quick look at the following visual for a better understanding:

So, if you are doing Ontological research, ensure that the questions focus on the “what” aspects of reality (the premise of your research) and opt for the nature of the knowledge for Epistemological research.
2. Choose the Right Structure
The structure of your research questions significantly impacts the depth and quality of data you collect. Opting for an open-ended format allows respondents the flexibility to express themselves freely, providing insights that pre-defined answers might miss.
- Open-ended format : These questions do not constrain respondents to a set of predetermined answers, unlike closed-ended questions. By allowing participants to articulate their thoughts in their own words, you can uncover nuances and complexities in their responses that might otherwise be overlooked.
- Avoid yes/no questions : Yes/no questions tend to limit the depth of responses. While they might be useful for gathering straightforward factual information, they are not conducive to exploring the depths and nuances that qualitative research seeks to uncover. Encouraging participants to elaborate on their experiences and perspectives leads to richer, more informative data.
For example, take a look at some qualitative questions examples shown in the following image:

3. Be Clear and Specific
Clarity and specificity in your questions are crucial to ensure that participants understand what is being asked and that their responses are relevant to your research objectives.
- Use clear language : Use straightforward, understandable language in your questions. Avoid jargon, acronyms, or overly technical terms that might confuse participants or lead to misinterpretation. The goal is to make your questions accessible to everyone involved in your study.
- Be specific : While maintaining the open-ended nature of qualitative questions, it’s important to narrow down your focus to specific aspects of the phenomenon you’re studying. This specificity helps guide participants’ responses and ensures that the data you collect directly relates to your research objectives.
4. Ensure Relevance and Feasibility
Each question should be carefully considered for its relevance to your research goals and its feasibility, given the constraints of your study.
- Relevance : Questions should be crafted to address the core objectives of your research directly. They should probe areas that are essential to understanding the phenomenon under investigation and should align with your theoretical framework or literature review findings.
- Feasibility : Consider the practical aspects of your research, including the time available for data collection and analysis, resources, and access to participants. Questions should be designed to elicit meaningful responses within the constraints of your study, ensuring that you can gather and analyze data effectively.
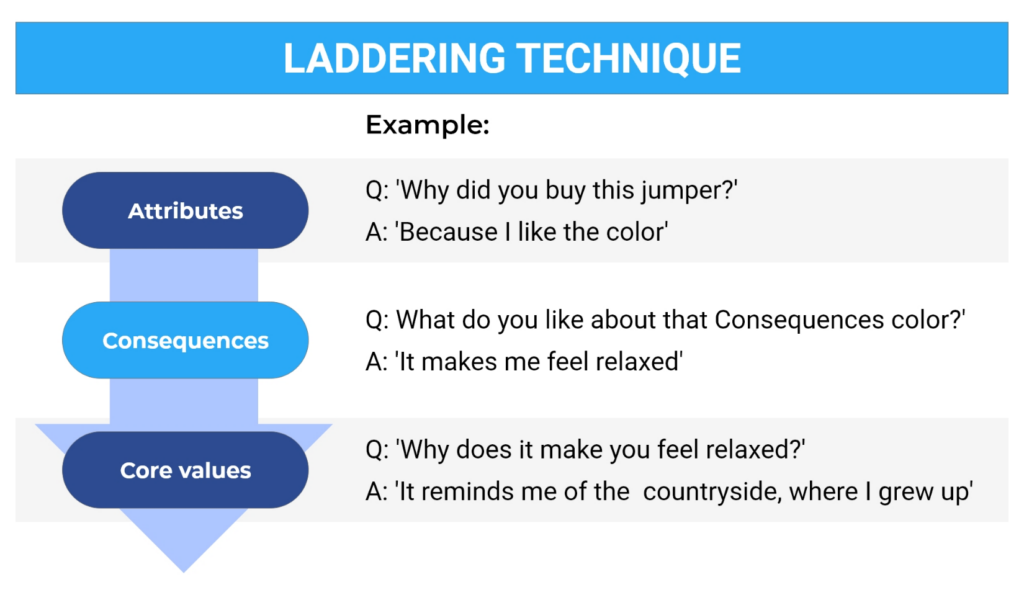
5. Focus on a Single Concept or Theme per Question
To ensure clarity and depth, each question should concentrate on a single idea or theme. However, if your main qualitative research question is tough to understand or has a complex structure, you can create sub-questions in limited numbers and with a “ladder structure”.
This will help your respondents understand the overall research objective in mind, and your research can be executed in a better manner.
For example, suppose your main question is – “What is the current state of illiteracy in your state?”
Then, you can create the following subquestions:
“How does illiteracy block progress in your state?”
“How would you best describe the feelings you have about illiteracy in your state?”
For an even better understanding, you can see the various qualitative research question examples in the following image:
| 📊 : Test them with a small group similar to your study population to ensure they are understood as intended and elicit the kind of responses you are seeking. : Be prepared to refine your questions based on pilot feedback or as your understanding of the topic deepens. |
Types of Qualitative Research Questions With Examples
Qualitative survey questions primarily focus on a specific group of respondents that are participating in case studies, surveys, ethnography studies, etc., rather than numbers or statistics.
As a result, the questions are mostly open-ended and can be subdivided into the following types as discussed below:
1. Descriptive Questions
Descriptive research questions aim to detail the “what” of a phenomenon, providing a comprehensive overview of the context, individuals, or situations under study. These questions are foundational, helping to establish a baseline understanding of the research topic.
- What are the daily experiences of teachers in urban elementary schools?
- What strategies do small businesses employ to adapt to rapid technological changes?
- How do young adults describe their transition from college to the workforce?
- What are the coping mechanisms of families with members suffering from chronic illnesses?
- How do community leaders perceive the impact of gentrification in their neighborhoods?
2. Interpretive Questions
Interpretive questions seek to understand the “how” and “why” behind a phenomenon, focusing on the meanings people attach to their experiences. These questions delve into the subjective interpretations and perceptions of participants.
- How do survivors of natural disasters interpret their experiences of recovery and rebuilding?
- Why do individuals engage in voluntary work within their communities?
- How do parents interpret and navigate the challenges of remote schooling for their children?
- Why do consumers prefer local products over global brands in certain markets?
- How do artists interpret the influence of digital media on traditional art forms?
3. Comparative Questions
Comparative research questions are designed to explore differences and similarities between groups, settings, or time periods. These questions can help to highlight the impact of specific variables on the phenomenon under study.
- How do the strategies for managing work-life balance compare between remote and office workers?
- What are the differences in consumer behavior towards sustainable products in urban versus rural areas?
- How do parenting styles in single-parent households compare to those in dual-parent households?
- What are the similarities and differences in leadership styles across different cultures?
- How has the perception of online privacy changed among teenagers over the past decade?
4. Process-oriented Questions
These questions focus on understanding the processes or sequences of events over time. They aim to uncover the “how” of a phenomenon, tracing the development, changes, or evolution of specific situations or behaviors.
- How do non-profit organizations develop and implement community outreach programs?
- What is the process of decision-making in high-stakes business environments?
- How do individuals navigate the process of career transition after significant industry changes?
- What are the stages of adaptation for immigrants in a new country?
- How do social movements evolve from inception to national recognition?
5. Evaluative Questions
Evaluative questions aim to assess the effectiveness, value, or impact of a program, policy, or phenomenon. These questions are critical for understanding the outcomes and implications of various initiatives or situations.
- How effective are online therapy sessions compared to in-person sessions in treating anxiety?
- What is the impact of community gardening programs on neighborhood cohesion?
- How do participants evaluate the outcomes of leadership training programs in their professional development?
- What are the perceived benefits and drawbacks of telecommuting for employees and employers?
- How do residents evaluate the effectiveness of local government policies on waste management?
6. One-on-One Questions
The one-on-one questions are asked to a single person and can be thought of as individual interviews that you can conduct online via phone and video chat as well.
The main aim of such questions is to ask your customers or people in the focus group a series of questions about their purchase motivations. These questions might also come with follow-ups, and if your customers respond with some interesting fact or detail, dig deeper and explore the findings as much as you want.
- What makes you happy in regard to [your research topic]?
- If I could make a wish of yours come true, what do you desire the most?
- What do you still find hard to come to terms with?
- Have you bought [your product] before?
- If so, what was your initial motivation behind the purchase?
7. Exploratory Questions
These questions are designed to enhance your understanding of a particular topic. However, while asking exploratory questions, you must ensure that there are no preconceived notions or biases to it. The more transparent and bias-free your questions are, the better and fair results you will get.
- What is the effect of personal smart devices on today’s youth?
- Do you feel that smart devices have positively or negatively impacted you?
- How do your kids spend their weekends?
- What do you do on a typical weekend morning?
8. Predictive Questions
The predictive questions are used for qualitative research that is focused on the future outcomes of an action or a series of actions. So, you will be using past information to predict the reactions of respondents to hypothetical events that might or might not happen in the future.
These questions come in extremely handy for identifying your customers’ current brand expectations, pain points, and purchase motivation.
- Are you more likely to buy a product when a celebrity promotes it?
- Would you ever try a new product because one of your favorite celebs claims that it actually worked for them?
- Would people in your neighborhood enjoy a park with rides and exercise options?
- How often would you go to a park with your kids if it had free rides?
9. Focus Groups
These questions are mostly asked in person to the customer or respondent groups. The in-person nature of these surveys or studies ensures that the group members get a safe and comfortable environment to express their thoughts and feelings about your brand or services.
- How would you describe your ease of using our product?
- How well do you think you were able to do this task before you started using our product?
- What do you like about our promotional campaigns?
- How well do you think our ads convey the meaning?
10. In-Home Videos
Collecting video feedback from customers in their comfortable, natural settings offers a unique perspective. At home, customers are more relaxed and less concerned about their mannerisms, posture, and choice of words when responding.
This approach is partly why Vogue’s 73 Questions Series is highly popular among celebrities and viewers alike. In-home videos provide insights into customers in a relaxed environment, encouraging them to be honest and share genuine experiences.
- What was your first reaction when you used our product for the first time?
- How well do you think our product performed compared to your expectations?
- What was your worst experience with our product?
- What made you switch to our brand?
11. Online Focus Groups
Online focus groups mirror the traditional, in-person format but are conducted virtually, offering a more cost-effective and efficient approach to gathering data. This digital format extends your reach and allows a rapid collection of responses from a broader audience through online platforms.
You can utilize social media and other digital forums to create communities of respondents and initiate meaningful discussions. Once you have them started, you can simply observe the exchange of thoughts and gather massive amounts of interesting insights!
- What do you like best about our product?
- How familiar are you with this particular service or product we offer?
- What are your concerns with our product?
- What changes can we make to make our product better?
Ask the Right Qualitative Research Questions for Meaningful Insights From Your Respondents
Watch: How to Create a Survey Using ProProfs Survey Maker
By now, you might have realized that manually creating a list of qualitative research questions is a daunting task. Keeping numerous considerations in mind, it’s easy to run out of ideas while crafting qualitative survey questions .
However, investing in smart survey tools, like ProProfs Survey Maker, can significantly streamline this process, allowing you to create various types of surveys in minutes.
With this survey tool , you can generate forms, NPS surveys , tests, quizzes, and assessments.
It’s also useful for conducting polls, sidebar surveys, and in-app surveys. Offering over 100 templates and more than 1,000,000 ready-to-use examples of phenomenological research questions, this software simplifies the task immensely.
Equipped with the right tools and the professional tips shared here, you’re well-prepared to conduct thorough research studies and obtain valuable insights that drive impactful results.
Frequently Asked Questions on Q ualitative Research Questions
1. how do you choose qualitative research questions.
To choose qualitative research questions, identify your main research goal, focus on exploring ‘how’ and ‘why’ aspects, ensure questions are open-ended, and align them with your theoretical framework and methodology.
2. Why are good qualitative research questions important?
Good qualitative research questions are important because they guide the research focus, enable the exploration of depth and complexity, and facilitate the gathering of rich, detailed insights into human experiences and behaviors.

About the author
Emma David is a seasoned market research professional with 8+ years of experience. Having kick-started her journey in research, she has developed rich expertise in employee engagement, survey creation and administration, and data management. Emma believes in the power of data to shape business performance positively. She continues to help brands and businesses make strategic decisions and improve their market standing through her understanding of research methodologies.
Related Posts

Multiple Choice Questions : With Types and Examples

100+ Customer Satisfaction Survey Questions to Ask in 2024

70+ Mental Health Survey Questionnaire for Students
75+ Student Survey Questions to Collect Valuable Students Feedback

75+ Fun Survey Questions to Create Engaging Surveys

What is Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI)? 25+ Survey Questions to Ask

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment Chapter 1 This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Seminal Authors
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Locating Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks This link opens in a new window
- Quantitative Research Questions
Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window

What’s in a Qualitative Research Question?
Qualitative research questions are driven by the need for the study. Ideally, research questions are formulated as a result of the problem and purpose, which leads to the identification of the methodology. When a qualitative methodology is chosen, research questions should be exploratory and focused on the actual phenomenon under study.
From the Dissertation Center, Chapter 1: Research Question Overview , there are several considerations when forming a qualitative research question. Qualitative research questions should
Below is an example of a qualitative phenomenological design. Note the use of the term “lived experience” in the central research question. This aligns with phenomenological design.
RQ1: “ What are the lived experiences of followers of mid-level managers in the financial services sector regarding their well-being on the job?”
If the researcher wants to focus on aspects of the theory used to support the study or dive deeper into aspects of the central RQ, sub-questions might be used. The following sub-questions could be formulated to seek further insight:
RQ1a. “How do followers perceive the quality and adequacy of the leader-follower exchanges between themselves and their novice leaders?”
RQ1b. “Under what conditions do leader-member exchanges affect a follower’s own level of well-being?”
Qualitative research questions also display the desire to explore or describe phenomena. Qualitative research seeks the lived experience, the personal experiences, the understandings, the meanings, and the stories associated with the concepts present in our studies.
We want to ensure our research questions are answerable and that we are not making assumptions about our sample. View the questions below:
How do healthcare providers perceive income inequality when providing care to poor patients?
In Example A, we see that there is no specificity of location or geographic areas. This could lead to findings that are varied, and the researcher may not find a clear pattern. Additionally, the question implies the focus is on “income inequality” when the actual focus is on the provision of care. The term “poor patients” can also be offensive, and most providers will not want to seem insensitive and may perceive income inequality as a challenge (of course!).
How do primary care nurses in outreach clinics describe providing quality care to residents of low-income urban neighborhoods?
In Example B, we see that there is greater specificity in the type of care provider. There is also a shift in language so that the focus is on how the individuals describe what they think about, experience, and navigate providing quality care.
Other Qualitative Research Question Examples
Vague : What are the strategies used by healthcare personnel to assist injured patients?
Try this : What is the experience of emergency room personnel in treating patients with a self-inflicted household injury?
The first question is general and vague. While in the same topic area, the second question is more precise and gives the reader a specific target population and a focus on the phenomenon they would have experienced. This question could be in line with a phenomenological study as we are seeking their experience or a case study as the ER personnel are a bounded entity.
Unclear : How do students experience progressing to college?
Try this : How do first-generation community members describe the aspects of their culture that promote aspiration to postsecondary education?
The first question does not have a focus on what progress is or what students are the focus. The second question provides a specific target population and provides the description to be provided by the participants. This question could be in line with a descriptive study.
- << Previous: Quantitative Research Questions
- Next: Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data >>
- Last Updated: Aug 30, 2024 8:27 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools


The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
- Introduction
Why are research questions so important?
Research question examples, types of qualitative research questions, writing a good research question, guiding your research through research questions.
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
- Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Case studies
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Research questions
The research question plays a critical role in the research process, as it guides the study design, data collection , analysis , and interpretation of the findings.
A research paper relies on a research question to inform readers of the research topic and the research problem being addressed. Without such a question, your audience may have trouble understanding the rationale for your research project.

People can take for granted the research question as an essential part of a research project. However, explicitly detailing why researchers need a research question can help lend clarity to the research project. Here are some of the key roles that the research question plays in the research process:
Defines the scope and focus of the study
The research question helps to define the scope and focus of the study. It identifies the specific topic or issue that the researcher wants to investigate, and it sets the boundaries for the study. A research question can also help you determine if your study primarily contributes to theory or is more applied in nature. Clinical research and public health research, for example, may be more concerned with research questions that contribute to practice, while a research question focused on cognitive linguistics are aimed at developing theory.
Provides a rationale for the study
The research question provides a rationale for the study by identifying a gap or problem in existing literature or practice that the researcher wants to address. It articulates the purpose and significance of the study, and it explains why the study is important and worth conducting.
Guides the study design
The research question guides the study design by helping the researcher select appropriate research methods , sampling strategies, and data collection tools. It also helps to determine the types of data that need to be collected and the best ways to analyze and interpret the data because the principal aim of the study is to provide an answer to that research question.

Shapes the data analysis and interpretation
The research question shapes the data analysis and interpretation by guiding the selection of appropriate analytical methods and by focusing the interpretation of the findings. It helps to identify which patterns and themes in the data are more relevant and worth digging into, and it guides the development of conclusions and recommendations based on the findings.
Generates new knowledge
The research question is the starting point for generating new knowledge. By answering the research question, the researcher contributes to the body of knowledge in the field and helps to advance the understanding of the topic or issue under investigation.
Overall, the research question is a critical component of the research process, as it guides the study from start to finish and provides a foundation for generating new knowledge.
Supports the thesis statement
The thesis statement or main assertion in any research paper stems from the answers to the research question. As a result, you can think of a focused research question as a preview of what the study aims to present as a new contribution to existing knowledge.
Here area few examples of focused research questions that can help set the stage for explaining different types of research questions in qualitative research . These questions touch upon various fields and subjects, showcasing the versatility and depth of research.
- What factors contribute to the job satisfaction of remote workers in the technology industry?
- How do teachers perceive the implementation of technology in the classroom, and what challenges do they face?
- What coping strategies do refugees use to deal with the challenges of resettlement in a new country?
- How does gentrification impact the sense of community and identity among long-term residents in urban neighborhoods?
- In what ways do social media platforms influence body image and self-esteem among adolescents?
- How do family dynamics and communication patterns affect the management of type 2 diabetes in adult patients?
- What is the role of mentorship in the professional development and career success of early-career academics?
- How do patients with chronic illnesses experience and navigate the healthcare system, and what barriers do they encounter?
- What are the motivations and experiences of volunteers in disaster relief efforts, and how do these experiences impact their future involvement in humanitarian work?
- How do cultural beliefs and values shape the consumer preferences and purchasing behavior of young adults in a globalized market?
- How do individuals whose genetic factors predict a high risk for developing a specific medical condition perceive, cope with, and make lifestyle choices based on this information?
These example research questions highlight the different kinds of inquiries common to qualitative research. They also demonstrate how qualitative research can address a wide range of topics, from understanding the experiences of specific populations to examining the impact of broader social and cultural phenomena.
Also, notice that these types of research questions tend to be geared towards inductive analyses that describe a concept in depth or develop new theory. As such, qualitative research questions tend to ask "what," "why," or "how" types of questions. This contrasts with quantitative research questions that typically aim to verify an existing theory. and tend to ask "when," "how much," and "why" types of questions to nail down causal mechanisms and generalizable findings.
Whatever your research inquiry, turn to ATLAS.ti
Powerful tools to help turn your research question into meaningful analysis, starting with a free trial.
As you can see above, the research questions you ask play a critical role in shaping the direction and depth of your study. These questions are designed to explore, understand, and interpret social phenomena, rather than testing a hypothesis or quantifying data like in quantitative research. In this section, we will discuss the various types of research questions typically found in qualitative research, making it easier for you to craft appropriate questions for your study.
Descriptive questions
Descriptive research questions aim to provide a detailed account of the phenomenon being studied. These questions usually begin with "what" or "how" and seek to understand the nature, characteristics, or functions of a subject. For example, "What are the experiences of first-generation college students?" or "How do small business owners adapt to economic downturns?"
Comparative questions
Comparative questions seek to examine the similarities and differences between two or more groups, cases, or phenomena. These questions often include the words "compare," "contrast," or "differences." For example, "How do parenting practices differ between single-parent and two-parent families?" or "What are the similarities and differences in leadership styles among successful female entrepreneurs?"
Exploratory questions
Exploratory research questions are open-ended and intended to investigate new or understudied areas. These questions aim to identify patterns, relationships, or themes that may warrant further investigation. For example, "How do teenagers use social media to construct their identities?" or "What factors influence the adoption of renewable energy technologies in rural communities?"
Explanatory questions
Explanatory research questions delve deeper into the reasons or explanations behind a particular phenomenon or behavior. They often start with "why" or "how" and aim to uncover underlying motivations, beliefs, or processes. For example, "Why do some employees resist organizational change?" or "How do cultural factors influence decision-making in international business negotiations?"
Evaluative questions
Evaluative questions assess the effectiveness, impact, or outcomes of a particular intervention, program, or policy. They seek to understand the value or significance of an initiative by examining its successes, challenges, or unintended consequences. For example, "How effective is the school's anti-bullying program in reducing incidents of bullying?" or "What are the long-term impacts of a community-based health promotion campaign on residents' well-being?"
Interpretive questions
Interpretive questions focus on understanding how individuals or groups make sense of their experiences, actions, or social contexts. These questions often involve the analysis of language, symbols, or narratives to uncover the meanings and perspectives that shape human behavior. For example, "How do cancer survivors make sense of their illness journey?" or "What meanings do members of a religious community attach to their rituals and practices?"
There are mainly two overarching ways to think about how to devise a research question. Many studies are built on existing research, but others can be founded on personal experiences or pilot research.
Using the literature review
Within scholarly research, the research question is often built from your literature review . An analysis of the relevant literature reporting previous studies should allow you to identify contextual, theoretical, or methodological gaps that can be addressed in future research.

A compelling research question built on a robust literature review ultimately illustrates to your audience what is novel about your study's objectives.
Conducting pilot research
Researchers may conduct preliminary research or pilot research when they are interested in a particular topic but don't yet have a basis for forming a research question on that topic. A pilot study is a small-scale, preliminary study that is conducted in order to test the feasibility of a research design, methods, and procedures. It can help identify unresolved puzzles that merit further investigation, and pilot studies can draw attention to potential issues or problems that may arise in the full study.
One potential benefit of conducting a pilot study in qualitative research is that it can help the researcher to refine their research question. By collecting and analyzing a small amount of data, the researcher can get a better sense of the phenomenon under investigation and can develop a more focused and refined research question for the full study. The pilot study can also help the researcher to identify key themes, concepts, or variables that should be included in the research question.
In addition to helping to refine the research question, a pilot study can also help the researcher to develop a more effective data collection and analysis plan. The researcher can test different methods for collecting and analyzing data, and can make adjustments based on the results of the pilot study. This can help to ensure that the full study is conducted in the most effective and efficient manner possible.
Overall, conducting a pilot study in qualitative research can be a valuable tool for refining the research question and developing a more effective research design, methods, and procedures. It can help to ensure that the full study is conducted in a rigorous and effective manner, and can increase the likelihood of generating meaningful and useful findings.
When you write a research question for your qualitative study, consider which type of question best aligns with your research objectives and the nature of the phenomenon you are investigating. Remember, qualitative research questions should be open-ended, allowing for a range of perspectives and insights to emerge. As you progress in your research, these questions may evolve or be refined based on the data you collect, helping to guide your analysis and deepen your understanding of the topic.

Use ATLAS.ti for every step of your research project
From the research question to the key insights, ATLAS.ti is there for you. See how with a free trial.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Qualitative Research Questions: What it is and how to write it

Qualitative research questions are like a compass that points researchers in the right direction to find rich stories, untangle complicated social relationships, and get a clear picture of how people act in subtle ways. Unlike their quantitative counterparts, these questions go beyond numbers and figures to explore the subjective, contextual, and complex parts of the human experience.
It’s well-established that all forms of research come with their own theories and implementation methods. Qualitative research is much the same. Qualitative research is conducted to understand the thought process of both the respondents as well as researchers. It usually is conducted in a natural setup where respondents will be their true selves and would respond transparently.
Results achieved from this research will not be generalized to the entire population but asked research questions , and their vocabulary gives away the researcher’s motive making it easier for respondents to participate in qualitative market research .
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
Qualitative research survey questions are created to understand a particular topic better or to inspect a new subject to understand the nerve of respondent experiences.
Content Index
What are qualitative research questions?
How to write qualitative research questions, types of qualitative research questions, how to choose qualitative research questions, what should be the process of forming qualitative research questions and questionnaires.
Qualitative research questions are the inquiries that lead to qualitative research studies and investigations. They are meant to help people explore and understand phenomena, experiences, meanings, and views from the participant’s point of view.
Different from quantitative research questions, which often try to measure and quantify variables, qualitative research questions try to understand the richness and complexity of human experiences and social events.
Most qualitative research questions are open-ended and allow for in-depth study. They want more than simple yes/no answers but instead want people to talk about their thoughts, feelings, views, and experiences. These questions try to find deeper meanings, patterns, and connections in a given situation.
Here are some examples of qualitative study questions in different fields:
- In psychology: How do individuals experience and cope with traumatic events?
- In sociology: What factors influence a student’s decision to pursue higher education?
- In anthropology: How do cultural norms and values shape gender roles in a specific community?
- In education: What are the challenges faced by teachers in implementing project-based learning in the classroom?
- In healthcare: What are the experiences and perspectives of patients undergoing long-term treatment for a chronic illness?
Qualitative research questions should be straightforward, specific, and tailored to the research’s goals. They guide the process of gathering data through interviews, observations, or document analysis and give a method for analyzing and interpreting data.
Writing the right qualitative research questions requires careful thought about the research goals, the event being studied, and the wanted level of understanding. Here are some tips to help you write good qualitative research questions:
Begin with a broad research question
Start by posing an all-encompassing question that probes the subject or phenomenon of interest. Exploring and learning from the answer to this open-ended question should be possible.
Specify the research objectives
Clearly state the objectives and purposes of your research. What do you want your qualitative study to accomplish? What facets or dimensions of the subject do you wish to investigate?
Focus on the phenomenon
Decide on whatever specific subject or phenomenon you want to research. Any pertinent topic, including social behavior, cultural customs, personal experiences, and more, may be used.
Use open-ended and exploratory language
In qualitative research, open-ended questions should be used to enable participants to offer thorough and in-depth responses. Avoid yes/no questions and queries with a one-word answer. Use words like “how,” “what,” “why,” or “describe” instead to compel people to express their thoughts and experiences.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Interview
Consider the context and participants
Consider your research’s background as well as the qualities of your subjects. Make sure your qualitative methods are specific to the people you will be studying so that they are pertinent and meaningful to them.
Incorporate theory and literature
Your research questions should be based on pertinent theories and available literature. This gives your investigation a theoretical foundation and places your study within the body of knowledge.
Balance breadth and depth
When formulating your research topics, try to strike a balance between depth and breadth. To fully understand the subject, you should investigate it broadly to get a variety of viewpoints and intensively delve into certain areas.
Avoid leading or biased questions
Ensure your questions are neutral and unbiased. Avoid leading participants towards a particular response. Instead, create questions that allow participants to express their thoughts and experiences freely.
Pilot test your questions
Pilot-test your research questions with a small group of people before finalizing them. This will make it easier to spot any possible problems, ambiguities, or places where clarity may be increased.
Revise and refine
Revise and clarify your research questions based on the comments and understandings received from the pilot testing. Aim for consistency, coherence, and congruence with your research goals.
Remember, qualitative market research questions should be flexible and adaptable throughout the research process. They serve as a guide but may evolve as you delve deeper into the data and discover new insights.
LEARN ABOUT: Steps in Qualitative Research
There are several types of qualitative research questions focus that can be used to guide qualitative studies. Here are some common types:
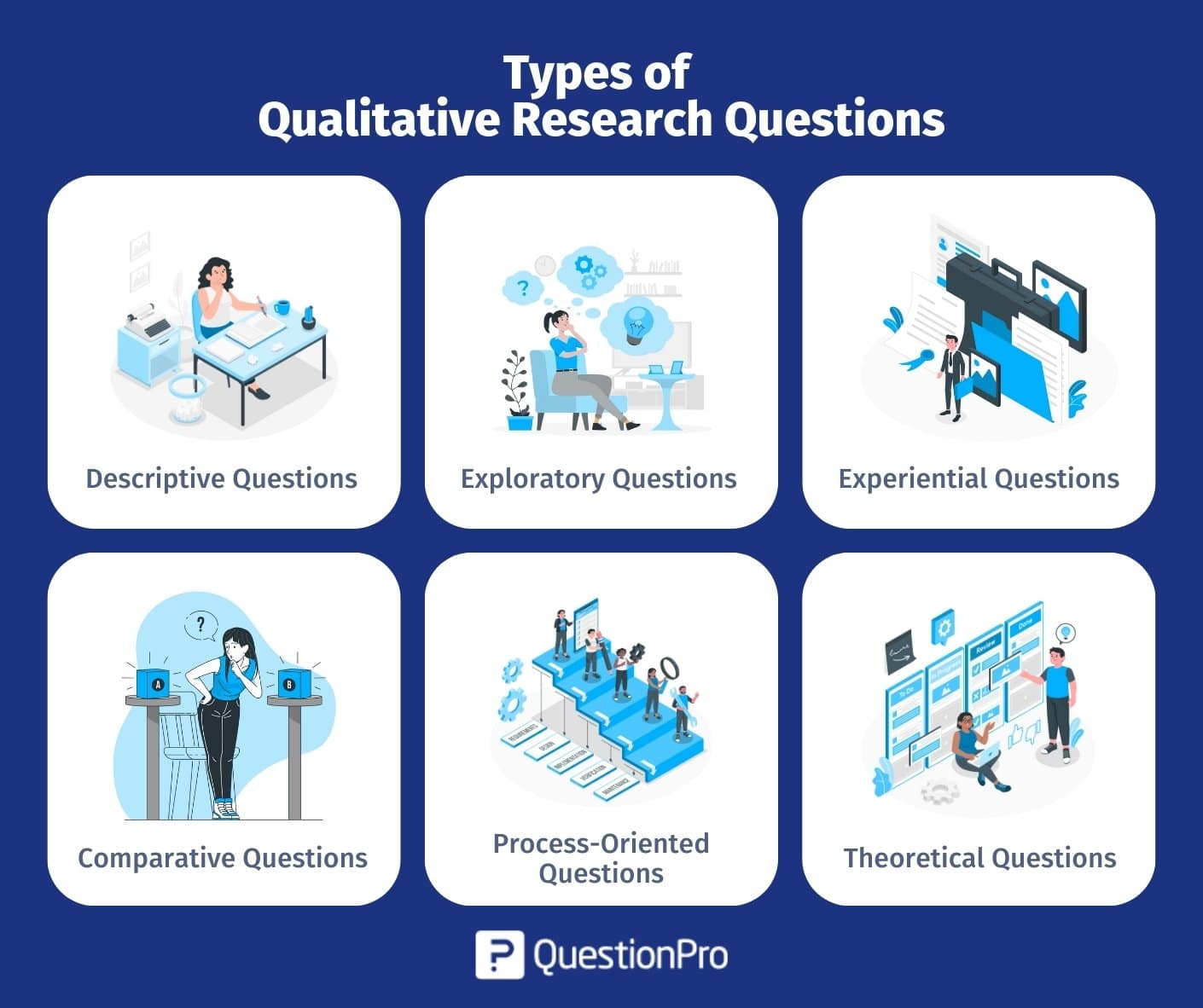
1. Descriptive questions
These questions aim to describe and understand a phenomenon or topic in detail. They focus on providing a comprehensive account of the subject matter. For example:
- What are the experiences of individuals living with chronic pain?
- How do employees perceive the organizational culture in a specific company?
2. Exploratory questions
These questions are used to explore new or under-researched areas. They seek to gain a deeper understanding of a topic or phenomenon. For example:
- What are the factors influencing consumers’ decision-making process when purchasing organic food?
- How do teachers perceive the implementation of project-based learning in the classroom?
3. Experiential questions
These questions focus on understanding individuals’ experiences, perspectives, and subjective meanings related to a particular phenomenon. They aim to capture personal experiences and emotions. For example:
- What are the challenges first-generation college students face during their transition to higher education?
- How do individuals with social anxiety disorder experience social interactions?
4. Comparative questions
These questions involve comparing and contrasting different groups, contexts, or perspectives to identify similarities, differences, or patterns. They explore variations in experiences or phenomena. For example:
- How do parenting practices differ between cultures A and B in terms of child discipline?
- What are the similarities and differences in the coping strategies used by individuals with individuals and depression questionnaire with anxiety disorders?
5. Process-oriented questions
These questions focus on understanding a phenomenon’s processes, mechanisms, or dynamics. They aim to uncover how and why certain outcomes or behaviors occur. For example:
- What are the processes by which teams in a workplace reach a consensus on decision-making?
- How does the negotiation process unfold during conflict resolution in interpersonal relationships?
6. Theoretical questions
These questions seek to generate or refine theory. They explore concepts, relationships, or theoretical frameworks to contribute to the existing body of knowledge. For example:
- How does the concept of “self-efficacy” manifest in the context of entrepreneurship?
- What underlying mechanisms explain the relationship between social support and mental health outcomes?
These are just a few examples of the types of qualitative research questions that can be used. The specific type of question you choose will depend on your research objectives, the phenomenon under investigation, and the depth of understanding you aim to achieve.
Explore Insightfully Contextual Inquiry in Qualitative Research
Choosing a good qualitative research question involves a thoughtful and systematic approach to ensure they align with the objectives of your study and allows for an in-depth exploration of the topic. Here are some steps to help you choose effective qualitative research questions:
Identify your research objectives
Clearly define the purpose of your study. What do you want to explore or understand? What specific insights or knowledge are you seeking to gain through your market research?
Review existing literature
Conduct a thorough review of relevant literature to identify existing research gaps or areas requiring further exploration. This will help you understand the current state of knowledge and inform the development of your research questions.
Brainstorm potential qualitative research question
Generate a list of potential research questions that address your research objectives. Consider different angles, perspectives, and dimensions of your topic. Creating open-ended questions that allow for in-depth exploration rather than simple yes/no answers is important.
Prioritize and refine the questions
Evaluate the generated questions based on their relevance to your research objectives, feasibility, and potential to yield meaningful insights. Prioritize the questions that are most likely to provide rich and valuable data. Refine and rephrase the questions as needed to ensure clarity and focus.
Consider the research design and methodology
Take into account the specific qualitative research design and methodology you plan to use. Different research approaches, such as ethnography, interviews, focus groups, or case studies, may require different types of research questions. Ensure that your questions align with your chosen methodology and will help you gather the desired data.
Pilot test the questions
Before finalizing your research questions, consider conducting a pilot test with a small group of participants. This will allow you to assess your questions’ clarity, appropriateness, and effectiveness. Make necessary revisions based on the feedback received.
Seek feedback
Share your research questions with colleagues, mentors, or experts in your field for feedback and suggestions. They can provide valuable insights and help you refine your questions further.
Finalize your research questions
Based on the steps above, select a set of research questions that are well-aligned with your research objectives, provide scope for exploration, and are feasible within the resources and time available for your study.
1. Mention the purpose of conducting qualitative research. It can be in the form of either of these sentences:
- This study will be on the topic of ….
- The reason for conducting this research is ….
2. Create qualitative statements with a defined objective that can be easily communicated to the target audience .
Keep these pointers in mind while designing this statement:
- Try and form single-sentence statements. Single statements can be much more effective than elaborate ones as they help in communicating important messages in an impactful manner in a short and succinct sentence.
- Clarify the purpose of conducting qualitative research in clear words so that respondents understand their contribution to this research.
- Mention the main topic of research that would prompt respondents to have a clearer idea about what they’re getting into.
- It’s the words that make all the difference. Use qualitative words that demonstrate the quality or feeling behind your purpose, such as understanding, describing, explore.
- Specify details that you would want to communicate to your respondents.
- Mention the name of the research website.
3. Other than the primary qualitative questions, you must create sub-questions so that the purpose is executed in a better manner.
- The main question might be – “What is the state of illiteracy in your state?”
- You can create sub-questions such as: “How does illiteracy hamper progress in your state?” or “How would you best describe your feelings about illiteracy?”
4. Highlight these questions using ‘qualitative’ words:
- Start the questions with “What” or “How” to make sure the respondents provide details about their feelings.
- Communicate what you’re trying to “understand,” “explore,” or “identify” using this Qualitative research online survey questionnaire.
- Questions such as “What happened” can be asked to develop a description of the topic.
- Questions about “how did respondents interpret the what happened question” can be asked to examine the outcome.
- Understand the entire qualitative research process by asking questions about “What happened to you with time?”
5. Develop a skeleton to design the primary questions and also the sub-questions. For example:
- Primary Qualitative research survey question: “How do you think _______ (the main topic of research) means?” or “Describe _____(the main topic of research) as you’ve experienced.”
- Sub-question for qualitative research: “What _________ (characteristic) does __________ (respondents) interest in as a _________ (main topic of research)?”
LEARN ABOUT: Structured Questionnaire
Qualitative research questions are key to giving research studies depth and breadth. These questions go into the details and complexities of human experiences, perceptions, and behaviors. This helps researchers get a full picture of a certain occurrence.
Qualitative research questions are meant to explore, describe, and make sense of subjective truths. Most of the time, they are open-ended, so people can say what they think and feel in their own words.
QuestionPro is an online poll and research platform with several tools and features that can make it easier to make and use qualitative research questions. Its easy-to-use design and variety of question types help researchers collect qualitative data quickly and easily, improving the whole research process.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Experimental vs Observational Studies: Differences & Examples
Sep 5, 2024
Interactive Forms: Key Features, Benefits, Uses + Design Tips
Sep 4, 2024

Closed-Loop Management: The Key to Customer Centricity
Sep 3, 2024

Net Trust Score: Tool for Measuring Trust in Organization
Sep 2, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

Chapter 4. Finding a Research Question and Approaches to Qualitative Research
We’ve discussed the research design process in general and ways of knowing favored by qualitative researchers. In chapter 2, I asked you to think about what interests you in terms of a focus of study, including your motivations and research purpose. It might be helpful to start this chapter with those short paragraphs you wrote about motivations and purpose in front of you. We are now going to try to develop those interests into actual research questions (first part of this chapter) and then choose among various “traditions of inquiry” that will be best suited to answering those questions. You’ve already been introduced to some of this (in chapter 1), but we will go further here.

Developing a Research Question
Research questions are different from general questions people have about the social world. They are narrowly tailored to fit a very specific issue, complete with context and time boundaries. Because we are engaged in empirical science and thus use “data” to answer our questions, the questions we ask must be answerable by data. A question is not the same as stating a problem. The point of the entire research project is to answer a particular question or set of questions. The question(s) should be interesting, relevant, practical, and ethical. Let’s say I am generally interested in the problem of student loan debt. That’s a good place to start, but we can’t simply ask,
General question: Is student loan debt really a problem today?
How could we possibly answer that question? What data could we use? Isn’t this really an axiological (values-based) question? There are no clues in the question as to what data would be appropriate here to help us get started. Students often begin with these large unanswerable questions. They are not research questions. Instead, we could ask,
Poor research question: How many people have debt?
This is still not a very good research question. Why not? It is answerable, although we would probably want to clarify the context. We could add some context to improve it so that the question now reads,
Mediocre research question: How many people in the US have debt today? And does this amount vary by age and location?
Now we have added some context, so we have a better idea of where to look and who to look at. But this is still a pretty poor or mediocre research question. Why is that? Let’s say we did answer it. What would we really know? Maybe we would find out that student loan debt has increased over time and that young people today have more of it. We probably already know this. We don’t really want to go through a lot of trouble answering a question whose answer we already have. In fact, part of the reason we are even asking this question is that we know (or think) it is a problem. Instead of asking what you already know, ask a question to which you really do not know the answer. I can’t stress this enough, so I will say it again: Ask a question to which you do not already know the answer . The point of research is not to prove or make a point but to find out something unknown. What about student loan debt is still a mystery to you? Reviewing the literature could help (see chapter 9). By reviewing the literature, you can get a good sense of what is still mysterious or unknown about student loan debt, and you won’t be reinventing the wheel when you conduct your research. Let’s say you review the literature, and you are struck by the fact that we still don’t understand the true impact of debt on how people are living their lives. A possible research question might be,
Fair research question: What impact does student debt have on the lives of debtors?
Good start, but we still need some context to help guide the project. It is not nearly specific enough.
Better research question: What impact does student debt have on young adults (ages twenty-five to thirty-five) living in the US today?
Now we’ve added context, but we can still do a little bit better in narrowing our research question so that it is both clear and doable; in other words, we want to frame it in a way that provides a very clear research program:
Optimal research question: How do young adults (ages twenty-five to thirty-five) living in the US today who have taken on $30,000 or more in student debt describe the impact of their debt on their lives in terms of finding/choosing a job, buying a house, getting married, and other major life events?
Now you have a research question that can be answered and a clear plan of how to answer it. You will talk to young adults living in the US today who have high debt loads and ask them to describe the impacts of debt on their lives. That is all now in the research question. Note how different this very specific question is from where we started with the “problem” of student debt.
Take some time practicing turning the following general questions into research questions:
- What can be done about the excessive use of force by police officers?
- Why haven’t societies taken firmer steps to address climate change?
- How do communities react to / deal with the opioid epidemic?
- Who has been the most adversely affected by COVID?
- When did political polarization get so bad?
Hint: Step back from each of the questions and try to articulate a possible underlying motivation, then formulate a research question that is specific and answerable.
It is important to take the time to come up with a research question, even if this research question changes a bit as you conduct your research (yes, research questions can change!). If you don’t have a clear question to start your research, you are likely to get very confused when designing your study because you will not be able to make coherent decisions about things like samples, sites, methods of data collection, and so on. Your research question is your anchor: “If we don’t have a question, we risk the possibility of going out into the field thinking we know what we’ll find and looking only for proof of what we expect to be there. That’s not empirical research (it’s not systematic)” ( Rubin 2021:37 ).
Researcher Note
How do you come up with ideas for what to study?
I study what surprises me. Usually, I come across a statistic that suggests something is common that I thought was rare. I tend to think it’s rare because the theories I read suggest it should be, and there’s not a lot of work in that area that helps me understand how the statistic came to be. So, for example, I learned that it’s common for Americans to marry partners who grew up in a different class than them and that about half of White kids born into the upper-middle class are downwardly mobile. I was so shocked by these facts that they naturally led to research questions. How do people come to marry someone who grew up in a different class? How do White kids born near the top of the class structure fall?
—Jessi Streib, author of The Power of the Past and Privilege Lost
What if you have literally no idea what the research question should be? How do you find a research question? Even if you have an interest in a topic before you get started, you see the problem now: topics and issues are not research questions! A research question doesn’t easily emerge; it takes a lot of time to hone one, as the practice above should demonstrate. In some research designs, the research question doesn’t even get clearly articulated until the end of data collection . More on that later. But you must start somewhere, of course. Start with your chosen discipline. This might seem obvious, but it is often overlooked. There is a reason it is called a discipline. We tend to think of “sociology,” “public health,” and “physics” as so many clusters of courses that are linked together by subject matter, but they are also disciplines in the sense that the study of each focuses the mind in a particular way and for particular ends. For example, in my own field, sociology, there is a loosely shared commitment to social justice and a general “sociological imagination” that enables its practitioners to connect personal experiences to society at large and to historical forces. It is helpful to think of issues and questions that are germane to your discipline. Within that overall field, there may be a particular course or unit of study you found most interesting. Within that course or unit of study, there may be an issue that intrigued you. And finally, within that issue, there may be an aspect or topic that you want to know more about.
When I was pursuing my dissertation research, I was asked often, “Why did you choose to study intimate partner violence among Native American women?” This question is necessary, and each time I answered, it helped shape me into a better researcher. I was interested in intimate partner violence because I am a survivor. I didn’t have intentions to work with a particular population or demographic—that came from my own deep introspection on my role as a researcher. I always questioned my positionality: What privileges do I hold as an academic? How has public health extracted information from institutionally marginalized populations? How can I build bridges between communities using my position, knowledge, and power? Public health as a field would not exist without the contributions of Indigenous people. So I started hanging out with them at community events, making friends, and engaging in self-education. Through these organic relationships built with Native women in the community, I saw that intimate partner violence was a huge issue. This led me to partner with Indigenous organizations to pursue a better understanding of how Native survivors of intimate partner violence seek support.
—Susanna Y. Park, PhD, mixed-methods researcher in public health and author of “How Native Women Seek Support as Survivors of Intimate Partner Violence: A Mixed-Methods Study”
One of the most exciting and satisfying things about doing academic research is that whatever you end up researching can become part of the body of knowledge that we have collectively created. Don’t make the mistake of thinking that you are doing this all on your own from scratch. Without even being aware of it, no matter if you are a first-year undergraduate student or a fourth-year graduate student, you have been trained to think certain questions are interesting. The very fact that you are majoring in a particular field or have signed up for years of graduate study in a program testifies to some level of commitment to a discipline. What we are looking for, ideally, is that your research builds on in some way (as extension, as critique, as lateral move) previous research and so adds to what we, collectively, understand about the social world. It is helpful to keep this in mind, as it may inspire you and also help guide you through the process. The point is, you are not meant to be doing something no one has ever thought of before, even if you are trying to find something that does not exactly duplicate previous research: “You may be trying to be too clever—aiming to come up with a topic unique in the history of the universe, something that will have people swooning with admiration at your originality and intellectual precociousness. Don’t do it. It’s safer…to settle on an ordinary, middle-of-the-road topic that will lend itself to a nicely organized process of project management. That’s the clever way of proceeding.… You can always let your cleverness shine through during the stages of design, analysis, and write-up. Don’t make things more difficult for yourself than you need to do” ( Davies 2007:20 ).
Rubin ( 2021 ) suggests four possible ways to develop a research question (there are many more, of course, but this can get you started). One way is to start with a theory that interests you and then select a topic where you can apply that theory. For example, you took a class on gender and society and learned about the “glass ceiling.” You could develop a study that tests that theory in a setting that has not yet been explored—maybe leadership at the Oregon Country Fair. The second way is to start with a topic that interests you and then go back to the books to find a theory that might explain it. This is arguably more difficult but often much more satisfying. Ask your professors for help—they might have ideas of theories or concepts that could be relevant or at least give you an idea of what books to read. The third way is to be very clever and select a question that already combines the topic and the theory. Rubin gives as one example sentencing disparities in criminology—this is both a topic and a theory or set of theories. You then just have to figure out particulars like setting and sample. I don’t know if I find this third way terribly helpful, but it might help you think through the possibilities. The fourth way involves identifying a puzzle or a problem, which can be either theoretical (something in the literature just doesn’t seem to make sense and you want to tackle addressing it) or empirical (something happened or is happening, and no one really understands why—think, for example, of mass school shootings).
Once you think you have an issue or topic that is worth exploring, you will need to (eventually) turn that into a good research question. A good research question is specific, clear, and feasible .
Specific . How specific a research question needs to be is somewhat related to the disciplinary conventions and whether the study is conceived inductively or deductively. In deductive research, one begins with a specific research question developed from the literature. You then collect data to test the theory or hypotheses accompanying your research question. In inductive research, however, one begins with data collection and analysis and builds theory from there. So naturally, the research question is a bit vaguer. In general, the more closely aligned to the natural sciences (and thus the deductive approach), the more a very tight and specific research question (along with specific, focused hypotheses) is required. This includes disciplines like psychology, geography, public health, environmental science, and marine resources management. The more one moves toward the humanities pole (and the inductive approach), the more looseness is permitted, as there is a general belief that we go into the field to find what is there, not necessarily what we imagine we are looking for (see figure 4.2). Disciplines such as sociology, anthropology, and gender and sexuality studies and some subdisciplines of public policy/public administration are closer to the humanities pole in this sense.
Regardless of discipline and approach, however, it is a good idea for beginning researchers to create a research question as specific as possible, as this will serve as your guide throughout the process. You can tweak it later if needed, but start with something specific enough that you know what it is you are doing and why. It is more difficult to deal with ambiguity when you are starting out than later in your career, when you have a better handle on what you are doing. Being under a time constraint means the more specific the question, the better. Questions should always specify contexts, geographical locations, and time frames. Go back to your practice research questions and make sure that these are included.
Clear . A clear research question doesn’t only need to be intelligible to any reader (which, of course, it should); it needs to clarify any meanings of particular words or concepts (e.g., What is excessive force?). Check all your concepts to see if there are ways you can clarify them further—for example, note that we shifted from impact of debt to impact of high debt load and specified this as beginning at $30,000. Ideally, we would use the literature to help us clarify what a high debt load is or how to define “excessive” force.
Feasible . In order to know if your question is feasible, you are going to have to think a little bit about your entire research design. For example, a question that asks about the real-time impact of COVID restrictions on learning outcomes would require a time machine. You could tweak the question to ask instead about the long-term impacts of COVID restrictions, as measured two years after their end. Or let’s say you are interested in assessing the damage of opioid abuse on small-town communities across the United States. Is it feasible to cover the entire US? You might need a team of researchers to do this if you are planning on on-the-ground observations. Perhaps a case study of one particular community might be best. Then your research question needs to be changed accordingly.
Here are some things to consider in terms of feasibility:
- Is the question too general for what you actually intend to do or examine? (Are you specifying the world when you only have time to explore a sliver of that world?)
- Is the question suitable for the time you have available? (You will need different research questions for a study that can be completed in a term than one where you have one to two years, as in a master’s program, or even three to eight years, as in a doctoral program.)
- Is the focus specific enough that you know where and how to begin?
- What are the costs involved in doing this study, including time? Will you need to travel somewhere, and if so, how will you pay for it?
- Will there be problems with “access”? (More on this in later chapters, but for now, consider how you might actually find people to interview or places to observe and whether gatekeepers exist who might keep you out.)
- Will you need to submit an application proposal for your university’s IRB (institutional review board)? If you are doing any research with live human subjects, you probably need to factor in the time and potential hassle of an IRB review (see chapter 8). If you are under severe time constraints, you might need to consider developing a research question that can be addressed with secondary sources, online content, or historical archives (see chapters 16 and 17).
In addition to these practicalities, you will also want to consider the research question in terms of what is best for you now. Are you engaged in research because you are required to be—jumping a hurdle for a course or for your degree? If so, you really do want to think about your project as training and develop a question that will allow you to practice whatever data collection and analysis techniques you want to develop. For example, if you are a grad student in a public health program who is interested in eventually doing work that requires conducting interviews with patients, develop a research question and research design that is interview based. Focus on the practicality (and practice) of the study more than the theoretical impact or academic contribution, in other words. On the other hand, if you are a PhD candidate who is seeking an academic position in the future, your research question should be pitched in a way to build theoretical knowledge as well (the phrasing is typically “original contribution to scholarship”).
The more time you have to devote to the study and the larger the project, the more important it is to reflect on your own motivations and goals when crafting a research question (remember chapter 2?). By “your own motivations and goals,” I mean what interests you about the social world and what impact you want your research to have, both academically and practically speaking. Many students have secret (or not-so-secret) plans to make the world a better place by helping address climate change, pointing out pressure points to fight inequities, or bringing awareness to an overlooked area of concern. My own work in graduate school was motivated by the last of these three—the not-so-secret goal of my research was to raise awareness about obstacles to success for first-generation and working-class college students. This underlying goal motivated me to complete my dissertation in a timely manner and then to further continue work in this area and see my research get published. I cared enough about the topic that I was not ready to put it away. I am still not ready to put it away. I encourage you to find topics that you can’t put away, ever. That will keep you going whenever things get difficult in the research process, as they inevitably will.
On the other hand, if you are an undergraduate and you really have very little time, some of the best advice I have heard is to find a study you really like and adapt it to a new context. Perhaps you read a study about how students select majors and how this differs by class ( Hurst 2019 ). You can try to replicate the study on a small scale among your classmates. Use the same research question, but revise for your context. You can probably even find the exact questions I used and ask them in the new sample. Then when you get to the analysis and write-up, you have a comparison study to guide you, and you can say interesting things about the new context and whether the original findings were confirmed (similar) or not. You can even propose reasons why you might have found differences between one and the other.
Another way of thinking about research questions is to explicitly tie them to the type of purpose of your study. Of course, this means being very clear about what your ultimate purpose is! Marshall and Rossman ( 2016 ) break down the purpose of a study into four categories: exploratory, explanatory, descriptive, and emancipatory ( 78 ). Exploratory purpose types include wanting to investigate little-understood phenomena, or identifying or discovering important new categories of meaning, or generating hypotheses for further research. For these, research questions might be fairly loose: What is going on here? How are people interacting on this site? What do people talk about when you ask them about the state of the world? You are almost (but never entirely) starting from scratch. Be careful though—just because a topic is new to you does not mean it is really new. Someone else (or many other someones) may already have done this exploratory research. Part of your job is to find this out (more on this in “What Is a ‘Literature Review’?” in chapter 9). Descriptive purposes (documenting and describing a phenomenon) are similar to exploratory purposes but with a much clearer goal (description). A good research question for a descriptive study would specify the actions, events, beliefs, attitudes, structures, and/or processes that will be described.
Most researchers find that their topic has already been explored and described, so they move to trying to explain a relationship or phenomenon. For these, you will want research questions that capture the relationships of interest. For example, how does gender influence one’s understanding of police brutality (because we already know from the literature that it does, so now we are interested in understanding how and why)? Or what is the relationship between education and climate change denialism? If you find that prior research has already provided a lot of evidence about those relationships as well as explanations for how they work, and you want to move the needle past explanation into action, you might find yourself trying to conduct an emancipatory study. You want to be even more clear in acknowledging past research if you find yourself here. Then create a research question that will allow you to “create opportunities and the will to engage in social action” ( Marshall and Rossman 2016:78 ). Research questions might ask, “How do participants problematize their circumstances and take positive social action?” If we know that some students have come together to fight against student debt, how are they doing this, and with what success? Your purpose would be to help evaluate possibilities for social change and to use your research to make recommendations for more successful emancipatory actions.
Recap: Be specific. Be clear. Be practical. And do what you love.
Choosing an Approach or Tradition
Qualitative researchers may be defined as those who are working with data that is not in numerical form, but there are actually multiple traditions or approaches that fall under this broad category. I find it useful to know a little bit about the history and development of qualitative research to better understand the differences in these approaches. The following chart provides an overview of the six phases of development identified by Denzin and Lincoln ( 2005 ):
Table 4.1. Six Phases of Development
| Year/Period | Phase | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-1945 | Traditional | Influence of positivism; anthropologists and ethnographers strive for objectivity when reporting observations in the field |
| 1945-1970 | Modernist | Emphasis of methodological rigor and procedural formalism as a way of gaining acceptance |
| 1970-1986 | Blurred genres | Large number of alternative approaches emerge, all competing with and contesting positivist and formalist approaches; e.g., structuralism, symbolic interactionism, ethnomethodology, constructionism |
| 1980s-1990s | Crisis of representation | Attention turns to issues of power and privilege and the necessity of reflexivity around race, class, gender positions and identities; traditional notions of validity and neutrality were undermined |
| 1990s-2000 | Triple crisis | Moving beyond issues of representation, questions raised about evaluation of qualitative research and the writing/presentation of it as well; more political and participatory forms emerge; qualitative research to advance social justice advocated |
| 2000s... | Postexperimental | Boundaries expanded to include creative nonfiction, autobiographical ethnography, poetic representation, and other creative approaches |
There are other ways one could present the history as well. Feminist theory and methodologies came to the fore in the 1970s and 1980s and had a lot to do with the internal critique of more positivist approaches. Feminists were quite aware that standpoint matters—that the identity of the researcher plays a role in the research, and they were ardent supporters of dismantling unjust power systems and using qualitative methods to help advance this mission. You might note, too, that many of the internal disputes were basically epistemological disputes about how we know what we know and whether one’s social location/position delimits that knowledge. Today, we are in a bountiful world of qualitative research, one that embraces multiple forms of knowing and knowledge. This is good, but it means that you, the student, have more choice when it comes to situating your study and framing your research question, and some will expect you to signal the choices you have made in any research protocols you write or publications and presentations.
Creswell’s ( 1998 ) definition of qualitative research includes the notion of distinct traditions of inquiry: “Qualitative research is an inquiry process of understanding based on distinct methodological traditions of inquiry that explore a social or human problem. The research builds complex, holistic pictures, analyzes words, reports detailed views of informants , and conducted the study in a natural setting” (15; emphases added). I usually caution my students against taking shelter under one of these approaches, as, practically speaking, there is a lot of mixing of traditions among researchers. And yet it is useful to know something about the various histories and approaches, particularly as you are first starting out. Each tradition tends to favor a particular epistemological perspective (see chapter 3), a way of reasoning (see “ Advanced: Inductive versus Deductive Reasoning ”), and a data-collection technique.
There are anywhere from ten to twenty “traditions of inquiry,” depending on how one draws the boundaries. In my accounting, there are twelve, but three approaches tend to dominate the field.
Ethnography
Ethnography was developed from the discipline of anthropology, as the study of (other) culture(s). From a relatively positivist/objective approach to writing down the “truth” of what is observed during the colonial era (where this “truth” was then often used to help colonial administrators maintain order and exploit people and extract resources more effectively), ethnography was adopted by all kinds of social science researchers to get a better understanding of how groups of people (various subcultures and cultures) live their lives. Today, ethnographers are more likely to be seeking to dismantle power relations than to support them. They often study groups of people that are overlooked and marginalized, and sometimes they do the obverse by demonstrating how truly strange the familiar practices of the dominant group are. Ethnography is also central to organizational studies (e.g., How does this institution actually work?) and studies of education (e.g., What is it like to be a student during the COVID era?).
Ethnographers use methods of participant observation and intensive fieldwork in their studies, often living or working among the group under study for months at a time (and, in some cases, years). I’ve called this “deep ethnography,” and it is the subject of chapter 14. The data ethnographers analyze are copious “field notes” written while in the field, often supplemented by in-depth interviews and many more casual conversations. The final product of ethnographers is a “thick” description of the culture. This makes reading ethnographies enjoyable, as the goal is to write in such a way that the reader feels immersed in the culture.
There are variations on the ethnography, such as the autoethnography , where the researcher uses a systematic and rigorous study of themselves to better understand the culture in which they find themselves. Autoethnography is a relatively new approach, even though it is derived from one of the oldest approaches. One can say that it takes to heart the feminist directive to “make the personal political,” to underscore the connections between personal experiences and larger social and political structures. Introspection becomes the primary data source.
Grounded Theory
Grounded Theory holds a special place in qualitative research for a few reasons, not least of which is that nonqualitative researchers often mistakenly believe that Grounded Theory is the only qualitative research methodology . Sometimes, it is easier for students to explain what they are doing as “Grounded Theory” because it sounds “more scientific” than the alternative descriptions of qualitative research. This is definitely part of its appeal. Grounded Theory is the name given to the systematic inductive approach first developed by Glaser and Strauss in 1967, The Discovery of Grounded Theory: Strategies for Qualitative Research . Too few people actually read Glaser and Strauss’s book. It is both groundbreaking and fairly unremarkable at the same time. As a historical intervention into research methods generally, it is both a sharp critique of positivist methods in the social sciences (theory testing) and a rejection of purely descriptive accounts-building qualitative research. Glaser and Strauss argued for an approach whose goal was to construct (middle-level) theories from recursive data analysis of nonnumerical data (interviews and observations). They advocated a “constant comparative method” in which coding and analysis take place simultaneously and recursively. The demands are fairly strenuous. If done correctly, the result is the development of a new theory about the social world.
So why do I call this “fairly unremarkable”? To some extent, all qualitative research already does what Glaser and Strauss ( 1967 ) recommend, albeit without denoting the processes quite so specifically. As will be seen throughout the rest of this textbook, all qualitative research employs some “constant comparisons” through recursive data analyses. Where Grounded Theory sets itself apart from a significant number of qualitative research projects, however, is in its dedication to inductively building theory. Personally, I think it is important to understand that Glaser and Strauss were rejecting deductive theory testing in sociology when they first wrote their book. They were part of a rising cohort who rejected the positivist mathematical approaches that were taking over sociology journals in the 1950s and 1960s. Here are some of the comments and points they make against this kind of work:
Accurate description and verification are not so crucial when one’s purpose is to generate theory. ( 28 ; further arguing that sampling strategies are different when one is not trying to test a theory or generalize results)
Illuminating perspectives are too often suppressed when the main emphasis is verifying theory. ( 40 )
Testing for statistical significance can obscure from theoretical relevance. ( 201 )
Instead, they argued, sociologists should be building theories about the social world. They are not physicists who spend time testing and refining theories. And they are not journalists who report descriptions. What makes sociologists better than journalists and other professionals is that they develop theory from their work “In their driving efforts to get the facts [research sociologists] tend to forget that the distinctive offering of sociology to our society is sociological theory, not research description” ( 30–31 ).
Grounded Theory’s inductive approach can be off-putting to students who have a general research question in mind and a working hypothesis. The true Grounded Theory approach is often used in exploratory studies where there are no extant theories. After all, the promise of this approach is theory generation, not theory testing. Flying totally free at the start can be terrifying. It can also be a little disingenuous, as there are very few things under the sun that have not been considered before. Barbour ( 2008:197 ) laments that this approach is sometimes used because the researcher is too lazy to read the relevant literature.
To summarize, Glaser and Strauss justified the qualitative research project in a way that gave it standing among the social sciences, especially vis-à-vis quantitative researchers. By distinguishing the constant comparative method from journalism, Glaser and Strauss enabled qualitative research to gain legitimacy.
So what is it exactly, and how does one do it? The following stages provide a succinct and basic overview, differentiating the portions that are similar to/in accordance with qualitative research methods generally and those that are distinct from the Grounded Theory approach:
Step 1. Select a case, sample, and setting (similar—unless you begin with a theory to test!).
Step 2. Begin data collection (similar).
Step 3. Engage data analysis (similar in general but specificity of details somewhat unique to Grounded Theory): (1) emergent coding (initial followed by focused), (2) axial (a priori) coding , (3) theoretical coding , (4) creation of theoretical categories; analysis ends when “theoretical saturation ” has been achieved.
Grounded Theory’s prescriptive (i.e., it has a set of rules) framework can appeal to beginning students, but it is unnecessary to adopt the entire approach in order to make use of some of its suggestions. And if one does not exactly follow the Grounded Theory rulebook, it can mislead others if you tend to call what you are doing Grounded Theory when you are not:
Grounded theory continues to be a misunderstood method, although many researchers purport to use it. Qualitative researchers often claim to conduct grounded theory studies without fully understanding or adopting its distinctive guidelines. They may employ one or two of the strategies or mistake qualitative analysis for grounded theory. Conversely, other researchers employ grounded theory methods in reductionist, mechanistic ways. Neither approach embodies the flexible yet systematic mode of inquiry, directed but open-ended analysis, and imaginative theorizing from empirical data that grounded theory methods can foster. Subsequently, the potential of grounded theory methods for generating middle-range theory has not been fully realized ( Charmaz 2014 ).
Phenomenology
Where Grounded Theory sets itself apart for its inductive systematic approach to data analysis, phenomenologies are distinct for their focus on what is studied—in this case, the meanings of “lived experiences” of a group of persons sharing a particular event or circumstance. There are phenomenologies of being working class ( Charlesworth 2000 ), of the tourist experience ( Cohen 1979 ), of Whiteness ( Ahmed 2007 ). The phenomenon of interest may also be an emotion or circumstance. One can study the phenomenon of “White rage,” for example, or the phenomenon of arranged marriage.
The roots of phenomenology lie in philosophy (Husserl, Heidegger, Merleau-Ponty, Sartre) but have been adapted by sociologists in particular. Phenomenologists explore “how human beings make sense of experience and transform experience into consciousness, both individually and as shared meaning” ( Patton 2002:104 ).
One of the most important aspects of conducting a good phenomenological study is getting the sample exactly right so that each person can speak to the phenomenon in question. Because the researcher is interested in the meanings of an experience, in-depth interviews are the preferred method of data collection. Observations are not nearly as helpful here because people may do a great number of things without meaning to or without being conscious of their implications. This is important to note because phenomenologists are studying not “the reality” of what happens at all but an articulated understanding of a lived experience. When reading a phenomenological study, it is important to keep this straight—too often I have heard students critique a study because the interviewer didn’t actually see how people’s behavior might conflict with what they say (which is, at heart, an epistemological issue!).
In addition to the “big three,” there are many other approaches; some are variations, and some are distinct approaches in their own right. Case studies focus explicitly on context and dynamic interactions over time and can be accomplished with quantitative or qualitative methods or a mixture of both (for this reason, I am not considering it as one of the big three qualitative methods, even though it is a very common approach). Whatever methods are used, a contextualized deep understanding of the case (or cases) is central.
Critical inquiry is a loose collection of techniques held together by a core argument that understanding issues of power should be the focus of much social science research or, to put this another way, that it is impossible to understand society (its people and institutions) without paying attention to the ways that power relations and power dynamics inform and deform those people and institutions. This attention to power dynamics includes how research is conducted too. All research fundamentally involves issues of power. For this reason, many critical inquiry traditions include a place for collaboration between researcher and researched. Examples include (1) critical narrative analysis, which seeks to describe the meaning of experience for marginalized or oppressed persons or groups through storytelling; (2) participatory action research, which requires collaboration between the researcher and the research subjects or community of interest; and (3) critical race analysis, a methodological application of Critical Race Theory (CRT), which posits that racial oppression is endemic (if not always throughout time and place, at least now and here).
Do you follow a particular tradition of inquiry? Why?
Shawn Wilson’s book, Research Is Ceremony: Indigenous Research Methods , is my holy grail. It really flipped my understanding of research and relationships. Rather than thinking linearly and approaching research in a more canonical sense, Wilson shook my world view by drawing me into a pattern of inquiry that emphasized transparency and relational accountability. The Indigenous research paradigm is applicable in all research settings, and I follow it because it pushes me to constantly evaluate my position as a knowledge seeker and knowledge sharer.
Autoethnography takes the researcher as the subject. This is one approach that is difficult to explain to more quantitatively minded researchers, as it seems to violate many of the norms of “scientific research” as understood by them. First, the sample size is quite small—the n is 1, the researcher. Two, the researcher is not a neutral observer—indeed, the subjectivity of the researcher is the main strength of this approach. Autoethnographies can be extremely powerful for their depth of understanding and reflexivity, but they need to be conducted in their own version of rigor to stand up to scrutiny by skeptics. If you are skeptical, read one of the excellent published examples out there—I bet you will be impressed with what you take away. As they say, the proof is in the pudding on this approach.
Advanced: Inductive versus Deductive Reasoning
There has been a great deal of ink shed in the discussion of inductive versus deductive approaches, not all of it very instructive. Although there is a huge conceptual difference between them, in practical terms, most researchers cycle between the two, even within the same research project. The simplest way to explain the difference between the two is that we are using deductive reasoning when we test an existing theory (move from general to particular), and we are using inductive reasoning when we are generating theory (move from particular to general). Figure 4.2 provides a schematic of the deductive approach. From the literature, we select a theory about the impact of student loan debt: student loan debt will delay homeownership among young adults. We then formulate a hypothesis based on this theory: adults in their thirties with high debt loads will be less likely to own homes than their peers who do not have high debt loads. We then collect data to test the hypothesis and analyze the results. We find that homeownership is substantially lower among persons of color and those who were the first in their families to graduate from college. Notably, high debt loads did not affect homeownership among White adults whose parents held college degrees. We thus refine the theory to match the new findings: student debt loads delay homeownership among some young adults, thereby increasing inequalities in this generation. We have now contributed new knowledge to our collective corpus.
The inductive approach is contrasted in figure 4.3. Here, we did not begin with a preexisting theory or previous literature but instead began with an observation. Perhaps we were conducting interviews with young adults who held high amounts of debt and stumbled across this observation, struck by how many were renting apartments or small houses. We then noted a pattern—not all the young adults we were talking to were renting; race and class seemed to play a role here. We would then probably expand our study in a way to be able to further test this developing theory, ensuring that we were not seeing anomalous patterns. Once we were confident about our observations and analyses, we would then develop a theory, coming to the same place as our deductive approach, but in reverse.
A third form of reasoning, abductive (sometimes referred to as probabilistic reasoning) was developed in the late nineteenth century by American philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce. I have included some articles for further reading for those interested.
Among social scientists, the deductive approach is often relaxed so that a research question is set based on the existing literature rather than creating a hypothesis or set of hypotheses to test. Some journals still require researchers to articulate hypotheses, however. If you have in mind a publication, it is probably a good idea to take a look at how most articles are organized and whether specific hypotheses statements are included.
Table 4.2. Twelve Approaches. Adapted from Patton 2002:132-133.
| Approach | Home discipline | /Data Collection Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Ethnography | Anthropology | Fieldwork/Observations + supplemental interviews |
| Grounded theory | Sociology | Fieldwork/Observations + Interviews |
| Phenomenology | Philosophy | In-depth interviews |
| Constructivism | Sociology | Focus Groups; Interviews |
| Heuristic inquiry | Psychology | Self-reflections and fieldnotes + interviews |
| Ethnomethodology | Sociology | In-depth interviews + Fieldwork, including social experiments |
| Symbolic interaction | Social psychology | Focus Groups + Interviews |
| Semiotics | Linguistics | Textual analyses + interviews/focus groups |
| Hermeneutics | Theology | Textual analyses |
| Narrative analysis | Literary criticism | Interviews, Oral Histories, Textual Analyses, Historical Artefacts, Content Analyses |
| Ecological psychology | Ecology | Observation |
| Orientational/Standpoint approaches (critical theory, feminist theory) | Law; Sociology | PAR, Interviews, Focus Groups |
Further Readings
The following readings have been examples of various approaches or traditions of inquiry:
Ahmed, Sara. 2007. “A Phenomenology of Whiteness.” Feminist Theory 8(2):149–168.
Charlesworth, Simon. 2000. A Phenomenology of Working-Class Experience . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.*
Clandinin, D. Jean, and F. Michael Connelly. 2000. Narrative Inquiry: Experience and Story in Qualitative Research . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Cohen, E. 1979. “A Phenomenology of Tourist Experiences.” Sociology 13(2):179–201.
Cooke, Bill, and Uma Kothari, eds. 2001. Participation: The New Tyranny? London: Zed Books. A critique of participatory action.
Corbin, Juliet, and Anselm Strauss. 2008. Basics of Qualitative Research: Techniques and Procedures for Developing Grounded Theory . 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Crabtree, B. F., and W. L. Miller, eds. 1999. Doing Qualitative Research: Multiple Strategies . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Creswell, John W. 1997. Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing among Five Approaches. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Glaser, Barney G., and Anselm Strauss. 1967. The Discovery of Grounded Theory: Strategies for Qualitative Research . New York: Aldine.
Gobo, Giampetro, and Andrea Molle. 2008. Doing Ethnography . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Hancock, Dawson B., and Bob Algozzine. 2016. Doing Case Study Research: A Practical Guide for Beginning Research . 3rd ed. New York: Teachers College Press.
Harding, Sandra. 1987. Feminism and Methodology . Bloomington: Indiana University Press.
Husserl, Edmund. (1913) 2017. Ideas: Introduction to Pure Phenomenology . Eastford, CT: Martino Fine Books.
Rose, Gillian. 2012. Visual Methodologies . 3rd ed. London: SAGE.
Van der Riet, M. 2009. “Participatory Research and the Philosophy of Social Science: Beyond the Moral Imperative.” Qualitative Inquiry 14(4):546–565.
Van Manen, Max. 1990. Researching Lived Experience: Human Science for an Action Sensitive Pedagogy . Albany: State University of New York.
Wortham, Stanton. 2001. Narratives in Action: A Strategy for Research and Analysis . New York: Teachers College Press.
Inductive, Deductive, and Abductive Reasoning and Nomothetic Science in General
Aliseda, Atocha. 2003. “Mathematical Reasoning vs. Abductive Reasoning: A Structural Approach.” Synthese 134(1/2):25–44.
Bonk, Thomas. 1997. “Newtonian Gravity, Quantum Discontinuity and the Determination of Theory by Evidence.” Synthese 112(1):53–73. A (natural) scientific discussion of inductive reasoning.
Bonnell, Victoria E. 1980. “The Uses of Theory, Concepts and Comparison in Historical Sociology.” C omparative Studies in Society and History 22(2):156–173.
Crane, Mark, and Michael C. Newman. 1996. “Scientific Method in Environmental Toxicology.” Environmental Reviews 4(2):112–122.
Huang, Philip C. C., and Yuan Gao. 2015. “Should Social Science and Jurisprudence Imitate Natural Science?” Modern China 41(2):131–167.
Mingers, J. 2012. “Abduction: The Missing Link between Deduction and Induction. A Comment on Ormerod’s ‘Rational Inference: Deductive, Inductive and Probabilistic Thinking.’” Journal of the Operational Research Society 63(6):860–861.
Ormerod, Richard J. 2010. “Rational Inference: Deductive, Inductive and Probabilistic Thinking.” Journal of the Operational Research Society 61(8):1207–1223.
Perry, Charner P. 1927. “Inductive vs. Deductive Method in Social Science Research.” Southwestern Political and Social Science Quarterly 8(1):66–74.
Plutynski, Anya. 2011. “Four Problems of Abduction: A Brief History.” HOPOS: The Journal of the International Society for the History of Philosophy of Science 1(2):227–248.
Thompson, Bruce, and Gloria M. Borrello. 1992. “Different Views of Love: Deductive and Inductive Lines of Inquiry.” Current Directions in Psychological Science 1(5):154–156.
Tracy, Sarah J. 2012. “The Toxic and Mythical Combination of a Deductive Writing Logic for Inductive Qualitative Research.” Qualitative Communication Research 1(1):109–141.
A place or collection containing records, documents, or other materials of historical interest; most universities have an archive of material related to the university’s history, as well as other “special collections” that may be of interest to members of the community.
A person who introduces the researcher to a field site’s culture and population. Also referred to as guides. Used in ethnography .
A form of research and a methodological tradition of inquiry in which the researcher uses self-reflection and writing to explore personal experiences and connect this autobiographical story to wider cultural, political, and social meanings and understandings. “Autoethnography is a research method that uses a researcher's personal experience to describe and critique cultural beliefs, practices, and experiences” ( Adams, Jones, and Ellis 2015 ).
The philosophical framework in which research is conducted; the approach to “research” (what practices this entails, etc.). Inevitably, one’s epistemological perspective will also guide one’s methodological choices, as in the case of a constructivist who employs a Grounded Theory approach to observations and interviews, or an objectivist who surveys key figures in an organization to find out how that organization is run. One of the key methodological distinctions in social science research is that between quantitative and qualitative research.
The process of labeling and organizing qualitative data to identify different themes and the relationships between them; a way of simplifying data to allow better management and retrieval of key themes and illustrative passages. See coding frame and codebook.
A later stage coding process used in Grounded Theory in which data is reassembled around a category, or axis.
A later stage-coding process used in Grounded Theory in which key words or key phrases capture the emergent theory.
The point at which you can conclude data collection because every person you are interviewing, the interaction you are observing, or content you are analyzing merely confirms what you have already noted. Achieving saturation is often used as the justification for the final sample size.
A methodological tradition of inquiry that focuses on the meanings held by individuals and/or groups about a particular phenomenon (e.g., a “phenomenology of whiteness” or a “phenomenology of first-generation college students”). Sometimes this is referred to as understanding “the lived experience” of a particular group or culture. Interviews form the primary tool of data collection for phenomenological studies. Derived from the German philosophy of phenomenology (Husserl 1913; 2017).
The number of individuals (or units) included in your sample
A form of reasoning which employs a “top-down” approach to drawing conclusions: it begins with a premise or hypothesis and seeks to verify it (or disconfirm it) with newly collected data. Inferences are made based on widely accepted facts or premises. Deduction is idea-first, followed by observations and a conclusion. This form of reasoning is often used in quantitative research and less often in qualitative research. Compare to inductive reasoning . See also abductive reasoning .
A form of reasoning that employs a “bottom-up” approach to drawing conclusions: it begins with the collection of data relevant to a particular question and then seeks to build an argument or theory based on an analysis of that data. Induction is observation first, followed by an idea that could explain what has been observed. This form of reasoning is often used in qualitative research and seldom used in qualitative research. Compare to deductive reasoning . See also abductive reasoning .
An “interpretivist” form of reasoning in which “most likely” conclusions are drawn, based on inference. This approach is often used by qualitative researchers who stress the recursive nature of qualitative data analysis. Compare with deductive reasoning and inductive reasoning .
A form of social science research that generally follows the scientific method as established in the natural sciences. In contrast to idiographic research , the nomothetic researcher looks for general patterns and “laws” of human behavior and social relationships. Once discovered, these patterns and laws will be expected to be widely applicable. Quantitative social science research is nomothetic because it seeks to generalize findings from samples to larger populations. Most qualitative social science research is also nomothetic, although generalizability is here understood to be theoretical in nature rather than statistical . Some qualitative researchers, however, espouse the idiographic research paradigm instead.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Usability testing
Run remote usability tests on any digital product to deep dive into your key user flows
- Product analytics
Learn how users are behaving on your website in real time and uncover points of frustration
- Research repository
A tool for collaborative analysis of qualitative data and for building your research repository and database.
- Trymata Blog
How-to articles, expert tips, and the latest news in user testing & user experience
- Knowledge Hub
Detailed explainers of Trymata’s features & plans, and UX research terms & topics
- Plans & Pricing
Get paid to test
- User Experience (UX) testing
- User Interface (UI) testing
- Ecommerce testing
- Remote usability testing
- Plans & Pricing
- Customer Stories
How do you want to use Trymata?
Conduct user testing, desktop usability video.
You’re on a business trip in Oakland, CA. You've been working late in downtown and now you're looking for a place nearby to grab a late dinner. You decided to check Zomato to try and find somewhere to eat. (Don't begin searching yet).
- Look around on the home page. Does anything seem interesting to you?
- How would you go about finding a place to eat near you in Downtown Oakland? You want something kind of quick, open late, not too expensive, and with a good rating.
- What do the reviews say about the restaurant you've chosen?
- What was the most important factor for you in choosing this spot?
- You're currently close to the 19th St Bart station, and it's 9PM. How would you get to this restaurant? Do you think you'll be able to make it before closing time?
- Your friend recommended you to check out a place called Belly while you're in Oakland. Try to find where it is, when it's open, and what kind of food options they have.
- Now go to any restaurant's page and try to leave a review (don't actually submit it).
What was the worst thing about your experience?
It was hard to find the bart station. The collections not being able to be sorted was a bit of a bummer
What other aspects of the experience could be improved?
Feedback from the owners would be nice
What did you like about the website?
The flow was good, lots of bright photos
What other comments do you have for the owner of the website?
I like that you can sort by what you are looking for and i like the idea of collections
You're going on a vacation to Italy next month, and you want to learn some basic Italian for getting around while there. You decided to try Duolingo.
- Please begin by downloading the app to your device.
- Choose Italian and get started with the first lesson (stop once you reach the first question).
- Now go all the way through the rest of the first lesson, describing your thoughts as you go.
- Get your profile set up, then view your account page. What information and options are there? Do you feel that these are useful? Why or why not?
- After a week in Italy, you're going to spend a few days in Austria. How would you take German lessons on Duolingo?
- What other languages does the app offer? Do any of them interest you?
I felt like there could have been a little more of an instructional component to the lesson.
It would be cool if there were some feature that could allow two learners studying the same language to take lessons together. I imagine that their screens would be synced and they could go through lessons together and chat along the way.
Overall, the app was very intuitive to use and visually appealing. I also liked the option to connect with others.
Overall, the app seemed very helpful and easy to use. I feel like it makes learning a new language fun and almost like a game. It would be nice, however, if it contained more of an instructional portion.
All accounts, tests, and data have been migrated to our new & improved system!
Use the same email and password to log in:
Legacy login: Our legacy system is still available in view-only mode, login here >
What’s the new system about? Read more about our transition & what it-->
25 Essential Qualitative Research Questions with Context
Conduct End-to-End User Testing & Research
- Health and Well-being:
Question: How do individuals with chronic illnesses perceive and manage their overall well-being?
Context: This question aims to explore the subjective experiences of individuals living with chronic illnesses, focusing on their perceptions of well-being and the strategies they employ to manage their health.
Question: What are the experiences of teachers implementing project-based learning in high school science classrooms?
Context: This question delves into the qualitative aspects of teaching practices, seeking to understand the lived experiences of teachers as they implement a specific instructional approach (project-based learning) in a particular academic context (high school science classrooms).
Question: How do marginalized communities perceive and navigate social inclusion in urban environments?
Context: This question addresses the sociological dimensions of social inclusion within urban settings, focusing on the perspectives and strategies of marginalized communities as they navigate societal structures.
- Psychology:
Question: What are the coping mechanisms employed by individuals facing post-traumatic stress disorder?
Context: This question explores the psychological experiences of individuals dealing with post-traumatic stress disorder, aiming to uncover the qualitative aspects of coping strategies and mechanisms.
- Anthropology:
Question: How does a specific cultural group express identity through traditional rituals and ceremonies?
Context: This anthropological question focuses on cultural practices and rituals as expressions of identity within a specific cultural group, aiming to uncover the meanings and functions of these traditions.
- Gender Studies:
Question: What are the lived experiences of transgender individuals in the workplace, particularly regarding inclusion and discrimination?
Context: This question within gender studies explores the qualitative dimensions of transgender individuals’ workplace experiences, emphasizing the nuanced aspects of inclusion and discrimination they may encounter.
- Environmental Studies:
Question: How do local communities perceive and respond to environmental conservation efforts in their region?
Context: This question addresses the intersection of environmental studies and sociology, aiming to understand the qualitative perspectives of local communities toward conservation initiatives, exploring their perceptions and responses.
- Business and Management:
Question: How do employees perceive leadership styles and their impact on workplace culture?
Context: Within the realm of business and management, this question explores the qualitative aspects of organizational culture, focusing on employees’ perceptions of leadership styles and their influence on the workplace environment.
- Technology and Society:
Question: What are the social implications and user experiences of emerging technologies in the context of augmented reality applications?
Context: This question within the field of technology and society investigates the qualitative dimensions of user experiences and social implications related to the adoption of augmented reality applications.
- Communication Studies:
Question: How do individuals from diverse cultural backgrounds interpret and respond to media representations of body image?
Context: This question explores the intersection of communication studies and cultural studies, aiming to understand the qualitative variations in how individuals from diverse cultural backgrounds interpret and respond to media depictions of body image.
- Political Science:
Question: What are the public perceptions and attitudes toward government policies on climate change?
Context: Within political science, this question delves into the qualitative aspects of public opinion, seeking to understand how individuals perceive and respond to government policies related to climate change.
- Cultural Studies:
Question: How do international students experience acculturation and adaptation in a foreign academic environment?
Context: This question within cultural studies explores the qualitative dimensions of acculturation and adaptation, focusing on the experiences of international students within the context of a foreign academic environment.
- Family Studies:
Question: How do families navigate and negotiate roles and responsibilities in the context of remote work?
Context: In the domain of family studies, this question addresses the qualitative aspects of family dynamics, examining how families navigate and negotiate roles and responsibilities in the context of remote work.
- Public Health:
Question: How do community members perceive and engage with public health campaigns aimed at promoting vaccination in underserved urban areas?
Context: This public health question investigates the qualitative aspects of community perceptions and engagement with vaccination campaigns, particularly in urban areas with limited access to healthcare resources.
- Urban Planning:
Question: What are the experiences of residents in gentrifying neighborhoods regarding changes in their community dynamics, affordability, and social cohesion?
Context: Within urban planning, this question explores the qualitative dimensions of gentrification, focusing on residents’ lived experiences and perceptions of neighborhood transformations.
- Literature and Cultural Criticism:
Question: How do contemporary authors use literature to critique and challenge societal norms around gender roles and identity?
Context: In the realm of literature and cultural criticism, this question examines the qualitative dimensions of literary works, exploring how authors use their craft to challenge and critique societal norms related to gender.
- Social Work:
Question: What are the perceptions of social workers regarding the challenges and opportunities in providing mental health support to homeless populations?
Context: This social work question addresses the qualitative aspects of mental health support within homeless populations, exploring social workers’ perspectives on challenges and opportunities in their roles.
- Tourism and Hospitality:
Question: How do tourists from different cultural backgrounds experience and interpret authenticity in local culinary traditions?
Context: Within tourism and hospitality, this question explores the qualitative aspects of cultural experiences, focusing on tourists’ perceptions and interpretations of authenticity in local culinary traditions.
- Media and Entertainment:
Question: How do audiences engage with and interpret representations of diverse identities in streaming platforms’ original content?
Context: In the realm of media and entertainment, this question investigates the qualitative dimensions of audience engagement and interpretation of diverse identities in content produced by streaming platforms.
- Historical Studies:
Question: What are the narratives and memories of individuals who lived through a significant historical event, and how have these narratives evolved over time?
Context: Within historical studies, this question explores the qualitative aspects of personal narratives and memory, investigating how individuals recall and frame their experiences of a significant historical event.
- Linguistics:
Question: How do multilingual individuals navigate language use and identity in diverse linguistic environments?
Context: In the field of linguistics, this question delves into the qualitative dimensions of language use and identity, focusing on how multilingual individuals navigate linguistic diversity in their environments.
- Cybersecurity:
Question: What are the perceptions and behaviors of employees in organizations regarding cybersecurity practices, and how do these perceptions influence organizational security?
Context: Within cybersecurity, this question explores the qualitative aspects of employees’ perceptions and behaviors related to cybersecurity practices, examining their impact on organizational security.
- Human-Computer Interaction:
Question: How do users experience and adapt to voice-controlled virtual assistants in their daily lives, considering factors such as privacy concerns and usability?
Context: In human-computer interaction, this question investigates the qualitative aspects of user experiences with voice-controlled virtual assistants, considering factors such as privacy concerns and usability challenges.
- International Development:
Question: How do local communities perceive and negotiate the impacts of international development projects on their cultural and economic landscapes?
Context: This international development question explores the qualitative dimensions of community perceptions and negotiations regarding the impacts of international development projects, considering cultural and economic factors.
- Sport Psychology:
Question: What are the psychological experiences and coping mechanisms of athletes during periods of extended competition hiatus, such as the postponement of major sporting events?
Context: In sport psychology, this question delves into the qualitative aspects of athletes’ psychological experiences and coping mechanisms during extended competition hiatus, such as the postponement of major sporting events.
These additional detailed examples provide a broader perspective on qualitative research questions, covering diverse fields of study and highlighting the nuanced inquiries within each domain.
Interested in learning more about the fields of product, research, and design? Search our articles here for helpful information spanning a wide range of topics!
What is a Software Testing Tool and Choosing the Best One
What is software testing types, methods, and more, importance of software testing life cycle in development, what are the types of software testing and techniques.

Research Question Examples 🧑🏻🏫
25+ Practical Examples & Ideas To Help You Get Started
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | October 2023
A well-crafted research question (or set of questions) sets the stage for a robust study and meaningful insights. But, if you’re new to research, it’s not always clear what exactly constitutes a good research question. In this post, we’ll provide you with clear examples of quality research questions across various disciplines, so that you can approach your research project with confidence!
Research Question Examples
- Psychology research questions
- Business research questions
- Education research questions
- Healthcare research questions
- Computer science research questions
Examples: Psychology
Let’s start by looking at some examples of research questions that you might encounter within the discipline of psychology.
How does sleep quality affect academic performance in university students?
This question is specific to a population (university students) and looks at a direct relationship between sleep and academic performance, both of which are quantifiable and measurable variables.
What factors contribute to the onset of anxiety disorders in adolescents?
The question narrows down the age group and focuses on identifying multiple contributing factors. There are various ways in which it could be approached from a methodological standpoint, including both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Do mindfulness techniques improve emotional well-being?
This is a focused research question aiming to evaluate the effectiveness of a specific intervention.
How does early childhood trauma impact adult relationships?
This research question targets a clear cause-and-effect relationship over a long timescale, making it focused but comprehensive.
Is there a correlation between screen time and depression in teenagers?
This research question focuses on an in-demand current issue and a specific demographic, allowing for a focused investigation. The key variables are clearly stated within the question and can be measured and analysed (i.e., high feasibility).

Examples: Business/Management
Next, let’s look at some examples of well-articulated research questions within the business and management realm.
How do leadership styles impact employee retention?
This is an example of a strong research question because it directly looks at the effect of one variable (leadership styles) on another (employee retention), allowing from a strongly aligned methodological approach.
What role does corporate social responsibility play in consumer choice?
Current and precise, this research question can reveal how social concerns are influencing buying behaviour by way of a qualitative exploration.
Does remote work increase or decrease productivity in tech companies?
Focused on a particular industry and a hot topic, this research question could yield timely, actionable insights that would have high practical value in the real world.
How do economic downturns affect small businesses in the homebuilding industry?
Vital for policy-making, this highly specific research question aims to uncover the challenges faced by small businesses within a certain industry.
Which employee benefits have the greatest impact on job satisfaction?
By being straightforward and specific, answering this research question could provide tangible insights to employers.
Examples: Education
Next, let’s look at some potential research questions within the education, training and development domain.
How does class size affect students’ academic performance in primary schools?
This example research question targets two clearly defined variables, which can be measured and analysed relatively easily.
Do online courses result in better retention of material than traditional courses?
Timely, specific and focused, answering this research question can help inform educational policy and personal choices about learning formats.
What impact do US public school lunches have on student health?
Targeting a specific, well-defined context, the research could lead to direct changes in public health policies.
To what degree does parental involvement improve academic outcomes in secondary education in the Midwest?
This research question focuses on a specific context (secondary education in the Midwest) and has clearly defined constructs.
What are the negative effects of standardised tests on student learning within Oklahoma primary schools?
This research question has a clear focus (negative outcomes) and is narrowed into a very specific context.
Need a helping hand?
Examples: Healthcare
Shifting to a different field, let’s look at some examples of research questions within the healthcare space.
What are the most effective treatments for chronic back pain amongst UK senior males?
Specific and solution-oriented, this research question focuses on clear variables and a well-defined context (senior males within the UK).
How do different healthcare policies affect patient satisfaction in public hospitals in South Africa?
This question is has clearly defined variables and is narrowly focused in terms of context.
Which factors contribute to obesity rates in urban areas within California?
This question is focused yet broad, aiming to reveal several contributing factors for targeted interventions.
Does telemedicine provide the same perceived quality of care as in-person visits for diabetes patients?
Ideal for a qualitative study, this research question explores a single construct (perceived quality of care) within a well-defined sample (diabetes patients).
Which lifestyle factors have the greatest affect on the risk of heart disease?
This research question aims to uncover modifiable factors, offering preventive health recommendations.

Examples: Computer Science
Last but certainly not least, let’s look at a few examples of research questions within the computer science world.
What are the perceived risks of cloud-based storage systems?
Highly relevant in our digital age, this research question would align well with a qualitative interview approach to better understand what users feel the key risks of cloud storage are.
Which factors affect the energy efficiency of data centres in Ohio?
With a clear focus, this research question lays a firm foundation for a quantitative study.
How do TikTok algorithms impact user behaviour amongst new graduates?
While this research question is more open-ended, it could form the basis for a qualitative investigation.
What are the perceived risk and benefits of open-source software software within the web design industry?
Practical and straightforward, the results could guide both developers and end-users in their choices.
Remember, these are just examples…
In this post, we’ve tried to provide a wide range of research question examples to help you get a feel for what research questions look like in practice. That said, it’s important to remember that these are just examples and don’t necessarily equate to good research topics . If you’re still trying to find a topic, check out our topic megalist for inspiration.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Research ideas on Political Science
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Copyright © SurveySparrow Inc. 2024 Privacy Policy Terms of Service SurveySparrow Inc.
Qualitative Research Survey Questions: Examples and Best Practices

Kate Williams
Last Updated: 12 August 2024
10 min read

Table Of Contents
- Qualitative Research Questions
General Qualitative Research Questions
Qualitative research questions in business, qualitative analysis questions, qualitative data questions, qualitative research questions in nursing, qualitative research questions in psychology, general qualitative interview questions.
- Semi-structured Interview Questions
Research is all about exploring domains and finding new insights, and one of the drivers of this is qualitative research questions.
When asked right, these questions can dive deep into a topic, unearthing new data, information, or trends. But, you already know…it’s one of the main reasons you are here. You want to learn about the qualitative research survey questions to ask and how to tailor questions.
Well, you have come to the right place. In this blog, we will discuss the following -
What Are Qualitative Research Questions?
Qualitative questionnaire examples, types of qualitative research questions, how to write a qualitative research question.
- The Best Tool to Run Qualitative Research
Let’s get started!
Qualitative research questions are questions used to understand complex human emotions. The answers to qualitative questions can shine insight into a person's sentiments , perceptions, experiences, and more.
More importantly, these questions can help you understand the "why" and "how" behind respondent behaviors.
Related Read: Qualitative vs Quantitative: A Detailed Comparison
If you are doing online research, then maybe the following template can be helpful. The template asks qualitative survey questions that focus on understanding why your customers are choosing you over your competitors.
Qualitative Reserach Survey
Preview Template

NOTE: The above template (and 1000+) from SurveySparrow is completely free to use. So if you like it, feel free to signup!
If you are looking for research questions on qualitative research, then read on because we will be touching on all aspects that are important.
For those who find it difficult to generate survey questions, try using AI. More specifically, SurveySparrow AI .
The tool is similar to ChatGPT. Just add in the prompt and generate questions that are more tailored to your needs. And that’s not it. With another click, you’ll have your survey ready to share. How great it that, right?
The feature is available on the free forever plan of SurveySparrow. So, don’t shy away from trying out the AI magic.
Create a Qualitative Research Survey
These, as the name indicates, are the most commonly used questions across research. The questions are aimed at understanding more about a person's feelings and perspective.
Some good qualitative research questions are as follows.
- How do individuals define success in their personal and professional lives?
- What are the common coping strategies used by people experiencing grief?
- How do cultural backgrounds influence individuals' perceptions of mental health?
- What factors contribute to the sense of community among residents in urban neighborhoods?
From helping understand consumer behavior to employee experience, these questions can unearth crucial insights. Businesses can understand the expectations (and the reasons behind them) of customers and employees and strive to satisfy both.
Here are some qualitative questions you can ask.
- What are the key motivations behind consumer loyalty to a brand?
- How do employees perceive the effectiveness of remote work policies in their organization?
- What challenges do small business owners face in adapting to digital marketing?
- How do team dynamics influence project outcomes in collaborative work environments?
These questions are mostly focused on analyzing qualitative data. The main aim is to seek and find themes, trends, or patterns within the data.
Here are some examples of qualitative analysis questions.
- What recurring themes emerge from interviews with patients regarding their treatment experiences?
- How do participants describe their feelings about the changes in their local healthcare services?
- What patterns can be identified in the narratives of individuals recovering from addiction?
- How do respondents articulate their experiences with workplace diversity initiatives?
These questions are often used during interviews or focus groups . You can use these types of qualitative questions if you want a more detailed response. In other words, it can capture more nuanced opinions and emotions of individuals.
Here are some questions to ask.
- How do individuals from different age groups perceive the impact of social media on relationships?
- What personal stories do participants share about their experiences with education during the pandemic?
- How do community members express their views on local environmental issues?
- What emotions do participants associate with their experiences of cultural identity?
These are more specific and targeted qualitative questions that can be included in healthcare surveys. It explores the patient experiences , the quality of service, and so on. The responses can help understand the challenges and coping strategies of nurses. You can use this to further improve workplace conditions and patient care.
Here are some examples of qualitative research questions in nursing.
- What are the experiences of nurses dealing with burnout in high-pressure environments?
- How do patients describe their interactions with healthcare providers during treatment?
- What factors influence nurses' decisions to stay in or leave their profession?
- How do patients perceive the quality of care received in outpatient settings?
This is yet another qualitative questionnaire with a healthcare focus. The questions asked here focus on understanding the mental health, behavior, and emotional experience of a person.
Some examples of qualitative research questions in psychology are as follows.
- How do individuals with depression describe their daily challenges and coping mechanisms?
- What are the lived experiences of people recovering from trauma?
- How do participants perceive the role of therapy in their mental health journey?
- What factors do individuals identify as contributing to their sense of self-worth?
Suggested Read: 70+ Mental Health Survey Questions for Students
Qualitative questions in interviews facilitate in-depth discussion during interviews. The questions are designed such that it encourages the participants to elaborate on their responses. These are general interview questions, so you can add them to your interviews if needed.
Here are the questions.
- Can you share a pivotal moment in your life that significantly influenced your career choices?
- How do you feel about the support systems available for mental health in your community?
- What challenges have you faced in maintaining work-life balance, and how have you addressed them?
- Can you describe your experience with a specific program or service that impacted your life?
Semi-structured Interview Questions in Qualitative Research
If you don't know, semi-structured interviews are those with some predetermined questions with the flexibility to explore more. The questions can help researchers gather specific information, all the while probing deeper into a participant's experience.
Some semi-structured interview questions to ask.
- What are the main challenges you encounter in your current role, and how do you address them?
- Can you describe a situation where you felt particularly supported or unsupported in your work?
- How do you think your background has shaped your approach to problem-solving in your field?
- What changes would you suggest to improve the current processes in your organization?
There are four main types of qualitative research questions. Each question helps the researchers explore a bit more about a specific topic.

Descriptive Questions
These are questions for capturing the essence of experiences, behaviors, or events. The main focus is to provide a complete overview of a specific aspect of interest.
An example question - " How does someone cope with trauma? "
As you can see, the answer to this question explores all kinda coping mechanisms. This way, researchers can gather diverse responses that reveal different strategies.
Evaluative Questions
These questions are used to understand the impact of certain practices or approaches on an individual or group. This type of qualitative question is mostly used in the education section.
An example question - " What are the challenges faced by teachers in the new era of education? "
In the example, the questions prompt educators to discuss the contemporary challenges faced by teachers. By understanding the challenges, educators can measure the impact of the current educational practices and policies.
Explanatory Questions
As the name indicates, these questions strive to understand the 'how' behind a subject. It allows researchers to draw connections between variables, helping them understand complex systems.
An example question - " How does an organizational culture affect employee satisfaction? "
The question is assessing how having a good culture interconnects with employee satisfaction . The discussion can prompt organizations to look into the communication style, values, and leadership practices and how they impact job satisfaction.
Exploratory Questions
Exploratory questions are used to look into areas where we don't know much yet. The questions help researchers understand things better. Also, they can be helpful when existing knowledge or theories don't fully explain a situation.
An example question - " What are the factors influencing a student's decision to pursue higher education? "
The response to the above question can offer insights into the factors that affect student's choice to go for higher education. Researchers can further notice the patterns and themes that otherwise might not be available to understand the reasons better.
Writing research questions for qualitative research can be tricky. The question needs to prompt the participants to explore more, all the while without straying from the core topic. To create a perfect qualitative research question, you should consider the following.

#1. Define Your Objective
This is a common practice to follow. Understanding what you really want to learn or explore can help you tailor the questions.
For example , your goal might be to understand how people cope with stress.
#2. Keep the Questions Specific
Broader research questions can skew the results. So, consider making your question more focused.
Here's an example.
Focused Question - What strategies do people use to manage stress in their daily lives?
Broad Question - What do people think about stress?
#3. Ensure Researchability
The questions created should be answerable through interviews, discussion, and observations. In other words, do go for simple "Yes or No" questions .
Good Question - How does stress affect people's daily routines?
Bad Question - Is stress bad?
#4. Use Simple Language
The simpler and clearer the questions are, the easier it will be for survey participants to respond to.
So, instead of asking - What are the psychological impacts of stress? - you should ask - How does stress affect your relationships with friends and family?
See, the questions are simple enough to understand and focus on at the same time.
#5. Be Original
Try to come up with questions that haven't been widely addressed. Uniqueness is always an attractive factor. Not to mention the raw and candid responses you can get from the participants.
Run Qualitative Research Surveys with SurveySparrow
Conducting research surveys is great, but collecting the responses and analyzing them can be a tough nut to crack. This is the case, especially when the research is online, and you have a high amount of responses. This is where survey tools like SurveySparrow come in handy.

The tool offers one of the best text analysis tools to analyze qualitative data. The feature analyzes the unstructured data, groups them into categories, and analyzes them to find actionable insights.
Some key insights you can expect are as follows.
- Customer sentiment
- Most discussed topics
- Most mentioned keywords
- Key drivers
Intrigued yet?
Get in touch with our team to learn more about the feature and see how helpful it can be in helping you with your research.

Content Marketer at SurveySparrow
You Might Also Like

11 Exclusive Insights Only Qualitative Market Research Can Offer

Customer Experience
Qualitative Feedback Guide: Importance, Analysis & Template

Top 5 Employee Surveys Every Organization Should Do Every Year

Survey Respondents: Who Are They, Types, and How to Find Them

15 Working NPS Follow-Up Questions That Get The Job Done!
Start your free trial today.
No Credit Card Required. 14-Day Free Trial
Request a Demo
Want to learn more about SurveySparrow? We'll be in touch soon!
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on October 26, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
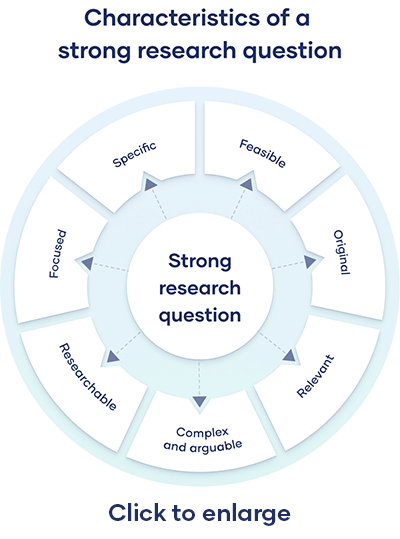
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, using sub-questions to strengthen your main research question, research questions quiz, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
| Research question formulations | |
|---|---|
| Describing and exploring | |
| Explaining and testing | |
| Evaluating and acting | is X |
Using your research problem to develop your research question
| Example research problem | Example research question(s) |
|---|---|
| Teachers at the school do not have the skills to recognize or properly guide gifted children in the classroom. | What practical techniques can teachers use to better identify and guide gifted children? |
| Young people increasingly engage in the “gig economy,” rather than traditional full-time employment. However, it is unclear why they choose to do so. | What are the main factors influencing young people’s decisions to engage in the gig economy? |
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Focused on a single topic | Your central research question should work together with your research problem to keep your work focused. If you have multiple questions, they should all clearly tie back to your central aim. |
| Answerable using | Your question must be answerable using and/or , or by reading scholarly sources on the to develop your argument. If such data is impossible to access, you likely need to rethink your question. |
| Not based on value judgements | Avoid subjective words like , , and . These do not give clear criteria for answering the question. |
Feasible and specific
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Answerable within practical constraints | Make sure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific. |
| Uses specific, well-defined concepts | All the terms you use in the research question should have clear meanings. Avoid vague language, jargon, and too-broad ideas. |
| Does not demand a conclusive solution, policy, or course of action | Research is about informing, not instructing. Even if your project is focused on a practical problem, it should aim to improve understanding rather than demand a ready-made solution. If ready-made solutions are necessary, consider conducting instead. Action research is a research method that aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as it is solved. In other words, as its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time. |

Complex and arguable
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Cannot be answered with or | Closed-ended, / questions are too simple to work as good research questions—they don’t provide enough for robust investigation and discussion. |
| Cannot be answered with easily-found facts | If you can answer the question through a single Google search, book, or article, it is probably not complex enough. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation prior to providing an answer. |
Relevant and original
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Addresses a relevant problem | Your research question should be developed based on initial reading around your . It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline. |
| Contributes to a timely social or academic debate | The question should aim to contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on. |
| Has not already been answered | You don’t have to ask something that nobody has ever thought of before, but your question should have some aspect of originality. For example, you can focus on a specific location, or explore a new angle. |
Chances are that your main research question likely can’t be answered all at once. That’s why sub-questions are important: they allow you to answer your main question in a step-by-step manner.
Good sub-questions should be:
- Less complex than the main question
- Focused only on 1 type of research
- Presented in a logical order
Here are a few examples of descriptive and framing questions:
- Descriptive: According to current government arguments, how should a European bank tax be implemented?
- Descriptive: Which countries have a bank tax/levy on financial transactions?
- Framing: How should a bank tax/levy on financial transactions look at a European level?
Keep in mind that sub-questions are by no means mandatory. They should only be asked if you need the findings to answer your main question. If your main question is simple enough to stand on its own, it’s okay to skip the sub-question part. As a rule of thumb, the more complex your subject, the more sub-questions you’ll need.
Try to limit yourself to 4 or 5 sub-questions, maximum. If you feel you need more than this, it may be indication that your main research question is not sufficiently specific. In this case, it’s is better to revisit your problem statement and try to tighten your main question up.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (“ x affects y because …”).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses . In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.

Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-questions/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

6 Main Qualitative Questions Examples
Qualitative vs. quantitative research, the importance of qualitative questions, key elements of effective qualitative research questions, role in the research design, 6 types and examples of qualitative questions, how to choose qualitative research questions, start collecting qualitative data right now, fullsession pricing plans.
- FAQs about Qualitative Research Questions
Qualitative research uncovers the details of human behavior, beliefs, and feelings. It gives us insights that numbers can't always tell.
These research questions help us understand the "how" and "why" of things.
In this article, we'll look at six examples of good qualitative questions. We aim to highlight how picking the right questions can improve your study.
It is important to understand the differences between qualitative and quantitative research.
Qualitative research questions aim to explore concepts, experiences, and perspectives. They offer the qualitative research expert an in-depth insight into the subject.
On the other hand, quantitative research questions focus on measurable aspects. They seek statistical comparisons to reach factual conclusions.
Both quantitative and qualitative questions have important roles in research. They serve unique purposes and provide different types of data.
Unlike quantitative research, qualitative questions aren't about numbers and statistical analysis. It's about understanding the reason behind data from a focus group.
Why pick qualitative research? When conducting qualitative research, you want to know why someone does something, not just count how many times they do it.
You ask, and you listen. That's the power of qualitative research. The right question is a key that unlocks valuable knowledge.
Effective qualitative research aims to unveil hidden truths. But how do you achieve it? With thought-provoking questions.
Here are the elements of the qualitative research questions for an in-depth exploration:
Open-ended and Exploratory
Qualitative research questions aim to understand the "how" and "why" of a topic. They invite people to share their views and stories.
Open-ended and exploratory questions help researchers grasp complex issues. These questions allow for diverse and detailed answers to a particular subject.
Clarity and Focus
Qualitative research questions need to be clear, focused, and brief. They help ensure the research meets its goals.
Being specific guides data collection and analysis, leading to valuable findings.
Relationships and Personal Experiences
Qualitative research questions examine how different factors relate to personal experiences and seek to understand why people act in certain ways.
They also explore how people respond to their surroundings, including culture and workplace rules.
Ethical Considerations
When creating qualitative research questions, it's important to think about ethics. Questions need to respect participants' dignity, privacy, and independence.
This makes sure that the research does not cause harm or distress. Ethics also matter when explaining and sharing results, as researchers must present data truthfully and with care.
The right qualitative research questions are crucial in the design of research projects for several reasons:
- Guidance on Research Methods: Directs the choice of qualitative research methods. Options include:
- Focus Groups: Small groups discuss topics with a moderator.
- In-Depth Interviews: Offers detailed insights from individual viewpoints.
- Qualitative Surveys: Gathers open-ended responses from a broad audience.
- Ensuring the Right Tools are Used: Matching objectives with the most suitable research tools. Enables thorough investigation and captures the complexity of experiences.
- Facilitating a Clear Understanding: Aims to uncover not just what is happening but why. Explores thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and the effects of various influences.
- Informing the Research Design: Influences all design aspects, including participant selection and analysis framework. Ensures ethical standards guide the research process.
Here are six types of qualitative questions with examples:
1. Descriptive
These questions are aimed at describing the characteristics or features of a product.
- Example 1: How do users describe their initial impressions when they first interact with our new software interface?
- Example 2: What are the specific colors and design elements that users notice about the new smartphone model when they see it for the first time?
2. Exploratory
Exploratory questions are designed to investigate how things work or how users interact with a product.
- Example 1: What strategies do users employ to navigate through the features of our newly launched app?
- Example 2: How do users attempt to solve problems when they encounter errors using our digital service platform?
3. Experiential
These questions focus on the user's experiences and emotions related to the product.
- Example 1: Can you describe a memorable experience you had while using our product?
- Example 2: What emotions do you feel when using our product under stressful conditions?
4. Comparative
Comparative questions look at differences between products, user groups, or other variables.
- Example 1: How do new users' experiences with our product compare to those of long-term users?
- Example 2: In what ways does our product perform better or worse than our main competitor's product in similar conditions?
5. Process-oriented
These questions delve into the processes or sequences of actions related to using the product.
- Example 1: Can you walk me through the process you typically follow when setting up our product for the first time?
- Example 2: What steps do you take when you troubleshoot an issue with our product?
6. Theoretical
Theoretical questions aim to understand the underlying principles or theories that explain user behavior or product dynamics.
- Example 1: What theories can explain why users prefer our product's design over traditional designs?
- Example 2: Based on your knowledge, what psychological principles might influence how users adapt to our product's innovative features?
When selecting qualitative questions, the aim is to deeply understand user interactions, perceptions, and experiences with the product.
Here are some key considerations for choosing good qualitative research questions:
- Define Your Objectives
Start by clearly defining the research objective of your product testing. What specific aspects of the product are you looking to evaluate? Are you interested in usability, aesthetics, functionality, or user satisfaction? Your objectives will guide the types of questions you need to ask. For example, if user satisfaction is your focus, you might ask about the user's emotional response to the product.
- Consider the Type of Qualitative Research
Different types of qualitative methods—such as ethnographic, narrative, phenomenological, or grounded theory—may influence the style and structure of your questions. For instance, narrative research focuses on stories and experiences, so your questions should encourage storytelling about product use.
- Ensure Questions are Open-Ended
Qualitative questions should be open-ended to allow for detailed responses that can reveal insights not anticipated by the researcher. Instead of asking, "Do you like our product?" which prompts a yes or no answer, ask, "How do you feel about our product?" to encourage a more detailed and nuanced response.
- Be Clear and Concise
While questions should allow for open-ended answers, they must also be clear and concise to avoid confusing the respondent. Ambiguity can lead to unreliable qualitative data , as different participants might interpret the questions differently.
- Sequence the Questions Logically
The order in which you ask questions can impact the flow of conversation and the quality of information gathered. Start with more general questions to make the respondent comfortable before moving to more specific or sensitive topics. This sequence helps build rapport and can lead to more honest and detailed responses later in the discussion.
- Consider the Participant
Tailor your questions to fit the background and experience level of your participants. Questions that are too technical or too basic can frustrate users or fail to elicit useful information. Understanding your audience allows you to frame questions that are appropriately challenging and engaging.
- Pilot Test Your Questions
Before finalizing your set of questions, conduct a pilot test with a small group of participants. This testing can reveal if any questions are confusing or ineffective at eliciting useful responses. Feedback from this phase can be invaluable in refining your questions.
- Be Prepared to Adapt
Finally, while it’s important to prepare your questions carefully, also be flexible during actual interactions. The conversation may reveal new paths of inquiry that are worth exploring. Being adaptive can help you capture deep insights that strictly adhering to a prepared list of questions might miss.
It takes less than 5 minutes to set up your first website or app feedback form, with FullSession , and it’s completely free!
After that, you will be able to collect high-quality feedback and avoid the guesswork.
The FullSession platform offers a 14-day free trial. It provides two paid plans—Basic and Business. Here are more details on each plan.
- The Basic plan costs $39/month and allows you to monitor up to 5,000 monthly sessions.
- The Business plan costs $149/month and helps you to track and analyze up to 25,000 monthly sessions.
- The Enterprise plan starts from 100,000 monthly sessions and has custom pricing.
If you need more information, you can get a demo.
FAQs about Qualitative Research Questions
What is a qualitative research question.
Qualitative research questions focus on ways to gather deep insights into people's experiences, beliefs, and perceptions. Such questions invite detailed narrative responses.
Can qualitative research questions change during the study?
It's not uncommon for qualitative research questions to evolve during the course of a study. As preliminary data is collected and analyzed, new insights may emerge that prompt a qualitative researcher to refine their questions.
How are qualitative questions used in business?
Businesses use qualitative questions to uncover valuable insights. They can explore customer behavior, employee satisfaction, or market trends. One example could be: "What factors drive consumer loyalty to our brand?"
Are there specific words to use in qualitative research questions?
Yes, use words like "describe," "explain," and "how" to frame qualitative questions. These terms promote more detailed and comprehensive answers. They are key to qualitative analysis.
Extract insights from Interviews. At Scale.
Research questions for qualitative research: examples.
Home » Research Questions for Qualitative Research: Examples
Qualitative Research Questions guide researchers in exploring complex human experiences, beliefs, and motivations. They delve into the "why" and "how" behind human behavior, allowing researchers to gain insights into participants' perspectives. By crafting effective questions, researchers can uncover deeper connections and meanings that quantitative data might overlook.
In the realm of qualitative research, understanding the nuances of individual experiences is crucial. These questions not only shape the direction of a study but also influence data collection methods and analysis. Developing well-formulated qualitative research questions is essential for drawing meaningful conclusions and enhancing the overall quality of research outcomes.
Importance of Qualitative Research Questions
Qualitative research questions hold significant importance in guiding effective research processes. These questions, when well-formed, illuminate the underlying motivations and perspectives of participants. They enable researchers to delve deep into complex topics, revealing nuanced insights that quantitative methods may overlook. Understanding the personal experiences and feelings of individuals is critical, especially when addressing sensitive or subjective subjects.
Moreover, qualitative research questions lay the foundation for data collection strategies, determining the types of interviews and focus groups conducted. Crafting clear and engaging questions fosters participant reflection and encourages richer responses. This richness in data empowers researchers to construct compelling narratives and more relevant findings. To maximize effectiveness, it's crucial to continually refine these questions based on initial findings, ensuring they remain aligned with the evolving landscape of the research topic. Through careful consideration of these elements, researchers can significantly enhance the quality and impact of their qualitative research.
Characteristics of Effective Qualitative Research Questions
Effective qualitative research questions serve as the cornerstone of any qualitative inquiry, guiding the research process and shaping the findings. The best qualitative research questions are open-ended, inviting participants to share their perspectives and experiences freely. This depth of engagement allows for a rich understanding of the subject matter, emphasizing the importance of context in qualitative research.
Additionally, effective questions should be clear and focused, ensuring that they address specific aspects of the phenomenon being studied. They should encourage exploration and reflection, prompting respondents to delve deeper into their thoughts. It's essential that these questions also align with the research objectives, providing a roadmap for data collection and analysis. Overall, well-crafted qualitative research questions will not only reflect the complexity of human experiences but also facilitate meaningful dialogue between researchers and participants.
Identifying the Right Qualitative Research Questions
Identifying the right qualitative research questions is crucial for obtaining meaningful insights. Effective qualitative research questions delve into participants' thoughts, feelings, and experiences to uncover rich narratives. Begin by considering the core objectives of your research. What specific phenomena or experiences do you wish to explore? This understanding will guide you in formulating questions that are open-ended and thought-provoking.
Reflect on the population or group you are studying. Who are they, and what unique perspectives might they offer? Questions should encourage respondents to share their personal viewpoints and stories. Moreover, employ techniques such as brainstorming or discussions with peers to refine your questions further. Aim for clarity and simplicity so your questions resonate with participants, encouraging deeper engagement. Remember, the quality of qualitative research questions directly influences the richness of the insights gained.
Examples of Qualitative Research Questions
Qualitative research questions aim to explore the depth of human experience and understanding. They can guide researchers in gaining insights into behaviors, motivations, and perspectives. Here are several examples that aptly illustrate this concept.
What factors influence individuals' perceptions of mental health treatment? This question seeks to understand the varying viewpoints on mental health support, potentially uncovering cultural stigmas or personal experiences that influence these perceptions.
How do parents navigate the challenges of remote learning during a pandemic? This question explores the experiences of parents, giving voice to their struggles and adaptations during unprecedented times.
What are the lived experiences of individuals who identify as LGBTQ+ in conservative communities? This inquiry invites participants to share their personal stories, shedding light on the intersection of identity and community values.
How do employees perceive workplace diversity initiatives? This question delves into the effectiveness and reception of diversity programs, revealing insights into employee sentiments and organizational culture.
These qualitative research questions exemplify the type of inquiries that can provide rich, nuanced data, enhancing our understanding of various social phenomena.
Examples in Social Sciences
Qualitative research questions in the social sciences can dramatically enhance our understanding of complex human behaviors and societal dynamics. For instance, researchers might explore how cultural narratives shape individual identities within diverse communities. Such inquiries not only reveal underlying motivations but also highlight the nuances of social interaction.
Another compelling example might involve examining the experiences of marginalized groups in educational settings. This line of questioning can uncover barriers to success and inform policies promoting equity. Ultimately, these qualitative research questions enable researchers to gather rich, descriptive data that offers deep insights into social phenomena. By focusing on lived experiences, qualitative research fosters a comprehensive understanding of the intricate web connecting individuals, their environments, and societal structures.
Examples in Education Research
In education research, qualitative research questions are essential for uncovering the complexities of teaching and learning experiences. Researchers might explore how specific educational practices influence student engagement and motivation. For instance, a question like, "How do teachers perceive the impact of technology in the classroom?" can lead to insightful narratives about educators' experiences and attitudes.
Another vital area of focus might involve understanding the challenges faced by diverse learners. Questions such as, "What are the lived experiences of students from underrepresented backgrounds in higher education?" can highlight disparities and inform strategies for improving inclusivity. By framing qualitative research questions in this manner, educators can gather rich, detailed data that informs policy, curriculum design, and pedagogical approaches, ultimately enhancing the educational experience for all students.
Conclusion on Qualitative Research Questions
Qualitative Research Questions serve as essential tools that guide the exploration of human experiences, behaviors, and emotions. These open-ended inquiries encourage deeper understanding and rich insights, allowing researchers to capture the nuances of complex phenomena. By framing effective qualitative research questions, researchers can encourage participants to share their stories, thus illuminating various aspects of the topic at hand.
In conclusion, crafting thoughtful qualitative research questions is a vital step in qualitative research design. Such questions not only drive data collection but also shape the analysis and interpretation process. Ultimately, well-formulated questions can lead to transformative findings that enhance our understanding of diverse social contexts and human experiences.
Turn interviews into actionable insights
On this Page
Random Sampling Definition in Research
You may also like, choosing the best tree testing software for ux.
Downloadable UX Research Template for Market Insights
10 usability testing questions to ask participants.
Unlock Insights from Interviews 10x faster
- Request demo
- Get started for free
Qualitative research: methods and examples
Last updated
13 April 2023
Reviewed by
Qualitative research involves gathering and evaluating non-numerical information to comprehend concepts, perspectives, and experiences. It’s also helpful for obtaining in-depth insights into a certain subject or generating new research ideas.
As a result, qualitative research is practical if you want to try anything new or produce new ideas.
There are various ways you can conduct qualitative research. In this article, you'll learn more about qualitative research methodologies, including when you should use them.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a broad term describing various research types that rely on asking open-ended questions. Qualitative research investigates “how” or “why” certain phenomena occur. It is about discovering the inherent nature of something.
The primary objective of qualitative research is to understand an individual's ideas, points of view, and feelings. In this way, collecting in-depth knowledge of a specific topic is possible. Knowing your audience's feelings about a particular subject is important for making reasonable research conclusions.
Unlike quantitative research , this approach does not involve collecting numerical, objective data for statistical analysis. Qualitative research is used extensively in education, sociology, health science, history, and anthropology.
- Types of qualitative research methodology
Typically, qualitative research aims at uncovering the attitudes and behavior of the target audience concerning a specific topic. For example, “How would you describe your experience as a new Dovetail user?”
Some of the methods for conducting qualitative analysis include:
Focus groups
Hosting a focus group is a popular qualitative research method. It involves obtaining qualitative data from a limited sample of participants. In a moderated version of a focus group, the moderator asks participants a series of predefined questions. They aim to interact and build a group discussion that reveals their preferences, candid thoughts, and experiences.
Unmoderated, online focus groups are increasingly popular because they eliminate the need to interact with people face to face.
Focus groups can be more cost-effective than 1:1 interviews or studying a group in a natural setting and reporting one’s observations.
Focus groups make it possible to gather multiple points of view quickly and efficiently, making them an excellent choice for testing new concepts or conducting market research on a new product.
However, there are some potential drawbacks to this method. It may be unsuitable for sensitive or controversial topics. Participants might be reluctant to disclose their true feelings or respond falsely to conform to what they believe is the socially acceptable answer (known as response bias).
Case study research
A case study is an in-depth evaluation of a specific person, incident, organization, or society. This type of qualitative research has evolved into a broadly applied research method in education, law, business, and the social sciences.
Even though case study research may appear challenging to implement, it is one of the most direct research methods. It requires detailed analysis, broad-ranging data collection methodologies, and a degree of existing knowledge about the subject area under investigation.
Historical model
The historical approach is a distinct research method that deeply examines previous events to better understand the present and forecast future occurrences of the same phenomena. Its primary goal is to evaluate the impacts of history on the present and hence discover comparable patterns in the present to predict future outcomes.
Oral history
This qualitative data collection method involves gathering verbal testimonials from individuals about their personal experiences. It is widely used in historical disciplines to offer counterpoints to established historical facts and narratives. The most common methods of gathering oral history are audio recordings, analysis of auto-biographical text, videos, and interviews.
Qualitative observation
One of the most fundamental, oldest research methods, qualitative observation , is the process through which a researcher collects data using their senses of sight, smell, hearing, etc. It is used to observe the properties of the subject being studied. For example, “What does it look like?” As research methods go, it is subjective and depends on researchers’ first-hand experiences to obtain information, so it is prone to bias. However, it is an excellent way to start a broad line of inquiry like, “What is going on here?”
Record keeping and review
Record keeping uses existing documents and relevant data sources that can be employed for future studies. It is equivalent to visiting the library and going through publications or any other reference material to gather important facts that will likely be used in the research.
Grounded theory approach
The grounded theory approach is a commonly used research method employed across a variety of different studies. It offers a unique way to gather, interpret, and analyze. With this approach, data is gathered and analyzed simultaneously. Existing analysis frames and codes are disregarded, and data is analyzed inductively, with new codes and frames generated from the research.
Ethnographic research
Ethnography is a descriptive form of a qualitative study of people and their cultures. Its primary goal is to study people's behavior in their natural environment. This method necessitates that the researcher adapts to their target audience's setting.
Thereby, you will be able to understand their motivation, lifestyle, ambitions, traditions, and culture in situ. But, the researcher must be prepared to deal with geographical constraints while collecting data i.e., audiences can’t be studied in a laboratory or research facility.
This study can last from a couple of days to several years. Thus, it is time-consuming and complicated, requiring you to have both the time to gather the relevant data as well as the expertise in analyzing, observing, and interpreting data to draw meaningful conclusions.
Narrative framework
A narrative framework is a qualitative research approach that relies on people's written text or visual images. It entails people analyzing these events or narratives to determine certain topics or issues. With this approach, you can understand how people represent themselves and their experiences to a larger audience.
Phenomenological approach
The phenomenological study seeks to investigate the experiences of a particular phenomenon within a group of individuals or communities. It analyzes a certain event through interviews with persons who have witnessed it to determine the connections between their views. Even though this method relies heavily on interviews, other data sources (recorded notes), and observations could be employed to enhance the findings.
- Qualitative research methods (tools)
Some of the instruments involved in qualitative research include:
Document research: Also known as document analysis because it involves evaluating written documents. These can include personal and non-personal materials like archives, policy publications, yearly reports, diaries, or letters.
Focus groups: This is where a researcher poses questions and generates conversation among a group of people. The major goal of focus groups is to examine participants' experiences and knowledge, including research into how and why individuals act in various ways.
Secondary study: Involves acquiring existing information from texts, images, audio, or video recordings.
Observations: This requires thorough field notes on everything you see, hear, or experience. Compared to reported conduct or opinion, this study method can assist you in getting insights into a specific situation and observable behaviors.
Structured interviews : In this approach, you will directly engage people one-on-one. Interviews are ideal for learning about a person's subjective beliefs, motivations, and encounters.
Surveys: This is when you distribute questionnaires containing open-ended questions
Free AI content analysis generator
Make sense of your research by automatically summarizing key takeaways through our free content analysis tool.
- What are common examples of qualitative research?
Everyday examples of qualitative research include:
Conducting a demographic analysis of a business
For instance, suppose you own a business such as a grocery store (or any store) and believe it caters to a broad customer base, but after conducting a demographic analysis, you discover that most of your customers are men.
You could do 1:1 interviews with female customers to learn why they don't shop at your store.
In this case, interviewing potential female customers should clarify why they don't find your shop appealing. It could be because of the products you sell or a need for greater brand awareness, among other possible reasons.
Launching or testing a new product
Suppose you are the product manager at a SaaS company looking to introduce a new product. Focus groups can be an excellent way to determine whether your product is marketable.
In this instance, you could hold a focus group with a sample group drawn from your intended audience. The group will explore the product based on its new features while you ensure adequate data on how users react to the new features. The data you collect will be key to making sales and marketing decisions.
Conducting studies to explain buyers' behaviors
You can also use qualitative research to understand existing buyer behavior better. Marketers analyze historical information linked to their businesses and industries to see when purchasers buy more.
Qualitative research can help you determine when to target new clients and peak seasons to boost sales by investigating the reason behind these behaviors.
- Qualitative research: data collection
Data collection is gathering information on predetermined variables to gain appropriate answers, test hypotheses, and analyze results. Researchers will collect non-numerical data for qualitative data collection to obtain detailed explanations and draw conclusions.
To get valid findings and achieve a conclusion in qualitative research, researchers must collect comprehensive and multifaceted data.
Qualitative data is usually gathered through interviews or focus groups with videotapes or handwritten notes. If there are recordings, they are transcribed before the data analysis process. Researchers keep separate folders for the recordings acquired from each focus group when collecting qualitative research data to categorize the data.
- Qualitative research: data analysis
Qualitative data analysis is organizing, examining, and interpreting qualitative data. Its main objective is identifying trends and patterns, responding to research questions, and recommending actions based on the findings. Textual analysis is a popular method for analyzing qualitative data.
Textual analysis differs from other qualitative research approaches in that researchers consider the social circumstances of study participants to decode their words, behaviors, and broader meaning.
Learn more about qualitative research data analysis software
- When to use qualitative research
Qualitative research is helpful in various situations, particularly when a researcher wants to capture accurate, in-depth insights.
Here are some instances when qualitative research can be valuable:
Examining your product or service to improve your marketing approach
When researching market segments, demographics, and customer service teams
Identifying client language when you want to design a quantitative survey
When attempting to comprehend your or someone else's strengths and weaknesses
Assessing feelings and beliefs about societal and public policy matters
Collecting information about a business or product's perception
Analyzing your target audience's reactions to marketing efforts
When launching a new product or coming up with a new idea
When seeking to evaluate buyers' purchasing patterns
- Qualitative research methods vs. quantitative research methods
Qualitative research examines people's ideas and what influences their perception, whereas quantitative research draws conclusions based on numbers and measurements.
Qualitative research is descriptive, and its primary goal is to comprehensively understand people's attitudes, behaviors, and ideas.
In contrast, quantitative research is more restrictive because it relies on numerical data and analyzes statistical data to make decisions. This research method assists researchers in gaining an initial grasp of the subject, which deals with numbers. For instance, the number of customers likely to purchase your products or use your services.
What is the most important feature of qualitative research?
A distinguishing feature of qualitative research is that it’s conducted in a real-world setting instead of a simulated environment. The researcher is examining actual phenomena instead of experimenting with different variables to see what outcomes (data) might result.
Can I use qualitative and quantitative approaches together in a study?
Yes, combining qualitative and quantitative research approaches happens all the time and is known as mixed methods research. For example, you could study individuals’ perceived risk in a certain scenario, such as how people rate the safety or riskiness of a given neighborhood. Simultaneously, you could analyze historical data objectively, indicating how safe or dangerous that area has been in the last year. To get the most out of mixed-method research, it’s important to understand the pros and cons of each methodology, so you can create a thoughtfully designed study that will yield compelling results.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- How it works

Qualitative Research Questionnaire – Types & Examples
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 19th, 2024 , Revised On August 20, 2024
Before you start your research, the first thing you need to identify is the research method . Depending on different factors, you will either choose a quantitative or qualitative study.
Qualitative research is a great tool that helps understand the depth and richness of human opinions and experiences. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data , qualitative research allows exploring and interpreting the experiences of the subject. Questionnaires, although mostly associated with quantitative research, can also be a valuable instrument in qualitative studies. Let’s explore what qualitative research questionnaires are and how you can create one.
What Is A Qualitative Research Questionnaire
Qualitative research questionnaires are a structured or semi-structured set of questions designed to gather detailed, open-ended participant responses. It allows you to uncover underlying reasons and opinions and provides insights into a particular phenomenon.
While quantitative questionnaires often have closed-ended questions and numerical responses, a qualitative questionnaire encourages participants to express themselves freely. Before you design your questionnaire, you should know exactly what you need so you can keep your questions specific enough for the participants to understand.
For example:
- Describe your experience using our product.
- How has technology impacted your work-life balance?
Types of Qualitative Research Questions With Examples
Now that you are familiar with what qualitative research questions are, let’s look at the different types of questions you can use in your survey .
Descriptive Questions
These are used to explore and describe a phenomenon in detail. It helps answer the “what” part of the research, and the questions are mostly foundational.
Example: How do students experience online learning?
Comparative Questions
This type allows you to compare and contrast different groups or situations. You can explore the differences and similarities to highlight the impact of specific variables.
Example: How do the study habits of first-year and fourth-year university students differ?
Interpretive Questions
These questions help you understand the meanings people attach to experiences or phenomena by answering the “how” and “why”.
Example: What does “success” mean to entrepreneurs?
Evaluative Questions
You can use these to assess the quality or value of something. These allow you to understand the outcomes of various situations.
Example: How effective is the new customer service training program?
Process-Oriented Questions
To understand how something happens or develops over time, researchers often use process-oriented questions.
Example: How do individuals develop their career goals?
Exploratory Questions
These allow you to discover new perspectives on a topic. However, you have to be careful that there must be no preconceived notions or research biases to it.
Example: What are the emerging trends in the mobile gaming industry?
How To Write Qualitative Research Questions?
For your study to be successful, it is important to consider designing a questionnaire for qualitative research critically, as it will shape your research and data collection. Here is an easy guide to writing your qualitative research questions perfectly.
Tip 1: Understand Your Research Goals
Many students start their research without clear goals, and they have to make substantial changes to their study in the middle of the research. This wastes time and resources.
Before you start crafting your questions, it is important to know your research objectives. You should know what you aim to discover through your research, or what specific knowledge gaps you are going to fill. With the help of a well-defined research focus, you can develop relevant and meaningful information.
Tip 2: Choose The Structure For Research Questions
There are mostly open-ended questionnaires in qualitative research. They begin with words like “how,” “what,” and “why.” However, the structure of your research questions depends on your research design . You have to consider using broad, overarching questions to explore the main research focus, and then add some specific probes to further research the particular aspects of the topic.
Tip 3: Use Clear Language
The more clear and concise your research questions are, the more effective and free from ambiguity they will be. Do not use complex terminology that might confuse participants. Try using simple and direct language that accurately conveys your intended meaning.
Here is a table to explain the wrong and right ways of writing your qualitative research questions.
| How would you characterise your attitude towards e-commerce transactions? | How do you feel about online shopping? |
| Could you elucidate on the obstacles encountered in your professional role? | What challenges do you face in your job? |
| What is your evaluation of the innovative product aesthetic? | What do you think about the new product design? |
| Can you elaborate on the influence of social networking platforms on your interpersonal connections? | How has social media impacted your relationships? |
Tip 4: Check Relevance With Research Goals
Once you have developed some questions, check if they align with your research objectives. You must ensure that each question contributes to your overall research questions. After this, you can eliminate any questions that do not serve a clear purpose in your study.
Tip 5: Concentrate On A Single Theme
While it is tempting to cover multiple aspects of a topic in one question, it is best to focus on a single theme per question. This helps to elicit focused responses from participants. Moreover, you have to avoid combining unrelated concepts into a single question.
If your main research question is complicated, you can create sub-questions with a “ladder structure”. These allow you to understand the attributes, consequences, and core values of your research. For example, let’s say your main broad research question is:
- How do you feel about your overall experience with our company?
The intermediate questions may be:
- What aspects of your experience were positive?
- What aspects of your experience were negative?
- How likely are you to recommend our company to a friend or colleague?
Types Of Survey Questionnaires In Qualitative Research
It is important to consider your research objectives, target population, resources and needed depth of research when selecting a survey method. The main types of qualitative surveys are discussed below.
Face To Face Surveys
Face-to-face surveys involve direct interaction between the researcher and the participant. This method allows observers to capture non-verbal cues, body language, and facial expressions, and helps adapt questions based on participant responses. They also let you clarify any misunderstandings. Moreover, there is a higher response rate because of personal interaction.
Example: A researcher conducting a study on consumer experiences with a new product might visit participants’ homes to conduct a detailed interview.
Telephone Surveys
These type of qualitative research survey questionnaires provide a less intrusive method for collecting qualitative data. The benefits of telephone surveys include, that it allows you to collect data from a wider population. Moreover, it is generally less expensive than face-to-face interviews and interviews can be conducted efficiently.
Example: A market research firm might conduct telephone surveys to understand customer satisfaction with a telecommunication service.
Online Surveys
Online survey questionnaires are a convenient and cost-effective way to gather qualitative data. You can reach a wide audience quickly, and participants may feel more comfortable sharing sensitive information because of anonymity. Additionally, there are no travel or printing expenses.
Example: A university might use online surveys to explore students’ perceptions of online learning experiences.
Strengths & Limitations Of Questionnaires In Qualitative Research
Questionnaires are undoubtedly a great data collection tool. However, it comes with its fair share of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s discuss the benefits of questionnaires in qualitative research and their cons as well.
| Can be inexpensive to distribute and collect | Can suffer from low response rates |
| Allow researchers to reach a wide audience | There is a lack of control over the environment |
| Consistent across participants | Once the questionnaire is distributed, it cannot be modified |
| Anonymity helps make participants feel more comfortable | Participants may not fully understand questions |
| Open-ended questions provide rich, detailed responses | Open-ended questions may not capture the right answers |
Qualitative Research Questionnaire Example
Here is a concise qualitative research questionnaire sample for research papers to give you a better idea of its format and how it is presented.
Thank you for participating in our survey. We value your feedback on our new mobile app. Your responses will help us improve the applications and better meet your needs.
Demographic Information
- Occupation:
- How long have you been using smartphones:
- How would you describe your overall experience with the new mobile app?
- What do you like most about the app?
- What do you dislike most about the app?
- Are there any specific features you find particularly useful or helpful? Please explain.
- Are there any features you think are missing or could be improved? Please elaborate.
- How easy is the app to navigate? Please explain any difficulties you encountered.
- How does this app compare to other similar apps you have used?
- What are your expectations for future updates or improvements to the app?
- Is there anything else you would like to share about your experience with the app?
Are questionnaires quantitative or qualitative research?
A survey research questionnaire can have both qualitative and quantitative questions. The qualitative questions are mostly open-ended, and quantitative questions take the form of yes/no, or Likert scale rating.
Can we use questionnaires in qualitative research?
Yes, survey questionnaires can be used in qualitative research for data collection. However, instead of a Likert scale or rating, you can post open-ended questions to your respondents. The participants can provide detailed responses to the questions asked.
Why are questionnaires good for qualitative research?
In qualitative research, questionnaires allow you to collect qualitative data. The open-ended and unstructured questions help respondents present their ideas freely and provide insights.
You May Also Like
In historical research, a researcher collects and analyse the data, and explain the events that occurred in the past to test the truthfulness of observations.
Struggling to figure out “whether I should choose primary research or secondary research in my dissertation?” Here are some tips to help you decide.
Baffled by the concept of reliability and validity? Reliability refers to the consistency of measurement. Validity refers to the accuracy of measurement.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Qualitative research examples

UserTesting

Qualitative research is a powerful tool that helps you unlock insights into the user experience—quintessential to building effective products and services. It provides a deeper understanding of complex behaviors, needs, and motivations. But what is qualitative research, and when is it ideal to use it? Let’s explore its methodologies and implementation with a few qualitative research examples.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a behavioral research method that seeks to understand the undertones, motivations, and subjective interpretations inherent in human behavior. It involves gathering nonnumerical data, such as text, audio, and video, allowing you to explore nuances and patterns that quantitative data can’t capture.
Instead of focusing on how many or how much, qualitative research questions delve into the why and how. This approach is instrumental in gaining a comprehensive understanding of a particular context, issue, or phenomenon from the perspective of those experiencing it. Examples of qualitative research questions include “How did you feel when you first used our product?” and “Could you describe your experience when you purchased a product from our website?”
Qualitative research methodology
Qualitative research design employs a variety of methodologies to collect and analyze data. The primary objective is to gather detailed and nuanced insights rather than generalizable findings. Steps include the following:
- Formulating research questions: Qualitative research begins by identifying specific research questions to guide the study. These questions should align with the research objectives and provide a clear focus for data collection and analysis.
- Selection of participants: Participant selection is a critical step in qualitative research. You must recruit participants who provide relevant and diverse perspectives on the research topic. It involves purposive sampling, where participants are chosen based on their knowledge or experiences related to the research questions.
- Data collection: Qualitative research uses various methods to collect data, such as interviews, focus groups, observation, and document analysis. You often employ multiple methods to comprehensively understand the research topic.
- Data analysis: Once the data is collected, it’s analyzed to identify recurring themes, patterns, and meanings. This analysis uses coding, thematic analysis, and constant comparison. The goal is to uncover the underlying perspectives of the participant.
- Interpretation and reporting: This is the final step in which findings are synthesized and interpreted, revealing their significance to the research questions. You can present your findings through descriptive narratives, quotes, and illustrative examples to provide a rich understanding of the research topic.
Types of qualitative research methods
The best qualitative research method primarily depends on your research questions and objectives. Different methods uncover different discernments.
One-on-one interviews
You often use one-on-one interviews to delve deep into a topic or understand individual experiences or perspectives. An interviewer asks a participant open-ended questions to understand their perspective, thoughts, feelings, and experiences regarding a specific topic, product, or service. Read about open ended vs closed ended questions to learn which questions will be most effective in an interview.
Say you’re developing a new electric vehicle mode. You can conduct one-on-one interviews to understand user experiences, probing into aspects such as comfort, design, driving experience, and more.
Focus groups
In-person or remote focus groups involve a small group of people (usually 6–10) discussing a given topic or question under the guidance of a moderator. This method is beneficial when you want to understand group dynamics or collective views. The interaction among group members can disclose awarenesses that may not arise in one-on-one interviews.
In the gaming industry, for example, you can use focus groups to explore player reactions to a new game design. You can encourage group interaction to spark discussions about usability, game mechanics, graphics, storyline, and other aspects.
Case study research
Case study research provides an in-depth analysis of a particular case (an individual, group, organization, event, etc.) within its real-life context. It’s a valuable method for exploring something in-depth and in its natural setting.
For instance, a healthcare case study could explore implementing a new electronic health record system in a hospital, focusing on challenges, successes, and lessons learned.
Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research (or an ethnographic stud y) involves an immersive investigation into a group’s behaviors, culture, and practices. It requires you to engage directly with the participants over a prolonged period in their natural environment. It can help uncover how people interact with products or services in natural settings.
A gaming organization may choose to study players in their natural gaming environments (such as home, game cafes, or e-sport tournaments) to understand their gaming habits, social interactions, and responses to specific features. These insights can inform the development of more engaging and user-friendly games.
Process of observation
The process of observation typically doesn’t involve the same level of immersion as ethnographic research. You observe and record behavior related to a specific context or activity. It can be in natural settings (naturalistic observation) or a controlled environment. It’s more about observing and recording specific behaviors or situations rather than cultural norms or dynamics.
For example, a consumer technology organization could observe how users interact with a new software interface, noting challenges, efficiencies, and overall user experience.
Record keeping
Record keeping refers to collecting and analyzing documents, records, and artifacts that provide an understanding of the study area. Record keeping allows you to access historical and contextual data that can be examined and reexamined. It’s a nonobtrusive method, meaning it doesn’t involve direct contact with the participants, nor does it affect or alter the situation you’re studying.
An online retailer might examine shopping cart abandonment records to identify at what point in the buying process customers tend to drop off. This information can help streamline the checkout process and improve conversion rates.
Qualitative research: Data collection and analysis
Data collection and analysis in qualitative research are closely linked processes that help generate meaningful and useful results.
Data collection
Data collection involves gathering rich, detailed materials to explain and understand the subject. These include interview transcripts, meeting notes, personal diaries, and photographs.
There are various qualitative data collection methods to consider depending on your research questions and the context of your study. For example, you could use one-on-one interviews to understand personal user experiences with a financial services app. A moderated focus group may be more appropriate to discuss user preferences in a new media and entertainment platform.
Data analysis
Once data are collected, the analysis process begins. It’s where you extract patterns, themes, and insights from the collected data. It’s one of the most critical aspects of qualitative research, turning raw, unstructured data into valuable insights.
Qualitative data analysis usually takes place with several steps, such as:
- Organizing and preparing the data for analysis
- Reading through the data
- Coding the data
- Generating themes or categories
- Interpreting the findings and
- Representing the data
Your choice of qualitative data analysis method depends on your research questions and the data type you collected. Common analysis methods include thematic, content, discourse, and narrative analysis. Some research platforms provide AI features that can do much of this analysis for researchers to speed up insight gathering.
When to use qualitative research
Qualitative techniques are ideal for understanding human experiences and perspectives. Here are common situations where qualitative research is invaluable:
- Exploring customer motivations, needs, behaviors, and pain points
- Gathering in-depth user feedback on products and services
- Understanding decision-making and buyer journeys
- Discovering barriers to adoption and satisfaction
- Developing hypotheses for future quantitative research
- Testing concepts , interfaces, or designs
- Identifying problems and improvement opportunities
- Learning about group norms, cultures, and social interactions
- Collecting evidence to develop theories and models
- Capturing complex, nuanced insights beyond numbers
Qualitative research methods vs. quantitative research methods
Qualitative and quantitative research differ in their approach to data collection, analysis, and the nature of the findings. Here are some key differences:
- Data collection: Qualitative research uses in-depth interviews , focus groups, observations, and analysis of documents to gather data. In contrast, quantitative research relies on structured surveys, experiments, and standard measurements.
- Analysis: Qualitative research involves analyzing textual or visual data through coding, categorization, and theme identification techniques. Quantitative research uses statistical analysis to examine numerical data for patterns, correlations, and trends.
- Sample size: Qualitative research typically involves smaller sample sizes, often selected through purposive sampling to ensure diversity and relevance. Quantitative research uses larger sample sizes to ensure statistical power and generalizability.
- Generalizability: Qualitative research seeks in-depth insight into specific contexts or groups and does not prioritize generalizability. On the other hand, quantitative research seeks to draw conclusions that apply to a broader context.
- Findings: Qualitative research generates descriptive and explanatory results that provide a deeper understanding of phenomena. Quantitative research produces numerical data that allows for statistical inferences and comparisons.
- Theory development: Qualitative research often contributes to theory development by generating new concepts, theories, or frameworks based on the rich and context-specific data collected. However, quantitative research tests preexisting theories and hypotheses using statistical models.
Advantages and strengths of qualitative research
Qualitative research enriches your research process and outcomes, making it an invaluable tool in many fields, including UX research, marketing, and digital product development.
In-depth understanding
Qualitative research provides a rich, detailed, in-depth understanding of the research subject. Proactive qualitative research takes this further with ongoing data collection, allowing organizations to continuously capture insights and adapt strategies based on evolving user needs.
Contextual data
Qualitative research collects contextually relevant data. It captures nuances that might be missed in numerically-based quantitative data, allowing you to understand the contexts in which behaviors and interactions occur.
Flexibility
The methods used in qualitative research, like interviews and focus groups, enable you to explore different topics in depth and adapt your approach based on the participants’ responses.
Human perspective
Qualitative research lets you capture human experiences and thoughts. It’s advantageous in fields such as UX research, where the human perspective is critical.
Hypothesis generation
The exploratory nature of qualitative research helps you identify new areas for exploration or generate hypotheses you can test using quantitative methods.
Trendspotting
Qualitative research reveals trends in thought and opinions, diving deeper into the problem. This is helpful when trying to understand behaviors, culture, and user interactions.
Disadvantages and limitations of qualitative research
While qualitative research offers many advantages, it’s essential to acknowledge its limitations.
Time-consuming
Collecting and analyzing qualitative data, particularly from in-depth interviews or focus groups, requires significant time investment.
Qualitative research relies on the skills and judgment of the researcher, introducing potential bias into the research process. The researcher may actively shape the research by posing questions, interpreting data, and influencing the findings.
Requires skilled researchers
The quality of qualitative research heavily depends on the researcher’s skills, experience, and perspective. A less experienced researcher may overlook important nuances, potentially affecting the depth and accuracy of the findings.
Lacks generalizability
Qualitative research often involves a smaller, nonrepresentative sample size than quantitative research. Therefore, the findings may not be generalizable to a larger context.
Limited numeric representation
Qualitative research usually focuses on words, observations, or experiences, so it doesn’t provide the numeric estimates often desired in research studies.
Challenging to replicate and standardize
Qualitative research’s inherent flexibility and context dependence make it challenging to repeat the study under the same conditions. This flexibility can often make it hard to standardize. Researchers approach and conduct the study in various ways, leading to inconsistent results and interpretations.
Difficult to measure reliability and validity
Assessing reliability and validity is more difficult with qualitative research since it relies on subjective human interpretation and has few established metrics and statistical tools compared to quantitative research. Triangulation and member checking add credibility but lack the discreteness of quantitative measures. However, there have been advancement s in the measurement of qualitative research that help to quantify its impact.
Qualitative research gives you the opportunity to dive deep into human behavior, experiences, and perceptions. It offers a prolific, intricate perspective that quantifiable data alone can’t provide. Combine qualitative research methodologies with techniques like A/B testing to gain a more holistic understanding of user experiences and preferences.
Despite its limitations, the depth and richness of data procured through qualitative research are undeniable assets. By understanding and utilizing its diverse methods, you will uncover detailed insights from your target audience and enhance your products or services to meet their needs.

The UX research methodology guidebook
Learn how to gather the user feedback you need to build best-in-class products.
In this Article
Get started now
Why is qualitative research important?
Qualitative research delves into subjective experiences and social contexts, providing in-depth insights and understanding. It provides a deep understanding of individuals’ needs, motivations, and preferences, allowing organizations to develop products and services that meet customer expectations.
What’s the difference between quantitative and qualitative methods?
Quantitative methods focus on numerical data and statistical analysis, aiming for generalizability and objectivity. Qualitative methods explore meanings, experiences, and behaviors, seeking in-depth understanding and detailed descriptions.
What are the main qualitative research approaches?
The main qualitative research approaches include one-on-one interviews, focus groups, case study research, ethnographic research, observation, and record-keeping. Each approach offers unique benefits and applications.
What is data collection?
Data collection in qualitative research involves gathering information through various methods such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and document analysis. It’s a critical step in generating meaningful insights and understanding human experiences.
How do you analyze qualitative data?
What are the ethical considerations in qualitative research.
Ethical considerations refer to the protection of participants’ rights, privacy, and confidentiality. You must obtain informed consent, maintain anonymity, and handle sensitive information responsibly. Additionally, maintaining transparency, addressing power imbalances, and conducting research unbiased and respectfully are vital ethical considerations in qualitative research.
How can I incorporate qualitative research into my study or project?
To incorporate qualitative research into your study, you must first define your research objectives to guide the choice of methodology. Next, choose a suitable qualitative method, such as interviews or focus groups. Then, collect and analyze the data using appropriate techniques and, finally, interpret and present the findings clearly and meaningfully. Remember to be mindful of the ethical considerations throughout the process.
How do you effectively communicate and present qualitative research findings to stakeholders?
For a quality presentation, create engaging visual representations, such as infographics or data visualizations, and use storytelling techniques to highlight key insights. Also, prepare concise and informative reports and organize interactive presentations or workshops to facilitate discussion and understanding.
How do you translate qualitative research findings into actionable insights?
Identify key themes linked to research goals and propose strategic solutions to address core needs and barriers. These solutions should be tailored to specific needs.
How can I ensure the validity and reliability of qualitative research findings?
About the author(s).
With UserTesting’s on-demand platform, you uncover ‘the why’ behind customer interactions. In just a few hours, you can capture the critical human insights you need to confidently deliver what your customers want and expect.
Related Blog Posts

How to build a business case for user feedback

Continuous discovery: all your questions answered

5 tips for retailers preparing for the 2024 holiday shopping season
Human understanding. Human experiences.
Get the latest news on events, research, and product launches
Oh no! We're unable to display this form.
Please check that you’re not running an adblocker and if you are please whitelist usertesting.com.
If you’re still having problems please drop us an email .
By submitting the form, I agree to the Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
Integrations
What's new?
In-Product Prompts
Participant Management
Interview Studies
Prototype Testing
Card Sorting
Tree Testing
Live Website Testing
Automated Reports
Templates Gallery
Choose from our library of pre-built mazes to copy, customize, and share with your own users
Browse all templates
Financial Services
Tech & Software
Product Designers
Product Managers
User Researchers
By use case
Concept & Idea Validation
Wireframe & Usability Test
Content & Copy Testing
Feedback & Satisfaction
Content Hub
Educational resources for product, research and design teams
Explore all resources
Question Bank
Maze Research Success Hub
Guides & Reports
Help Center
Future of User Research Report
The Optimal Path Podcast
User Research
Aug 19, 2024 • 17 minutes read
Qualitative research examples: How to unlock, rich, descriptive insights
Qualitative research uncovers in-depth user insights, but what does it look like? Here are seven methods and examples to help you get the data you need.

Armin Tanovic
Behind every what, there’s a why . Qualitative research is how you uncover that why. It enables you to connect with users and understand their thoughts, feelings, wants, needs, and pain points.
There’s many methods for conducting qualitative research, and many objectives it can help you pursue—you might want to explore ways to improve NPS scores, combat reduced customer retention, or understand (and recreate) the success behind a well-received product. The common thread? All these metrics impact your business, and qualitative research can help investigate and improve that impact.
In this article, we’ll take you through seven methods and examples of qualitative research, including when and how to use them.
Qualitative UX research made easy
Conduct qualitative research with Maze, analyze data instantly, and get rich, descriptive insights that drive decision-making.

7 Qualitative research methods: An overview
There are various qualitative UX research methods that can help you get in-depth, descriptive insights. Some are suited to specific phases of the design and development process, while others are more task-oriented.
Here’s our overview of the most common qualitative research methods. Keep reading for their use cases, and detailed examples of how to conduct them.
Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|
User interviews | |||
Focus groups | |||
Ethnographic research | |||
Qualitative observation | |||
Case study research | |||
Secondary research | |||
Open-ended surveys | to extract descriptive insights. |
1. User interviews
A user interview is a one-on-one conversation between a UX researcher, designer or Product Manager and a target user to understand their thoughts, perspectives, and feelings on a product or service. User interviews are a great way to get non-numerical data on individual experiences with your product, to gain a deeper understanding of user perspectives.
Interviews can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured . Structured interviews follow a strict interview script and can help you get answers to your planned questions, while semi and unstructured interviews are less rigid in their approach and typically lead to more spontaneous, user-centered insights.
When to use user interviews
Interviews are ideal when you want to gain an in-depth understanding of your users’ perspectives on your product or service, and why they feel a certain way.
Interviews can be used at any stage in the product design and development process, being particularly helpful during:
- The discovery phase: To better understand user needs, problems, and the context in which they use your product—revealing the best potential solutions
- The design phase: To get contextual feedback on mockups, wireframes, and prototypes, helping you pinpoint issues and the reasons behind them
- Post-launch: To assess if your product continues to meet users’ shifting expectations and understand why or why not
How to conduct user interviews: The basics
- Draft questions based on your research objectives
- Recruit relevant research participants and schedule interviews
- Conduct the interview and transcribe responses
- Analyze the interview responses to extract insights
- Use your findings to inform design, product, and business decisions
💡 A specialized user interview tool makes interviewing easier. With Maze Interview Studies , you can recruit, host, and analyze interviews all on one platform.
User interviews: A qualitative research example
Let’s say you’ve designed a recruitment platform, called Tech2Talent , that connects employers with tech talent. Before starting the design process, you want to clearly understand the pain points employers experience with existing recruitment tools'.
You draft a list of ten questions for a semi-structured interview for 15 different one-on-one interviews. As it’s semi-structured, you don’t expect to ask all the questions—the script serves as more of a guide.
One key question in your script is: “Have tech recruitment platforms helped you find the talent you need in the past?”
Most respondents answer with a resounding and passionate ‘no’ with one of them expanding:
“For our company, it’s been pretty hit or miss honestly. They let just about anyone make a profile and call themselves tech talent. It’s so hard sifting through serious candidates. I can’t see any of their achievements until I invest time setting up an interview.”
You begin to notice a pattern in your responses: recruitment tools often lack easily accessible details on talent profiles.
You’ve gained contextual feedback on why other recruitment platforms fail to solve user needs.
2. Focus groups
A focus group is a research method that involves gathering a small group of people—around five to ten users—to discuss a specific topic, such as their’ experience with your new product feature. Unlike user interviews, focus groups aim to capture the collective opinion of a wider market segment and encourage discussion among the group.
When to use focus groups
You should use focus groups when you need a deeper understanding of your users’ collective opinions. The dynamic discussion among participants can spark in-depth insights that might not emerge from regular interviews.
Focus groups can be used before, during, and after a product launch. They’re ideal:
- Throughout the problem discovery phase: To understand your user segment’s pain points and expectations, and generate product ideas
- Post-launch: To evaluate and understand the collective opinion of your product’s user experience
- When conducting market research: To grasp usage patterns, consumer perceptions, and market opportunities for your product
How to conduct focus group studies: The basics
- Draft prompts to spark conversation, or a series of questions based on your UX research objectives
- Find a group of five to ten users who are representative of your target audience (or a specific user segment) and schedule your focus group session
- Conduct the focus group by talking and listening to users, then transcribe responses
- Analyze focus group responses and extract insights
- Use your findings to inform design decisions
The number of participants can make it difficult to take notes or do manual transcriptions. We recommend using a transcription or a specialized UX research tool , such as Maze, that can automatically create ready-to-share reports and highlight key user insights.
Focus groups: A qualitative research example
You’re a UX researcher at FitMe , a fitness app that creates customized daily workouts for gym-goers. Unlike many other apps, FitMe takes into account the previous day’s workout and aims to create one that allows users to effectively rest different muscles.
However, FitMe has an issue. Users are generating workouts but not completing them. They’re accessing the app, taking the necessary steps to get a workout for the day, but quitting at the last hurdle.
Time to talk to users.
You organize a focus group to get to the root of the drop-off issue. You invite five existing users, all of whom have dropped off at the exact point you’re investigating, and ask them questions to uncover why.
A dialog develops:
Participant 1: “Sometimes I’ll get a workout that I just don’t want to do. Sure, it’s a good workout—but I just don’t want to physically do it. I just do my own thing when that happens.”
Participant 2: “Same here, some of them are so boring. I go to the gym because I love it. It’s an escape.”
Participant 3: “Right?! I get that the app generates the best one for me on that specific day, but I wish I could get a couple of options.”
Participant 4: “I’m the same, there are some exercises I just refuse to do. I’m not coming to the gym to do things I dislike.”
Conducting the focus groups and reviewing the transcripts, you realize that users want options. A workout that works for one gym-goer doesn’t necessarily work for the next.
A possible solution? Adding the option to generate a new workout (that still considers previous workouts)and the ability to blacklist certain exercises, like burpees.
3. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research is a research method that involves observing and interacting with users in a real-life environment. By studying users in their natural habitat, you can understand how your product fits into their daily lives.
Ethnographic research can be active or passive. Active ethnographic research entails engaging with users in their natural environment and then following up with methods like interviews. Passive ethnographic research involves letting the user interact with the product while you note your observations.
When to use ethnographic research
Ethnographic research is best suited when you want rich insights into the context and environment in which users interact with your product. Keep in mind that you can conduct ethnographic research throughout the entire product design and development process —from problem discovery to post-launch. However, it’s mostly done early in the process:
- Early concept development: To gain an understanding of your user's day-to-day environment. Observe how they complete tasks and the pain points they encounter. The unique demands of their everyday lives will inform how to design your product.
- Initial design phase: Even if you have a firm grasp of the user’s environment, you still need to put your solution to the test. Conducting ethnographic research with your users interacting with your prototype puts theory into practice.
How to conduct ethnographic research:
- Recruit users who are reflective of your audience
- Meet with them in their natural environment, and tell them to behave as they usually would
- Take down field notes as they interact with your product
- Engage with your users, ask questions, or host an in-depth interview if you’re doing an active ethnographic study
- Collect all your data and analyze it for insights
While ethnographic studies provide a comprehensive view of what potential users actually do, they are resource-intensive and logistically difficult. A common alternative is diary studies. Like ethnographic research, diary studies examine how users interact with your product in their day-to-day, but the data is self-reported by participants.
⚙️ Recruiting participants proving tough and time-consuming? Maze Panel makes it easy, with 400+ filters to find your ideal participants from a pool of 3 million participants.
Ethnographic research: A qualitative research example
You're a UX researcher for a project management platform called ProFlow , and you’re conducting an ethnographic study of the project creation process with key users, including a startup’s COO.
The first thing you notice is that the COO is rushing while navigating the platform. You also take note of the 46 tabs and Zoom calls opened on their monitor. Their attention is divided, and they let out an exasperated sigh as they repeatedly hit “refresh” on your website’s onboarding interface.
You conclude the session with an interview and ask, “How easy or difficult did you find using ProFlow to coordinate a project?”
The COO answers: “Look, the whole reason we turn to project platforms is because we need to be quick on our feet. I’m doing a million things so I need the process to be fast and simple. The actual project management is good, but creating projects and setting up tables is way too complicated.”
You realize that ProFlow ’s project creation process takes way too much time for professionals working in fast-paced, dynamic environments. To solve the issue, propose a quick-create option that enables them to move ahead with the basics instead of requiring in-depth project details.
4. Qualitative observation
Qualitative observation is a similar method to ethnographic research, though not as deep. It involves observing your users in a natural or controlled environment and taking notes as they interact with a product. However, be sure not to interrupt them, as this compromises the integrity of the study and turns it into active ethnographic research.
When to qualitative observation
Qualitative observation is best when you want to record how users interact with your product without anyone interfering. Much like ethnographic research, observation is best done during:
- Early concept development: To help you understand your users' daily lives, how they complete tasks, and the problems they deal with. The observations you collect in these instances will help you define a concept for your product.
- Initial design phase: Observing how users deal with your prototype helps you test if they can easily interact with it in their daily environments
How to conduct qualitative observation:
- Recruit users who regularly use your product
- Meet with users in either their natural environment, such as their office, or within a controlled environment, such as a lab
- Observe them and take down field notes based on what you notice
Qualitative observation: An qualitative research example
You’re conducting UX research for Stackbuilder , an app that connects businesses with tools ideal for their needs and budgets. To determine if your app is easy to use for industry professionals, you decide to conduct an observation study.
Sitting in with the participant, you notice they breeze past the onboarding process, quickly creating an account for their company. Yet, after specifying their company’s budget, they suddenly slow down. They open links to each tool’s individual page, confusingly switching from one tab to another. They let out a sigh as they read through each website.
Conducting your observation study, you realize that users find it difficult to extract information from each tool’s website. Based on your field notes, you suggest including a bullet-point summary of each tool directly on your platform.
5. Case study research
Case studies are a UX research method that provides comprehensive and contextual insights into a real-world case over a long period of time. They typically include a range of other qualitative research methods, like interviews, observations, and ethnographic research. A case study allows you to form an in-depth analysis of how people use your product, helping you uncover nuanced differences between your users.
When to use case studies
Case studies are best when your product involves complex interactions that need to be tracked over a longer period or through in-depth analysis. You can also use case studies when your product is innovative, and there’s little existing data on how users interact with it.
As for specific phases in the product design and development process:
- Initial design phase: Case studies can help you rigorously test for product issues and the reasons behind them, giving you in-depth feedback on everything between user motivations, friction points, and usability issues
- Post-launch phase: Continuing with case studies after launch can give you ongoing feedback on how users interact with the product in their day-to-day lives. These insights ensure you can meet shifting user expectations with product updates and future iterations
How to conduct case studies:
- Outline an objective for your case study such as examining specific user tasks or the overall user journey
- Select qualitative research methods such as interviews, ethnographic studies, or observations
- Collect and analyze your data for comprehensive insights
- Include your findings in a report with proposed solutions
Case study research: A qualitative research example
Your team has recently launched Pulse , a platform that analyzes social media posts to identify rising digital marketing trends. Pulse has been on the market for a year, and you want to better understand how it helps small businesses create successful campaigns.
To conduct your case study, you begin with a series of interviews to understand user expectations, ethnographic research sessions, and focus groups. After sorting responses and observations into common themes you notice a main recurring pattern. Users have trouble interpreting the data from their dashboards, making it difficult to identify which trends to follow.
With your synthesized insights, you create a report with detailed narratives of individual user experiences, common themes and issues, and recommendations for addressing user friction points.
Some of your proposed solutions include creating intuitive graphs and summaries for each trend study. This makes it easier for users to understand trends and implement strategic changes in their campaigns.
6. Secondary research
Secondary research is a research method that involves collecting and analyzing documents, records, and reviews that provide you with contextual data on your topic. You’re not connecting with participants directly, but rather accessing pre-existing available data. For example, you can pull out insights from your UX research repository to reexamine how they apply to your new UX research objective.
Strictly speaking, it can be both qualitative and quantitative—but today we focus on its qualitative application.
When to use secondary research
Record keeping is particularly useful when you need supplemental insights to complement, validate, or compare current research findings. It helps you analyze shifting trends amongst your users across a specific period. Some other scenarios where you need record keeping include:
- Initial discovery or exploration phase: Secondary research can help you quickly gather background information and data to understand the broader context of a market
- Design and development phase: See what solutions are working in other contexts for an idea of how to build yours
Secondary research is especially valuable when your team faces budget constraints, tight deadlines, or limited resources. Through review mining and collecting older findings, you can uncover useful insights that drive decision-making throughout the product design and development process.
How to conduct secondary research:
- Outline your UX research objective
- Identify potential data sources for information on your product, market, or target audience. Some of these sources can include: a. Review websites like Capterra and G2 b. Social media channels c. Customer service logs and disputes d. Website reviews e. Reports and insights from previous research studies f. Industry trends g. Information on competitors
- Analyze your data by identifying recurring patterns and themes for insights
Secondary research: A qualitative research example
SafeSurf is a cybersecurity platform that offers threat detection, security audits, and real-time reports. After conducting multiple rounds of testing, you need a quick and easy way to identify remaining usability issues. Instead of conducting another resource-intensive method, you opt for social listening and data mining for your secondary research.
Browsing through your company’s X, you identify a recurring theme: many users without a background in tech find SafeSurf ’s reports too technical and difficult to read. Users struggle with understanding what to do if their networks are breached.
After checking your other social media channels and review sites, the issue pops up again.
With your gathered insights, your team settles on introducing a simplified version of reports, including clear summaries, takeaways, and step-by-step protocols for ensuring security.
By conducting secondary research, you’ve uncovered a major usability issue—all without spending large amounts of time and resources to connect with your users.
7. Open-ended surveys
Open-ended surveys are a type of unmoderated UX research method that involves asking users to answer a list of qualitative research questions designed to uncover their attitudes, expectations, and needs regarding your service or product. Open-ended surveys allow users to give in-depth, nuanced, and contextual responses.
When to use open-ended surveys
User surveys are an effective qualitative research method for reaching a large number of users. You can use them at any stage of the design and product development process, but they’re particularly useful:
- When you’re conducting generative research : Open-ended surveys allow you to reach a wide range of users, making them especially useful during initial research phases when you need broad insights into user experiences
- When you need to understand customer satisfaction: Open-ended customer satisfaction surveys help you uncover why your users might be dissatisfied with your product, helping you find the root cause of their negative experiences
- In combination with close-ended surveys: Get a combination of numerical, statistical insights and rich descriptive feedback. You��’ll know what a specific percentage of your users think and why they think it.
How to conduct open-ended surveys:
- Design your survey and draft out a list of survey questions
- Distribute your surveys to respondents
- Analyze survey participant responses for key themes and patterns
- Use your findings to inform your design process
Open-ended surveys: A qualitative research example
You're a UX researcher for RouteReader , a comprehensive logistics platform that allows users to conduct shipment tracking and route planning. Recently, you’ve launched a new predictive analytics feature that allows users to quickly identify and prepare for supply chain disruptions.
To better understand if users find the new feature helpful, you create an open-ended, in-app survey.
The questions you ask your users:
- “What has been your experience with our new predictive analytics feature?"
- “Do you find it easy or difficult to rework your routes based on our predictive suggestions?”
- “Does the predictive analytics feature make planning routes easier? Why or why not?”
Most of the responses are positive. Users report using the predictive analytics feature to make last-minute adjustments to their route plans, and some even rely on it regularly. However, a few users find the feature hard to notice, making it difficult to adjust their routes on time.
To ensure users have supply chain insights on time, you integrate the new feature into each interface so users can easily spot important information and adjust their routes accordingly.
💡 Surveys are a lot easier with a quality survey tool. Maze’s Feedback Surveys solution has all you need to ensure your surveys get the insights you need—including AI-powered follow-up and automated reports.
Qualitative research vs. quantitative research: What’s the difference?
Alongside qualitative research approaches, UX teams also use quantitative research methods. Despite the similar names, the two are very different.
Here are some of the key differences between qualitative research and quantitative research .
Research type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Qualitative research | . | |||
Quantitative research |
Before selecting either qualitative or quantitative methods, first identify what you want to achieve with your UX research project. As a general rule of thumb, think qualitative data collection for in-depth understanding and quantitative studies for measurement and validation.
Conduct qualitative research with Maze
You’ll often find that knowing the what is pointless without understanding the accompanying why . Qualitative research helps you uncover your why.
So, what about how —how do you identify your 'what' and your 'why'?
The answer is with a user research tool like Maze.
Maze is the leading user research platform that lets you organize, conduct, and analyze both qualitative and quantitative research studies—all from one place. Its wide variety of UX research methods and advanced AI capabilities help you get the insights you need to build the right products and experiences faster.
Frequently asked questions about qualitative research examples
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a research method that aims to provide contextual, descriptive, and non-numerical insights on a specific issue. Qualitative research methods like interviews, case studies, and ethnographic studies allow you to uncover the reasoning behind your user’s attitudes and opinions.
Can a study be both qualitative and quantitative?
Absolutely! You can use mixed methods in your research design, which combines qualitative and quantitative approaches to gain both descriptive and statistical insights.
For example, user surveys can have both close-ended and open-ended questions, providing comprehensive data like percentages of user views and descriptive reasoning behind their answers.
Is qualitative or quantitative research better?
The choice between qualitative and quantitative research depends upon your research goals and objectives.
Qualitative research methods are better suited when you want to understand the complexities of your user’s problems and uncover the underlying motives beneath their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Quantitative research excels in giving you numerical data, helping you gain a statistical view of your user's attitudes, identifying trends, and making predictions.
What are some approaches to qualitative research?
There are many approaches to qualitative studies. An approach is the underlying theory behind a method, and a method is a way of implementing the approach. Here are some approaches to qualitative research:
- Grounded theory: Researchers study a topic and develop theories inductively
- Phenomenological research: Researchers study a phenomenon through the lived experiences of those involved
- Ethnography: Researchers immerse themselves in organizations to understand how they operate
Qualitative Research Definition
Qualitative research methods and examples, advantages and disadvantages of qualitative approaches, qualitative vs. quantitative research, showing qualitative research skills on resumes, what is qualitative research methods and examples.
- Share on Twitter Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn Share on LinkedIn

Forage puts students first. Our blog articles are written independently by our editorial team. They have not been paid for or sponsored by our partners. See our full editorial guidelines .
Table of Contents
Qualitative research seeks to understand people’s experiences and perspectives by studying social organizations and human behavior. Data in qualitative studies focuses on people’s beliefs and emotional responses. Qualitative data is especially helpful when a company wants to know how customers feel about a product or service, such as in user experience (UX) design or marketing .
Researchers use qualitative approaches to “determine answers to research questions on human behavior and the cultural values that drive our thinking and behavior,” says Margaret J. King, director at The Center for Cultural Studies & Analysis in Philadelphia.
Data in qualitative research typically can’t be assessed mathematically — the data is not sets of numbers or quantifiable information. Rather, it’s collections of images, words, notes on behaviors, descriptions of emotions, and historical context. Data is collected through observations, interviews, surveys, focus groups, and secondary research.
However, a qualitative study needs a “clear research question at its base,” notes King, and the research needs to be “observed, categorized, compared, and evaluated (along a scale or by a typology chart) by reference to a baseline in order to determine an outcome with value as new and reliable information.”

Quantium Data Analytics
Explore the power of data and its ability to power breakthrough possibilities for individuals, organisations and societies with this free job simulation from Quantium.
Avg. Time: 4 to 5 hours
Skills you’ll build: Data validation, data visualisation, data wrangling, programming, data analysis, commercial thinking, statistical testing, presentation skills
Who Uses Qualitative Research?
Researchers in social sciences and humanities often use qualitative research methods, especially in specific areas of study like anthropology, history, education, and sociology.
Qualitative methods are also applicable in business, technology , and marketing spaces. For example, product managers use qualitative research to understand how target audiences respond to their products. They may use focus groups to gain insights from potential customers on product prototypes and improvements or surveys from existing customers to understand what changes users want to see.
Other careers that may involve qualitative research include:
- Marketing analyst
- UX and UI analyst
- Market researcher
- Statistician
- Business analyst
- Data analyst
- Research assistant
- Claims investigator

Electronic Arts Product Management
Learn how product managers leverage qualitative and other types of research to build and improve products in this free job simulation from EA.
Avg. Time: 1 to 2 hours
Skills you’ll build: Critical thinking, problem solving, performance metrics, written communication, project planning
Good research begins with a question, and this question informs the approach used by qualitative researchers.
Grounded Theory
Grounded theory is an inductive approach to theory development. In many forms of research, you begin with a hypothesis and then test it to see if you’re correct. In grounded theory, though, you go in without any assumptions and rely on the data you collect to form theories. You start with an open question about a phenomenon you are studying and collect and analyze data until you can form a fully-fledged theory from the information.
Example: A company wants to improve its brand and marketing strategies. The company performs a grounded theory approach to solving this problem by conducting interviews and surveys with past, current, and prospective customers. The information gathered from these methods helps the company understand what type of branding and marketing their customer-base likes and dislikes, allowing the team to inductively craft a new brand and marketing strategy from the data.
Action Research
Action research is one part study and one part problem-solving . Through action research, analysts investigate a problem or weakness and develop practical solutions. The process of action research is cyclical —- researchers assess solutions for efficiency and effectiveness, and create further solutions to correct any issues found.
Example: A manager notices her employees struggle to cooperate on group projects. She carefully reviews how team members interact with each other and asks them all to respond to a survey about communication. Through the survey and study, she finds that guidelines for group projects are unclear. After changing the guidelines, she reviews her team again to see if there are any changes to their behavior.
>>MORE: Explore how action research helps consultants serve clients with Accenture’s Client Research and Problem Identification job simulation .
Phenomenological Research
Phenomenological research investigates a phenomenon in depth, looking at people’s experiences and understanding of the situation. This sort of study is primarily descriptive and seeks to broaden understanding around a specific incident and the people involved. Researchers in phenomenological studies must be careful to set aside any biases or assumptions because the information used should be entirely from the subjects themselves.
Example : A researcher wants to better understand the lived experience of college students with jobs. The purpose of this research is to gain insights into the pressures of college students who balance studying and working at the same time. The researcher conducts a series of interviews with several college students, learning about their past and current situations. Through the first few interviews, the researcher builds a relationship with the students. Later discussions are more targeted, with questions prompting the students to discuss their emotions surrounding both work and school and the difficulties and benefits arising from their situation. The researcher then analyzes these interviews, and identifies shared themes to contextualize the experiences of the students.

GE Aerospace Human Resources
Learn the research and conflict resolution skills necessary for a career in human resources in this free job simulation from GE.
Avg. Time: 3 to 4 hours
Skills you’ll build: Feedback giving, communication skills, empowering with insights, basics of lean, process mapping, continuous improvement tools, dataset handling in Excel
Ethnography
Ethnography is an immersive study of a particular culture or community. Through ethnographic research, analysts aim to learn about a group’s conventions, social dynamics, and cultural norms. Some researchers use active observation methods, finding ways to integrate themselves into the culture as much as possible. Others use passive observation, watching closely from the outside but not fully immersing themselves.
Example: A company hires an external researcher to learn what their company’s culture is actually like. The researcher studies the social dynamics of the employees and may even look at how these employees interact with clients and with each other outside of the office. The goal is to deliver a comprehensive report of the company’s culture and the social dynamics of its employees.
Case Studies
A case study is a type of in-depth analysis of a situation. Case studies can focus on an organization, belief system, event, person, or action. The goal of a case study is to understand the phenomenon and put it in a real-world context. Case studies are also commonly used in marketing and sales to highlight the benefits of a company’s products or services.
Example: A business performs a case study of its competitors’ strategies. This case study aims to show why the company should adopt a specific business strategy. The study looks at each competitor’s business structure, marketing campaigns, product offerings, and historical growth trends. Then, using this data on other businesses, the researcher can theorize how that strategy would benefit their company.
>>MORE: Learn how companies use case study interviews to assess candidates’ research and problem-solving skills.
Qualitative research methods are great for generating new ideas. The exploratory nature of qualitative research means uncovering unexpected information, which often leads to new theories and further research topics. Additionally, qualitative findings feel meaningful. These studies focus on people, emotions, and societies and may feel closer to their communities than quantitative research that relies on more mathematical and logical data.
However, qualitative research can be unreliable at times. It’s difficult to replicate qualitative studies since people’s opinions and emotions can change quickly. For example, a focus group has a lot of variables that can affect the outcome, and that same group, asked the same questions a year later, may have entirely different responses. The data collection can also be difficult and time-consuming with qualitative research. Ultimately, interviewing people, reviewing surveys, and understanding and explaining human emotions can be incredibly complex.
Find your career fit
See what career path is right for you with our free career quiz!
While qualitative research deals with data that isn’t easily manipulated by mathematics, quantitative research almost exclusively involves numbers and numerical data. Quantitative studies aim to find concrete details, like units of time, percentages, or statistics.
Besides the types of data used, a core difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the idea of control and replication.
“Qualitative is less subject to control (as in lab studies) and, therefore, less statistically measurable than quantitative approaches,” says King.
One person’s interview about a specific topic can have completely different responses than every other person’s interview since there are so many variables in qualitative research. On the other hand, quantitative studies can often be replicated. For instance, when testing the effects of a new medication, quantifiable data, like blood test results, can be repeated. Qualitative data, though, like how people feel about the medication, may differ from person to person and from moment to moment.

JPMorgan Quantitative Research
Discover how bankers use quantitative methods to analyze businesses and industry trends with this free job simulation.
Avg. Time: 6 to 7 hours
Skills you’ll build: Programming, data analysis, Python, critical thinking, statistics, dynamic programming
You can show your experience with qualitative research on your resume in your skills or work experience sections and your cover letter .
- In your skills section , you can list types of qualitative research you are skilled at, like conducting interviews, performing grounded theory research, or crafting case studies.
- In your work or internship experience descriptions , you can highlight specific examples, like talking about a time you used action research to solve a complex issue at your last job.
- In your cover letter , you can discuss in-depth qualitative research projects you’ve completed. For instance, say you spent a summer conducting ethnographic research or a whole semester running focus groups to get feedback on a product. You can talk about these experiences in your cover letter and note how these skills make you a great fit for the job.
Grow your skills and explore your career options with Forage’s free job simulations .
Image credit: Canva

Related Posts
6 negotiation skills to level up your work life, how to build conflict resolution skills: case studies and examples, what is github uses and getting started, upskill with forage.

Top companies are hiring now!

Login | Register
- Current Issues
- Previous Issues
- Editorial Team
- Managerial Board
- Become a Reviewer
- Submission Guidelines
- Harvard Citation Style
- Vancouver Citation Style
- APA Citation Style
- Download RIS
- Download BibTeX
Thematically Synthesizing the Qualitative Evidence Reporting the Impact of Poverty Alleviation Programs in Low-income Communities in South Africa: A Review
- Madoda Sitshange (University of Stellenbosch)
Significant poverty levels raise critical questions about the impact of poverty eradication programs. Literature reviews play a critical role in highlighting impactful and ineffective socio-economic approaches. This article presents a review of nine qualitative studies that were reported between 2006 and 2013 in poor urban, semi-rural, and rural communities in South Africa. The main goal of this paper is to describe how low-income communities were impacted by programs to reduce poverty. Themes on strength-based interventions, participation, and holistic-multidimensional approaches, emerge from the content analysis as the best account of the impact of community-based poverty eradication programs. Due to the qualitative nature of the small sample of studies under review, a thematic synthesis of the qualitative data provides baseline evidence for further research to assess progress in the provision of development programs, and to generate more insight to strengthen evidence-informed approaches to address persistently high rates of poverty.
Keywords: poverty eradication, community-based programs, thematic synthesis, systematic review, qualitative evidence, social development
Sitshange, M., (2024) “Thematically Synthesizing the Qualitative Evidence Reporting the Impact of Poverty Alleviation Programs in Low-income Communities in South Africa: A Review”, Social Development Issues 46(3): 7. doi: https://doi.org/10.3998/sdi.6771
Downloads: Download XML Download PDF
15 Downloads
Published on 05 sep 2024, peer reviewed, creative commons attribution 4.0, introduction.
A higher rate of poverty indicates that South Africa might not reach the 2030 National Development Plan (NDP) target of reducing poverty-induced hunger to 0 percent ( National Development Plan, 2012 ). The Human Development Report (HDR) presented data showing that 18.9 percent of the population, about 11 million South Africans, live on less than R28 ($1.90) for a day. In terms of the Human Development Index, a measurement of equality developed by the United Nations (UN) that ranks countries by analyzing their quality of life against their rate of industrial development, ranked South Africa 114 out of 189 countries due to its declining standard of living and deepening income inequality ( Human Development Report, 2022 ). Since the COVID-19 pandemic, inequality worsened as the country has dropped two levels lower on the index as a result of more than 2 million job losses ( Human Development Report, 2022 ; World Bank, 2022 ).
Consistent with the statistics that are reported by global development agencies, Statistics South Africa reported that 55.5 percent of the South African population could not afford to meet their basic needs ( Stats SA, 2017 ). In terms of the Gini coefficient index, which measures inequality on a scale from 0 to 1 (where the higher values indicate higher inequality), inequality rose from 0.66 in 1993 to 0.72 in 2006: despite a decrease from 2006 to 0.68 in 2015, South Africa is the most unequal country in the world ( Stats SA, 2017 ). The World Inequality Report presented data showing that in 2014 the richest 10 percent of the population received two-thirds of the national income, while the top 1 percent received 20 percent of the national income ( Alvaredo, Chancel, Piketty, Saez, & Zucman, 2018 ).
Women make up a large percentage of the poor. Compared to male-headed households, poverty is consistently higher in female-headed households. In 2015, poverty was found to be 51.2 percent among female-headed households compared to 31.4 percent in male-headed households ( Stats SA, 2019 ). Gender “…disparities are still predominant in South Africa’s labor market with unemployment at 29.5 for women and 26.1 for men” (National Development Agency, 2019:10). In addition to gender inequality, racial disparities continue to define post-apartheid South Africa socio-economic fault lines. While the post-1994 government social and economic transformation policies improved the living conditions of many black South Africans, many still live in poverty. Unemployment rates are 30.5 percent for black Africans and 8 percent for whites. Race still affects the ability to find a job, as well as the wages received once employed ( World Bank, 2018 ).
Literature Review
The reviewer’s content analysis of the qualitative studies under review was guided by theoretical perspectives in poverty studies. According to Bradshaw (2007) , five main theoretical perspectives provide a comprehensive view of the causes, effects, and solutions to poverty: (1) Individual deficiencies, (2) Cultural belief systems that support subcultures in poverty, (3) Political-economic distortions, (4) Geographical disparities, or (5) Cumulative and circumstantial origins.
Theoretical perspectives on poverty that proffer individualistic, systematic, and cyclical explanations are summarized in Table 1 advanced into a variety of multidimensional perspectives that inform contemporary analysis and research. According to Adetoro, Ngidi, and Danso-Abbeam (2023), “a multidimensional approach has been developed to analyze a wide range of multiple poverty interrelated levels involving severe deprivation of basic human needs, such as health, education, income-generation and living standards”. The Human Development Report (2022) links the concept of multidimensional poverty with a lack of clean water, inadequate access to healthcare services, malnutrition, poor health, and poor housing conditions.
Five theories of poverty
Theory | Causes | Effects | Solutions/Interventions/Programs |
|---|---|---|---|
Individual | Individual laziness, incompetence, inherent disabilities. | Rewards winners and punish those that don’t work hard or are lucky. | Use training and counselling to help poor individuals to overcome poverty. Safety nets to be accessible to the less fortunate. |
Cultural | Adoption of values of a sub-culture that is non-productive and contrary to success. | Re-socialization through the formation of new peer groups. | Asset-based community development. Head-start program for after-school leadership development within subculture. |
Political-economic structure | Systematic and structural barriers prevent the poor from accessing jobs, health, education, savings, and assets. | Selection criteria directly or indirectly exclude some groups based on a set of political conditions. | Policies to enforce inclusion and empowerment. |
Geographic | Socio-economic advantage is heavily determined by geographic location. | Resource distribution and economics of scale as poverty determining factors. | Area redevelopment programs, rural development policies, and urban revitalization. |
Cumulative and cyclical | Spirals of poverty are interdependent and strongly related to community dynamics. | Poverty is systematic and related to community cycles and levels of stability. | Periodic community development programs to build assets targeted at addressing individual deficiencies. |
Source: Adopted from Bradshaw (2007) .
There seem to be definite areas of alignment between the South African social security system and the multidimensional poverty formulation. The Department of Social Development provides comprehensive social assistance programs for indigent individuals and families to access a range of benefits such as cash transfers, food aid, and a range of welfare services. Free basic education, free health care, and free social housing are part of social benefits that are provided by housing, health, and education government departments. A multi-departmental approach that collectively provides a range of poverty reduction programs is consistent with a multidimensional theoretical approach to poverty that is applied on a national scale to address inequality, vulnerability, and urban-to-rural poverty ( Mert & Kadioglu, 2016 ). Uni-dimensional assessments of poverty that look at monetary value and consumption, in conjunction with broader multi-dimensional approaches that focus on child poverty, early childhood development and literacy, are indicative of a dynamic theory of poverty that incorporates most of the elements in Bradshaw’s (2007) theory of poverty which considers individualistic to economic-political factors.
Zizzamia, Schotte, and Leibbrandt (2019) posit the concept of poverty dynamics, as referring to a fluid state where individuals, families, and communities experience cyclical periods of chronic poverty, transient poverty, and vulnerable poverty. In expanding on the poverty dynamics perspective, Schotte, Zizzamia, and Leibbrandt (2018) define fluid and cyclical poverty situations as conditions where the chronic poor are trapped in poverty, the transient poor are classified as below the poverty line but with above-average chances of escaping poverty, and the vulnerable are classified as above the poverty line but with above-average chances of falling into poverty. In terms of the poverty dynamics theory, a considerable share of the South African population can be classified as the transient poor and the vulnerable group, estimated as 27 percent of the population ( Zizzamia et al., 2019 ). The poverty dynamics theory draws attention to the rural and urban working poor as most vulnerable due to economic instability and volatile labor markets, irregular forms of employment, and government incompetence, which makes poverty a constant threat in their daily lives, hence are the largest population group that are beneficiaries of poverty alleviation programs.
Contextualization
Meta-synthesizing several qualitative studies sharing similar themes and methods is a well-tested scientific method for assessing and presenting broader experiences ( Graham & Masters-Awatere, 2020 ), which only some research studies can provide. The overriding aim of this article is to present a review of a small sample of primary research studies, that apply qualitative procedures to report data on the impact of poverty eradication programs, by addressing the following questions: In what ways did beneficiaries of community-based poverty eradication programs describe, in their own words, their impact? How did the beneficiaries of poverty eradication programs perceive the extent to which their living conditions improved because of poverty eradication programs?
The two research questions that guide the content analysis of qualitative studies are aimed at highlighting practices and approaches that are associated with positive and negative program outcomes. A review that focuses on program impact might contribute to the knowledge that the implementers of social development interventions need to strengthen the provision of poverty eradication programs. Global, regional, national, and/or local poverty eradication program providers require analysis of program impact to reduce high rates of poverty. Drawing key lessons from systematic reviews, using a review of literature in the paper is in line with the consensus in the research literature that (reviews) play an important role in documenting and disseminating scientific evidence on the impact of programs ( Hlongwa & Hlongwana, 2020 ; Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ).
A review of poverty eradication programs implemented between 2006 and 2013 is intended to contribute to Lombard’s (2008) 10-year review of the implementation of the White Paper for Social Welfare (1997). The reviewer’s intention in presenting a thematic synthesis of studies focusing on poverty eradication is motivated by a need to provide another perspective on the progress of the social development approach by addressing both the root causes and effects of poverty.
Methodology
A thematic synthesis of qualitative studies on poverty eradication is guided by the question: How were the intended beneficiaries impacted by community-based poverty eradication programs? In addressing the research question, the reviewer sought to highlight themes and trends that may assist in reporting progress in the implementation of social development approaches.
The following keywords in the research report titles, abstracts, keywords, and text, guided the search for qualitative studies: “poverty/poverty-eradication/poverty-alleviation/poverty-reduction/anti-poverty”, “social exclusion”, “community-based program(s)/project(s)”, and “program/project impact”. The reviewer sourced relevant literature through an electronic search using the following databases: Social Science Citation Index on the Web of Science, Google Scholar, and the Social Science Database. A desktop internet search formed a critical part of the search, and some unpublished studies were accessed through the expert opinion of social development researchers. An online search of research reports in development studies, economics, social work, social development, politics, public health, sociology, psychology, and related social sciences and/or humanities disciplines, formed an essential part of the desktop internet search. Peer-reviewed online scientific publications were also examined. University websites were also searched for unpublished dissertations and technical research reports that focus on poverty eradication programs.
The entire search yielded studies that were reported during 2006–2013. This 10-year period is crucial for tracking and assessing progress since the social development approach became official policy, through the White Paper for Social Welfare (1997). The search for qualitative studies produced 76 research reports. The reviewer screened the 76 research studies using the inclusion and exclusion criteria, as presented in Table 2 .
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria |
|---|---|
After a comprehensive search of the literature, the reviewer applied the inclusion and exclusion criteria on the titles, abstracts, keywords, and text of the 76 reports to remove excluded and duplicated reports. While this is a review of literature, the Preferred Re-porting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) ( Shamseer et al., 2015 ) was applied by the reviewer, to explain the process used to arrive at studies selected for thematic synthesis, as outlined in Figure 1 .

Systematic review process-map.
Of the 76 studies, 16 studies were sourced through a desktop internet search, while an electronic database search yielded 60 studies. Of the 76 studies that represent data on issues related to poverty eradication, social exclusion, and community-based programs, 59 were excluded: 47 mainly because they are quantitative studies, eight use poverty definitions that are inconsistent with the literature review, another set of eight studies did not report the impact of community-based programs, while six studies neither indicate whether ethics clearance was obtained nor peer-review was conducted. Of the 17 studies that complied with the inclusion criteria, further screening narrowed down the number to 15, because two studies were duplicates. After further full-text eligibility assessment, the reviewer narrowed down the number to nine short-listed studies. After re-applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria on the short-listed studies, the reviewer arrived at nine final qualitative studies to be reviewed.
A blind procedure, where a second reviewer, without knowledge of the nine short-listed studies, repeated the process-map that is outlined above, by applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria to the 76 selected studies. The second reviewer confirmed the suitability of the nine studies selected for inclusion in the systematic review. All the included studies were debated to address any inconsistencies and areas of ambiguity as far as the inclusion and exclusion criteria required, and whether the processing of studies through the process-map was standardized and replicable. All nine studies listed in Table 2 are included mainly because of three factors: they all address “‘poverty/poverty-eradication/poverty-alleviation/poverty-reduction/anti-poverty”, “social exclusion”, “community-based program(s)/project(s)”, present qualitative data, and underwent ethics clearance or were peer-reviewed. Adato, Carter, and May (2006) explore household poverty traps and social exclusion. Mashau (2006) and Nkosi (2010) investigate the poverty situation and the impact of a strategy for poverty alleviation in rural and urban areas, while Van der Merwe (2006) provides a description and analysis of the very personal, subjective experience of poverty by Afrikaans-speaking people.
Stephen (2008) , explores factors that might have an impact on the communities’ anti-poverty projects. The study focuses on four projects: two agricultural projects and two non-agricultural projects. Blaauw, Viljoen, and Schenck’s (2011) study sought to determine the prevalence of child-headed households in Gauteng in order to establish a database and to ensure access to aid programs by needy child-headed households. Strydom, Wessels, and Strydom’s (2010) study assesses the effects of health issues and poverty on families in rural areas. Kaeana and Ross (2012) investigated beneficiaries’ perceptions of income-generating projects as alleviators or perpetrators of poverty, and lastly, Sikrweqe (2013) assessed whether a local program contributed towards achieving the goals of poverty reduction.
Table 3 further outlines the sample number and type, the age range of the participants, data collection procedures, and the geographical locations where each study was conducted. All the studies present qualitative data. A study with the smallest sample number reported four participants and a study with the largest sample size reported 700 participants. The age range of the respondents in all nine studies fell within the 18–60 bracket. All the studies (n = 9) interviewed people living and working in underprivileged communities. An overview of geographical areas where the qualitative data were collected shows that the studies were collected in five provinces in South Africa: Gauteng (n = 3), KwaZulu-Natal (n = 2), Limpopo (n = 2), Northern Cape (n = 1), and the Eastern Cape (n = 1).
Studies included in the systematic review.
Publication | Aim of study | Sample size | Sample type | Age | Data | Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explores household poverty traps and social exclusion | 50 households | Poorest households in rural, semi-urban, and urban areas | Not specified | In-depth, semi-structured interviews | KwaZulu-Natal |
| To investigate the poverty situation and outline a strategy for poverty alleviation in the rural area of Mashau | 118 households | Key role-players | 18–21 | In-depth, semi-structured interviews | Limpopo Province, Mashau Village |
| To provide a description and analysis of the very personal, subjective experience of poverty by this group of Afrikaans-speaking people | 4 households | Residents of a shelter for destitute individuals and families | Not specified | Individual unstructured interviews | Vaal Triangle, Southern Gauteng |
| To explore factors that might have an impact on the communities’ anti-poverty projects. The study focuses on four projects: two agricultural projects and two non-agricultural projects | 49 households | Members of a community-based program | 18–35 | Self-administered questionnaires and structured interviews | Limpopo Province, Ga-Molepo |
| To assess the effects of health issues and poverty on families in rural areas. | 700 households | Low-income residents | Not specified | Semi-structured interviews | Northern Cape, in Heuningvlei |
| To assess the impact of the Mashunka Flagship project as an approach to poverty alleviation | 20 households | Members of the Mashunka flagship program | 18–50 | In-depth interviews | KwaZulu-Natal, Msinga Municipality |
| To determine the prevalence of child-headed households in Gauteng in order to establish a database and to ensure access to aid programs by needy child-headed households | 61 households | Residents of Gauteng | Not specified | Semi-structured interviews and questionnaires | Gauteng Province |
| To investigate beneficiaries’ perceptions of income-generating projects as alleviators or perpetrators of poverty | 20 households | Beneficiaries of an income-generating project | 20–60 | Semi-structured interviews | Sedibeng, Gauteng Province |
| To establish whether KSD municipality’s IDP contributes towards achieving the goals of poverty reduction | 20 households | Residents and municipal directors | 30–49 | Questionnaire and semi-structured interviews | Eastern Cape, King Sabata Dalindyebo |
Guided by relevant theoretical perspectives in poverty, social development, and community-based programs, the reviewer content analyzed the studies by coding of text “line-by-line”; followed by the development of “descriptive themes”; and lastly, the generation of “analytical themes” ( Thomas & Harden, 2008 ; Tong, Palmer, Craig, & Strippoli, 2016 ). “Thematic analysis” completed the identification and confirmation of emerging themes ( Thomas & Harden, 2008 ), and allowed the reviewer to present the qualitative evidence directly from the studies under review. The procedure that was followed by the reviewer enabled explicit translation of the qualitative data by “…synthesizing them in a transparent way, and facilitating the explicit production of new concepts and hypotheses” ( Thomas & Harden, 2008 , p. 1).
Results and Discussion
A thematic synthesis of 2006 to 2013 qualitative studies on the impact of community-based women empowerment programs.
The discussion of findings is presented under three themes: strength-based interventions, participation, and holistic, multi-dimensional approaches. Guided by the literature on poverty eradication, social exclusion, and community-based programs, a comprehensive content analysis of the qualitative data from the studies selected for review enabled the extraction and presentation of the following discussion of the research results.
Strength-based interventions
A content analysis of community-based poverty eradication programs shows that developing the strength of indigent individuals and families is crucial. Strydom et al.’s (2010) study highlights the importance of linkages between the well-being and happiness of beneficiaries and social services providers’ acceptance and enhancement of their (i.e., beneficiaries of poverty-eradication programs) strengths, and material and human resources. The impact of programs, in other words, will be greatly enhanced by leveraging underutilized personal and group coping and survival capabilities. Leveraging underutilized coping and survival capabilities might sustain the structure and functioning of indigent individuals, families, and communities ( Strydom et al., 2010 ). In an urban setting, Van der Merwe (2006 , p.141) posits that psychosocial programs “…need to capitalise on existing strengths and cultivate new personal strengths such as self-confidence, creativity, and capacity for hard work, self-determination, optimism and faith”.
Authors specifically identify social connections, as opposed to social isolation and social exclusion, as crucial for community-based programs to empower indigent individuals and families, to access income-generating opportunities or to cope better in times of periodical cycles of vulnerability to poverty ( Adato et al., 2006 ; Blaauw et al., 2011 ; Sikrweqe, 2013 ; Strydom et al., 2010 ).
Community-based poverty eradication programs that focus on building the strengths of women and children report a crucial area that social service providers need to focus on. Nkosi’s (2010) study found that child-headed and female-headed households went beyond being passive beneficiaries of cash transfers, to using limited savings to access crucial life-skills that translated into increased school attendance, fewer risks of malnutrition, and exposure to abuse. According to Blaauw et al. (2011) , school-based poverty eradication programs play a crucial role in improving the socioeconomic circumstances of child-headed households, primarily by directly linking the development of strengths to child-headed households to directly accessing social services and cash-transfers, rather than relying on adults who might abuse the resources. Even though poverty and the scarcity of resources can cause conflict in households, the respondents in Strydom et al.’s (2010) study felt strongly that the family was their important strength. As a strength that poverty eradication programs must build on, authors present data confirming the family as a form of social capital that is best placed to stabilize basic livelihood levels, owing to the observation that families have the capacity to adapt, change, and become closer in times of social and economic shocks ( Mashau, 2006 ; Stephen, 2008 ).
Gaps in eradicating poverty through the development of individual and family strengths receive great attention in the research literature. According to Adato et al. (2006 , p. 226), for individuals and families that are considered to be living below the poverty line, “…social capital at best helps stabilize livelihoods at low levels and does little to promote upward mobility”. Access to programs that provide a combination of assets with financial value, income-generating capabilities, and access to markets to build on assets over time, could sustainably address both the root causes and effects of poverty, and upward social mobility ( Adato et al., 2006 ; Stephen, 2008 ; Van der Merwe, 2006 ). Focusing poverty eradication programs on individuals and families has its critical limitations. According to Blaauw et al.’s (2011) post-intervention analysis, 26.2 percent of households cannot support even one person with their total monthly income, while less than 40 percent would be able to support a household of two to three members, with only 11.5 percent able to support a household size of four people, and none of the respondents’ households able to support a household size of six members. Holistic and multi-dimensional poverty eradication programs require evidence-informed approaches to supplement and complement strength-based interventions that support individuals, families, and larger communities.
Participation
Participation allowed the beneficiaries of community-based poverty eradication programs to highlight progress and identify gaps in service delivery ( Kaeana & Ross, 2012 ). Sikrweqe’s (2013) study echoes the theme of opening program monitoring and evaluating the voices of the beneficiaries, by presenting data showing that ward committees went beyond improving the participation of beneficiaries, and ensuring that the beneficiaries directly influence decisions about future developments in the neighborhood. The ability of ordinary members of society to influence decisions about development issues deepens democratic practices and governance ( Sikrweqe, 2013 ). Mashau’s (2006) assessment of a flagship local job creation project, highlights a human-centered approach to a collaborative approach to poverty eradication, that brought together the combined strengths of all key stakeholders, ordinary community members, government officials, business people, and non-governmental and faith-based organizations.
At a more practical level, Van der Merwe’s (2006) study emphasizes that, where possible, the beneficiaries must participate in all important areas and phases of program implementation to promote the type of community ownership that will invest in long-term sustainability. In recognition that participation in community-based poverty eradication programs is easier said than done, authors recommend further in-depth research analysis of the impact of participation on the outcomes of poverty eradication programs ( Blaauw et al., 2011 ; Kaeana & Ross, 2012 ; Mashau, 2006 ; Nkosi, 2010 ; Stephen, 2008 ; Van der Merwe, 2006 ). According to Stephen (2008) , least participatory programs tended to have pensioners as the majority of beneficiaries, thereby sensitizing social service providers to be more realistic and strategic in customizing models of participation to be more consistent with the capabilities of the intended beneficiaries.
The main conclusion in Kaeana and Ross’s (2012) study is that income-generating projects achieved their aims to some extent, but there were areas of improvement in terms of the participation of beneficiaries in decision-making. In reiterating the theme of the importance and limitations of participation, Adato et al. (2006) assert that while the impact of the beneficiaries’ participation in poverty eradication programs cannot be denied, there is no compelling evidence that community participation in poverty eradication translated directly into economic advancement and the accumulation of assets with long-term financial value. The link between the level of beneficiary participation in program processes to the reduction of poverty appears to be complex and still to be sufficiently examined, especially when participation occurs within holistic and multi-dimensional approaches.
Holistic and multi-dimensional approaches
A comprehensive and integrated research-informed approach to establish a local and contextually grounded database, according to Blaauw et al. (2011) and Strydom et al. (2010) , sets a standard for poverty to be addressed as the main target of health, development, education, employment creation, and environmental programs. A holistic, multi-disciplinary, and multi-dimensional approach to poverty eradication could be more impactful, in respect of the data that shows that poverty mainly manifests itself in the deprivation of income-generating opportunities, housing, lack of clean water, sanitation, health services, electricity, literacy, public infra-structure, and so on ( Mashau, 2006 ; Sikrweqe, 2012; Stephen, 2008 ; Strydom et al., 2010 ).
According to Kaeana and Ross’s (2012) study, a holistic and multi-pronged approach to poverty eradication needs to integrate income generation and employment creation, the provision of social and physical infrastructure including clinics and schools, measures to address social exclusion and institutionalized racism, xenophobia and sexism, the promotion of sustainable livelihoods, and the dissemination of the type of knowledge and skills that fosters human development at the community level. Community-based programs to raise awareness, through education and skills development are central themes that are frequently reported by the studies under review. For instance, more impactful community-based poverty eradication programs had more beneficiaries with secondary school education, while the worst performing were fewer ( Blaauw et al., 2011 ; Mashau, 2006 ; Nkosi, 2010 ; Van Der Merwe, 2006 ).
Deeper structural changes require innovative and novel approaches in light of growing levels of poverty, unemployment, and socio-economic inequality. According to some authors, the broader problem of “…poverty alleviation seems unlikely to be resolved until deeper structural changes make time and markets work more effectively for the broader community of all South Africans” ( Adato et al., 2006 , p. 245). A theme that cuts across most studies is that current social security programs play a significant role in alleviating poverty, but because of the growing inequality, the social security systems need to be improved to address gaps and shortcomings ( Adato et al., 2006 ; Kaeana & Ross, 2012 ; Sikrweqe, 2012). The research participants in Nkosi’s (2010) study, correctly recommend that gaps and weaknesses in social security programs can be best addressed through intersectoral collaborations between governmental and non-governmental service providers, in conjunction with the training of beneficiaries as a key element towards the sustenance of program impact and comprehensive service delivery. The findings are consistent will the assertion that policymakers recognize the integrated approach as more effective in low-middle-income countries ( Kumar & Cheng, 2024 ).
Recommendations
Similar to systematic reviews, literature reviews analyze an ever-growing scope of research on “best practices” for policy-making and policy evaluation ( Sundberg & Taylor-Gooby, 2013 ; Van Rooyen, Steward, & De Wet, 2012 ). This paper reviews the qualitative evidence to highlight approaches in poverty eradication that can be inferred as impactful and ineffective, subject to more advanced analysis through large-scale reviews that apply qualitative and quantitative methods. This article recommends further systematic reviews that will analyze studies conducted between 2016 and 2023, to provide a more recent and comprehensive picture of the progress and challenges related to social development programs. Reviews place greater emphasis on transparency and accountability ( Thomas & Harden, 2008 ), by providing an overview of impactful and ineffective approaches that no single study can provide. Themes on beneficiaries’ strengths and direct involvement in crucial phases of holistic and multi-multidimensional community-development processes, emerge in the paper as significant to track in forthcoming systematic reviews. Training and research in the three themes outlined above are key areas of focus in assessing progress in the implementation of the social development approach. As noted in a related paper, training “emerges as an important option in expanding the prospects of the intended beneficiaries of community-based programs” ( Sitshange, 2022 ).
Conclusions
Reviews are critical in evaluating the impact of poverty eradication programs. According to the authors, poverty alleviation programs have been ineffective and unsustainable ( Dipela & Mohapi, 2021 ; Raniga, 2018 ), hence high rates of poverty are consistently reported by statisticians. Reviewers of research studies have a responsibility to beyond painting the impact of poverty through numbers, to highlighting the impact of programs using the voices of community members. The thematic synthesis of qualitative research studies in poverty eradication notes a gap between theory and practice. While laws, policies, and institutions are in place to eradicate poverty, reviews need to empower relevant laws, policies, and institutions to prove impact and sustainability using evidence-based frames of reference. While the review that is presented in the paper is qualitative and limited, it lays a basis for more advanced studies on the impact of poverty eradication programs on individuals and groups.
Adato, M., Carter, M. R., & May, J. (2006). Exploring poverty traps and social exclusion in South Africa using qualitative and quantitative data. The Journal of Development Studies , 42(2), 226–247. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220380500405345 https://doi.org/10.1080/00220380500405345
Adetoro, A. A., Ngidi, M. S. C., & Danso-Abbeam, G. (2023). Towards the global zero poverty agenda: Examining the multidimensional poverty situation in South Africa. SN Social Sciences , 3(148), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-023-00735-2 https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-023-00735-2
Alvaredo, F., Chancel, L., Piketty, T., Saez, E., & Zucman, G. (2018). World Inequality Report 2018, World Inequality Lab.
Blaauw, D., Viljoen, K., & Schenck, R. (2011). “Life is not pap and vleis”: Poverty in child-headed households in Gauteng. Social Work/Maatskaplike Werk , 47(2), 138–154. https://doi.org/10.15270/47-2-132 https://doi.org/10.15270/47-2-132
Bradshaw, T. K. (2007). Theories of poverty and anti-poverty programs in community development. Journal of the Community Development Society , 38(1), 7–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/15575330709490182 https://doi.org/10.1080/15575330709490182
Dipela, M. P., & Mohapi, B. (2021). Barriers affecting effective monitoring and evaluation of poverty alleviation projects within Waterberg District. Social Work/Maatskaplike Werk , 57(3), 278–301. https://doi.org/10.15270/57-3-948 https://doi.org/10.15270/57-3-948
Graham, R., & Masters-Awatere, B. (2020). Experiences of Māori of Aotearoa New Zealand’s public health system: A systematic review of two decades of published qualitative research. Aust NZ J Public Health , 44(3), 193–200. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-6405.12971 https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-6405.12971
Hlongwa, M., & Hlongwana, K. (2020). Men’s perspectives on HIV self-testing in sub-Saharan Africa: A qualitative systematic review protocol. JBI Evid Synth , 18(3), 571–575. https://doi.org/10.11124/JBISRIR-D-19-00097 https://doi.org/10.11124/JBISRIR-D-19-00097
Human Development Report. (2022). Report to explore uncertainty in the Anthropocene . United Nations: Geneva.
Kaeana, R., & Ross, E. (2012). Income-generating projects: Alleviating or perpetuating poverty. Social Work/Maatskaplike Werk , 48(1), 17–34. https://doi.org/10.15270/48-1-102 https://doi.org/10.15270/48-1-102
Kearney, M. H. (2001). Enduring love: Grounded formal theory of women’s experience of domestic violence. Research in Nursing and Health , 24(4), 270–282. https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.1029 https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.1029
Kumar, V., & Cheng, S. C. (2024). A comparative literature review of integrated approach in health care in high and low-middle-income countries. Social Development Issues , 46(1), 25–44. https://doi.org/10.3998/sdi.5294 https://doi.org/10.3998/sdi.5294
Lombard, A. (2008). The implementation of the white paper for social welfare. The Social Work Practitioner-Researcher , 20(2), 154–173. http://hdl.handle.net/2263/9739 http://hdl.handle.net/2263/9739
Mashau, T. D. (2006). Towards a strategy for poverty alleviation in Mashau . Master’s diss., North-West University.
Mert, K., & Kadioglu, H. (2016). Nursing interventions to help prevent children from working on the streets. International Nursing Review , 63(3), 429–436. https://doi.org/10.1111/inr.12301. Epub 2016 Jul 19. PMID: 27430362. https://doi.org/10.1111/inr.12301. Epub 2016 Jul 19. PMID: 27430362.
National Development Plan. (2012). National Development Plan 2030: Our future make it work . Pretoria: National Planning Commission.
Nkosi, B. W. G. (2010). An impact of flagship program: An approach to poverty alleviation . Master’s diss., University of Zululand.
Petticrew, M., & Roberts, H. (2006). Systematic reviews in the social sciences . Oxford: Blackwell.
Porritt, K., Gomersall, J. C., & Lockwood, C. S. (2014). Study selection and critical appraisal. AJN American Journal of Nurs-ing , 114(6), 47–52. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.NAJ.0000450430.97383.64 https://doi.org/10.1097/01.NAJ.0000450430.97383.64
Raniga, T. (2018). Poverty alleviation, social protection policy and sustainability of economic development cooperatives: Voices of women residing in Bhambhayi, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Social Work/Maatskaplike Werk , 54(4), 394–406. https://doi.org/10.15270/54-4-668 https://doi.org/10.15270/54-4-668
Republic of South Africa (RSA). (1997). Ministry of Welfare and Population. White Paper for Social Welfare. Notice 1008 of 1997. Government Gazette , 368, (18166). Pretoria: Government Printer.
Schotte, S., Zizzamia, R., & Leibbrandt, M. (2018). A poverty dynamics approach to social stratification: The South Africa case. World Development , 110 (2018), 88–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2018.05.024 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2018.05.024
Shamseer, L., Moher, D., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., et al. (2015). Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P): Elaboration and explanation. BMJ , 586, 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g7647 https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g7647
Sikrweqe, N. P. (2013). Integrated development planning as a poverty reduction strategy in the King Sabata Dalindyebo Municipality, Eastern Cape Province . Master’s diss., University of South Africa.
Sitshange, M. (2022). A thematic synthesis of income-generating studies conducted from 2007 to 2012 in Gauteng, Limpopo and KwaZulu-Natal: A systematic review of the qualitative evidence. Social Work/Maatskaplike Werk , 58(4), 382–393. https://doi.org/10.15270/58-4-1072 https://doi.org/10.15270/58-4-1072
Statistics South Africa (Stats SA). (2017). Poverty Trends in South Africa. An examination of absolute poverty between 2006 and 2015 . Pretoria: Statistics South Africa.
Statistics South Africa (Stats SA). (2019). Marginalised Groups Indicator Report. Report No. 0319-05. Retrieved from https://www.statssa.gov.za/publications/03-19-05/03-19-052019.pdf https://www.statssa.gov.za/publications/03-19-05/03-19-052019.pdf
Stephen, K. (2008). The impact of poverty alleviation projects in Ga-Molepo area in Polokwane Municipality, Limpopo Province . Master’s diss., University of Limpopo.
Strydom, C., Wessels, C., & Strydom, H. (2010). The role of the social worker to empower families in a deep rural community. Social Work/Maatskaplike Werk , 46(2), 175–191. https://doi.org/10.15270/46-2-172 https://doi.org/10.15270/46-2-172
Sundberg, T., & Taylor-Gooby, P. (2013). A systematic review of comparative studies of attitudes to social policy. Social Policy & Administration , 47(4), 416–433. ISSN 0144-5596. https://doi.org/10.1111/spol.12027 https://doi.org/10.1111/spol.12027
Thomas, J., & Harden, A. (2008). Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 8(45), 1471–2288. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-8-45 https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-8-45
Tong, A., Palmer, S., Craig, J. C., & Strippoli, G. F. M. (2016). A guide to reading and using systematic reviews of qualitative research. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation , 31(6), 897–903. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfu354 https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfu354
Van der Merwe, K. (2006). The phenomenology of experiencing poverty – An exploration. The Journal for Transdisciplinary Research in Southern Africa , 2(1), 131–144. https://doi.org/10.4102/td.v2i1.311 https://doi.org/10.4102/td.v2i1.311
Van Rooyen, C., Steward, R., & De Wet, T. (2012). The impact of microfinance in Sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review of the evidence. World Development , 40(11), 2249–2262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2012.03.012 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2012.03.012
World Bank. (2018). Overcoming poverty and inequality in South Africa: An assessment of drivers, constraints and opportunities. Retrieved from https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/530481521735906534/pdf/124521-rev-ouo-south-africa-povertyand-inequality-assessment-report-2018-fnal-web.pdf https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/530481521735906534/pdf/124521-rev-ouo-south-africa-povertyand-inequality-assessment-report-2018-fnal-web.pdf
World Bank. (2022). Report on inequality in Southern Africa: An assessment of the Southern African Customs Union. Retrieved from https://www.worldbank.org/en/events/2022/03/09/inequality-in-southern-africa-an-assessment-of-the-southern-african-customs-union https://www.worldbank.org/en/events/2022/03/09/inequality-in-southern-africa-an-assessment-of-the-southern-african-customs-union
Zizzamia, R., Schotte, S., & Leibbrandt, M. (2019). Snakes and ladders and loaded dice: Poverty dynamics and inequality in South Africa, 2008-2017 , WIDER Working Paper Series wp-2019-25, World Institute for Development Economic Research (UNU-WIDER).
Madoda Sitshange, Department of Social Work, University of Stellenbosch, South Africa and Department of Politics and International Relations, University of Johannesburg, South Africa. He can be contacted at [email protected]
Harvard-Style Citation
Sitshange, M. (2024) 'Thematically Synthesizing the Qualitative Evidence Reporting the Impact of Poverty Alleviation Programs in Low-income Communities in South Africa: A Review', Social Development Issues . 46(3) doi: 10.3998/sdi.6771
Show: Vancouver Citation Style | APA Citation Style
Vancouver-Style Citation
Sitshange, M. Thematically Synthesizing the Qualitative Evidence Reporting the Impact of Poverty Alleviation Programs in Low-income Communities in South Africa: A Review. Social Development Issues. 2024 9; 46(3) doi: 10.3998/sdi.6771
Show: Harvard Citation Style | APA Citation Style
APA-Style Citation
Sitshange, M. (2024, 9 4). Thematically Synthesizing the Qualitative Evidence Reporting the Impact of Poverty Alleviation Programs in Low-income Communities in South Africa: A Review. Social Development Issues 46(3) doi: 10.3998/sdi.6771
Show: Harvard Citation Style | {% trans 'Vancouver Citation Style' %}
Non Specialist Summary
This article has no summary

Market Research Plan

In 1970, food and drink sales of the US restaurant industry reached only 42.8 billion US dollars, which is way behind the 745.61 billion US dollar sales of 2015. According to the statistic posted in statista, this number should grow in the next few years. In fact, the website reported that from the 2015’s over 14 million employees of the restaurant industry, it should increase up to 16 million in 2026. However, as a result of this growth, there will be possibilities that the market will be saturated and more competitive. Thus, as a business owner, you will need to gear up and gain an edge to stand out in the market. By conducting market research for a restaurant, you can prepare your business to become more competitive and strategic, which will ensure its success.
What Do You Need to Know About Market Research?
Market research is an essential component of a business plan which aims to get information concerning the target market of a business. Through this study, you will determine the chances of a proposed service or new product to survive in the market. As part of market research, you need to develop a research plan.
What is Market Research Plan?
In general, market research plan is the foundation of a detailed research proposal . This document contains the initial thoughts about the research project that you are planning to take place logically and concisely, which is a crucial content of market research. Simply put, by obtaining a market research plan, you can thoroughly examine how your product or service will proceed in a specific domain.
2+ Market Research Plan Examples
Conducting market research will give significant benefits to your business. However, to materialize it, you may need to ensure that you build your market research plan correctly. Below is a list of the market research plan samples and templates that you can use as a guide.
1. Market Research Plan Template

- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
Size: 19 KB
2. Sample Market Research Plan Example
Size: 68 KB
3. Basic Market Research Plan Example
Size: 151 KB
4. Market Research Business Plan Example

Size: 600 KB
How to Develop a Strong Market Research Project Plan?
Now that you know how a marketing research plan should look, make a secure market research plan by following the steps below:
1. Set Goals and Objectives
What do you want to attain with your research? Your goals and objectives should answer that question. You can start by forming a general marketing goal . You will, then, make it more specific. This goal will help you focus and direct the entire research process to make the best data-driven marketing decisions. To determine the most critical issue, you may conduct qualitative research . This research methodology ensures that you address the issue that really requires an urgent solution.
2. Determine Your Target Respondents and Appropriate Distribution Method
In this step, you will identify the right people to get the information that you need to create the right decision for your marketing goals. After that, list down the best possible ways for the data gathering. For example, your target market is veterans. You may want to use more appropriate channels such as direct mails, phone, or personal interview. Once you have chosen the most appropriate data collection method, create an outline that will allow your team to get the most relevant information from your target market or audience.
4. Brainstorm for the Right Questions
In deciding the right questions for your marketing research, it is crucial to keep your study goals in mind. Only include items that are relevant to the study to come up with the best business decisions. Asking the wrong questions may lead to inadequate conclusions. Data-driven solutions mostly obtained through quantitative research questions. You can still use qualitative research questions but make it minimal to avoid making the respondents bored and held up, which can lead to survey abandonment. As much as possible, make your survey short and answerable in less than 5 minutes. Otherwise, you may want to find an alternative option in getting the desired data. Also, it would help if you will consider other factors in building the right questions. Refrain from asking sensitive, personal, and offensive questions. To do it, research your target audience.
5. Analyze the Data
Start this step by cleaning your survey data. To do it, filter out any low-quality responses. These items can affect your decision-making negatively. Basing on the set standards, remove the outlier responses. To do that, determine if the respondents answered in the desired format. If not, especially if it has become a trend, disqualify the question or conduct another data-gathering or investigation for this question. In this process, you will also find out if the answers of the participants are contributing to your research goals. At the end of this stage, you will, then, share your findings. To effectively show your results, you can use data visualization methods such as charts, graphs, and infographics.
6. Create a Data-Driven Marketing Decisions
Now that you have the necessary market research data, you can come up with a data-driven decision. Whether you are running a pharmaceutical firm or a corporal business such as Coca Cola, you can develop a new marketing campaign and other relevant business actions without unnecessary worries since you have directly reached out to your target market.
In a market that is becoming more competitive, creating a market research plan for a new product of your business can give you an advantage and an edge over your opponents. This type of method will also save your time, effort, and money because it allows you to determine the proper actions that you can take towards the corporate goals in terms of marketing and other relevant sectors.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The UK Data Service describes this perfectly, saying, "The value of qualitative research is that it gives a voice to the lived experience.". Read on to see seven use cases and 83 qualitative research questions, with the added bonus of examples that show how to get similar insights faster with Similarweb Research Intelligence.
5. Ask something researchable. Big questions, questions about hypothetical events or questions that would require vastly more resources than you have access to are not useful starting points for qualitative studies. Qualitative words or subjective ideas that lack definition are also not helpful.
25 examples of expertly crafted qualitative research questions. It's easy enough to cover the theory of writing a qualitative research question, but sometimes it's best if you can see the process in practice. In this section, we'll list 25 examples of B2B and B2C-related qualitative questions. Let's begin with five questions.
1. Begin with Your Research Goals. The first step in formulating qualitative research questions is to have a clear understanding of what you aim to discover or understand through your research. There are two types of qualitative questionnaires or research - Ontological and Epistemological. Finding out the nature of your research influences ...
10 Research Question Examples to Guide your ...
Qualitative Research Questions - Research Writing and Analysis
Here area few examples of focused research questions that can help set the stage for explaining different types of research questions in qualitative research. These questions touch upon various fields and subjects, showcasing the versatility and depth of research. ... Remember, qualitative research questions should be open-ended, allowing for a ...
In qualitative research, open-ended questions should be used to enable participants to offer thorough and in-depth responses. Avoid yes/no questions and queries with a one-word answer. Use words like "how," "what," "why," or "describe" instead to compel people to express their thoughts and experiences. LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative ...
Finding a Research Question and Approaches to Qualitative Research We've discussed the research design process in general and ways of knowing favored by qualitative researchers. In chapter 2, I asked you to think about what interests you in terms of a focus of study, including your motivations and research purpose.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis. Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, history, etc. Qualitative research question examples
Context: Within tourism and hospitality, this question explores the qualitative aspects of cultural experiences, focusing on tourists' perceptions and interpretations of authenticity in local culinary traditions. Media and Entertainment: Question: How do audiences engage with and interpret representations of diverse identities in streaming ...
Research Question Examples 🧑🏻🏫. 25+ Practical Examples & Ideas To Help You Get Started. By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | October 2023. A well-crafted research question (or set of questions) sets the stage for a robust study and meaningful insights. But, if you're new to research, it's not always clear what exactly constitutes a good ...
To create a perfect qualitative research question, you should consider the following. #1. Define Your Objective. This is a common practice to follow. Understanding what you really want to learn or explore can help you tailor the questions. For example, your goal might be to understand how people cope with stress. #2.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
reference and deconstruct a sample research question. The sample is derived from my dissertation that launched a significant portion of my research agenda through the ensuing decades. In this chapter, I dissect the sample question to reveal and brieflydefine the six parts of the Anatomy of a Qualitative Research Question. In the ensuing ...
Qualitative research uncovers the details of human behavior, beliefs, and feelings. It gives us insights that numbers can't always tell. These research questions help us understand the "how" and "why" of things. In this article, we'll look at six examples of good qualitative questions. We aim to highlight how picking the right questions can ...
Examples of Qualitative Research Questions. Qualitative research questions aim to explore the depth of human experience and understanding. They can guide researchers in gaining insights into behaviors, motivations, and perspectives. Here are several examples that aptly illustrate this concept.
Qualitative research is a broad term describing various research types that rely on asking open-ended questions. Qualitative research investigates "how" or "why" certain phenomena occur. ... Everyday examples of qualitative research include: Conducting a demographic analysis of a business. For instance, suppose you own a business such ...
The following are examples of qualita tive research questions drawn from several types of strategies. 131 Example 7.1 A Qualitative Central Question From an Ethnography Finders (1996) used ethnographic procedures to document the reading of teen magazines by middle-class European American seventh-grade girls. By exam-
Qualitative research questionnaires are a structured or semi-structured set of questions designed to gather detailed, open-ended participant responses. It allows you to uncover underlying reasons and opinions and provides insights into a particular phenomenon. While quantitative questionnaires often have closed-ended questions and numerical ...
Qualitative research is a behavioral research method that seeks to understand the undertones, motivations, and subjective interpretations inherent in human behavior. It involves gathering nonnumerical data, such as text, audio, and video, allowing you to explore nuances and patterns that quantitative data can't capture.
5. Case study research. Case studies are a UX research method that provides comprehensive and contextual insights into a real-world case over a long period of time. They typically include a range of other qualitative research methods, like interviews, observations, and ethnographic research.
Qualitative Research Methods and Examples. Good research begins with a question, and this question informs the approach used by qualitative researchers. Grounded Theory. Grounded theory is an inductive approach to theory development. In many forms of research, you begin with a hypothesis and then test it to see if you're correct.
Significant poverty levels raise critical questions about the impact of poverty eradication programs. Literature reviews play a critical role in highlighting impactful and ineffective socio-economic approaches. This article presents a review of nine qualitative studies that were reported between 2006 and 2013 in poor urban, semi-rural, and rural communities in South Africa. The main goal of ...
2+ Market Research Plan Examples. Conducting market research will give significant benefits to your business. ... Data-driven solutions mostly obtained through quantitative research questions. You can still use qualitative research questions but make it minimal to avoid making the respondents bored and held up, which can lead to survey ...
Qualitative research methods such as participant observation as a mode of gathering and producing data remain marginal in educational research about international students in Anglophone countries. It is suggested that educational research about international students will benefit from scholars' use of a more diverse set of qualitative ...