How to Set, Track, and Achieve Business Objectives with 60 Examples
By Kate Eby | April 10, 2023
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Businesses that set objectives make better decisions. Business objectives allow companies to focus their efforts, track progress, and visualize future success. We’ve worked with experts to create the most comprehensive guide to business objectives.
Included in this article, you’ll find the differences between business objectives and business goals , the four main business objectives , and the benefits of setting business objectives . Plus, find 60 examples of business objectives , which you can download in Microsoft Word.

What Is a Business Objective?
A business objective is a specific, measurable outcome that a company works to achieve. Company leaders set business objectives that help the organization meet its long-term goals. Business objectives should be recorded so that teams can easily access them.
Business objectives cover many different factors of a company’s success, such as financial health, operations, productivity, and growth.
One easy way to make sure that you are setting the right business objectives is to follow the SMART goal framework . SMART objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
To learn about setting project objectives using the SMART framework, see this comprehensive guide to writing SMART project objectives .
Business Objectives vs. Business Goal
A business goal is a broad, long-term outcome that a company works toward. Goals usually inform which strategies that department leaders will implement. A business objective , however, is a specific, short-term outcome or action that helps the company achieve long-term goals.
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, goals and objectives are not the same . In general, goals are broad in scope and describe an outcome, while objectives are narrow in scope and describe a specific action or step.
While these differences are important to understand, many of the common frameworks for successful goal-setting — such as SMART, objectives and key results ( OKRs ), and management by objectives (MBO) — can be useful when writing business objectives.
When deciding on objectives for a team or department, keep in mind the overarching goals of a business. Each objective should move the company closer to its long-term goals.
Project Goals and Objectives Template
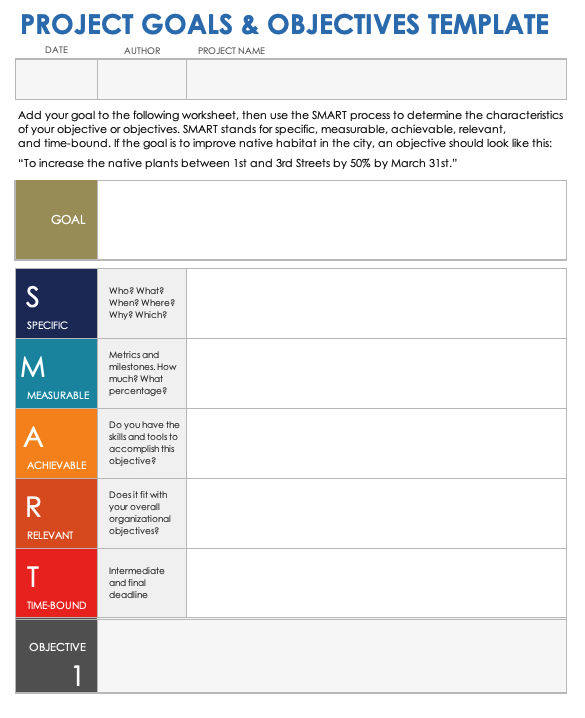
Download the Project Goals and Objectives Template for Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Use this free, printable template to learn how to break down project goals into individual objectives using the SMART framework. Write the primary goal at the top of the worksheet, then follow the SMART process to create one or more specific objectives that will help you achieve that goal.
For resources to help with setting and tracking goals at your company, see this all-inclusive list of goal tracking and setting templates .
What Are the Four Main Business Objectives?
The four main business objectives are economic, social, human, and organic. Each can help a business ensure their prolonged health and growth. For example, human objectives refer to employees’ well-being, while economic objectives refer to the company’s financial health.
These are the four main business objectives:
- Example: Reduce spending on paid advertisements by 20 percent.
- Example: Reduce average customer wait times from eight minutes to four minutes.
- Example: Hire two new chemical engineers by the end of Q2.
- Example: Improve the efficiency of a specific software product by 15 percent.
Types of Business Objectives
There are many types of business objectives beyond the main four. These range from regulation objectives to environmental objectives to municipal objectives. For example, a global objective might be to distribute a product to a new country.
In addition to economic, social, human, and organic objectives, here are some other types of business objectives companies might set:
- Regulatory: These objectives relate to compliance requirements, such as meeting quality standards or conducting internal audits.
- National: These objectives relate to a company’s place in and how they contribute to the country they operate in, such as promoting social justice causes and creating employment opportunities.
- Global: These objectives relate to a company’s place in and its contribution to many countries, such as improving living standards and responding to global demands for products and services.
- Environmental: These objectives relate to a company’s environmental impact, such as reducing chemical waste or making eco-friendly investments.
- Healthcare: These objectives relate to the health and well-being of a population, whether within or outside an organization. These objectives might be improving healthcare benefit options for employees or refining a drug so that it has fewer side effects.
The Importance of Having Business Objectives
Teams need business objectives to stay focused on the company’s long-term goals. Business objectives help individual employees understand how their roles contribute to the larger mission of the organization. Setting business objectives facilitates effective planning.
Here are some benefits to setting business objectives:

- Develops Leadership: Company leaders are more effective when they have a clear vision and can delegate tasks to make it a reality. Setting objectives is a great way to improve one’s leadership skills.
- Increases Motivation: People tend to be more invested in work when they have clear, attainable objectives to achieve. Plus, each completed objective provides a morale boost to keep teams happy and productive.
- Encourages Innovation and Productivity: With increased motivation and workplace satisfaction come more innovations. Set attainable but challenging objectives, and watch teams come up with creative solutions to get things done.
- Improves Strategy: Setting objectives that align with overarching company goals means that everyone across the company can stay aligned on strategic implementation.
- Enhances Customer Satisfaction: Overall customer satisfaction is more likely to increase over time when measurable quality improvements are in place.
- Improves Prioritization: When they are being able to see all of the current objectives, team members can more easily prioritize their work, which in turn makes their workloads feel more manageable.
- Improves Financial Health: Setting economic objectives in particular can help companies stay on top of their financial goals.
60 Examples of Business Objectives
Company leaders can use business objectives to improve every facet of an organization, from customer satisfaction to market share to employee well-being. Here are 60 examples of business objectives that can help a company achieve its goals.
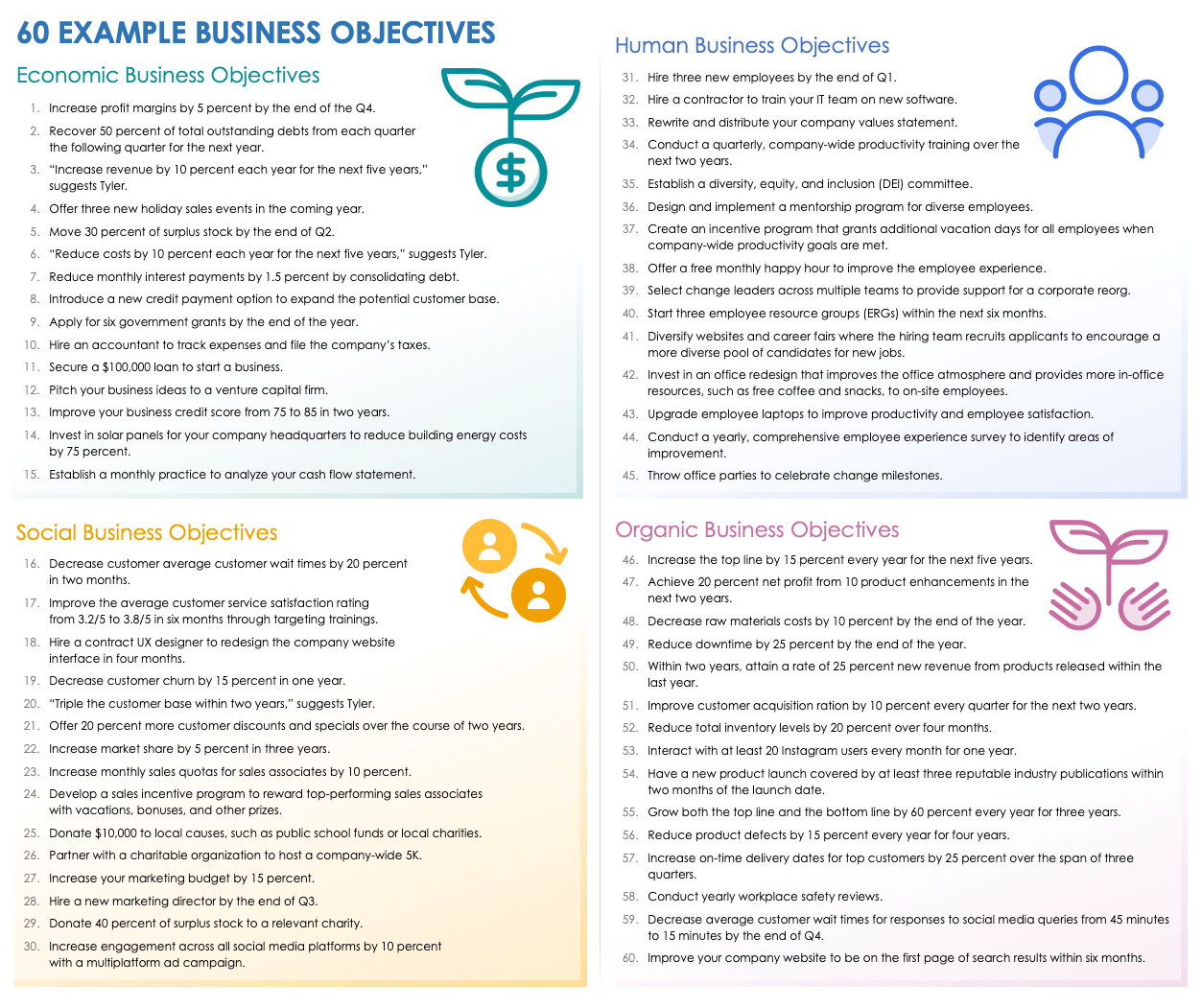
Economic Business Objectives
- Increase profit margins by 5 percent by the end of the Q4.
- Recover 50 percent of total outstanding debts from each quarter the following quarter for the next year.
- “Increase revenue by 10 percent each year for the next five years,” suggests Tyler.
- Offer three new holiday sales events in the coming year.
- Move 30 percent of surplus stock by the end of Q2.
- “Reduce costs by 10 percent each year for the next five years,” suggests Tyler.
- Reduce monthly interest payments by 1.5 percent by consolidating debt.
- Introduce a new credit payment option to expand the potential customer base.
- Apply for six government grants by the end of the year.
- Hire an accountant to track expenses and file the company’s taxes.
- Secure a $100,000 loan to start a business.
- Pitch your business ideas to a venture capital firm.
- Improve your business credit score from 75 to 85 in two years.
- Invest in solar panels for your company headquarters to reduce building energy costs by 75 percent.
- Establish a monthly practice to analyze your cash flow statement.
Social Business Objectives
- Decrease customer average customer wait times by 20 percent in two months.
- Improve the average customer service satisfaction rating from 3.2/5 to 3.8/5 in six months through targeting trainings.
- Hire a contract UX designer to redesign the company website interface in four months.
- Decrease customer churn by 15 percent in one year.
- “Triple the customer base within two years,” suggests Tyler.
- Offer 20 percent more customer discounts and specials over the course of two years.
- Increase market share by 5 percent in three years.
- Increase monthly sales quotas for sales associates by 10 percent.
- Develop a sales incentive program to reward top-performing sales associates with vacations, bonuses, and other prizes.
- Donate $10,000 to local causes, such as public school funds or local charities.
- Partner with a charitable organization to host a company-wide 5K.
- Increase your marketing budget by 15 percent.
- Hire a new marketing director by the end of Q3.
- Donate 40 percent of surplus stock to a relevant charity.
- Increase engagement across all social media platforms by 10 percent with a multiplatform ad campaign.
Human Business Objectives
- Hire three new employees by the end of Q1.
- Hire a contractor to train your IT team on new software.
- Rewrite and distribute your company values statement.
- Conduct a quarterly, company-wide productivity training over the next two years.
- Establish a diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) committee.
- Design and implement a mentorship program for diverse employees.
- Create an incentive program that grants additional vacation days for all employees when company-wide productivity goals are met.
- Offer a free monthly happy hour to improve the employee experience.
- Select change leaders across multiple teams to provide support for a corporate reorg.
- Start three employee resource groups (ERGs) within the next six months.
- Diversify websites and career fairs where the hiring team recruits applicants to encourage a more diverse pool of candidates for new jobs.
- Invest in an office redesign that improves the office atmosphere and provides more in-office resources, such as free coffee and snacks, to on-site employees.
- Upgrade employee laptops to improve productivity and employee satisfaction.
- Conduct a yearly, comprehensive employee experience survey to identify areas of improvement.
- Throw office parties to celebrate change milestones.
Organic Business Objectives
- Increase the top line by 15 percent every year for the next five years.
- Achieve 20 percent net profit from 10 product enhancements in the next two years.
- Decrease raw materials costs by 10 percent by the end of the year.
- Reduce downtime by 25 percent by the end of the year.
- Within two years, attain a rate of 25 percent new revenue from products released within the last year.
- Improve customer acquisition ration by 10 percent every quarter for the next two years.
- Reduce total inventory levels by 20 percent over four months.
- Interact with at least 20 Instagram users every month for one year.
- Have a new product launch covered by at least three reputable industry publications within two months of the launch date.
- Grow both the top line and the bottom line by 60 percent every year for three years.
- Reduce product defects by 15 percent every year for four years.
- Increase on-time delivery dates for top customers by 25 percent over the span of three quarters.
- Conduct yearly workplace safety reviews.
- Decrease average customer wait times for responses to social media queries from 45 minutes to 15 minutes by the end of Q4.
- Improve your company website to be on the first page of search results within six months.
Download 60 Example Business Objectives for
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Track the Progress of Business Objectives with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Need a business plan? Call now:
Talk to our experts:
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB1 Business Plan
- EB2 Visa Business Plan
- EB5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- UK Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- UK Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Planning
- Landlord Business Plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- eCommerce business plan
- Online Boutique Business Plan
- Daycare business plan
- Mobile Application Business Plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food Delivery Business Plan
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Buy Side Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Templates
Goals and Objectives for Business Plan with Examples
Published Nov.05, 2023
Updated Apr.23, 2024
By: Jakub Babkins
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 2
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Table of Content
Every business needs a clear vision of what it wants to achieve and how it plans to get there. A business plan is a document that outlines the goals and objectives of a business, as well as the strategies and actions to achieve them. A well-written business plan from business plan specialists can help a business attract investors, secure funding, and guide its growth.
Understanding Business Objectives
Business objectives are S pecific, M easurable, A chievable, R elevant, and T ime-bound (SMART) statements that describe what a business wants to accomplish in a given period. They are derived from the overall vision and mission of the business, and they support its strategic direction.
Business plan objectives can be categorized into different types, depending on their purpose and scope. Some common types of business objectives are:
- Financial objectives
- Operational objectives
- Marketing objectives
- Social objectives
For example, a sample of business goals and objectives for a business plan for a bakery could be:
- To increase its annual revenue by 20% in the next year.
- To reduce its production costs by 10% in the next six months.
- To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
- To improve its customer satisfaction rating by 15% in the next month.
The Significance of Business Objectives
Business objectives are important for several reasons. They help to:
- Clarify and direct the company and stakeholders
- Align the company’s efforts and resources to a common goal
- Motivate and inspire employees to perform better
- Measure and evaluate the company’s progress and performance
- Communicate the company’s value and advantage to customers and the market
For example, by setting a revenue objective, a bakery can focus on increasing its sales and marketing efforts, monitor its sales data and customer feedback, motivate its staff to deliver quality products and service, communicate its unique selling points and benefits to its customers, and adjust its pricing and product mix according to market demand.
Advantages of Outlining Business Objectives
Outlining business objectives is a crucial step in creating a business plan. It serves as a roadmap for the company’s growth and development. Outlining business objectives has several advantages, such as:
- Clarifies the company’s vision, direction, scope, and boundaries
- Break down the company’s goals into smaller tasks and milestones
- Assigns roles and responsibilities and delegates tasks
- Establishes standards and criteria for success and performance
- Anticipates risks and challenges and devises contingency plans
For example, by outlining its business objective for increasing the average revenue per customer in its business plan, a bakery can:
- Attract investors with its viable business plan for investors
- Secure funding from banks or others with its realistic financial plan
- Partner with businesses or organizations that complement or enhance its products or services
- Choose the best marketing, pricing, product, staff, location, etc. for its target market and customers
Setting Goals and Objectives for a Business Plan
Setting goals and objectives for a business plan is not a one-time task. It requires careful planning, research, analysis, and evaluation. To set effective goals and objectives for a business plan, one should follow some best practices, such as:
OPTION 1: Use the SMART framework. A SMART goal or objective is clear, quantifiable, realistic, aligned with the company’s mission and vision, and has a deadline. SMART stands for:
- Specific – The goal or objective should be clear, concise, and well-defined.
- Measurable – The goal or objective should be quantifiable or verifiable.
- Achievable – The goal or objective should be realistic and attainable.
- Relevant – The goal or objective should be aligned with the company’s vision, mission, and values.
- Time-bound – The goal or objective should have a deadline or timeframe.
For example, using the SMART criteria, a bakery can refine its business objective for increasing the average revenue per customer as follows:
- Specific – Increase revenue with new products and services from $5 to $5.50.
- Measurable – Track customer revenue monthly with sales reports.
- Achievable – Research the market, develop new products and services, and train staff to upsell and cross-sell.
- Relevant – Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, profitability and cash flow, and market competitiveness.
- Time-bound – Achieve this objective in six months, from January 1st to June 30th.
OPTION 2: Use the OKR framework. OKR stands for O bjectives and K ey R esults. An OKR is a goal-setting technique that links the company’s objectives with measurable outcomes. An objective is a qualitative statement of what the company wants to achieve. A key result is a quantitative metric that shows how the objective will be achieved.
OPTION 3: Use the SWOT analysis. SWOT stands for S trengths, W eaknesses, O pportunities, and T hreats. A SWOT analysis is a strategic tool that helps the company assess the internal and external factors that affect its goals and objectives.
- Strengths – Internal factors that give the company an advantage over others.
- Weaknesses – Internal factors that limit the company’s performance or growth.
- Opportunities – External factors that allow the company to improve or expand.
- Threats – External factors that pose a risk or challenge to the company.
For example, using these frameworks, a bakery might set the following goals and objectives for its SBA business plan :
Objective – To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
Key Results:
- Research gluten-free cake market demand and preferences by month-end.
- Create and test 10 gluten-free cake recipes by next month-end.
- Make and sell 100 gluten-free cakes weekly online or in-store by quarter-end.
SWOT Analysis:
- Expertise and experience in baking and cake decorating.
- Loyal and satisfied customer base.
- Strong online presence and reputation.
Weaknesses:
- Limited production capacity and equipment.
- High production costs and low-profit margins.
- Lack of knowledge and skills in gluten-free baking.
Opportunities:
- Growing demand and awareness for gluten-free products.
- Competitive advantage and differentiation in the market.
- Potential partnerships and collaborations with health-conscious customers and organizations.
- Increasing competition from other bakeries and gluten-free brands.
- Changing customer tastes and preferences.
- Regulatory and legal issues related to gluten-free labeling and certification.
Examples of Business Goals and Objectives
To illustrate how to write business goals and objectives for a business plan, let’s use a hypothetical example of a bakery business called Sweet Treats. Sweet Treats is a small bakery specializing in custom-made cakes, cupcakes, cookies, and other baked goods for various occasions.
Here are some examples of possible startup business goals and objectives for Sweet Treats:
Earning and Preserving Profitability
Profitability is the ability of a company to generate more revenue than expenses. It indicates the financial health and performance of the company. Profitability is essential for a business to sustain its operations, grow its market share, and reward its stakeholders.
Some possible objectives for earning and preserving profitability for Sweet Treats are:
- To increase the gross profit margin by 5% in the next quarter by reducing the cost of goods sold
- To achieve a net income of $100,000 in the current fiscal year by increasing sales and reducing overhead costs
Ensuring Consistent Cash Flow
Cash flow is the amount of money that flows in and out of a company. A company needs to have enough cash to cover its operating expenses, pay its debts, invest in its growth, and reward its shareholders.
Some possible objectives for ensuring consistent cash flow for Sweet Treats are:
- Increase monthly operating cash inflow by 15% by the end of the year by improving the efficiency and productivity of the business processes
- Increase the cash flow from investing activities by selling or disposing of non-performing or obsolete assets
Creating and Maintaining Efficiency
Efficiency is the ratio of output to input. It measures how well a company uses its resources to produce its products or services. Efficiency can help a business improve its quality, productivity, customer satisfaction, and profitability.
Some possible objectives for creating and maintaining efficiency for Sweet Treats are:
- To reduce the production time by 10% in the next month by implementing lean manufacturing techniques
- To increase the customer service response rate by 20% in the next week by using chatbots or automated systems
Winning and Keeping Clients
Clients are the people or organizations that buy or use the products or services of a company. They are the source of revenue and growth for a company. Therefore, winning and keeping clients is vital to generating steady revenue, increasing customer loyalty, and enhancing word-of-mouth marketing.
Some possible objectives for winning and keeping clients for Sweet Treats are:
- To acquire 100 new clients in the next quarter by launching a referral program or a promotional campaign
- To retain 90% of existing clients in the current year by offering loyalty rewards or satisfaction guarantees
Building a Recognizable Brand
A brand is the name, logo, design, or other features distinguishing a company from its competitors. It represents the identity, reputation, and value proposition of a company. Building a recognizable brand is crucial for attracting and retaining clients and creating a loyal fan base.
Some possible objectives for building a recognizable brand for Sweet Treats are:
- To increase brand awareness by 50% in the next six months by creating and distributing engaging content on social media platforms
- To improve brand image by 30% in the next year by participating in social causes or sponsoring events that align with the company’s values
Expanding and Nurturing an Audience with Marketing
An audience is a group of people interested in or following a company’s products or services. They can be potential or existing clients, fans, influencers, or partners. Expanding and nurturing an audience with marketing is essential for increasing a company’s visibility, reach, and engagement.
Some possible objectives for expanding and nurturing an audience with marketing for Sweet Treats are:
- To grow the email list by 1,000 subscribers in the next month by offering a free ebook or a webinar
- To nurture leads by sending them relevant and valuable information through email newsletters or blog posts
Strategizing for Expansion
Expansion is the process of increasing a company’s size, scope, or scale. It can involve entering new markets, launching new products or services, opening new locations, or forming new alliances. Strategizing for expansion is important for diversifying revenue streams, reaching new audiences, and gaining competitive advantages.
Some possible objectives for strategizing for expansion for Sweet Treats are:
- To launch a new product or service line by developing and testing prototypes
- To open a new branch or franchise by securing funding and hiring staff
Template for Business Objectives
A template for writing business objectives is a format or structure that can be used as a guide or reference for creating your objectives. A template for writing business objectives can help you to ensure that your objectives are SMART, clear, concise, and consistent.
To use this template, fill in the blanks with your information. Here is an example of how you can use this template:
Example of Business Objectives
Our business is a _____________ (type of business) that provides _____________ (products or services) to _____________ (target market). Our vision is to _____________ (vision statement) and our mission is to _____________ (mission statement).
Our long-term business goals and objectives for the next _____________ (time period) are:
S pecific: We want to _____________ (specific goal) by _____________ (specific action).
M easurable: We will measure our progress by _____________ (quantifiable indicator).
A chievable: We have _____________ (resources, capabilities, constraints) that will enable us to achieve this goal.
R elevant: This goal supports our vision and mission by _____________ (benefit or impact).
T ime-bound: We will complete this goal by _____________ (deadline).
Repeat this process for each goal and objective for your business plan.
How to Monitor Your Business Objectives?
After setting goals and objectives for your business plan, you should check them regularly to see if you are achieving them. Monitoring your business objectives can help you to:
- Track your progress and performance
- Identify and overcome any challenges
- Adjust your actions and strategies as needed
Some of the tools and methods that you can use to monitor your business objectives are:
- Dashboards – Show key data and metrics for your objectives with tools like Google Data Studio, Databox, or DashThis.
- Reports – Get detailed information and analysis for your objectives with tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, or SEMrush.
- Feedback – Learn from your customers and their needs and expectations with tools like SurveyMonkey, Typeform, or Google Forms.
Strategies for Realizing Business Objectives
To achieve your business objectives, you need more than setting and monitoring them. You need strategies and actions that support them. Strategies are the general methods to reach your objectives. Actions are the specific steps to implement your strategies.
Different objectives require different strategies and actions. Some common types are:
- Marketing strategies
- Operational strategies
- Financial strategies
- Human resource strategies
- Growth strategies
To implement effective strategies and actions, consider these factors:
- Alignment – They should match your vision, mission, values, goals, and objectives
- Feasibility – They should be possible with your capabilities, resources, and constraints
- Suitability – They should fit the context and needs of your business
How OGSCapital Can Help You Achieve Your Business Objectives?
We at OGSCapital can help you with your business plan and related documents. We have over 15 years of experience writing high-quality business plans for various industries and regions. We have a team of business plan experts who can assist you with market research, financial analysis, strategy formulation, and presentation design. We can customize your business plan to suit your needs and objectives, whether you need funding, launching, expanding, or entering a new market. We can also help you with pitch decks, executive summaries, feasibility studies, and grant proposals. Contact us today for a free quote and start working on your business plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the goals and objectives in business.
Goals and objectives in a business plan are the desired outcomes that a company works toward. To describe company goals and objectives for a business plan, start with your mission statement and then identify your strategic and operational objectives. To write company objectives, you must brainstorm, organize, prioritize, assign, track, and review them using the SMART framework and KPIs.
What are the examples of goals and objectives in a business plan?
Examples of goals and objectives in a business plan are: Goal: To increase revenue by 10% each year for the next five years. Objective: To launch a new product line and create a marketing campaign to reach new customers.
What are the 4 main objectives of a business?
The 4 main objectives of a business are economic, social, human, and organic. Economic objectives deal with financial performance, social objectives deal with social responsibility, human objectives deal with employee welfare, and organic objectives deal with business growth and development.
What are goals and objectives examples?
Setting goals and objectives for a business plan describes what a business or a team wants to achieve and how they will do it. For example: Goal: To provide excellent customer service. Objective: To increase customer satisfaction scores by 20% by the end of the quarter.
At OGSCapital, our business planning services offer expert guidance and support to create a realistic and actionable plan that aligns with your vision and mission. Get in touch to discuss further!
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Bowling Alley Business Plan Sample

Nightclub Business Plan (2024): A Comprehensive Guide

Rabbit Farming Business Plan

Beverages Business Plan

Private Schools Business Plan

Business Plan for a Lounge

Any questions? Get in Touch!
We have been mentioned in the press:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Search the site:
Business growth
Business tips
Business objectives: How to set them (with 5 examples and a template)
As anyone who played rec league sports in the '90s might remember, being on a team for some reason required you to sell knockoff candy bars to raise funds. Every season, my biggest customer was always me. Some kids went door-to-door, some set up outside local businesses, some sent boxes to their parents' jobs—I just used my allowance to buy a few for myself.
Aside from initiative, what my approach lacked was a plan, a goal, and accountability. A lot to ask of an unmotivated nine-year-old, I know, but 100% required for anyone who runs an actual business.
Business objectives help companies avoid my pitfalls by laying the groundwork for all the above so they can pursue achievable growth.
Table of contents:
What are business objectives?
What you want the company to achieve
How you can measure success
Which players are involved in driving success
The timelines needed to plan, initiate, and implement steps
How, if successful, these actions can be integrated sustainably going forward
Business objectives vs. goals
Here's what that breakdown could have looked like for nine-year-old me selling candy for my little league team:
Business objective: I will increase my sales output by learning and implementing point-of-sale conversion frameworks. I'll measure success by comparing week-over-week sales growth to median sales across players on my baseball team.
Business goal: I will sell more candy bars than anyone on my team and earn the grand prize: a team party at Pizza Hut.
The benefits of setting business objectives
You might think it's good enough to continue working status quo toward your goals, but as the cliche goes, good enough usually isn't. Establishing and following defined, actionable steps through business objectives can:
Help establish clear roadmaps: You can translate your objectives into time-sensitive sequences to chart your path toward growth.
Set groundwork for culture: Clear objectives should reflect the culture you envision, and, in turn, they should help guide your team to foster it.
Influence talent acquisition: Once you know your objectives, you can use them to find the people with the specific skills and experiences needed to actualize them.
Encourage teamwork: People work together better when they know what they're working toward.
Establish accountability: By measuring progress, you can see where errors and inefficiencies come from.
Drive productivity: The endgame of an objective is to make individual team members and processes more effective.
How to set business objectives
Setting business objectives takes a thoughtful, top-to-bottom approach. At every level of your business—whether you're a massive candy corporation or one kid selling chocolate almond bars door-to-door—there are improvements to make, steps to take, and players with stakes (or in my case, bats) in the game.

1. Establish clear goals
You can't hit a home run without a fence, and you can't reach a goal without setting it. Before you start brainstorming your objectives, you need to know what your objectives will help you work toward.
Increase total revenue by 25% over the next two years
Reduce production costs by 10% by the end of the year
Provide health insurance for employees by next fiscal year
Grow design department to 10+ employees this year
Reach 100k Instagram followers ahead of new product launch
Implement full rebrand before new partnership announcement
Once you have these goals in place, you can establish individual objectives that position your company to reach them.
2. Set a baseline
Like a field manager before a game, you've got to set your baselines. (Very niche pun, I know.) With a definite goal in mind, the only way to know your progress is to know where you're starting from.
Analyzing your baselines could also help you recalibrate your goals. You may have decided abstractly that you want conversion rates to double in six months, but is that really possible? If your measurables show there's potentially a heavier lift involved than you expected, you can always roll back the goal performance or expand the timeline.
3. Involve players at all levels in the conversation
Too often, the most important people are left out of conversations about goals and objectives. The more levels of complexity and oversight, the more important it is to hear from everyone—yet the more likely it is that some will be excluded.
Let's say you want to reduce overhead by 5% over the next two years for your sporting goods manufacturing outfit. At a high level, your team finds you can reduce production costs by using cheaper materials for baseball gloves. A member of your sales team points out that the reduction in quality, which your brand is famous for, could lead to losses that offset those savings. Meanwhile, a factory representative points out that replacing outdated machines would be expensive initially but would increase efficiency, reduce defects, and cut maintenance costs, breaking even in four years.
By involving various teams at multiple levels, you find it's worth it to extend timelines from two to four years. Your overhead reduction may be lower than 5% by year two but should be much higher than that by year four based on these changes.
The takeaway from this pretty crude example is that it's helpful to make sure every team that touches anything related to your objective gets consulted. They should give valuable, practical input thanks to their boots- (or cleats-) on-the-ground experience.
4. Define measurable outcomes
An objective should be exactly that. Using KPIs (key performance indicators) to apply a level of objectivity to your action steps allows you to measure their progress and success over time and either adapt as you go along or stay the course.
How do you know if your specific objectives are leading to increased web traffic, or if that's just natural (or even incidental) growth? How do you know if your recruiting efforts lead to better candidates, or whether your employees are actually more satisfied? Here are a few examples of measurable outcomes to show proof:
Percentage change (15% overall increase in revenue)
Goal number (10,000 subscribers)
Success range (five to 10 new clients)
Clear change (new company name)
Executable action (weekly newsletter launch)
5. Outline a roadmap with a schedule
You've got your organizational goals defined, logged your baselines, sourced objectives from across your company, and know your metrics for defining success. Now it's time to set an actionable plan you can execute.
Your objectives roadmap should include all involved team members and departments and clear timelines for reaching milestones. Within your objectives, set action items with deadlines to stay on track, along with corresponding progress markers. For the objective of "increase lead conversion efficiency by 10%," that could look like:
May 15: Begin time logging
June 1: Register team members for productivity seminar
June 15: Integrate Trello for managing processes
June 15: Audit time log
August 1: Audit time log—goal efficiency increase of 5%
6. Integrate successful changes
You've successfully achieved your objectives—great! But as Yogi Berra famously said, "It ain't over till it's over," and it ain't over yet.
Don't let this win be a one-off accomplishment. Berra also said "You can observe a lot by just watching," and applying what you observed from this process will help you continue growing your company. Take what worked, and integrate it into your business processes for sustainable improvement. Then create new objectives, so you can continue the cycle.
Examples of business objectives and goals
Business objectives aren't collated plans or complicated flowcharts—they're short, impactful statements that are easy to memorize and communicate. There are four basic components every business objective should have:
A growth-oriented intention (improve efficiency)
One or more actions (implement monthly training sessions)
A measurement for success (20% increase)
A timeline to reach success (by end of year)
Our SaaS product's implementation team will grow to five during the next fiscal year. This will require us to submit a budget proposal by the end of the quarter and look into restructured growth tracks, new job posting templates, and revised role descriptions by the start of next fiscal year.
We will increase customer satisfaction for our mobile app product demonstrably by the end of the year by integrating a new AI chatbot feature. To measure the change in customer satisfaction, we will monitor ratings in the app store, specifically looking for decreases in rates of negative reviews by 5%-10% as well as increases in overall positive reviews by 5%-10%.
Each of our water filtration systems will achieve NSF certification ahead of the launch of our rebranding campaign. Our product team will establish a checklist of changes necessary for meeting certification requirements and communicate timelines to the marketing team.
HR will implement bi-annual performance reviews starting next year. Review timelines will be built into scheduling software, and HR will automate email reminders to managers to communicate to their teams.
Business objective template
Business objectives can be as simple as one action or as complex as a multi-year roadmap—but they should be able to fall into a clear, actionable framework.
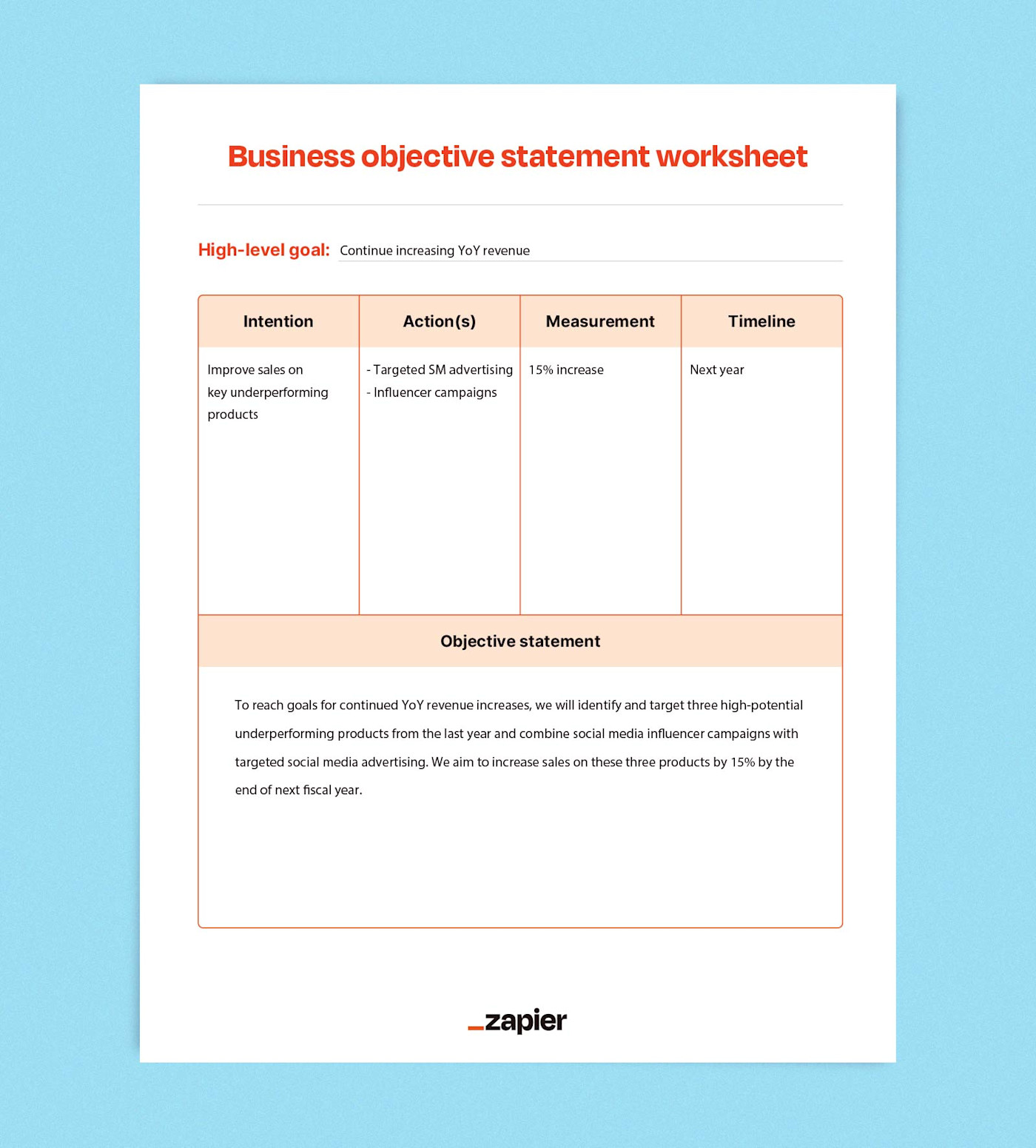
Tips for achieving business objectives
Calling your shot to the left centerfield wall and hitting a ball over that wall are two different things—the same goes for setting an objective and actualizing it.
Start with clear, attainable goals: Objectives should position your business to reach broader growth goals, so start by establishing those.
Align decisions with objectives: Once you set objectives, they should inform other decisions. Decision-makers should think about how changes they make along the way affect their objectives' timelines and execution.
Listen to team members at all levels: Those most affected by organizational changes can be the ones with the least say in the matter. Great ideas and insights can come from any level—even if they're only tangentially related to an outcome.
What makes business objectives so useful is that they can help you build a plan with defined steps to reach obtainable growth goals. As (one more time) Yogi Berra also once said, "You've got to be very careful if you don't know where you are going, because you might not get there."
As you outline your objectives, here are some guides that can help you find KPIs and improvement opportunities:
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Bryce Emley
Currently based in Albuquerque, NM, Bryce Emley holds an MFA in Creative Writing from NC State and nearly a decade of writing and editing experience. His work has been published in magazines including The Atlantic, Boston Review, Salon, and Modern Farmer and has received a regional Emmy and awards from venues including Narrative, Wesleyan University, the Edward F. Albee Foundation, and the Pablo Neruda Prize. When he isn’t writing content, poetry, or creative nonfiction, he enjoys traveling, baking, playing music, reliving his barista days in his own kitchen, camping, and being bad at carpentry.
- Small business
- Sales & business development
Related articles

Project milestones for improved project management
Project milestones for improved project...

14 data visualization examples to captivate your audience
14 data visualization examples to captivate...

61 best businesses to start with $10K or less
61 best businesses to start with $10K or...
SWOT analysis: A how-to guide and template (that won't bore you to tears)
SWOT analysis: A how-to guide and template...
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

Guide To Starting A Business
4. how to write objectives for your business plan.
Next Read: 6 Types of Business Plans
- How to Write Objectives for Your Business Plan

Table of Contents
As a small business owner, setting objectives is a key part of your company’s success—both now and in the future. Business objectives not only help you envision the results you hope your company will achieve, they enable you to map out a plan to accomplish them.
The following guide will help you understand what business objectives are and how to create personalized objectives for your own business plan. You’ll also discover why not setting business objectives can be a dangerous small business mistake to make.
What are business objectives?
Business objectives are written statements that define results you want your company to achieve and detail how and when it will achieve them. These objectives typically focus on key areas (i.e., growth , revenue, productivity, operational efficiency, etc.) that can bring you closer to your long-term business vision.
A successful business objective should keep you and your employees motivated and focused. And there’s nothing wrong with a goal that’s a bit of a challenge. At the same time, the most effective business objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. (More on that below.)
Benefits of business objectives.
There are many reasons why you should consider incorporating written business objectives into your own business plan . Whether you’re a small business owner running a one-person startup or you’re managing a fast-growing company, business objectives could help you:
- Provide your company with a sense of direction
- Motivate business owners and employees
- Boost employee retention
- Increase business revenue
- Improve workplace productivity
- Enhance company culture
- Provide a mechanism to measure performance
- Enhance customer service
- Improve company reputation
How to set your business objectives.
Different businesses tend to have different approaches to the business objective-writing process. And this process may evolve over time as your business grows. If you’re setting business objectives for the first time, the four steps below are a good starting point.
Step one: Identify what you want to achieve and why.
For each business objective that you set in your business plan, it’s important to begin with a brainstorming session to identify what it is that you want your company to accomplish. During this process, remember that there’s a difference between goals and objectives.
A goal might look something like, “We want to be the largest home remodeling company in the greater Chicago area.” And while there’s nothing wrong with setting a goal, what makes the previous statement fall short of being an objective is that it isn’t specific, measurable, or time-bound. An objective, on the other hand, might look like, “We will boost revenue by 20% by the end of 2023 by partnering with five new referral partners.”
As you brainstorm ideas for your business objectives, consider asking employees to contribute ideas. You’ll likely come up with multiple objectives that you can work to narrow down to the most important categories you want to focus on for the upcoming year.
Step two: Consider your “why”.
Before you finalize your business objectives, it’s important to identify or keep in mind the underlying reason why you want your business to thrive in the first place. You can discover your “why” by answering the following question: What is it that drives you to succeed?
Perhaps you’re working to make a difference in your community. Other small business owners may desire to provide financial stability for their families and employees. Some entrepreneurs dream of financial freedom or an early retirement. Whatever your definition of success looks like, make sure that your business objectives support these overarching goals.
Step three: Get organized.
At the end of the brainstorming process, you may begin to notice patterns of overlapping information. Numerous goals, for example, might pertain to increasing business revenue and profits. You might have several ideas on how to improve customer satisfaction, employee productivity, marketing reach, sales, and more.
If you try to implement too many changes at once, you and your staff could become overwhelmed. However, it might be possible to combine common ideas together to create enhanced business objectives that are better than they were in their original form.
Step four: Write and review.
As you sit down to write, remember that each business objective needs five components to be effective. A business objective should be SMART:
- M easurable
- A chievable
- T ime-Bound
When an objective is specific, anyone reading the business plan understands what the business is working to accomplish and who is responsible for each role in the process. The more details you can provide, the better.
A business objective should also cover how success will be measured. How will the business owner, employees, stakeholders, and others know if the business is on track to reach its goals?
An achievable business objective is realistic. Again, it’s fine to stretch yourself and your team. But you should also consider employee morale and avoid setting expectations that could discourage rather than motivate.
Relevant business objectives focus on the mission of the organization. Additionally, make sure you assign the right responsibilities to the right team members as you work toward accomplishing goals.
Time-bound objectives set a deadline. Without a date in mind for when you want your business to reach the goals it has set, you’ll never know if you cross the finish line on time.
Business objective examples.
Now you have a basic understanding of how to set business objectives for your business plan. Here are four examples of business objectives in different categories.
Example #1: Customer service business objective.
Our business will reduce customer complaints by 25% this year. To accomplish this goal, we will hire three new team members to decrease time spent on hold for customers, add an online chat support option, and invest in training to help our staff manage angry customers.
Example #2: Revenue business objective.
Our company will increase overall revenue by 20% this year. To accomplish this goal, we will introduce a customer referral program and sales bonus opportunities for all employees in Q1. We will also conduct surveys to find out how targeted customers discovered our brand in the past and increase marketing spending in those areas by 25%.
Example #3: Online brand awareness.
Our business will boost brand awareness by doubling our number of Instagram and/or TikTok followers by the end of the year. To accomplish this goal, we’ll hire a full-time social media manager and dedicate an additional 10% in marketing dollars to social media campaigns and advertising.
Example #4: Improve employee retention.
Our company will reduce employee turnover by 40% this year. To accomplish this goal, we will implement a new employee incentive program by the end of Q1. We will also schedule bi-weekly meetings between employees and managers to give team members an opportunity to discuss frustrations and strengthen relationships.
Bottom line
There are many tips and tools you can use to grow your small business . Yet, creating solid business objectives should be at the top of your list. Whether your business is brand new or has been around for decades, taking the time to define where you want your business to go and how you intend to get there can be a powerful exercise.
Creating business objectives for your business plan may also benefit you when you apply for certain types of business loans . And even though some lenders might want your business plan to focus on how your business intends to use the funds it borrows, the more details you can provide about your company’s future goals and objectives, the better.
Compare loan options from multiple funders.
Applying is free and won’t impact your credit., talk to a rep at (855) 853-6346 mon-fri 7:30am-5pm mst, information provided on this blog is for educational purposes only, and is not intended to be business, legal, tax, or accounting advice. the views and opinions expressed in this blog are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of lendio. while lendio strives to keep its content up-to-date, it is only accurate as of the date posted. offers or trends may expire, or may no longer be relevant..

About the author
Michelle lambright black.
Michelle Lambright Black is a nationally recognized credit expert with two decades of experience. Founder of CreditWriter.com—an online community that helps busy moms take control of their credit and finances—Michelle's work has been published thousands of times by FICO, Experian, Forbes, Bankrate, MarketWatch, Parents, U.S. News & World Report, and many more.
Up next in this guide:
5. 6 Types of Business Plans
Explore Guide Topics:
- How to Start a Business in 19 Steps
- How to Perform Market Research for a New Small Business
- The Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Business Plan
- 6 Types of Business Plans
- How to Present a Business Plan
- Funding Your Small Business: How to do It
- How Much Does it Cost to Start a Business?
- 10 Funding Strategies to Keep Your Business Growing
- How to Choose a Business Location
- What You Need to Know About Small Business Zoning Laws
- Business Structures: Choose One for Your Business
- How to Name Your New Small Business
- How to Check if a Business Name is Available
- How to Register a Business
- How to Get a Business Tax ID Number
- How to Get a Business License
- How to Open a Business Bank Account
- Benefits of Having a Business Bank Account
- Business Insurance: Why You Need it and How to Get It

Starting a business
Get a copy of the guide in your email.

Business insights right to your inbox
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter for industry news and business strategies and tips
Subscribe to the newsletter
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter for industry news and business strategies and tips.
Terms & Agreements
Your Privacy Choices
Find a Local Representative
Life at Lendio
Lendio Gives
Business Success Stories
Lendio Reviews
Business Financing
How It Works
Small Business Loans
Building Business Credit
Business Loans Near Me
Resources For Lenders
- Filling out an Application for business funding, and submission to our funding partners will not impact your personal credit score, but, depending on the product, accepting an offer may result in a hard inquiry.
- Time to fund depends upon the product that you select, and can be as little as 24 hours, but may be longer.
- Funding amounts and number of total loans funded include loans funded under the Paycheck Protection Program.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- United Kingdom
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
Plan Your Business Plan Before you put pen to paper, find out how to assess your business's goals and objectives.
You've decided to write a business plan, and you're ready to get started. Congratulations. You've just greatly increased the chances that your business venture will succeed. But before you start drafting your plan, you need to--you guessed it--plan your draft.
One of the most important reasons to plan your plan is that you may be held accountable for the projections and proposals it contains. That's especially true if you use your plan to raise money to finance your company. Let's say you forecast opening four new locations in the second year of your retail operation. An investor may have a beef if, due to circumstances you could have foreseen, you only open two. A business plan can take on a life of its own, so thinking a little about what you want to include in your plan is no more than common prudence.
Second, as you'll soon learn if you haven't already, business plans can be complicated documents. As you draft your plan, you'll be making lots of decisions on serious matters, such as what strategy you'll pursue, as well as less important ones, like what color paper to print it on. Thinking about these decisions in advance is an important way to minimize the time you spend planning your business and maximize the time you spend generating income.
To sum up, planning your plan will help control your degree of accountability and reduce time-wasting indecision. To plan your plan, you'll first need to decide what your goals and objectives in business are. As part of that, you'll assess the business you've chosen to start, or are already running, to see what the chances are that it will actually achieve those ends. Finally, you'll take a look at common elements of most plans to get an idea of which ones you want to include and how each will be treated.
Determine Your Objectives Close your eyes. Imagine that the date is five years from now. Where do you want to be? Will you be running a business that hasn't increased significantly in size? Will you command a rapidly growing empire? Will you have already cashed out and be relaxing on a beach somewhere, enjoying your hard-won gains?
Answering these questions is an important part of building a successful business plan. In fact, without knowing where you're going, it's not really possible to plan at all.
Now is a good time to free-associate a little bit--to let your mind roam, exploring every avenue that you'd like your business to go down. Try writing a personal essay on your business goals. It could take the form of a letter to yourself, written from five years in the future, describing all you have accomplished and how it came about.
As you read such a document, you may make a surprising discovery, such as that you don't really want to own a large, fast-growing enterprise but would be content with a stable small business. Even if you don't learn anything new, though, getting a firm handle on your goals and objectives is a big help in deciding how you'll plan your business.
Goals and Objectives Checklist If you're having trouble deciding what your goals and objectives are, here are some questions to ask yourself:
- How determined am I to see this succeed?
- Am I willing to invest my own money and work long hours for no pay, sacrificing personal time and lifestyle, maybe for years?
- What's going to happen to me if this venture doesn't work out?
- If it does succeed, how many employees will this company eventually have?
- What will be its annual revenues in a year? Five years?
- What will be its market share in that time frame?
- Will it be a niche marketer, or will it sell a broad spectrum of good and services?
- What are my plans for geographic expansion? Local? National? Global?
- Am I going to be a hands-on manager, or will I delegate a large proportion of tasks to others?
- If I delegate, what sorts of tasks will I share? Sales? Technical? Others?
- How comfortable am I taking direction from others? Could I work with partners or investors who demand input into the company's management?
- Is it going to remain independent and privately owned, or will it eventually be acquired or go public?
Your Financing Goals
It doesn't necessarily take a lot of money to make a lot of money, but it does take some. That's especially true if, as part of examining your goals and objectives, you envision very rapid growth.
Energetic, optimistic entrepreneurs often tend to believe that sales growth will take care of everything, that they'll be able to fund their own growth by generating profits. However, this is rarely the case, for one simple reason: You usually have to pay your own suppliers before your customers pay you. This cash flow conundrum is the reason so many fast-growing companies have to seek bank financing or equity sales to finance their growth. They are literally growing faster than they can afford.
Start by asking yourself what kinds of financing you're likely to need--and what you'd be willing to accept. It's easy when you're short of cash, or expect to be short of cash, to take the attitude that almost any source of funding is just fine. But each kind of financing has different characteristics that you should take into consideration when planning your plan. These characteristics take three primary forms:
- First, there's the amount of control you'll have to surrender. An equal partner may, quite naturally, demand approximately equal control. Venture capitalists often demand significant input into management decisions by, for instance, placing one or more people on your board of directors. Angel investors may be very involved or not involved at all, depending on their personal style. Bankers, at the other end of the scale, are likely to offer no advice whatsoever as long as you make payments of principal and interest on time and are not in violation of any other terms of your loan.
- You should also consider the amount of money you're likely to need. Any amount less than several million dollars is too small to be considered for a standard initial public offering of stock, for example. Venture capital investors are most likely to invest amounts of $250,000 to $3 million. On the other hand, only the richest angel investor will be able to provide more than a few hundred thousand dollars, if that.
Almost any source of funds, from a bank to a factor, has some guidelines about the size of financing it prefers. Anticipating the size of your needs now will guide you in preparing your plan.
- The third consideration is cost. This can be measured in terms of interest rates and shares of ownership as well as in time, paperwork and plain old hassle.
How Will You Use Your Plan
Believe it or not, part of planning your plan is planning what you'll do with it. No, we haven't gone crazy--at least not yet. A business plan can be used for several things, from monitoring your company's progress toward goals to enticing key employees to join your firm. Deciding how you intend to use yours is an important part of preparing to write it.
Do you intend to use your plan to help you raise money? In that case, you'll have to focus very carefully on the executive summary, the management, and marketing and financial aspects. You'll need to have a clearly focused vision of how your company is going to make money. If you're looking for a bank loan, you'll need to stress your ability to generate sufficient cash flow to service loans. Equity investors, especially venture capitalists, must be shown how they can cash out of your company and generate a rate of return they'll find acceptable.
Do you intend to use your plan to attract talented employees? Then you'll want to emphasize such things as stock options and other aspects of compensation as well as location, work environment, corporate culture and opportunities for growth and advancement.
Do you anticipate showing your plan to suppliers to demonstrate that you're a worthy customer? A solid business plan may convince a supplier of some precious commodity to favor you over your rivals. It may also help you arrange supplier credit. You may want to stress your blue-ribbon customer list and spotless record of repaying trade debts in this plan.
Assessing Your Company's Potential
For most of us, unfortunately, our desires about where we would like to go aren't as important as our businesses' ability to take us there. Put another way, if you choose the wrong business, you're going nowhere.
Luckily, one of the most valuable uses of a business plan is to help you decide whether the venture you have your heart set on is really likely to fulfill your dreams. Many, many business ideas never make it past the planning stage because their would-be founders, as part of a logical and coherent planning process, test their assumptions and find them wanting.
Test your idea against at least two variables. First, financial, to make sure this business makes economic sense. Second, lifestyle, because who wants a successful business that they hate?
Answer the following questions to help you outline your company's potential. There are no wrong answers. The objective is simply to help you decide how well your proposed venture is likely to match up with your goals and objectives.
- What initial investment will the business require?
- How much control are you willing to relinquish to investors?
- When will the business turn a profit?
- When can investors, including you, expect a return on their money?
- What are the projected profits of the business over time?
- Will you be able to devote yourself full time to the business, financially?
- What kind of salary or profit distribution can you expect to take home?
- What are the chances the business will fail?
- What will happen if it does?
- Where are you going to live?
- What kind of work are you going to be doing?
- How many hours will you be working?
- Will you be able to take vacations?
- What happens if you get sick?
- Will you earn enough to maintain your lifestyle?
- Does your family understand and agree with the sacrifices you envision?
Sources: The Small Business Encyclopedia , Business Plans Made Easy, Start Your Own Business and Entrepreneur magazine.
Continue on to the next section of our Business Plan How-To >> Elements of a Business Plan
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- His Ex-Boss Issued Him a Cease-and-Desist Order . Neither Man Expected What Happened in a Parking Lot Next: 'I Bleed This Business. It's Cold-Blooded.'
- Lock 8 Evening Routines With Surprising Effects on Your Ability to Get Things Done
- Why Are Nvidia Earnings So Important? They Could Be a 'Market Mover,' Says Expert.
- Lock I Sent My Role Model a DM, Never Imagining She'd Respond — Then This Happened
- Lock This Couple's Weekend Side Hustle Began With a $50 Facebook Marketplace Purchase — Now It Earns Millions of Dollars a Year: 'You Don't Need Money to Start'
- Walmart and Burger King's New Partnership Is Poised to Give a Boost to Franchise Traffic
Most Popular Red Arrow
Why being a more generous leader will create a more successful business.
There is no time like the present to think more about others than oneself. Give generously in all you do: your time, energy, enthusiasm, caring and financial impact. Your company, clients, community and team will thank you.
These Are the Best Jobs for Every Personality Type, According to a New Report
You don't have to be an extrovert to find a job that aligns with your strengths.
Apple Just Conducted a Rare Round of Layoffs. Here Are the Teams and Roles Affected.
Apple has over 160,000 employees.
63 Small Business Ideas to Start in 2024
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
Double Your Organic Traffic and Boost Your Sales With This SEO Guide for Ecommerce Businesses
Discover proven SEO tips to double organic traffic to your ecommerce business and drive more sales.
What Is Elon Musk's New Master Plan For Tesla? Original Blueprint Disappears From Tesla's Website After 18 years
Tesla seems to have removed Musk's original master plan (and the follow-up) from its website.
Successfully copied link
- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Capacity planning
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- 22 types of business objectives to meas ...
22 types of business objectives to measure success

Clear business objectives help you achieve your mission statement and long-term company vision. These objectives can range from financial objectives to organization specific objectives. Take a look at 22 types of business objectives you can set—plus, learn when to use business objectives vs. 14 other goal frameworks.
Whether you work at a small business, a start up, or as a team lead at a larger enterprise, as a key business owner, you’re responsible for identifying the business objectives that will help your organization hit its long-term goals. Setting goals and strategic objectives is the best way to know where you’re going and how to get there.
In this article, learn about 22 different types of business objectives and how to make them achievable. Then, take a look at the 15 different types of goals you can set, depending on why you’re setting those goals.
What is a business objective?
Business objectives are the results you are aiming to achieve in order to accomplish your longer-term company vision. Think of business objectives as metrics to measure your overall business success.
Hitting your business objectives means you’re on the path towards achieving larger company goals. As such, business objectives should focus on large-scale organizational impact. Good business objectives are measurable, specific, and time-bound.
Unlock the true business value of Asana
Discover IDC's insights on how Asana helps businesses overcome tool overload, streamline decision-making, and boost productivity. Learn how Asana delivers 57% more on-time projects, 82% higher employee satisfaction, and an impressive ROI.
22 types of business objectives
Set business objectives based on factors that measure and impact your organization’s success. For example, you might set the following business objectives:
Financial business objectives
1. Profitability: A profitability-focused business objective is important if your company is relying on outside investors. Achieving—and maintaining—profitability ensures your long-term success so you can make progress towards your overall company mission.
2. Revenue: Revenue-focused business objectives help you balance your income with your costs in order to stay in business. You might set business objectives to achieve a certain annual revenue goal, or to increase revenue by a certain percentage over a period of time.
3. Costs: Costs refer to how much money you’re spending on your business. Reducing costs can help you increase revenue and achieve profitability. Business objectives related to cost can help you control production or operations cost to improve your business’s financial performance.
4. Cash flow: Cash flow refers to the money moving into and out of your business. Cash flow can be positive—when you’re making more than you’re spending—or negative—when you’re spending more than you’re making. Similar to profitability, a cash flow-oriented business objective can help set you up for long term financial success.
5. Sustainable growth: In order to grow as a business, you need to grow sustainably. Setting business objectives around sustainable growth can help you plan your financial projections, employee costs, and other financial considerations.
Customer-centric business objectives
6. Competitive positioning: A big element of your business strategy is thinking about how your product or service compares to others in the same market. By setting a business objective focused on competitive positioning, you can ensure your product or service reaches parity with what’s expected in the market, or use competitive positioning to outdo your competitors in a key area.
8. Customer satisfaction: In order to succeed as a business, you need happy customers. Focusing on a customer satisfaction-based business objective can help you better serve your customers. Depending on the business objective, this might focus on a customer advocacy program, a better help desk, or something similarly customer-facing.
9. Brand awareness: Your brand is what makes your organization stand out from the crowd. Brand awareness is an important way to understand how your customers think of your brand, and how aware they are of your distinct brand vs. your competitors. Understanding—and increasing—brand awareness is a key part of your long-term marketing strategy .
10. Sales: You’ll often find business objectives related to improving or refining the sales cycle. This could include anything from reducing customer acquisition cost (CAC), developing better lead tracking, increasing cross-selling, or something else.
11. Churn: In business, your churn rate refers to how many customers you lose over a set period of time. Reducing churn is a great way to increase your revenue and ensure your customers are satisfied with the product or service you provide.
Internal business objectives
12. Employee satisfaction and engagement: Part of your business is how your employees feel about working there, too. Increasing employee satisfaction and engagement leads to happier employees, reduced burnout , and more effective teams.
13. Employee retention: A key internal business objective is how long your employees spend at your company. Increasing tenure and reducing turnover can help you achieve more complex projects with knowledgeable employees.
14. Company growth: In order to grow your business, you also need to grow the number of people you employ. Growing your company sustainably can be difficult—which is why businesses often set company growth as a key business objective.
15. Organizational culture: Organizational culture is the ideals, values, and group norms that shape how team members interact within your company. Good culture drives employee engagement and increases retention, which is one of the key reasons so many companies set organizational culture-focused business objectives.
16. Change management: Smoothly implement large-scale organizational change with change management . Though you typically won’t see organizations set this type of business objective year after year, it can be a helpful objective to set if you have large changes on the horizon.
17. Productivity: At Asana, we don’t think of productivity as “doing the most you can,” but rather as a way to optimize your time and get your best work done. Increasing employee productivity can help your teams achieve their high-impact work more efficiently.
18. Employee effectiveness: Teams don’t just need to be efficient—they also need to know the right things to work on. The best companies aim for efficiency and effectiveness—which is where an effectiveness-based business objective comes into play. To learn more, read our article about the difference between efficiency and effectiveness .
19. Diversity and inclusion: A big part of a welcoming company culture is making sure your employees feel like they belong. Investing in diversity and inclusion programs can help your business be more welcoming to your current and potential employees.
Regulation related business objectives
20. Quality control: Implementing quality control measures as a business objective can help you ensure your product or services are at the level you want them to be. This in turn leads to better customer relationships and overall increase in revenue.
21. Compliance: If your business has any compliance needs to meet in the near future, setting those compliance requirements as a business objective will ensure you hit your targets on time.
22. Sustainability or waste reduction: Some businesses set business objectives to reduce waste or increase sustainability. While this may not directly impact your business, proving that you’re environmentally minded can help you reach specific audiences you’re targeting.
Which goal framework is right for you?
Figuring out exactly what type of goal you need to set can be tricky. Each goal framework is slightly different—and implementing the right one can help you achieve success.
The type of goal you set will depend on the business activities you’re running and the specific goals you have. If your goals have a set time frame, you may want to go with short-term objectives, whereas larger goals have their own unique frameworks.
If you’re not sure where to start, check out these 15 goal frameworks for different situations:
1. Business objectives: Set goals based on operating factors that impact your company’s long-term success.
2. Business plan : Also called a business strategy plan. Document your business’ goals and plan out how you’ll get there.
3. Vision statement : Set an organization-wide North Star.
4. Big Hairy Audacious Goals (BHAGs) : Set organization-sized stretch goals .
5. Company values : Align your team around core principles.
6. Strategic plan : Clarify your three to five year company goals during the strategic planning process.
7. Strategic goal : Set the goals you want to achieve by the end of your strategic plan.
8. Critical success factors : Clarify the high-level goals you need to achieve in order to achieve your strategic goals.
9. Strategic management : Execute against your strategic plan in order to achieve your company goals.
10. Business goals : Set predetermined targets to achieve in a set period of time.
11. Objectives and key results (OKRs) : Set and communicate annual company goals.
12. Key performance indicators (KPIs) : Set quantitative goals.
13. Project objectives : Share what you want to achieve by the end of a project.
14. Project deliverables : Identify a project’s output.
15. Project milestones : Mark specific checkpoints along a project’s timeline.
More goal setting resources
Clear goals are critical to keep your organization functioning. In addition to business objectives, check out our goal setting resource hub for tips on setting goals and achieving high-impact results. Then when you’re ready, get started with Asana for goal tracking. With Asana , you can connect your company goals to the work that supports them—all in one place.
Related resources

What's the difference between accuracy and precision?

How Asana streamlines strategic planning with work management
What is management by objectives (MBO)?

7 steps to complete a social media audit (with template)
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
How To Write A Business Plan (2024 Guide)

Updated: Apr 17, 2024, 11:59am

Table of Contents
Brainstorm an executive summary, create a company description, brainstorm your business goals, describe your services or products, conduct market research, create financial plans, bottom line, frequently asked questions.
Every business starts with a vision, which is distilled and communicated through a business plan. In addition to your high-level hopes and dreams, a strong business plan outlines short-term and long-term goals, budget and whatever else you might need to get started. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to write a business plan that you can stick to and help guide your operations as you get started.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
$0 + State Fee
On Formations' Website
Drafting the Summary
An executive summary is an extremely important first step in your business. You have to be able to put the basic facts of your business in an elevator pitch-style sentence to grab investors’ attention and keep their interest. This should communicate your business’s name, what the products or services you’re selling are and what marketplace you’re entering.
Ask for Help
When drafting the executive summary, you should have a few different options. Enlist a few thought partners to review your executive summary possibilities to determine which one is best.
After you have the executive summary in place, you can work on the company description, which contains more specific information. In the description, you’ll need to include your business’s registered name , your business address and any key employees involved in the business.
The business description should also include the structure of your business, such as sole proprietorship , limited liability company (LLC) , partnership or corporation. This is the time to specify how much of an ownership stake everyone has in the company. Finally, include a section that outlines the history of the company and how it has evolved over time.
Wherever you are on the business journey, you return to your goals and assess where you are in meeting your in-progress targets and setting new goals to work toward.
Numbers-based Goals
Goals can cover a variety of sections of your business. Financial and profit goals are a given for when you’re establishing your business, but there are other goals to take into account as well with regard to brand awareness and growth. For example, you might want to hit a certain number of followers across social channels or raise your engagement rates.
Another goal could be to attract new investors or find grants if you’re a nonprofit business. If you’re looking to grow, you’ll want to set revenue targets to make that happen as well.
Intangible Goals
Goals unrelated to traceable numbers are important as well. These can include seeing your business’s advertisement reach the general public or receiving a terrific client review. These goals are important for the direction you take your business and the direction you want it to go in the future.
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you’re offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are providing something necessary or entirely new. If you have any patents or trademarks, this is where you can include those too.
If you have any visual aids, they should be included here as well. This would also be a good place to include pricing strategy and explain your materials.
This is the part of the business plan where you can explain your expertise and different approach in greater depth. Show how what you’re offering is vital to the market and fills an important gap.
You can also situate your business in your industry and compare it to other ones and how you have a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Other than financial goals, you want to have a budget and set your planned weekly, monthly and annual spending. There are several different costs to consider, such as operational costs.
Business Operations Costs
Rent for your business is the first big cost to factor into your budget. If your business is remote, the cost that replaces rent will be the software that maintains your virtual operations.
Marketing and sales costs should be next on your list. Devoting money to making sure people know about your business is as important as making sure it functions.
Other Costs
Although you can’t anticipate disasters, there are likely to be unanticipated costs that come up at some point in your business’s existence. It’s important to factor these possible costs into your financial plans so you’re not caught totally unaware.
Business plans are important for businesses of all sizes so that you can define where your business is and where you want it to go. Growing your business requires a vision, and giving yourself a roadmap in the form of a business plan will set you up for success.
How do I write a simple business plan?
When you’re working on a business plan, make sure you have as much information as possible so that you can simplify it to the most relevant information. A simple business plan still needs all of the parts included in this article, but you can be very clear and direct.
What are some common mistakes in a business plan?
The most common mistakes in a business plan are common writing issues like grammar errors or misspellings. It’s important to be clear in your sentence structure and proofread your business plan before sending it to any investors or partners.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best VPN Services
- Best Project Management Software
- Best Web Hosting Services
- Best Antivirus Software
- Best LLC Services
- Best POS Systems
- Best Business VOIP Services
- Best Credit Card Processing Companies
- Best CRM Software for Small Business
- Best Fleet Management Software
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Software
- Best Business Apps
- Best Free Software For Business
- How to Start a Business
- How To Make A Small Business Website
- How To Trademark A Name
- What Is An LLC?
- How To Set Up An LLC In 7 Steps
- What is Project Management?
- How To Write An Effective Business Proposal

What Is SNMP? Simple Network Management Protocol Explained
What Is A Single-Member LLC? Definition, Pros And Cons
What Is Penetration Testing? Definition & Best Practices
What Is Network Access Control (NAC)?
What Is Network Segmentation?

How To Start A Business In Louisiana (2024 Guide)
Julia is a writer in New York and started covering tech and business during the pandemic. She also covers books and the publishing industry.
- Newsletters
- Best Industries
- Business Plans
- Home-Based Business
- The UPS Store
- Customer Service
- Black in Business
- Your Next Move
- Female Founders
- Best Workplaces
- Company Culture
- Public Speaking
- HR/Benefits
- Productivity
- All the Hats
- Digital Transformation
- Artificial Intelligence
- Bringing Innovation to Market
- Cloud Computing
- Social Media
- Data Detectives
- Exit Interview
- Bootstrapping
- Crowdfunding
- Venture Capital
- Business Models
- Personal Finance
- Founder-Friendly Investors
- Upcoming Events
- Inc. 5000 Vision Conference
- Become a Sponsor
- Cox Business
- Verizon Business
- Branded Content
- Apply Inc. 5000 US
Inc. Premium

- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Overview and Objectives
The third in a comprehensive series to help you craft the perfect business plan for your startup.

This article is part of a series on how to write a great business plan .
Providing an overview of your business can be tricky, especially when you're still in the planning stages. If you already own an existing business, summarizing your current operation should be relatively easy; it can be a lot harder to explain what you plan to become .
So start by taking a step back.
Think about what products and services you will provide, how you will provide those items, what you need to have in order to provide those items, exactly who will provide those items... and most importantly, whom you will provide those items to.
Consider our bicycle rental business example. It's serves retail customers. It has an online component, but the core of the business is based on face-to-face transactions for bike rentals and support.
So you'll need a physical location, bikes, racks and tools and supporting equipment, and other brick-and-mortar related items. You'll need employees with a very particular set of skills to serve those customers, and you'll need an operating plan to guide your everyday activities.
Sound like a lot? It boils down to:
- What you will provide
- What you need to run your business
- Who will service your customers, and
- Who your customers are
In our example, defining the above is fairly simple. You know what you will provide to meet your customer's needs. You will of course need a certain quantity of bikes to service demand, but you will not need a number of different types of bikes. You need a retail location, furnished to meet the demands of your business. You need semi-skilled employees capable of sizing, customizing, and repairing bikes.
And you know your customers: Cycling enthusiasts.
In other businesses and industries answering the above questions can be more difficult. If you open a restaurant, what you plan to serve will in some ways determine your labor needs, the location you choose, the equipment you need to purchase... and most importantly will help define your customer. Changing any one element may change other elements; if you cannot afford to purchase expensive kitchen equipment, you may need to adapt your menu accordingly. If you hope to attract an upscale clientele, you may need to invest more in purchasing a prime location and creating an appealing ambience.
So where do you start? Focus on the basics first:
- Identify your industry: Retail, wholesale, service, manufacturing, etc. Clearly define your type of business.
- Identify your customer. You cannot market and sell to customers until you know who they are.
- Explain the problem you solve. Successful businesses create customer value by solving problems. In our rental example, one problem is cycling enthusiasts who don't--or can't--travel with bikes. Another problem is casual cyclists who can't--or choose not to--spend significant sums on their own bikes. The rental shop will solve that problem by offering a lower-cost and convenient alternative.
- Show how you will solve that problem. Our rental shop will offer better prices and enhanced services like remote deliveries, off-hours equipment returns, and online reservations.
If you are still stuck, try answering these questions. Some may pertain to you; others may not.
- Who is my average customer? Who am I targeting? (Unless you plan to open a grocery store, you should be unlikely to answer, "Everyone!")
- What problem do I solve for my customers?
- How will I solve that problem?
- Where will I fail to solve a customer problem... and what can I do to overcome that issue? (In our rental example, one problem is a potential lack of convenience; we will overcome that issue by offering online reservations, on-resort deliveries, and drive-up equipment returns.)
- Where will I locate my business?
- What products, services, and equipment do I need to run my business?
- What skills do my employees need, and how many do I need?
- How will I beat my competition?
- How can I differentiate myself from my competition in the eyes of my customers? (You can have a great plan to beat your competition but you also must win the perception battle among your customers. If customers don't feel you are different... then you aren't truly different. Perception is critical.)
Once you work through this list you will probably end up with a lot more detail than is necessary for your business plan. That is not a problem: Start summarizing the main points. For example, your Business Overview and Objectives section could start something like this:
History and Vision
Blue Mountain Cycle Rentals is a new retail venture that will be located at 321 Mountain Drive, directly adjacent to an extremely popular cycling destination. Our initial goal is to become the premier provider for bicycle rentals. We will then leverage our customer base and position in the market to offer new equipment sales as well as comprehensive maintenance and service, custom equipment fittings, and expert trail advice.
- Achieve the largest market share bicycle rentals in the area
- Generate a net income of $235,000 at the end of the second year of operation
- Minimize rental inventory replacement costs by maintaining a 7% attrition rate on existing equipment (industry average is 12%)
Keys to Success
- Provide high quality equipment, sourcing that equipment as inexpensively as possible through existing relationships with equipment manufacturers and other cycling shops
- Use signage to attract visitors traveling to the national forest, highlighting our cost and service advantage
- Create additional customer convenience factors to overcome a perceived lack of convenience for customers planning to ride roads and trails some distance away from our shop
- Develop customer incentive and loyalty programs to leverage customer relationships and create positive word of mouth
You could certainly include more detail in each section; this is simply a quick guide. And if you plan to develop a product or service, you should thoroughly describe the development process as well as the end result.
The key is to describe what you will do for your customers--if you can't, you won't have any customers.
Next time we'll look at another major component in a business plan: your Products and Services .
More in this series:
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Key Concepts
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: the Executive Summary
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Products and Services
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Market Opportunities
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Sales and Marketing
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Competitive Analysis
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Operations
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Management Team
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Financial Analysis
The Daily Digest for Entrepreneurs and Business Leaders
Privacy Policy
Table of Contents
How to make a business plan
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Plans and pricing.
6 examples of objectives for a small business plan
Table of Contents
1) Becoming and staying profitable
2) maintaining cash flow , 3) establishing and sustaining productivity , 4) attracting and retaining customers , 5) developing a memorable brand and marketing strategy, 6) planning for growth , track your business objectives and more with countingup.
Your new company’s business plan is a crucial part of your success, as it helps you set up your business and secure the necessary funding. A major part of this plan is your objectives or the outcomes you aim to reach. If you’re unsure where to start, this list of business objective examples can help.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- Becoming and staying profitable
- Maintaining cash flow
- Establishing and sustaining productivity
- Attracting and retaining customers
- Developing a memorable brand
- Reaching and growing an audience through marketing
- Planning for growth
One of the key objectives you may consider is establishing and maintaining profitability . In short, you’ll aim to earn more than you spend and pay off your startup costs. To do this, you’ll need to consider your business’s starting budget and how you’ll stick to it.
To create an objective around profitability, you’ll need to calculate how much you spend to start your business and how much you’ll have to spend regularly to run it. Knowing these numbers will help you determine the earnings you’ll need to become profitable. From there, you can factor in the pricing of your products or services and create sales goals .
For example, say you spend £2,000 on startup costs and expect to spend about £200 monthly to cover business expenses. To earn a profit, you’ll first need to earn back that £2,000 then make more than £200 monthly.
Once you know what you’ll need to earn to become profitable, you can create a realistic timeline to achieve it. If demand and sales forecasts suggest you could earn about £700 monthly, you may create a timeline of 5 months to become profitable.
We have created a free profit margin calculator tool which can help you work out your profit margins.
Maintaining cash flow is another financial objective you could include in your business plan. While profitability means you’ll make more money than you spend, cash flow is the cash running in and out of your business over a given time. This flow is crucial to your company’s success because you need available cash to cover business expenses .
When you complete services, clients may not pay out an invoice right away, meaning you won’t see the cash until they do. If you make enough sales but have low cash flow, you’ll struggle to run your business. So, create an achievable and measurable plan for how you’ll maintain the cash flow you need.
For example, if you spend £500 monthly, you’ll need to ensure you have at least that much available cash. On top of that, anticipate and save for unexpected or emergency expenses, such as broken equipment. To maintain your cash flow, you may want to prioritise cash payments, introduce a realistic deadline for invoices, or create a system to turn your profit to cash.
Aside from financial objectives, another example of objectives for a business plan is sustaining productivity . When you run a business, it can be overwhelming and challenging to stay on top of all the tasks you have to get done. But, if you aim to remain productive and create a clear plan as to how, you can better manage your to-do list.
For example, you may find project management tools that can help you track what you need to do and how to organise your priorities. You may also plan to outsource some aspects of your business eventually, such as investing in an accountant.
Other than planning how you’ll get things done, you may want to create an objective for developing and retaining a customer base. Here, you may outline your efforts to find leads and recruit customers. So, establish goals for how many customers you want to find in your business’s first month, quarter, or year. Your market research can help you understand demand and create realistic sales goals.
If you start a business that customers regularly need, like hairdressing, you may also want to create a strategy for how you’ll retain customers you earn. For example, you could introduce a loyalty program or prioritise customer service to build strong relationships.
Another example of objectives for a business plan is to develop a memorable brand and overall marketing strategy . Your brand is how you present your business to the public, including its unique tone and design. So, here you might research how to make a brand memorable and consider what colour scheme and style will best reach your target audience.
To measure your brand’s progress, you could hold focus groups on understanding what people think of your overall look. Then, surveys can help you grasp the reach of your reputation over time.
Aside from tracking the success of your brand strategy, you may want to consider your business’s marketing approach. For example, you might invest in paid advertising and use social media. You can measure the progress of this over time by using tools like Google Analytics to track your following and reach.
Finally, creating an objective for your company’s growth will help you understand and plan for where you want to go. For example, you may want to expand your services or open a second location for a shop. Whatever ideas you have for the future of your business, try to create a clear, measurable way of getting there, including a timeline. You may also want to include steps towards this goal and savings goals for growth.
To achieve and track your business plan objectives, you’ll need to organise your finances well. But, financial management can be stressful and time-consuming when you’re self-employed. That’s why thousands of business owners use the Countingup app to make their financial admin easier.
Countingup is the business account with built-in accounting software that allows you to manage all your financial data in one place. With the cash flow insights feature, you can confidently keep on top of your finances wherever you are. Plus, the app lets you track and manage what you spend on your business with automatic expense categorisation. This way, you can stick to your budget and plan to accomplish your objectives.

- Counting Up on Facebook
- Counting Up on Twitter
- Counting Up on LinkedIn
Related Resources
Business insurance from superscript.
We’re partnered with insurance experts, Superscript to provide you with small business insurance.
How to register a company in the UK
There are over five million companies registered in the UK and 500,000 new
How to set up a TikTok shop (2024)
TikTok can be an excellent platform for growing a business, big or small.
Best Side Hustle Ideas To Make Extra Money In 2024 (UK Edition)
Looking to start a new career? Or maybe you’re looking to embrace your
How to throw a launch party for a new business
So your business is all set up, what next? A launch party can
How to set sales goals
Want to make manageable and achievable sales goals for your business? Find out
10 key tips to starting a business in the UK
10 things you need to know before starting a business in the UK
How to set up your business: Sole trader or limited company
If you’ve just started a business, you’ll likely be faced with the early
How to register as a sole trader
Running a small business and considering whether to register as a sole trader?
How to open a Barclays business account
When starting a new business, one of the first things you need to
How to start a successful business during a recession
Starting a business during a recession may sound like madness, but some big
What is a mission statement (and how to write one)
When starting a small business, you’ll need a plan to get things up
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many, or all, of the products featured on this page are from our advertising partners who compensate us when you take certain actions on our website or click to take an action on their website. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

LLC Formation
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan helps keep the executive team focused on short- and long-term objectives.
- There's no single required format for a business plan, but certain key elements are essential for most companies.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't.
A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities.
While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below.
A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices.
Common elements in many business plans include:
- Executive summary : This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services : Describe the products and services the company offers or plans to introduce. Include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique consumer benefits. Mention production and manufacturing processes, relevant patents , proprietary technology , and research and development (R&D) information.
- Market analysis : Explain the current state of the industry and the competition. Detail where the company fits in, the types of customers it plans to target, and how it plans to capture market share from competitors.
- Marketing strategy : Outline the company's plans to attract and retain customers, including anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. Describe the distribution channels that will be used to deliver products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections : Established businesses should include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. This section may also include any funding requests.
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These are detailed and lengthy, requiring more effort to create but offering comprehensive information that can be persuasive to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These are concise, sometimes just one page, and focus on key elements. While they save time, companies should be ready to provide additional details if requested by investors or lenders.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth.
As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone.
University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey.
Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ."
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/marketing-plan-ff4bce0e2c52493f909e631039c8f4ca.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Write your business plan
Business plans help you run your business.
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You’ll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It’s a way to think through the key elements of your business.
Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners. Investors want to feel confident they’ll see a return on their investment. Your business plan is the tool you’ll use to convince people that working with you — or investing in your company — is a smart choice.
Pick a business plan format that works for you
There’s no right or wrong way to write a business plan. What’s important is that your plan meets your needs.
Most business plans fall into one of two common categories: traditional or lean startup.
Traditional business plans are more common, use a standard structure, and encourage you to go into detail in each section. They tend to require more work upfront and can be dozens of pages long.
Lean startup business plans are less common but still use a standard structure. They focus on summarizing only the most important points of the key elements of your plan. They can take as little as one hour to make and are typically only one page.
Traditional business plan

Lean startup plan
Traditional business plan format
You might prefer a traditional business plan format if you’re very detail-oriented, want a comprehensive plan, or plan to request financing from traditional sources.
When you write your business plan, you don’t have to stick to the exact business plan outline. Instead, use the sections that make the most sense for your business and your needs. Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections.
Executive summary
Briefly tell your reader what your company is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your company’s leadership team, employees, and location. You should also include financial information and high-level growth plans if you plan to ask for financing.
Company description
Use your company description to provide detailed information about your company. Go into detail about the problems your business solves. Be specific, and list out the consumers, organization, or businesses your company plans to serve.
Explain the competitive advantages that will make your business a success. Are there experts on your team? Have you found the perfect location for your store? Your company description is the place to boast about your strengths.
Market analysis
You'll need a good understanding of your industry outlook and target market. Competitive research will show you what other businesses are doing and what their strengths are. In your market research, look for trends and themes. What do successful competitors do? Why does it work? Can you do it better? Now's the time to answer these questions.
Organization and management
Tell your reader how your company will be structured and who will run it.
Describe the legal structure of your business. State whether you have or intend to incorporate your business as a C or an S corporation, form a general or limited partnership, or if you're a sole proprietor or limited liability company (LLC).
Use an organizational chart to lay out who's in charge of what in your company. Show how each person's unique experience will contribute to the success of your venture. Consider including resumes and CVs of key members of your team.
Service or product line
Describe what you sell or what service you offer. Explain how it benefits your customers and what the product lifecycle looks like. Share your plans for intellectual property, like copyright or patent filings. If you're doing research and development for your service or product, explain it in detail.
Marketing and sales
There's no single way to approach a marketing strategy. Your strategy should evolve and change to fit your unique needs.
Your goal in this section is to describe how you'll attract and retain customers. You'll also describe how a sale will actually happen. You'll refer to this section later when you make financial projections, so make sure to thoroughly describe your complete marketing and sales strategies.
Funding request
If you're asking for funding, this is where you'll outline your funding requirements. Your goal is to clearly explain how much funding you’ll need over the next five years and what you'll use it for.
Specify whether you want debt or equity, the terms you'd like applied, and the length of time your request will cover. Give a detailed description of how you'll use your funds. Specify if you need funds to buy equipment or materials, pay salaries, or cover specific bills until revenue increases. Always include a description of your future strategic financial plans, like paying off debt or selling your business.
Financial projections
Supplement your funding request with financial projections. Your goal is to convince the reader that your business is stable and will be a financial success.
If your business is already established, include income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements for the last three to five years. If you have other collateral you could put against a loan, make sure to list it now.
Provide a prospective financial outlook for the next five years. Include forecasted income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and capital expenditure budgets. For the first year, be even more specific and use quarterly — or even monthly — projections. Make sure to clearly explain your projections, and match them to your funding requests.
This is a great place to use graphs and charts to tell the financial story of your business.
Use your appendix to provide supporting documents or other materials were specially requested. Common items to include are credit histories, resumes, product pictures, letters of reference, licenses, permits, patents, legal documents, and other contracts.
Example traditional business plans
Before you write your business plan, read the following example business plans written by fictional business owners. Rebecca owns a consulting firm, and Andrew owns a toy company.
Lean startup format
You might prefer a lean startup format if you want to explain or start your business quickly, your business is relatively simple, or you plan to regularly change and refine your business plan.
Lean startup formats are charts that use only a handful of elements to describe your company’s value proposition, infrastructure, customers, and finances. They’re useful for visualizing tradeoffs and fundamental facts about your company.
There are different ways to develop a lean startup template. You can search the web to find free templates to build your business plan. We discuss nine components of a model business plan here:

Key partnerships
Note the other businesses or services you’ll work with to run your business. Think about suppliers, manufacturers, subcontractors, and similar strategic partners.
Key activities
List the ways your business will gain a competitive advantage. Highlight things like selling direct to consumers, or using technology to tap into the sharing economy.
Key resources
List any resource you’ll leverage to create value for your customer. Your most important assets could include staff, capital, or intellectual property. Don’t forget to leverage business resources that might be available to women , veterans , Native Americans , and HUBZone businesses .
Value proposition
Make a clear and compelling statement about the unique value your company brings to the market.
Customer relationships
Describe how customers will interact with your business. Is it automated or personal? In person or online? Think through the customer experience from start to finish.
Customer segments
Be specific when you name your target market. Your business won’t be for everybody, so it’s important to have a clear sense of whom your business will serve.
List the most important ways you’ll talk to your customers. Most businesses use a mix of channels and optimize them over time.
Cost structure
Will your company focus on reducing cost or maximizing value? Define your strategy, then list the most significant costs you’ll face pursuing it.
Revenue streams
Explain how your company will actually make money. Some examples are direct sales, memberships fees, and selling advertising space. If your company has multiple revenue streams, list them all.
Example lean business plan
Before you write your business plan, read this example business plan written by a fictional business owner, Andrew, who owns a toy company.
Need help? Get free business counseling
How to Set Goals and Objectives in Your Business Plan
Writing out a business plan is a vital step in starting a new company. It helps you create a roadmap of the future of your company and it's the first place investors look to see if you're for real. However, if your company goals aren't laid out clearly or they're unrealistic, investors won't get on board with your vision.
To guide your company toward success, you need to know what success entails. You'll have a much greater chance of making it if you have a direction to move toward. Goal setting gives your company a target to shoot for in the future.
Big goals don't happen all at once, however. You have to take them step by step and you need to know the objectives you'll have to complete on the way. In this article, we'll show you how to create manageable goals for your business and design a series of actionable objectives leading up to them.
What Are Goals and Objectives for Your Business?
Goals are the big targets in your business planning, while objectives are the actions or landmarks that make up the end goal. Clear goals serve to inspire and rally your team to perform but they're not immediately actionable, specific, or measurable. For example, let's say your business sells computers and your goal this year is to increase your gross revenue. How much gross revenue do you want to bring in? You need an objective amount to aim for.
Let's say you decide to shoot for $300,000 in gross revenue. That means your monthly objective is to make $25,000 in gross revenue ($300,000/12). Your direct cost to make each computer is $500 and you sell each computer for $1,500. That means you need to sell 25 computers a month.
Now, you have a measurable monthly objective, but it's not actionable. You need to give your team specific objectives that will lead them toward achieving the goal. How will they sell an average of 25 computers every month?
Here's a list of some actionable objectives your marketing team could complete to help you reach your sales goal. You should assign objectives directly to an individual or department within your business. Of course, if you're the only member of your business, you'll be doing everything yourself.
- Create two blog posts every week using search engine optimization (SEO) to increase brand awareness.
- Create one product video every month and feature it on social media sites like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
- Create an email list for consumers who fill out a form on your website. Send out a weekly email with exclusive news and promotions about the product.
- Use key performance indicators (KPIs) for the company website to identify the top exit page (where the most visitors leave). Redesign the page.
Decide on Goals for Your Business
How do you decide what your goals should be for your company? Each business's goals will be unique depending on its particular business model. A great place to start the decision-making process is your mission statement. Let's use the same computer company in the following example.
Your mission statement is "to create affordable, easy-to-use computers and offer knowledgeable, friendly, and fast technical support and customer service." There are several keywords in the statement that you can use to develop goals. If you use "fast technical support," your goal might be to increase the speed at which your team responds to customer inquiries.
You can also use other methods to decide your company goals. You might hold a brainstorming session with your team to create your goals or you can set goals about how you'll outperform or reach a different market segment than your competitors.
Here are a few types of goals you might create for your business.
- Operational goals: To be more efficient in your work processes and business strategy
- Profit goals: To increase revenue, reduce costs, or increase market share
- Staff development goals: To train your team, increase their knowledge, or improve their customer satisfaction scores
- Goals for handling problems: To be proactive in dealing with possible market, manufacturer, staff, or product issues and things like natural disasters
- Product goals: To create and release a new product or improve a current one
Evaluate Your Business Goals and Objectives
One of the quickest ways to turn investors off is to include outlandish goals in your business plan. Before they put money into your company, they'll want to know that your goal-setting process is sensible. Both your short-term goals and long-term goals need to be realistic and attainable.
You may believe that your company is capable of achieving incredible results, but investors are practical. For example, no one will believe that your computer shop that currently makes $100,000 in gross revenue will be more profitable than Microsoft in five years.
To prove that your goals are realistic, you'll have to show your work. Create a believable forecast of your future business revenue by analyzing things like your business costs, profit margins, market share, and expected growth.
Using SMART to Analyze Your Business Goals
One way to evaluate your business goals for effectiveness is to use SMART goals . Each letter of the acronym represents a quality that your business goals should have. Here's a breakdown you can follow to make sure you have smart goals:
- Specific: Your objectives should be clear, specific actions. It should also be clear who's responsible for them. For example, your marketing team needs to create an email list.
- Measurable: You should be able to easily gauge your success. For example, you need to sell 25 computers a month to reach your goal. If you sell 23, you may need to adjust your method.
- Attainable: Goals need to be realistic. If you currently sell 15 computers a month, it's very unlikely that you'll immediately start selling 1,000 a month.
- Relevant: Your goals need to be in line with your higher-level goals. Creating a blog and optimizing it to appear high on a search engine results page (SERP) will increase brand awareness and provide a bigger audience of possible new customers.
- Time-bound: Create deadlines for your goals or they'll never get done. For example, your sales team must redesign the landing page for your Facebook Ads by Friday, Nov. 3.
Using OKRs to Measure Business Objectives
Another system you can use for managing goals and objectives is the objective and key results (OKR) method. In the OKR system, the O (objective) is representative of a larger goal, while the KR (key results) represent the smaller objectives you use to measure your progress. Here's an OKR model for your computer sales goal.
- O: Increase profitability for the computer company.
- KR1: Make $300,000 in gross profit for the year.
- KR2: Sell 25 computers every month.
Skynova Can Help You Manage All Your Accounting Goals
Generally, investors are more interested in where your company is going than where it currently is. If they're going to put money into it, they need to see that you have the initiative to grow your business and give them a big return on their investment. Use your business plan to give them a clear understanding of your goals and objectives and you'll have a greater chance of getting their backing.
No matter what type of business you run, you likely want to spend your time growing it, not doing administration. Skynova's software products can help you manage your accounting tasks quickly and easily. Take a look at how simple our business templates and accounting software can make your business processes.
Notice to the Reader
The content within this article is designed to provide a basic explanation of goal- and objective-setting for a small business. It isn't tailored to any specific type of business and may not fit your particular company. Before making any big business decisions that could affect your bottom line or presenting your company objectives to investors, you should seek the advice of a certified professional.
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Setting Business Goals & Objectives: 4 Considerations

- 31 Oct 2023
Setting business goals and objectives is important to your company’s success. They create a roadmap to help you identify and manage risk , gain employee buy-in, boost team performance , and execute strategy . They’re also an excellent marker to measure your business’s performance.
Yet, meeting those goals can be difficult. According to an Economist study , 90 percent of senior executives from companies with annual revenues of one billion dollars or more admitted they failed to reach all their strategic goals because of poor implementation. In order to execute strategy, it’s important to first understand what’s attainable when developing organizational goals and objectives.
If you’re struggling to establish realistic benchmarks for your business, here’s an overview of what business goals and objectives are, how to set them, and what you should consider during the process.
Access your free e-book today.
What Are Business Goals and Objectives?
Business objectives dictate how your company plans to achieve its goals and address the business’s strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities. While your business goals may shift, your objectives won’t until there’s an organizational change .
Business goals describe where your company wants to end up and define your business strategy’s expected achievements.
According to the Harvard Business School Online course Strategy Execution , there are different types of strategic goals . Some may even push you and your team out of your comfort zone, yet are important to implement.
For example, David Rodriguez, global chief human resources officer at Marriott, describes in Strategy Execution the importance of stretch goals and “pushing people to not accept today's level of success as a final destination but as a starting point for what might be possible in the future.”
It’s important to strike a balance between bold and unrealistic, however. To do this, you must understand how to responsibly set your business goals and objectives.
Related: A Manager’s Guide To Successful Strategy Implementation
How to Set Business Goals and Objectives
While setting your company’s business goals and objectives might seem like a simple task, it’s important to remember that these goals shouldn’t be based solely on what you hope to achieve. There should be a correlation between your company’s key performance indicators (KPIs)—quantifiable success measures—and your business strategy to justify why the goal should, and needs to, be achieved.
This is often illustrated through a strategy map —an illustration of the cause-and-effect relationships that underpin your strategy. This valuable tool can help you identify and align your business goals and objectives.
“A strategy map gives everyone in your business a road map to understand the relationship between goals and measures and how they build on each other to create value,” says HBS Professor Robert Simons in Strategy Execution .
While this roadmap can be incredibly helpful in creating the right business goals and objectives, a balanced scorecard —a tool to help you track and assess non-financial measures—ensures they’re achievable through your current business strategy.
“Ask yourself, if I picked up a scorecard and examined the measures on that scorecard, could I infer what the business's strategy was,” Simon says. “If you've designed measures well, the answer should be yes.”
According to Strategy Execution , these measures are necessary to ensure your performance goals are achieved. When used in tandem, a balanced scorecard and strategy map can also tell you whether your goals and objectives will create value for you and your customers.
“The balanced scorecard combines the traditional financial perspective with additional perspectives that focus on customers, internal business processes, and learning and development,” Simons says.
These four perspectives are key considerations when setting your business goals and objectives. Here’s an overview of what those perspectives are and how they can help you set the right goals for your business.
4 Things to Consider When Setting Business Goals and Objectives
1. financial measures.
It’s important to ensure your plans and processes lead to desired levels of economic value. Therefore, some of your business goals and objectives should be financial.
Some examples of financial performance goals include:
- Cutting costs
- Increasing revenue
- Improving cash flow management
“Businesses set financial goals by building profit plans—one of the primary diagnostic control systems managers use to execute strategy,” Simons says in Strategy Execution . “They’re budgets drawn up for business units that have both revenues and expenses, and summarize the anticipated revenue inflows and expense outflows for a specified accounting period.”
Profit plans are essential when setting your business goals and objectives because they provide a critical link between your business strategy and economic value creation.
According to Simons, it’s important to ask three questions when profit planning:
- Does my business strategy generate enough profit to cover costs and reinvest in the business?
- Does my business generate enough cash to remain solvent through the year?
- Does my business create sufficient financial returns for investors?
By mapping out monetary value, you can weigh the cost of different strategies and how likely it is you’ll meet your company and investors’ financial expectations.
2. Customer Satisfaction
To ensure your business goals and objectives aid in your company’s long-term success, you need to think critically about your customers’ satisfaction. This is especially important in a world where customer reviews and testimonials are crucial to your organization’s success.
“Everything that's important to the business, we have a KPI and we measure it,” says Tom Siebel, founder, chairman, and CEO of C3.ai, in Strategy Execution . “And what could be more important than customer satisfaction?”
Unlike your company’s reputation, measuring customer satisfaction has a far more personal touch in identifying what customers love and how to capitalize on it through future strategic initiatives .
“We do anonymous customer satisfaction surveys every quarter to see how we're measuring up to our customer expectations,” Siebel says.
While this is one example, your customer satisfaction measures should reflect your desired market position and focus on creating additional value for your audience.
Related: 3 Effective Methods for Assessing Customer Needs
3. Internal Business Processes
Internal business processes is another perspective that should factor into your goal setting. It refers to several aspects of your business that aren’t directly affected by outside forces. Since many goals and objectives are driven by factors such as business competition and market shifts, considering internal processes can create a balanced business strategy.
“Our goals are balanced to make sure we’re holistically managing the business from a financial performance, quality assurance, innovation, and human talent perspective,” says Tom Polen, CEO and president of Becton Dickinson, in Strategy Execution .
According to Strategy Execution , internal business operations are broken down into the following processes:
- Operations management
- Customer management
While improvements to internal processes aren’t driven by economic value, these types of goals can still reap a positive return on investment.
“We end up spending much more time on internal business process goals versus financial goals,” Polen says. “Because if we take care of them, the financial goals will follow at the end of the day.”
4. Learning and Growth Opportunities
Another consideration while setting business goals and objectives is learning and growth opportunities for your team. These are designed to increase employee satisfaction and productivity.
According to Strategy Execution , learning and growth opportunities touch on three types of capital:
- Human: Your employees and the skills and knowledge required for them to meet your company’s goals
- Information: The databases, networks, and IT systems needed to support your long-term growth
- Organization: Ensuring your company’s leadership and culture provide people with purpose and clear objectives
Employee development is a common focus for learning and growth goals. Through professional development opportunities , your team will build valuable business skills and feel empowered to take more risks and innovate.
To create a culture of innovation , it’s important to ensure there’s a safe space for your team to make mistakes—and even fail.
“We ask that people learn from their mistakes,” Rodriguez says in Strategy Execution . “It's really important to us that people feel it’s safe to try new things. And all we ask is people extract their learnings and apply it to the next situation.”

Achieve Your Business Goals
Business goals aren’t all about your organization’s possible successes. It’s also about your potential failures.
“When we set goals, we like to imagine a bright future with our business succeeding,” Simons says in Strategy Execution . “But to identify your critical performance variables, you need to engage in an uncomfortable exercise and consider what can cause your strategy to fail.”
Anticipating potential failures isn’t easy. Enrolling in an online course—like HBS Online’s Strategy Execution —can immerse you in real-world case studies of past strategy successes and failures to help you better understand where these companies went wrong and how to avoid it in your business.
Do you need help setting your business goals and objectives? Explore Strategy Execution —one of our online strategy courses —and download our free strategy e-book to gain the insights to create a successful strategy.

About the Author
The 10 Components of a Business Plan

Whether you’re planning to open a shop that makes the best coffee or you want to sell eco-friendly office supplies, you’ll need to explain why your business is necessary and how it’ll differ from its competitors. That’s where your business plan comes in. It provides investors, lenders and potential partners with an understanding of your company’s structure and goals. If you want to gain the financial autonomy to run a business or become an entrepreneur, a financial advisor can help align your finances.
1. Executive Summary
Your executive summary should appear first in your business plan. It should summarize what you expect your business to accomplish. Since it’s meant to highlight what you intend to discuss in the rest of the plan, the Small Business Administration suggests that you write this section last.
A good executive summary is compelling. It reveals the company’s mission statement, along with a short description of its products and services. It might also be a good idea to briefly explain why you’re starting your company and include details about your experience in the industry that you’re entering.
2. Company Description
A company description includes key information about your business, goals and the target customers that you want to serve. This is where you explain why your company stands out from other competitors in the industry and break down its strengths, including how it offers solutions for customers, and the competitive advantages that will give your business an edge to succeed.
3. Market Analysis
This is where you show that you have a key understanding of the ins and outs of the industry and the specific market you plan to enter. Here you will substantiate the strengths that you highlighted in your company description with data and statistics that break down industry trends and themes. Show what other businesses are doing and how they are succeeding or failing. Your market analysis should also help visualize your target customers. This includes how much money they make, what their buying habits are, which services they want and need, among other target customer preferences. Above all, the numbers should help answer why your business can do it better.
4. Competitive Analysis

A good business plan will present a clear comparison of your business vs your direct and indirect competitors. This is where you prove your knowledge of the industry by breaking down their strengths and weaknesses. Your end goal is show how your business will stack up. And if there are any issues that could prevent you from jumping into the market, like high upfront costs, this is where you will need to be forthcoming. Your competitive analysis will go in your market analysis section.
5. Description of Management and Organization
Your business must also outline how your organization is set up. Introduce your company managers here and summarize their skills and primary job responsibilities. An effective way could be to create a diagram that maps out your chain of command.
Don’t forget to indicate whether your business will operate as a partnership, a sole proprietorship or a business with a different ownership structure. If you have a board of directors, you’ll need to identify the members.
6. Breakdown of Your Products and Services
While your company description is an overview, a detailed breakdown of your products and services is intended to give a complementary but fuller description about the products that you are creating and selling, how long they could last and how they will meet existing demand.
This is where you should mention your suppliers, as well as other key information about how much it will cost to make your products and how much money you are hoping to bring in. You should also list here all relevant information pertaining to patents and copyright concerns as well.
7. Marketing Plan
This is where you describe how you intend to get your products and services in front of your target customers. Break down here the steps that you will take to promote your products and the budget that you will need to implement your strategies.
8. Sales Strategy
This section should answer how you will sell the products that you are building or carry out the services that you intend to offer. Your sales strategy must be specific. Break down how many sales reps you will need to hire and how you will recruit them and bring them on board. Make sure to include your sales targets as well.
9. Request for Funding
If you need funding, this section focuses on the amount of money that you need to set up your business and how you plan to use the capital that you are raising. You might want to include a timeline here for additional funding that you may require to complete other important projects.
10. Financial Projections

This final section breaks down the financial goals and expectations that you’ve set based on market research. You’ll report your anticipated revenue for the first 12 months and your annual projected earnings for the second, third, fourth and fifth years of business.
If you’re trying to apply for a personal loan or a small business loan, you can always add an appendix or another section that provides additional financial or background information.
Bottom Line
Every company is different so your business plan might look nothing like another entrepreneur’s. But there are key components that every good plan needs to have, and it’s always a good idea to provide a clear and accurate summary of your business goals in your business plan.
Tips for Business Owners
- A financial advisor can help you align your personal finances to give you an edge as a business owner or an entrepreneur. Finding a financial advisor doesn’t have to be hard. SmartAsset’s free tool matches you with up to three vetted financial advisors who serve your area, and you can have a free introductory call with your advisor matches to decide which one you feel is right for you. If you’re ready to find an advisor who can help you achieve your financial goals, get started now .
- If you are thinking of buying real estate, equipment, developing new products and other big-ticket activities for your business, you should consider using a capital asset pricing model to determine whether an investment is worth your risk.
Photo credit: ©iStock.com/nandyphotos, ©iStock.com/shironosov, ©iStock.com/cigdemhizal
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

7 Business Plan Examples to Inspire Your Own (2024)
Need support creating your business plan? Check out these business plan examples for inspiration.

Any aspiring entrepreneur researching how to start a business will likely be advised to write a business plan. But few resources provide business plan examples to really guide you through writing one of your own.
Here are some real-world and illustrative business plan examples to help you craft your business plan .
7 business plan examples: section by section
The business plan examples in this article follow this template:
- Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business.
- Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists.
- Market analysis. Research-based information about the industry and your target market.
- Products and services. What you plan to offer in exchange for money.
- Marketing plan. The promotional strategy to introduce your business to the world and drive sales.
- Logistics and operations plan. Everything that happens in the background to make your business function properly.
- Financial plan. A breakdown of your numbers to show what you need to get started as well as to prove viability of profitability.
- Executive summary
Your executive summary is a page that gives a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. It’s easiest to save this section for last.
In this free business plan template , the executive summary is four paragraphs and takes a little over half a page:

- Company description
You might repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page, social media profile pages, or other properties that require a boilerplate description of your small business.
Soap brand ORRIS has a blurb on its About page that could easily be repurposed for the company description section of its business plan.

You can also go more in-depth with your company overview and include the following sections, like in the example for Paw Print Post:
- Business structure. This section outlines how you registered your business —as an LLC , sole proprietorship, corporation, or other business type . “Paw Print Post will operate as a sole proprietorship run by the owner, Jane Matthews.”
- Nature of the business. “Paw Print Post sells unique, one-of-a-kind digitally printed cards that are customized with a pet’s unique paw prints.”
- Industry. “Paw Print Post operates primarily in the pet industry and sells goods that could also be categorized as part of the greeting card industry.”
- Background information. “Jane Matthews, the founder of Paw Print Post, has a long history in the pet industry and working with animals, and was recently trained as a graphic designer. She’s combining those two loves to capture a niche in the market: unique greeting cards customized with a pet’s paw prints, without needing to resort to the traditional (and messy) options of casting your pet’s prints in plaster or using pet-safe ink to have them stamp their ‘signature.’”
- Business objectives. “Jane will have Paw Print Post ready to launch at the Big Important Pet Expo in Toronto to get the word out among industry players and consumers alike. After two years in business, Jane aims to drive $150,000 in annual revenue from the sale of Paw Print Post’s signature greeting cards and have expanded into two new product categories.”
- Team. “Jane Matthews is the sole full-time employee of Paw Print Post but hires contractors as needed to support her workflow and fill gaps in her skill set. Notably, Paw Print Post has a standing contract for five hours a week of virtual assistant support with Virtual Assistants Pro.”
Your mission statement may also make an appearance here. Passionfruit shares its mission statement on its company website, and it would also work well in its example business plan.
- Market analysis
The market analysis consists of research about supply and demand, your target demographics, industry trends, and the competitive landscape. You might run a SWOT analysis and include that in your business plan.
Here’s an example SWOT analysis for an online tailored-shirt business:
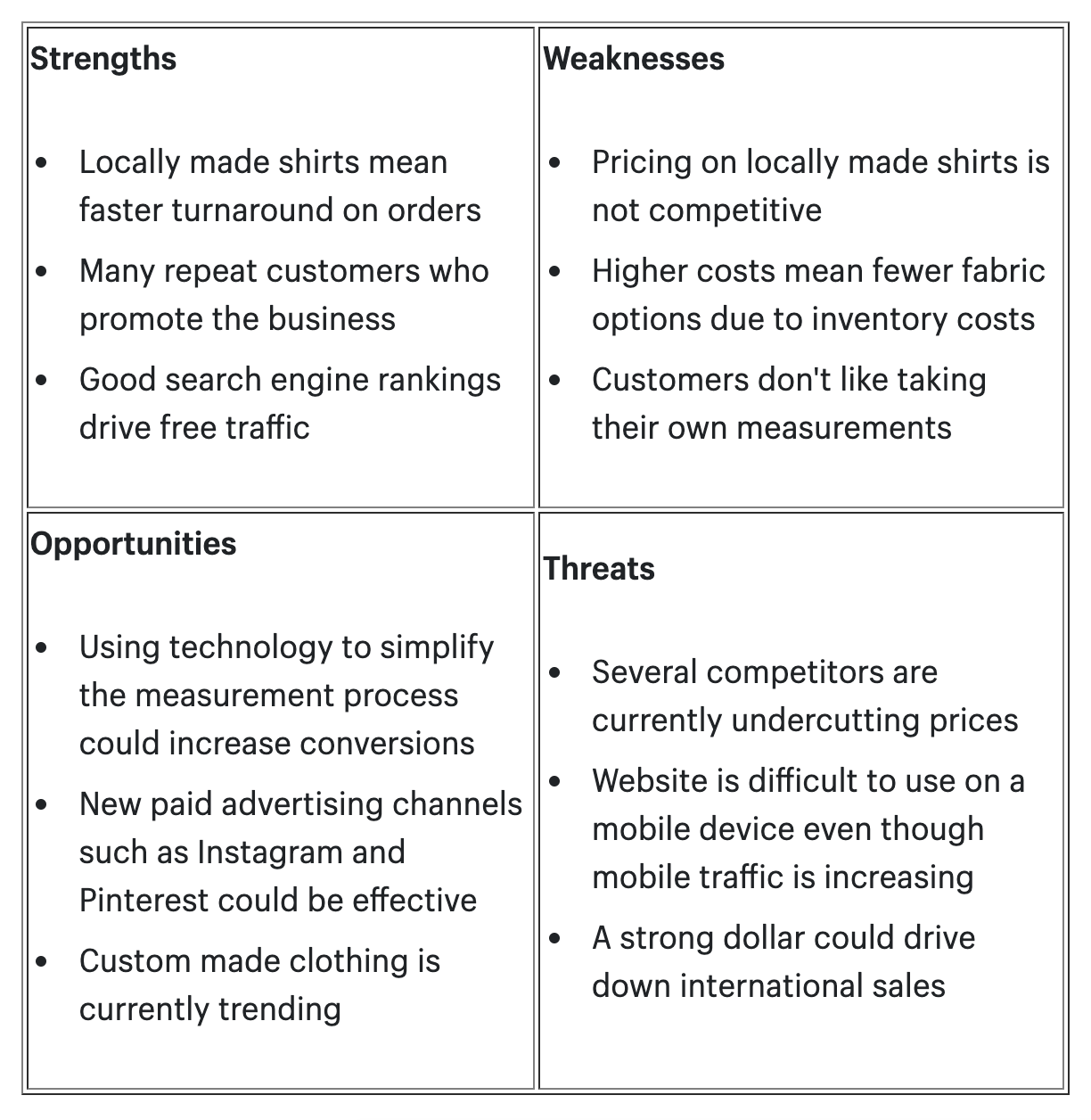
You’ll also want to do a competitive analysis as part of the market research component of your business plan. This will tell you who you’re up against and give you ideas on how to differentiate your brand. A broad competitive analysis might include:
- Target customers
- Unique value add or what sets their products apart
- Sales pitch
- Price points for products
- Shipping policy
- Products and services
This section of your business plan describes your offerings—which products and services do you sell to your customers? Here’s an example for Paw Print Post:

- Marketing plan
It’s always a good idea to develop a marketing plan before you launch your business. Your marketing plan shows how you’ll get the word out about your business, and it’s an essential component of your business plan as well.
The Paw Print Post focuses on four Ps: price, product, promotion, and place. However, you can take a different approach with your marketing plan. Maybe you can pull from your existing marketing strategy , or maybe you break it down by the different marketing channels. Whatever approach you take, your marketing plan should describe how you intend to promote your business and offerings to potential customers.
- Logistics and operations plan
The Paw Print Post example considered suppliers, production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory.
Financial plan
The financial plan provides a breakdown of sales, revenue, profit, expenses, and other relevant financial metrics related to funding and profiting from your business.
Ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy’s financial plan breaks down predicted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.
It then dives deeper into the financials to include:
- Funding needs
- Projected profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
- Projected cash-flow statement
You can use this financial plan spreadsheet to build your own financial statements, including income statement, balance sheet, and cash-flow statement.
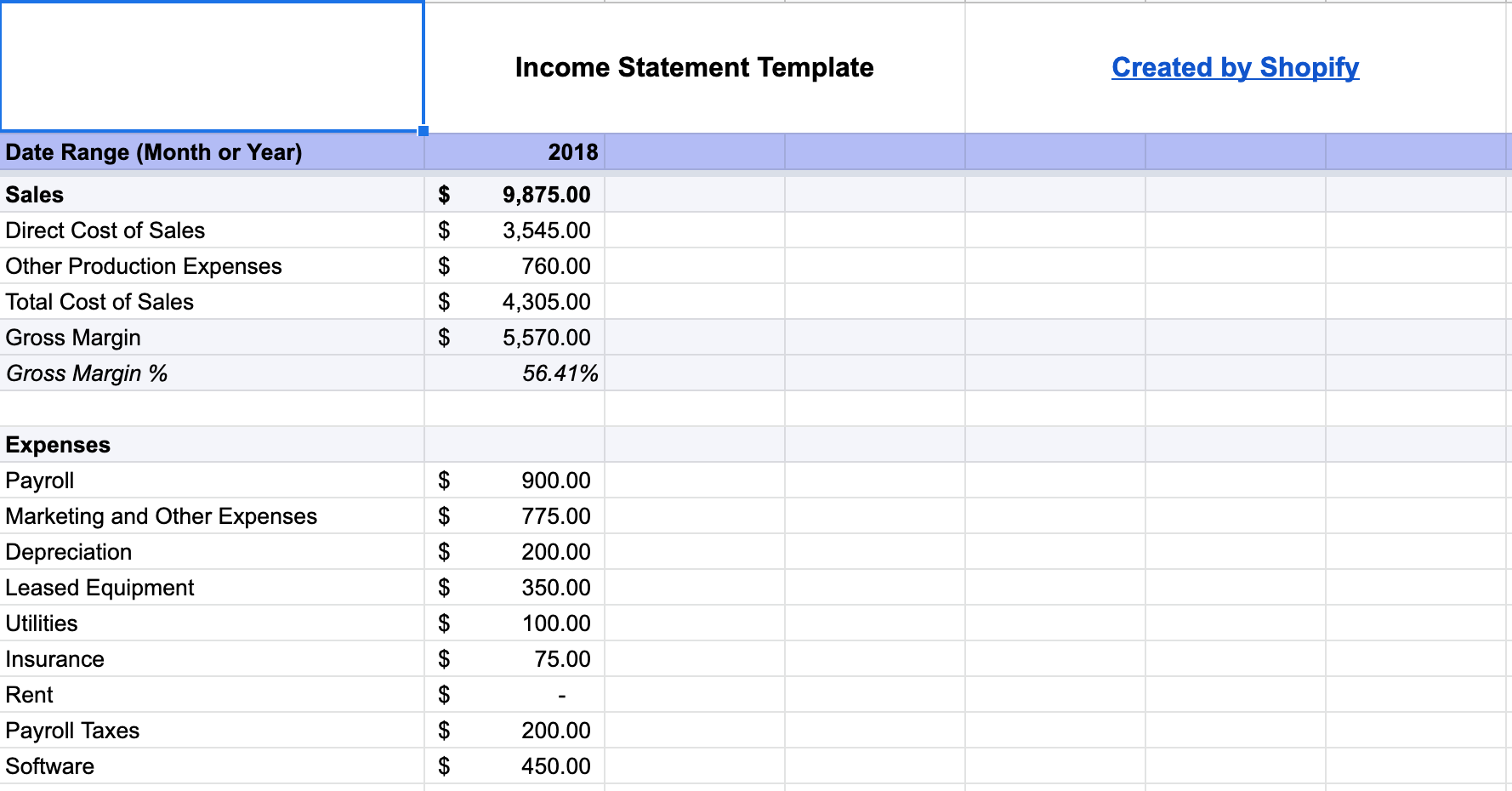
Types of business plans, and what to include for each
A one-page business plan is meant to be high level and easy to understand at a glance. You’ll want to include all of the sections, but make sure they’re truncated and summarized:
- Executive summary: truncated
- Market analysis: summarized
- Products and services: summarized
- Marketing plan: summarized
- Logistics and operations plan: summarized
- Financials: summarized
A startup business plan is for a new business. Typically, these plans are developed and shared to secure outside funding . As such, there’s a bigger focus on the financials, as well as on other sections that determine viability of your business idea—market research, for example.
- Market analysis: in-depth
- Financials: in-depth
Your internal business plan is meant to keep your team on the same page and aligned toward the same goal.
A strategic, or growth, business plan is a bigger picture, more-long-term look at your business. As such, the forecasts tend to look further into the future, and growth and revenue goals may be higher. Essentially, you want to use all the sections you would in a normal business plan and build upon each.
- Market analysis: comprehensive outlook
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Marketing plan: comprehensive outlook
- Logistics and operations plan: comprehensive outlook
- Financials: comprehensive outlook
Feasibility
Your feasibility business plan is sort of a pre-business plan—many refer to it as simply a feasibility study. This plan essentially lays the groundwork and validates that it’s worth the effort to make a full business plan for your idea. As such, it’s mostly centered around research.
Set yourself up for success as a business owner
Building a good business plan serves as a roadmap you can use for your ecommerce business at launch and as you reach each of your business goals. Business plans create accountability for entrepreneurs and synergy among teams, regardless of your business model .
Kickstart your ecommerce business and set yourself up for success with an intentional business planning process—and with the sample business plans above to guide your own path.
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- The 13 Best Dropshipping Suppliers in 2024
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- 25+ Ideas for Online Businesses To Start Now (2024)
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- How to Build a Business Website for Beginners
- 7 Inspiring Marketing Plan Examples (and How You Can Implement Them)
- 10 Ways to Write Product Descriptions That Persuade (2024)
- Get Guidance- 6 Business Plan Software to Help Write Your Future
- Business Valuation- Learn the Value of Your Business
Business plan examples FAQ
How do i write a simple business plan, what is the best format to write a business plan, what are the 4 key elements of a business plan.
- Executive summary: A concise overview of the company's mission, goals, target audience, and financial objectives.
- Business description: A description of the company's purpose, operations, products and services, target markets, and competitive landscape.
- Market analysis: An analysis of the industry, market trends, potential customers, and competitors.
- Financial plan: A detailed description of the company's financial forecasts and strategies.
What are the 3 main points of a business plan?
- Concept: Your concept should explain the purpose of your business and provide an overall summary of what you intend to accomplish.
- Contents: Your content should include details about the products and services you provide, your target market, and your competition.
- Cashflow: Your cash flow section should include information about your expected cash inflows and outflows, such as capital investments, operating costs, and revenue projections.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Aug 28, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
Financial modeling spreadsheets and templates in Excel & Google Sheets
- Your cart is empty.

What are the 12 Components of a Business Plan You Need to Know

Crafting a business plan is a crucial step for any entrepreneur aiming to start or grow a business. This foundational document not only sets the vision and direction for the venture but also provides a structured approach to achieving objectives. A well-thought-out business plan encompasses various elements that collectively form a comprehensive strategy. By understanding and implementing these key components, business owners can ensure they are well-prepared to navigate challenges and seize opportunities as they arise. Moreover, this plan acts as a bridge, communicating your business potential to investors and other stakeholders effectively.
The intricacies of what are the 12 components of a business plan stretch far beyond mere bullet points; each segment serves a distinct purpose in the framework of your business strategy. These components range from the Executive Summary, that encapsulates the essence of the plan, to financial projections that detail the anticipated economic performance. Attention to each part ensures clarity and thoroughness, thereby enhancing the credibility of the business plan. Emphasizing these components helps in identifying any gaps or weaknesses early, enabling proactive adjustments to strengthen the overall business strategy.
Understanding the 12 Components of a Business Plan
Creating a successful business requires a well-structured plan that serves as a roadmap for growth and accountability. The blueprint for this endeavor is composed of 12 essential components, each playing a critical role in guiding a venture towards its goals. By understanding these components, aspiring entrepreneurs can articulate their vision clearly and attract potential investors and partners.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is often considered the heart of the business plan. This section condenses the entire plan into a brief overview, providing a concise summary of the objectives and key elements of the venture. It should capture attention and compel the reader to explore further.
2. Company Description
A detailed company description follows the executive summary. This section outlines the business’s history, mission statement, vision, and objectives. When detailing your company, emphasize what sets it apart from competitors and its unique value proposition.
3. Market Analysis
Understanding your market is crucial. A comprehensive market analysis includes research on industry trends, target demographics, and competitive landscape. This data helps in identifying potential customer segments and validates the need for your service or product.
4. Organization and Management
In this component, you present the organizational structure of your business. Clarify who is responsible for what, outlining the management team, their qualifications, and roles within the organization. A clear organizational chart can enhance understanding.
5. Service or Product Line
This section delves into the products or services your business will offer. Describe their benefits, lifecycle, and potential for growth. It’s essential to show how your offerings address specific customer needs and what differentiates them from others in the market.
6. Marketing and Sales Strategy
The marketing and sales strategy outlines how you plan to attract and retain customers. Discuss your branding approach, marketing channels, and sales techniques. Highlight any anticipated challenges and how you intend to overcome them to create a sustainable customer base.
7. Funding Request
If you’re seeking funding, this element is vital. Clearly indicate how much money you need, the purpose of the funds, and the type of funding you are seeking—be it equity, loans , or grants. Make sure to present a well-reasoned case for your request based on solid financial projections.
8. Financial Projections
Financial projections provide an outlook on the expected revenue and expenses over a specific period, often spanning three to five years. Include income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. These documents help reinforce the viability of your business plan to investors.
9. Appendix
The appendix serves as a supplementary section for additional information that enhances your business plan. Include resumes, legal agreements, product images, or any market research data here. This allows readers to delve deeper into specifics if they choose to.
10. Implementation Plan
Your implementation plan outlines actionable steps required to launch and operate your business effectively. It should present a timeline of critical milestones and measurable objectives to track progress, ensuring that the venture remains on course.
11. Exit Strategy
An exit strategy details your plan for the future, whether you intend to sell the business, pass it on to heirs, or close it down. Addressing this component shows potential investors that you have considered long-term sustainability and potential returns on their investment.
12. Risk Assessment
Every business faces risks, and a thoughtful risk assessment identifies potential challenges and their possible impact. Address market fluctuations, competition, and operational risks, and articulate your plans to mitigate these issues. This demonstrates proactive management techniques to investors.
When composing a business plan, integrating these 12 components ensures a comprehensive, detailed, and compelling document. Each section serves a purpose, contributing to the overall narrative of your business and reinforcing your vision. By carefully addressing these elements, entrepreneurs can pave the way for their business’s success and secure the necessary support to fulfill their aspirations.
The Importance of Market Analysis in Business Planning
Effective business planning hinges on numerous crucial factors, but few are as vital as understanding the market landscape. A detailed market analysis empowers entrepreneurs to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and seize opportunities that may not be immediately apparent. This detailed approach helps ensure that businesses are not only prepared to enter the market but are also strategically aligned with consumer needs and industry trends.
One of the core reasons for conducting a market analysis lies in identifying and understanding target demographics. By gathering demographic data, businesses can delineate their potential customer base, paying attention to factors such as age, gender, income level, and lifestyle. This information is pivotal in shaping marketing strategies and product development.
Analyzing Market Trends
Market analysis also includes scrutinizing current trends and forecasting future developments. Understanding these trends provides a roadmap for businesses, allowing them to adapt their offerings promptly. Consideration of elements such as:
- Consumer behavior
- Technological advancements
- Economic indicators
- Regulatory changes
These factors play a considerable role in shaping market dynamics and influencing business strategies.
Competitive Analysis
Another essential component of market analysis is competitive assessment. Gaining insight into competitors helps businesses ascertain their strengths and weaknesses relative to the market. This competitive analysis involves examining:
- Market share of competitors
- Their pricing strategies
- Their marketing approaches
- Their product or service offerings
By understanding where they stand in comparison to competitors, businesses can position themselves more effectively and discover gaps in the market that they can exploit.
Identifying Opportunities and Risks
Through thorough market analysis, businesses can identify both opportunities and risks. Opportunities might arise from underserved customer needs or niche markets that have not been fully capitalized. Conversely, understanding risks involves being aware of potential challenges that could hinder growth, such as economic downturns, increasing competition, or shifting regulations. Businesses can formulate strategies to mitigate these risks, ensuring their plans are resilient and adaptable.
Setting Realistic Goals
Furthermore, a well-rounded market analysis helps in setting realistic and measurable objectives. Knowledge of market conditions allows businesses to create goals that are attainable based on empirical evidence instead of mere speculation. This data-driven approach ensures that targets are both challenging yet achievable, fostering a culture of accountability and success.
Tailoring Marketing Strategies
With insights gleaned from market analysis, businesses can tailor their marketing strategies to engage effectively with their target audience. This can include selecting the most effective channels for advertising, such as social media, email campaigns, or traditional media. A clear understanding of customer preferences informs the creation of marketing messages that resonate with potential customers, ultimately boosting conversion rates.
Enhancing Product Development
Market analysis also informs product development. By understanding customer needs and preferences, businesses can design products or services that directly cater to market demands. This alignment between product offerings and consumer expectations increases the likelihood of successful market entry and customer satisfaction.
In addition to driving product innovation, a comprehensive market analysis allows businesses to assess pricing strategies accurately. Understanding the perceived value of offerings in the context of competition helps in setting competitive yet profitable pricing structures. This analysis ultimately supports sustainable revenue growth.
Incorporating market analysis into business planning promotes an agile approach. In a rapidly changing business environment, having a finger on the pulse of the market allows companies to pivot quickly when necessary, adapting their strategies to align with evolving trends and consumer preferences. This flexibility is crucial for long-term viability and success.
The importance of market analysis in business planning cannot be overstated. It is a multi-faceted tool that aids in understanding the market landscape, identifying opportunities, minimizing risks, setting realistic goals, and ultimately driving successful business outcomes. By prioritizing a thorough market analysis, businesses can create robust strategies that pave the way for sustained growth and success.
Crafting an Effective Executive Summary
Creating an effective executive summary is a crucial part of any business plan. This section serves as the first impression for your readers, often determining whether they will engage with the rest of your document. A concise and compelling executive summary not only encapsulates key elements of your business plan but also highlights the unique aspects that set your business apart from the competition.
To craft a narrative that is engaging and informative, consider the following components to include:
- Business Overview: Start with a brief description of your business. Clearly state what your company does, the products or services offered, and your target market. This sets the stage for the rest of the summary.
- Mission Statement: Include your mission statement to communicate your core purpose. This should convey the essence of your business and what you aim to achieve in the long term.
- Market Opportunity: Describe the market needs your business addresses. Present any data or insights that demonstrate a clear opportunity for growth, indicating why your business is well-positioned to succeed.
- Business Model: Explain how your business plans to make money. Clearly outline the revenue streams, pricing strategies, and any unique selling propositions that differentiate you from competitors.
- Target Audience: Detail your target audience. Understanding your ideal customer is vital for tailoring your services and marketing strategies effectively.
- Competitive Advantage: Discuss how your business stands out in the marketplace. Highlight any unique skills, technologies, or intellectual property that provides an edge over competitors.
- Financial Projections: Provide an overview of expected revenue and profitability. Use clear, concise figures instead of jargon to make the information easily digestible.
- Funding Requirements: If applicable, outline your funding needs. Specify how much money you are looking to raise, how it will be used, and the expected outcomes from these investments.
- Milestones and Objectives: List critical milestones across the timeline of your business. It could include product launches, partnership agreements, or sales targets that mark your path to success.
- Management Team: Introduce key members of your team. Highlight their experience, qualifications, and roles within the company, demonstrating that you have the right people in place to execute your plan.
- Call to Action: End with a compelling call to action. Encourage readers to take the next step, whether it’s to schedule a meeting or to delve deeper into the complete business plan.
As you compile these elements into your summary, remember to keep it focused and to the point. Ideally, the executive summary should be no longer than one to two pages. Strive for clarity and engage the reader immediately; your writing should possess a natural flow.
When drafting, use active voice to convey confidence and directness. Phrases like “We provide innovative solutions” rather than “Innovative solutions are provided by us” create a stronger sense of ownership and commitment. Furthermore, breaking up lengthy sentences will help maintain the reader’s attention. Short, impactful sentences mirror how people communicate in conversations.
Another essential factor is the tone. Although it’s crucial to maintain a professional demeanor, you should also express enthusiasm for your business. Show potential investors or stakeholders why they should be excited about your company.
Visual elements can also enhance engagement. bullet points, bolding essential terms, or including charts can help your executive summary stand out. Visuals break down complex information, making it more accessible for the reader.
Before finalizing your executive summary, solicit feedback. Share it with colleagues or mentors to get their perspective. A fresh set of eyes can identify areas that might be unclear or unconvincing. Consider their feedback seriously and make revisions accordingly.
Crafting an effective executive summary requires careful thought and consideration. By focusing on the key components outlined, maintaining a clear and engaging style, and utilizing feedback, you can create a summary that captivates and informs your audience. Remember, this is your chance to make a remarkable first impression—so invest the time needed to make it outstanding.
Financial Projections: Building a Sustainable Budget
Building a sustainable budget requires careful planning and financial projections serve as the backbone of that process. Without clear projections, businesses can find themselves floundering as they navigate financial challenges. Understanding how to create reliable financial projections can help businesses not only survive but thrive in competitive environments. Here’s an insightful breakdown of how to approach this important aspect of business planning.
Understanding Financial Projections
Financial projections are essentially estimates of future income and expenses. They help business owners regulate their budgets, make informed decisions, and allocate resources efficiently. These projections typically cover a specific period, often three to five years, and consist of several key components that provide a roadmap for businesses.
The 12 Key Components for Effective Financial Projections
To create a robust financial projection, consider including the following components:
- Sales Forecast: Estimate the expected revenue based on past performance, market trends, and sales strategies. Use data analytics to support your forecasts.
- Expense Forecast: Outline operational costs, including both fixed and variable expenses. Understanding where your money will go is crucial for financial health.
- Cash Flow Projections: Analyze incoming and outgoing cash to anticipate liquidity needs and maintain solvency. This will reveal how much cash is available at any given time.
- Profit and Loss Statement: This projected income statement details expected revenues, costs, and profits over time, providing insights into overall profitability.
- Balance Sheet Forecast: Include projections about the assets, liabilities, and equity of the business to understand its financial position at various points in the future.
- Break-even Analysis: Determine the level of sales needed to cover costs, indicating when the business will start generating profits.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Analyze how changes in key assumptions, like sales volume or cost increases, can impact financial outcomes.
- Funding Requirements: Identify how much capital the business needs, when it will be needed, and possible sources to secure that funding.
- Investment and Capital Expenditure Projections: Outline anticipated investments in long-term assets and how they align with expected revenue growth.
- Assumptions and Methodologies: Clearly state the assumptions behind each projection, including market conditions and business strategies.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish metrics to measure financial health and performance against projections.
- Scenario Planning: Prepare for varying outcomes by developing best-case, worst-case, and expected-case scenarios to ensure flexibility.
Creating the Budget
Once you have gathered all necessary projections, you can start creating a sustainable budget. This involves allocating funds based on your forecasts while regularly revisiting your projections. You might find the following strategies helpful:
- Prioritize Expenses: Categorize essential and non-essential expenses to focus spending on what drives your business forward.
- Incorporate Flexibility: Allow a buffer in your budget for unpredicted costs or changes in market conditions.
- Regular Reviews: Schedule monthly or quarterly reviews of your budget against actual performance to adjust your plans as necessary.
- Use Software Tools: Implement budgeting software to help streamline the planning process and maintain organization.
The Importance of Accurate Data
In crafting financial projections, the quality of your data is key. Utilize reliable sources and incorporate historical data for accuracy. Always validate your numbers through alternative methods, like industry benchmarking. This not only improves the reliability of your projections but also instills trust among stakeholders.
Engaging Professionals
If you’re feeling overwhelmed, don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance. Financial consultants can provide expert insights, ensuring that your projections are realistic and aligned with industry standards. They can help identify potential pitfalls before they become issues, ultimately supporting a sustainable financial future.
By understanding and implementing these components, you create a comprehensive framework for financial projections and budgeting. Doing so helps position your business for sustainable growth and operational stability. Remember, the most effective budgets evolve over time, reflecting the changing dynamics of the market and your business’s unique circumstances.
Target Audience: Defining Your Market Segment
Identifying your target audience is a critical step when launching any business or service. Understanding who will buy your product or use your service allows you to shape your marketing strategies effectively. You can optimize your efforts and resources by tailoring your message to the right individuals or groups.
First, begin with demographic information. This is the basic data that encompasses age, gender, income level, marital status, and education. Gathering this info gives you a foundational understanding of who your audience is. For instance, a luxury spa might target affluent women aged 30-50, while a budget gym could focus on young adults in their 20s. The clearer you define your demographics, the more effectively you can tailor your approach.
Next, delve into psychographics, which offer insights into the values, interests, and lifestyles of your potential customers. These factors go beyond basic demographics and reveal what truly motivates your audience. For example, a company selling eco-friendly products may appeal to consumers who value sustainability and are environmentally conscious. Understanding psychographics allows you to create messages that speak directly to the needs and desires of your audience.
Another valuable aspect to consider is geographic segmentation. The location of your audience can significantly impact their purchasing behavior. A business operating in an urban area may adopt a different strategy than one in a rural setting. For instance, a coffee shop in a city might need to focus on convenience and quick service, while a shop in a quieter town can offer a more relaxed environment. Tailoring your approach based on where your audience lives can enhance engagement and drive sales.
Behavioral segmentation is also crucial. This considers how customers interact with your brand, including purchasing habits, brand loyalty, and usage frequency. By analyzing these behaviors, you can generate insights into how to market your product or service effectively. For example, if consumers frequently purchase a specific item, consider promoting it more prominently in your marketing campaigns to foster loyalty.
To help clarify these concepts, here’s a formatted list that encapsulates key steps for defining your target audience:
- Conduct Market Research: Use surveys, interviews, and focus groups to gather insights directly from potential customers.
- Analyze Existing Customers: Look at your current customer base to identify shared characteristics and preferences.
- Utilize Data Analytics: Make use of web analytics and social media insights to track user behavior and preferences.
- Develop Customer Personas: Create fictional profiles that represent segments of your audience to guide marketing strategies.
- Test and Adapt: Regularly revisit your audience definition as markets and consumer preferences can change.
Also, don’t underestimate the power of competition analysis. Examining who your competitors are targeting can reveal valuable insights. If a competitor targets a similar market segment but offers a slightly different product, you may find an opportunity to differentiate yourself further and capture a unique niche.
As you define your market segment, remember that reaching your target audience effectively involves utilizing the right channels. Whether through social media, email marketing, or traditional advertising, understanding where your audience spends their time helps guide your strategy. Using channels that align with your audience’s preferences boosts engagement and conversion rates.
In addition, it’s essential to stay flexible. As customer preferences and market dynamics change, so should your approach. Regularly collecting feedback allows you to refine your audience definition and marketing strategies continuously. Whether it’s adjusting messaging, changing visuals, or trying new platforms, adaptability can set you apart from rigid competitors.
Defining your target audience is not just about identifying who might buy your product. It’s about understanding them on a deeper level—demographics, psychographics, geographical location, behaviors, and preferences all intertwine to create a picture of your ideal customer. By investing the time and resources to accurately define and continuously adapt your market segment, you position your business for success.
Operational Plan: Structuring Your Business for Success
Building a successful business requires more than just a great idea; it demands a well-structured operational plan that lays out the pathway to achieving your goals. An effective operational plan details the processes, resources, and strategies you’ll employ to ensure your business runs smoothly. It’s a crucial element that aligns your operational activities with your overall strategy. Here’s how you can structure your operational plan to set your business up for success.
Define Your Business Objectives
The first step in creating an operational plan is to define your business objectives clearly. What do you want to achieve in the short and long term? Having concrete objectives will guide every aspect of your operational strategy. Consider using the SMART criteria—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound—to formulate your goals.
Identify Key Functional Areas
Your operational plan will span several key functional areas of your business. These typically include:
- Production or Service Delivery
- Marketing and Sales
- Customer Support
- Human Resources
- Finance and Accounting
Identifying these areas helps in allocating resources more effectively and facilitates streamlined operations.
Detail Your Processes
Creating a detailed outline of your business processes is essential. This includes how products will be created or how services will be delivered. Break down your processes into specific steps:
- Input: What materials, resources, or data do you need?
- Activity: What actions will be taken using these inputs?
- Output: What will the final product or service look like?
Having a clear picture of these processes helps to minimize errors and enhance efficiency.
Establish Performance Metrics
To gauge the success of your operational strategies, you need to establish key performance indicators (KPIs). These are measurable values that help you track progress toward your objectives. Consider metrics like:
- Customer satisfaction scores
- Operational costs
- Production times
- Employee turnover rates
Choosing relevant KPIs allows you to make data-driven decisions and adjust strategies as needed.
Resource Allocation
Effective resource allocation is crucial in an operational plan. Identify what resources you need to achieve your objectives, including:
- Financial Investments
- Materials and Supplies
Ensuring that resources are appropriately allocated will minimize waste and maximize outputs.
Create a Timeline
Alongside your budget and resources, create a timeline for implementation. Outline when specific tasks will be completed and who will be responsible for them. This timeline provides accountability, ensuring tasks are completed on schedule.
Risk Management Strategy
Every operational plan must include a risk management component. Identify potential risks that could disrupt operations and create contingency plans to address them. This could involve:
- Insurance covering potential losses
- Backup suppliers for key materials
- Strategies to handle personnel shortages
A strong risk management strategy can save your business from unexpected setbacks.
Regular Review and Updates
Your operational plan should be a living document. Make it a habit to review your operational outcomes regularly. Are your objectives being met? Are adjustments needed in processes, resource allocation, or timelines? Regular updates can ensure your operational plan remains aligned with your business goals.
By following these steps, you can construct an operational plan that not only guides your daily operations but also serves as a compass that points your business toward sustained success. Keep your focus on clear objectives, efficient processes, and strategic planning to turn your vision into reality.
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators in Business Plans
In the world of business, the quest for success is often defined by measurable outcomes. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) serve as critical tools in a business plan, guiding both strategists and stakeholders toward objectives that lead to growth and profitability. By clearly determining what success looks like, companies can effectively track performance and make informed decisions.
KPIs are quantifiable metrics that help businesses assess their progress in achieving specific goals. These indicators can vary widely depending on the industry and the specific aspirations of a business. However, a few essential KPIs consistently stand out as vital components across various sectors.
Defining Financial KPIs
Financial performance is paramount for any business. Key financial KPIs often include:
- Revenue Growth Rate: Measures the increase in a company’s sales over a specified period, indicating market demand.
- Net Profit Margin: This figure shows what percentage of revenue remains after expenses, reflecting overall profitability.
- Operating Cash Flow: A gauge of cash generated from operational activities, providing insight into liquidity and financial health.
Understanding Customer-Centric KPIs
Monitoring customer engagement and satisfaction is crucial for sustainable growth. Consider these essential customer KPIs:
- Customer Retention Rate: Represents the percentage of customers retained over a given period, demonstrating loyalty and satisfaction.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measures customer willingness to recommend a business, indicating overall satisfaction.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This metric calculates the cost involved in gaining a new customer, critical for evaluating marketing efficiency.
Operational Efficiency Indicators
To determine how effectively resources are utilized, businesses can leverage operational KPIs. Key metrics include:
- Inventory Turnover: The frequency at which inventory is sold and replaced, indicating efficiency in inventory management.
- Employee Productivity: This can be measured through output per employee or revenue per employee, highlighting workforce effectiveness.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) Compliance: For service-oriented businesses, tracking the adherence to predefined service standards is essential.
Setting Targets and Benchmarks
Establishing clear targets for each KPI is crucial. Each metric should align with the overall business objectives while considering industry standards. For instance, a startup might aim for a high customer acquisition rate in the early stages, while an established company may focus on enhancing profit margins through operational efficiencies.
Benchmarking your KPIs against competitors or industry standards can help contextualize performance. Understanding where a business stands in relation to its peers can provide valuable insights for improvement.
Regular Monitoring and Analysis
Success in business is not static; it requires continuous assessment and adjustment. Regularly reviewing KPIs allows businesses to adapt their strategies in real-time. For example, if customer acquisition costs are climbing, a company might need to revise its marketing strategy or explore different channels.
Furthermore, incorporating data analytics tools can facilitate deeper insights into KPI trends. Visual representations through dashboards can make complex data more intuitive, enabling quick adjustments and informed decision-making.
The Impact on Strategic Planning
Integrating KPIs into the business planning process solidifies their importance across all organizational levels. From executive to operational roles, every stakeholder can align their efforts toward common objectives. This fosters accountability and drives a performance-oriented culture within the organization.
Ultimately, the use of KPIs in business plans isn’t just about numbers; it’s about creating a narrative around performance and progress. It helps businesses identify strengths and weaknesses, make informed decisions, and ensure long-term success. By focusing on the right indicators, organizations can sustain growth, adapt to market changes, and enhance overall stakeholder satisfaction.
Understanding and measuring success through KPIs is fundamental to any business strategy. By continually evaluating performance against clear metrics, companies can navigate the complexities of the market and achieve their desired outcomes.
Creating a thorough business plan is undeniably a crucial step for any entrepreneur. Each of the 12 components serves as a building block that supports the overall structure of your business strategy. They collectively provide a roadmap, guiding you through the intricate process of establishing and growing your business. By understanding each component, you can ensure that your business plan is not only detailed but also functional and aligned with your goals.
Market analysis stands out as a fundamental aspect of successful business planning. It allows you to gain insights into your competitors and understand the dynamics within your industry. A well-researched market analysis equips you with data that aids in making informed decisions, helping you adapt to market trends and consumer demands. By identifying potential opportunities and risks, you can position your business strategically for success.
The executive summary, often the first section potential investors or partners will read, encapsulates the key highlights of your entire business plan. Crafting an effective summary requires not just a brief overview of your business, but also a compelling narrative that grabs attention. It should effectively communicate your mission, vision, and values while summarizing your financial projections and market analysis. A strong executive summary can set the tone for the rest of the plan, making it imperative to take time perfecting this element.
Financial projections are essential for building a sustainable business budget. They provide a realistic outlook on your anticipated income, expenses, and profit margins over a specified time. Investors and stakeholders often look for solid financial plans that indicate growth potential and profitability. By meticulously forecasting your finances, you create trust in your business acumen while also highlighting your understanding of cash flow management, break-even analysis, and how to handle financial contingencies.
Defining your target audience is another critical component that amplifies your business strategy. By identifying specific market segments, you can tailor your products or services to meet their unique needs and preferences. Understanding who your customers are allows for more effective marketing efforts and better product development. A targeted approach helps in maximizing customer satisfaction and loyalty, which in turn will reflect positively on your bottom line.
The operational plan is the skeleton of your business strategy, showcasing how all the pieces work together. This is where you detail the day-to-day operations, management structure, and the logistics that drive your business forward. An effective operational plan not just outlines what needs to be done but also who will be responsible for each task. This clarity is vital for fostering accountability and ensuring that everyone in your team is aligned towards common objectives.
Measuring success is an ongoing endeavor, and establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) reflects your organization’s commitment to continuous improvement. These metrics allow you to gauge performance across various aspects of your business, aligning them with your strategic goals. Whether it’s sales growth, customer retention rates, or market reach, having specific KPIs set in advance offers a benchmark against which you can measure success, adapt strategies, and make informed decisions.
Each component of your business plan intricately weaves into the others, creating a cohesive strategy that supports long-term objectives. They enable you to stay organized, focused, and adaptable in an ever-changing landscape. The journey of entrepreneurship is filled with challenges and uncertainties, but a detailed business plan rooted in the 12 components can instill confidence in your path forward.
By investing the time and resources into building a comprehensive business plan, you are laying the groundwork for sustainable growth and success. Ultimately, the clarity and direction provided by these carefully devised sections can serve as a catalyst for your business, attracting investment and fostering stakeholder interest. Moving forward, remember that writing a business plan isn’t merely a checkbox activity; it’s an ongoing process that should evolve as your business grows. Engage with your classmates, mentors, and peers, and continually refine your business plan to ensure it remains relevant and strategically sound in navigating your entrepreneurial journey.

Freight Brokerage Financial Model Excel Template
Discover Freight Brokerage Pro Forma Projection. Impress bankers and investors with a proven, strategic business plan that impresses every time.... read more
- Excel - Multi-User – $129.00
- Excel - Single-User – $99.00
- Free Demo – $0.00

Port Operator Financial Model
Port Operator Financial Model presents the business case of an already operating port terminal (with planned refurbishments) and an investment in a ne... read more
- Excel Model – $119.00
- Free PDF – $0.00

Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Financial Model
Financial Model presenting development and operating scenarios of various projects under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) agreement.
- Excel Financial Model – $119.00 Version 1
- PDF Free Demo – $0.00 Version 1

Airport Financial Model (Development, Operation & Valuation)
Financial Model presenting a development and operating scenario of an Airport under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) agreement.
- Excel Financial Model – $149.00 Version 1

Project Finance Excel Model – 10 Year Projection
The template creates a financial model for your individual project finance initiative The model is suitable for any type of business / industry Includ... read more
- Full Version – $79.00 Version 3
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Sign up for our newsletter for product updates, new blog posts, and the chance to be featured in our Small Business Spotlight!

The importance of a business plan

Business plans are like road maps: it’s possible to travel without one, but that will only increase the odds of getting lost along the way.
Owners with a business plan see growth 30% faster than those without one, and 71% of the fast-growing companies have business plans . Before we get into the thick of it, let’s define and go over what a business plan actually is.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a 15-20 page document that outlines how you will achieve your business objectives and includes information about your product, marketing strategies, and finances. You should create one when you’re starting a new business and keep updating it as your business grows.
Rather than putting yourself in a position where you may have to stop and ask for directions or even circle back and start over, small business owners often use business plans to help guide them. That’s because they help them see the bigger picture, plan ahead, make important decisions, and improve the overall likelihood of success.
Why is a business plan important?
A well-written business plan is an important tool because it gives entrepreneurs and small business owners, as well as their employees, the ability to lay out their goals and track their progress as their business begins to grow. Business planning should be the first thing done when starting a new business. Business plans are also important for attracting investors so they can determine if your business is on the right path and worth putting money into.
Business plans typically include detailed information that can help improve your business’s chances of success, like:
- A market analysis : gathering information about factors and conditions that affect your industry
- Competitive analysis : evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors
- Customer segmentation : divide your customers into different groups based on specific characteristics to improve your marketing
- Marketing: using your research to advertise your business
- Logistics and operations plans : planning and executing the most efficient production process
- Cash flow projection : being prepared for how much money is going into and out of your business
- An overall path to long-term growth
What is the purpose of a business plan?
A business plan is like a map for small business owners, showing them where to go and how to get there. Its main purposes are to help you avoid risks, keep everyone on the same page, plan finances, check if your business idea is good, make operations smoother, and adapt to changes. It's a way for small business owners to plan, communicate, and stay on track toward their goals.
10 reasons why you need a business plan
I know what you’re thinking: “Do I really need a business plan? It sounds like a lot of work, plus I heard they’re outdated and I like figuring things out as I go...”.
The answer is: yes, you really do need a business plan! As entrepreneur Kevin J. Donaldson said, “Going into business without a business plan is like going on a mountain trek without a map or GPS support—you’ll eventually get lost and starve! Though it may sound tedious and time-consuming, business plans are critical to starting your business and setting yourself up for success.
To outline the importance of business plans and make the process sound less daunting, here are 10 reasons why you need one for your small business.
1. To help you with critical decisions
The primary importance of a business plan is that they help you make better decisions. Entrepreneurship is often an endless exercise in decision making and crisis management. Sitting down and considering all the ramifications of any given decision is a luxury that small businesses can’t always afford. That’s where a business plan comes in.
Building a business plan allows you to determine the answer to some of the most critical business decisions ahead of time.
Creating a robust business plan is a forcing function—you have to sit down and think about major components of your business before you get started, like your marketing strategy and what products you’ll sell. You answer many tough questions before they arise. And thinking deeply about your core strategies can also help you understand how those decisions will impact your broader strategy.
Send invoices, estimates, and other docs:
- via links or PDFs
- automatically, via Wave
*While subscribed to Wave’s Pro Plan, get 2.9% + $0 (Visa, Mastercard, Discover) and 3.4% + $0 (Amex) per transaction for the first 10 transactions of each month of your subscription, then 2.9% + $0.60 (Visa, Mastercard, Discover) and 3.4% + $0.60 (Amex) per transaction. Discover processing is only available to US customers. See full terms and conditions for the US and Canada . See Wave’s Terms of Service for more information.
Send invoices, get paid, track expenses, pay your team, and balance your books with our financial management software.
2. To iron out the kinks
Putting together a business plan requires entrepreneurs to ask themselves a lot of hard questions and take the time to come up with well-researched and insightful answers. Even if the document itself were to disappear as soon as it’s completed, the practice of writing it helps to articulate your vision in realistic terms and better determine if there are any gaps in your strategy.
3. To avoid the big mistakes
Only about half of small businesses are still around to celebrate their fifth birthday . While there are many reasons why small businesses fail, many of the most common are purposefully addressed in business plans.
According to data from CB Insights , some of the most common reasons businesses fail include:
- No market need : No one wants what you’re selling.
- Lack of capital : Cash flow issues or businesses simply run out of money.
- Inadequate team : This underscores the importance of hiring the right people to help you run your business.
- Stiff competition : It’s tough to generate a steady profit when you have a lot of competitors in your space.
- Pricing : Some entrepreneurs price their products or services too high or too low—both scenarios can be a recipe for disaster.
The exercise of creating a business plan can help you avoid these major mistakes. Whether it’s cash flow forecasts or a product-market fit analysis , every piece of a business plan can help spot some of those potentially critical mistakes before they arise. For example, don’t be afraid to scrap an idea you really loved if it turns out there’s no market need. Be honest with yourself!
Get a jumpstart on your business plan by creating your own cash flow projection .
4. To prove the viability of the business
Many businesses are created out of passion, and while passion can be a great motivator, it’s not a great proof point.
Planning out exactly how you’re going to turn that vision into a successful business is perhaps the most important step between concept and reality. Business plans can help you confirm that your grand idea makes sound business sense.

A critical component of your business plan is the market research section. Market research can offer deep insight into your customers, your competitors, and your chosen industry. Not only can it enlighten entrepreneurs who are starting up a new business, but it can also better inform existing businesses on activities like marketing, advertising, and releasing new products or services.
Want to prove there’s a market gap? Here’s how you can get started with market research.
5. To set better objectives and benchmarks
Without a business plan, objectives often become arbitrary, without much rhyme or reason behind them. Having a business plan can help make those benchmarks more intentional and consequential. They can also help keep you accountable to your long-term vision and strategy, and gain insights into how your strategy is (or isn’t) coming together over time.
6. To communicate objectives and benchmarks
Whether you’re managing a team of 100 or a team of two, you can’t always be there to make every decision yourself. Think of the business plan like a substitute teacher, ready to answer questions any time there’s an absence. Let your staff know that when in doubt, they can always consult the business plan to understand the next steps in the event that they can’t get an answer from you directly.
Sharing your business plan with team members also helps ensure that all members are aligned with what you’re doing, why, and share the same understanding of long-term objectives.
7. To provide a guide for service providers
Small businesses typically employ contractors , freelancers, and other professionals to help them with tasks like accounting , marketing, legal assistance, and as consultants. Having a business plan in place allows you to easily share relevant sections with those you rely on to support the organization, while ensuring everyone is on the same page.
8. To secure financing
Did you know you’re 2.5x more likely to get funded if you have a business plan?If you’re planning on pitching to venture capitalists, borrowing from a bank, or are considering selling your company in the future, you’re likely going to need a business plan. After all, anyone that’s interested in putting money into your company is going to want to know it’s in good hands and that it’s viable in the long run. Business plans are the most effective ways of proving that and are typically a requirement for anyone seeking outside financing.
Learn what you need to get a small business loan.
9. To better understand the broader landscape
No business is an island, and while you might have a strong handle on everything happening under your own roof, it’s equally important to understand the market terrain as well. Writing a business plan can go a long way in helping you better understand your competition and the market you’re operating in more broadly, illuminate consumer trends and preferences, potential disruptions and other insights that aren’t always plainly visible.
10. To reduce risk
Entrepreneurship is a risky business, but that risk becomes significantly more manageable once tested against a well-crafted business plan. Drawing up revenue and expense projections, devising logistics and operational plans, and understanding the market and competitive landscape can all help reduce the risk factor from an inherently precarious way to make a living. Having a business plan allows you to leave less up to chance, make better decisions, and enjoy the clearest possible view of the future of your company.
Business plan FAQs
How does having a business plan help small business owners make better decisions.
Having a business plan supports small business owners in making smarter decisions by providing a structured framework to assess all parts of their businesses. It helps you foresee potential challenges, identify opportunities, and set clear objectives. Business plans help you make decisions across the board, including market strategies, financial management, resource allocation, and growth planning.
What industry-specific issues can business plans help tackle?
Business plans can address industry-specific challenges like regulatory compliance, technological advancements, market trends, and competitive landscape. For instance, in highly regulated industries like healthcare or finance, a comprehensive business plan can outline compliance measures and risk management strategies.
How can small business owners use their business plans to pitch investors or apply for loans?
In addition to attracting investors and securing financing, small business owners can leverage their business plans during pitches or loan applications by focusing on key elements that resonate with potential stakeholders. This includes highlighting market analysis, competitive advantages, revenue projections, and scalability plans. Presenting a well-researched and data-driven business plan demonstrates credibility and makes investors or lenders feel confident about your business’s potential health and growth.
Understanding the importance of a business plan
Now that you have a solid grasp on the “why” behind business plans, you can confidently move forward with creating your own.
Remember that a business plan will grow and evolve along with your business, so it’s an important part of your whole journey—not just the beginning.
Related Posts
Now that you’ve read up on the purpose of a business plan, check out our guide to help you get started.
The information and tips shared on this blog are meant to be used as learning and personal development tools as you launch, run and grow your business. While a good place to start, these articles should not take the place of personalized advice from professionals. As our lawyers would say: “All content on Wave’s blog is intended for informational purposes only. It should not be considered legal or financial advice.” Additionally, Wave is the legal copyright holder of all materials on the blog, and others cannot re-use or publish it without our written consent.

Blog · OKRs
May 4, 2022
Performance Objectives - What Are the 5 Business Objectives?
The five key business performance objectives for any organization include quality, speed, dependability, flexibility, and cost.
by Joseph Garvey

Join IONA - A different way of networking
Meet one new person every day. That's 30 new people a month. That's 365 real connections a year.
When it comes to business performance objectives you're likely aware that efficiency and productivity are crucial. But how do you successfully achieve these? The key to having good all-round performance is five performance objectives: quality, speed, dependability, flexibility and cost.

Performance Objective 1: Quality
Quality is the visual sign of how well an operation does what it does. It's a consistent indicator which customers and staff base their expectations around.
Does the product work as it should? Or has it been made with low-value parts that undermine its integrity? Quality is a fundamental aspect of performance and, because of this, has a huge influence on whether a customer is satisfied or not.
For example, giving each individual warehouse packer the responsibility to pack their own boxes improves quality as mis-packs are made less likely to occur.
In terms of the operation principles, quality can create the potential for better services and products which reduce costs in the long run thanks to having more satisfied customers.

Performance Objective 2: Speed
Speed is the turnaround time between customers ordering a product or service and the point at which they receive it. When an organization delivers the goods or services on time, the more likely a customer is to be satisfied with their experience.
If you can provide a service or product faster than other companies without compromising on quality then you are already off to a winning start.
In terms of operation principles, high speed can allow for faster delivery of services, therefore saving costs.

How can you keep track of your business performance objectives? Goal setting , whether it's through Objectives & Key Results or SMART Goals gives you a framework to track your targets, progress and results, and helps you to communicate these company-wide.
Performance Objective 3: Dependability
Dependability means that customers can rely on your organization to receive their goods and/or services as and when promised. While this may not affect the chances of a customer selecting the service - as they have already 'consumed' the product - it influences whether the customer returns to make a future purchase or recommends your business.
No matter how cheap or fast a pizza is made by a takeaway company, if the customer can't depend on it to be delivered on time or to the correct address, then they will go elsewhere.
In terms of operation principles, dependability is important in providing the reliable delivery of service and products.

The Essential Guide to OKRs will show you how to create an Objectives & Key Results process that you can implement across the organization to track your performance objectives.
Performance Objective 4: Flexibility
Flexibility is the means of changing an operation to match a customer's requirements. This may involve changing what the operation does or how it works so that the service is bespoke.
Customers are likely to require change for four reasons:
- Product/service flexibility occurs in order to introduce a new or modified product.
- Mix flexibility is the ability to have the variety of products available grow.
- Volume flexibility involves the output of a process and being able to produce different quantities/volumes.
- Delivery flexibility is being able to change the timings of delivery in a product/service.
Being flexible gives the potential for a business to hold a competitive edge due to their wider variety, different volumes and varying delivery dates.

Performance Objective 5: Cost
Cost is an important factor for companies which compete directly on rates. The lower a company can keep its production costs, the lower they can have their customer-facing prices.
Even companies who do not compete on price want to keep their costs as low as possible while still maintaining the levels of quality, speed, dependability and flexibility that their customers demand.
The minimalization of costs is as important so that resources can be spared to grow other areas of the business.

These performance metrics are relatively straightforward and should be applied to all aspects of your business operatiosn. By achieving each of these performance objectives you can satisfy customers and improve your profit.
Build any HR process on PeopleGoal.
Create an account and start building on the PeopleGoal platform. All accounts start with a 7-day free trial and can be cancelled at any time.
Further Reading
Related articles from our blog, read on

How to choose a performance review software that adds value
A performance review software can help you identify top talent and reword your people. Sometimes it's difficult to find the right softaware that adds value to your organization. Read on to find out what you should consider...

Sophie Smith-Watkins

Employee Manager One on One Meeting: A Guide
Your complete guide to help you through the dreaded employee manager one-on-one meeting
Joseph Garvey

6 Tips to Prevent Work Burnout
What is work burnout and how can you prevent its appearance?

PeopleGoal Team

How to Write Your Career Goals
Career goals are a great way to establish a foundation for what you want to achieve and stay on track with your progress.

7 Characteristics of a Good Manager
Learn how to become a better manager by focusing on 7 management traits.
Employee Performance Management Software : 9 Key Features
Effective performance management software.

James Strickland
Ready to see PeopleGoal in action? Start your free trial today.
- Local Markets
- Development
- Performance
- How it Works
- Case studies
- Whitepapers
- Landing Pages

Subscribe to our newsletter
The latest news, articles, and resources, sent to your inbox weekly.
© 2024 PeopleGoal, Inc. All rights reserved.

Structuring Employee Stock Option Plans Strategically
Structuring an employee stock option plan requires a strategic approach that aligns with a company's overall objectives and goals. Defining clear company goals and objectives is vital, as it provides a framework for evaluating employee performance and determining stock option vesting and payout. Selecting the appropriate Employee Stock Ownership Plan type and determining fair market value are also critical components. Additionally, setting vesting periods and terms, managing financial and tax implications, and ensuring regulatory compliance are imperative. By understanding these key elements, organizations can create a tailored incentive program that drives business success; exploring these concepts further can reveal the full potential of a well-structured ESOP.
Table of Contents
Defining Company Goals and Objectives
Establishing well-defined company goals and objectives is a crucial precursor to structuring employee stock options, as it facilitates organizations to align their compensation strategies with overall business objectives. By doing so, companies can guarantee that their employee stock option plans are designed to drive desired behaviors and outcomes that support the achievement of their strategic objectives.
To effectively align their strategy, organizations must identify and establish clear, measurable, and achievable performance metrics that are tied to specific business outcomes. These metrics serve as the foundation for evaluating employee performance and determining the vesting and payout of stock options. By linking performance metrics to business objectives, companies can create a direct line of sight between employee efforts and organizational success. This approach enables organizations to incentivize and reward employees for making meaningful contributions to the company's growth and profitability. Ultimately, well-defined company goals and objectives provide the necessary framework for structuring employee stock options that drive business success and align employee interests with those of the organization.
Choosing the Right ESOP Type
As organizations venture into structuring their employee stock option plans, selecting the appropriate Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) type is critical, as it directly impacts the plan's effectiveness in driving desired behaviors and outcomes. The choice of ESOP type should be informed by a thorough understanding of employee demographics, including job roles, tenure, and performance levels. For instance, a non-qualified stock option plan may be more suitable for senior executives, while a qualified incentive stock option plan may be more appealing to rank-and-file employees.
Industry benchmarks can also provide valuable insights into the types of ESOPs that are commonly used in a particular sector or industry. For example, technology startups often favor restricted stock units (RSUs) due to their flexibility and simplicity, while large corporations may prefer traditional stock options. It is vital to evaluate the pros and cons of each ESOP type, considering factors such as tax implications, vesting periods, and exercise prices. By selecting the right ESOP type, organizations can create a tailored incentive program that aligns with their goals and objectives, ultimately driving employee motivation and retention.
In addition, a crucial step in designing an effective ESOP is to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each option, taking into account the organization's specific needs and priorities.
Determining Fair Market Value
Determining fair market value is a critical component of structuring employee stock options, as it directly impacts the strike price and overall value of the options. To accurately determine fair market value, companies must employ appropriate valuation methodologies, taking into account relevant market data sources. This process involves a thorough assessment of various factors to establish a reliable strike price that reflects the underlying stock's true value.
Valuation Methodologies Used
Fair market value, a critical component in structuring employee stock options, is typically ascertained through the application of various valuation methodologies. These methodologies enable companies to determine the fair market value of their shares, which is vital for option pricing and equity analytics. The choice of valuation methodology depends on the company's specific circumstances, industry, and stage of development.
| Valuation Methodology | Description | Applicability |
|---|---|---|
| Income Approach | Estimates fair market value based on expected future cash flows | Suitable for companies with stable cash flows |
| Market Approach | Uses market data to estimate fair market value | Applicable to companies with publicly traded peers |
| Asset-Based Approach | Values a company based on its net asset value | Relevant for companies with significant tangible assets |
| Hybrid Approach | Combines multiple approaches to estimate fair market value | Used for companies with complex financial structures |
Each valuation methodology has its strengths and weaknesses, and companies may choose to use a single approach or a combination of approaches to determine fair market value. By selecting the most appropriate valuation methodology, companies can accurately price their employee stock options, which is crucial for attracting and retaining top talent.
Determining Strike Price
The strike price of an employee stock option, a vital component in option valuation, is directly tied to the fair market value of the underlying shares, necessitating a precise determination of this value to facilitate accurate option pricing. This determination is pivotal, as it profoundly impacts the option's intrinsic value and ultimately affects the employee's compensation package. Market volatility, a key consideration in option pricing, can profoundly influence the fair market value of the underlying shares, making it imperative to establish a robust methodology for strike price determination.
A thorough understanding of the underlying share's fair market value enables companies to set a strike price that accurately reflects the option's value, allowing them to record the compensation expense accurately. In addition, an accurately determined strike price helps to prevent over- or under-compensation, which can have substantial implications for the company's financial performance. By adopting a rigorous approach to determining the strike price, companies can confirm that their employee stock option plans are structured strategically, aligning with their overall compensation and retention objectives.
Market Data Sources
Accurate valuation of employee stock options hinges on the reliability of market data, which serves as the foundation for determining the fair market value of the underlying shares. This reliability is critical in ensuring that the strike price is set fairly, and that the options are accurately valued for accounting and tax purposes.
When selecting a market data source, companies must prioritize data quality and vendor selection. The following table highlights the key considerations for evaluating market data sources:
| Exchange Data | High | Evaluate vendor's data processing and storage capabilities |
| Market Data Vendors | Medium | Assess vendor's experience in providing market data for similar companies |
| Internal Data | Low | Consider the company's ability to collect and maintain accurate data internally |
| Third-Party Providers | Medium | Evaluate vendor's methodology for determining fair market value |
Setting Vesting Periods and Terms
When structuring employee stock options, setting vesting periods and terms is a critical component. This involves determining the length of time employees must wait before they can exercise their options, as well as the specific conditions that must be met for vesting to occur. The key considerations in this process include the ideal vesting period length, the variety of vesting terms to be offered, and the rules governing accelerated vesting.
Vesting Period Length
Determining the ideal vesting period length is crucial, as it directly impacts the alignment of employee interests with those of the company and influences the overall effectiveness of the employee stock option plan. A vesting period that is too short may not provide sufficient incentive for employees to remain with the company long-term, undermining employee retention. Conversely, a vesting period that is too long may lead to frustration and disengagement among employees.
When setting the vesting period length, companies should consider their specific goals and objectives. For instance, if the primary objective is to drive employee retention, a longer vesting period may be more effective. On the other hand, if the goal is to incentivize employees to meet specific performance metrics, a shorter vesting period may be more suitable. Ultimately, the vesting period length should be tailored to the company's unique needs and aligned with its overall strategic objectives. By doing so, companies can guarantee that their employee stock option plan is optimized to drive desired behaviors and outcomes.
Vesting Terms Variety
Companies can implement a vesting terms variety by offering different vesting periods and terms to cater to diverse employee groups, performance metrics, or business objectives. This approach enables organizations to tailor their employee stock option plans to meet specific needs and goals, thereby enhancing their overall effectiveness.
By incorporating vesting flexibility and term innovation, companies can create a more nuanced and adaptive compensation strategy. For instance:
- Tiered vesting : Offering different vesting periods for distinct employee groups, such as executive, management, and staff levels.
- Performance-based vesting : Tying vesting to specific performance metrics, such as revenue growth or product development milestones.
- Time-based vesting : Implementing a standard vesting period, such as three or five years, for all employees.
- Hybrid vesting : Combining time-based and performance-based vesting terms to incentivize both tenure and achievement.
- Customized vesting : Designing unique vesting terms for individual employees or teams based on their specific roles, responsibilities, or contributions.
Accelerated Vesting Rules
Establishing accelerated vesting rules allows organizations to set vesting periods and terms that align with their business objectives, providing flexibility in response to changing market conditions or exceptional employee performance. This approach enables companies to adapt their employee stock option plans to meet shifting priorities, such as responding to market downturns or recognizing outstanding contributions. Accelerated vesting rules can be triggered by specific events, such as a change in control, initial public offering, or significant milestones. By doing so, organizations can modify their retention strategy to better align with their current needs. For instance, accelerated vesting can be used to retain key employees during periods of high turnover or to incentivize them to stay with the company during times of uncertainty. In addition, change incentives can be built into the plan, allowing organizations to adjust the vesting terms based on individual or company performance. By incorporating accelerated vesting rules into their employee stock option plans, organizations can create a more agile and responsive retention strategy that drives business success.
Managing Financial and Tax Implications
Optimizing the financial and tax implications of employee stock options requires a thorough understanding of the complex rules and regulations governing their treatment. A well-structured employee stock option plan can have a significant impact on a company's financial performance and tax liability. Effective management of financial and tax implications is essential to achieve tax efficiency and cost mitigation.
To achieve this, companies should consider the following strategies:
- *Designing option plans with tax-efficient exercise provisions to minimize tax liabilities*
- *Implementing cashless exercise features to reduce the financial burden on employees*
- *Offering net settlement arrangements to reduce the number of shares issued and minimize dilution*
- *Utilizing hedging strategies to mitigate the financial impact of option exercises*
- *Monitoring and optimizing the plan's financial performance through regular reporting and analysis*
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
In addition to managing financial and tax implications, a well-structured employee stock option plan must also navigate the complex web of regulatory requirements to guarantee compliance and avoid potential legal and reputational risks. Adherence to regulatory requirements is vital to maintain the integrity of the plan and avoid potential penalties.
To maintain compliance, it is imperative to establish a robust system for tracking and recording all plan-related activities, including grant dates, vesting periods, and exercise prices. This will create an audit trail that can be used to verify conformance with regulatory requirements.
| Disclosure Obligations | Establish a system for timely and accurate disclosure of plan information to participants and regulatory bodies |
| Audit Trails | Implement a robust system for tracking and recording all plan-related activities |
| Tax Compliance | Guarantee compliance with tax laws and regulations governing employee stock options |
| Plan Documentation | Maintain accurate and up-to-date plan documentation, including plan terms and conditions |
| Reporting Requirements | Establish a system for timely and accurate reporting of plan information to regulatory bodies
Measuring Plan Effectiveness
A well-structured employee stock option plan's effectiveness can be measured by its ability to align with the organization's overall strategic objectives, drive desired employee behaviors, and provide a competitive advantage in the marketplace. To gauge plan effectiveness, organizations should establish clear Plan Metrics that measure success factors such as employee engagement, retention, and performance.
Some key metrics to examine include:
- *Employee participation rates*: The percentage of eligible employees participating in the plan.
- *Option exercise rates*: The frequency at which employees exercise their options.
- *Employee retention rates*: The percentage of employees retained over a specific period.
- *Performance metrics*: Correlation between option grants and employee performance.
- *Cost and expense management*: The plan's impact on the organization's financial performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can employees sell their options on the open market immediately?.
Generally, employees cannot sell their options on the open market immediately, as they are typically subject to vesting schedules and blackout periods, limiting immediate liquidity and exposing them to market volatility.
How Do ESOPS Impact Employee Benefit Programs Like 401(K)?
Employee Stock Option Plans (ESOPs) can impact employee benefit programs like 401(k) by introducing tax implications, potentially reducing retirement savings contributions, and altering overall compensation packages, necessitating careful integration and planning to optimize benefits for employees.
Are There Limits on the Number of Options an Employee Can Receive?
There are typically no statutory limits on the number of options an employee can receive, but companies often impose internal limits. Vesting periods, which dictate when options can be exercised, can also influence the number of options granted to employees.
Can ESOPS Be Used to Attract and Retain Independent Contractors?
Independent contractors can be incentivized through ESOPs, fostering contractor loyalty and building a talent pipeline, as they become more invested in the organization's success, potentially leading to longer-term collaborations and reduced turnover rates.
Do ESOPS Require a Board of Directors Approval for Implementation?
In general, implementation of ESOPs typically necessitates approval from the Board of Directors, ensuring alignment with corporate governance principles and fostering healthy board dynamics, as directors oversee the plan's administration and potential impact on company ownership.

UNLOCK YOUR COPY
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- U.S. Open Tennis
- College football
- Auto Racing
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Israel-Hamas war latest: Blinken visits Gaza mediators in pursuit of cease-fire deal
Palestinian officials said on Tuesday that an Israeli airstrike on a school-turned-shelter in Gaza City killed at least 10 people. (Production: Wafaa Shurafa)
US Secretary of State Antony Blinken met Qatari Minister of State Mohammed bin Abdulaziz Al Khulaifi in Lusail Palace after his arrival in Doha on Tuesday evening. Blinken was visiting fellow mediators Egypt and Qatar as he pressed ahead Tuesday with the latest diplomatic mission to secure a cease-fire in the war in Gaza, even as Hamas and Israel signalled that challenges remain.
Tents are crammed together as displaced Palestinians camp on the beach, west of Deir al-Balah, Gaza Strip, Tuesday, Aug. 20, 2024. (AP Photo/Abdel Kareem Hana)
Protesters stand with large cutout photos of slain hostages and other hostages with relatives of hostages taken by Hamas militants to the Gaza Strip, to honor the memories of six men whose bodies were returned and to call for a deal to release the remaining captives, in Tel Aviv, Israel, Tuesday, Aug. 20, 2024. (AP Photo/Ariel Schalit)
Israeli police officers move a demonstrator blocking a street during a protest, in Jerusalem, Tuesday, Aug. 20, 2024. People gather to honor the memories of six men whose bodies were returned and to call for a deal to release the remaining captives. (AP Photo/Leo Correa)
People hold portraits of the hostages taken in Hamas’ Oct. 7 attack, in Jerusalem, Tuesday, Aug. 20, 2024. People gather to honor the memories of six men whose bodies were returned and to call for a deal to release the remaining captives. (AP Photo/Leo Correa)
A demonstrator holds a banner with a portrait of the slain hostage Yoram Metzger, who was taken by Hamas militants to the Gaza Strip in Oct. 7 attack, during a protest, in Jerusalem, Tuesday, Aug. 20, 2024. People gather to honor the memories of six men whose bodies were returned and to call for a deal to release the remaining captives. (AP Photo/Leo Correa)
A protester holds a poster showing Shiri Bibas and her child, Kfir, hostages taken with their family by Hamas militants to the Gaza Strip, to honor the memories of six men whose bodies were returned and to call for a deal to release the remaining captives, in Tel Aviv, Tuesday, Aug. 20, 2024. (AP Photo/Ariel Schalit)
Displaced Palestinians walk past tents pitched on the beach, west of Deir al-Balah, Gaza Strip, Tuesday, Aug. 20, 2024. (AP Photo/Abdel Kareem Hana)
Displaced Palestinians camp on the beach, west of Deir al-Balah, Gaza Strip, Tuesday, Aug. 20, 2024. (AP Photo/Abdel Kareem Hana)
- Copy Link copied
U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken visited fellow mediators Egypt and Qatar as he pressed ahead Tuesday with the latest diplomatic mission to secure a cease-fire in the war in Gaza , even as Hamas and Israel signaled that challenges remain.
Hamas in a new statement called the latest proposal presented to it a “reversal” of what it agreed to previously and accused the U.S. of acquiescing to what it called “new conditions” from Israel. There was no immediate U.S. response.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu told relatives of hostages in Gaza that a key goal is to “preserve our strategic security assets in the face of great pressures from home and abroad.”
Netanyahu’s meeting with the families came as Israel’s military said it recovered the bodies of six hostages taken in Hamas’ Oct. 7 attack that started the war, bringing fresh grief for many Israelis who have long pressed Netanyahu to agree to a cease-fire that would bring remaining hostages home.
Blinken’s meetings in Egypt and Qatar came a day after he met in Israel with Netanyahu and said the prime minister had accepted a U.S. proposal to bridge gaps separating Israel and Hamas. Blinken called on the militant group to do the same.
But there still appear to be wide gaps between the two sides.
Here’s the latest:
Israeli strikes in Lebanon kill 1 and injure 19
BEIRUT — At least one person was killed and 19 injured in a series of Israeli strikes in Lebanon’s eastern Bekaa Valley early Wednesday, Lebanon’s public health ministry said. It was not immediately clear what the target was.
Hospital officials said the wounded included children.
Earlier in the week, the Israeli army said it hit “a number of Hezbollah weapons storage facilities” in the Bekaa Valley. Videos from the scene showed a large fire and multiple explosions following the initial strike.
Israel and the Lebanese militant group have traded near-daily strikes for more than 10 months against the backdrop of Israel’s war against Hezbollah’s ally, Hamas, in Gaza. The exchanges have killed more than 500 people in Lebanon — mostly militants but also including around 100 civilians and non-combatants — and 23 soldiers and 26 civilians in Israel.
Israel says military is shifting its attention to the border with Lebanon
TEL AVIV, Israel — Defense Minister Yoav Gallant says Israel’s military is shifting its attention from Gaza to the border with Lebanon.
Touring northern Israel on Tuesday, Gallant said Israel has scaled back its activities in Gaza, where it has been fighting a war against Hamas for nearly a year, and turned its focus to Hezbollah militants in Lebanon.
“Our strongholds are moving from the south to the north, we are gradually changing, we still have a number of missions in the south,” Gallant told troops.
Hezbollah began striking Israel almost immediately after Hamas’ Oct. 7 attack. The sides have been engaged in almost daily fighting since then, raising fears of a broader regionwide war. Those fears have grown as Hezbollah has vowed retaliation for an Israeli strike in Beirut last month that killed a top Hezbollah commander.
Hezbollah launched more than 120 projectiles towards northern Israel on Tuesday, causing damage to a home and sparking a number of fires. Israel said it was striking the source of the launches.
More than 500 people have been killed in Lebanon, including at least 100 civilians. In Israel, 23 soldiers and 26 civilians have been killed.
Some kibbutzim will boycott official memorial commemorating Hamas’ Oct. 7 attack
JERUSALEM — Some small towns and communal farms in southern Israel that were devastated during the Oct. 7 Hamas attack plan to boycott an official government memorial commemorating the first anniversary.
Kibbutz Nirim said Tuesday that not a single government representative had come to visit or take responsibility for the failures on Oct. 7. Israeli media said at least five other hard-hit kibbutzim have said will not join the government event and will hold their own ceremonies instead.
Many residents of the small towns in the south have said they felt abandoned by the government during the attack, when Hamas militants stormed the border and killed approximately 1,200 people and took 250 others hostage, as well as in the ensuing 10 months.
It took Israeli forces hours to respond to the attack. Dozens of hostages, many from border communities, remain in captivity in Gaza. Many community members accuse the government of dragging its feet in cease-fire talks.
The official government memorial ceremony for the attack will be overseen by Transportation Minister Miri Regev, one of Netanyahu’s staunchest supporters in his Likud party. In June, Israeli police raided Regev’s Jerusalem office after the state attorney ordered an investigation into whether Regev gave preferential treatment to Israeli cities and towns whose officials supported her politically.
Israeli airstrike on school-turned-shelter in Gaza kills at least 10 people, Palestinian officials say
DEIR AL-BALAH, Gaza Strip — Palestinian officials say an Israeli airstrike on a school-turned-shelter in Gaza City killed at least 10 people.
The Israeli military said Tuesday’s strike on the Mustafa Hafez school targeted Hamas militants who had set up a command center inside and were planning and launching attacks.
The Palestinian Civil Defense, first responders operating under the Hamas-run government, said the strike killed at least 10 people and that they were still searching for survivors. It said around 700 people were sheltering at the school when it was hit.
Earlier on Tuesday, a strike in the Bureij refugee camp in central Gaza killed five children and their mother, according to the Al-Aqsa Martyrs Hospital, where an Associated Press reporter counted the bodies.
The hospital said the father, Alaa Abu Zeid, a schoolteacher, has been in Israeli detention for the last nine months.
Bureij is one of several crowded, built-up refugee camps in Gaza that date back to the 1948 war surrounding Israel’s creation.
Israel says it tries to avoid harming civilians and blames their deaths on Hamas because the militants operate in dense residential areas. It has struck several schools-turned-shelters in recent weeks, accusing Hamas fighters of sheltering inside them.
Israeli military says it has recovered the bodies of 6 hostages in a Gaza operation
JERUSALEM — The Israeli military says it has recovered the bodies of six hostages taken in Hamas’ Oct. 7 attack that started the Gaza war.
The military said in a statement Tuesday that its forces recovered the bodies in an overnight operation in southern Gaza. It identified the hostages as Yagev Buchshtab, Alexander Dancyg, Avraham Munder, Yoram Metzger, Nadav Popplewell, and Haim Perry, without saying when or how they died.
The recovery came as the United States, Egypt and Qatar were trying to mediate a cease-fire agreement between Israel and Hamas that would see the release of scores of hostages held by the militant group.
Hamas is still believed to be holding around 110 hostages captured in the Oct. 7 attack. Israeli authorities estimate around a third of them are dead.
Israeli military says 55 rockets from Lebanon ignite fires in northern Israel
JERUSALEM — Israel’s military said that a barrage of 55 rockets from Lebanon has ignited fires in northern Israel.
The military said Tuesday that only some of the projectiles were intercepted by Israel’s air defense systems, while others fell in open areas. Firefighters were working to contain the blazes.
Lebanon’s Hezbollah militant group said it fired “intense barrages of missiles” at military positions in Israel’s north. Israel said it struck the areas where the missiles were launched in Lebanon.
Israel and Hezbollah have been exchanging fire since Oct. 8, causing widespread damage on both sides of the border and killing civilians and combatants on both sides.
Fears have increased in recent weeks of a larger escalation, with Hezbollah vowing retaliation for an Israeli strike last month in Beirut that killed one of its top commanders.
Bodies of 2 hostages returned to Israel from Gaza, their communal farm says
JERUSALEM — The bodies of two hostages were returned from the Gaza Strip, the communal farm they lived on announced Tuesday.
Kibbutz Nirim said that the bodies of Yagev Buchshtav and Nadav Popplewell had been returned to Israel from the Gaza Strip overnight. The kibbutz did not provide additional information and the Israeli military did not immediately confirm the information.
Israeli media reported that the two men — along with Avraham Munder, whose death his kibbutz announced Tuesday — were part of a larger military hostage extraction operation overnight.
Popplewell was declared dead by the Israeli military in June. Hamas said in May that Popplewell had died after being wounded in an Israeli airstrike. Israel’s military announced Buchshtav’s death in July.
The men were taken hostage by militants who stormed the border on Oct. 7, killing some 1,200 people, mostly civilians, and taking roughly 250 hostages. About 110 hostages kidnapped that day remain in the strip. About a third of them are believed to be dead.
Israel’s retaliatory offensive on Gaza has killed over 40,000 Palestinians, according to the territory’s Health Ministry.
Another Israeli hostage dies in Hamas captivity, his village says
JERUSALEM — Another male hostage has died in Hamas captivity, his communal farming village announced Tuesday.
Kibbutz Nir Oz said that Avraham Munder had been killed while held hostage in Gaza “after enduring months of physical and mental torture.” It was not clear from the statement whether his body had been recovered. Israel’s military did not immediately confirm the information.
Of some 110 hostages remaining in Gaza who were captured in Hamas’ Oct. 7 attack, around 40 are believed to be dead, their bodies held in Gaza.
The kibbutz remembered Munder for his “clear voice, warm smile, and boundless love for his family and the kibbutz.”
Militants kidnapped Munder on Oct. 7 when they stormed Nir Oz , dragging some 80 of its residents back to Gaza.
Munder’s wife, daughter, and grandson were also taken hostage, but released during a brief cease-fire in November in exchange for the release of Palestinians imprisoned by Israel. His son was killed on Oct. 7.
In total, militants killed some 1,200 people, mostly civilians, across southern Israel and took about 250 hostages back to Gaza. Israel’s retaliatory offensive in Gaza has killed over 40,000 Palestinians, according to local health officials.
UN chief calls for ‘constructive dialogue’ as a former Israeli ambassador to the UN returns to the post
UNITED NATIONS – From the early days of the Israel-Hamas war, Israel’s U.N. Ambassador Gilad Erdan attacked U.N. Secretary-General Antonio Guterres, accusing him of being “an accomplice to terrorism” and calling for his resignation.
Now, Israel has a new ambassador, and the U.N. chief is calling for “a constructive dialogue.”
However, Danny Danon, who served as Israel’s U.N. ambassador from 2015-2020 and presented his credentials to the secretary-general on Monday, made clear he would be following in Erdan’s footsteps when it comes to Israel’s views about the United Nations.
Danon said he’s returning to the U.N. at a time of “immense challenges” for Israel and its people, saying 115 Israelis are still being held hostage in Gaza and face “ongoing atrocities and suffering.”
“I am committed to represent my country to show the real face of Israel, and to push back the lies and the hypocrisy that we unfortunately have to deal with here at this building,” he said.
Neither the U.N. Security Council nor the General Assembly have condemned Hamas’ Oct. 7 attack that killed about 1,200 people and triggered the war, though Guterres has repeatedly called for a cease-fire and the release of all hostages. He has also criticized the killing of over 40,000 Palestinians in Gaza, including many women and children, mainly in Israeli airstrikes, as well as Israel’s obstruction to humanitarian aid deliveries.
For his part, Guterres said that “for the U.N., it is extremely important to have an objective relationship with Israel.”
“We have different points of view in many aspects in relation to the two-state solution, in relation to what has been happening recently,” Guterres said, “but that doesn’t mean that we should not have a constructive dialogue based on truth.”
Multiple Israeli airstrikes reported in Lebanon
BEIRUT — The Israeli army said it hit “a number of Hezbollah weapons storage facilities” in Lebanon’s eastern Bekaa Valley Monday night.
At least three Israeli airstrikes hit towns in the Baalbek district, Lebanese state media reported.
Videos from the scene showed a large fire and multiple explosions following the initial strike.
“Following the strikes, secondary explosions were identified, indicating the presence of large amounts of weapons in the facilities struck,” the Israeli army statement said.
A spokesperson for the Lebanese militant group Hezbollah did not immediately respond to requests for comment on the strike.
A similar scene took place last month after an Israeli airstrike on the southern coastal village of Adloun hit an arms depot, setting off a series of explosions that hit nearby villages with shrapnel.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Economic Business Objective: Also called financial objectives, economic objectives relate to the financial health and growth of the company. These objectives can involve profits, revenue, costs, cash flow, sustainable growth, debt management, and investments. Example: Reduce spending on paid advertisements by 20 percent.
Social objectives. For example, a sample of business goals and objectives for a business plan for a bakery could be: To increase its annual revenue by 20% in the next year. To reduce its production costs by 10% in the next six months. To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
There are four basic components every business objective should have: A growth-oriented intention (improve efficiency) One or more actions (implement monthly training sessions) A measurement for success (20% increase) A timeline to reach success (by end of year) Example objective #1: Percentage change.
Step one: Identify what you want to achieve and why. For each business objective that you set in your business plan, it's important to begin with a brainstorming session to identify what it is that you want your company to accomplish. During this process, remember that there's a difference between goals and objectives.
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
To plan your plan, you'll first need to decide what your goals and objectives in business are. As part of that, you'll assess the business you've chosen to start, or are already running, to see ...
8. Critical success factors: Clarify the high-level goals you need to achieve in order to achieve your strategic goals. 9. Strategic management: Execute against your strategic plan in order to achieve your company goals. 10. Business goals: Set predetermined targets to achieve in a set period of time. 11.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Focus on the basics first: Identify your industry: Retail, wholesale, service, manufacturing, etc. Clearly define your type of business. Identify your customer. You cannot market and sell to ...
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
In addition to providing a framework for innovation at every level of a company's operations, business objectives can help: Increase revenue. Recruit and retain high-quality employees. Enhance customer satisfaction. Improve company culture. Maximize workplace safety. Develop leadership. Expand productivity. Increase product quality.
Aside from financial objectives, another example of objectives for a business plan is sustaining productivity. When you run a business, it can be overwhelming and challenging to stay on top of all the tasks you have to get done. But, if you aim to remain productive and create a clear plan as to how, you can better manage your to-do list.
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business. Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners.
In the OKR system, the O (objective) is representative of a larger goal, while the KR (key results) represent the smaller objectives you use to measure your progress. Here's an OKR model for your computer sales goal. O: Increase profitability for the computer company. KR1: Make $300,000 in gross profit for the year.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
4. Learning and Growth Opportunities. Another consideration while setting business goals and objectives is learning and growth opportunities for your team. These are designed to increase employee satisfaction and productivity. According to Strategy Execution, learning and growth opportunities touch on three types of capital: Human: Your ...
To improve brand and reputation. To grow production size to meet demand. 4. Social objectives. Social business objectives are created to help or give back to society in some way. Businesses often set social goals: To ensure better quality products for customers.
That's where your business plan comes in. It provides investors, lenders and potential partners with an understanding of your company's structure and goals. If you want to gain the financial autonomy to run a business or become an entrepreneur, a financial advisor can help align your finances. 1. Executive Summary.
7 business plan examples: section by section. The business plan examples in this article follow this template: Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business. Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists. Market analysis.
Include income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. These documents help reinforce the viability of your business plan to investors. 9. Appendix. The appendix serves as a supplementary section for additional information that enhances your business plan. Include resumes, legal agreements, product images, or any market research ...
To outline the importance of business plans and make the process sound less daunting, here are 10 reasons why you need one for your small business. 1. To help you with critical decisions. The primary importance of a business plan is that they help you make better decisions. Entrepreneurship is often an endless exercise in decision making and ...
These performance metrics are relatively straightforward and should be applied to all aspects of your business operatiosn. By achieving each of these performance objectives you can satisfy customers and improve your profit. The five key business performance objectives for any organization include quality, speed, dependability, flexibility, and ...
By doing so, companies can guarantee that their employee stock option plan is optimized to drive desired behaviors and outcomes. Vesting Terms Variety. Companies can implement a vesting terms variety by offering different vesting periods and terms to cater to diverse employee groups, performance metrics, or business objectives.
Plan and track enterprise projects, gain visibility into capacity, ensure alignment to business objectives, monitor insights and results, and support data-driven decision-making. Make informed decisions and gather insights by building effective dashboards with user-friendly, visual tools.
U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken visited fellow mediators Egypt and Qatar as he pressed ahead Tuesday with the latest diplomatic mission to secure a cease-fire in the war in Gaza, even as Hamas and Israel signaled that challenges remain.. Hamas in a new statement called the latest proposal presented to it a "reversal" of what it agreed to previously and accused the U.S. of ...