Home — Essay Samples — History — History of the United States — American Revolution

Essays on American Revolution
Compare and contrast the american and french revolution, articles of confederation failure essay, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
What Were The 13 Colonies Similarities
How and why the american revolution started, overview of the events of the american revolution, the effects of the american revolution, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
The History of American Revolution - Timeline, Facts & Causes
The major aspects and key achievements during the american revolution, coming of the american revolution: boston tea party, american revolution and relationship between americans and british, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
How Did The War Between Britain and America Benefit Others
The american revolutionary war: the battles of lexington and concord, the role of women during the american revolution, revolutionary mothers by carol berkin: the role of founding mothers during the american revolution, differences between british and american soldiers in the american revolution, american revolution's negative impact on native american history, the role of boston tea party in the american revolution, establishment of american ideals during american revolution, the spies of the american revolution: nathan hale, the revolution of 1800, role and concequences of the articles of confederation, the second american revolution: its impact and legacy, the impact of valley forge on the american revolution , analysis of the main causes of the american revolution, war on the colonies: french, indian war and american revolution, a history of the enlightenment inspired revolutions, a study of major revolution events in america, the american revolution: how women and wives influenced husbands and friends, main minuses of the articles of confederation, insurgency and asymmetric warfare in the american revolutionary war .
22 March 1765 – 14 January 1784
Thirteen Colonies (United States)
Dutch Republic, France, Loyalist, Spain, United Kingdom, United States, American colonies
The Boston Tea Party (1773), The Battles of Lexington and Concord (1775), The Declaration of Independence (1776), The Battle of Saratoga (1777), The Siege of Yorktown (1781)
George Washington: As the commander-in-chief of the Continental Army, George Washington emerged as a central figure in the revolution. His strategic brilliance, perseverance, and moral character helped inspire and lead the troops through challenging times, ultimately leading to victory. Thomas Jefferson: Known for his eloquence and intellect, Thomas Jefferson was the principal author of the Declaration of Independence. His ideas and ideals, including the belief in natural rights and self-governance, greatly influenced the revolutionary cause. Benjamin Franklin: A polymath and influential statesman, Benjamin Franklin played a vital role in rallying support for the revolution. He traveled to Europe as a diplomat, securing crucial aid from France and other countries, and his scientific discoveries further enhanced his reputation. John Adams: A passionate advocate for independence, John Adams was instrumental in driving the revolutionary movement forward. He served as a diplomat, including as a representative to France and as the second President of the United States, and his contributions to shaping the nation were significant. Abigail Adams: Abigail Adams, wife of John Adams, was an influential figure in her own right. Her letters to her husband and other prominent figures provided valuable insights and perspectives on the revolution, and she became an early advocate for women's rights and equality.
In the 18th century, the thirteen American colonies were under British rule. Over time, tensions began to rise as the colonists developed a distinct identity and desired greater autonomy. Several key factors contributed to the buildup of resentment and ultimately led to the revolution. One crucial prerequisite was the concept of colonial self-government. The colonists enjoyed a degree of self-rule, which allowed them to develop their own institutions and local governments. However, as British policies, such as the Stamp Act and Townshend Acts, imposed new taxes and regulations on the colonies, the sense of self-government and individual liberties were threatened. Another significant factor was the Enlightenment era, which spread ideas of natural rights, individual freedoms, and representative government. Influential thinkers like John Locke and Thomas Paine advocated for the rights of the people and challenged the legitimacy of monarchy. The causes of the American Revolution were diverse and multifaceted. The colonists' grievances included taxation without representation, restrictions on trade, and the presence of British troops in the colonies. The Boston Massacre in 1770 and the Boston Tea Party in 1773 further heightened tensions and solidified the resolve for independence. Ultimately, the outbreak of armed conflict in 1775 at Lexington and Concord marked the beginning of the Revolutionary War. The Declaration of Independence, adopted on July 4, 1776, served as a powerful statement of the colonists' grievances and their determination to establish a free and sovereign nation. The historical context of the American Revolution reflects the culmination of colonial aspirations for self-government, Enlightenment ideas of individual rights, and a series of grievances against British rule.
Establishment of the United States as a sovereign nation; the creation of a new form of government based on democratic principles; adoption of the United States Constitution; redefinition of citizenship; abolition of feudalism; expansion of territorial boundaries, etc.
One of the major effects of the American Revolution was the establishment of a new form of government based on the principles of democracy and individual rights. The United States Constitution, born out of the revolution, served as a model for constitutional governments around the world. The idea of a government by the people and for the people spread, inspiring future revolutions and movements for independence. The revolution also challenged the existing colonial powers, particularly the British Empire, and set in motion a wave of decolonization throughout the world. The success of the American colonies in breaking free from British rule demonstrated that colonies could successfully achieve independence, fueling nationalist movements in other parts of the world and ultimately leading to the dissolution of empires. The American Revolution also had significant economic effects. It established the United States as a new economic power and opened up opportunities for trade and commerce. The revolution encouraged the development of industry and innovation, setting the stage for the industrial revolution that would follow. Furthermore, the American Revolution had a profound impact on the institution of slavery. While the revolution did not immediately abolish slavery, it planted the seeds of abolitionism and sparked debates on the issue of human rights and equality. Lastly, the American Revolution inspired and influenced subsequent revolutions and movements for independence, such as the French Revolution, which drew inspiration from the ideals of liberty, equality, and popular sovereignty championed by the American colonists.
Public opinion on the American Revolution varied greatly during the time period and continues to be interpreted differently today. In the 18th century, support for the revolution was not unanimous. Some colonists were loyal to the British Crown and opposed the revolutionary movement, while others actively supported the cause of independence. Public opinion shifted over time as events unfolded and more people became aware of the grievances and aspirations of the revolutionaries. Many colonists, especially those who felt oppressed by British policies, embraced the ideals of liberty, self-determination, and representation. They saw the revolution as a necessary step towards achieving these principles and securing their rights as free individuals. Others were motivated by economic factors, such as trade restrictions and taxation without representation, which fueled their support for independence. However, there were also segments of the population that remained loyal to Britain. Some believed in the benefits of British rule, such as protection and stability, while others feared the potential chaos and uncertainty that could result from a revolution. In modern times, public opinion on the American Revolution tends to be positive, with many viewing it as a pivotal moment in history that laid the foundation for democratic governance and individual freedoms. The ideals and principles that emerged from the revolution continue to shape American identity and influence public discourse on issues of liberty, equality, and self-governance.
1. The American Revolution lasted for eight years, from 1775 to 1783, making it one of the longest and most significant conflicts in American history. 2. The American Revolution had a profound impact on the world stage. It inspired other countries and movements seeking independence and democracy, such as the French Revolution that followed in 1789. 3. While often overlooked, women made significant contributions to the American Revolution. They served as spies, messengers, nurses, and even soldiers. Some notable examples include Deborah Sampson, who disguised herself as a man to join the Continental Army, and Abigail Adams, who advocated for women's rights.
The topic of the American Revolution holds immense importance for academic exploration and essay writing due to its profound impact on the world and the enduring legacy it left behind. Firstly, the American Revolution marked a pivotal moment in history where thirteen colonies fought for their independence from British rule, leading to the formation of the United States of America. It represents a significant event in the development of democracy and self-governance, serving as an inspiration for subsequent revolutions worldwide. Studying the American Revolution allows us to understand the principles and ideals that shaped the nation's foundation, such as liberty, equality, and the pursuit of happiness. It sheds light on the struggles and sacrifices made by individuals who fought for their rights and paved the way for the establishment of a democratic government. Furthermore, exploring this topic provides insights into the complexities of colonial society, the causes of the revolution, the role of key figures, and the social, economic, and political consequences of the conflict.
1. Bailyn, B. (1992). The Ideological Origins of the American Revolution. Belknap Press. 2. Ellis, J. J. (2013). American Creation: Triumphs and Tragedies at the Founding of the Republic. Vintage. 3. Ferling, J. E. (2015). Whirlwind: The American Revolution and the War That Won It. Bloomsbury Publishing. 4. Fischer, D. H. (2006). Washington's Crossing. Oxford University Press. 5. Maier, P. (1997). American Scripture: Making the Declaration of Independence. Vintage. 6. Middlekauff, R. (2005). The Glorious Cause: The American Revolution, 1763-1789. Oxford University Press. 7. Middlekauff, R. (2007). The Glorious Cause: The American Revolution, 1763-1789. Oxford University Press. 8. Nash, G. B. (2006). The Unknown American Revolution: The Unruly Birth of Democracy and the Struggle to Create America. Penguin Books. 9. Tuchman, B. W. (1989). The First Salute: A View of the American Revolution. Random House. 10. Wood, G. S. (1992). The Radicalism of the American Revolution. Vintage.
Relevant topics
- Industrial Revolution
- Manifest Destiny
- Great Depression
- Pearl Harbor
- Westward Expansion
- Civil Rights Movement
- Frederick Douglass
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Bibliography
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
American Revolution
The Revolutionary War waged by the American colonies against Britain influenced political ideas and revolutions around the globe, as a small fledgling nation won its freedom from the greatest military force of its time.

Revolutionary War
The Revolutionary War (1775-1783) arose from growing tensions between residents of Great Britain’s 13 North American colonies and the colonial government. The American colonists, led by General George Washington, won political independence and eventually formed the United States of America.

Battles of Lexington and Concord
Lead-Up to the Battles of Lexington and Concord Starting in 1764, Great Britain enacted a series of measures aimed at raising revenue from its 13 American colonies. Many of those measures, including the Sugar Act, Stamp Act and Townshend Acts, generated fierce resentment among the colonists, who protested against “taxation without representation.” Boston, the site […]

Dunmore’s Proclamation
Loyalist Governor Sought to Expand His Troops The proclamation was months in the making, as Dunmore was in a vulnerable position as throngs of rebels filled the Virginia capital of Williamsburg, prompting the loyalist governor to depart for Norfolk. Worsening matters for him was that many of his forces had deserted him, leaving him with […]

Continental Congress
Britain and the Imperial Crises Throughout most of colonial history, the British Crown was the only political institution that united the American colonies. The Imperial Crises of the 1760s and 1770s, found England saddled with crippling debt, incurred in large part by wars such as the French and Indian War. The British government responded by […]

Global Impact of the American Revolution
The American Revolution influenced political ideals and revolutions across the globe.

American Revolution History
Did you know that Paul Revere didn’t ride alone, and there were women on the Revolutionary War battlefields? Find out more about the war’s lesser-known patriots.

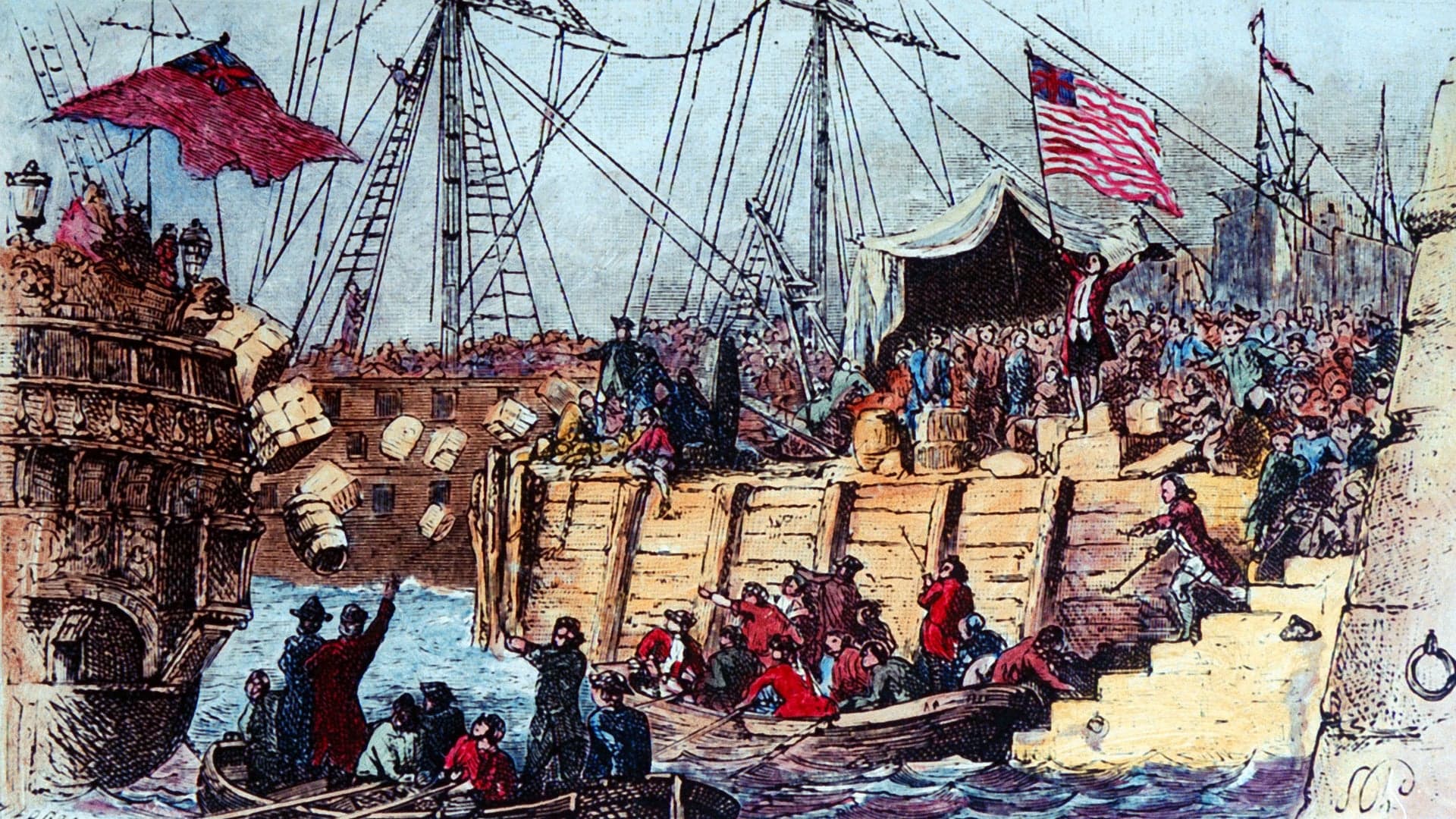
Boston Massacre Sparks a Revolution
The shooting of several men by British soldiers in 1770 inflames passions in the colonies.

The Tea Act of 1773, an act of Great Britain’s Parliament, was the catalyst for some of the most important moments of the lead-up to the Revolutionary War.

7 Events That Enraged Colonists and Led to the American Revolution
Colonists didn’t just take up arms against the British out of the blue. A series of events escalated tensions that culminated in America’s war for independence.

The Declaration of Independence Was Also a List of Grievances
The document was designed to prove to the world (especially France) that the colonists were right to defy King George III’s rule.

7 Hard-Fought Battles That Helped Win the American Revolution
While the British were often better equipped and trained, these events proved critical in ultimately securing Americans’ victory in the war.

7 Surprising Facts About the Boston Tea Party
For starters, the colonists weren’t protesting higher taxes on tea.
This Day in History

This Day in History Video: What Happened on July 4

This Day in History Video: What Happened on September 21

This Day in History Video: What Happened on December 16
This Day in History Video: What Happened on October 19

“Swamp Fox” routs Loyalists while Gates’ men fall ill
Congress issues a “declaration on the causes and necessity of taking up arms”.
Open Yale Courses
You are here, the american revolution.

The American Revolution entailed some remarkable transformations–converting British colonists into American revolutionaries, and a cluster of colonies into a confederation of states with a common cause–but it was far more complex and enduring than the fighting of a war. As John Adams put it, “The Revolution was in the Minds of the people… before a drop of blood was drawn at Lexington”–and it continued long past America’s victory at Yorktown. This course will examine the Revolution from this broad perspective, tracing the participants’ shifting sense of themselves as British subjects, colonial settlers, revolutionaries, and Americans.
This Yale College course, taught on campus twice per week for 50 minutes, was recorded for Open Yale Courses in Spring 2010.
Bailyn, Bernard. Faces of Revolution: Personalities and Themes in the Struggle for American Independence . New York: Knopf, 1990.
Brown, Richard D., ed. Major Problems in the Era of the American Revolution, 1760-1791 . 2nd ed. Stamford, CT: Cengage Learning, 1999.
Cray, Robert E. Jr., “Major John Andre and the Three Captors: Class Dynamics and Revolutionary Memory Wars in the Early Republic, 1780-1831,” Journal of the Early Republic, Vol. 17, No. 3. Autumn, 1997.
Gross, Robert A. The Minutemen and Their World . Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 2001.
Hamilton, Alexander, James Madison, and John Jay. The Federalist Papers . New York: Penguin, 1987.
McDonnell, Michael. “Popular Mobilization and Political Culture in Revolutionary Virginia: The Failure of the Minutemen and the Revolution from Below,” Journal of American History, Vol. 85, No. 3. December, 1998.
Paine, Thomas. Common Sense . New York: Penguin, 1982.
Raphael, Ray. A People’s History of the American Revolution . New York: HarperCollins, 2002.
Schwartz, Barry. “George Washington and the Whig Conception of Heroic Leadership,” American Sociological Review, Vol. 48, No. 1. February, 1983.
Wood, Gordon S. The Radicalism of the American Revolution . New York: Knopf, 1992.
Wood, Gordon S. The American Revolution: A History . New York: Modern Library, 2002. [optional]
Exams There is one midterm exam covering material discussed up through Lecture 13. The final exam covers material from the entire course.
Papers One paper, 3-5 pages long, is due the day of Lecture 9. A second paper, 7-9 pages in length, is due the day of Lecture 23.
First paper: 15% Midterm exam: 20% Second paper: 25% Final exam: 30% Discussion section participation: 10%

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.3: The Causes of the American Revolution
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 9360

- American YAWP
- Stanford via Stanford University Press
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Most immediately, the American Revolution resulted directly from attempts to reform the British Empire after the Seven Years’ War. The Seven Years’ War culminated nearly a half century of war between Europe’s imperial powers. It was truly a world war, fought between multiple empires on multiple continents. At its conclusion, the British Empire had never been larger. Britain now controlled the North American continent east of the Mississippi River, including French Canada. It had also consolidated its control over India. But the realities and responsibilities of the postwar empire were daunting. War (let alone victory) on such a scale was costly. Britain doubled the national debt to 13.5 times its annual revenue. Britain faced significant new costs required to secure and defend its far-flung empire, especially the western frontiers of the North American colonies. These factors led Britain in the 1760s to attempt to consolidate control over its North American colonies, which, in turn, led to resistance.
King George III took the crown in 1760 and brought Tories into his government after three decades of Whig rule. They represented an authoritarian vision of empire in which colonies would be subordinate. The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was Britain’s first major postwar imperial action targeting North America. The king forbade settlement west of the Appalachian Mountains in an attempt to limit costly wars with Native Americans. Colonists, however, protested and demanded access to the territory for which they had fought alongside the British.
In 1764, Parliament passed two more reforms. The Sugar Act sought to combat widespread smuggling of molasses in New England by cutting the duty in half but increasing enforcement. Also, smugglers would be tried by vice-admiralty courts and not juries. Parliament also passed the Currency Act, which restricted colonies from producing paper money. Hard money, such as gold and silver coins, was scarce in the colonies. The lack of currency impeded the colonies’ increasingly sophisticated transatlantic economies, but it was especially damaging in 1764 because a postwar recession had already begun. Between the restrictions of the Proclamation of 1763, the Currency Act, and the Sugar Act’s canceling of trials-by-jury for smugglers, some colonists began to fear a pattern of increased taxation and restricted liberties.
In March 1765, Parliament passed the Stamp Act. The act required that many documents be printed on paper that had been stamped to show the duty had been paid, including newspapers, pamphlets, diplomas, legal documents, and even playing cards. The Sugar Act of 1764 was an attempt to get merchants to pay an already existing duty, but the Stamp Act created a new, direct (or “internal”) tax. Parliament had never before directly taxed the colonists. Instead, colonies contributed to the empire through the payment of indirect, “external” taxes, such as customs duties. In 1765, Daniel Dulany of Maryland wrote, “A right to impose an internal tax on the colonies, without their consent for the single purpose of revenue, is denied, a right to regulate their trade without their consent is, admitted.” 7 Also, unlike the Sugar Act, which primarily affected merchants, the Stamp Act directly affected numerous groups throughout colonial society, including printers, lawyers, college graduates, and even sailors who played cards. This led, in part, to broader, more popular resistance.
Resistance to the Stamp Act took three forms, distinguished largely by class: legislative resistance by elites, economic resistance by merchants, and popular protest by common colonists. Colonial elites responded by passing resolutions in their assemblies. The most famous of the anti-Stamp Act resolutions were the Virginia Resolves, passed by the House of Burgesses on May 30, 1765, which declared that the colonists were entitled to “all the liberties, privileges, franchises, and immunities . . . possessed by the people of Great Britain.” When the Virginia Resolves were printed throughout the colonies, however, they often included a few extra, far more radical resolutions not passed by the Virginia House of Burgesses, the last of which asserted that only “the general assembly of this colony have any right or power to impose or lay any taxation” and that anyone who argued differently “shall be deemed an enemy to this his majesty’s colony.” 8 These additional items spread throughout the colonies and helped radicalize subsequent responses in other colonial assemblies. These responses eventually led to the calling of the Stamp Act Congress in New York City in October 1765. Nine colonies sent delegates, who included Benjamin Franklin, John Dickinson, Thomas Hutchinson, Philip Livingston, and James Otis. 9
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=397&height=438)
The Stamp Act Congress issued a “Declaration of Rights and Grievances,” which, like the Virginia Resolves, declared allegiance to the king and “all due subordination” to Parliament but also reasserted the idea that colonists were entitled to the same rights as Britons. Those rights included trial by jury, which had been abridged by the Sugar Act, and the right to be taxed only by their own elected representatives. As Daniel Dulany wrote in 1765, “It is an essential principle of the English constitution, that the subject shall not be taxed without his consent.” 10 Benjamin Franklin called it the “prime Maxim of all free Government.” 11 Because the colonies did not elect members to Parliament, they believed that they were not represented and could not be taxed by that body. In response, Parliament and the Crown argued that the colonists were “virtually represented,” just like the residents of those boroughs or counties in England that did not elect members to Parliament. However, the colonists rejected the notion of virtual representation, with one pamphleteer calling it a “monstrous idea.” 12
The second type of resistance to the Stamp Act was economic. While the Stamp Act Congress deliberated, merchants in major port cities were preparing nonimportation agreements, hoping that their refusal to import British goods would lead British merchants to lobby for the repeal of the Stamp Act. In New York City, “upwards of two hundred principal merchants” agreed not to import, sell, or buy “any goods, wares, or merchandises” from Great Britain. 13 In Philadelphia, merchants gathered at “a general meeting” to agree that “they would not Import any Goods from Great-Britain until the Stamp-Act was Repealed.” 14 The plan worked. By January 1766, London merchants sent a letter to Parliament arguing that they had been “reduced to the necessity of pending ruin” by the Stamp Act and the subsequent boycotts. 15
The third, and perhaps, most crucial type of resistance was popular protest. Riots broke out in Boston. Crowds burned the appointed stamp distributor for Massachusetts, Andrew Oliver, in effigy and pulled a building he owned “down to the Ground in five minutes.” 16 Oliver resigned the position the next day. The following week, a crowd also set upon the home of his brother-in-law, Lieutenant Governor Thomas Hutchinson, who had publicly argued for submission to the stamp tax. Before the evening was over, much of Hutchinson’s home and belongings had been destroyed. 17
Popular violence and intimidation spread quickly throughout the colonies. In New York City, posted notices read:
PRO PATRIA, The first Man that either distributes or makes use of Stampt Paper, let him take care of his House, Person, & Effects. Vox Populi; We dare.” 18
By November 16, all of the original twelve stamp distributors had resigned, and by 1766, groups calling themselves the Sons of Liberty were formed in most colonies to direct and organize further resistance. These tactics had the dual effect of sending a message to Parliament and discouraging colonists from accepting appointments as stamp collectors. With no one to distribute the stamps, the act became unenforceable.
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=423&height=545)
Pressure on Parliament grew until, in February 1766, it repealed the Stamp Act. But to save face and to try to avoid this kind of problem in the future, Parliament also passed the Declaratory Act, asserting that Parliament had the “full power and authority to make laws . . . to bind the colonies and people of America . . . in all cases whatsoever.” However, colonists were too busy celebrating the repeal of the Stamp Act to take much notice of the Declaratory Act. In New York City, the inhabitants raised a huge lead statue of King George III in honor of the Stamp Act’s repeal. It could be argued that there was no moment at which colonists felt more proud to be members of the free British Empire than 1766. But Britain still needed revenue from the colonies. 19
The colonies had resisted the implementation of direct taxes, but the Declaratory Act reserved Parliament’s right to impose them. And, in the colonists’ dispatches to Parliament and in numerous pamphlets, they had explicitly acknowledged the right of Parliament to regulate colonial trade. So Britain’s next attempt to draw revenues from the colonies, the Townshend Acts, were passed in June 1767, creating new customs duties on common items, like lead, glass, paint, and tea, instead of direct taxes. The acts also created and strengthened formal mechanisms to enforce compliance, including a new American Board of Customs Commissioners and more vice-admiralty courts to try smugglers. Revenues from customs seizures would be used to pay customs officers and other royal officials, including the governors, thereby incentivizing them to convict offenders. These acts increased the presence of the British government in the colonies and circumscribed the authority of the colonial assemblies, since paying the governor’s salary had long given the assemblies significant power over them. Unsurprisingly, colonists, once again, resisted.
Even though these were duties, many colonial resistance authors still referred to them as “taxes,” because they were designed primarily to extract revenues from the colonies not to regulate trade. John Dickinson, in his “Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania,” wrote, “That we may legally be bound to pay any general duties on these commodities, relative to the regulation of trade, is granted; but we being obliged by her laws to take them from Great Britain, any special duties imposed on their exportation to us only, with intention to raise a revenue from us only, are as much taxes upon us, as those imposed by the Stamp Act.” Hence, many authors asked: once the colonists assented to a tax in any form , what would stop the British from imposing ever more and greater taxes on the colonists? 20
New forms of resistance emerged in which elite, middling, and working-class colonists participated together. Merchants reinstituted nonimportation agreements, and common colonists agreed not to consume these same products. Lists were circulated with signatories promising not to buy any British goods. These lists were often published in newspapers, bestowing recognition on those who had signed and led to pressure on those who had not.
Women, too, became involved to an unprecedented degree in resistance to the Townshend Acts. They circulated subscription lists and gathered signatures. The first political commentaries in newspapers written by women appeared. 21 Also, without new imports of British clothes, colonists took to wearing simple, homespun clothing. Spinning clubs were formed, in which local women would gather at one of their homes and spin cloth for homespun clothing for their families and even for the community. 22
Homespun clothing quickly became a marker of one’s virtue and patriotism, and women were an important part of this cultural shift. At the same time, British goods and luxuries previously desired now became symbols of tyranny. Nonimportation and, especially, nonconsumption agreements changed colonists’ cultural relationship with the mother country. Committees of Inspection monitored merchants and residents to make sure that no one broke the agreements. Offenders could expect to be shamed by having their names and offenses published in the newspaper and in broadsides.
Nonimportation and nonconsumption helped forge colonial unity. Colonies formed Committees of Correspondence to keep each other informed of the resistance efforts throughout the colonies. Newspapers reprinted exploits of resistance, giving colonists a sense that they were part of a broader political community. The best example of this new “continental conversation” came in the wake of the Boston Massacre. Britain sent regiments to Boston in 1768 to help enforce the new acts and quell the resistance. On the evening of March 5, 1770, a crowd gathered outside the Custom House and began hurling insults, snowballs, and perhaps more at the young sentry. When a small number of soldiers came to the sentry’s aid, the crowd grew increasingly hostile until the soldiers fired. After the smoke cleared, five Bostonians were dead, including one of the ringleaders, Crispus Attucks, a former slave turned free dockworker. The soldiers were tried in Boston and won acquittal, thanks, in part, to their defense attorney, John Adams. News of the Boston Massacre spread quickly through the new resistance communication networks, aided by a famous engraving initially circulated by Paul Revere, which depicted bloodthirsty British soldiers with grins on their faces firing into a peaceful crowd. The engraving was quickly circulated and reprinted throughout the colonies, generating sympathy for Boston and anger with Britain.
.png?revision=1)
Resistance again led to repeal. In March 1770, Parliament repealed all of the new duties except the one on tea, which, like the Declaratory Act, was left, in part, to save face and assert that Parliament still retained the right to tax the colonies. The character of colonial resistance had changed between 1765 and 1770. During the Stamp Act resistance, elites wrote resolves and held congresses while violent, popular mobs burned effigies and tore down houses, with minimal coordination between colonies. But methods of resistance against the Townshend Acts became more inclusive and more coordinated. Colonists previously excluded from meaningful political participation now gathered signatures, and colonists of all ranks participated in the resistance by not buying British goods and monitoring and enforcing the boycotts.
Britain’s failed attempts at imperial reform in the 1760s created an increasingly vigilant and resistant colonial population and, most importantly, an enlarged political sphere—both on the colonial and continental levels—far beyond anything anyone could have imagined a few years earlier. A new sense of shared grievances began to join the colonists in a shared American political identity.
American Revolution: Reclaiming Rights and Powers Essay
The American Revolution was the war between the British Crown and American colonies, which led to the formation of the independent United States. The American Revolution was an attempt to rewrite the norms of a daily life and to break away from monarchial system that guided both personal and political behavior. The beginning of the American Revolution can be traced back to the 1763 when the British Government began to reassert control over its American colonies. During this period, the British government was fighting to protect its colonies from its French and Native enemies.
As a result, British Government Pursued policies of the kind embodied in the proclamation of the 1763 and the Quebec act that gave Quebec the right to many Indian lands claimed by the American colonists to ensure future domestic tranquility (Sidney 54). Besides the Quebec act, The British Government also began to institute new taxes and enforce old ones in order to pay for its wartime expenses.
Many colonists opposed the new policies implemented by the British government as they felt that the British government was taking away their right and powers. This paper seeks to discuss the key rights and powers that the American believed were being taken way by the British Crown. The paper will also provide the evidences the colonist had to support their beliefs.
The key rights and powers that Americans believed were being taken away by the British government
While reasserting control over its American colonies in 1763, British government came up with various policies. Many Americans felt that these policies were taking way their rights and powers. The key rights and powers that the Americans believed were being taken away include the rights and powers to own land, and the right to pay taxes.
The right and power to own land
When the British government came up with the proclamation of 1763, many colonists felt that the British government was violating their fundamental rights. In regards to the proclamation of the 1763, the British government forbade settlement west of the Appalachian Mountains in an attempt to secure peace with powerful Native Americans neighbors. However, Colonists reacted to this policy in different ways. In their views, the proclamation of 1763 was the first of many imperial insults.
Many colonists believed that the Britsh Crown was taking away their key rights and powers to own land. As a matter of fact, when the British Crown came up with the proclamation of 1763, many eastern and western farmers were frustrated. Colonists felt that such actions cut off opportunities for land speculators and western farmers, many of whom were already coveting or squatting on these lands. From the vantage point of the colonialists, the British government seemed to be sacrificing the ambitions of the colonialist in favor of the Indians.
The colonialist, therefore, felt that the Crown was taking away their right to possess lands and giving them to Indians. As a result, colonists responded to the proclamation of 1763 and other new policies of the British crown through the written word. Sidney (89) reveals that the colonists wrote petitions, public letters, broadsides, and sermons. According to Sidney (90), the colonist sang songs, wrote poetries, and otherwise voiced their displeasures with the British crown and their growing desire of independence. The struggles over lands predated the revolution by more than a century, and they shaped the participation of white settlers and Native Americans during the war.
The Burden Taxes
Besides, the proclamation of 1763, the colonists also disputed the new tax policies that the British government implemented. When the crown implemented the new taxes, Americans took to the streets to protest them, and for more than a decade, they signed petitions to claim their liberties as loyal English citizens. For instance, the colonial response to the stamp act and sugar act demonstrated the power of the masses.
Many Bostonians took to the street in august 1765 to protest the new tax on stamps used for legal documents. The angry protestors destroyed the personal property of the stamp distributor for the colony and then hanged and beheaded him in effigy. The outrage spread throughout the colonies, as indebted colonists were now facing greater fees after they were taken to court.
Colonists were expressing their dissatisfaction with the tax policies because they felt that the stamp act and the sugar act violated the rights of levying taxes conferred by charter solely upon the state legislature. Tandem to this, the colonist had no direct representation in the British parliament, thus, they felt that it was unfair for them to be subject taxation without representation (Sidney 130).
In fact, Americans believed that the new tax policies demonstrated that the British government was not acting precipitately. Colonists saw that the government had no intentions to subvert colonial liberties but merely to raise revenue in the most expeditious and least burdensome manner possible.
Colonist’s dissatisfaction with the new tax system could also be witnessed four months later after the Boston riot. Many frustrated colonists engaged in similar public protest in all of the other colonies. Protestors from Carolina also demonstrated their opposition to the tax policy as well as their solidarity with protestors from Boston.
Small farmers and herders in the colonial backcountry similarly voiced their frustrations through various act of civil unrest. Because of the protests, many stamp distributors resigned forcing the British Crown to repeal the tax act (Goldfield, et al. 80). This protest had apparently made the Colonists intention clear. Obviously, they believed that the Crown was taking away their legal rights by implementing new tax laws.
The general warrants
Besides the burden tax, the British Crown had also issued a general warrant that allowed the British to search homes and seize property without specific search warrants. Many colonists felt that the British government was violating their personal rights. Therefore, they decided to oppose this act by demonstrating on the streets.
Tandem to this, the quartering of the British troops in personal homes, without the consent of the owners, was also a source of dislike towards the British Crown. From these three perspectives, one can justify that the American Revolution was fundamentally conservative as many colonists were fighting to protect the rights and powers they had.
Conclusively, According to Sidney (234), the dispute was waged over the nature of the British constitution and the rights of subject; the goals of the colonist were to reform the British Empire, not to withdraw from it. In fact, the colonists did not see themselves as revolutionaries; they saw themselves as English citizens who were only defending their rights to own properties. Therefore, in response to British action, the colonist established a continental congress in 1774 to organize their resistance effort and coordinate their policies towards the crown (Goldfield, et al. 89).
Works Cited
Goldfield, David, et al . American Journey: A History of The United States. 2nd Ed. Vol. 2 Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Publishers, 2011. Print.
Sidney, Barclay. American Revolution . Charleston, SC: BiblioLife Publishers, 2009. Print.
- The American Revolution From 1763 to 1777
- Literature Analysis of Faulkner Journeys
- Cancellation and Termination of Contract
- Women Status after the American Revolution
- American Revolution of 1774
- Slavery and the Abolition of Slave Trade
- the Principle of Term Limits for Members of Congress
- Confederation Articles and 1787 Constitution
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, May 2). American Revolution: Reclaiming Rights and Powers. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-american-revolution-essay/
"American Revolution: Reclaiming Rights and Powers." IvyPanda , 2 May 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/the-american-revolution-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'American Revolution: Reclaiming Rights and Powers'. 2 May.
IvyPanda . 2020. "American Revolution: Reclaiming Rights and Powers." May 2, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-american-revolution-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "American Revolution: Reclaiming Rights and Powers." May 2, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-american-revolution-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "American Revolution: Reclaiming Rights and Powers." May 2, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-american-revolution-essay/.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Without cookies your experience may not be seamless.

- Essays on the American Revolution
In this Book

- Stephen G. Kurtz
- Published by: The University of North Carolina Press
- Series: Published for the Omohundro Institute of Early American History and Culture, Williamsburg, Virginia
Table of Contents

- Title page, Copyright
- pp. vii-viii
- Introduction
- 1. The Central Themes of the American Revolution: An Interpretation
- BERNARD BAILYN
- 2. An Uneasy Connection: An Analysis of the Preconditions of the American Revolution
- JACK P. GREENE
- 3. Violence and the American Revolution
- RICHARD MAXWELL BROWN
- 4. The American Revolution: The Military Conflict Considered as a Revolutionary War
- pp. 121-156
- 5. The Structure of Politics in the Continental Congress
- H. JAMES HENDERSON
- pp. 157-196
- 6. The Role of Religion in the Revolution: Liberty of Conscience and Cultural Cohesion in the New Nation
- WILLIAM G. McLOUGHLIN
- pp. 197-255
- 7. Feudalism, Communalism, and the Yeoman Freeholder: The American Revolution Considered as a Social Accident
- ROWLAND BERTHOFF AND JOHN M. MURRIN
- pp. 256-288
- 8. Conflict and Consensus in the American Revolution
- EDMUND S. MORGAN
- pp. 289-310
- pp. 311-318
- Notes on the Contributors
- pp. 319-320
Additional Information
Project MUSE Mission
Project MUSE promotes the creation and dissemination of essential humanities and social science resources through collaboration with libraries, publishers, and scholars worldwide. Forged from a partnership between a university press and a library, Project MUSE is a trusted part of the academic and scholarly community it serves.

2715 North Charles Street Baltimore, Maryland, USA 21218
+1 (410) 516-6989 [email protected]
©2024 Project MUSE. Produced by Johns Hopkins University Press in collaboration with The Sheridan Libraries.
Now and Always, The Trusted Content Your Research Requires

Built on the Johns Hopkins University Campus
- The Legacy of the Revolution
Why the American Revolution Matters
Posted February 18, 2019 / Basic Principles , History Education , The Legacy of the Revolution

The American Revolution was shaped by high principles and low ones, by imperial politics, dynastic rivalries, ambition, greed, personal loyalties, patriotism, demographic growth, social and economic changes, cultural developments, British intransigence, and American anxieties. It was shaped by conflicting interests between Britain and America, between regions within America, between families and between individuals. It was shaped by religion, ethnicity, and race, as well as by tensions between rich and poor. It was shaped, perhaps above all else, by the aspirations of ordinary people to make fulfilling lives for themselves and their families, to be secure in their possessions, safe in their homes, free to worship as they wished, and to improve their lives by availing themselves of opportunities that seemed to lie within their grasp.
No one of these factors, nor any specific combination of them, can properly be said to have caused the American Revolution. An event as vast as the American Revolution is simply too complex to assign it neatly to particular causes. Although we can never know the causes of the American Revolution with precision, we can see very clearly the most important consequences of the Revolution. They are simply too large and important to miss, and so clearly related to the Revolution that they cannot be traced to any other sequence of events. Every educated American should understand and appreciate them.
First, the American Revolution secured the independence of the United States from the dominion of Great Britain and separated it from the British Empire. While it is altogether possible that the thirteen colonies would have become independent during the nineteenth or twentieth century, as other British colonies did, the resulting nation would certainly have been very different than the one that emerged, independent, from the Revolutionary War. The United States was the first nation in modern times to achieve its independence in a national war of liberation and the first to explain its reasons and its aims in a declaration of independence, a model adopted by national liberation movements in dozens of countries over the last 250 years.
Second, the American Revolution established a republic , with a government dedicated to the interests of ordinary people rather than the interests of kings and aristocrats. The United States was the first large republic since ancient times and the first one to emerge from the revolutions that rocked the Atlantic world, from South America to Eastern Europe, through the middle of the nineteenth century. The American Revolution influenced, to varying degrees, all of the subsequent Atlantic revolutions, most of which led to the establishment of republican governments, though some of those republics did not endure. The American republic has endured, due in part to the resilience of the Federal Constitution, which was the product of more than a decade of debate about the fundamental principles of republican government. Today most of the world’s nations are at least nominal republics due in no small way to the success of the American republic.
Third, the American Revolution created American national identity , a sense of community based on shared history and culture, mutual experience, and belief in a common destiny. The Revolution drew together the thirteen colonies, each with its own history and individual identity, first in resistance to new imperial regulations and taxes, then in rebellion, and finally in a shared struggle for independence. Americans inevitably reduced the complex, chaotic and violent experiences of the Revolution into a narrative of national origins, a story with heroes and villains, of epic struggles and personal sacrifices. This narrative is not properly described as a national myth, because the characters and events in it, unlike the mythic figures and imaginary events celebrated by older cultures, were mostly real. Some of the deeds attributed to those characters were exaggerated and others were fabricated, usually to illustrate some very real quality for which the subject was admired and held up for emulation. The Revolutionaries themselves, mindful of their role as founders of the nation, helped create this common narrative as well as symbols to represent national ideals and aspirations.
American national identity has been expanded and enriched by the shared experiences of two centuries of national life, but those experiences were shaped by the legacy of the Revolution and are mostly incomprehensible without reference to the Revolution. The unprecedented movement of people, money and information in the modern world has created a global marketplace of goods, services, and ideas that has diluted the hold of national identity on many people, but no global identity has yet emerged to replace it, nor does this seem likely to happen any time in the foreseeable future.
Fourth, the American Revolution committed the new nation to ideals of liberty, equality, natural and civil rights, and responsible citizenship and made them the basis of a new political order. None of these ideals was new or originated with Americans. They were all rooted in the philosophy of ancient Greece and Rome, and had been discussed, debated and enlarged by creative political thinkers beginning with the Renaissance. The political writers and philosophers of the eighteenth-century Enlightenment disagreed about many things, but all of them imagined that a just political order would be based on these ideals. What those writers and philosophers imagined, the American Revolution created—a nation in which ideals of liberty, equality, natural and civil rights, and responsible citizenship are the basis of law and the foundation of a free society.
The revolutionary generation did not complete the work of creating a truly free society, which requires overcoming layers of social injustice, exploitation, and other forms of institutionalized oppression that have accumulated over many centuries, as well as eliminating the ignorance, bigotry, and greed that support them. One of the fundamental challenges of a political order based on principles of universal right is that it empowers ignorant, bigoted, callous, selfish, and greedy people in the same way it empowers the wise and virtuous. For this reason, political progress in free societies can be painfully, frustratingly slow, with periods of energetic change interspersed with periods of inaction or even retreat. The wisest of our Revolutionaries understood this, and anticipated that creating a truly free society would take many generations. The flaw lies not in our Revolutionary beginnings or our Revolutionary ideals, but in human nature. Perseverance alone is the answer.
Our independence, our republic, our national identity and our commitment to the high ideals that form the basis of our political order are not simply the consequences of the Revolution, to be embalmed in our history books. They are living legacies of the Revolution, more important now as we face the challenges of the modern world than ever before. Without understanding them, we find our history incomprehensible, our present confused, and our future dark. Understanding them, we recognize our common origins, appreciate our present challenges, and can advocate successfully for the Revolutionary ideals that are the only foundation for the future happiness of the world.
Above: Detail of Liberty by an unidentified American artist, ca. 1800-1820, National Gallery of Art.
If you share our concern about ensuring that all Americans understand and appreciate the constructive achievements of the American Revolution, we invite you to join our movement. Sign up for news and notices from the American Revolution Institute. It costs nothing to express your commitment to thoughtful, responsible, balanced, non-partisan history education.
- Basic Principles
- History Education
- Material Culture
- Revolutionary Characters
- Revolutionary Events
- Revolutionary Ideals

Latest Posts
- The Mysterious Hero’s Return
- The People’s Constitution
- Richard Henry Lee: Gentleman Revolutionary
- El General Washington
- Lessons from the Boston Massacre
American Revolution - List of Essay Samples And Topic Ideas
The American Revolution, a pivotal period from 1765 to 1783, led to the thirteen American colonies’ independence from British rule. Essays could delve into the various factors that contributed to the revolution, the key battles, and notable figures who played significant roles. They might also explore the ideological underpinnings of the revolutionaries, the impact of Enlightenment thought, and the subsequent formulation of a new governmental system. Discussions might further extend to the revolution’s global repercussions, its effect on American society, and the enduring legacy of the values and institutions established during this period. A vast selection of complimentary essay illustrations pertaining to American Revolution you can find in Papersowl database. You can use our samples for inspiration to write your own essay, research paper, or just to explore a new topic for yourself.

Women after the American Revolution
Although the Revolutionary War provided a new perspective of women’s roles in politics and the household, there was not lasting change after the end of the war. Coverture is the status that a woman is essentially property of her husband, and is to remain under his command. During the post-revolutionary era, ideas of coverture still existed in America, even if new rights given to women began to spark their want for equality. Before the American Revolution, women had a very […]
Was the American Revolution Really Revolutionary?
During the Age of Revolution (1774-1849), many revolutionary movements occurred in Europe and the Americas. One of the most revolutionary revolutions was the French Revolution, a period of social and political upheaval in France that resulted in an upswing of nationalism, as well as the decline of monarchies and the rise of Democracy. The entire political and social structure of France was overthrown as a result of The French Revolution, making it one of the most radical revolutions of its […]
Was the Revolutionary War Actually Revolutionary?
The Revolutionary War could perhaps be called the greatest thing to ever happen to us. But, was it really? Just how revolutionary was the Revolutionary War? Some may say it was extremely revolutionary but, was it even revolutionary at all? This subject is very contradictory to various groups of people . To some it was very revolutionary but to others at just a glance it was revolutionary but, once you take a deeper look you'd find it was not very […]
We will write an essay sample crafted to your needs.
Why was the American Revolution a Conservative Movement?
The American Revolution is often analyzed by historians as a conservative movement to maintain the status quo. However, the American Revolution was partially conservative and partially liberal, contributing to the nuance of the issue. Politically, the revolution was revolutionary because the governmental institutions that resulted from it were radically different than the inherited governmental systems of Great Britain. These governmental establishments amplified Enlightenment ideas and divided sovereignty (federalism), notably different from Britain’s political system. Additionally, the Bill of Rights was […]
Role of Women in the American Revolutionary War
The achievements of men usually overshadow the role of women in the history of America. However, women have been very important in establishing liberal America that people live in today. The accomplishments of women in the American revolutionary war is hardly reported in historical books. During the American Revolution (1775-1783), women played a role in a variety of ways, including the creation of organizations, becoming camp followers, and by gathering intelligence for the Patriot cause. One of the roles of […]
Nation-state Building in the United States
Nation-state Building in the United States from the American Revolution to the Civil War Era A major component of Nation-state building in the U.S included and started with westward expansion. There was a collective belief that God had foreordained the United States to cover the entire continent, thus began the territorial expansion of the U.S.; which was pursued under the doctrine of manifest destiny. The initial westward expansion conquest, beyond the original thirteen colonies, was the Ohio River Valley, but […]
Three Phases of American Revolution
What were the three phases of American revolution? What were the developments in the three phases of American revolution during the seventeenth century? How did the three phases of American revolution evolve? In 1754, war erupted on the North American continent which was known as the French and Indian War. The fighting lasted until 1763, when Britain and its colonists emerged victorious and seized nearly all French land in North America. The victory, however, only led to growing tensions between […]
Is the American Revolution Radical?
Radical is a word that means change. If something is radical it means a change has occurred. The American Revolution was a war that broke that began in 1775. There was conflict between the colonies and Great Britain. War broke out when the 13 colonies revolted against the Britain rulers. There were many events that made up the revolution. There was chaos all over the 13 colonies. The American revolution brought a lot of change and shaped a new nation. […]
A War of the Thirteen Colonies against Great Britain
Parliament's passage of the Intolerable Acts in 1774 intensified the conflict between the colonies and Great Britain. Americans came to the conclusion that the only solution to their dilemma with the British government was to sever all ties with it. The American Revolution was the radical breakthrough in which the thirteen colonies fought a war against Great Britain in order to become independent. The initiation that caused the American Revolution was the Lexington and Concord in which British troops and […]
The Major Trigger for the American Revolution
The French-Indian War was the major trigger for the American Revolution for independence also referred to as the Seven Years War', the conflict was between France and Great Britain with both countries believing they were the inhibitors of Ohio River Valley. Subsequent to the seven years of disputes and fights over the ownership, Britain won and took victory over the land (Thompson, 2017). Over the next 15 years, the French government yearned for revenge and recovery of its former colonies. […]
How the American Revolution had Influenced on France
The American Revolution had surfaced from the adversary between the British and the American colonists in the New World who were fighting desperately for their independence. The French and Indian War contributed greatly to this fight for independence, as the cost of the war was abundant and prompted the British to initiate harsh taxes on the American colonists, such as the Sugar Act. Along with the high costs, what additionally resulted from the French and Indian War was the French […]
MYP Individuals in Society
The American Revolution was a war that took place between 1775-1783. During this period of time, the British and the 13 colonies fought. Many soldiers and militiamen died either because of diseases, lack of supplies, natural disasters, or battles. The battle of Lexington and Concord was the battle that started the American Revolution. It all started on April 18 when British troops arrived at Boston. They proceeded to take the militia's goods. Luckily, Paul Revere, a patriot, warned the colonists […]
The American Revolution and the United States of America
The American Revolution was the true beginning of the United States of America. The colonists fought the British long and hard for seven years and gained their independence. Many people doubted the colonists, but they persevered and defeated one of the greatest armies in the world. This allowed the colonists to build a nation based off of four main principles: religious tolerance, economic opportunity, self-government, and individual liberty. In the early 1600's, many people began to migrate to the Americas […]
What Lead to the American Revolution
The American Revolution is a major part of our history today. Without the revolution, we would not be where we are today. The reason our country is what it is today is because of the American Revolution. America is its own country because of the revolution. The first settlers came over here in the name of England, but years after, we were fighting against them to become a separate nation. But it all had to start somewhere. What lead up […]
About Women in American Revolution
In our well-developed, better-than-ever society, we are still fighting for women's rights and equality between genders. Waiting for a police officer or a neurologist to arrive, we are usually surprised when we see a woman approaching. While reading an article about the death toll in the Syrian Civil War, we easily assume all late soldiers were males. Does this approach differ from the one that was two hundred and fifty years ago? The role of women was crucial during the […]
American Revolution in United States History
A profound turning point in United States history between the period of 1754-1800 was the American Revolution. It elevated recognition of social inequality, which drove some people and groups to call for the abolition of slavery and greater political democracy in the new state and national governments. This war can be understood in the historical context of Britain's threats to assert stricter authority over the North American colonies, through the imposition of taxes without representation in the British Parliament. This […]
An Eventful Time in American History
An eventful time in American History, full of pride, bloodshed, self-realization, and building of an independent nation. A nation was fought for and built, created things, the very things that make America the great country it is today. A rebellion would change the world, in a matter of nearly a decade of unrest and hostility. The rejection of the British Parliament's authority due to taxation, rising prices of many things needed to sustain life under British rule. Brought about a […]
The American People and the American Revolution
This essay will talk about the main point and details of the American Revolution and American People. Which is where the Americans get Independence from the British. The main topics that it will inform in this essay is the Second Continental Army, the Declaration of Independence, and the Surrender of Yorktown which were important events that lead to Independence of the Americans. Also what the British did to the Americans like taxation with the products they used a lot back […]
American Revolution: Series of Crisis
American Revolution was brought about by a series of crisis between the British colonizers and the Americans. The crisis was caused by various acts made by the colonizers to get taxes from the colonies. This was after the British government was involved in a war between French and Indians which took seven years. The war caused the government to be in a debt because of the soldiers who were employed to fight together with the British government. Imposition of sugar […]
The American Revolution
Role of slaves and Native Americans in the RevolutionThousands of African slaves and the Native American involvement in the fight for independence against the British colonial masters. Most of them were actively involved in the forefront of the war. They refused to stand aside and took the side of the war that they felt had an upper arm in winning and of course the one that offered better terms of their freedom when the war is won. The war was […]
The American Revolution and a Political and Social Partition
It would be agreed that for the British Colonists, the year of 1763 was seen as a great watershed in American History. On that note, throughout the years of 1756-1763, was a time period of salutary neglect that lead to the French and Indian war, in which the British called it the Seven Years War. At first it began as a local war in North America battled by the Colonists against the coalition of the French and Indians, however it […]
Western Constitutionalism and his Influence in the USA
One of the short stories of the West (the American one) appears before us as an exemplary, intense and exalting adventure. In an area of about nine and a half million square kilometers, a handful of men of disparate origins could make their new homeland, the first economic and political power of the planet by dint of determination, heroism and strength. The year 1607 was the year in which the first expeditions were made in Virginia, which did not find […]
About American Revolutionary War
More than two million people lived in the new thirteen original American colonies during the mid-1700s. Some were born naturally in the New World, while others moved to America to create a new home. Many immigrants left Great Britain to come to America. People left for various reasons like religious persecution, war, disease, famine, and some just wanted a fresh start. Many less than fortunate people sold themselves as indentured servants to the wealthy and in return they would receive […]
Many Reasons for the American Revolution
The American Revolution was a very interesting event in American History. It caused many great changes to the way we live. In my opinion, this topic is one of the most fascinating topics in American history because of the many complex pieces that come together to form the story of the revolution and the way that it has affected the way we live our lives today. Although there were many reasons for the American Revolution, a few of the major […]
The American Revolution and Society History
The American Revolution was the thirteen colonies fight for independence from Great Britain that began in 1775 in Lexington and Concord, Massachusetts. It is considered a revolution because it was the first successful economic and political reformation in a society that served to inspire worldwide revolutions. It occured after the French and Indian War (1745-1763) when a profound feeling of disunity and betrayal was felt among the colonies. During this time the British empire's expansion and large financial debt caused […]
How the American Revolution Led to the French Revolution
In the American Revolution, the thirteen colonies were able to gain independence from Great Britain and an important cause of the victory was the help of the French who made a major impact on the war and were allies of the colonists. They fought together closely and exchanged several ideas, which included thinking that led to the start of the American Revolution. After the war of almost eight years, there were many parts of French culture that had been affected […]
The American and the French Revolutions
The right of revolution was an idea proposed by Enlightenment Philosopher John Locke, which inspired and challenged the colonies in America and the people of France to revolt. Displeased with their current positions with their governments, they mustered up the courage and strength to challenge authority. Through their battles and hardships, both revolutions sought a government that mirrored the Enlightenment beliefs of natural rights, power of the people, and equality. With those goals in mind, they demonstrated the idea that […]
The American Patriots and the American Revolution
Throughout history, many revolutions have occurred and the reasonings behind them are many. Some of these revolutions occur because people want freedom. An example of this type of revolution would be the American Revolution. The American Revolution was a colonial revolt that took place in 1775 through 1783. The American Patriots in the Thirteen Colonies won independence from Great Britain, becoming the United States of America. They defeated the British in the American Revolutionary War which took place between 1775-1783 […]
American Revolution and Nathanael Greene
Nathanael Greene - Nathanael Greene was a Patriot Major General who had extreme military potential from a young age. He was born into a very faithful and determind Quaker family in Rhode Island. Nathanael Greene's family did not believe or agree with military goals. However he ended up choosing the milatary before his family's beliefs. He became the youngest Patriot brigadier general at the age of 34 and reached that rank in one year. Greene was in command of Boston […]
The Effect that the Enlightenment had on the American Revolution
The Declaration of independence, document declaring the US to be independent of the British Crown, signed by the congressional representatives of the Thirteen Colonies, including Thomas Jefferson, Benjamin Franklin, and John Adams, and ratified on July 4, 1776. This was just one of the first set of foundation to the united states. Second came the constitution. The Constitution of the United States is a document that embodies the fundamental laws and principles by which the United States is governed. It […]
Additional Example Essays
- Enlightenment and The French Revolution
- Was the French Revolution Successful
- Compare And Contrast In WW1 And WW2
- Why College Should Not Be Free
- Shakespeare's Hamlet Character Analysis
- A Raisin in the Sun Theme
- Logical Fallacies in Letter From Birmingham Jail
- How the Roles of Women and Men Were Portrayed in "A Doll's House"
- Martin Luther King Speech Evaluation
- A Rose for Emily Setting
- Abraham Lincoln and the Gettysburg Address
- Greek and Roman affects on Western Civilization
How To Write an Essay About American Revolution
Understanding the american revolution.
Before writing an essay about the American Revolution, it is crucial to understand its historical context and significance. The American Revolution, occurring from 1765 to 1783, was a pivotal event in which the Thirteen Colonies in North America won independence from Great Britain and formed the United States. Start by outlining the key events that led to the revolution, including the French and Indian War, the Stamp Act, the Boston Tea Party, and the Battles of Lexington and Concord. Familiarize yourself with the major figures involved, such as George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, and King George III, and understand the ideological underpinnings of the revolution, including concepts of liberty, democracy, and taxation without representation. This foundational knowledge will provide a solid basis for your essay.
Developing a Focused Thesis Statement
A strong essay on the American Revolution should be centered around a clear, concise thesis statement. This statement should present a specific viewpoint or argument about the revolution. For example, you might argue that the American Revolution was primarily a political and ideological revolution rather than just a military conflict, or analyze the impact of the revolution on the development of American political thought. Your thesis will guide the direction of your essay and ensure a structured and coherent analysis.
Gathering Historical Evidence
To support your thesis, gather historical evidence from credible sources. This might include primary sources like letters, speeches, and contemporary accounts, as well as secondary sources like scholarly articles and history books. Analyze this evidence critically, considering the reliability and perspective of each source. Use this evidence to build your argument and provide depth to your analysis of the American Revolution.
Analyzing Key Events and Figures
Dedicate a section of your essay to analyzing key events and figures of the American Revolution. Discuss how these events were pivotal in the progress of the revolution and examine the roles and contributions of significant figures. For example, explore how the Declaration of Independence encapsulated the revolutionary ideals or how diplomatic efforts with foreign nations were crucial to the colonial victory. This analysis will help readers understand the complexities and nuances of the revolution.
Concluding the Essay
Conclude your essay by summarizing the main points of your discussion and restating your thesis in light of the evidence presented. Your conclusion should tie together your analysis and emphasize the significance of the American Revolution in shaping American history and identity. You might also want to reflect on the broader implications of the revolution, such as its impact on global politics or its legacy in contemporary America.
Reviewing and Refining Your Essay
After completing your essay, review and edit it for clarity and coherence. Ensure that your arguments are well-structured and supported by historical evidence. Check for grammatical accuracy and ensure that your essay flows logically from one point to the next. Consider seeking feedback from peers or instructors to further refine your essay. A well-crafted essay on the American Revolution will not only demonstrate your understanding of this pivotal event in history but also your ability to engage critically with historical narratives.
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The History of American Revolution - Timeline, Facts & Causes. Essay grade: Poor. 2 pages / 1137 words. The army for the Patriots in the Revolutionary War was called the Continental ArmyThe essay lacks a clear thesis statement, making it difficult for the reader to understand the purpose of the essay.
The American Revolution was an insurrection carried out by 13 of Great Britain's North American colonies that began in 1775 and ended with a peace treaty in 1783. The colonies won political independence and went on to form the United States of America.The war followed more than a decade of growing estrangement between the British crown and a large and influential segment of its North ...
The American Revolution, also known as the Revolutionary War, was a time of revolting and political uprising, in which the 13 colonies separated from the British Empire, forming the independent nation known as the United States of America. Though the American Revolution began because the colonies wanted independence from Britain, many important ...
The Revolutionary War (1775-83), also known as the American Revolution, arose from growing tensions between residents of Great Britain's 13 North American colonies and the colonial government ...
American Revolution, also known as Revolutionary War, occurred in the second half of the 18th century. Among its causes was a series of acts established by the Crown. These acts placed taxes on paint, tea, glass, and paper imported to the colonies. As a result of the war, the thirteen American colonies gained independence from the British Crown ...
Revolutionary War. The Revolutionary War (1775-1783) arose from growing tensions between residents of Great Britain's 13 North American colonies and the colonial government. The American ...
The American Revolution was a rebellion and political movement in the Thirteen Colonies which peaked when colonists initiated an ultimately successful war for independence against the Kingdom of Great Britain. ... (although there were a few Loyalist papers) and printed many pamphlets, announcements, patriotic letters, and pronouncements.
American Revolution Timeline. List of some of the major causes and effects of the American Revolution. The revolution began after Britain imposed new taxes and trade restrictions on the 13 American colonies, fueling growing resentment and strengthening the colonists' objection to their lack of representation in the British Parliament.
These eight original essays by a group of America's most distinguished scholars include the following themes: the meaning and significance of the Revolutio...
The American Revolution entailed some remarkable transformations-converting British colonists into American revolutionaries, and a cluster of colonies into a confederation of states with a common cause-but it was far more complex and enduring than the fighting of a war. ... Papers One paper, 3-5 pages long, is due the day of Lecture 9. A ...
Introduction to the American Revolution (1775-1783)The American Revolutionary War (1775-1783) resulted from a conflict between the British government and British subjects living in the thirteen American colonies. Between the years 1764 and 1774, the crown and his majesty's legislature passed a number of tax measures, which the colonists fiercely opposed.
Most immediately, the American Revolution resulted directly from attempts to reform the British Empire after the Seven Years' War. The Seven Years' War culminated nearly a half century of war between Europe's imperial powers. It was truly a world war, fought between multiple empires on multiple continents. At its conclusion, the British ...
American Revolution: Reclaiming Rights and Powers Essay. The American Revolution was the war between the British Crown and American colonies, which led to the formation of the independent United States. The American Revolution was an attempt to rewrite the norms of a daily life and to break away from monarchial system that guided both personal ...
March 13, the French minister in London informs King George III that France recognizes the United States. May 4, Congress ratifies the Treaty of Alliance with France, and further military and financial assistance follows. By June, France and England are at war. The American Revolution has become an international war.
Essays on the American Revolution. These eight original essays by a group of America's most distinguished scholars include the following themes: the meaning and significance of the Revolution; the long-term, underlying causes of the war; violence and the Revolution; the military conflict; politics in the Continental Congress; the role of ...
The American Revolution was shaped by high principles and low ones, by imperial politics, dynastic rivalries, ambition, greed, personal loyalties, patriotism, demographic growth, social and economic changes, cultural developments, British intransigence, and American anxieties. It was shaped by conflicting interests between Britain and America ...
This essay about the Battle of Saratoga highlights the pivotal conflict in the American Revolutionary War. It explores the strategic maneuvers of British General John Burgoyne and American General Horatio Gates, emphasizing the significant roles played by American patriots.
99 essay samples found. The American Revolution, a pivotal period from 1765 to 1783, led to the thirteen American colonies' independence from British rule. Essays could delve into the various factors that contributed to the revolution, the key battles, and notable figures who played significant roles. They might also explore the ideological ...
Eliga H. Gould | University of New Hampshire. The American Revolution was a civil war in every sense of the word, a fratricidal conflict that divided men and women throughout the Empire, in Britain no less than the American colonies. For the metropolitan public, however, the American Revolution was a very different war from the one experienced ...
The Stamp Act crisis. 1. Focusing on the British government and the problems it faced in 1764, explained why its ministers considered introducing a stamp tax in colonial America. 2. Explain the purpose of a colonial stamp tax, how it would be implemented and which people or groups it would affect. 3.
American Revolution Essay: American Revolution is also known as United States War of Independence. This American Revolutionary War started in 1775 and ended in the year 1783 and was between Great Britain and North America. In this revolutionary war, Great Britain's 13 of North American colonies were given political independence. Local militiamen clashed with the […]
The following pages contain informative but concise summaries of key American Revolution topics. All pages have been written by Alpha History authors. If you would like to suggest a topic article, please contact Alpha History. We are currently reviewing, rewriting and expanding these pages through January-February 2024. Thank you for your patience.