IEEE Account
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address

Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- PubMed/Medline
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Mimo antennas: design approaches, techniques and applications.

1. Introduction
2. mimo antenna design approaches, 2.1. envelope correlation coefficient (ecc), 2.2. diversity gain (dg), 2.3. channel capacity loss (ccl), 2.4. mean effective gain (meg), 2.5. total active reflection coefficient (tarc), 3. ultra-wideband (uwb) mimo antenna designs, 4. dual-band mimo antenna designs, 5. circularly polarized mimo antenna design approaches, 6. mimo antennas in indoor environment, 7. mimo characteristics for 6g technology, 8. conclusions, author contributions, institutional review board statement, informed consent statement, data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
- Tao, J.; Feng, Q. Compact ultra-wideband MIMO antenna with half-slot structure. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016 , 16 , 792–795. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Xu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wen, S.; Wang, H. Vertically polarized quasi-Yagi MIMO antenna for 5G N78 band application. IEEE Access 2021 , 9 , 7836–7844. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sakli, H.; Abdelhamid, C.; Essid, C.; Sakli, N. Metamaterial-based antenna performance enhancement for MIMO system applications. IEEE Access 2021 , 9 , 38546–38556. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Garg, P.; Jain, P. Isolation improvement of MIMO antenna using a novel flower shaped metamaterial absorber at 5.5GHz WiMAX band. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2020 , 67 , 675–679. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Cai, Y.; Zheng, S.; Yin, Y. A meta-surface antenna array decoupling (MAAD) method for mutual coupling reduction in a MIMO antenna system. Sci. Rep. 2018 , 8 , 3152–3159. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Xue, C.D.; Zhang, X.Y.; Cao, Y.F.; Hou, Z.; Ding, C.F. MIMO antenna using hybrid electric and magnetic coupling for isolation enhancement. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017 , 65 , 5162–5170. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yang, C.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Wee, J.; Kim, B.; Jung, C. Quad-band antenna with high isolation MIMO and broadband SCS for broadcasting and telecommunication services. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2010 , 9 , 584–587. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Roy, B. Investigations on an extremely compact MIMO antenna with enhanced isolation and bandwidth. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020 , 62 , 845–851. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Larsson, E.G.; Edfors, O.; Tufvesson, F.; Marzetta, T.L. Massive MIMO for next generation wireless systems. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014 , 52 , 186–195. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Pei, T.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, W. A low-profile decoupling structure for mutual coupling suppression in MIMO patch antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021 , 69 , 6145–6153. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tiwari, R.N.; Singh, P.; Kumar, P.; Kanaujia, B.K. High isolation 4-port UWB MIMO antenna with novel decoupling structure for high speed and 5G communication. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications (ICEAA), Cape Town, South Africa, 5–9 September 2022; pp. 336–339. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ghalib, A.; Sharawi, M.S. TCM analysis of defected ground structures for MIMO antenna designs in mobile terminals. IEEE Access 2017 , 5 , 19680–19692. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pan, B.C.; Cui, T.J. Broadband decoupling network for dual-band microstrip patch antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017 , 65 , 5595–5598. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Khalid, M.; Iffat Naqvi, S.; Hussain, N.; Rahman, M.; Mirjavadi, S.S.; Khan, M.J.; Amin, Y. 4-port MIMO antenna with defected ground structure for 5G millimeter wave applications. Electronics 2020 , 9 , 71. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Niu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhong, T. Isolation enhancement for 1 × 3 closely spaced E-plane patch antenna array using defect ground structure and metal-vias. IEEE Access 2019 , 7 , 119375–119383. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Federal Communications Commission. First Report and Order Revision of Part 15 of the Commission’s Rules Regarding Ultra-Wideband Transmission Systems FCC 02-48 ; Federal Communications Commission: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Wong, K.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, W.Y. Decoupled compact ultra-wideband MIMO antennas covering 3300~6000 MHz for the fifth-generation mobile and 5GHz-WLAN operations in the future smartphone. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2018 , 60 , 2345–2351. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jehangir, S.S.; Sharawi, M.S. A miniaturized UWB biplanar Yagi-like MIMO antenna system. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017 , 16 , 2320–2323. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chen, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Yin, Y. A dual-feed MIMO antenna pair with one shared radiator and two isolated ports for fifth generation mobile communication band. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Aided Eng. 2017 , 27 , e21146. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, L.; Cai, Y.M. A MIMO antenna decoupling network composed of inverters and coupled split ring resonators. Prog. Electromagnet. Res. C 2017 , 79 , 175–183. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Pandit, S.; Mohan, A.; Ray, P. A compact four-element MIMO antenna for WLAN applications. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2018 , 60 , 289–295. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tiwari, R.N.; Singh, P.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Srivastava, K. Neutralization technique based two and four port high isolation MIMO antennas for UWB communication. Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEU) 2019 , 110 , 152828. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tang, X.; Yao, Z.; Li, Y.; Zong, W.; Liu, G.; Shan, F. A high performance UWB MIMO antenna with defected ground structure and U-shape branches. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Aided Eng. 2020 , 31 , e22270. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tiwari, R.N.; Singh, P.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Kumar, P. UWB MIMO antenna with decoupling strip for 5G applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium (ACES), Hamilton, ON, Canada, 1–5 August 2021; pp. 1–4. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Katie, M.O.; Jamlos, M.F.; Alqadami, A.S.M.; Jamlos, M.A. Isolation enhancement of compact dual-wideband MIMO antenna using Flag-shaped stub. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2017 , 59 , 1028–1032. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tiwari, R.N.; Singh, P.; Kanaujia, B.K. A compact UWB MIMO antenna with neutralization line for WLAN/ISM/mobile applications. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Aided Eng. 2019 , 29 , e21907. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, E.; Wang, W.; Tan, X.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y. A UWB slot antenna using defected ground structure for high isolation. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Aided Eng. 2020 , 30 , e22155. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tebache, S.; Belouchrani, A.; Ghanem, F.; Mansoul, A. Novel reliable and practical decoupling mechanism for strongly coupled antenna array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019 , 67 , 5892–5899. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Barani, I.R.R.; Wong, K.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, W.Y. Low-profile wideband conjoined open-slot antennas fed by grounded coplanar waveguides for 4 × 4 5G MIMO operation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020 , 68 , 2646–2657. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Saadh, A.W.M.; Ramaswamy, P.; Ali, T. A CPW fed two and four element antenna with reduced mutual coupling between the antenna elements for wireless applications. Appl. Phys. A 2021 , 127 , 88. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ali, W.A.E.; Ibrahim, A.A. A compact double-sided MIMO antenna with an improved isolation for UWB applications. Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEU) 2017 , 82 , 7–13. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Roshna, T.K.; Deepak, U.; Mohananl, P. Compact UWB MIMO antenna for tridirectional pattern diversity characteristics. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2017 , 11 , 2059–2065. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mendez, J.A.T.; Aguilar, H.J.; Merino, A.R.; Toledo, L.A.V.; Villanueva, R.G. Four ports wideband drop-shaped slot antenna for MIMO applications. J. Electromagnet. Waves Applicat. 2020 , 34 , 1159–1179. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ahmed, B.T.; Rodriguez, I.F. Compact high isolation UWB MIMO antennas. Wirel. Netw. 2022 , 28 , 1977–1999. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, L.; Du, Z.; Yang, H.; Ma, R.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, X.; Xi, X. Compact UWB MIMO antenna with high isolation using fence-type decoupling structure. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019 , 18 , 1641–1645. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, M.; Nan, J.; Liu, J. High-isolation UWB MIMO antenna with multiple X-shaped stubs loaded between ground planes. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2021 , 2021 , 1155471. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Addepalli, T.; Anitha, V.R. A very compact and closely spaced circular shaped UWB MIMO antenna with improved isolation. Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEU) 2020 , 114 , 153016. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sharma, M.; Dhasarathan, V.; Patel, S.K.; Nguyen, T.K. An ultra-compact four-port 4 × 4 superwideband MIMO antenna including mitigation of dual notched bands characteristics designed for wireless network applications. Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEU) 2020 , 123 , 153332. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sharma, A.; Sarkar, A.; Biswas, A.; Akhtar, M.J. A-shaped wideband dielectric resonator antenna for wireless communication systems and its MIMO implementation. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Eng. 2018 , 28 , e21402. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sharma, A.; Biswas, A. Wideband multiple-input-multiple-output dielectric resonator antenna. IET Microw. Antenna Propag. 2017 , 11 , 496–502. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gotra, S.; Varshney, G.; Pandey, V.S.; Yaduvanshi, R.S. Super-wideband multi-input-multi-output dielectric resonator antenna. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2020 , 14 , 21–27. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tiwari, R.N.; Singh, P.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, S.K. A low profile dual band MIMO antenna for LTE/Bluetooth /Wi-Fi/WLAN applications. J. Electromagnet. Wave Applicat. 2020 , 34 , 1239–1253. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Liu, P.; Sun, D.; Wang, P.; Gao, P. Design of a dual-band MIMO antenna with high isolation for WLAN applications. Prog. Electromagnet. Res. Lett. 2018 , 74 , 23–30. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Nirmal, P.C.; Nandgaonkar, A.; Nalbalwar, S.; Gupta, R.K. A compact dual-band MIMO antenna with improved isolation for WI-MAX and WLAN applications. Prog. Electromagnet. Res. M 2018 , 68 , 69–77. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ren, J.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Dual-band planar MIMO antenna for WLAN application. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2015 , 57 , 2257–2262. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wu, Y.T.; Chu, Q.X. Dual-band multiple input multiple output antenna with slitted ground. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2014 , 8 , 1007–1013. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Islam, S.K.N.; Das, S. Dual-band CPW fed MIMO antenna with polarization diversity and improved gain. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Aided Eng. 2020 , 30 , e22128. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tiwari, R.N.; Singh, P.; Panday, S.; Anand, R.; Singh, D.K.; Kanaujia, B.K. Swastika shaped slot embedded two port dual frequency band MIMO antenna for wireless applications. Analog Integra. Circuits Signal Process. 2021 , 109 , 103–113. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sharma, P.; Tiwari, R.N.; Singh, P.; Kanaujia, B.K. Dual-band trident shaped MIMO antenna with novel ground plane for 5G applications. Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEU) 2022 , 155 , 154364. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Luo, X.; Yuan, J.; Chen, K. Compact and low profile MIMO antenna for dual-WLAN-band access points. Prog. Electromagnet. Res. Lett. 2017 , 67 , 97–102. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Deng, J.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Zhao, L.; Guo, L.X. A dual-band inverted-F MIMO antenna with enhanced isolation for WLAN applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017 , 16 , 2270–2273. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yang, R.; Xi, S.; Cai, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, G. A compact planar dual-band multiple-input and multiple-output antenna with high isolation for 5G and 4G applications. Micromachines 2021 , 12 , 544. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhao, N.; Tian, W.P. CPW-fed dual-band MIMO antenna with common radiating element. Prog. Electromagnet. Res. Lett. 2016 , 62 , 71–75. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yang, M.; Zhou, J. A compact pattern diversity MIMO antenna with enhanced bandwidth and high-isolation characteristics for WLAN/5G/WiFi applications. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020 , 62 , 2353–2364. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sarkar, D.; Srivastava, K.V. Compact four-element SRR-loaded dual-band MIMO antenna for WLAN/WiMAX/WiFi/4G-LTE and 5G applications. Electron. Lett. 2017 , 53 , 1623–1624. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ding, K.; Gao, C.; Qu, D.; Yin, Q. Compact broadband MIMO antenna with parasitic strip. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017 , 16 , 2349–2353. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tiwari, R.N.; Singh, P.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Kumar, P. Dual band 4-port MIMO antenna for Bluetooth/5G applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (APS/URSI), Singapore, 4–10 December 2021; pp. 1941–1942. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shen, X.; Liu, F.; Zhao, L.; Huang, G.L.; Shi, X.; Huang, Q.; Chen, A. Decoupling of two strongly coupled dual-band antennas with reactively loaded dummy element array. IEEE Access 2019 , 7 , 154672–154682. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kumar, A.; Ansari, A.Q.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Kishor, J. A novel ITI-shaped isolation structure placed between two-port CPW-fed dual-band MIMO antenna for high isolation. Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEU) 2019 , 104 , 35–43. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Desai, A.; Upadhyaya, T.; Palandoken, M.; Gocen, C. Dual band transparent antenna for wireless MIMO system applications. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2019 , 61 , 1845–1856. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Peng, H.; Zhi, R.; Yang, Q.; Cai, J.; Wan, Y.; Liu, G. Design of a MIMO antenna with high gain and enhanced isolation for WLAN applications. Electronics 2021 , 10 , 1659. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Maturi, T.; Harikrishna, B. Electronic band-gap integrated low mutual coupling dual band MIMO antenna. Int. J. Electron. 2020 , 107 , 1166–1176. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Abdulkawi, W.M.; Malik, W.A.; Rehman, S.U.; Aziz, A.; Sheta, A.F.A.; Alkanhal, M.A. Design of a compact dual-band MIMO antenna system with high-diversity gain performance in both frequency bands. Micromachines 2021 , 12 , 383. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y. Isolation enhancement in dual band monopole antenna for 5G applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp Briefs 2021 , 68 , 1867–1871. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Soltani, S.; Lotfi, P.; Murch, R.D. A dual-band multiport MIMO slot antenna for WLAN applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016 , 16 , 529–532. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Nandi, S.; Mohan, A. A compact dual-band MIMO slot antenna for WLAN applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017 , 16 , 2457–2460. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Khan, A.A.; Jamaluddin, M.H.; Aqeel, S.; Nasir, J.; Kazim, J.U.R.; Owais, O. Dual-band MIMO dielectric resonator antenna for WiMAX/WLAN applications. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2017 , 11 , 113–120. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kumar, A.; Agrawal, T. High performance circularly polarized MIMO antenna with polarization independent metamaterial. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021 , 16 , 3205–3216. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Malviya, L.; Panigrahi, R.K.; Kartikeyan, M.V. Circularly polarized 2 × 2 MIMO antenna for WLAN applications. Prog. Electromagnet. Res. C 2016 , 66 , 97–107. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Hussine, U.U.; Huang, Y.; Song, C. A new circularly polarized antenna for GNSS applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 11th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), Paris, France, 19–24 March 2017; pp. 1954–1956. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tiwari, R.N.; Singh, P.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Kumar, P. Compact circularly polarized MIMO printed antenna with novel ground structure for wideband applications. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Aided Eng. 2021 , 31 , e22737. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jaiswal, R.K.; Kumari, K.; Sim, C.Y.D.; Srivastava, K.V. Three-port circularly polarized MIMO antenna for WLAN application with pattern and polarization diversity. Microw Opt. Technol. Lett. 2021 , 63 , 1927–1934. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tran, H.H.; Hussain, H.; Le, T.T. Low-profile wideband circularly polarized MIMO antenna with polarization diversity for WLAN applications. Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEU) 2019 , 108 , 172–180. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chen, H.N.; Song, J.M.; Park, J.D. A compact circularly polarized MIMO dielectric resonator antenna over electromagnetic band-gap surface for 5G applications. IEEE Access 2019 , 7 , 140889–140898. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sahu, N.K.; Das, G.; Gangwar, R.K. Dual polarized triple-band dielectric resonator based hybrid MIMO antenna for WLAN/WiMAX applications. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2018 , 60 , 1033–1041. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dicandia, F.A.; Genovesi, S.; Monorchio, A. Analysis of the performance enhancement of MIMO systems employing circular polarization. IEEE Trans. Antenna Propag. 2017 , 65 , 4824–4835. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sahu, N.K.; Das, G.; Gangwar, R.K. L-shaped dielectric resonator based circularly polarized multi-input-multi-output (MIMO) antenna for wireless local area network (WLAN) applications. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Aided Eng. 2018 , 28 , e21426. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Iqbal, J.; Illahi, U.; Sulaiman, M.I.; Alam, M.M.; Suud, M.M.; Yasin, M.N.M. Mutual coupling reduction using hybrid technique in wideband circularly polarized MIMO antenna for WiMAX applications. IEEE Access 2019 , 7 , 40951–40958. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Varshney, G.; Singh, R.; Pandey, V.S.; Yaduvanshi, R.S. Circularly polarized two-port MIMO dielectric resonator antenna. Prog. Electromagnet. Res. M 2020 , 91 , 19–28. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Varshney, G.; Gotra, S.; Chaturvedi, S.; Pandey, V.S.; Yaduvanshi, R.S. Compact four-port MIMO dielectric resonator antenna with pattern diversity. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2019 , 13 , 2193–2198. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Das, G.; Sharma, A.; Gangwar, R.K. Dielectric resonator based circularly polarized MIMO antenna with polarization diversity. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2018 , 60 , 685–693. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Khan, I.; Wu, Q.; Ullah, I.; Rahman, S.U.; Ullah, H.; Zhang, K. Designed circularly polarized two-port microstrip MIMO antenna for WLAN applications. Appl. Sci. 2022 , 12 , 1068. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bhadade, R.S.; Mahajan, S.P. Circularly polarized 4 × 4 MIMO antenna for WLAN applications. Electromagnetics 2019 , 39 , 325–342. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kumar, S.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, H.C.; Kim, K.W. Dual circularly polarized planar four-port MIMO antenna with wide axial-ratio bandwidth. Sensors 2020 , 20 , 5610. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jamal, M.Y.; Li, M.; Yeung, K.L. Isolation enhancement of closely packed dual circularly polarized MIMO antenna using hybrid technique. IEEE Access 2020 , 8 , 11241–11247. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dwivedi, A.K.; Sharma, A.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, V. Design of dual band four port circularly polarized MIMO DRA for WLAN/WiMAX applications. J. Electromagnet. Waves Applicat. 2020 , 34 , 1990–2009. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dwivedi, A.K.; Sharma, A.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, V. Circularly polarized two port MIMO cylindrical DRA for 5G applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on UK-China Emerging Technologies (UCET), Glasgow, UK, 20–21 August 2020; pp. 1–4. [ Google Scholar ]
- Thi, P.K.; Tran, H.H.; Le, T.T. Circularly polarized MIMO antenna utilizing parasitic elements for simultaneous improvements in isolation, bandwidth and gain. Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEU) 2021 , 135 , 153727. [ Google Scholar ]
- Adam, I.; Yasin, M.N.M.; Ramli, N.; Jusoh, M.; Rahim, H.A.; Latef, T.B.A.; Izam, T.F.T.M.N.; Sabapathy, T. Mutual coupling reduction of a wideband circularly polarized microstrip MIMO antenna. IEEE Access 2019 , 7 , 97838–97845. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dwivedi, A.K.; Sharma, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Singh, V. Two port circularly polarized MIMO antenna design and investigation for 5G communication systems. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021 , 120 , 2085–2099. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Iqbal, A.; Smida, A.; Alazemi, A.J.; Waly, M.I.; Mallat, N.K.; Kim, S. Wideband circularly polarized MIMO antenna for high data wearable biotelemetric devices. IEEE Access 2020 , 8 , 17935–17944. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Cho, S.; Hong, I. Reduction of wireless signals in indoor environments by using an active frequency selective wall based on spectrum sensing. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2017 , 30 , e3370. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yin, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, T.; Min, X. A novel compact dual-band frequency selective surface for GSM shielding by utilizing a 2.5-dimensional structure. IEEE Trans. Electromag. Compat. 2018 , 60 , 2057–2060. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Rodriguez, J.V.; Gustafsson, M.; Pardo, J.M.M.G.; Llacer, L.J.; Rodriguez, I.R. Frequency-selective wallpaper for indoor interference reduction and MIMO capacity improvement. Symmetry 2020 , 12 , 695. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yoo, I.; Smith, D.R. Dynamic metasurface antennas for higher-order MIMO systems in indoor environments. IEEE Wirel. Communica. Lett. 2020 , 9 , 1129–1132. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Alsabah, M.; Naser, M.A.; Mahmmod, B.M.; Abdulhussain, S.H.; Eissa, M.R.; Baidhani, A.A.; Noordin, N.K.; Sait, S.M.; Utaibi, K.A.A.; Hashim, F. 6G Wireless communications networks: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access 2021 , 9 , 148191–148243. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mahmood, N.H.; Alves, H.; López, O.A.; Shehab, M.; Osorio, D.P.M.; Aho, M.L. Six key features of machine type communication in 6G. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd 6G Wireless Summit (6G SUMMIT), Levi, Finland, 17–20 March 2020; pp. 1–5. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen, R.; Liu, M.; Hui, Y.; Cheng, N.; Li, J. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for 6G IoT wireless positioning: A contemporary survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022 , 1–13. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Oh, J. Large-aperture metamaterial lens antenna for multi-layer MIMO transmission for 6G. IEEE Access 2022 , 10 , 20486–20495. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dicandia, F.A.; Fonseca, N.J.G.; Bacco, M.; Mugnaini, S.; Genovesi, S. Space-air-ground integrated 6G wireless communication networks: A review of antenna technologies and application scenarios. Sensors 2022 , 22 , 3136. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
Click here to enlarge figure
| Ref. | MIMO Element | Antenna Size (mm ) | Antenna Frequency Band (GHz) | Bandwidth Improvement Technique | Isolation (dB) with Decoupling Techniques | Gain (dBi) | Efficiency (%) | ECC | CCL (bits/s/Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [ ] | 4 × 4 | 48 × 34 × 1.6 | 3.52–10.08 | Modified rectangular patch | ≤−23 Neutralization line | 0.95–2.91 | 70.01–79.87 | ≤0.039 | ≤0.29 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 25 × 36 × 1.6 | 2.78–17.43 | Corner-truncated rhombus-shaped (CTRS) | <−19 Rectangular strip connected with GP | - | - | <0.008 | <0.31 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 36 × 22 × 1.6 | 2.5–2.85/4.82–6.1 | Square radiating patch | <−18 Flag-shaped stub connected with middle GP | 9.992 | - | <0.05 | - |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 21 × 34 × 1.6 | 3.52–9.89 | Dome-shaped patch | ≤−22 Neutralization line | 3.08–5.12 | >62 | ≤0.005 | <0.26 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 30 × 50 × 1 | 3–10.9 | F-shaped radiators with L-shaped open-slots | ≤−20 Fork-shaped slots | 1.9–38 | - | <0.06 | - |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 22 × 43.5 × 1 | 2.45 | L-shaped radiating patch | <−40 Tapered slot | 1.9 | 81.7 | 0.06 | - |
| [ ] | 4 × 4 | 42 × 42 × 1 | 3.3–4.2 | Four conjoined slots | <−10 Circular slot | - | 47–64 | <0.06 | - |
| [ ] | 4 × 4 | 45 × 45 × 1.6 | 4.3–6.45 | Split-shaped radiating patch | <−20 Decoupling structure | 4.0–5.0 | 90 | <0.2 | <0.018 |
| [ ] | 4 × 4 | 40 × 40 × 1.6 | 3.1–11 | Circular patch | <−20 Decoupling structure | 3.28 (avg. gain) | - | <0.004 | <0.4 |
| [ ] | 3 × 3 | 45 × 25 × 1.588 | 3.1–11.5 | Staircase-shaped radiators | ≤−19 Spatial diversity | 5.5 (peak gain) | 61–98 | ≤ 0.2 | - |
| [ ] | 4 × 4 | 110 × 110 × 1.45 | 1.7–7.2 | Kraus technique | <−20 Electro-magnetic walls | 3.0–5.2 | 90 | 0.0025 | - |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 29.5 × 60 × 1.6 | 3.05–20 | L-like stubs | <−20 Metallic barriers | 3.36–4.92 | 83 | <0.00012 | 0.325 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 50 × 35 × 1 | 3.0–11 | L-shaped parasitic branches | <−25 Fence-type decoupling structure | above 3 dB | >80 | <0.004 | - |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 18 × 28 × 1.6 | 1.9–14 | Three crossed X-shaped stubs | <−15.5 X-shaped stubs in ground planes | 0.4–4.8 | - | <0.09 | <0.4 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 16 × 26 × 1.6 | 2.82–14.45 | Circular radiator | <−22 Stubs and protruded strip | 0.7–6.86 | ≥91.7 | <0.08 | - |
| Ref. No. | MIMO Element | Antenna Size (mm ) | Antenna Frequency Band (GHz) | Technique to Achieve Dual-band | Isolation (dB) with Decoupling TECHNIQUES | Gain (dBi) | Efficiency (%) | ECC | CCL (bits/s/Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 20 × 34 × 16 | 2.11–4.19/4.98–6.81 | Embedding a pair of comb-shaped slots in the GP | <−21 T-stub with comb-shaped slots | 2.75–4.19 | >70 | <0.004 | <0.32 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 46 × 30 × 1.6 | 1.85–3.63/5.07–7.96 | Swastika-shaped slot in the rectangular patch | <−17.21 T-shaped narrow conducting strip in GP | 1.14–4.12/1.42–4.78 | 71.21–92.69/70.55–90.99 | <0.003 | <0.35 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 62 × 25.6 × 1.524 | 2.99–3.61/4.53–4.92 | Arrow-shaped strip in between the U-shaped patch | <−16 Defected ground with L-shaped slot with strip | 2.96–3.14/3.69–3.84 | 72.68–80.24 | <0.002 | <0.32 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 69 × 34 × 4.2 | 2.375–2.52/4.98–5.88 | Inverted F-shaped | <−18 Slots on GP | 2.66/5.18 | - | <0.01 | - |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 52 × 77.5 × 1.6 | 2.4–2.48/5.15–5.825 | Horizontal U-strip | <−15 Inverted T-slot and meander line resonancebranch | - | - | <0.2 | - |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 32 × 32 × 1.59 | 2.36–2.59/3.17–3.77 | T-shaped strip and rectangular strip | <−15 Rectangular microstrip stub with defected GP | 5.8 (peak gain) | 76 | <0.02 | - |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 30 × 30 × 1.6 | 3.32–3.74/5.45–6.05 | Trapezoidal-shaped patch | <−20 T-shaped branch | <1.5/3.5 (peak gain both band) | - | - | - |
| [ ] | 4 × 4 | 30 × 30 × 0.8 | 4.58–6.12 | Rectangular patch | <−15.4 Swastika- shaped decoupling strip | 4.02 | 67–82 | <0.15 | - |
| [ ] | 4 × 4 | 40 × 40 × 1.6 | 2.93/5.68 | L-shaped with split ring resonator | <−14 SRR | 4 | 83.48–89.55 | <0.05 | <0.5 |
| [ ] | 4 × 4 | 85 × 85 × 0.8 | 2.32–2.95 | Metal strip | <−14 Parasitic element | 5.5 | 83 −90 | <0.008 | - |
| [ ] | 4 × 4 | 38 × 38 × 1.6 | 2.38–2.45/2.96–4.01 | Two asymmetric U-shaped slots in the radiating patch | ≤−18 Four metallic strips in the GP | - | - | <0.008 | <0.35 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 70 × 70 × 0.8 | 2.4~2.5/5.6~5.8 | Width of branches | <−25 Loadeddummy elements | - | Not given value | Not given value | - |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 72 × 56 × 0.8 | 2.24–2.90/3.9–7.55 | Rectangle split-ring-resonator | <−24 ITI-shaped structure | 2.5–5.6 | - | <0.04 | <0.4 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 105 × 105 × 1.83 | 2.23–2.46/3.22–4.04 | Slotted interconnected ring resonator | <−12 | 3.6/7.1 (peak gain) | 74–84 | 0.002 | - |
| [ ] | 1 × 2 | 51 × 29.6 × 1.6 | 2.4/5.2 | Slotted rectangular patch | <−25 EBG structure | 2.2/3.8 (peak gain) | - | 0.07 | - |
| [ ] | 4 × 4 | 58 × 60 × 1.6 | 1.55–2.65/3.35–3.65 | Two opposite slots in the radiating elements | <−10 Orthogonal plus-shaped partial ground | 2.2/3.8 | - | <0.08 | <0.4 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 38.6 × 56.4 × 1.524 | 3.5/4.85 | L-shaped branches | <−29 DGS and ground branches | 2.45/4.56 | - | <0.005 | - |
| Ref. | MIMO Element | Antenna Size (mm ) | Frequency Band (GHz) | 3-dB AR Bandwidth (GHz) | CP Technique | Gain (dBi) | Isolation (dB) | ECC | CCL bits/s/Hz |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 24 × 24 × 1.6 | 3.04–8.11 | 4.42–6.11 | Asymmetric Z-shaped patch with stub loaded defected GP | 0.28–2.76 | <−16 | <0.004 | <0.32 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 56 × 32 × 3 | 5.10–5.85 | 5.10–5.85 | Truncated corner patch with defected periodic GP | 5.8 | ≤−20 | - | - |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 95 × 49.7 × 1.6 | 3.15–3.93 | 3.3–3.8 | Cross ring slot with DRA truncation | 4.83 | <−26 | < 0.03 | <0.10 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 50 × 70 × 1.6 | 2.21–3.13/3.40–3.92/5.30–6.10 | 5.62–5.86 | Dual strips along with single slot in the GP | 4.1 | <−28 | <0.15 | <0.23 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 40 × 65 × 1.6 | 5.16–6.30 | 5.20–5.58 | L-shaped DRA | 4.011 | 22.284 | <0.112 | <0.338 |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 350 × 350 × 26.1 | 3.50–4.95 | 3.58–4.40 | Rectangular DRA with parasitic patch | 6.2 | <−28 | <0.04 | - |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 22.5 × 50 × 1.6 | 5.2–6.4 | 5.37–5.72 | Square slot cut in the corner of the GP | 6 (Peak gain) | <−20 | 0.001 | - |
| [ ] | 4 × 4 | 70 × 68 × 1.6 | 4–13 | 4.2–8.5 | Cross-shaped structure on ground | 6.4 (Peak gain) | ≤−18 | <0.25 | - |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 150 × 100 × 0.8 | 2.47–2.55 | 2.50–2.66 | Offset feeding | 6.1 (Peak gain) | ≤−20 | 0.003 | - |
| [ ] | 4 × 4 | 80 × 80 × 11.6 | 3.35–3.82/5.09–5.41 | 3.54–3.72/5.04–5.16 | Z-shaped slots | 5.0–6.8 | <−18 | <0.04 | - |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | 80 × 40 × 1.6 | 2.9–3.2/3.44–3.64/4.75–5.5 | 3.32–3.58/ 5.0–5.32 | Z-shaped slots in the GP | 2 | ≤−15 | <0.2 | - |
| [ ] | 2 × 2 | - | 4.75–5.9 | 5.1–5.8 | Parasitic elements | 7.5–8.2 | ≤−22 | - | - |
| MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
Share and Cite
Sharma, P.; Tiwari, R.N.; Singh, P.; Kumar, P.; Kanaujia, B.K. MIMO Antennas: Design Approaches, Techniques and Applications. Sensors 2022 , 22 , 7813. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207813
Sharma P, Tiwari RN, Singh P, Kumar P, Kanaujia BK. MIMO Antennas: Design Approaches, Techniques and Applications. Sensors . 2022; 22(20):7813. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207813
Sharma, Preeti, Rakesh N. Tiwari, Prabhakar Singh, Pradeep Kumar, and Binod K. Kanaujia. 2022. "MIMO Antennas: Design Approaches, Techniques and Applications" Sensors 22, no. 20: 7813. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207813
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals
Challenges and Endeavors of Radiated Radio Frequency Tests for 5G Radios
Share this page:
Submission Deadline: 31 January 2021
IEEE Access invites manuscript submissions in the area of Challenges and Endeavors of Radiated Radio Frequency Tests for 5G Radios.
By now, we have entered the fifth generation (5G) era with intensive research and development (R&D) of various 5G applications from both industry and academia. The 5G systems promise higher spectral efficiency/energy efficiency, lower latency, and more reliable communications. These advantages are supported by millimeter wave (mmWave) and/or massive multiple-input multiple-output (M-MIMO) techniques.
Cable conducted testing has been the dominant testing method for sub-6 GHz conventional communication systems, where antenna ports are mostly accessible for conducted testing. In the conducted testing, antenna characteristics are omitted completely by testing from antenna ports. However, for M-MIMO antenna systems with hundreds of antenna elements, conducted testing obviously becomes infeasible. Moreover, it is likely that mmWave systems will not have standard antenna ports, rendering over-the-air (OTA) the only testing solution. However, many challenges for OTA testing of 5G devices arise, e.g., the lack of antenna connectors especially at frequency region (FR) 2, the high number of antenna connectors at RF1 for base stations; the complicated and expensive system resource requirement for testing electrically large 5G devices; the time-consuming array diagnosis and calibration for M-MIMO and millimeter-wave systems; the large measurement range requirement in the test system to meet the far field assumption; the link budget issue at FR2, etc. Besides conventional antenna and radio frequency (RF) testing, it is necessary as well to test both mmWave and M-MIMO systems with appropriate channel models due to the fact that the use of beamforming and spatial filtering is sensitive to time-variant radio channel conditions.
In addition, the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) problems of 5G systems become very serious due to the existence of complicated circuits and numerous wireless components. In practice, the EMC test needs to not only evaluate the radiated/conducted emission/susceptibility, but also identify the key sources of EMC failures. Due to the complexity of 5G systems, the identification of EMC failure source is especially challenging. Therefore, new testing solutions and post-processing techniques are needed to address the challenges of 5G EMC tests, also accounting for coexistence with existing fixed and mobile installations.
The objective of this Special Section is to address the challenges in OTA/EMC tests for 5G Technologies. The topics of interest include, but are not limited to:
- Anechoic chamber based testing methods for 5G applications
- Reverberation chambers based testing methods for 5G applications
- M-MIMO antenna array diagnosis and calibration
- Millimeter-wave antenna array diagnosis and calibration
- Numerical modeling and simulation methods for M-MIMO systems and 5G applications
- OTA testing of 5G base stations and terminals
- EMC tests of 5G devices and coexisting issues
- Virtual drive testing
- Performance evaluation of communication systems in critical propagation scenarios
- Progress in standardization of 5G metrology
- Developments 5G channel model, radio channel emulator, and other testbeds for performance testing
- OTA methods of fading emulation for demodulation and radio resource management (RRM) testing
- OTA methods for RF performance testing
- Uncertainty analyses for OTA/EMC tests
We also highly recommend the submission of multimedia with each article as it significantly increases the visibility and downloads of articles.
Associate Editor: Wei Fan, Aalborg University, Denmark Huapeng Zhao, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, China
Guest Editors:
- Xiaoming Chen, Xi’an Jiao tong University, China
- Su Yan, Howard University, USA
- Pekka Kyösti, Keysight technologies and Oulu University, Finland
- Jukka-Pekka Nuutinen, Spirent Technologies, USA
- Valter Mariani Primiani, Università Politecnica delle Marche – Ancona, Italy
Relevant IEEE Access Special Sections:
Antenna and Propagation for 5G and Beyond
5g and beyond mobile wireless communications enabling intelligent mobility, millimeter-wave and terahertz propagation, channel modeling and applications.
IEEE Access Editor-in-Chief: Prof. Derek Abbott, University of Adelaide
Article submission: Contact Associate Editor and submit manuscript to: http://ieee.atyponrex.com/journal/ieee-access
For inquiries regarding this Special Section, please contact: [email protected] .
Body Area Networks
Submission Deadline: 30 July 2020
IEEE Access invites manuscript submissions in the area of body area networks, wireless sensors networks, medical ICT, intelligent health management, and big data analysis.
Wearable communications and personal health management are the future trends of the healthcare industry. To make this happen, new technologies are required to provide trustable measurement and communication mechanisms, from the data source to medical health databases. Wireless body area networks (WBAN) are the focus of this Special Section, not just on-body devices, but also technologies providing information from inside the body. Dependable communications combined with accurate localization and behavior analysis will benefit WBAN technology and make healthcare processes more effective.
The topics of interest include, but are not limited to:
- Wearable computing
- Embedded devices and medical applications
- In-, on- and off-body communications & networking
- Antennas and propagation
- Security and privacy of health data communications
- Smart BAN for social inclusion
- Socio-economic aspects of health caring
- Medical device regulation
- Human bond communications
- Remote patient management and preventive care
- Radio coexistence and interference management
- Rehabilitation and activity monitoring
- Wellness and sport applications of body area networks
- ICT solutions for health and wellness education
- Molecular communications
- WBANs supporting cognitive impairments
We also highly recommend the submission of multimedia with each article as it significantly increases the visibility, downloads, and citations of articles.
Associate Editor: Lorenzo Mucchi, University of Florence, Italy
- Matti Hämäläinen, University of Oulu, Finland
- Massimiliano Pierobon, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, USA
- Diep Nguyen, University of Technology Sydney, Australia
- Hirokazu Tanaka, Hiroshima Hiroshima City University, Dept. of Biomedical Information Sciences
- Wearable and Implantable Devices and Systems
- Molecular Communication Networks
- Advances of Multisensory Services and Technologies for Healthcare in Smart Cities
For inquiries regarding this Special Section, please contact: [email protected] .
Energy Harvesting Technologies for Wearable and Implantable Devices
Submission Deadline: 31 December 2020
IEEE Access invites manuscript submissions in the area of Energy Harvesting Technologies for Wearable and Implantable Devices.
Implantable and wearable electronic devices can improve the quality of life as well as the life expectancy of many chronically ill patients, provided that certain biological signs can be accurately monitored. Thanks to advances in packaging and nanofabrication, it is now possible to embed various microelectronic and micromechanical sensors (such as gyroscopes, accelerometers and image sensors) into a small area on a flexible substrate and at a relatively low cost. Furthermore, these devices have been integrated with wireless communication technologies to enable the transmission of both signals and energy. However, to ensure that these devices can truly improve a patient’s quality of life, new preventative, diagnostic and therapeutic devices that can provide hassle-free, long-term, continuous monitoring will need to be developed, which must rely on novel energy harvesting solutions that are non-obstructive to their wearer. So far, research in the field has focussed on materials, new processing techniques and one-off devices. However, existing progress is not sufficient for future electronic devices to be useful in any new application and a great demand exists towards scaling up the research towards circuits and systems. A few interesting developments in this direction indicate that special attention should be given towards the design, simulation and modeling of energy harvesting techniques while keeping system integration and power management in mind.
- Novel piezoelectric, thermoelectric and photovoltaic energy harvesting technologies that lead to enhanced efficiency and controllability under standard or varying working conditions
- Novel control strategies for achieving maximum or optimum energy harvesting
- Power management circuits for energy harvesters
- Novel data driven techniques for optimizing and forecasting the amount of energy that can be harvested
- Low-Power circuits and sensors
- Flexible sensors, circuits and energy harvesters for wearables
- Implantable electronics
- Novel wireless power transfer and delivery techniques
- Numerical and computational modeling techniques
Associate Editor: Hadi Heidari, University of Glasgow, UK
- Mehmet Ozturk, North Carolina State University, USA
- Rami Ghannam,University of Glasgow, UK
- Law Man Kay, University of Macau, China
- Hamideh Khanbareh, University of Bath, UK
- Abdul Halim Miah, University of Florida, USA
- Smart Health Sensing and Computational Intelligence: From Big Data to Big Impacts
- Neural Engineering Informatics
For inquiries regarding this Special Section, please contact: [email protected] .
Submission Deadline: 31 December 2019
IEEE Access invites manuscript submissions in the area of Antenna and Propagation for 5G and Beyond.
5G is not just the next evolution of 4G technology; it’s a paradigm shift. “5G and Beyond” will enable bandwidth in excess of 100s of Mb/s with latency of less than 1 ms, in addition to providing connectivity to billions of devices. The verticals of 5G and beyond are not limited to smart transportation, industrial IoT, eHealth, smart cities, and entertainment services; transforming the way humanity lives, works, and engages with its environment.
“5G and beyond” is an enormous opportunity but the widespread deployment of 5G still faces many challenges, including reliable connectivity, a wide range of bands to support ranging from the 600 MHz UHF band to the mm-wave 60 GHz V-band, dynamic spectrum sharing, channel modeling and wave propagation for ultra-dense wireless networks, as well as price pressures. Besides other required features, the choice of an antenna system will be a critical component of all the node end devices. Choosing the right antenna for an application presents a key design challenge. Creating effective antenna performance requires engineers to examine several factors including antenna size, from what is needed to what is possible, antenna shape, and placement. As consumer electronic modules continue to shrink, incorporating more wireless technologies, making space for antennas is becoming an increasingly significant challenge. Thus, the antenna designers face the restrictions of maintaining reasonable performance in ever-shrinking footprints and under extreme interference conditions. Since high frequency bands are expected to be used in 5G, the propagation characteristics such as propagation loss and multipath characteristics must be evaluated for mm Wave frequencies and beyond. Therefore, new radio propagation modeling and prediction techniques need to be developed to cover the new frequency bands for future 5G wireless systems.
The explosive growth of 5G creates many scientific and engineering challenges that call for ingenious research efforts from both academia and industry. This Special Section in IEEE Access brings together scholars, professors, researchers, engineers, and administrators to find new approaches for exploiting challenging propagation channels and the development of efficient, cost-effective, scalable, and reliable antenna systems/solutions. Further, this Special Section will allow researchers to identify new opportunities for this exciting field.
- Massive MIMO Antenna Systems: design and applications
- Distributed Massive MIMO
- Smart Reconfigurable Antenna Design and Systems
- Antenna and propagation for smart wearables IoT
- Base Station and Terminal Antennas
- Antennas for Machine to Machine (M2M) Connection
- mm Wave Antennas
- Antennas for Terahertz applications
- Antennas for Driverless Cars
- Phased Array Antennas
- Antenna Beamforming
- Channel enhancement techniques
- Propagation modeling for 5G
- Channel modeling and wave propagation for smart cities
- Electromagnetic wave attenuation and RF signal propagation in smart cities
Associate Editor: Muhammad Ali Imran, University of Glasgow, UK
- Asimina Kiourti, The Ohio State University, USA
- Hassan Tariq Chattha, Islamic University of Madinah, Saudi Arabia
- Yejun He, Shenzhen University, China
- Akram Alomainy, Queen Mary University of London, UK
- Raheel M. Hashmi, Macquarie University, NSW, Australia
- Muhammad Zulfiker Alam, Queens University, Kingston, Canada
- Qammer H. Abbasi, University of Glasgow, UK
Advances in Statistical Channel Modeling for Future Wireless Communications Networks
For inquiries regarding this Special Section, please contact: [email protected] ; [email protected] .
Submission Deadline: 30 September 2019
IEEE Access invites manuscript submissions in the area of 5G and Beyond Mobile Wireless Communications Enabling Intelligent Mobility.
Increasing urbanization is one major trend that shapes tomorrow’s society; by 2050 more than 85% of the developed world’s population will live in a comparatively small number of ever-growing cities. Within such cities and their commuter belts, reliable high-rate wireless communication will not only be required for (quasi-) static users, but also for hosts of people moving in public and private transportation networks. Yet, wireless connectivity is not restricted to people; frictionless functioning of such a society in motion is supported by Intelligent Mobility where each connected transportation vehicle (car, train, bus, ship, aircraft, motorcycle, bicycle) is expected to be a smart object equipped with a powerful multi-sensor platform, communication capability, computing units, and Internet protocol (IP)-based connectivity, such as to be highly efficient in various vehicular and transportation applications. This vision requires a more pervasive and ubiquitous communications and networking core, which will not be only driven by the existing research on 5G, but also enabled by future mobile wireless communications which employ new concepts, such as data analytics, artificial intelligence, machine learning, cloud-computing, etc. Therefore, this Special Section in IEEE Access focuses on various theoretical and experimental views on researching and developing the required technological enhancements of 5G and beyond mobile wireless communications to efficiently support the vision of intelligent mobility, providing mobility as a service and enabling dependable Internet services.
- Propagation and channel measurement and modeling for connected cars, trains, ships, and aircrafts, especially at new frequency bands
- Integrated space-air-vehicle-ground networks
- Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into new wireless systems solutions and applications for intelligent mobility
- Data analytics for intelligent transportation systems
- Cloud- and edge based high-performance computing techniques for mobile networks
- MIMO and Massive MIMO for intelligent transportation systems
- Radio technologies for high mobility transportation systems
- Physical layer techniques for connected vehicles, public transportation control and signaling
- Wireless technologies for automated and connected vehicles
- Millimeter wave, sub-millimeter wave, and THz communications enabling intelligent mobility
- Heterogeneous networks and distributed antenna systems
- Novel physical layer waveforms and modulation schemes
Associate Editor: Ke Guan, Beijing Jiaotong University, China
- Markus Rupp, Vienna University of Technology, Austria
- Thomas Kürner, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Germany
- Cesar Briso, Polytechnic University of Madrid, Spain
- David W. Matolak, University of South Carolina, USA
- Jun-ichi Takada, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan
- Wei Wang, Chang’an University, China
- Network Resource Management in Flying Ad Hoc Networks: Challenges, Potentials, Future Applications, and Wayforward
Paper submission: Contact Associate Editor and submit manuscript to: http://ieee.atyponrex.com/journal/ieee-access
For inquiries regarding this Special Section, please contact: [email protected] .
Submission Deadline: 30 June 2019
IEEE Access invites manuscript submissions in the area of Advances in Statistical Channel Modeling for Future Wireless Communications Networks.
Wireless communication technology, including both radio and optical frequencies, has become an important aspect of modern life. The accurate depiction of wireless signals is paramount. Statistical channel modeling is of great importance, as accurate characterization of the propagation channel is essential for different applications like system design and performance analysis.
Recently, various types of new wireless communication systems have emerged, such as device-to-device, millimeter wave, and massive multiple-input multiple output (MIMO) systems. However, traditional and well-established fading models, such as Rayleigh, Rician, and Nakagami- m , may not accurately model the random fluctuations of the received signal. There is a strong, credible body of evidence, suggesting that the complex electromagnetic propagation phenomena involved in new wireless communications should be taken into account by general and unifying, physically based channel models. Researchers have been making great efforts to propose appropriate channel models and readers of IEEE Access have keen interest in the research advances in this fundamental and important area.
- Backscatter communications
- Collocated, distributed and cell-free massive MIMO communications
- Millimeter wave communications
- Device-to-device communications
- Satellite communications
- UAV communications
- Underwater and marine communications
- Vehicular communications
- Visible light/free-space optical communications
- High-speed mobility scenarios
- Wireless body area networks
- Internet of Things in smart factories
- Physical layer security of wireless communications
Associate Editor: Daniel Benevides da Costa, Federal University of Ceará, Brazil
- Jiayi Zhang, Beijing Jiaotong University, China
- George K. Karagiannidis, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece
- Kostas P. Peppas, University of Peloponnese, Greece
- Michail Matthaiou, Queen’s University of Belfast, UK
- Octavia A. Dobre, Memorial University, Canada
- Big Data Analytics in Internet-of-Things And Cyber-Physical System
- Optical Wireless Technologies for 5G Communications and Beyond
- Modelling, Analysis, and Design of 5G Ultra-Dense Networks
IEEE Access Editor-in-Chief: Michael Pecht, Professor and Director, CALCE, University of Maryland
For inquiries regarding this Special Section, please contact: [email protected]
Submission Deadline: 31 October 2019
IEEE Access invites manuscript submissions in the area of Millimeter-wave and Terahertz Propagation, Channel Modeling and Applications.
The demand for ever-increasing wireless data-transmission rates and throughput area-densities is common to several wireless services and application areas, from ultra-dense cellular networks to internet access, wireless networks on-chip, back-hauling, device-to-device communications and sensing techniques. This need is fostering the exploration of new spectrum in the millimeter-wave (30 to 300 GHz) and Terahertz (0.1 to 10 THz) bands and the study of techniques for multi-Gigabit transmission based on very high-gain antennas or using massive antenna arrays (massive-MIMO, i.e. massive Multiple Input Multiple Output systems).
Besides the greater spectrum availability, mm-wave and THz communications can benefit from the small wavelength, which allows for the design of compact, massive antenna arrays with very narrow beams and therefore of powerful beamforming techniques (pencil-beamforming) that yield optimum spectrum spatial re-use and consistently high signal to interference ratio.
Beamforming is likely to be of great interest for far-field Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) techniques, recently proposed to energize small, battery-less devices and sensors and foster the development of the Internet of Things (IoT). For example, small, low-cost passive tags could be attached to products in a warehouse and high gain mm-wave beam-scanning antenna arrays could be used to localize them and at the same time to acquire sensing information about them. Furthermore, the use of multiple bands in the mm-wave and Terahertz frequency ranges will allow the implementation of very high-accuracy sensing and localization techniques. This will enable a variety of applications, with special regard to security enforcing and vehicular systems, such as the detection and/or localization of drones or the accurate localization of vehicles in urban environment using multi-static cooperative radar techniques for safety and traffic control.
To fully exploit the potential of mm-wave and THz spectrum a deep understanding of the propagation channel will be required, including aspects such as materials’ electromagnetic properties, blockage and scattering due to people, vehicles, drones, as well as multidimensional, multi-frequency channel characterization. Moreover, multi-disciplinary studies on link components such as antennas, devices, pointing systems, etc., will be necessary, especially for the development of reliable THz communications systems.
The goal of this Special Section in IEEE Access is to provide insight into the peculiar characteristics of electromagnetic propagation at millimeter wave and THz frequencies, to investigate and compare different channel modeling approaches, application scenarios, system architectures, information and power transmission techniques as well as novel localization and sensing solutions that the use of such frequency bands will foster.
The topics of interests include, but are not limited to:
- Millimeter and Terahertz Wave Propagation
- Millimeter and Sub-Millimeter Wave Measurements
- Scattering and Blockage from Humans and Objects
- Diffuse Scattering Modeling
- Ray Tracing Propagation Modeling
- Empirical / Statistical Propagation Modeling
- Material Characterization at mm-wave and THz Frequencies
- Mm-wave and THz Channel Modeling
- Vehicular Communications
- Railway Communications
- Air-to-Ground Communications
- 5G and Beyond Mobile Communications
- Radar Techniques for Safety and Traffic Control
- Mm-wave and THz Remote Sensing and Imaging Techniques
- High Accuracy Localization Techniques
- Localization and Mapping Techniques
- Inter- and Intra-chip Wireless Networks
- Device-to-Device and Rack-to-Rack Communications
- Gigabit and Terabit Wireless Links for Back-Hauling and High-Speed Access
- Mm-wave and Terahertz Transmission Techniques and System Architectures
- Massive MIMO Communications Techniques
- Analog and Digital Beamforming Techniques
- Multi-user Beamforming and Space Division techniques
- Internet of Things
- Mm-wave RFID techniques
- Far-field Wireless Power Transmission
- Wireless Power Focusing techniques and Frequency Diverse Arrays
- Mm-wave and THz Antennas, Rectennas and Devices
- Submillimeter Wave Technology
Associate Editor: Vittorio Degli-Esposti and Franco Fuschini, University of Bologna, Italy
- Henry L. Bertoni, NYU School of Engineering, New York, USA
- Reiner Thomä, Technische Hochschule Ilmenau, Germany
- Xuefeng Yin, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
- Ke Guan, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China
- Roadmap to 5G: Rising to the Challenge
- Multi-Function RF Components for Current and Future 5G Wireless Communications
- Modelling, Analysis, and Design of 5G Ultra-Dense Networks
For inquiries regarding this Special Section, please contact: : [email protected] , [email protected]
Wireless Body Area Networks
Submission Deadline: 31 March 2019
IEEE Access invites manuscript submissions in the area of Wireless Body Area Networks.
This Special Section collects extended versions of the best-ranked papers presented in Bodynets 2018 Conference in Oulu, Finland. In addition, other researchers are encouraged to submit their recent research work for possible publication in the Special Section.
Wearable devices and wireless communications combined with a personalized health management are the future trends of healthcare practices and procedures. To make this progress happen, new technologies and methods are required to provide reliable measuring, end-to-end communications and data analysis mechanisms from the data source to medical health records. Wireless body area networks (WBAN) are one major element in this process. Not limited to only on-body WBAN devices but also benefiting technologies which can distribute vital information inside a human body, or allow control of implantable devices are also the main focus of this Special Section. Dependable wireless communications combined with versatile application areas, such as accurate localization or behavior analysis techniques, remote monitoring, adoption of vital sensors and actuators, etc. can benefit the increased use of new WBAN technologies in various healthcare related studies. Eventually, this will make the healthcare processes more effective and user friendly, and simultaneously increase the safety of (out)patients.
This Special Section in IEEE Access focuses on various theoretical and experimental views on the WBAN applications, technologies, implementations and utilizations based on the extended versions of the best-evaluated papers from Bodynets 2018. Articles should be extended versions of the 2018 Bodynets Conference articles since only 35% overlap is allowed. Original and new research articles are also welcome.
- In-, on- and off-body communications and networking
- Embedded devices
- Medical applications
- WBAN radio channel modeling
- WBAN antennas
- Security aspects of WBAN or security for medical ICT
- Experimentations of WBAN technologies and services
- Utilization of WBAN in general
Associate Editor: Matti Hämäläinen, University of Oulu, Finland.
- Daizuke Anzai, Nagoya Institute of Technology, Japan
- Giancarlo Fortino, University of Calabria, Italy
- Jari Iinatti, University of Oulu, Finland
- Lorenzo Mucchi, University of Florence, Italy
- Carlos Pomalaza-Raez, Purdue University, USA
- Advanced Information Sensing and Learning Technologies for Data-centric Smart Health Applications
- Trends, Perspectives and Prospects of Machine Learning Applied to Biomedical Systems in Internet of Medical Things
For inquiries regarding this Special Section, please contact: [email protected]
Wirelessly Powered Networks: Algorithms, Applications and Technologies
Submission Deadline: 31 October 2018
IEEE Access invites manuscript submissions in the area of Wirelessly Powered Networks: Algorithms, Applications and Technologies.
Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) is, by definition, a process that occurs in any system where electrical energy is transmitted from a power source to a load without the connection of electrical conductors. WPT is the driving technology that will enable the next stage in the current consumer electronics revolution, including battery-less sensors, passive RF identification (RFID), passive wireless sensors, the Internet of Things and 5G, and machine-to-machine solutions. WPT-enabled devices can be powered by harvesting energy from the surroundings, including electromagnetic (EM) energy, leading to a new communication networks paradigm, the Wirelessly Powered Networks.
While recent advances in wireless utensils appear to be unlimited, the dependence of their operation on batteries remains a weakness, mainly because batteries come with a limited lifetime and require a fast charge time to achieve continuous operation. This is where the technologies of WPT become useful, bringing together wireless energy and data transmission. WPT technologies substitute the traditional powering concept, where a cable or a battery is connected to the wireless device, by the transmission of energy over the air in an efficient way to power-up the device.
Wirelessly Powered Networks have recently evolved into a very active research field, as well as a topic of rapid technological progress, emerging practical developments and standardization activities. However, a solid foundational, technological, and applied background is still necessary for Wirelessly Powered Networks to achieve their full potential. The provisioning of relevant technological models, algorithmic design and analysis methods, networking principles, circuit and system design, and application methodologies is a challenging task. This Special Section in IEEE Access invites academic and industrial experts to make their contributions on Wirelessly Powered Networks. It will selectively span a coherent, large spectrum of fundamental aspects of WPT, and will focus on three main thematic pillars and relevant themes: Algorithms, Applications and Technologies.
- Optimization and approximation algorithms (mobility/energy/data management)
- Joint operation scheduling (routing, data gathering, ambient harvesting)
- Precise algorithmic models and efficient distributed protocols
- WPT devices deployment
- Safety provisioning through EM radiation control algorithms
- Peer-to-peer and crowd charging algorithms
- Algorithms for simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT)
Applications
- Medical implants and wearable devices
- Automotive technology and electric vehicles
- Mobile communications, wireless sensor networks and UAVs
- Spacecraft engineering
- Home/Industrial appliances
- Standardization, regulations and biological effects
- Solutions for SWIPT
Technologies
- RF energy harvesting, rectennas and rectenna arrays
- High-frequency rectifying circuits, power transmitters and devices
- Near-field (inductive, resonant) energy transfer
- Microwave transmission and beaming
- Novel materials, fabrication techniques
- Energy storage elements, RFID-related electronics and self-powered sensors
- Measurement and characterization approaches for WPT components
Associate Editor: Theofanis P. Raptis, National Research Council, Italy
- Nuno Borges Carvalho, University of Aveiro, Portugal
- Diego Masotti, University of Bologna, Italy
- Lei Shu, Nanjing Agricultural University, China / University of Lincoln, UK
- Cong Wang, Old Dominion University, USA
- Yuanyuan Yang, Stony Brook University, USA
- Energy Efficient Wireless Communications with Energy Harvesting and Wireless Power Transfer
- Exploiting the Benefits of Interference in Wireless Networks: Energy Harvesting and Security
- Energy Harvesting and Scavenging: Technologies, Algorithms, and Communication Protocols
For inquiries regarding this Special Section, please contact: [email protected]
Multi-Function RF Components for Current and Future 5G Wireless Communications
Submission Deadline: 31 May 2018
IEEE Access invites manuscript submissions in the area of Multi-Function RF Components for Current and Future 5G Wireless Communications.
With the increasing demand of wireless connection, wireless communication including 5G is continuously and rapidly growing. Modern wireless communication systems, such as 5G, bring great challenges on radio frequency (RF) sub-systems, which should support multiple RF chains operating at different frequency bands and for various modes. In the 5G RF sub-systems, massive multi-input multi-output (MIMO) antennas are the key technology for the success of 5G in which there are tens or even hundreds of RF chains. In these cases, a large number of transceivers and other components must co-exist within a limited volume. The power consumption and size of RF components are problematic issues, which play an important role in the overall behavior of wireless systems. To solve this problem, extensive work has been done, focusing on the reduction of power consumption and size of various RF components. Although great advances have recently been made, current techniques are still lacking in successful implementations of compact and low-power RF sub-systems fulfilling the increasing demand. It is therefore urgent to develop new techniques which can support the requirements of multiple RF chains in current and future 5G wireless systems.
Fortunately, the technique of co-designing multiple RF operational functionalities to realize multi-function components has exhibited the potential to achieve compact size and low power consumption. Further progress in this area will be made by studying the theory and techniques of multi-component co-design so that the resulting multi-function RF devices outperform the classic cascades of multiple mono-function components.
The objective of this Special Section in IEEE Access is to identify and discuss technical challenges and recent results related to multi-function RF components for current and future wireless communication system with emphasis on 5G. For this Special Section, we seek prospective authors to submit their high-quality original and unpublished contributions, surveys, and case studies on this research area.
- Co-design of antennas and filters
- Antennas with integrated power combining capability
- Power amplifiers with integrated filtering responses
- Filtering power dividers/couplers
- Filtering matching networks/transformers
- Filtering phase shifters
- Filtering with differential-mode operation.
- Rectennas with integrated design of antenna and rectifier
- Multi-function reconfigurable filters (simultaneous bandpass, bandstop, all-pass and/or all-reject response)
- Novel analysis method for multi-function RF components
We also highly recommend the submission of multimedia with each article as it significantly increases the visibility, downloads, and citations of articles.
Associate Editor: Xiu Yin Zhang, South China University of Technology, China
- Roberto Gómez-García , University of Alcala, Spain
- Guoan Wang, University of South Carolina, USA
- Yi Wang, University of Greenwich, UK
- Tunable devices for modern communications: materials, integration, modeling, and applications
- Recent Advances on Radio Access and Security Methods in 5G Networks
For inquiries regarding this Special Section, please contact: [email protected]
At a Glance
- Journal: IEEE Access
- Format: Open Access
- Frequency: Continuous
- Submission to Publication: 4-6 weeks (typical)
- Topics: All topics in IEEE
- Average Acceptance Rate: 27%
- Impact Factor: 3.4
- Model: Binary Peer Review
- Article Processing Charge: US $1,995
Featured Articles
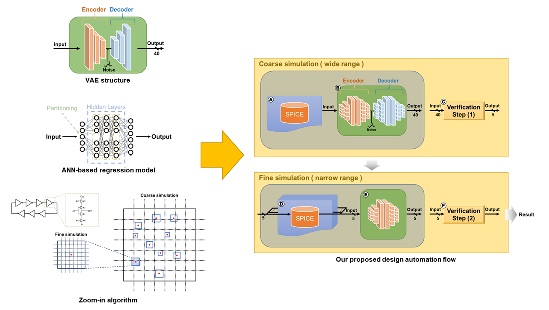
AMS Circuit Design Optimization Technique Based on ANN Regression Model With VAE Structure
View in IEEE Xplore
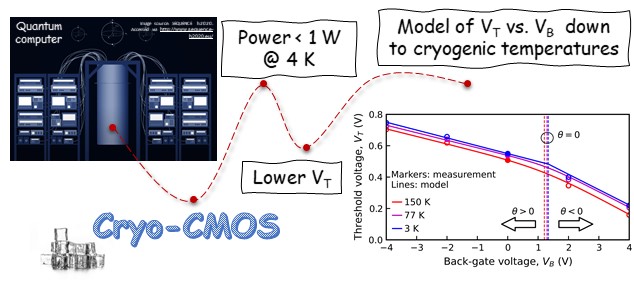
Novel Approach to FDSOI Threshold Voltage Model Validated at Cryogenic Temperatures
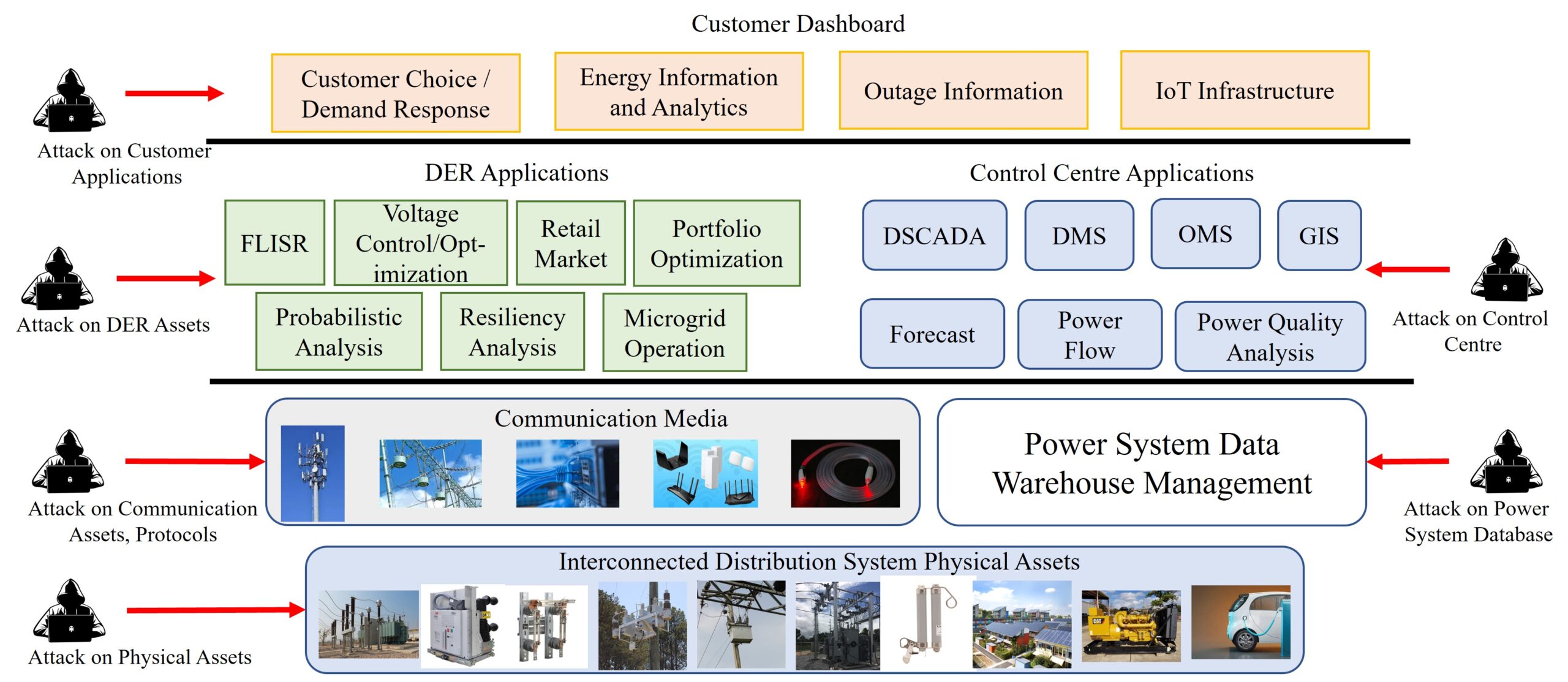
On the Cyber-Physical Needs of DER-Based Voltage Control/Optimization Algorithms in Active Distribution Network
Submission guidelines.
© 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this website signifies your agreement to the IEEE TERMS AND CONDITIONS.
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world’s largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity.
AWARD RULES:
NO PURCHASE NECESSARY TO ENTER OR WIN. A PURCHASE WILL NOT INCREASE YOUR CHANCES OF WINNING.
These rules apply to the “2024 IEEE Access Best Video Award Part 1″ (the “Award”).
- Sponsor: The Sponsor of the Award is The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Incorporated (“IEEE”) on behalf of IEEE Access , 445 Hoes Lane, Piscataway, NJ 08854-4141 USA (“Sponsor”).
- Eligibility: Award is open to residents of the United States of America and other countries, where permitted by local law, who are the age of eighteen (18) and older. Employees of Sponsor, its agents, affiliates and their immediate families are not eligible to enter Award. The Award is subject to all applicable state, local, federal and national laws and regulations. Entrants may be subject to rules imposed by their institution or employer relative to their participation in Awards and should check with their institution or employer for any relevant policies. Void in locations and countries where prohibited by law.
- Agreement to Official Rules : By participating in this Award, entrants agree to abide by the terms and conditions thereof as established by Sponsor. Sponsor reserves the right to alter any of these Official Rules at any time and for any reason. All decisions made by Sponsor concerning the Award including, but not limited to the cancellation of the Award, shall be final and at its sole discretion.
- How to Enter: This Award opens on January 1, 2024 at 12:00 AM ET and all entries must be received by 11:59 PM ET on June 30, 2024 (“Promotional Period”).
Entrant must submit a video with an article submission to IEEE Access . The video submission must clearly be relevant to the submitted manuscript. Only videos that accompany an article that is accepted for publication in IEEE Access will qualify. The video may be simulations, demonstrations, or interviews with other experts, for example. Your video file should not exceed 100 MB.
Entrants can enter the Award during Promotional Period through the following method:
- The IEEE Author Portal : Entrants can upload their video entries while submitting their article through the IEEE Author Portal submission site .
- Review and Complete the Terms and Conditions: After submitting your manuscript and video through the IEEE Author Portal, entrants should then review and sign the Terms and Conditions .
Entrants who have already submitted a manuscript to IEEE Access without a video can still submit a video for inclusion in this Award so long as the video is submitted within 7 days of the article submission date. The video can be submitted via email to the article administrator. All videos must undergo peer review and be accepted along with the article submission. Videos may not be submitted after an article has already been accepted for publication.
The criteria for an article to be accepted for publication in IEEE Access are:
- The article must be original writing that enhances the existing body of knowledge in the given subject area. Original review articles and surveys are acceptable even if new data/concepts are not presented.
- Results reported must not have been submitted or published elsewhere (although expanded versions of conference publications are eligible for submission).
- Experiments, statistics, and other analyses must be performed to a high technical standard and are described in sufficient detail.
- Conclusions must be presented in an appropriate fashion and are supported by the data.
- The article must be written in standard English with correct grammar.
- Appropriate references to related prior published works must be included.
- The article must fall within the scope of IEEE Access
- Must be in compliance with the IEEE PSPB Operations Manual.
- Completion of the required IEEE intellectual property documents for publication.
- At the discretion of the IEEE Access Editor-in-Chief.
- Disqualification: The following items will disqualify a video from being considered a valid submission:
- The video is not original work.
- A video that is not accompanied with an article submission.
- The article and/or video is rejected during the peer review process.
- The article and/or video topic does not fit into the scope of IEEE Access .
- The article and/or do not follow the criteria for publication in IEEE Access .
- Videos posted in a comment on IEEE Xplore .
- Content is off-topic, offensive, obscene, indecent, abusive or threatening to others.
- Infringes the copyright, trademark or other right of any third party.
- Uploads viruses or other contaminating or destructive features.
- Is in violation of any applicable laws or regulations.
- Is not in English.
- Is not provided within the designated submission time.
- Entrant does not agree and sign the Terms and Conditions document.
Entries must be original. Entries that copy other entries, or the intellectual property of anyone other than the Entrant, may be removed by Sponsor and the Entrant may be disqualified. Sponsor reserves the right to remove any entry and disqualify any Entrant if the entry is deemed, in Sponsor’s sole discretion, to be inappropriate.
- Entrant’s Warranty and Authorization to Sponsor: By entering the Award, entrants warrant and represent that the Award Entry has been created and submitted by the Entrant. Entrant certifies that they have the ability to use any image, text, video, or other intellectual property they may upload and that Entrant has obtained all necessary permissions. IEEE shall not indemnify Entrant for any infringement, violation of publicity rights, or other civil or criminal violations. Entrant agrees to hold IEEE harmless for all actions related to the submission of an Entry. Entrants further represent and warrant, if they reside outside of the United States of America, that their participation in this Award and acceptance of a prize will not violate their local laws.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Entrant grants Sponsor an irrevocable, worldwide, royalty free license to use, reproduce, distribute, and display the Entry for any lawful purpose in all media whether now known or hereinafter created. This may include, but is not limited to, the IEEE A ccess website, the IEEE Access YouTube channel, the IEEE Access IEEE TV channel, IEEE Access social media sites (LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, IEEE Access Collabratec Community), and the IEEE Access Xplore page. Facebook/Twitter/Microsite usernames will not be used in any promotional and advertising materials without the Entrants’ expressed approval.
- Number of Prizes Available, Prizes, Approximate Retail Value and Odds of winning Prizes: Two (2) promotional prizes of $350 USD Amazon gift cards. One (1) grand prize of a $500 USD Amazon gift card. Prizes will be distributed to the winners after the selection of winners is announced. Odds of winning a prize depend on the number of eligible entries received during the Promotional Period. Only the corresponding author of the submitted manuscript will receive the prize.
The grand prize winner may, at Sponsor’ discretion, have his/her article and video highlighted in media such as the IEEE Access Xplore page and the IEEE Access social media sites.
The prize(s) for the Award are being sponsored by IEEE. No cash in lieu of prize or substitution of prize permitted, except that Sponsor reserves the right to substitute a prize or prize component of equal or greater value in its sole discretion for any reason at time of award. Sponsor shall not be responsible for service obligations or warranty (if any) in relation to the prize(s). Prize may not be transferred prior to award. All other expenses associated with use of the prize, including, but not limited to local, state, or federal taxes on the Prize, are the sole responsibility of the winner. Winner(s) understand that delivery of a prize may be void where prohibited by law and agrees that Sponsor shall have no obligation to substitute an alternate prize when so prohibited. Amazon is not a sponsor or affiliated with this Award.
- Selection of Winners: Promotional prize winners will be selected based on entries received during the Promotional Period. The sponsor will utilize an Editorial Panel to vote on the best video submissions. Editorial Panel members are not eligible to participate in the Award. Entries will be ranked based on three (3) criteria:
- Presentation of Technical Content
- Quality of Video
Upon selecting a winner, the Sponsor will notify the winner via email. All potential winners will be notified via their email provided to the sponsor. Potential winners will have five (5) business days to respond after receiving initial prize notification or the prize may be forfeited and awarded to an alternate winner. Potential winners may be required to sign an affidavit of eligibility, a liability release, and a publicity release. If requested, these documents must be completed, signed, and returned within ten (10) business days from the date of issuance or the prize will be forfeited and may be awarded to an alternate winner. If prize or prize notification is returned as undeliverable or in the event of noncompliance with these Official Rules, prize will be forfeited and may be awarded to an alternate winner.
- General Prize Restrictions: No prize substitutions or transfer of prize permitted, except by the Sponsor. Import/Export taxes, VAT and country taxes on prizes are the sole responsibility of winners. Acceptance of a prize constitutes permission for the Sponsor and its designees to use winner’s name and likeness for advertising, promotional and other purposes in any and all media now and hereafter known without additional compensation unless prohibited by law. Winner acknowledges that neither Sponsor, Award Entities nor their directors, employees, or agents, have made nor are in any manner responsible or liable for any warranty, representation, or guarantee, express or implied, in fact or in law, relative to any prize, including but not limited to its quality, mechanical condition or fitness for a particular purpose. Any and all warranties and/or guarantees on a prize (if any) are subject to the respective manufacturers’ terms therefor, and winners agree to look solely to such manufacturers for any such warranty and/or guarantee.
11.Release, Publicity, and Privacy : By receipt of the Prize and/or, if requested, by signing an affidavit of eligibility and liability/publicity release, the Prize Winner consents to the use of his or her name, likeness, business name and address by Sponsor for advertising and promotional purposes, including but not limited to on Sponsor’s social media pages, without any additional compensation, except where prohibited. No entries will be returned. All entries become the property of Sponsor. The Prize Winner agrees to release and hold harmless Sponsor and its officers, directors, employees, affiliated companies, agents, successors and assigns from and against any claim or cause of action arising out of participation in the Award.
Sponsor assumes no responsibility for computer system, hardware, software or program malfunctions or other errors, failures, delayed computer transactions or network connections that are human or technical in nature, or for damaged, lost, late, illegible or misdirected entries; technical, hardware, software, electronic or telephone failures of any kind; lost or unavailable network connections; fraudulent, incomplete, garbled or delayed computer transmissions whether caused by Sponsor, the users, or by any of the equipment or programming associated with or utilized in this Award; or by any technical or human error that may occur in the processing of submissions or downloading, that may limit, delay or prevent an entrant’s ability to participate in the Award.
Sponsor reserves the right, in its sole discretion, to cancel or suspend this Award and award a prize from entries received up to the time of termination or suspension should virus, bugs or other causes beyond Sponsor’s control, unauthorized human intervention, malfunction, computer problems, phone line or network hardware or software malfunction, which, in the sole opinion of Sponsor, corrupt, compromise or materially affect the administration, fairness, security or proper play of the Award or proper submission of entries. Sponsor is not liable for any loss, injury or damage caused, whether directly or indirectly, in whole or in part, from downloading data or otherwise participating in this Award.
Representations and Warranties Regarding Entries: By submitting an Entry, you represent and warrant that your Entry does not and shall not comprise, contain, or describe, as determined in Sponsor’s sole discretion: (A) false statements or any misrepresentations of your affiliation with a person or entity; (B) personally identifying information about you or any other person; (C) statements or other content that is false, deceptive, misleading, scandalous, indecent, obscene, unlawful, defamatory, libelous, fraudulent, tortious, threatening, harassing, hateful, degrading, intimidating, or racially or ethnically offensive; (D) conduct that could be considered a criminal offense, could give rise to criminal or civil liability, or could violate any law; (E) any advertising, promotion or other solicitation, or any third party brand name or trademark; or (F) any virus, worm, Trojan horse, or other harmful code or component. By submitting an Entry, you represent and warrant that you own the full rights to the Entry and have obtained any and all necessary consents, permissions, approvals and licenses to submit the Entry and comply with all of these Official Rules, and that the submitted Entry is your sole original work, has not been previously published, released or distributed, and does not infringe any third-party rights or violate any laws or regulations.
12.Disputes: EACH ENTRANT AGREES THAT: (1) ANY AND ALL DISPUTES, CLAIMS, AND CAUSES OF ACTION ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THIS AWARD, OR ANY PRIZES AWARDED, SHALL BE RESOLVED INDIVIDUALLY, WITHOUT RESORTING TO ANY FORM OF CLASS ACTION, PURSUANT TO ARBITRATION CONDUCTED UNDER THE COMMERCIAL ARBITRATION RULES OF THE AMERICAN ARBITRATION ASSOCIATION THEN IN EFFECT, (2) ANY AND ALL CLAIMS, JUDGMENTS AND AWARDS SHALL BE LIMITED TO ACTUAL OUT-OF-POCKET COSTS INCURRED, INCLUDING COSTS ASSOCIATED WITH ENTERING THIS AWARD, BUT IN NO EVENT ATTORNEYS’ FEES; AND (3) UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES WILL ANY ENTRANT BE PERMITTED TO OBTAIN AWARDS FOR, AND ENTRANT HEREBY WAIVES ALL RIGHTS TO CLAIM, PUNITIVE, INCIDENTAL, AND CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, AND ANY OTHER DAMAGES, OTHER THAN FOR ACTUAL OUT-OF-POCKET EXPENSES, AND ANY AND ALL RIGHTS TO HAVE DAMAGES MULTIPLIED OR OTHERWISE INCREASED. ALL ISSUES AND QUESTIONS CONCERNING THE CONSTRUCTION, VALIDITY, INTERPRETATION AND ENFORCEABILITY OF THESE OFFICIAL RULES, OR THE RIGHTS AND OBLIGATIONS OF ENTRANT AND SPONSOR IN CONNECTION WITH THE AWARD, SHALL BE GOVERNED BY, AND CONSTRUED IN ACCORDANCE WITH, THE LAWS OF THE STATE OF NEW JERSEY, WITHOUT GIVING EFFECT TO ANY CHOICE OF LAW OR CONFLICT OF LAW, RULES OR PROVISIONS (WHETHER OF THE STATE OF NEW JERSEY OR ANY OTHER JURISDICTION) THAT WOULD CAUSE THE APPLICATION OF THE LAWS OF ANY JURISDICTION OTHER THAN THE STATE OF NEW JERSEY. SPONSOR IS NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY TYPOGRAPHICAL OR OTHER ERROR IN THE PRINTING OF THE OFFER OR ADMINISTRATION OF THE AWARD OR IN THE ANNOUNCEMENT OF THE PRIZES.
- Limitation of Liability: The Sponsor, Award Entities and their respective parents, affiliates, divisions, licensees, subsidiaries, and advertising and promotion agencies, and each of the foregoing entities’ respective employees, officers, directors, shareholders and agents (the “Released Parties”) are not responsible for incorrect or inaccurate transfer of entry information, human error, technical malfunction, lost/delayed data transmissions, omission, interruption, deletion, defect, line failures of any telephone network, computer equipment, software or any combination thereof, inability to access web sites, damage to a user’s computer system (hardware and/or software) due to participation in this Award or any other problem or error that may occur. By entering, participants agree to release and hold harmless the Released Parties from and against any and all claims, actions and/or liability for injuries, loss or damage of any kind arising from or in connection with participation in and/or liability for injuries, loss or damage of any kind, to person or property, arising from or in connection with participation in and/or entry into this Award, participation is any Award-related activity or use of any prize won. Entry materials that have been tampered with or altered are void. If for any reason this Award is not capable of running as planned, or if this Award or any website associated therewith (or any portion thereof) becomes corrupted or does not allow the proper playing of this Award and processing of entries per these rules, or if infection by computer virus, bugs, tampering, unauthorized intervention, affect the administration, security, fairness, integrity, or proper conduct of this Award, Sponsor reserves the right, at its sole discretion, to disqualify any individual implicated in such action, and/or to cancel, terminate, modify or suspend this Award or any portion thereof, or to amend these rules without notice. In the event of a dispute as to who submitted an online entry, the entry will be deemed submitted by the authorized account holder the email address submitted at the time of entry. “Authorized Account Holder” is defined as the person assigned to an email address by an Internet access provider, online service provider or other organization responsible for assigning email addresses for the domain associated with the email address in question. Any attempt by an entrant or any other individual to deliberately damage any web site or undermine the legitimate operation of the Award is a violation of criminal and civil laws and should such an attempt be made, the Sponsor reserves the right to seek damages and other remedies from any such person to the fullest extent permitted by law. This Award is governed by the laws of the State of New Jersey and all entrants hereby submit to the exclusive jurisdiction of federal or state courts located in the State of New Jersey for the resolution of all claims and disputes. Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, G+, YouTube, IEEE Xplore , and IEEE TV are not sponsors nor affiliated with this Award.
- Award Results and Official Rules: To obtain the identity of the prize winner and/or a copy of these Official Rules, send a self-addressed stamped envelope to Kimberly Rybczynski, IEEE, 445 Hoes Lane, Piscataway, NJ 08854-4141 USA.

Fully Open Access Topical Journals

A Growing Collection of Gold Fully Open Access (OA) Options
IEEE offers more options than ever to authors with the launch of new gold fully open access journals spanning a wide range of technologies. These journals are significant additions to IEEE’s well-known and respected portfolio of fully open access journals. In addition, many of the journals featured here target an accelerated publication time frame of 10 weeks for most accepted papers to help get your research exposed faster. Visit the publication home page of each title for details.
The fully open access journals are accepting submissions. Please see each journal’s description below for more details. All of the titles are fully compliant with funder mandates including Plan S. All IEEE Open Access titles, current and new, will be hosted on the IEEE Xplore ® platform.
Call for Papers
Submit a paper to an ieee fully open access journal.

IEEE Open Journal of Antennas and Propagation
High-quality, peer reviewed research covering antennas, including analysis, design, development, measurement, standards, and testing; radiation, propagation, and the interaction of electromagnetic waves with discrete and continuous media.
This fully open access journal publishes high-quality, peer reviewed papers covering antennas, including analysis, design, development, measurement, standards, and testing; radiation, propagation, and the interaction of electromagnetic waves with discrete and continuous media; and applications and systems pertinent to antennas, propagation, and sensing, such as applied optics, millimeter-and sub-millimeter-wave techniques, antenna signal processing and control, radio astronomy, and propagation and radiation aspects of terrestrial and space-based communication, including wireless, mobile, satellite, and telecommunications at all frequencies. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Konstantina (Nantia) Nikita Professor National Technical University of Athens, Greece
Learn More and Submit a Paper
IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing
Addresses the growing field of applications in Earth observations and remote sensing and provides a venue for the rapidly expanding special issues that are being sponsored by the IEEE Geosciences and Remote Sensing Society.
The IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing addresses the growing field of applications in Earth observations and remote sensing, and also provides a venue for the rapidly expanding special issues that are being sponsored by the IEEE Geosciences and Remote Sensing Society. The journal draws upon the experience of the highly successful “IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing” and provide a complementary medium for the wide range of topics in applied earth observations. Papers should address current issues and techniques in applied remote and in situ sensing, their integration, and applied modeling and information creation for understanding the Earth. Applications are for the Earth, oceans and atmosphere. Topics can include observations, derived information such as forecast data, simulated information, data assimilation and Earth information techniques to address science and engineering issues of the Earth system. The technical content of papers must be both new and significant.

IEEE Open Journal of Circuits and Systems
Featuring high-quality peer reviewed research covering the theory, analysis, design, tools, and implementation of circuits and systems.
This fully open access journal publishes high-quality, peer-reviewed papers covering the theory, analysis, design, tools, and implementation of circuits and systems. This includes their theoretical foundations, applications, and architectures, as well as circuits and systems implementation of algorithms for signal and information processing. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Gabriele Manganaro, Ph.D., FIEEE Technology Director Analog Devices, Inc., USA

IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society
Featuring high-quality peer reviewed research covering science, technology, applications and standards for information organization, collection and transfer using electronic, optical and wireless channels and networks.
As a fully open access journal publishing high-quality peer reviewed papers, IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society covers science, technology, applications and standards for information organization, collection and transfer using electronic, optical and wireless channels and networks, including but not limited to: Systems and network architecture, control and management; Protocols, software and middleware; Quality of service, reliability and security; Modulation, detection, coding, and signaling; Switching and routing; Mobile and portable communications; Terminals and other end-user devices; Networks for content distribution and distributed computing; and Communications-based distributed resources control. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Octavia A. Dobre, Dipl.-Ing., Ph.D. Professor and Research Chair Memorial University, Canada

IEEE Open Journal of the Computer Society
Forum for rapid publication of open access articles describing high-impact results in all aspects of theory, design, practice, and application relating to computer and information processing science and technology.
The IEEE Open Journal of the Computer Society (OJ-CS) is a rigorously peer-reviewed forum for rapid publication of open access articles describing high-impact results in all areas of interest to the IEEE Computer Society. This new fully open access journal complements existing IEEE Computer Society publications by providing a rapid review cycle and a thorough review of technical articles. It is dedicated to publishing articles on the latest emerging topics and trends in all aspects of computing with a scope that encompasses all aspects of theory, design, practice, and application relating to computer and information processing science and technology. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Dr. Song Guo Department of Computing The Hong Kong Polytechnic University

IEEE Open Journal of Control Systems
Publication of the IEEE Control Systems Society, this journal aims to publish high-quality papers on the theory, design, optimization, and applications of dynamic systems and control.
The IEEE Open Journal of Control Systems covers the theory, design, optimization, and applications of dynamic systems and control. The field integrates elements of sensing, communication, decision and actuation components, as relevant for the analysis, design and operation of dynamic systems and control. The systems considered include: technological, physical, biological, economic, organizational and other entities, and combinations thereof. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Sonia Martínez University of California, San Diego United States

IEEE Data Descriptions
Now Accepting Submissions! This new publication is a peer-reviewed journal that publishes short articles on all aspects of data: data descriptors, data collections, and metadata.
IEEE Data Descriptions is a peer-reviewed journal that publishes short articles on all aspects of data: data descriptors, data collections, and metadata. Its overarching purpose is to promote publicly available datasets (open access or subscription-based access) in support of reproducible science while at the same time bringing insights into the associated dataset, data collection methods, and data quality. The metadata collected provides enhanced dataset discoverability and creates a foundation for future data science tools such as auto-discovery and mashups.
Datasets described in IEEE Data Descriptions must be findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable. The dataset needs to be of a quality high enough that other researchers can use it for their research experimentation and have some permanence. Articles describing datasets must be comprehensive and follow the outlined sections listed in Author Information. The preference is for data to be stored within IEEE DataPort, however, IEEE Data Descriptions accepts submissions where data is stored at other persistent/permanent locations.
Editor-in-Chief: Stephen Makonin Simon Fraser University Vancouver, Canada

IEEE Journal of the Electron Devices Society
Featuring high quality research in the field of electron and ion devices ranging from fundamentals to applied research.
Featuring high-quality research in the field of electron and ion devices ranging from fundamentals to applied research, this journal provides authors an affordable outlet for rapid publishing and universal access, coupled with superior technical quality.

IEEE Open Journal of Engineering in Medicine and Biology
High-quality research covering the development and application of engineering concepts and methods to biology, medicine and health sciences.
As a fully open access journal publishing high-quality peer reviewed papers, IEEE Open Journal of Engineering in Medicine and Biology covers the development and application of engineering concepts and methods to biology, medicine and health sciences to provide effective solutions to biological, medical and healthcare problems. It encompasses the development of mathematical theories, physical, biological and chemical principles, computational models and algorithms, devices and systems for clinical, industrial and educational applications. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Paolo Bonato Associate Professor Harvard University, USA
IEEE Journal on Exploratory Solid-State Computational Devices and Circuits
Multi-disciplinary research in solid-state circuits using exploratory materials and devices for novel energy efficient computation beyond standard CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) technology.
Multi-disciplinary research in solid-state circuits using exploratory materials and devices for novel energy efficient computation beyond standard CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) technology. Focus is on the exploration of materials, devices and computation circuits to enable Moore’s Law to continue for computation beyond a 10 to 15 year horizon (beyond end of the roadmap for CMOS technologies) with the associated density scaling and improvement in energy efficiency.
IEEE Open Journal on Immersive Displays
Now Accepting Submissions! New publication will be home to publications in display science and applications.
The IEEE Open Journal on Immersive Displays (OJID) will be home to publications in display science and applications. The field of displays is diverse, ranging from the science and engineering of materials and devices to their application in high definition, form-factor-independent displays featuring interactivity, virtual and augmented reality, and 3D content. Submissions on advanced fabrication processing, thin film active and passive devices, and lifetime and reliability evaluation are welcome when display is the focus or where there is a direct relationship to the nature of the display system. Tutorial and review papers extending the frontiers of immersive display technologies and novel applications are also published.
Editor-in-Chief: Arokia Nathan University of Cambridge Hertfordshire, U.K.

IEEE Journal of Indoor and Seamless Positioning and Navigation
Publishes original research in the fields of localization and tracking of people, robots, and objects.
IEEE Journal of Indoor and Seamless Positioning and Navigation (J-ISPIN) publishes original research in the fields of localization and tracking of people, robots, and objects. It covers all aspects of localization systems, including sensing, communications, location-based services, mapping, protocols, human interfaces and standards. The scope includes methods and systems addressing indoor environments as well as those enabling seamless transition between heterogeneous indoor contexts or between indoor and outdoor environments, for example where Global Navigation Satellites Systems are underperforming or unavailable.
Editor-in-Chief: Valérie Renaudin Senior Researcher University Gustave Eiffel, France

IEEE Open Journal of the Industrial Electronics Society
Featuring high quality research covering the theory and applications of electronics, controls, communications, instrumentation and computational intelligence to industrial and manufacturing systems and processes.
This fully open access journal publishes high-quality, peer-reviewed papers covering the theory and applications of electronics, controls, communications, instrumentation and computational intelligence to industrial and manufacturing systems and processes. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Dr. Leopoldo Garcia Franquelo Professor, Electronics Engineering Universidad de Sevilla, Spain

IEEE Open Journal of Industry Applications
Covering the advancement of the theory and practice of electrical and electronic engineering in the development, design, manufacture and application of electrical systems, apparatus, devices, and controls to the processes and equipment of industry and commerce.
As a fully open access journal publishing high-quality peer reviewed papers, IEEE Open Journal of Industry Applications covers the advancement of the theory and practice of electrical and electronic engineering in the development, design, manufacture and application of electrical systems, apparatus, devices, and controls to the processes and equipment of industry and commerce; the promotion of safe, reliable, and economic installations; industry leadership in energy conservation and environmental, health, and safety issues; the creation of voluntary engineering standards and recommended practices; and the professional development of its readers. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Professor Pericle Zanchetta Fellow IEEE Faculty of Engineering University of Nottingham, UK

IEEE Open Journal of Instrumentation and Measurement
Publication of the Instrumentation and Measurement Society, this journal publishes papers on the science, technology, and application of instrumentation and measurement.
The IEEE Open Journal of Instrumentation and Measurement publishes papers on the science, technology, and application of instrumentation and measurement. Instrumentation and measurement, in the current context of the IEEE IMS community, consists of methods, instruments, systems, and applications for measurement, detection, tracking, monitoring, characterization, identification, sensing, estimation, recognition, or diagnosis of a physical phenomenon; or metrology and measurement theory including measurement uncertainty, instrument precision, calibration, etc.
Editor-in-Chief: Shervin Shirmohammadi University of Ottawa Canada
IEEE Open Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems
Featuring high-quality research covering the theoretical, experimental and operational aspects of electrical and electronics engineering and information technologies as applied to Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS).
As a fully open access journal publishing high-quality peer reviewed papers, IEEE Open Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems covers theoretical, experimental and operational aspects of electrical and electronics engineering and information technologies as applied to Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS), defined as those systems utilizing synergistic technologies and systems engineering concepts to develop and improve transportation systems of all kinds. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Dr. Bart van Arem Full Professor of Transport Modelling Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands

IEEE Transactions on Machine Learning in Communications and Networking
Featuring high-quality manuscripts on advances in machine learning methods for and applications to communications and networking.
The IEEE Transactions on Machine Learning in Communications and Networking publishes high-quality manuscripts on advances in machine learning methods for and applications to communications and networking. Furthermore, articles developing novel communication and networking techniques for distributed machine learning algorithms are of interest. Both theoretical contributions (including new theories, techniques, concepts, algorithms, and analyses) and practical contributions (including system experiments, prototypes, and new applications) are encouraged.
Editor-in-Chief: Walid Saad Professor Virginia Tech Research Center – Arlington, USA


IEEE Journal of Microwaves
Covering articles on the theory, techniques and applications of guided wave and wireless technologies and spanning the electromagnetic spectrum from RF/microwave through millimeter-waves and terahertz.
The IEEE Journal of Microwaves is a fully open access publication covering the complete scope of the Microwave Theory and Techniques Society which includes articles on the theory, techniques and applications of guided wave and wireless technologies and spanning the electromagnetic spectrum from RF/microwave through millimeter-waves and terahertz, covering the aspects of materials, components, devices, circuits, modules, and systems which involve the generation, modulation, demodulation, control, transmission, sensing and effects of electromagnetic signals.
Editor-in-Chief: Peter H. Siege THz Global, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology Pasadena, California

IEEE Open Journal of Nanotechnology
Featuring high-quality, peer reviewed research covering the theory, design, and development of nanotechnology and its scientific, engineering, and industrial applications.
As a fully open access journal publishing high-quality peer reviewed papers, IEEE Open Journal of Nanotechnology covers the theory, design, and development of nanotechnology and its scientific, engineering, and industrial applications. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Co-Editors-in-Chief: Professor Wen J. Li Chair Professor of Biomedical Engineering Associate Provost City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Professor Jin-Woo Kim Professor of Biological Engineering and Nanoscience & Engineering University of Arkansas, USA
Professor Seiji Samukawa Director of Innovative Energy Research Center, Institute of Fluid Science (IFS) Principal Investigator of Advance Institute for Materials Research (AIMR) Tohoku University, Japan

IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering
Covering the rehabilitative and neural aspects of biomedical engineering, including functional electrical stimulation, acoustic dynamics, human performance measurement, and more.
Rehabilitative and neural aspects of biomedical engineering, including functional electrical stimulation, acoustic dynamics, human performance measurement and analysis, nerve stimulation, electromyography, motor control and stimulation; and hardware and software applications for rehabilitation engineering and assistive devices.

IEEE Photonics Journal
Dedicated to the rapid disclosure of research at the forefront of all areas of photonics and addressing issues ranging from fundamental understanding to emerging technologies.
Breakthroughs in the generation of light and its control and utilization have given rise to the field of Photonics: a rapidly expanding area of science and technology with major technological and economic impact. IEEE Photonics Journal is an online-only journal dedicated to the rapid disclosure of top-quality peer-reviewed research at the forefront of all areas of photonics. Contributions addressing issues ranging from fundamental understanding to emerging technologies and applications are within the scope of the Journal.

IEEE Open Access Journal of Power and Energy
High-quality, peer reviewed research covering the development, planning, design, construction, maintenance, installation, and operation of equipment, structures, power systems and usage of electric energy, including its measurement and control.
As a fully open access journal publishing high-quality peer reviewed papers, the IEEE Open Access Journal of Power and Energy publishes articles focused on the development, planning, design, construction, maintenance, installation, and operation of equipment, structures, and power systems for the safe, sustainable, economic, and reliable conversion, generation, transmission, distribution, storage, and usage of electric energy, including its measurement and control. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Fangxing “Fran” Li The University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN 37996 USA [email protected]

IEEE Open Journal of Power Electronics
Covering the development and application of power electronic systems and technologies, which encompass the effective use of electronic components, the application of circuit theory and design techniques and the development of analytical methods and tools.
The IEEE Open Journal of Power Electronics covers the development and application of power electronic systems and technologies, which encompass the effective use of electronic components, the application of circuit theory and design techniques and the development of analytical methods and tools toward efficient electronic conversion, control and conditioning of electric power to enable the sustainable use of energy. As a fully open access journal publishing high-quality peer reviewed papers, the Society’s aim is to publish novel developments as well as tutorial and survey articles including those of value to both the R&D and practicing professionals in the field. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Alan Mantooth, Ph.D., P.E., FIEEE Distinguished Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas, USA

IEEE Transactions on Privacy
Now Accepting Submissions! New publication will provide a multidisciplinary forum for theoretical, methodological, engineering, and applications aspects of privacy and data protection, including specification, design, implementation, testing, and validation.
The IEEE Transactions on Privacy provides a multidisciplinary forum for theoretical, methodological, engineering, and applications aspects of privacy and data protection, including specification, design, implementation, testing, and validation. Privacy, in this context, is defined as the freedom from unauthorized intrusion in its broadest sense, arising from any activity in information collection, information processing, information dissemination or invasion. The transactions publishes articles reporting significant advances in theoretical models and formalization as well as engineering tools supporting the above activities, design frameworks and languages, architectures, infrastructures, model-based approaches, study cases, and standards.

IEEE Transactions on Quantum Engineering
Publishing regular, review, and tutorial articles based on the engineering applications of quantum phenomena, including quantum computation, information, communication, software, hardware, devices, and metrology.
Publishes regular, review, and tutorial articles based on the engineering applications of quantum phenomena, including quantum computation, information, communication, software, hardware, devices, and metrology. Articles also address quantum-engineering aspects of superconductivity, magnetics, microwave techniques, photonics, and signal processing.

IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Sensors
Now Accepting Submissions! New publication of the IEEE Sensors Council, this journal publishes papers in all areas of the field of interest of the IEEE Sensors Council.
The IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Sensors publishes papers in all areas of the field of interest of the IEEE Sensors Council, i.e., the theory, design, simulation, fabrication, manufacturing and application of devices for sensing and transducing physical, chemical, and biological phenomena, with emphasis on the electronics, physics and reliability aspects of sensors and integrated sensor-actuators. The Journal is built exclusively from papers on selected topics of current interest to the Sensors community.
Editor-in-Chief: Chonggang Wang InterDigital, Inc. USA

IEEE Open Journal of Signal Processing
High-quality, peer reviewed research covering the enabling technology for the generation, transformation, extraction, and interpretation of information.
This fully open access journal publishes high-quality, peer-reviewed papers covering the enabling technology for the generation, transformation, extraction, and interpretation of information. It comprises the theory, algorithms with associated architectures and implementations, and applications related to processing information contained in many different formats broadly designated as signals. Signal processing uses mathematical, statistical, computational, heuristic, and/or linguistic representations, formalisms, modeling techniques and algorithms for generating, transforming, transmitting, and learning from signals. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Brendt Wohlberg Los Alamos National Laboratory, USA

IEEE Open Journal of the Solid-State Circuits Society
High-quality, peer reviewed research covering the design, implementation, and application of solid-state integrated circuits.
As a fully open access journal publishing high-quality peer reviewed papers, IEEE Open Journal of the Solid-State Circuits Society covers design, implementation and application of solid-state integrated circuits. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Jan Craninckx Distinguished Member of Technical Staff IMEC, Belgium

IEEE Open Journal of Systems Engineering
Provides a forum for practitioners, scientists, academics, and researchers engaged in the discipline of Systems Engineering.
The IEEE Open Journal of Systems Engineering (OJSE) is an open access journal that is sponsored by the consortium of IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Society, IEEE Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Society, and the IEEE Systems Council. OJSE provides a forum for practitioners, scientists, academics, and researchers engaged in the discipline of Systems Engineering. Multidisciplinary aspects of systems engineering is a focus of this journal. Methodologies, tools, principles, and applied engineering aspects of the process of systems engineering for complex systems are of interest. The methodologies, tools, and principles include such elements as model-based systems engineering; digital thread; requirements generation, flowdown, tracking, needs analysis, validation/verification; integration and test; and full life cycle of the target system. OJSE deals primarily with the science, methodology, and tools of systems engineering, rather than the results of the application of systems engineering that is the focus of other IEEE journals.
Editor-in-Chief: W. Dale Blair Principal Research Engineer Georgia Tech Research Institute, USA

IEEE Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Letters
Now Accepting Submissions! New publication of the IEEE Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Society (SMC), this journal covers the ultimate aims and key strategies of the SMC society towards the next generation of symbiotic human and machine intelligence systems.
IEEE Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Letter (SMC-L) will cover the ultimate aims and key strategies of the SMC society towards the next generation of symbiotic human and machine intelligence systems. The feature of SMC-L is highlighted by its rapid publication of peer-reviewed short articles within 5 pages, which provide a timely and concise account of innovative research ideas, novel application results, and significant theoretical findings, as well as analyses of emerging trends and groundbreakingly work in SMC fields. SMC-L will provide a new means for members and readers to complement established SMC transactions.
Editor-in-Chief: Prof. Yingxu Wang Editor-In-Chief Univ. of Calgary, Canada
IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine
Bridges the engineering and clinical worlds, focusing on detailed descriptions of advanced technical solutions to a clinical need along with clinical results and healthcare relevance.
This journal bridges the engineering and clinical worlds, focusing on detailed descriptions of advanced technical solutions to a clinical need along with clinical results and healthcare relevance. Its aim is to provide a platform for state-of-the-art technology directions in the interdisciplinary field of biomedical engineering, embracing engineering, life sciences and medicine. The journal provides an active forum for clinical research and relevant state-of-the-art technology for members of all the IEEE societies that have an interest in biomedical engineering as well as reaching out directly to physicians and the medical community through the American Medical Association (AMA) and other clinical societies.

IEEE Open Journal of Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control
Covering high-quality, peer reviewed research theory, technology, materials, and applications relating to the generation, transmission, and detection of ultrasonic waves and related phenomena.
OJ-UFFC covers theory, technology, materials, and applications relating to: the generation, transmission, and detection of ultrasonic waves and related phenomena; medical ultrasound, and associated technologies; ferroelectric, piezoelectric, and piezomagnetic materials; frequency generation and control, timing, and time coordination and distribution. This interest ranges from fundamental studies to the design and/or applications of devices, sensors, systems and manufacturing technologies within the general scope defined above. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Steven Freear University of Leeds, School of Electronic and Electrical Engineering Leeds, United Kingdom

IEEE Open Journal of Vehicular Technology
Featuring high-quality, peer reviewed research on the theoretical, experimental and operational aspects of electrical and electronics engineering in mobile radio, motor vehicles and land transportation.
This fully open access journal publishes high-quality, peer-reviewed papers covering the theoretical, experimental and operational aspects of electrical and electronics engineering in mobile radio, motor vehicles and land transportation. (a) Mobile radio shall include all terrestrial mobile services. (b) Motor vehicles shall include the components and systems and motive power for propulsion and auxiliary functions. (c) Land transportation shall include the components and systems used in both automated and non-automated facets of ground transport technology. The journal peer-review process targets a publication period of 10 weeks from submission to online publication.
Editor-in-Chief: Dr. Sumei Sun Fellow of the IEEE Principal Scientist, Institute for Infocomm Research Adjunct Professor, National University of Singapore, Singapore
Sign up for IEEE open access news
Sign Up Now
Institutions
Learn about open access options
Answers to common questions on open access
Society Members
APC discounts now available
- Antennas and Propagation
- Engineering
- Telecommunications Engineering
- Patch Antenna
Design and Analysis of Microstrip Patch Antenna for Wireless Communication

- University of Petroleum & Energy Studies

- Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies

- The ICFAI University, Jaipur

- NRIITM,gwalior
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Santhakumar Govindasamy
- Jothi Chitra Ratha Krishnan
- Bello Abdullahi Muhammad
- Mohd Nazri Mahmud

- Mohd Fadzil Ain
- WIRELESS PERS COMMUN

- K S Joseph Wilson
- Bambang Bagus
- Sukahir Sukahir

- Fatmawati Sabur
- B G Sathish Kumar
- M H Priyadarshini

- Nitin D. Sali
- Sangeeta Kumari
- Arvind Kumar
- Ettiyappan Anbalagan
- Manoj Sharma
- Aditi Bhardwaj

- MICROW OPT TECHN LET

- Kin-Lu Wong
- Chia-Lun Tang

- Dong-Zo Kim

- Ramesh Garg
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Wireless receiver blocks interference for better mobile device performance
Press contact :, media download.

*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."

Previous image Next image
The growing prevalence of high-speed wireless communication devices, from 5G mobile phones to sensors for autonomous vehicles, is leading to increasingly crowded airwaves. This makes the ability to block interfering signals that can hamper device performance an even more important — and more challenging — problem.
With these and other emerging applications in mind, MIT researchers demonstrated a new millimeter-wave multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) wireless receiver architecture that can handle stronger spatial interference than previous designs. MIMO systems have multiple antennas, enabling them to transmit and receive signals from different directions. Their wireless receiver senses and blocks spatial interference at the earliest opportunity, before unwanted signals have been amplified, which improves performance.
Key to this MIMO receiver architecture is a special circuit that can target and cancel out unwanted signals, known as a nonreciprocal phase shifter. By making a novel phase shifter structure that is reconfigurable, low-power, and compact, the researchers show how it can be used to cancel out interference earlier in the receiver chain.
Their receiver can block up to four times more interference than some similar devices. In addition, the interference-blocking components can be switched on and off as needed to conserve energy.
In a mobile phone, such a receiver could help mitigate signal quality issues that can lead to slow and choppy Zoom calling or video streaming.
“There is already a lot of utilization happening in the frequency ranges we are trying to use for new 5G and 6G systems. So, anything new we are trying to add should already have these interference-mitigation systems installed. Here, we’ve shown that using a nonreciprocal phase shifter in this new architecture gives us better performance. This is quite significant, especially since we are using the same integrated platform as everyone else,” says Negar Reiskarimian, the X-Window Consortium Career Development Assistant Professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS), a member of the Microsystems Technology Laboratories and Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE), and the senior author of a paper on this receiver .
Reiskarimian wrote the paper with EECS graduate students Shahabeddin Mohin, who is the lead author, Soroush Araei, and Mohammad Barzgari, an RLE postdoc. The work was recently presented at the IEEE Radio Frequency Circuits Symposium and received the Best Student Paper Award.
Blocking interference
Digital MIMO systems have an analog and a digital portion. The analog portion uses antennas to receive signals, which are amplified, down-converted, and passed through an analog-to-digital converter before being processed in the digital domain of the device. In this case, digital beamforming is required to retrieve the desired signal.
But if a strong, interfering signal coming from a different direction hits the receiver at the same time as a desired signal, it can saturate the amplifier so the desired signal is drowned out. Digital MIMOs can filter out unwanted signals, but this filtering occurs later in the receiver chain. If the interference is amplified along with the desired signal, it is more difficult to filter out later.
“The output of the initial low-noise amplifier is the first place you can do this filtering with minimal penalty, so that is exactly what we are doing with our approach,” Reiskarimian says.
The researchers built and installed four nonreciprocal phase shifters immediately at the output of the first amplifier in each receiver chain, all connected to the same node. These phase shifters can pass signal in both directions and sense the angle of an incoming interfering signal. The devices can adjust their phase until they cancel out the interference.
The phase of these devices can be precisely tuned, so they can sense and cancel an unwanted signal before it passes to the rest of the receiver, blocking interference before it affects any other parts of the receiver. In addition, the phase shifters can follow signals to continue blocking interference if it changes location.
“If you start getting disconnected or your signal quality goes down, you can turn this on and mitigate that interference on the fly. Because ours is a parallel approach, you can turn it on and off with minimal effect on the performance of the receiver itself,” Reiskarimian adds.
A compact device
In addition to making their novel phase shifter architecture tunable, the researchers designed them to use less space on the chip and consume less power than typical nonreciprocal phase shifters.
Once the researchers had done the analysis to show their idea would work, their biggest challenge was translating the theory into a circuit that achieved their performance goals. At the same time, the receiver had to meet strict size restrictions and a tight power budget, or it wouldn’t be useful in real-world devices.
In the end, the team demonstrated a compact MIMO architecture on a 3.2-square-millimeter chip that could block signals which were up to four times stronger than what other devices could handle. Simpler than typical designs, their phase shifter architecture is also more energy efficient.
Moving forward, the researchers want to scale up their device to larger systems, as well as enable it to perform in the new frequency ranges utilized by 6G wireless devices. These frequency ranges are prone to powerful interference from satellites. In addition, they would like to adapt nonreciprocal phase shifters to other applications.
This research was supported, in part, by the MIT Center for Integrated Circuits and Systems.
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Negar Reiskarimian
- Research Laboratory of Electronics
- Microsystems Technology Laboratories
- Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Related Topics
- Electronics
- Computer chips
- Mobile devices
- Internet of things
- Computer science and technology
- Electrical Engineering & Computer Science (eecs)
Related Articles
New chip for mobile devices knocks out unwanted signals
Miniscule device could help preserve the battery life of tiny sensors

A new chip for decoding data transmissions demonstrates record-breaking energy efficiency
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

MIT researchers identify routes to stronger titanium alloys
Read full story →
Implantable microphone could lead to fully internal cochlear implants

The tenured engineers of 2024
Detachable cardiac pacing lead may improve safety for cardiac patients

A prosthesis driven by the nervous system helps people with amputation walk naturally

“Rollerama” roller rink opens in Kendall Square
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
ieee antennas propagation society engineers education students
Antenna signal processing radio astronomy engineering space communication, wireless mobile satellite telecommunications applied optics electromagnetic waves.

- New AP-S Logo File Originals
- Our Field of Interest
- History of AP-S
- Recent Featured Articles
- In Memoriam
- Past Announcements
- Book Reviews
- IEEE Open Journal of Antennas and Propagation
- IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine
- IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation
- IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters
- IEEE Journal on Multiscale and Multiphysics Computational Techniques (JMMCT)
- Call for Papers: IEEE Journal of Electromagnetics, RF and Microwaves in Medicine and Biology (J-ERM)
- Future Conferences and Calls for Papers
- AP-S/URSI 2023
- AP-S/URSI 2022
- AP-S/URSI 2021
- AP-S/URSI 2020
- AP-S/URSI 2019
- AP-S/URSI 2017
- Meetings Handbook for Joint Symposia
- Summary of Past Symposia
- Requests for IEEE AP-S Sponsorship of Conferences
- Worldwide Chapters
- nanoVNA Program
- Volunteer Opportunities
- Current Committee Members
- Society Representatives
- IEEE Young Professionals Program
- IEEE AP-S Young Professional Ambassador Program
- Call for Nominations for Consideration for the Ballot
- Officers and AdCom Members
- Editors and Committee Chairs
- Constitution
- Operating Manual
- Standing Committee Charters
- Strategic and Operation Plans 2019 -2023
- Membership Benefits
- To All IEEE Life Members
- AP-S AdCom Meeting Minutes
- IEEE Expense Policy
- DL Program Handbook
- DLP Chair’s Note
- Current Distinguished Lecturers
- Past Distinguished Lecturers
- Joint AP-S/MTT-S/EMC-S/GRSS DL Programs
- Recent DL Visits / Tours
- Second Call for 2024 MTT-AP ISDL
- First Call for 2024 AP-S DL Nominations
- Complete List of AP-S Awards
- Call for Nominations for the 2024 AP-S Field Awards
- 2023 AP-S Award Recipients
- Past IEEE and AP-S Award Winners
- AP-S Student Paper Contest Winners
- AP-S Student Design Contest Winners
- AP-S Doctoral and Pre-Doctoral Research Grant Recipients
- AP-S Fellowship Awards
- 2024 Raj Mittra Travel Grant awarded
- IEEE AP-S Fellows
- 2024 IEEE AP-S Student Design Contest Finalists
- Educational Resources
- IEEE Resources
- IEEE AP-S Student Paper Competition Rules and Guidelines
- Apply for 2024 Undergraduate Summer Research Scholarship
- Call for Educational Initiative Proposals
- AP-S YP Ambassadors
- AP-S COPE Activities
- The First Wireless Radio Broadcast
- James Clerk Maxwell Glenlair Trust
- Current Research and Travel Grants
- Contest Submissions and Judging Area
rigorous peer review | rapid publication | open access
Recent Advances in Compact/Integrated Antenna Techniques for 5G Applications
Download Call for Papers (PDF)
Submission Deadline: 30 June 2022
Antenna designs as the critical technology of all nodes and devices face challenges for the fully widespread deployment of 5G. The antenna’s footprint is a challenging task due to the ever-shrinking size of the electronic modules/devices. Thus, the compact/integrated antenna designs with reasonable performance are highly demanded in the extremely limited space and strong interference scenario. As more frequency bands are deployed for various purposes, antenna techniques that can support multiple frequency bands are desirable for the purpose of reducing the aperture, especially the technology integrating frequency bands with large frequency ratio. Also, antennas bundling multiple functionalities, realizing a multi-function RF element, constitute a challenging but effective approach to fully use the limited footprint and reduce the power consumption. Simultaneously, techniques of antenna-in-package (AiP) in the millimeter-wave frequency band are also encouraged, especially those capable of producing multiple or agilely steering beams to achieve high capacity, high agility, and high integrity in 5G mobile communications. This Special Section also welcomes papers on rectenna techniques for 5G-IoT applications that can be employed to power up the geographically located low power consumption nodes or devices. The integration of rectenna platform and communication module sharing the same space is another challenge, demanding substantial research.
This Special Section focuses on challenges for compact/integrated antenna designs in 5G and related applications. It will serve as a venue for sharing innovative concepts, recent advances, and prospective opportunities of antenna design techniques in 5G applications for researchers from both academia and industry.
Potential topics include but are not limited to the following:
- Wideband and low profile antennas
- Dual/multi-frequency antenna with a large frequency ratio
- Co-design of antennas and filters
- Techniques for millimeter wave antenna array
- Rectennas with integrated design of antenna and rectifier
- Antenna-in-package
- MIMO antenna
- Compact wideband antenna
- Multi-frequency/function antenna
- Millimeter wave antenna
Lead Guest Editor
Guest Editors
- IEEE Xplore Digital Library
- IEEE Standards
- IEEE Spectrum
- IEEE Collabratec
- DOI: 10.1109/APCAP59480.2023.10470176
- Corpus ID: 268610665
A Suspended Stacked Patch Antenna for Terahertz Applications
- Junyao Tan , Yujian Li , Junhong Wang
- Published in IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference… 22 November 2023
- Engineering, Physics
Figures from this paper

7 References
A compact 267 ghz shorted annular ring antenna with surface wave suppression in 130 nm sige bicmos, a 320 ghz octagonal shorted annular ring on-chip antenna array, 340-ghz low-cost and high-gain on-chip higher order mode dielectric resonator antenna for thz applications, a 270 ghz × 9 multiplier chain mmic with on-chip dielectric-resonator antenna, opening terahertz for everyday applications, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers

COMMENTS
The antenna is a critical part of the RF front end of a communication system. In this study, we present some of the major applications of artificial intelligence (AI) to antenna design. We review the previous research and applications of several AI techniques such as evolutionary algorithms, machine learning, and knowledge representation ontologies. Applications may vary from antenna design to ...
Wearable antennas are the vital components for Body Centric Communication (BCC). These antennas have recently gained the attention of researchers and have received a great deal of popularity due to their attractive characteristics and opportunities. They are fundamental in the Wireless Body Area Networks (WBANs) for health care, military, sports, and identification purposes. Compared to ...
The exponential growth of digital platforms and the increasing user base in wireless communication has created a need for communication systems that can provide high data speeds, reliability, and strong transmission links. The limitations of single antenna systems have led to an increased focus on multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) antennas in order to address the requirements of modern ...
This paper discusses various challenges related to the antenna design process for 5G communications focusing on the 26 GHz band. In a first example, an 8 element wideband array antenna is optimized for use in a mobile phone. The antenna performance is investigated, including gain, coupling and beamsteering. Aspects related to the antenna integration workflows are also discussed. In a second ...
In this review the author traces the history of antennas and some of the most basic radiating elements, demonstrates the fundamental principles of antenna radiation, reviews Maxwell's equations and electromagnetic boundary conditions, and outlines basic procedures and equations of radiation. Modeling of antenna source excitation is illustrated, and antenna parameters and figures-of-merit are ...
Welcome to the web site of. Since 1952, this journal has delivered many thousands of articles on a wide range of topics of interest to specialists, practicing engineers, educators and students in the field of interest of the IEEE Antennas & Propagation Society (see Scope of Articles in the Transactions ). The Transactions publishes 12 issues ...
Antennas are a critical component in any wireless link. The significance of their role continues to grow, together with the rise of machine-to-machine (M2M) communications and telecommunications starting to shift from the fourth generation (4G, or Long-Term Evolution, LTE) into the fifth generation (5G) and beyond 5G (B5G), and also due to the prominence of the convenience promised by the ...
In general, the term "Antenna" is derived from the latin word, which means something that is used for transmitting and retrieving both the messages and signals. The proposed research work aims to design one such system in our study, to aid the future of communication technologies. This research work has performed an in-depth analysis of the electromagnetics study.
A co-axial feed Microstrip Patch Antenna (MPA) operating at 4.6 GHz frequency, with four symmetric L shaped slots is presented in this paper. The proposed antenna is designed using Roger RT Duroid 5880 substrate material having dielectric constant 2.2 and thickness 4.0 mm. This antenna with Full Ground Plane (FGP) has return loss is -17.91dB and gain 7.9dB is achieved but by defecting the ...
Call for Papers The 2020 IEEE Texas Symposium on Wireless & Microwave Circuits & Systems Baylor University, Waco, Texas April 2-3, 2020 ... IEEE ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION MAGAZINE EDITORIAL BOARD IEEE prohibits discrimination, harassment, and bullying. ... engineering, manufacturing, and scientific research. See how you can apply it to ...
The IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine publishes feature articles and columns that describe engineering activities within its scope, taking place in industry, government, and universities. Emphasis is placed on providing the reader with a general understanding of either a particular subject or of the technical challenges being addressed by ...
This manuscript covers two aspects of parallel plate slot array antennas for synthetic aperture radar. The first pertains to a series-fed slot array antenna, which employs a non-inclined slot array to excite a plane wave within a parallel plate waveguide, resulting in enhanced aperture efficiency. Our investigations yield 1.2 dBi directivity and a 21.0% improvement in aperture efficiency ...
The excessive use of digital platforms with rapidly increasing users in the wireless domain enforces communication systems to provide information with high data rates, high reliability and strong transmission connection quality. Wireless systems with single antenna elements are not able to accomplish the desired needs. Therefore, multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) antennas are getting more ...
Submission Deadline: 31 December 2019 IEEE Access invites manuscript submissions in the area of Antenna and Propagation for 5G and Beyond.. 5G is not just the next evolution of 4G technology; it's a paradigm shift. "5G and Beyond" will enable bandwidth in excess of 100s of Mb/s with latency of less than 1 ms, in addition to providing connectivity to billions of devices.
Founded in 1949, the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society is an international organization active in over 40 countries. ... The top cited research paper from the last decade (2012-2022) is dated 2013 and is co-authored by T. S. Rappaport et al. This article was the first to provide propagation measurements to characterize the use of millimeter ...
This paper demonstrates that the proposed approach can achieve higher than 3.8 dB enhancement in peak gain compared to the antenna without the U-shaped lens when the phase offset (PO) is 0°.
These journals are significant additions to IEEE's well-known and respected portfolio of fully open access journals. In addition, many of the journals featured here target an accelerated publication time frame of 10 weeks for most accepted papers to help get your research exposed faster. Visit the publication home page of each title for details.
Call for Papers: Advances in Antenna Design and Radio Propagation for Integrated Sensing and Communications. Deadline for submissions: March 31, 2025; May 13, 2024. Call For Proposals: Special Sections of the IEEE Open Journal of Antennas and Propagation. Deadline for submissions: 15 June 2024; Apr 30, 2024
This paper presents the evolution of the publication of microstrip antenna papers in the IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation. Both the number of papers and the topics of the papers are ...
IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine; ... Call for Papers: IEEE Journal of Electromagnetics, RF and Microwaves in Medicine and Biology (J-ERM) Conferences. Future Conferences and Calls for Papers; Most Recent AP-S/URSI Conference ... AP-S Doctoral and Pre-Doctoral Research Grant Recipients; AP-S Fellowship Awards; 2024 Raj Mittra Travel Grant ...
This paper proposed a novel patch antenna loaded with L-shaped slots and opposite corner of Square patch is trimmed to achieve dual band operation at 3.43 GHz and 4.75 GHz (the ratio of operating ...
MIMO systems have multiple antennas, enabling them to transmit and receive signals from different directions. ... The work was recently presented at the IEEE Radio Frequency Circuits Symposium and received the Best Student Paper Award. Blocking interference. Digital MIMO systems have an analog and a digital portion. The analog portion uses ...
IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine; IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation; IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters; IEEE Journal on Multiscale and Multiphysics Computational Techniques (JMMCT) Call for Papers: IEEE Journal of Electromagnetics, RF and Microwaves in Medicine and Biology (J-ERM) Conferences. Future Conferences ...
A dual-band antenna-on-chip (AoC) with a loop-type antenna at 120 GHz and a 1-by-2 dipole-type array at 280 GHz realized in a shared structure was presented. The AoC utilizes micro-bumps in a standard flip-chip assembly process, showing radiation gains of -5.71 dBi and 7.32 dBi, as well as maximum efficiency of 13.56% and 52.14% at two bands, respectively.
Array antenna is a type of antenna composed of many antenna radiation units arranged according to certain rules or randomly, which is widely used in many fields such as communications, radar, navigation and satellites. In this paper, a conformal array antenna with a hemisphere structure is designed. The array consists of 91 antenna elements, each of which is the same left-handed doubly-fed ...
As for the return loss of the antennas, the −10 dB impedance bandwidths of the antennas range from 3.47 to 3.52 GHz approximately in both the coupled and decoupled situations. In the decoupled array, S 11 and S 22 are not identical because the introduction of the DFL leads to the differentiation of the boundary conditions of Antenna A and B ...
Call for Papers: Modeling, Analysis, and Design Methods for Embedded Antennas in IoT Wireless Devices. Deadline for submissions: 31 December 2024; April 18, 2024. Call for Papers: Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-based Antenna and Field Measurements. Deadline for submissions: 30 June 2024; Feb 02, 2024. Winner of the Second IEEE OJAP Video Contest
DOI: 10.1016/j.aeue.2024.155417 Corpus ID: 270827477; Null-filled high gain airborne antenna with metasurface for emergency communication @article{Zhou2024NullfilledHG, title={Null-filled high gain airborne antenna with metasurface for emergency communication}, author={WenQiang Zhou and Linyan Guo and Xiaofei Wang and Jinfeng Yan and Chunyu Pan}, journal={AEU - International Journal of ...
The antenna has been successfully applied in practical vehicle systems with good results. In this paper, a near vertical incident skywave (NVIS) shortwave magnetic loop antenna suitable for engineering applications is proposed and designed, and the effects of its structural form, size, and impedance matching on antenna performance is analyzed ...
In this paper, a wideband suspended stacked patch antenna is investigated. The approach involves the creation of parasitic patches through spin-coating a conductive silver paste onto the underside of the suspension structure, resulting in a terahertz antenna with wideband characteristics. The application of an adjustable suspension bracket method within the structure ensures precise alignment ...