
- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Learning Style’s Fleming’s VARK
Published by Flora Scott Modified over 6 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Learning Style’s Fleming’s VARK"— Presentation transcript:

Teachingenglish-TKT Essentials

V isual. A uditory. R eading. K inesthetic. From the Training Room to the Call Center Floor: How to be a Success!

What makes a good teaching session? Jayne Jefferies - NICE.

6 th Grade PEP Academic Planning Overview 1)Watch fun learning styles video 2)Complete intro to learning styles activity 3)Complete learning styles inventory.

Learning Styles Mrs. Sterbinsky. EQ: How do I learn best?

Non-Linguistic Representation Web 2.0 Tools Helping students understand and represent knowledge non- linguistically is the most under-used instructional.
Lori Pitcock REED 663 Dr. Pitcher Fall 2010

The VARK Model ( Copyright Version 7.0 (1992) held by Neil D. Fleming, Christchurch, New Zealand and Charles C. Bonwell, Springfield, MO 65804, USA.) V.

Learning Styles.

IDENTIFYING LEARNING STYLES PASS How Would You Do It? Cooking a new dish for dinner… Read a recipe (from a cookbook or online). Watch and.

Learning Styles, Part II: Different Ways of Teaching A KIT workshop.

By Jessica Gibbs. Students with Disabilities Working with students with disabilities while keeping the rest of the class on track and moving forward can.

Level 2: Chapter 10. Understand that the term “learning styles” can be defined in several ways. Use a simple inventory to determine learning style.

Kaumudi Nagaraju, EnhanceEdu Pedagogy and Learning Styles.

WHAT WE WILL COVER What is a learning style VARK Explained Test Yourself.

Learning Styles and Strategies Make the most of the yourself!
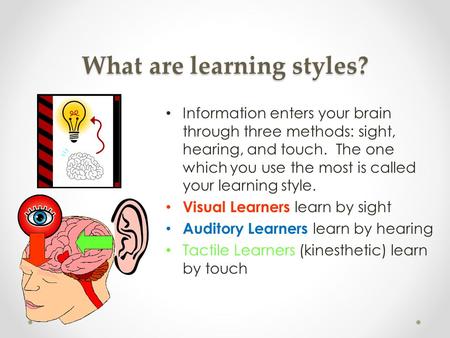
What are learning styles?

Collaborative learning Learning styles Technology

Learning Styles Business and Management Department.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
VARK Learning Styles PPT assignment with links

Description
Use this PPT to introduce your students to VARK four learning styles (visual, auditory, reading/writing, and kinesthetic).
Includes links to an online VARK learning style inventory, learning style infographics, and student/teacher resources, and two great study videos.
Questions & Answers
Firingdendrites.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Overview of VARK Learning Styles
Sam Edwards / Getty Images
VARK Learning Styles
- Find Your Style
- Kinesthetic
Why It Matters
Frequently asked questions.
Learning styles are a popular concept in psychology and education and are intended to identify how people learn best. VARK learning styles suggest that there are four main types of learners: visual, auditory, reading/writing, and kinesthetic.
The idea that students learn best when teaching methods and school activities match their learning styles, strengths, and preferences grew in popularity in the 1970s and 1980s. However, most evidence suggests that personal learning preferences have little to no actual influence on learning outcomes.
While the existing research has found that matching teaching methods to learning styles has no influence on educational outcomes, the concept of learning styles remains extremely popular.
There are many different ways of categorizing learning styles , but Neil Fleming's VARK model is one of the most popular. Fleming introduced an inventory in 1987 that was designed to help students and others learn more about their individual learning preferences.
According to the VARK model, learners are identified by whether they have a preference for:
- Visual learning (pictures, movies, diagrams)
- Auditory learning (music, discussion, lectures)
- Reading and writing (making lists, reading textbooks, taking notes)
- Kinesthetic learning (movement, experiments, hands-on activities)
The VARK model refers to the four sensory modalities that describe different learning preferences. The model suggests that these modalities reflect how students learn best.
What Type of Learner Are You?
In order to identify which type of learner people are, Fleming developed a self-report inventory that posed a series of situations. Respondents select the answers that best match their preferred approach to learning.
Imagine that you are learning how to perform a new physical skill such as riding a bike or dancing a certain style of dance. In which way would you learn this skill the best?
- Look at pictures of people performing the skill. (Visual)
- Listen to an expert explain how to do the task. (Auditory)
- Read about how to perform the task in a book. (Reading/Writing)
- Watch someone else perform the skill and then trying it yourself. (Kinesthetic)
Visual Learners
Visual learners learn best by seeing. Graphic displays such as charts, diagrams, illustrations, handouts, and videos are all helpful learning tools for visual learners.
Visual learners prefer this type of learning would rather see information presented in a visual rather than in written form.
Do you think you might be a visual learner? Then consider the following questions:
- Are art, beauty, and aesthetics important to you?
- Does visualizing information in your mind help you remember it better?
- Do you have to see information in order to remember it?
- Do you pay close attention to body language ?
If you can answer yes to most of these questions, chances are good that you have a visual learning style. You may find it helpful to incorporate things like pictures and graphs when you are learning new information.
Aural Learners
Aural (or auditory) learners learn best by hearing information. They tend to get a great deal out of lectures and are good at remembering things they are told.
Are you an auditory learner? Consider the following questions:
- Do you create songs to help remember information?
- Does reading out loud help you remember information better?
- Do you prefer to listen to class lectures rather than reading from the textbook?
- Would you prefer to listen to a recording of your class lectures or a podcast rather than going over your class notes?
If you answered yes to most of these questions, then you are probably an auditory learner. You might find things like audiobooks and podcasts helpful for learning new things.
Reading and Writing Learners
Reading and writing learners prefer to take in information that is displayed as words and text. Could you be a reading and writing learner? Read through the following questions and think about whether they might apply to you.
- Do you enjoy making lists, reading definitions, and creating presentations?
- Do you find reading your textbook to be a great way to learn new information?
- Do you take a lot of notes during class and while reading textbooks?
- Do you prefer it when teachers make use of overheads and handouts?
If you answered yes to these questions, it is likely that you have a strong preference for the reading and writing style of learning. You might find it helpful to write down information in order to help you learn and remember it.
Kinesthetic Learners
Kinesthetic (or tactile) learners learn best by touching and doing. Hands-on experience is important for kinesthetic learners.
Not sure if you're a kinesthetic learner? Answer these questions to find out:
- Are you good at applied activities such as painting, cooking, mechanics, sports, and woodworking?
- Do you enjoy performing tasks that involve directly manipulating objects and materials?
- Do you have to actually practice doing something in order to learn it?
- Is it difficult for you to sit still for long periods of time?
If you responded yes to these questions, then you are most likely a kinesthetic learner. Taking classes that give you practical, hands-on experience may be helpful when you want to acquire a new skill.
The validity of the VARK model as well as other learning style theories has been questioned and criticized extensively. Some critics have suggested that labeling students as having one specific learning style can actually be a hindrance to learning.
One large-scale look at learning style models suggested that the instruments designed to assess individual learning styles were questionable.
The VARK model remains fairly popular among both students and educators despite these criticisms. Students may feel drawn to a particular learning style. Others may find that their learning preferences lie somewhere in the middle, such as finding both visual and auditory learning equally appealing.
People might find that understanding their own learning preferences can be helpful. If you know that visual learning appeals to you most, using visual study strategies in conjunction with other learning methods might help you remember and enjoy your studies more.
If no single learning preference calls out to you or you change preferences based on the situation or the type of information you are learning, you probably have what is known as a multimodal style .
For example, you might rely on your reading and writing preferences when you are dealing with a class that requires a great deal of book reading and note-taking, such as a history of psychology course. During an art class, you might depend more on your visual and kinesthetic preferences as you take in pictorial information and learn new techniques.
The four VARK learning styles are visual learners, aural learners, reading and writing learners, and kinesthetic learners.
According to some data, the most common is a multimodal learning style referred to as VARK Type Two, which involves exhibiting a range of learning preferences. People with this learning style tend to collect information more slowly and take time to make decisions.
In terms of single preferences, kinesthetic is by far the most common, accounting for 22.8% of respondents.
Pashler H, Mcdaniel M, Rohrer D, Bjork R. Learning styles: concepts and evidence . Psychol Sci Public Interest . 2008;9(3):105-19. doi:10.1111/j.1539-6053.2009.01038.x
VARK Learn Limited. VARK research - what do we know about VARK ?
Fleming N. Introduction to Vark .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
| . |
| VARK is a simple taxonomy for learning styles. It abbreviates . It is attributed to . Sometimes, this is augmented to 7 learning styles, adding components. Up to 70 learning styles have since been introduced! What learning type are you? V,A,R or K? It can be complicated. I consider myself very much a V type as I think often in pictures, but I also find R appealing as precise statements more clear than pictures; we have learned in mathematics that pictures can mislead. I also like to hear things from an expert, additionally to see a lecture. In some parts, I'm also very Kinesthetic in that I like to hold in hand an object. which definitely belongs to V and which is definitely belongs to K. As illustrates, there is little scientific evidence that a VARK classification really works. Note, that this does not mean that Fleming and Mills got the taxonomy wrong. It means that we often draw from additional assumptions which are not justified. One assumption is that and that this . Both additional statements were not done by Fleming and Mills but just assumed to be true because it seems to fit our experiences. The Veratesium video comes with lots of references and also explanations. One explanation given by a psychologist in the movie is that if you believe to be a visual learner and a picture convinces you, then you attribute that to your learning style. If it ``clicks" while listing, you might not notice because of your predisposition ``I'm a visual learner". More important appears to be . One can also recall it as effect. To remember it, just imagine the different colors of the M & M candy. Material presented in various ways sticks better. Again, the above video gives lots of references which illustrate this. There is little to add except maybe that learning also very much depends on subject and abstraction level. Subjects like the theory of schemes or abstract algebra can be visualized less well than differential geometry or topology. The next time you teach or present remember: . ( to make it stick!) |

- Alternatives
VARK Learning Styles | Finding Your 2024 Ideal Learning Method
Jane Ng • 15 December, 2023 • 10 min read
Today, we will explore four VARK Learning Styles : visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and reading/writing. By understanding how these styles impact learning experiences, we can design educational strategies that engage and connect with each learner's strengths and preferences. Get ready to uncover the secret to unlocking the potential of every individual!
| Who created VARK learning styles? | Neil Fleming |
| When was the VARK learning style created? | 1987 |
Tips For Better Class Engagement
- Types of Learning Styles
- Honey and mumford learning styles
- Auditory Learner

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next class. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
Table of Contents
What are the vark learning styles, why is it important to understand your vark learning styles , how to find your ideal vark learning styles, key takeaways.
The VARK learning styles are a model developed by Neil Fleming, which categorizes learners into four main types:
- Visual learners (V) : These individuals learn best through visual aids and images.
- Auditory learners (A): These individuals excel in learning through listening and speaking.
- Read/Write learners (R): People who learn best through reading and writing activities.
- Kinesthetic learners (K): These individuals who learn best through physical activities and experiences.

Understanding your VARK learning style is important for several reasons:
- It helps you to choose strategies and resources that align with your strengths, making the learning process more efficient and enjoyable.
- It helps you to work collaboratively with teachers to create a learning environment that supports your needs and facilitates your academic progress.
- It empowers you to continue your personal and professional development, making your ongoing learning journey more effective.
We will delve into the 4 types of VARK learning styles, exploring their unique characteristics and discovering strategies to facilitate effective learning for each style.
#1 - Visual Learners - The VARK Learning Styles
How to identify visual learners.
Visual learners prefer to process information through visual aids and imagery. They rely on seeing information in graphs, diagrams, charts, or other visual representations. Here are some simple ways to identify visual learners:
- Strong visual preference: You strongly favor visual materials and tools. To properly understand and retain knowledge, you rely on visualizing information through visuals, graphs, charts, and videos. For example, you may enjoy looking at infographics instead of listening to a lecture.
- Good visual memory: You have a good memory for visual details. You remember things they have seen more easily than information they have heard. For instance, you might recall specific images or illustrations from a lesson.
- Love for visual arts and imagery: Visual learners are often interested in activities that involve visual perception and creativity. So you may enjoy drawing, painting, or photography. For example, you may be more likely to choose art-related projects or electives.
- Strong observation skills: You can notice patterns, colors, and shapes more readily. For example, you might quickly spot a specific diagram or image within a larger document or presentation.
Learning Strategies For Visual Learners
If you are a
Use Visual aids and materials:
Incorporate visual aids, such as charts, diagrams, and images, into your teaching. These visual representations help visual learners grasp concepts more effectively.
- Example: When learning about the water cycle, use a colorful diagram to illustrate the different stages and processes involved.
Mind mapping:
You can create mind maps to organize thoughts and make connections between ideas. This visual representation helps them see the big picture and the relationships between different concepts.
Incorporate color coding:
Use color coding to highlight important information, categorize content, or differentiate key concepts. Color coding helps visual learners process and remember information more effectively.
Engage in visual storytelling:
You can use images, props, or videos to create a visual narrative that connects with the content of the lessons.
- Example: When learning historical events, use photographs or primary source documents to tell the story visually and evoke an emotional connection.
Visual reflection and expression:
Visual learners can benefit from expressing their understanding through visual means. So you can create visual presentations, drawings, or diagrams to showcase your comprehension.
- Example: After reading a book, you can create a visual representation of your favorite scene or draw a comic strip summarizing the main events.


#2 - Auditory Learners - The VARK Learning Styles
How to identify auditory learners.
Auditory learners learn best through sound and auditory input. They excel in listening and verbal communication. Here are some characteristics:
- Enjoy spoken instruction: You tend to favor verbal instructions over written or visual materials. You may request explanations or seek out opportunities for discussions. If given instructions, you often ask for clarification or prefer to hear the instructions explained aloud rather than read them silently.
- Strong listening skills : You show active listening skills during class or discussions. You maintain eye contact, nod, and respond when information is presented verbally.
- Enjoy participating in conversations and discussions: You contribute your thoughts, ask questions, and engage in dialogue to deepen your understanding. You might find that auditory learner eagerly raises their hand during class discussions and enthusiastically shares their ideas with peers.
- Love oral activities: You often derive pleasure from activities that involve listening, such as audiobooks, podcasts, or oral storytelling. You actively seek out opportunities to engage with spoken content.
Learning Strategies For Auditory Learners
If you are an auditory learner, you can employ the following strategies to enrich your learning experience:
Participate in group discussions:
Engage in discussions, group activities, or study groups where you can explain and discuss concepts with others. This verbal interaction helps reinforce your understanding of the material.
Use audio resources:
Incorporate audio materials such as audiobooks, podcasts, or recorded lectures into your learning process. These resources allow you to reinforce your learning through auditory repetition.
Read aloud:
You can read aloud to reinforce your understanding of written texts. This technique combines with the visual input from reading, enhancing comprehension and retention.
Use mnemonic devices:
You can remember information by employing mnemonic devices that involve verbal elements.
- For instance, creating rhymes, acronyms, or jingles can assist in retaining and recalling key concepts.

#3 - Read/Write Learners - The VARK Learning Styles
How to identify read/write learners.
Read/Write Learners learn best by engaging with written materials, taking detailed notes, and creating lists or written summaries. They may benefit from textbooks, handouts, and written assignments to reinforce their understanding.
To identify read/write learners, look for the following characteristics and preferences:
- Preference for reading: You enjoy reading books, articles, and written materials to gain knowledge and understanding. You may often be found engrossed in a book during your free time or show excitement when presented with written information.
- Strong note-taking skills: You excel at taking detailed notes during lectures or when studying. During a class lecture, you diligently write down key points, using bullet points, headings, and subheadings to categorize your notes.
- Appreciate written assignments: You thrive in tasks that involve writing, such as essays, reports, and written projects. You can effectively research, analyze information, and present it in a written format.
- Memorize through writing: You find that writing information helps you memorize and retain it more effectively. You rewrite or summarize important details as a study technique.
Learning Strategies For Read/Write Learners
Here are some specific learning strategies tailored for Read/Write learners:
Highlight and underline:
You can highlight or underline key information while reading. This activity helps you focus on important details and facilitates better retention.
- For example, you can use colored highlighters or underline key phrases in their textbooks or study materials.
Create study guides or flashcards:
By organizing important concepts and information in a written format, you can engage actively with the content and reinforce your understanding. Your
Use writing prompts:
You can use writing prompts related to the subject matter. These prompts can be thought-provoking questions, scenario-based prompts, or open-ended statements that support critical thinking and written exploration of the topic.
Write practice essays or journal entries:
Practice your writing skills by composing essays or journal entries on relevant topics. This activity allows you to express your thoughts, reflect on your learning, and strengthen your ability to articulate ideas effectively in written form.

#4 - Kinesthetic Learners - The VARK Learning Styles
How to identify kinesthetic learners.
Kinesthetic learners prefer a hands-on approach to learning. They learn best through physical activities, movement, and direct experiences.
To recognize kinesthetic learners, look for the following characteristics and behaviors:
- Enjoy hands-on activities: You love activities that involve physical movement, manipulation of objects, and practical application of concepts, such as science experiments, building models, or engaging in sports and physical activities.
- Need for movement: You find it difficult to sit still for long periods. You may fidget, tap your feet, or use gestures while learning or listening to instructions. You frequently shift positions, pace around the room, or use hand movements to express yourself .
- Improve learning through physical involvement: You often retain information better when you can physically interact with it by acting it out, such as simulating historical events or using physical objects to represent mathematical operations.
- Use gestures and body language: You often use gestures, body movements, and facial expressions to communicate and express your thoughts.
Learning Strategies For Kinesthetic Learners
Hands-on activities:
Engage in activities that involve physical movement, such as experiments, simulations, or practical tasks. This allows you to learn by doing and directly experience the concepts being taught.
- Example: In a science class, instead of just reading about chemical reactions, perform hands-on experiments to see and feel the changes happening.
Engage in Sports or Physical Activities:
Participate in sports or physical activities that require coordination and body movement. These activities stimulate your kinesthetic learning style while providing a break from traditional study methods.
- Example: Join a dance class, participate in team sports, or engage in activities like yoga or martial arts to enhance your learning experience.
Study with Kinesthetic Techniques:
Incorporate physical movement into your study routine. This can include pacing while reciting information, using gestures to reinforce concepts, or using flashcards and physically arranging them to form connections.
- Example: When memorizing vocabulary words, walk around the room while saying the words aloud or use hand motions to associate meanings with each word.
Incorporate physical breaks:
Kinesthetic learners benefit from short breaks. So you should stretch, walk around, or engage in light physical activity, which can improve focus and retention.

Understanding the
And don't forget AhaSlides is a versatile interactive presentation platform that allows for dynamic engagement and customization templates . With features like interactive polls , quizzes , and collaborative activities, AhaSlides help educators to adapt their teaching methods to different learning styles and capture the attention and participation of all students.
What is VARK preferred learning style?
The VARK model does not prioritize or suggest a single preferred learning style. Instead, it recognizes that individuals may have a preference for one or more of the four learning styles: visual, auditory, reading/writing, and kinesthetic.
What are VAK or VARK models?
VAK and VARK are two similar models that categorize learning styles. VAK stands for Visual, Auditory, and Kinesthetic, while VARK includes an additional category of reading/writing. Both models aim to categorize learners based on their preferred modes of receiving and processing information.
What is VAK teaching method?
The VAK teaching method refers to an instructional approach that incorporates visual, auditory, and kinesthetic elements to engage learners with different learning styles.
Ref: Rasmussen | Very Well Mind

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides


What Is the VARK Learning Style Model?
If you look at recent academic trends, people are continuously moving towards innovative education models. Moving away from traditional teacher-centred…

If you look at recent academic trends, people are continuously moving towards innovative education models. Moving away from traditional teacher-centred methods, where instructors had a lot of control over what someone would learn or gain, we have identified personalized methods of education. The core need gap that encouraged such transformation was the need to accommodate different learning styles.
Everyone has a unique learning style, whether they are in academic institutions or in the workplace. Various learning styles also inform various working styles of employees. Managers and team leaders shoulder the responsibility of not only leading their team but also providing direction and guidance. This is why it’s important to understand individual learning and working styles. The VARK Model is one of the most popular instruments for gauging someone’s learning style. Let’s explore the VARK Model in detail.
Understanding The VARK Model Of Learning
Why managers need the vark model, applying the vark learning style model.
To understand the VARK learning style , we need to learn about the context in which it developed. It was Neil D. Fleming, a teacher from New Zealand, who developed the VARK test in a 1992 study. After several hours of classroom observation, he developed a questionnaire that helped determine the personal learning preferences of an individual. The preference represents how an individual likes to learn and gain new information. Understanding the preferences can help individuals choose the most suitable medium through which they want to acquire new information. ( Ambien )
- VARK stands for Visual (V), Aural (A), Read/Write (R) and Kinesthetic (K), which classified the four types of learning preferences. Identifying one’s VARK learning style has been instrumental in overcoming several challenges such as
- It helps in effective learning as individuals have a personalized experience of gaining new knowledge or information
- It explores the science behind how people learn; therefore, different (and unconventional) learning tools can be used for studying, teaching or learning
- Different learning tools stimulate learners, making the experience more engaging; learners are likely to become more attentive and involved
- In short, the VARK Model provides learners with much-needed flexibility to fit in with their learning environments
Managers across any functional level need to communicate and collaborate with multiple team members at any given moment. While they have the primary task of delegating responsibilities, they are instrumental in guiding and supporting employees. Now, every team member will have a unique approach to work as everyone has a unique learning and working style. If managers and team leaders want to effectively provide guidance, they need to navigate different learning styles. This is where the VARK learning style makes a difference. You can support and manage your employees with greater efficiency with the VARK Model of learning :
1. Visual Learners
In this type of VARK learning style , individuals learn best through visual or graphical representation. They rely on graphics, videos and written information to gain new knowledge. For example, PowerPoint presentations are useful in communicating to visual learners. Even graphs, charts and other visual information are helpful.
2. Aural Learners
Also known as auditory learners, such individuals learn best by listening to the information being conveyed to them. They pay attention to what someone has to say and gather new inputs simply by listening. They benefit from group discussions and brainstorming sessions because ideas are shared out loud. Some other learning tools include voice-over videos and audio recordings.
3. Reading/Writing Learners
These learners prefer to learn new information when presented in text format. Whether it’s a PowerPoint presentation or handing out a report, they find it easier to process information after reading it. Even during discussions or meetings, they prefer taking notes and reading them to understand the information being conveyed.
4. Kinesthetic Learners
Such individuals retain information through their senses. Simply put, they learn through hands-on experiences. Their strengths lie in tasks that involve engaging with materials or objects. For example, an employee understands a project better when they have on-site experience, communicate with stakeholders involved and play a pivotal role in documentation and organization of all the activities involved.
If you want to make the most of your team’s goals and expectations, then understanding individual learning styles won’t suffice. To go above and beyond, you need to foster team spirit and collaborate effectively. Harappa’s Managing Teamwork course will teach you how to navigate and harness different skills of team members and successfully collaborate with them through open dialogue and discussion. The Social Styles Model framework will help you understand four common work styles and lead them to success. Manage effectively to lead successfully. Start your free trial today!
Explore Harappa Diaries to learn more about topics such as Detailed Guide To Blended Learning , Meaning Of Visual Learning Style , Meaning Of Microlearning and Multimodal Learning to upgrade your knowledge and skills.


Understanding the VARK Learning Styles: Visual, Auditory, Reading/Writing, and K
Apr 12, 2024
0 likes | 4 Views
Kinesthetic learners often excel in subjects like physical education, where they can apply their skills in a practical setting
Share Presentation

Presentation Transcript
Introduction In the world of education, it is crucial to recognize that not all students learn in the same way. Each individual has their own unique learning style, which affects how they process and retain information. One popular model for understanding these different learning styles is the VARK model, which categorizes learners into four main styles: visual, auditory, reading/writing, and kinesthetic. By understanding these learning styles and tailoring teaching methods to suit each student's preferences, educators can create a more effective and inclusive learning environment. What are the VARK Learning Styles? The VARK model was developed by Neil Fleming in 1987 as a way to identify and cater to different learning preferences. Learning Optimization It stands for Visual, Auditory, Reading/Writing, and Kinesthetic – representing four distinct ways in which individuals prefer to learn. Visual Learner Characteristics Auditory Learning Techniques Reading/Writing Learning Strategies Kinesthetic Learning Activities Visual Learner Characteristics Visual learners are those who prefer to process information through images and spatial representations. They have a knack for visualizing concepts and tend to rely on charts, graphs, diagrams, and other visual aids when studying or learning new material. Some common characteristics of visual learners include: Strong visualization skills Excellent spatial awareness Preference for color-coded notes or study materials Enjoyment of visual arts or activities To accommodate visual learners in the classroom or during study sessions, teachers can incorporate various techniques such as: Utilizing visual aids like charts or diagrams Encouraging the use of color-coding or highlighting important information Providing opportunities for drawing or sketching to reinforce concepts Auditory Learning Techniques Auditory learners, on the other hand, thrive when information is presented through sound and speech. They learn best through listening and verbal communication. Some common characteristics of auditory learners include: Good listening skills Strong verbal communication abilities Enjoyment of discussions or lectures Preference for audio materials like podcasts or recordings To cater to auditory learners, educators can utilize the following techniques: Incorporating group discussions or debates into lessons Providing audio recordings or podcasts for review Encouraging students to explain concepts verbally or present their knowledge through oral presentations Reading/Writing Learning Strategies Reading/writing learners prefer to process information through written words. They are skilled at reading, writing, and organizing their thoughts on paper. Some common characteristics of reading/writing learners include: Strong reading comprehension skills Enjoyment of reading and writing activities Preference for taking notes during lectures or while studying Effective use of written resources and materials To support reading/writing learners, teachers can incorporate the following strategies: Assigning reading materials and providing study guides Encouraging note-taking during lectures and discussions Incorporating writing assignments or essay questions to reinforce understanding Kinesthetic Learning Activities
Kinesthetic learners excel in hands-on activities that involve physical movement and manipulation. They learn best when they can engage their senses and actively participate in the learning process. Some common characteristics of kinesthetic learners include: Strong physical coordination and motor skills Tendency to fidget or move while learning Enjoyment of activities such as experiments, role-playing, or simulations Preference for interactive learning experiences To engage kinesthetic learners effectively, educators can implement the following activities: Hands-on experiments or demonstrations Role-playing exercises to simulate real-life scenarios Incorporating movement breaks throughout the lesson to keep students engaged How to Identify Your Learning Style? Now that we have explored the different VARK learning styles, you may be wondering how to identify your own learning style. Understanding your preferred learning style can help you tailor your study habits and maximize your learning potential. Here are a few methods to identify your learning style: Learning Style Questionnaire Educational Methods VARK Student Learning Preferences Learning Style Questionnaire There are various online quizzes and questionnaires available that can help you determine your learning style. These quizzes typically involve answering a series of questions about your preferences, strengths, and study habits. By analyzing your responses, the questionnaire will provide insights into which learning style suits you best. Educational Methods VARK Another method is to reflect on past educational experiences and assess which methods or activities have been most effective for you. Did you find yourself excelling in hands-on activities? Did listening to lectures help you retain information better? Evaluating your past experiences can give you valuable clues about your preferred learning style. Student Learning Preferences Additionally, observing how you naturally approach learning can also provide insights into your learning style. Do you often find yourself doodling or drawing diagrams when trying to understand new concepts? Do you prefer discussing ideas with others rather than reading textbooks alone? Paying attention to these tendencies can help uncover your unique learning preferences. How to Improve Study Habits Based on VARK? Now that we have identified the different VARK learning styles and discussed how to identify your own, let's explore some strategies for improving study habits based on these styles. Visual vs Auditory vs Kinesthetic Best Learning Practices for VARK Learning Style Assessment Customize Learning Approach Visual vs Auditory vs Kinesthetic Understanding the differences between visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners can guide us in developing effective study habits tailored to each style: Visual learners benefit from utilizing visual aids such as graphs, charts, and diagrams during their studies. Auditory learners should focus on listening to lectures, podcasts, or recordings to reinforce their understanding. Kinesthetic learners thrive when engaged in hands-on activities and movement-based learning experiences. By recognizing your learning style and incorporating techniques that align with it, you can enhance your study habits and improve knowledge retention. Best Learning Practices for VARK
In addition to tailoring study habits to individual learning styles, there are some general best practices that can benefit all types of learners: Create a structured study schedule: Establishing a consistent study routine helps maintain focus and productivity. Break down complex information: Divide large amounts of information into smaller, manageable chunks to make studying more manageable. Utilize mnemonic devices: Mnemonics, such as acronyms or visual associations, can aid in memorization and recall. Teach others: Explaining concepts to someone else helps reinforce your own understanding while also benefiting the person you are teaching. Learning Style Assessment Regularly assessing and reflecting on your learning style is crucial for ongoing improvement. As you progress through different subjects or stages of education, you may find that your preferred learning style evolves. Continuously reassessing your learning preferences allows you to adapt your study habits accordingly and optimize your educational experience. Customize Learning Approach Remember that each individual's learning style is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. It is essential to customize your learning approach based on your specific needs and preferences. Experiment with different study methods, techniques, and resources until you find what suits you best. VARK Learning Examples To further illustrate how the VARK model can be applied in different educational contexts, let's explore some examples: Science Class: Visual learners benefit from observing experiments or demonstrations. Auditory learners can benefit from listening to explanations or participating in class discussions. Reading/writing learners should focus on taking detailed notes during lectures or researching additional information. Kinesthetic learners can engage in hands-on activities, such as conducting their experiments or building models. Language Learning: Visual learners can benefit from using flashcards or visual aids to learn vocabulary. Auditory learners should focus on listening to native speakers or engaging in conversation practice. Reading/writing learners can enhance their language skills by reading books, writing essays, or keeping a language journal. Kinesthetic learners can engage in role-playing exercises or interactive language games. Maximizing Learning Efficiency with VARK Regardless of your learning style, there are some general tips and strategies that can help maximize your learning efficiency: Create a conducive learning environment: Find a quiet and comfortable space where you can focus without distractions. Use technology wisely: Leverage educational resources and tools that align with your learning style, such as online tutorials or interactive apps. Take breaks: Regularly taking short breaks during study sessions helps prevent burnout and promotes better information retention. Seek support: Don't hesitate to ask for help from teachers, classmates, or tutors if you are struggling with certain concepts. Understanding the VARK Model: A Summary The VARK model provides valuable insights into the different ways individuals prefer to learn – visually, auditorily, through reading/writing, or kinesthetically. By identifying your own learning style and understanding how it impacts your study habits, you can optimize your educational journey and improve knowledge retention. Remember that everyone's learning style is unique and may evolve over time. Continuously reassessing your preferences and adapting your study methods accordingly ensures that you are always making the most of your educational experience.
In conclusion, understanding the VARK learning styles is essential for educators and students alike. By recognizing the diverse ways in which individuals process information, we can create inclusive and effective learning environments that cater to every learner's needs. So, embrace your learning style and tailor your study habits accordingly – the rewards will be well worth the effort.
- More by User
- Preferences

VARK - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

VARK Learning Styles VARK Learning Styles Record answer on sheet by circling the VARK that corresponds to answer choice Focus on your preference Okay to choose ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
- Learning Styles
- 5 multi-disciplinary teams
- 7 communicate effectively
- Record answer on sheet by circling the VARK that corresponds to answer choice
- Focus on your preference
- Okay to choose more than one answer
- a. go with her.
- b. tell her the directions.
- c. write down the directions.
- d. draw or give her a map.
- a. look it up in the dictionary.
- b. see that word in your mind and choose by the way it looks.
- c. sound it out in your mind.
- d. write both versions down on paper and choose one.
- a. describe some of the highlights.
- b. use a map or website to show them the places.
- c. give them a copy of the printed itinerary.
- d. phone, text, or e-mail them.
- a. cook something you know without the need for instructions.
- b. ask friends for suggestions.
- c. look through the cookbook for ideas from the pictures.
- d. use a cookbook where you know there is a good recipe.
- a. talk about, or arrange a talk for them about parks or wildlife reserves.
- b. show them internet pictures, photographs, or picture books.
- c. take them to a park or wildlife reserve and walk with them.
- d. give them a book or pamphlets about the parks or wildlife reserves.
- a. Trying or testing it.
- b. Reading the details about its features.
- c. It is a modern design and looks good.
- d. The salesperson telling you about its features.
- a. watching a demonstration.
- b. listening to somebody explaining it and asking questions.
- c. diagrams and charts - visual clues.
- d. written instructions e.g. a manual or textbook.
- a. gave you a something to read to explain what was wrong.
- b. used a plastic model to show what was wrong.
- c. described what was wrong.
- d. showed you a diagram of what was wrong.
- a. read the written instructions that came with the program.
- b. talk with people who know about the program.
- c. use the controls or keyboard.
- d. follow the diagrams in the book that came with it.
- a. things you can click on, shift, or try.
- b. interesting design and visual features.
- c. interesting written descriptions, lists, and explanations.
- d. audio channels where you can hear music, radio programs, or interviews.
- a. The way it looks is appealing.
- b. Quickly reading parts of it.
- c. A friend talks about it and recommends it.
- d. It has real-life stories, experiences, and examples.
- a. a chance to ask questions and talk about the camera and its features.
- b. clear written instructions with lists and bullet points about what to do.
- c. diagrams showing the camera and what each part does.
- d. many examples of good and poor photos and how to improve them.
- a. demonstrations, models, or practical sessions.
- b. question and answer, talk, group discussion, or guest speakers.
- c. handouts, books, or readings.
- d. diagrams, charts, or graphs.
- a. using examples from what you have done.
- b. using a written description of your results.
- c. from somebody who talks it through with you.
- d. using graphs showing what you had achieved.
- a. choose something that you have had there before.
- b. listen to the waiter or ask friends to recommend choices.
- c. choose from the descriptions in the menu.
- d. look at what others are eating or look at pictures of each dish.
- a. make diagrams or get graphs to help explain things.
- b. write a few key words and practice saying your speech over and over.
- c. write out your speech and learn from reading it over several times.
- d. gather many examples and stories to make the talk real and practical.
- Total the number of Vs, As, Rs, and Ks
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.


COMMENTS
The VARK Model of Learning To find out more about how students learn, I'm going to focus on the VARK model of learning. Let's start by explaining what VARK is; The VARK model of learning is a model designed by Neil D. Fleming, and it refers to the four types of learning styles: Visual, auditory, reading/reading, and kinesthetic (Learning styles, 2008).
1 Learning Style's Fleming's VARK. IMMANUEL VICTOR GEORGE ILTA 07/06/2016. 2 Microteaching Structure. Intended learning outcomes Approaches and activities Assessment Active learning session Participative exercises Contributions Questions One minute paper at the end (Biggs's Constructive Alignment, 2006) 3 Intended Learning Outcomes.
PowerPoint Presentation. Chapter 4. Determinants of Learning. 9.VARK Learning Style VARK is a sensory model and it is an extension of the neuro-linguistic model. In the acronym VARK, V stands for visual, A for aural, R for read/write and K for kinesthetic. According to Fleming (2006), VARK refers to category of communication preference.
Use this PPT to introduce your students to VARK four learning styles (visual, auditory, reading/writing, and kinesthetic). Includes links to an online VARK learning style inventory, learning style infographics, and student/teacher resources, and two great study videos.
4.1 Vark And Learning Preferences - Visual Knowing and Taking Advantage of Learning Styles in a Way That Works for You Visual Learning Preference Sit in class where you can see PowerPoint slides and other visual presentations Pay attention to your textbooks' illustrations and diagrams Use a visual approach in your class notes
The VARK learning styles are a way to categorize different modes of learning. The VARK model determines visual, auditory, reading/writing, and kinesthetic learners.
VARK is a simple taxonomy for learning styles. It abbreviates Visual, Aural/Auditory, Read/Write, and Kinesthetic . It is attributed to Neil D. Fleming and Colleen Mills from 1992 [PDF] . Sometimes, this is augmented to 7 learning styles, adding Social, Solitary and Logical components.
By embracing the importance of understanding VARK and customizing our approach to education, we can create inclusive and effective learning environments that cater to the unique needs of each individual learner. So take the time to assess your learning style, adapt your study habits, and embark on a journey of efficient and enjoyable learning.
VARK. Unlock the knowledge... know your learning style! Learning Styles: Visual, Auditory, Read/Write, Kinesthetic. There are many models and theories about learning styles. This particular system about an individual's learning preference is known as VARK—Visual, Auditory, Read/Write, and Kinesthetic (hands-on) Know your tutee's learning ...
Remember, every student is unique, and by embracing their individual learning styles, we can cultivate a love for learning that lasts a lifetime. So dive deep into VARK and unlock the potential of every learner!
The VARK learning styles are a model developed by Neil Fleming, which categorizes learners into four main types: Visual learners (V): These individuals learn best through visual aids and images. Auditory learners (A): These individuals excel in learning through listening and speaking. Read/Write learners (R): People who learn best through ...
VARK Learning Styles by Jackie Cintel on Prezi. Blog. June 30, 2024. Everything you need to know about creating a research presentation. June 28, 2024. Mastering internal communication: The key to business success. May 31, 2024. How to create and deliver a winning team presentation.
VARK. Learning Styles. VARK - Learning Styles. Record answer on sheet by circling the VARK that corresponds to answer choice Focus on your preference Okay to choose more than one answer.
VARK Model provides learners with much-needed flexibility to fit in with their learning environments. Go through the VARK learning style by Harappa to explore the science behind how people learn, engage, and gain new information.
Download Presentation Understanding the VARK Learning Styles: Visual, Auditory, Reading/Writing, and K
VARK Learning Styles VARK Learning Styles Record answer on sheet by circling the VARK that corresponds to answer choice Focus on your preference Okay to choose ... - A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as an HTML5 slide show) on PowerShow.com - id: 754d08-MzI2Z