
TOPIC SENTENCE/ In his numerous writings, Marx critiques capitalism by identifying its flaws. ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ By critiquing the political economy and capitalism, Marx implores his reader to think critically about their position in society and restores awareness in the proletariat class. EVIDENCE/ To Marx, capitalism is a system characterized by the “exploitation of the many by the few,” in which workers accept the exploitation of their labor and receive only harm of “alienation,” rather than true benefits ( MER 487). He writes that “labour produces for the rich wonderful things – but for the worker it produces privation. It produces palaces—but for the worker, hovels. It produces beauty—but for the worker, deformity” (MER 73). Marx argues capitalism is a system in which the laborer is repeatedly harmed and estranged from himself, his labor, and other people, while the owner of his labor – the capitalist – receives the benefits ( MER 74). And while industry progresses, the worker “sinks deeper and deeper below the conditions of existence of his own class” ( MER 483). ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ But while Marx critiques the political economy, he does not explicitly say “capitalism is wrong.” Rather, his close examination of the system makes its flaws obvious. Only once the working class realizes the flaws of the system, Marx believes, will they - must they - rise up against their bourgeois masters and achieve the necessary and inevitable communist revolution.
Not every paragraph will be structured exactly like this one, of course. But as you draft your own paragraphs, look for all three of these elements: topic sentence, evidence, and analysis.
- picture_as_pdf Anatomy Of a Body Paragraph

How to Write a Body Paragraph for a College Essay
- Body paragraphs play an essential role in crafting a successful college essay.
- The basic body paragraph structure has six parts, including a topic sentence and evidence.
- Key paragraphing tips include moving transitions and avoiding repetition in your essay.
Paragraphing is an essential key to successful academic writing. A writer’s organizing decisions control the reader’s (i.e., your professor’s) attention by raising or decreasing engagement with the subject. Writing an effective paragraph includes determining what goes into each paragraph and how your paragraphs and ideas relate to one another.
The first paragraph in any academic essay is the introduction , and the last is the conclusion, both of which are critical to crafting a compelling essay. But what is a body paragraph? The body paragraphs — all the paragraphs that come between the intro and conclusion — comprise the bulk of the essay and together form the student’s primary argument.
In this article, we look at the function of a body paragraph and provide guidance on how to write a good body paragraph for any college essay.
What Is the Purpose of a Body Paragraph?
Body paragraphs play an indispensable role in proving the essay’s thesis , which is presented in the introduction. As a sequence, body paragraphs provide a path from the introduction — which forecasts the structure of the essay’s content — to the conclusion, which summarizes the arguments and looks at how final insights may apply in different contexts. Each body paragraph must therefore relate logically to the one immediately before and after it.
If you can eliminate a paragraph without losing crucial information that supports your thesis claim, then that paragraph is a divergence from this path and should be edited so that it fits with the rest of your essay and contains necessary evidence, context, and/or details.
Each body paragraph must relate logically to the one immediately before and after it, and must also focus on a single topic or idea.
Each paragraph must also focus on a single topic or idea. If the topic is complex or has multiple parts, consider whether each would benefit from its own paragraph.
People tend to absorb information in short increments, and readers usually time mental breaks at paragraph ends. This stop is also where they pause to consider content or write notes. As such, you should avoid lengthy paragraphs.
Finally, most academic style conventions frown upon one-sentence paragraphs. Similar to how body paragraphs can be too long and messy, one-sentence paragraphs can feel far too short and underdeveloped. Following the six steps below will allow you to avoid this style trap.
Popular Online Programs
Learn about start dates, transferring credits, availability of financial aid, and more by contacting the universities below.
6 Steps for Writing an Effective Body Paragraph
There are six main steps to crafting a compelling body paragraph. Some steps are essential in every paragraph and must appear in a fixed location, e.g., as the first sentence. Writers have more flexibility with other steps, which can be delayed or reordered (more on this later).
Step 1: Write a Topic Sentence
Consider the first sentence in a body paragraph a mini-thesis statement for that paragraph. The topic sentence should establish the main point of the paragraph and bear some relationship to the essay’s overarching thesis statement.
In theory, by reading only the topic sentence of every paragraph, a reader should be able to understand a summary outline of the ideas that prove your paper’s thesis. If the topic sentence is too complex, it’ll confuse the reader and set you up to write paragraphs that are too long-winded.
Step 2: Unpack the Topic Sentence
Now, it’s time to develop the claims in your paragraph’s topic sentence by explaining or expanding all the individual parts. In other words, you’ll parse out the discussion points your paragraph will address to support its topic sentence.
You may use as many sentences as necessary to achieve this step, but if there are too many components, consider writing a paragraph for each of them, or for a few that fit particularly well together. In this case, you’ll likely need to revise your topic sentence. The key here is only one major idea per paragraph.
Step 3: Give Evidence
The next step is to prove your topic sentence’s claim by supplying arguments, facts, data, and quotations from reputable sources . The goal is to offer original ideas while referencing primary sources and research, such as books, journal articles, studies, and personal experiences.
Step 4: Analyze the Evidence
Never leave your body paragraph’s evidence hanging. As the writer, it’s your job to do the linking work, that is, to connect your evidence to the main ideas the paragraph seeks to prove. You can do this by explaining, expanding, interpreting, or commentating on your evidence. You can even debunk the evidence you’ve presented if you want to give a counterargument.
Step 5: Prove Your Objective
This next step consists of two parts. First, tie up your body paragraph by restating the topic sentence. Be sure to use different language so that your writing is not repetitive. Whereas the first step states what your paragraph will prove, this step states what your paragraph has proven .
Second, every three or four paragraphs, or where it seems most fitting, tie your proven claim back to the paper’s thesis statement on page 1. Doing so makes a concrete link between your discussion and the essay’s main claim.
Step 6: Provide a Transition
A transition is like a bridge with two ramps: The first ramp takes the reader out of a topic or paragraph, whereas the second deposits them into a new, albeit related, topic. The transition must be smooth, and the connection between the two ideas should be strong and clear.
Purdue University lists some of the most commonly used transition words for body paragraphs.
Body Paragraph Example
Here is an example of a well-structured body paragraph, and the beginning of another body paragraph, from an essay on William Shakespeare’s play “Twelfth Night.” See whether you can identify the topic sentence and its development, the evidence, the writer’s analysis and proof of the objective, and the transition to the next paragraph.
As well as harmony between parent and child, music represents the lasting bond between romantic couples. Shakespeare illustrates this tunefulness in the relationship between Viola and Orsino. Viola’s name evokes a musical instrument that fits between violin and cello when it comes to the depth of tone. Orsino always wants to hear sad songs until he meets Viola, whose wit forces him to be less gloomy. The viola’s supporting role in an orchestra, and Orsino’s need for Viola to break out of his depression, foreshadow the benefits of the forthcoming marriage between the two. The viola is necessary in both lamenting and celebratory music. Shakespeare uses the language of orchestral string music to illustrate how the bonds of good marriages often depend on mediating between things.
The play also references cacophonous music. The unharmonious songs that Sir Toby and Andrew sing illustrate how indulging bad habits is bad for society as a whole. These characters are always drunk, do no work, play mean tricks, and are either broke or squander their money. …
Strategies for Crafting a Compelling Body Paragraph
Break down complex topic sentences.
A topic sentence with too many parts will force you to write a lot of support. But as you already know, readers typically find long paragraphs more difficult to absorb. The solution is to break down complicated topic sentences into two or more smaller ideas, and then devote a separate paragraph for each.
Move the Transition to the Following Paragraph
Though a body paragraph should always begin with a topic sentence and end with proof of your objective — sometimes with a direct connection to the essay’s thesis — you don’t need to include the transition in that paragraph; instead, you may insert it right before the topic sentence of the next paragraph.
For example, if a body paragraph is already incredibly long, you might want to avoid adding a transition at the end.
Your body paragraphs should be no longer than half to three-quarters of a double-spaced page with 1-inch margins in Times New Roman 12-point font. A little longer is sometimes acceptable, but you should generally avoid writing paragraphs that fill or exceed one page.
Shift Around Some of the Paragraph Steps Above
The steps above are a general guide, but you may change the order of them (to an extent). For instance, if your topic sentence is fairly complicated, you might need to unpack it into several parts, with each needing its own evidence and analysis.
You could also swap steps 3 and 4 by starting with your analysis and then providing evidence. Even better, consider alternating between giving evidence and providing analysis.
The idea here is that using more than one design for your paragraphs usually makes the essay more engaging. Remember that monotony can make a reader quickly lose interest, so feel free to change it up.
Don’t Repeat the Same Information Between Paragraphs
If similar evidence or analysis works well for other paragraphs too, you need to help the reader make these connections. You can do this by incorporating signal phrases like “As the following paragraph also indicates” and “As already stated.”
Explore More College Resources

How to Choose Your College Class Schedule
Learn how to create the best class schedule each semester by considering important academic and nonacademic factors.

by Steve Bailey
Updated March 22, 2023

Full-Time vs. Part-Time Student: What’s the Difference?
Discover the challenges and opportunities full-time vs. part-time students face and get tips on which college experience is right for you.

by Marisa Upson
Updated October 12, 2023

Summer Semester: When Does It Start? And Should You Enroll?
School’s out — or, rather, in — for summer. Discover the pros and cons of enrolling in an optional summer semester in college.

by Anne Dennon
Updated March 20, 2023

How to write an essay: Body
- What's in this guide
- Introduction
- Essay structure
- Additional resources
Body paragraphs
The essay body itself is organised into paragraphs, according to your plan. Remember that each paragraph focuses on one idea, or aspect of your topic, and should contain at least 4-5 sentences so you can deal with that idea properly.
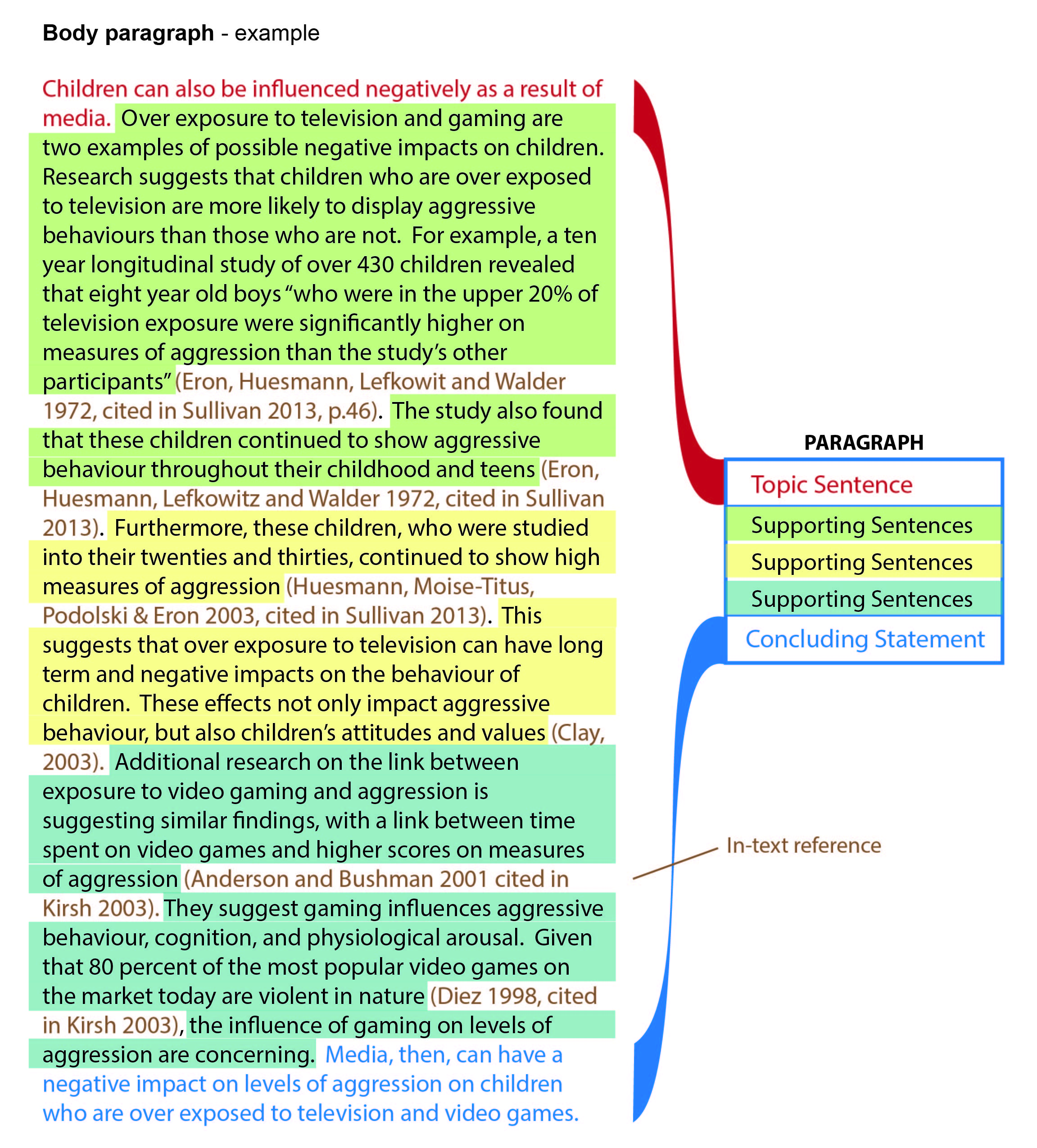
Each body paragraph has three sections. First is the topic sentence . This lets the reader know what the paragraph is going to be about and the main point it will make. It gives the paragraph’s point straight away. Next – and largest – is the supporting sentences . These expand on the central idea, explaining it in more detail, exploring what it means, and of course giving the evidence and argument that back it up. This is where you use your research to support your argument. Then there is a concluding sentence . This restates the idea in the topic sentence, to remind the reader of your main point. It also shows how that point helps answer the question.

Pathways and Academic Learning Support

- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Nov 29, 2023 1:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.2 Writing Body Paragraphs
Learning objectives.
- Select primary support related to your thesis.
- Support your topic sentences.
If your thesis gives the reader a roadmap to your essay, then body paragraphs should closely follow that map. The reader should be able to predict what follows your introductory paragraph by simply reading the thesis statement.
The body paragraphs present the evidence you have gathered to confirm your thesis. Before you begin to support your thesis in the body, you must find information from a variety of sources that support and give credit to what you are trying to prove.
Select Primary Support for Your Thesis
Without primary support, your argument is not likely to be convincing. Primary support can be described as the major points you choose to expand on your thesis. It is the most important information you select to argue for your point of view. Each point you choose will be incorporated into the topic sentence for each body paragraph you write. Your primary supporting points are further supported by supporting details within the paragraphs.
Remember that a worthy argument is backed by examples. In order to construct a valid argument, good writers conduct lots of background research and take careful notes. They also talk to people knowledgeable about a topic in order to understand its implications before writing about it.
Identify the Characteristics of Good Primary Support
In order to fulfill the requirements of good primary support, the information you choose must meet the following standards:
- Be specific. The main points you make about your thesis and the examples you use to expand on those points need to be specific. Use specific examples to provide the evidence and to build upon your general ideas. These types of examples give your reader something narrow to focus on, and if used properly, they leave little doubt about your claim. General examples, while they convey the necessary information, are not nearly as compelling or useful in writing because they are too obvious and typical.
- Be relevant to the thesis. Primary support is considered strong when it relates directly to the thesis. Primary support should show, explain, or prove your main argument without delving into irrelevant details. When faced with lots of information that could be used to prove your thesis, you may think you need to include it all in your body paragraphs. But effective writers resist the temptation to lose focus. Choose your examples wisely by making sure they directly connect to your thesis.
- Be detailed. Remember that your thesis, while specific, should not be very detailed. The body paragraphs are where you develop the discussion that a thorough essay requires. Using detailed support shows readers that you have considered all the facts and chosen only the most precise details to enhance your point of view.
Prewrite to Identify Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
Recall that when you prewrite you essentially make a list of examples or reasons why you support your stance. Stemming from each point, you further provide details to support those reasons. After prewriting, you are then able to look back at the information and choose the most compelling pieces you will use in your body paragraphs.
Choose one of the following working thesis statements. On a separate sheet of paper, write for at least five minutes using one of the prewriting techniques you learned in Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
- Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
- Students cheat for many different reasons.
- Drug use among teens and young adults is a problem.
- The most important change that should occur at my college or university is ____________________________________________.
Select the Most Effective Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
After you have prewritten about your working thesis statement, you may have generated a lot of information, which may be edited out later. Remember that your primary support must be relevant to your thesis. Remind yourself of your main argument, and delete any ideas that do not directly relate to it. Omitting unrelated ideas ensures that you will use only the most convincing information in your body paragraphs. Choose at least three of only the most compelling points. These will serve as the topic sentences for your body paragraphs.
Refer to the previous exercise and select three of your most compelling reasons to support the thesis statement. Remember that the points you choose must be specific and relevant to the thesis. The statements you choose will be your primary support points, and you will later incorporate them into the topic sentences for the body paragraphs.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
When you support your thesis, you are revealing evidence. Evidence includes anything that can help support your stance. The following are the kinds of evidence you will encounter as you conduct your research:
- Facts. Facts are the best kind of evidence to use because they often cannot be disputed. They can support your stance by providing background information on or a solid foundation for your point of view. However, some facts may still need explanation. For example, the sentence “The most populated state in the United States is California” is a pure fact, but it may require some explanation to make it relevant to your specific argument.
- Judgments. Judgments are conclusions drawn from the given facts. Judgments are more credible than opinions because they are founded upon careful reasoning and examination of a topic.
- Testimony. Testimony consists of direct quotations from either an eyewitness or an expert witness. An eyewitness is someone who has direct experience with a subject; he adds authenticity to an argument based on facts. An expert witness is a person who has extensive experience with a topic. This person studies the facts and provides commentary based on either facts or judgments, or both. An expert witness adds authority and credibility to an argument.
- Personal observation. Personal observation is similar to testimony, but personal observation consists of your testimony. It reflects what you know to be true because you have experiences and have formed either opinions or judgments about them. For instance, if you are one of five children and your thesis states that being part of a large family is beneficial to a child’s social development, you could use your own experience to support your thesis.
Writing at Work
In any job where you devise a plan, you will need to support the steps that you lay out. This is an area in which you would incorporate primary support into your writing. Choosing only the most specific and relevant information to expand upon the steps will ensure that your plan appears well-thought-out and precise.
You can consult a vast pool of resources to gather support for your stance. Citing relevant information from reliable sources ensures that your reader will take you seriously and consider your assertions. Use any of the following sources for your essay: newspapers or news organization websites, magazines, encyclopedias, and scholarly journals, which are periodicals that address topics in a specialized field.
Choose Supporting Topic Sentences
Each body paragraph contains a topic sentence that states one aspect of your thesis and then expands upon it. Like the thesis statement, each topic sentence should be specific and supported by concrete details, facts, or explanations.
Each body paragraph should comprise the following elements.
topic sentence + supporting details (examples, reasons, or arguments)
As you read in Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” , topic sentences indicate the location and main points of the basic arguments of your essay. These sentences are vital to writing your body paragraphs because they always refer back to and support your thesis statement. Topic sentences are linked to the ideas you have introduced in your thesis, thus reminding readers what your essay is about. A paragraph without a clearly identified topic sentence may be unclear and scattered, just like an essay without a thesis statement.
Unless your teacher instructs otherwise, you should include at least three body paragraphs in your essay. A five-paragraph essay, including the introduction and conclusion, is commonly the standard for exams and essay assignments.
Consider the following the thesis statement:
Author J.D. Salinger relied primarily on his personal life and belief system as the foundation for the themes in the majority of his works.
The following topic sentence is a primary support point for the thesis. The topic sentence states exactly what the controlling idea of the paragraph is. Later, you will see the writer immediately provide support for the sentence.
Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from posttraumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced themes in many of his works.
In Note 9.19 “Exercise 2” , you chose three of your most convincing points to support the thesis statement you selected from the list. Take each point and incorporate it into a topic sentence for each body paragraph.
Supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Topic sentence: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
Draft Supporting Detail Sentences for Each Primary Support Sentence
After deciding which primary support points you will use as your topic sentences, you must add details to clarify and demonstrate each of those points. These supporting details provide examples, facts, or evidence that support the topic sentence.
The writer drafts possible supporting detail sentences for each primary support sentence based on the thesis statement:
Thesis statement: Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
Supporting point 1: Dogs can scare cyclists and pedestrians.
Supporting details:
- Cyclists are forced to zigzag on the road.
- School children panic and turn wildly on their bikes.
- People who are walking at night freeze in fear.
Supporting point 2:
Loose dogs are traffic hazards.
- Dogs in the street make people swerve their cars.
- To avoid dogs, drivers run into other cars or pedestrians.
- Children coaxing dogs across busy streets create danger.
Supporting point 3: Unleashed dogs damage gardens.
- They step on flowers and vegetables.
- They destroy hedges by urinating on them.
- They mess up lawns by digging holes.
The following paragraph contains supporting detail sentences for the primary support sentence (the topic sentence), which is underlined.
Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from posttraumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced the themes in many of his works. He did not hide his mental anguish over the horrors of war and once told his daughter, “You never really get the smell of burning flesh out of your nose, no matter how long you live.” His short story “A Perfect Day for a Bananafish” details a day in the life of a WWII veteran who was recently released from an army hospital for psychiatric problems. The man acts questionably with a little girl he meets on the beach before he returns to his hotel room and commits suicide. Another short story, “For Esmé – with Love and Squalor,” is narrated by a traumatized soldier who sparks an unusual relationship with a young girl he meets before he departs to partake in D-Day. Finally, in Salinger’s only novel, The Catcher in the Rye , he continues with the theme of posttraumatic stress, though not directly related to war. From a rest home for the mentally ill, sixteen-year-old Holden Caulfield narrates the story of his nervous breakdown following the death of his younger brother.
Using the three topic sentences you composed for the thesis statement in Note 9.18 “Exercise 1” , draft at least three supporting details for each point.
Thesis statement: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Supporting details: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
You have the option of writing your topic sentences in one of three ways. You can state it at the beginning of the body paragraph, or at the end of the paragraph, or you do not have to write it at all. This is called an implied topic sentence. An implied topic sentence lets readers form the main idea for themselves. For beginning writers, it is best to not use implied topic sentences because it makes it harder to focus your writing. Your instructor may also want to clearly identify the sentences that support your thesis. For more information on the placement of thesis statements and implied topic statements, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
Print out the first draft of your essay and use a highlighter to mark your topic sentences in the body paragraphs. Make sure they are clearly stated and accurately present your paragraphs, as well as accurately reflect your thesis. If your topic sentence contains information that does not exist in the rest of the paragraph, rewrite it to more accurately match the rest of the paragraph.
Key Takeaways
- Your body paragraphs should closely follow the path set forth by your thesis statement.
- Strong body paragraphs contain evidence that supports your thesis.
- Primary support comprises the most important points you use to support your thesis.
- Strong primary support is specific, detailed, and relevant to the thesis.
- Prewriting helps you determine your most compelling primary support.
- Evidence includes facts, judgments, testimony, and personal observation.
- Reliable sources may include newspapers, magazines, academic journals, books, encyclopedias, and firsthand testimony.
- A topic sentence presents one point of your thesis statement while the information in the rest of the paragraph supports that point.
- A body paragraph comprises a topic sentence plus supporting details.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How To Write Essay Body Paragraphs

- 3-minute read
- 4th October 2022
Writing essays is an unavoidable part of student life . And even if you’re not pursuing a career that involves much writing, if you can boost the quality of your essays , you’ll improve your grades and have a better chance of reaching your goals.
One effective way to improve your writing is to strengthen your essay body paragraphs. Those are the paragraphs between the introduction and the conclusion. In our guide below, we’ll consider four components of body paragraphs:
● Purpose
● Evidence
● Analysis
● Connection
For each paragraph you write , ask yourself: Why are you writing this paragraph? What point are you trying to make? This can be turned into a topic sentence, which is a brief sentence at the beginning of the paragraph clearly stating its focus.
Let’s say our essay is arguing that Fall is the best season, and, in this paragraph, we’re promoting the enjoyableness of Fall activities. Our topic sentence could be something like:
Fall activities, like apple picking, visiting a pumpkin patch, and playing in the leaves, are more enjoyable than activities in other seasons.
Now that you have a clear idea of the point you’d like to make, you must support it with facts. You can do this by citing scientific and/or academic sources; sharing data from case studies; and providing information that you’ve discovered yourself, such as by conducting your own study or describing a real-life experience.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
We sent a survey to 100 participants. One question asked: “Which activity do you prefer: apple picking, building a snowman, planting flowers, or kayaking?” Sixty percent of respondents chose apple picking.
Now that you’ve provided evidence, critically analyzing it is key to strengthening your essay. This involves explaining how the presented facts support your argument, what counterarguments exist, and if there are any alternative points of view.
Although the response to one question indicated that 55% of respondents prefer swimming to jumping in piles of leaves, the responses to the rest of the questions in the survey showed that most participants chose Fall activities as their favorites. These findings indicate that Fall activities are more enjoyable than other types of activities.
Each paragraph must be connected to the paragraphs around it and the main point. You can achieve this by using transitional words and sentences at the end of the paragraph to summarize the current paragraph’s findings and introduce the next one. Transition words include likewise , however , furthermore , accordingly , and in summary .
Therefore, Fall is the best season when it comes to activities. Furthermore, the clothing worn during this season is also superior.
Proofreading and Editing
This step should not be overlooked. Even the best writers will miss errors in their own writing, so it’s crucial to have an outside pair of eyes check your work for spelling, grammar, punctuation, sentence structure, and readability.
Our expert editors can also ensure your referencing style is followed correctly, offer suggestions for areas where your meaning isn’t clear, and even format your document for you! Try our service for free today by uploading a 500-word sample .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

COMMENTS
You can work through the body in three main stages: Create an outline of what you want to say and in what order. Write a first draft to get your main ideas down on paper. Write a second draft to clarify your arguments and make sure everything fits together. This article gives you some practical tips for how to approach each stage.
Your essay’s body paragraphs are where you support your thesis statement with facts and evidence. Each body paragraph should focus on one supporting argument for your thesis by discussing related data, content, or events.
When you write strong, clear paragraphs, you are guiding your readers through your argument by showing them how your points fit together to support your thesis. The number of paragraphs in your essay should be determined by the number of steps you need to take to build your argument.
A body paragraph is any paragraph in the middle of an essay, paper, or article that comes after the introduction but before the conclusion. Generally, body paragraphs support the work’s thesis and shed new light on the main topic, whether through empirical data, logical deduction, deliberate persuasion, or anecdotal evidence.
In this article, we’ll explore how to write a body paragraph for an essay and what methods to use to make it impactful. We’ll walk you through the body paragraph format, purpose, and principal elements, Cover using evidence wisely and make sure your sentences connect well,
But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and organize your text logically.
Body paragraphs play an essential role in crafting a successful college essay. The basic body paragraph structure has six parts, including a topic sentence and evidence. Key paragraphing tips include moving transitions and avoiding repetition in your essay. Paragraphing is an essential key to successful academic writing.
Each body paragraph has three sections. First is the topic sentence. This lets the reader know what the paragraph is going to be about and the main point it will make. It gives the paragraph’s point straight away. Next – and largest – is the supporting sentences.
Each body paragraph contains a topic sentence that states one aspect of your thesis and then expands upon it. Like the thesis statement, each topic sentence should be specific and supported by concrete details, facts, or explanations. Each body paragraph should comprise the following elements.
One effective way to improve your writing is to strengthen your essay body paragraphs. Those are the paragraphs between the introduction and the conclusion. In our guide below, we’ll consider four components of body paragraphs: Purpose. Evidence. Analysis. Connection.