- How it works


How to Write a Statement of a Problem in Research with Steps
Published by Grace Graffin at August 11th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
Research is a systematic investigation to find new techniques, products or processes to solve problems. Apart from being systematic, research is empirical in nature: it’s based on observations and measurement of those observations.
It’s what comes before the development. Impacts and policies that are born in society are borne out of the research.
The most important step to perform any research is to identify a problem that needs to be solved. Therefore, it is necessary to define a research problem before starting the actual research process. Once a research problem has been identified, the next step is to write a problem statement.
Philosopher Kaoru Ishikawa said: “You will have a problem half-solved by defining it correctly on the first day.”
This quote perfectly reflects the importance of a problem statement in research. Before writing a problem statement, it is essential to pinpoint a specific problem, the difficulties you can expect to face as you try to solve it and the research gaps you aim to fill with your research.
The last part—how your research aims to fill a gap in the existing literature—will act as a springboard to the solution(s) that policy makers, for instance, might eventually take to solve that problem.
Filling a gap, therefore, is very important towards solving an existing problem.
What is a Problem Statement?
A problem statement is a clear and concise description of an issue or challenge that needs to be addressed. It typically outlines the existing gap between the current state (what currently is) and the desired state (what should be). Crafting a well-defined problem statement is critical for problem-solving, research, or project planning, as it serves as a guidepost and sets the direction for the subsequent steps.
Research Problem and Research Method – A Cyclical Process
The type of research strategy used in research determines whether you will be analysing theoretical problems to add value to existing knowledge, discussing practical issues to become an agent of change for an organisation or industry or looking at both aspects in relation to any given problem.
However, the kind of problem you aim to tackle with your research, to begin with, will also help you narrow down which research design , method or strategy to opt for.
This is therefore a cyclical process. Your research aim guides your research design can help you focus on a specific kind of research gap/problem.
However, generally, your research will focus on one or the other.
Here is all you need to know about how to write a statement of the problem in research, also called problem statement by some research writers .
Why do you Need a Statement of the Problem, to Begin with?
You need a statement of the problem to transform a generalised problem into a well-defined, brief, targeted statement to perform research in the decision-making process. The problem statement helps the researcher to identify the purpose of the ongoing research.
The problem statement in the dissertation is the pillar of the introduction chapter through which the reader can understand the research questions and scope of the project. If you do not define the problem statement properly, the results might become unmanageable.
Writing Problem Statement for a Business or Organisation
In the business world, problem statements provide the basis for the enhancement and refinement of projects. Without identifying and understanding the problem, it will be hard to find and effectively implement solutions.
A stand-alone document that solely provides an in-depth and detailed problem statement is usually the answer for organisations and businesses when it becomes imperative to find the solution to a problem.
Writing Problem Statement for Academic Research
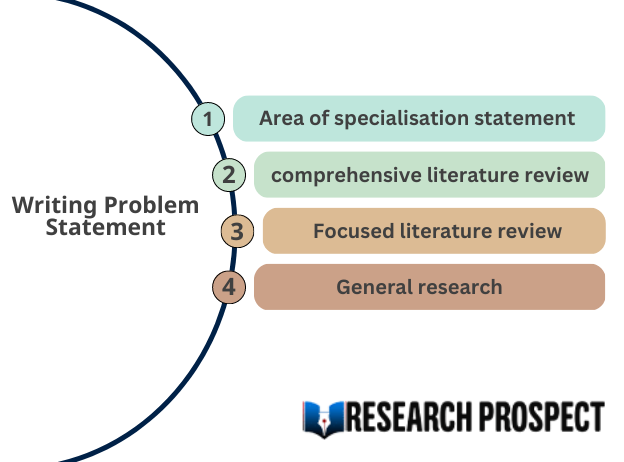
Hire an Expert Writer
Proposal and dissertation orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Plagiarism free
- 100% Confidential
- Never Resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements
Problem Statement – How to Write it
Ask yourself the following questions before writing the problem statement:
- What is wrong in the research area/subarea XYZ?
- Where did it happen?
- When did it happen?
- To what extent (how much)?
- I know that because…(evidence)
‘What’ always defines the defect of the problem at hand and explains why it matters? ‘Where’ defines the geological location of the problem. ‘When’ defines the history and the pattern of the problem, the goal of the stated problem and the scope of research.
‘How much’ defines the trend of the problem as to how many objects are facing the same defect and to what extent. The last part, ‘I know this because…’, will help the researcher identify the standard(s) that he must meet.
Step 1: Understanding the Problem
The problem statement should provide a clear and concise background to the research problem you are investigating. Before starting your research , review the literature about the specific problem and find a gap to fill with your own research.
Practical Research Problem Statement
If you are doing experimental research , you can identify problems by talking to people working in a relevant field, studying research reports, and reviewing previous research. Here are some examples of practical research problems:
- A problem that hinders the efficiency of a company
- An institutional process that needs interventions
- An area of concern in your field/sub-field of interest
- Members of a society facing a specific difficulty
The problem statement should focus on the details related to the problem, such as:
- When and where was the problem observed?
- Who is/are affected by it?
- What research has been conducted and what practical steps have been taken to resolve the problem?
Example of Practical Research Problem Statement
The production of a company is low for the months of July and August every year. Initial research has been conducted by the company, which revealed poor production in July and August is due to the unavailability of local raw material.
The company has made some effective attempts at engaging the local suppliers to ensure an uninterrupted supply of the raw material, but these efforts are yet to have any significant impact on the production levels.
Theoretical Research Problem Statement
According to USC Libraries, “A theoretical framework consists of concepts and, together with their definitions and reference to relevant scholarly literature, existing theory that is used for your particular study…theoretical framework must demonstrate an understanding of theories and concepts…relevant to the topic of your research paper and that relate to the broader areas of knowledge being considered.”
The theoretical research indirectly contributes to the change by identifying the problem, expanding knowledge and improving understanding. The researcher can find a specific problem by brainstorming the topic and reviewing already published theories and research.
When writing a problem statement based on a theoretical research problem , it is important to recognise the historical, geographical, social and scientific background. Here are the elements of the theoretical problem statement framework that you should consider:
- What are the facts about the problem?
- Does the problem relate to a certain geographical area or time period?
- How is the problem discussed and explained in the existing literature?
Example of Theoretical Research Problem Statement
The production of a company is low for July and August every year. Initial research has been conducted by the company, which revealed poor production in July and August is due to the unavailability of local raw material. The company has made some effective attempts to engage the local suppliers to ensure an uninterrupted raw material supply. Still, these efforts are yet to have any significant impact on the production levels.
Looking for Dissertation Help?
Researchprospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with dissertations across a variety of STEM disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

Step 2 – Show why it’s Important and Relevant
By discussing the importance of the problem under investigation, you are demonstrating the relevance of your research. However, this does not mean that you will end up discovering something unimaginable or extraordinary.
The objective here is to clearly state how and why your research problem is relevant in your chosen area of study and why it requires further research.
As indicated previously, practical research deals with a problem affecting society, social group, firm or organisation on a broader scale. To elaborate on why it is important to solve this problem and why your research is significant, you could consider the following questions:
- What will be the consequences if the problem remains unsolved?
- Who do these consequences have the most implications for?
- What is the wider relevance of the problem being investigated?
Low production in July and August negatively affects the company’s marketing capital, thereby becoming an area of deep concern for the directors and stakeholders. The marketing budget cut in July and August is hindering its ability to promote its products uninterruptedly.
Addressing this problem will have practical benefits for the company and help establish the reasons for disruption in raw material supply.
The relevance of all theoretical issues may not be too obvious, even though most theoretical problems do have practical implications. Here are some questions for you to ponder to establish the importance of your research problem:
- Will your research help to advance understanding of the topic under investigation?
- Are there any benefits of you resolving the problem for other researchers who wish to explore this topic further in the future?
- What are the direct or indirect implications (s) of the problem you are trying to solving?
The new forms of employment such as freelance, contract-based work and zero-hour work arrangements are recognised as either a manipulative last option or a flexible active choice. It is necessary to conduct comprehensive qualitative research to uncover why fresh graduates take up these types of employment in the gig economy. There is a need to advance more vigorous concepts relating to instability and flexibility in modern forms of employment from employees’ perspectives, which will also help shape future policies.
Also see: How to Write the Abstract for Dissertation
Step 3 – Declaring the Problem
Before you jump on to state your research’s problem statements, it’s important to devote a sentence or two to let your readers know the precise, narrowed-down research problem you will be discussing about.
For language clarity purposes, here are some strong opening statements to achieve this step:
- Recently, there has been growing interest in …
- The possibility of…has generated wide interest in …
- The development of…is a classic problem in…
- The development of…has led to the hope that …
- The…has become a favourite topic for analysis …
- Knowledge of…has great importance for …
- The study of…has become an important aspect of …
- A central issue in…is…
- The…has been extensively studied in recent years.
- Many investigators have recently turned to …
- The relationship between…has been investigated by many researchers.
- Many recent studies have found out…
Step 4 – Establishing Aim and Objectives
The last step in writing a problem statement is to provide a framework for solving the problem. This will help you, the researcher, stay focused on your research aims and not stray; it will also help you readers keep in mind the reason as to why you conducted this study, to begin with.
A good problem statement does not provide the exact solution to any problem. Rather, it focuses more on how to effectively understand or tackle a problem by establishing the possible causes.
The aim of a research study is its end goal or overall purpose. Following are some examples of how you can craft your research aim statements:
- This research study aims to investigate…
- This paper is aimed at exploring…
- This research aims to identify…
On the other hand, objectives are the smaller steps that a researcher must take to address the aim of the research. Once you have laid out the research problem your research will deal with, it’s important to next mention the how behind that. Objectives are mostly imperative statements, often beginning with transitive verbs like ‘to analyse,’ ‘to investigate,’ etc.
Some more examples are:
- Statistical analysis will be conducted to determine…
- Both quantitative and qualitative research methods will be employed to probe…
- Face-to-face interviews will be carried out with the participants to establish…
Practical Research Aim and Objectives
This project aims to identify the causes of disturbed supply of raw material in the region, which resulted in low production for the company in July and August. This will be achieved by conducting interviews and surveys with the suppliers to understand why the supply is unpredictable in those two months and what can be done to ensure orderliness. Practical experiments will also be conducted to observe the effectiveness of proposed solutions.
Theoretical Research Aim and Objectives
This study aims to understand and unearth the experiences of fresh graduates in the modern economy. The sample population will participate in this study through qualitative research methods, which are expected to provide a deeper insight into the perceptions and motives of these fresh graduates working as freelancers and contract-based employees. The data collected from this exercise and the existing literature on the topic will be analysed in statistical analysis software.
TIP: Search the common themes of the problem statement in your field of research before writing a problem statement.
Also see: Argumentative Essay Writing Service
Problem Statement versus Significance of the Study
Even though both may sound similar, the statement of the problem and the significance of your study are going to be different. The latter does develop upon and from the former, though.
The problem statement tells your readers what’s wrong, whereas the significance of the study will tell them how your research contributed to that problem. You can’t have a significance of a study without mentioning the problem statement first.
Furthermore, signifying your study implies mentioning 4 key points related to it:
- How your study will further develop the theory behind the existing problem
- Practical solutions that might be implemented to solve the problem (especially in field research work)
- Whether your study or research will pave way for innovative methods to solve the existing problem.
- How your study can help in policy making and implementation, impact studies, etc.
Problem statement in research is the description of an existing issue that needs to be addressed. The problem statement is a focal point of any research and a bridge between the literature review and the research methodology .
Problem statement often has three elements; the problem itself, the method of solving the problem, and the purpose. There are five aspects of every problem: What, Where, When, to what extent, and what defects you know about the topic. Here is an example of a problem statement in a research proposal for your better understanding.
If you wish to know more about how to start your research process, then you might want to take a look at the “ Starting the Research Process ” section on our website, which has several articles relating to a research problem , problem statement, research aim and objectives, and research proposal .
ResearchProspect is a UK-registered business that offers academic support and assistance to students across the globe. Our writers can help you with individual chapters of your dissertation or the full dissertation writing service , no matter how urgent or complex your requirements might be.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it necessary to write a problem statement.
Yes, the most important step to perform any research is to identify a problem that needs to be solved. Therefore, it is necessary to define a research problem before starting the actual research process .
How is a problem statement different from a problem statement written for an organisation?
In the business world, problem statements provide the basis for the enhancement and refinement of projects. Whereas, in academic research, A problem statement helps researchers understand and realise organised the significance of a research problem .
What is a practical research problem?
Doing experimental research can identify problems by talking to people working in a relevant field, studying research reports, and reviewing previous research.
What is a theoretical research problem?
A theoretical research problem is when the researcher finds a specific problem by brainstorming and reviewing already published theories and research.
You May Also Like
Writing a dissertation can be tough if this is the first time you are doing it. You need to look into relevant literature, analyze past researches, conduct surveys, interviews etc.
Have you failed dissertation, assignment, exam or coursework? Don’t panic because you are not alone. Get help from our professional UK qualified writers!
Table of contents is an essential part of dissertation paper. Here is all you need to know about how to create the best table of contents for dissertation.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

- Research Process
What is a Problem Statement? [with examples]
- 5 minute read
- 985.7K views
Table of Contents
The statement of the problem is one of the first things that a colleague or potential client will read. With the vastness of the information available at one’s fingertips in the online9 world, your work may have just a few seconds to draw in a reader to take a deeper look at your proposal before moving on to the next option. It explains quickly to the reader, the problem at hand, the need for research, and how you intend to do it.
A strong, clear description of the problem that drew you to your research has to be straightforward, easy to read and, most important, relevant. Why do you care about this problem? How can solving this problem impact the world? The problem statement is your opportunity to explain why you care and what you propose to do in the way of researching the problem.
A problem statement is an explanation in research that describes the issue that is in need of study . What problem is the research attempting to address? Having a Problem Statement allows the reader to quickly understand the purpose and intent of the research. The importance of writing your research proposal cannot be stressed enough. Check for more information on Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal .
It is expected to be brief and concise , and should not include the findings of the research or detailed data . The average length of a research statement is generally about one page . It is going to define the problem, which can be thought of as a gap in the information base. There may be several solutions to this gap or lack of information, but that is not the concern of the problem statement. Its purpose is to summarize the current information and where a lack of knowledge may be presenting a problem that needs to be investigated .
The purpose of the problem statement is to identify the issue that is a concern and focus it in a way that allows it to be studied in a systematic way . It defines the problem and proposes a way to research a solution, or demonstrates why further information is needed in order for a solution to become possible.
What is Included in a Problem Statement?
Besides identifying the gap of understanding or the weakness of necessary data, it is important to explain the significance of this lack.
-How will your research contribute to the existing knowledge base in your field of study?
-How is it significant?
-Why does it matter?
Not all problems have only one solution so demonstrating the need for additional research can also be included in your problem statement. Once you identify the problem and the need for a solution, or for further study, then you can show how you intend to collect the needed data and present it.
How to Write a Statement of Problem in Research Proposal
It is helpful to begin with your goal. What do you see as the achievable goal if the problem you outline is solved? How will the proposed research theoretically change anything? What are the potential outcomes?
Then you can discuss how the problem prevents the ability to reach your realistic and achievable solution. It is what stands in the way of changing an issue for the better. Talk about the present state of affairs and how the problem impacts a person’s life, for example.
It’s helpful at this point to generally layout the present knowledge and understanding of the subject at hand, before then describing the gaps of knowledge that are currently in need of study. Your problem statement is a proposed solution to address one of these gaps.
A good problem statement will also layout the repercussions of leaving the problem as it currently stands. What is the significance of not addressing this problem? What are the possible future outcomes?
Example of Problem Statement in Research Proposal
If, for example , you intended to research the effect of vitamin D supplementation on the immune system , you would begin with a review of the current knowledge of vitamin D’s known function in relation to the immune system and how a deficiency of it impacts a person’s defenses.
You would describe the ideal environment in the body when there is a sufficient level of vitamin D. Then, begin to identify the problems associated with vitamin D deficiency and the difficulty of raising the level through supplementation, along with the consequences of that deficiency. Here you are beginning to identify the problem of a common deficiency and the current difficulty of increasing the level of vitamin D in the blood.
At this stage, you may begin to identify the problem and narrow it down in a way that is practical to a research project. Perhaps you are proposing a novel way of introducing Vitamin D in a way that allows for better absorption by the gut, or in a combination with another product that increases its level in the blood.
Describe the way your research in this area will contribute to the knowledge base on how to increase levels of vitamin D in a specific group of subjects, perhaps menopausal women with breast cancer. The research proposal is then described in practical terms.
How to write a problem statement in research?
Problem statements differ depending on the type and topic of research and vary between a few sentences to a few paragraphs.
However, the problem statement should not drag on needlessly. Despite the absence of a fixed format, a good research problem statement usually consists of three main parts:
Context: This section explains the background for your research. It identifies the problem and describes an ideal scenario that could exist in the absence of the problem. It also includes any past attempts and shortcomings at solving the problem.
Significance: This section defines how the problem prevents the ideal scenario from being achieved, including its negative impacts on the society or field of research. It should include who will be the most affected by a solution to the problem, the relevance of the study that you are proposing, and how it can contribute to the existing body of research.
Solution: This section describes the aim and objectives of your research, and your solution to overcome the problem. Finally, it need not focus on the perfect solution, but rather on addressing a realistic goal to move closer to the ideal scenario.
Here is a cheat sheet to help you with formulating a good problem statement.
1. Begin with a clear indication that the problem statement is going to be discussed next. You can start with a generic sentence like, “The problem that this study addresses…” This will inform your readers of what to expect next.
2. Next, mention the consequences of not solving the problem . You can touch upon who is or will be affected if the problem continues, and how.
3. Conclude with indicating the type of research /information that is needed to solve the problem. Be sure to reference authors who may have suggested the necessity of such research.
This will then directly lead to your proposed research objective and workplan and how that is expected to solve the problem i.e., close the research gap.
Language Editing Plus
Elsevier Language Editing Plus service will provide you with a thorough language review of your thesis, article or presentation. It offers review of logic and flow, reference checks, document formatting, a customized cover letter and more.

- Manuscript Preparation
What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research?

How to Use Tables and Figures effectively in Research Papers
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

Research Problem Statement — Find out how to write an impactful one!
Table of Contents
What Is a Research Problem Statement?
A research problem statement is a clear, concise, and specific statement that describes the issue or problem that the research project addresses. It should be written in a way that is easily understandable to both experts and non-experts in the field.
To write a research problem statement, you should:
- Identify the general area of interest: Start by identifying the general area of research that interests you.
- Define the specific problem: Narrow down the general area of interest to a specific problem or issue.
- Explain the significance of the problem: Provide context for the problem by explaining why it is important to study and what gap in current knowledge or understanding it fills.
- Provide a clear and concise statement: State the problem in a clear and concise manner, making sure to use language that is easily understood by your intended audience.
- Use a scientific and objective tone: The problem statement should be written in a neutral and objective tone, avoiding any subjective language and personal bias .
An Example of a Research Problem Statement
“The increasing prevalence of obesity in children is a growing public health concern. Despite the availability of information on healthy eating and physical activity, many children are still not engaging in healthy lifestyle behaviors. The problem this study addresses is the lack of understanding of the barriers and facilitators to healthy lifestyle behaviors in children.”
When to Write a Problem Statement in Research?
A research problem statement should be written at the beginning of the research process, before any data collection or analysis takes place. This is because the statement sets the foundation for the entire research project by clearly defining the problem that the research is trying to address.
Writing a problem statement early in the research process helps to guide the research design and methodology , and ensures that the research is focused on addressing the specific problem at hand. It also helps to ensure that the research is relevant and addresses a gap in current knowledge or understanding.
In addition, a well-written problem statement effectively communicates the purpose and significance of the research to potential funders, collaborators, and other stakeholders. It also generates interest and support for the research project.
It’s also important to note that, during the research process, the statement can be refined or updated as new information is discovered or as the research progresses. This is normal and it’s a good idea to revise the statement as needed to ensure that it remains clear and concise and that it accurately reflects the current focus of the research project.
What Does a Research Problem Statement Include?
A research problem statement typically includes the following elements:
1. The research topic:
The general area of interest or field of study that the research project addresses.
2. The specific problem or issue:
A clear and concise statement of the problem or issue that the research project aims to address.
3. The significance of the problem:
A discussion of why the problem is important and what gap in current knowledge or understanding it fills.
4. The research questions:
A set of questions that the research project aims to answer, in order to address the problem or issue.
5. The research objectives:
A set of specific and measurable objectives that the research project aims to achieve.
6. The scope of the research:
A description of the specific population, setting, or context that the research project will focus on.
7. The theoretical framework:
A discussion of the theoretical concepts and principles that inform the research project.
8. The research design:
A description of the research methodologies that will be used to collect and analyze data in order to address the research questions and objectives.
It’s important to note that the problem statement is usually brief and concise, typically a few sentences or a short paragraph. But it should provide enough information to convey the main idea of the research project.
Important Features of Research Problem Statement
The problem statement should be clear and easy to understand. Write it in a way that is accessible to both experts and non-experts in the field.
2. Specificity
The statement should be specific and clearly define the problem or issue that the research project aims to address. It should be narrow enough to be manageable, but broad enough to be of interest to others in the field.
3. Significance
The statement should explain why the problem is important and what gap in current knowledge or understanding it fills. It should provide context for the research project and help to justify its importance.
4. Relevance
The statement should be relevant to the field of study and address an issue that is currently of concern to researchers.
5. Research questions
The statement should include a set of research questions that the research project aims to answer in order to address the problem or issue.
6. Research objectives
The statement should include a set of specific and measurable objectives that the research project aims to achieve.
The statement should define the specific population, setting, or context that the research project will focus on.
8. Theoretical framework
The statement should provide an overview of the theoretical concepts and principles that inform the research project.
9. Research design
The statement should provide an overview of the research methodologies. This will be useful collect and analyze data in order to address the research questions and objectives.
Difference Between a Thesis Statement and a Problem Statement
A thesis statement and a problem statement are related but distinct elements of a research project.
A thesis statement is a statement that summarizes the central argument or claim of a research paper or essay. It presents the main idea of the paper and sets the direction for the rest of the content. It’s usually located at the end of the introduction, and it’s often one sentence.
A problem statement, on the other hand, is a statement that describes a specific problem or issue that the research project aims to address. It sets the foundation for the entire research project by clearly defining the research problem. It is usually located at the beginning of a research paper or proposal, and is of one or a few paragraphs.
In summary, a thesis statement is a summary of the main point or key argument of the research paper. A problem statement describes the specific issue that the research project aims to address. A thesis statement is more focused on the final outcome of the research. While a problem statement is focused on the current state of knowledge and the gap in understanding that the research project aims to fill.
In Conclusion
A problem statement is a critical component of the research project, as it provides a clear and concise roadmap for the research, and helps to ensure that the research is well-designed and addresses a significant and relevant issue.
We hope this blog has clarified your doubts and confusion associated with research problem statement and helps you write an effective statement for your research project!
comprehensive contents. thanks!
Very good writing and easy to understand
WOW..its easy to understand…
This has opened up my mind, Systematically outlined steps.
Wow I’ve gained Alot from this!
WOW…This was much helpful.
Good and straightforward explanations with ease of understanding for all the students and teachers alike.
Beautiful work
I enjoy and understand every bit of the explanations on each topic. Kudos to the team.
very clear and easy to understand. i really benefited
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
![how to write research problem in research paper What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Diversity and Inclusion
The Silent Struggle: Confronting gender bias in science funding
In the 1990s, Dr. Katalin Kariko’s pioneering mRNA research seemed destined for obscurity, doomed by…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Demystifying the Role of Confounding Variables in Research

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 1. Choosing a Research Problem
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
In the social and behavioral sciences, the subject of analysis is most often framed as a problem that must be researched in order to obtain a greater understanding, formulate a set of solutions or recommended courses of action, and/or develop a better approach to practice. The research problem, therefore, is the main organizing principle guiding the analysis of your research. The problem under investigation establishes an occasion for writing and a focus that governs what you want to say. It represents the core subject matter of scholarly communication and the means by which scholars arrive at other topics of conversation and the discovery of new knowledge and understanding.
Alvesson, Mats and Jörgen Sandberg. Constructing Research Questions: Doing Interesting Research . London: Sage, 2013; Jacobs, Ronald L. “Developing a Dissertation Research Problem: A Guide for Doctoral Students in Human Resource Development and Adult Education.” New Horizons in Adult Education and Human Resource Development 25 (Summer 2013): 103-117; Chapter 1: Research and the Research Problem. Nicholas Walliman . Your Research Project: Designing and Planning Your Work . 3rd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2011.
Choosing a Research Problem / How to Begin
Do not assume that identifying a research problem to investigate will be a quick and easy task! You should be thinking about it during the beginning of the course. There are generally three ways you are asked to write about a research problem : 1) your professor provides you with a general topic from which you study a particular aspect; 2) your professor provides you with a list of possible topics to study and you choose a topic from that list; or, 3) your professor leaves it up to you to choose a topic and you only have to obtain permission to write about it before beginning your investigation. Here are some strategies for getting started for each scenario.
I. How To Begin: You are given the topic to write about
Step 1 : Identify concepts and terms that make up the topic statement . For example, your professor wants the class to focus on the following research problem: “Is the European Union a credible security actor with the capacity to contribute to confronting global terrorism?" The main concepts in this problem are: European Union, security, global terrorism, credibility [ hint : focus on identifying proper nouns, nouns or noun phrases, and action verbs in the assignment description]. Step 2 : Review related literature to help refine how you will approach examining the topic and finding a way to analyze it . You can begin by doing any or all of the following: reading through background information from materials listed in your course syllabus; searching the USC Libraries Catalog to find a recent book on the topic and, if appropriate, more specialized works about the topic; conducting a preliminary review of the research literature using multidisciplinary databases such as ProQuest or subject-specific databases from the " By Subject Area " drop down menu located above the list of databases.
Choose the advanced search option in the database and enter into each search box the main concept terms you developed in Step 1. Also consider using their synonyms to retrieve additional relevant records. This will help you refine and frame the scope of the research problem. You will likely need to do this several times before you can finalize how to approach writing about the topic. NOTE : Always review the references from your most relevant research results cited by the authors in footnotes, endnotes, or a bibliography to locate related research on your topic. This is a good strategy for identifying important prior research about the topic because titles that are repeatedly cited indicate their significance in laying a foundation for understanding the problem. However, if you’re having trouble at this point locating relevant research literature, ask a librarian for help!
ANOTHER NOTE : If you find an article from a database that's particularly helpful, paste it into Google Scholar , placing the title of the article in quotes. If the article record appears, look for a "cited by" reference followed by a number [e.g., C ited by 37] just below the record. This link indicates how many times other scholars have subsequently cited that article in their own research since it was first published. This is an effective strategy for identifying more current, related research on your topic. Finding additional cited by references from your original list of cited by references helps you navigate through the literature and, by so doing, understand the evolution of thought around a particular research problem. Step 3 : Since social science research papers are generally designed to encourage you to develop your own ideas and arguments, look for sources that can help broaden, modify, or strengthen your initial thoughts and arguments. For example, if you decide to argue that the European Union is inadequately prepared to take on responsibilities for broader global security because of the debt crisis in many EU countries, then focus on identifying sources that support as well as refute this position. From the advanced search option in ProQuest , a sample search would use "European Union" in one search box, "global security" in the second search box, and adding a third search box to include "debt crisis."
There are least four appropriate roles your related literature plays in helping you formulate how to begin your analysis :
- Sources of criticism -- frequently, you'll find yourself reading materials that are relevant to your chosen topic, but you disagree with the author's position. Therefore, one way that you can use a source is to describe the counter-argument, provide evidence from your own review of the literature as to why the prevailing argument is unsatisfactory, and to discuss how your approach is more appropriate based upon your interpretation of the evidence.
- Sources of new ideas -- while a general goal in writing college research papers in the social sciences is to examine a research problem with some basic idea of what position you'd like to take and on what basis you'd like to defend your position, it is certainly acceptable [and often encouraged] to read the literature and extend, modify, and refine your own position in light of the ideas proposed by others. Just make sure that you cite the sources !
- Sources for historical context -- another role your related literature plays in formulating how to begin your analysis is to place issues and events in proper historical context. This can help to demonstrate familiarity with developments in relevant scholarship about your topic, provide a means of comparing historical versus contemporary issues and events, and identifying key people, places, and events that had an important role related to the research problem. Given its archival journal coverage, a good multidisciplnary database to use in this case is JSTOR .
- Sources of interdisciplinary insight -- an advantage of using databases like ProQuest to begin exploring your topic is that it covers publications from a variety of different disciplines. Another way to formulate how to study the topic is to look at it from different disciplinary perspectives. If the topic concerns immigration reform, for example, ask yourself, how do studies from sociological journals found by searching ProQuest vary in their analysis from those in political science journals. A goal in reviewing related literature is to provide a means of approaching a topic from multiple perspectives rather than the perspective offered from just one discipline.
NOTE : Remember to keep careful notes at every stage or utilize a citation management system like EndNotes or RefWorks . You may think you'll remember what you have searched and where you found things, but it’s easy to forget or get confused. Most databases have a search history feature that allows you to go back and see what searches you conducted previously as long as you haven't closed your session. If you start over, that history could be deleted.
Step 4 : Assuming you have done an effective job of synthesizing and thinking about the results of your initial search for related literature, you're ready to prepare a detailed outline for your paper that lays the foundation for a more in-depth and focused review of relevant research literature [after consulting with a librarian, if needed!]. How will you know you haven't done an effective job of synthesizing and thinking about the results of our initial search for related literature? A good indication is that you start composing the outline and gaps appear in how you want to approach the study. This indicates the need to gather further background information and analysis about the research problem.
II. How To Begin: You are provided a list of possible topics to choose from Step 1 : I know what you’re thinking--which topic on this list will be the easiest to find the most information on? An effective instructor would never include a topic that is so obscure or complex that no research is available to examine and from which to design an effective study. Therefore, don't approach a list of possible topics to study from the perspective of trying to identify the path of least resistance; choose a topic that you find interesting in some way, that is controversial and that you have a strong opinion about, that has some personal meaning for you, or relates to your major or a minor. You're going to be working on the topic for quite some time, so choose one that you find interesting and engaging or that motivates you to take a position. Embrace the opportunity to learn something new! Once you’ve settled on a topic of interest from the list provided by your professor, follow Steps 1 - 4 listed above to further develop it into a research paper.
NOTE : It’s ok to review related literature to help refine how you will approach analyzing a topic, and then discover that the topic isn’t all that interesting to you. In that case, choose a different topic from the list. Just don’t wait too long to make a switch and, of course, be sure to inform your professor that you are changing your topic.
III. How To Begin: Your professor leaves it up to you to choose a topic
Step 1 : Under this scenario, the key process is turning an idea or general thought into a topic that can be configured into a research problem. When given an assignment where you choose the topic, don't begin by thinking about what to write about, but rather, ask yourself the question, "What do I want to understand or learn about?" Treat an open-ended research assignment as an opportunity to gain new knowledge about something that's important or exciting to you in the context of the overall subject of the course.
Step 2 : If you lack ideas, or wish to gain focus, try any or all of the following strategies:
- Review your course readings, particularly the suggested readings, for topic ideas. Don't just review what you've already read, but jump ahead in the syllabus to readings that have not been covered yet.
- Search the USC Libraries Catalog for a recently published book and, if appropriate, more specialized works related to the discipline area of the course [e.g., for the course SOCI 335: Society and Population, search for books on "population and society" or "population and social impact"]. Reviewing the contents of a book about your area of interest can give you insight into what conversations scholars are having about the topic and, thus, how you might want to contribute your own ideas to these conversations through the research paper you write for the class.
- Browse through some current scholarly [a.k.a., academic, peer reviewed] journals in your subject discipline. Even if most of the articles are not relevant, you can skim through the contents quickly. You only need one to be the spark that begins the process of wanting to learn more about a topic. Consult with a librarian and/or your professor about what constitutes the core journals within the subject area of the writing assignment.
- Think about essays you have written for other courses you have taken or academic lectures and programs you have attended outside of class. Thinking back, ask yourself why did you want to take this class or attend this event? What interested you the most? What would you like to know more about? Place this question in the context of the current course assignment. Note that this strategy also applies to anything you've watched on TV or has been shared on social media.
- Search online news media sources, such as CNN , the Los Angeles Times , Huffington Post , MSNBC , Fox News , or Newsweek , to see if your idea has been covered by the media. Use this coverage to refine your idea into something that you'd like to investigate further, but in a more deliberate, scholarly way in relation to a particular problem that needs to be researched.
Step 3 : To build upon your initial idea, use the suggestions under this tab to help narrow , broaden , or increase the timeliness of your idea so you can write it out as a research problem.
Once you are comfortable with having turned your idea into a research problem, follow Steps 1 - 4 listed in Part I above to further develop it into an outline for a research paper.
Alderman, Jim. "Choosing a Research Topic." Beginning Library and Information Systems Strategies. Paper 17. Jacksonville, FL: University of North Florida Digital Commons, 2014; Alvesson, Mats and Jörgen Sandberg. Constructing Research Questions: Doing Interesting Research . London: Sage, 2013; Chapter 2: Choosing a Research Topic. Adrian R. Eley. Becoming a Successful Early Career Researcher . New York: Routledge, 2012; Answering the Question. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra; Brainstorming. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University; Brainstorming. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Chapter 1: Research and the Research Problem. Nicholas Walliman . Your Research Project: Designing and Planning Your Work . 3rd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2011; Choosing a Topic. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Mullaney, Thomas S. and Christopher Rea. Where Research Begins: Choosing a Research Project That Matters to You (and the World) . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2022; Coming Up With Your Topic. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College; How To Write a Thesis Statement. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Identify Your Question. Start Your Research. University Library, University of California, Santa Cruz; The Process of Writing a Research Paper. Department of History. Trent University; Trochim, William M.K. Problem Formulation. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006.
Resources for Identifying a Topic
Resources for Identifying a Research Problem
If you are having difficulty identifying a topic to study or need basic background information, the following web resources and databases can be useful:
- CQ Researcher -- a collection of single-themed public policy reports that provide an overview of an issue. Each report includes background information, an assessment of the current policy situation, statistical tables and maps, pro/con statements from representatives of opposing positions, and a bibliography of key sources.
- New York Times Topics -- each topic page collects news articles, reference and archival information, photos, graphics, audio and video files. Content is available without charge on articles going back to 1981.
- Opposing Viewpoints In Context -- an online resource covering a wide range of social issues from a variety of perspectives. The database contains a media-rich collection of materials, including pro/con viewpoint essays, topic overviews, primary source materials, biographies of social activists and reformers, journal articles, statistical tables, charts and graphs, images, videos, and podcasts.
- Policy Commons -- platform for objective, fact-based research from the world’s leading policy experts, nonpartisan think tanks, and intergovernmental and non-governmental organizations. The database provides advanced searching across millions of pages of books, articles, working papers, reports, policy briefs, data sets, tables, charts, media, case studies, and statistical publications, including archived reports from more than 200 defunct think tanks. Coverage is international in scope.
Descriptions of resources are adapted or quoted from vendor websites.
Writing Tip
Not Finding Anything on Your Topic? Ask a Librarian!
Don't assume or jump to the conclusion that your topic is too narrowly defined or obscure just because your initial search has failed to identify relevant research. Librarians are experts in locating and critically assessing information and how it is organized. This knowledge will help you develop strategies for analyzing existing knowledge in new ways. Therefore, always consult with a librarian before you consider giving up on finding information about the topic you want to investigate. If there isn't a lot of information about your topic, a librarian can help you identify a closely related topic that you can study. Use the Ask-A-Librarian link above to identify a librarian in your subject area.
Another Writing Tip
Don't be a Martyr!
In thinking about what to study, don't adopt the mindset of pursuing an esoteric or overly complicated topic just to impress your professor but that, in reality, does not have any real interest to you. Choose a topic that is challenging but that has at least some interest to you or that you care about. Obviously, this is easier for courses within your major, but even for those nasty prerequisite classes that you must take in order to graduate [and that provide an additional tuition revenue for the university], try to apply issues associated with your major to the general topic given to you. For example, if you are an international relations major taking a GE philosophy class where the assignment asks you to apply the question of "what is truth" to some aspect of life, you could choose to study how government leaders attempt to shape truth through the use of nationalistic propaganda.
Still Another Writing Tip
A Research Problem is Not a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement and a research problem are two different parts of the introduction section of your paper. The thesis statement succinctly describes in one or two sentences, usually in the last paragraph of the introduction, what position you have reached about a topic. It includes an assertion that requires evidence and support along with your opinion or argument about what you are researching. There are three general types of thesis statements: analytical statements that break down and evaluate the topic; argumentative statements that make a claim about the topic and defend that claim; and, expository statements that present facts and research about the topic. Each are intended to set forth a claim that you will seek to validate through the research you describe in your paper.
Before the thesis statement, your introduction must include a description of a problem that describes either a key area of concern, a condition to be improved upon, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling issue that exists . The research problem describes something that can be empirically verified and measured; it is often followed by a set of questions that underpin how you plan to approach investigating that problem. In short, the thesis statement states your opinion or argument about the research problem and summarizes how you plan to address it.
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Write a Strong Thesis Statement! The Writing Center, University of Evansville; Thesis Statements. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tutorial #26: Thesis Statements and Topic Sentences. Writing Center, College of San Mateo; Creswell, John W. and J. David Creswell. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . 5th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2017.
- << Previous: Glossary of Research Terms
- Next: Reading Research Effectively >>
- Last Updated: May 21, 2024 11:14 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications . If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
How to Write a Statement of the Problem for Your Research Proposal
Defining your research problem is essential when conducting an experiment. In this article, you will learn how to write a statement of the problem for your research proposal. Learn about the characteristics of a good statement of the problem and examples of research questions.
Updated on May 17, 2022

You are a great researcher. You are full of ideas and questions as to where to go next with your work. You would not be in this position if you were not good at coming up with interesting questions within your area.
One problem, though, is knowing where to spend your time, energy, and money. Which ideas, questions, and problems are worthwhile?
You need to be able to define a good research problem. A research problem addresses an existing gap in knowledge in your field and leads to further investigations by you and other researchers. Inspiring others with your research problem will lead to citations, enhancing your and your institution's impact.
In order to write a clear and useful problem statement, you need to describe a question and its consequences.
One key way to assess the ‘usefulness' of your research ideas is to learn how to express them as clear problems.
In this article, we will talk about how to write a statement of the problem for your next research proposal. This is important not just for assessing the ‘usefulness' of research ideas, but also for formulating a grant application or proposal. We'll talk about how to explain your research ideas to others in the form of a problem statement in your proposal.
What is a statement of the problem in research?
All research projects should start with a clear problem statement. A problem statement is a formulation of an issue which is usually a ‘gap' within your area. A research gap is an unanswered question, an issue, controversy, or untested hypothesis that has not yet been addressed.
The trick with research problems is working out whether they are actually worth investing the time, energy, and money to figure out. This comes with experience, or you could just read on!
Since a clear problem statement is going to form the basis of your next research project, the question is: How can I write one?
How is this done? The first step is to become familiar with the basic elements of a problem statement in effective research.
Characteristics of a problem statement
A research problem statement has two key attributes:
- The problem must be challenging and original, but also potentially achievable by your team.
- The problem must not be incremental. In other words, don't try to address a small change or advance on an existing study that leads to no new scientific insight. This could be damaging to your and your team's reputation, and will likely not lead to a meaningful publication.
Developing a ‘good' research problem statement, therefore, involves systematic planning and setting time-based, realistic objectives. Your problem has to be achievable.
You'll also need to apply feasible research methods based on an approach that best suits the research question. Your methods have to make sense. They must be usable. In other words, you must be able to acquire statistically sufficient and relevant data that is reproducible.
Finally, the problem you define means you'll need to train team members in this particular research area and methods.
Writing a statement of the problem
Stating a research problem is done by defining it within the general area of your research. This depends on your previous work and experience. It may be an area you want to move into or a topic related to what you have already worked on as a researcher. Examples could include a question in astrophysics within physics, robotics within engineering, nutrition within medicine, or marine biology within ocean and Earth science.
Once you've determined your overall area (and you'll know this already of course), it's time to drill down, decide, and define a research problem within that field.
First , your statement should identify a problem that needs to be addressed within your selected sub-area.
This will almost certainly require literature work, but the idea may arise from:
- Discussions you've had with colleagues;
- Discussions at a conference;
- A paper you've read.
Second , your problem statement should be a “good research problem.” This will require further investigation and reading as you consider “what has been done?” and “what needs to be done?”
Third , search for more information, perhaps by:
- Locating relevant books, papers and other materials;
- Evaluating the quality and authority of the information collected;
- Maintaining a regular literature review throughout the project;
- Making regular notes on background material;
- Deciding how this literature search will be carried out within the research group;
- Deciding how information gained will be disseminated to the group (e.g., via each researcher carrying out a regular literature review in their sub-area and information disseminated at group meetings or via email at regular intervals).
This process may well change or modify how your research problem is stated or formulated.
Once your research problem has been identified, research questions within the problem need to be specified.
How long should your statement of the problem be?
Not too long. One page is more than enough for a clear and effective problem statement.
Research questions within your problem
The first stage of writing your research problem statement involves formulating your questions in a meaningful way. In the context of important questions, we are looking for things that many readers across different disciplines find to be interesting. But at the same time, set your question within your field.
Thus, once a research problem has been established, several questions can be written down. These questions should specify exactly what needs to be determined to address the problem.
These questions should also be specific enough that they can be answered using appropriate available research methods - or methods that could be made available to the research group (e.g. by buying or borrowing equipment).
These questions should require complex in-depth investigation, analysis, and argument. They should not be simple enough that they can be answered easily with well-established facts or yes/no answers.
All research questions should be focused, specific, appropriately complex, and relevant to the overall aims of the project.
Examples of questions and next steps
- How do government regulations prevent companies from polluting water systems?
- What factors have influenced population growth in the fastest growing countries?
- How can a bespoke thermal desorption unit be designed and built for use in detection of trace particulate matter in a polluted environment (e.g., a busy city street)?
- What methods and procedures can be used to understand, and hence control, fundamental chemical processes that occur in flames?
- How can measurement protocols used in mass spectrometry in a university research laboratory be developed and standardized to enable direct comparison with related measurements in a government laboratory?
Once the problem and questions have been identified, the resources required to carry out the research will need to be assessed. This will involve:
- Identifying the equipment needed. Find out what is available and what needs to be purchased.
- Assessing which consumables (e.g., chemicals) are needed for the project, and determining if they can be obtained on a regular basis (i.e., in the right quantities at the appropriate times).
- Identifying the software, data-analyses and other computer support needed. Assess what needs to be purchased.
- Assessing what laboratory and office space is needed. And if more is required, discuss this with the relevant laboratory manager.
- Identifying what support for travel is needed for the group, as well as what resources are required for the group to attend relevant conferences and training of group personnel.
Final thoughts
Defining and writing a clear statement of a problem as the basis of a project is the first - and most important - step in any research. The tips and ideas in this article will help you clearly identify the purpose of the research you are developing.
A clear research problem statement will likely form the skeleton of the Introduction of your final article. If you are able to clearly direct your reader (the most important person in the publishing process) to an important and interesting question, they will likely stay engaged, and use and cite your article in the future.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples
How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples
Published on 8 November 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George.
A research problem is a specific issue or gap in existing knowledge that you aim to address in your research. You may choose to look for practical problems aimed at contributing to change, or theoretical problems aimed at expanding knowledge.
Some research will do both of these things, but usually the research problem focuses on one or the other. The type of research problem you choose depends on your broad topic of interest and the type of research you think will fit best.
This article helps you identify and refine a research problem. When writing your research proposal or introduction , formulate it as a problem statement and/or research questions .

Table of contents
Why is the research problem important, step 1: identify a broad problem area, step 2: learn more about the problem, frequently asked questions about research problems.
Having an interesting topic isn’t a strong enough basis for academic research. Without a well-defined research problem, you are likely to end up with an unfocused and unmanageable project.
You might end up repeating what other people have already said, trying to say too much, or doing research without a clear purpose and justification. You need a clear problem in order to do research that contributes new and relevant insights.
Whether you’re planning your thesis , starting a research paper , or writing a research proposal , the research problem is the first step towards knowing exactly what you’ll do and why.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
As you read about your topic, look for under-explored aspects or areas of concern, conflict, or controversy. Your goal is to find a gap that your research project can fill.
Practical research problems
If you are doing practical research, you can identify a problem by reading reports, following up on previous research, or talking to people who work in the relevant field or organisation. You might look for:
- Issues with performance or efficiency
- Processes that could be improved
- Areas of concern among practitioners
- Difficulties faced by specific groups of people
Examples of practical research problems
Voter turnout in New England has been decreasing, in contrast to the rest of the country.
The HR department of a local chain of restaurants has a high staff turnover rate.
A non-profit organisation faces a funding gap that means some of its programs will have to be cut.
Theoretical research problems
If you are doing theoretical research, you can identify a research problem by reading existing research, theory, and debates on your topic to find a gap in what is currently known about it. You might look for:
- A phenomenon or context that has not been closely studied
- A contradiction between two or more perspectives
- A situation or relationship that is not well understood
- A troubling question that has yet to be resolved
Examples of theoretical research problems
The effects of long-term Vitamin D deficiency on cardiovascular health are not well understood.
The relationship between gender, race, and income inequality has yet to be closely studied in the context of the millennial gig economy.
Historians of Scottish nationalism disagree about the role of the British Empire in the development of Scotland’s national identity.
Next, you have to find out what is already known about the problem, and pinpoint the exact aspect that your research will address.
Context and background
- Who does the problem affect?
- Is it a newly-discovered problem, or a well-established one?
- What research has already been done?
- What, if any, solutions have been proposed?
- What are the current debates about the problem? What is missing from these debates?
Specificity and relevance
- What particular place, time, and/or group of people will you focus on?
- What aspects will you not be able to tackle?
- What will the consequences be if the problem is not resolved?
Example of a specific research problem
A local non-profit organisation focused on alleviating food insecurity has always fundraised from its existing support base. It lacks understanding of how best to target potential new donors. To be able to continue its work, the organisation requires research into more effective fundraising strategies.
Once you have narrowed down your research problem, the next step is to formulate a problem statement , as well as your research questions or hypotheses .
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarise the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2022, November 08). How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/define-research-problem/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, example theoretical framework of a dissertation or thesis, how to write a strong hypothesis | guide & examples.

Organizing Academic Research Papers: The Research Problem/Question
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
A research problem is a statement about an area of concern, a condition to be improved, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or in practice that points to the need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation. In some social science disciplines the research problem is typically posed in the form of a question. A research problem does not state how to do something, offer a vague or broad proposition, or present a value question.
Importance of...
The purpose of a problem statement is to:
- Introduce the reader to the importance of the topic being studied . The reader is oriented to the significance of the study and the research questions or hypotheses to follow.
- Places the problem into a particular context that defines the parameters of what is to be investigated.
- Provides the framework for reporting the results and indicates what is probably necessary to conduct the study and explain how the findings will present this information.
In the social sciences, the research problem establishes the means by which you must answer the "So What?" question. The "So What?" question refers to a research problem surviving the relevancy test [the quality of a measurement procedure that provides repeatability and accuracy]. Note that answering the "So What" question requires a commitment on your part to not only show that you have researched the material, but that you have thought about its significance.
To survive the "So What" question, problem statements should possess the following attributes:
- Clarity and precision [a well-written statement does not make sweeping generalizations and irresponsible statements],
- Identification of what would be studied, while avoiding the use of value-laden words and terms,
- Identification of an overarching question and key factors or variables,
- Identification of key concepts and terms,
- Articulation of the study's boundaries or parameters,
- Some generalizability in regards to applicability and bringing results into general use,
- Conveyance of the study's importance, benefits, and justification [regardless of the type of research, it is important to address the “so what” question by demonstrating that the research is not trivial],
- Does not have unnecessary jargon; and,
- Conveyance of more than the mere gathering of descriptive data providing only a snapshot of the issue or phenomenon under investigation.
Castellanos, Susie. Critical Writing and Thinking . The Writing Center. Dean of the College. Brown University; Ellis, Timothy J. and Yair Levy Nova Framework of Problem-Based Research: A Guide for Novice Researchers on the Development of a Research-Worthy Problem. Informing Science: the International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline 11 (2008); Thesis and Purpose Statements . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Thesis Statements . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Types and Content
There are four general conceptualizations of a research problem in the social sciences:
- Casuist Research Problem -- this type of problem relates to the determination of right and wrong in questions of conduct or conscience by analyzing moral dilemmas through the application of general rules and the careful distinction of special cases.
- Difference Research Problem -- typically asks the question, “Is there a difference between two or more groups or treatments?” This type of problem statement is used when the researcher compares or contrasts two or more phenomena.
- Descriptive Research Problem -- typically asks the question, "what is...?" with the underlying purpose to describe a situation, state, or existence of a specific phenomenon.
- Relational Research Problem -- suggests a relationship of some sort between two or more variables to be investigated. The underlying purpose is to investigate qualities/characteristics that are connected in some way.
A problem statement in the social sciences should contain :
- A lead-in that helps ensure the reader will maintain interest over the study
- A declaration of originality [e.g., mentioning a knowledge void, which would be supported by the literature review]
- An indication of the central focus of the study, and
- An explanation of the study's significance or the benefits to be derived from an investigating the problem.
II. Sources of Problems for Investigation
Identifying a problem to study can be challenging, not because there is a lack of issues that could be investigated, but due to pursuing a goal of formulating a socially relevant and researchable problem statement that is unique and does not simply duplicate the work of others. To facilitate how you might select a problem from which to build a research study, consider these three broad sources of inspiration:
Deductions from Theory This relates to deductions made from social philosophy or generalizations embodied in life in society that the researcher is familiar with. These deductions from human behavior are then fitted within an empirical frame of reference through research. From a theory, the research can formulate a research problem or hypothesis stating the expected findings in certain empirical situations. The research asks the question: “What relationship between variables will be observed if theory aptly summarizes the state of affairs?” One can then design and carry out a systematic investigation to assess whether empirical data confirm or reject the hypothesis and hence the theory.
Interdisciplinary Perspectives Identifying a problem that forms the basis for a research study can come from academic movements and scholarship originating in disciplines outside of your primary area of study. A review of pertinent literature should include examining research from related disciplines, which can expose you to new avenues of exploration and analysis. An interdisciplinary approach to selecting a research problem offers an opportunity to construct a more comprehensive understanding of a very complex issue than any single discipline might provide.
Interviewing Practitioners The identification of research problems about particular topics can arise from formal or informal discussions with practitioners who provide insight into new directions for future research and how to make research findings increasingly relevant to practice. Discussions with experts in the field, such as, teachers, social workers, health care providers, etc., offers the chance to identify practical, “real worl” problems that may be understudied or ignored within academic circles. This approach also provides some practical knowledge which may help in the process of designing and conducting your study.
Personal Experience Your everyday experiences can give rise to worthwhile problems for investigation. Think critically about your own experiences and/or frustrations with an issue facing society, your community, or in your neighborhood. This can be derived, for example, from deliberate observations of certain relationships for which there is no clear explanation or witnessing an event that appears harmful to a person or group or that is out of the ordinary.
Relevant Literature The selection of a research problem can often be derived from an extensive and thorough review of pertinent research associated with your overall area of interest. This may reveal where gaps remain in our understanding of a topic. Research may be conducted to: 1) fill such gaps in knowledge; 2) evaluate if the methodologies employed in prior studies can be adapted to solve other problems; or, 3) determine if a similar study could be conducted in a different subject area or applied to different study sample [i.e., different groups of people]. Also, authors frequently conclude their studies by noting implications for further research; this can also be a valuable source of problems to investigate.
III. What Makes a Good Research Statement?
A good problem statement begins by introducing the broad area in which your research is centered and then gradually leads the reader to the more narrow questions you are posing. The statement need not be lengthy but a good research problem should incorporate the following features:
Compelling topic Simple curiosity is not a good enough reason to pursue a research study. The problem that you choose to explore must be important to you and to a larger community you share. The problem chosen must be one that motivates you to address it. Supports multiple perspectives The problem most be phrased in a way that avoids dichotomies and instead supports the generation and exploration of multiple perspectives. A general rule of thumb is that a good research problem is one that would generate a variety of viewpoints from a composite audience made up of reasonable people. Researchable It seems a bit obvious, but you don't want to find yourself in the midst of investigating a complex research project and realize that you don't have much to draw on for your research. Choose research problems that can be supported by the resources available to you. Not sure? Seek out help from a librarian!
NOTE: Do not confuse a research problem with a research topic. A topic is something to read and obtain information about whereas a problem is something to solve or framed as a question that must be answered.
IV. Mistakes to Avoid
Beware of circular reasoning . Don’t state that the research problem as simply the absence of the thing you are suggesting. For example, if you propose, "The problem in this community is that it has no hospital."
This only leads to a research problem where:
- The need is for a hospital
- The objective is to create a hospital
- The method is to plan for building a hospital, and
- The evaluation is to measure if there is a hospital or not.
This is an example of a research problem that fails the "so what?" test because it does not reveal the relevance of why you are investigating the problem of having no hospital in the community [e.g., there's a hospital in the community ten miles away] and because the research problem does not elucidate the significance of why one should study the fact that no hospital exists in the community [e.g., that hospital in the community ten miles away has no emergency room].
Choosing and Refining Topics . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Ellis, Timothy J. and Yair Levy Nova Framework of Problem-Based Research: A Guide for Novice Researchers on the Development of a Research-Worthy Problem. Informing Science: the International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline 11 (2008); How to Write a Research Question . The Writing Center. George Mason University; Invention: Developing a Thesis Statement . The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; Problem Statements PowerPoint Presentation . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Procter, Margaret. Using Thesis Statements . University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Trochim, William M.K. Problem Formulation . Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Thesis and Purpose Statements . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Thesis Statements . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
- << Previous: Background Information
- Next: Theoretical Framework >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Methodology
Definition:
Research Methodology refers to the systematic and scientific approach used to conduct research, investigate problems, and gather data and information for a specific purpose. It involves the techniques and procedures used to identify, collect , analyze , and interpret data to answer research questions or solve research problems . Moreover, They are philosophical and theoretical frameworks that guide the research process.
Structure of Research Methodology
Research methodology formats can vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project, but the following is a basic example of a structure for a research methodology section:
I. Introduction
- Provide an overview of the research problem and the need for a research methodology section
- Outline the main research questions and objectives
II. Research Design
- Explain the research design chosen and why it is appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Discuss any alternative research designs considered and why they were not chosen
- Describe the research setting and participants (if applicable)
III. Data Collection Methods
- Describe the methods used to collect data (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations)
- Explain how the data collection methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or instruments used for data collection
IV. Data Analysis Methods
- Describe the methods used to analyze the data (e.g., statistical analysis, content analysis )
- Explain how the data analysis methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or software used for data analysis
V. Ethical Considerations
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise from the research and how they were addressed
- Explain how informed consent was obtained (if applicable)
- Detail any measures taken to ensure confidentiality and anonymity
VI. Limitations
- Identify any potential limitations of the research methodology and how they may impact the results and conclusions
VII. Conclusion
- Summarize the key aspects of the research methodology section
- Explain how the research methodology addresses the research question(s) and objectives
Research Methodology Types
Types of Research Methodology are as follows:
Quantitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of numerical data using statistical methods. This type of research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Qualitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
Mixed-Methods Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that combines elements of both quantitative and qualitative research. This approach can be particularly useful for studies that aim to explore complex phenomena and to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular topic.
Case Study Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves in-depth examination of a single case or a small number of cases. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and anthropology to gain a detailed understanding of a particular individual or group.
Action Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves a collaborative process between researchers and practitioners to identify and solve real-world problems. Action research is often used in education, healthcare, and social work.
Experimental Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the manipulation of one or more independent variables to observe their effects on a dependent variable. Experimental research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Survey Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection of data from a sample of individuals using questionnaires or interviews. Survey research is often used to study attitudes, opinions, and behaviors.
Grounded Theory Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the development of theories based on the data collected during the research process. Grounded theory is often used in sociology and anthropology to generate theories about social phenomena.
Research Methodology Example
An Example of Research Methodology could be the following:
Research Methodology for Investigating the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Reducing Symptoms of Depression in Adults
Introduction:
The aim of this research is to investigate the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. To achieve this objective, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) will be conducted using a mixed-methods approach.
Research Design:
The study will follow a pre-test and post-test design with two groups: an experimental group receiving CBT and a control group receiving no intervention. The study will also include a qualitative component, in which semi-structured interviews will be conducted with a subset of participants to explore their experiences of receiving CBT.
Participants:
Participants will be recruited from community mental health clinics in the local area. The sample will consist of 100 adults aged 18-65 years old who meet the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder. Participants will be randomly assigned to either the experimental group or the control group.
Intervention :
The experimental group will receive 12 weekly sessions of CBT, each lasting 60 minutes. The intervention will be delivered by licensed mental health professionals who have been trained in CBT. The control group will receive no intervention during the study period.
Data Collection:
Quantitative data will be collected through the use of standardized measures such as the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7). Data will be collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at a 3-month follow-up. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a subset of participants from the experimental group. The interviews will be conducted at the end of the intervention period, and will explore participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-tests, and mixed-model analyses of variance (ANOVA) to assess the effectiveness of the intervention. Qualitative data will be analyzed using thematic analysis to identify common themes and patterns in participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Ethical Considerations:
This study will comply with ethical guidelines for research involving human subjects. Participants will provide informed consent before participating in the study, and their privacy and confidentiality will be protected throughout the study. Any adverse events or reactions will be reported and managed appropriately.
Data Management:
All data collected will be kept confidential and stored securely using password-protected databases. Identifying information will be removed from qualitative data transcripts to ensure participants’ anonymity.
Limitations:
One potential limitation of this study is that it only focuses on one type of psychotherapy, CBT, and may not generalize to other types of therapy or interventions. Another limitation is that the study will only include participants from community mental health clinics, which may not be representative of the general population.
Conclusion:
This research aims to investigate the effectiveness of CBT in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. By using a randomized controlled trial and a mixed-methods approach, the study will provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying the relationship between CBT and depression. The results of this study will have important implications for the development of effective treatments for depression in clinical settings.
How to Write Research Methodology
Writing a research methodology involves explaining the methods and techniques you used to conduct research, collect data, and analyze results. It’s an essential section of any research paper or thesis, as it helps readers understand the validity and reliability of your findings. Here are the steps to write a research methodology:
- Start by explaining your research question: Begin the methodology section by restating your research question and explaining why it’s important. This helps readers understand the purpose of your research and the rationale behind your methods.
- Describe your research design: Explain the overall approach you used to conduct research. This could be a qualitative or quantitative research design, experimental or non-experimental, case study or survey, etc. Discuss the advantages and limitations of the chosen design.
- Discuss your sample: Describe the participants or subjects you included in your study. Include details such as their demographics, sampling method, sample size, and any exclusion criteria used.
- Describe your data collection methods : Explain how you collected data from your participants. This could include surveys, interviews, observations, questionnaires, or experiments. Include details on how you obtained informed consent, how you administered the tools, and how you minimized the risk of bias.
- Explain your data analysis techniques: Describe the methods you used to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, content analysis, thematic analysis, or discourse analysis. Explain how you dealt with missing data, outliers, and any other issues that arose during the analysis.
- Discuss the validity and reliability of your research : Explain how you ensured the validity and reliability of your study. This could include measures such as triangulation, member checking, peer review, or inter-coder reliability.
- Acknowledge any limitations of your research: Discuss any limitations of your study, including any potential threats to validity or generalizability. This helps readers understand the scope of your findings and how they might apply to other contexts.
- Provide a summary: End the methodology section by summarizing the methods and techniques you used to conduct your research. This provides a clear overview of your research methodology and helps readers understand the process you followed to arrive at your findings.
When to Write Research Methodology
Research methodology is typically written after the research proposal has been approved and before the actual research is conducted. It should be written prior to data collection and analysis, as it provides a clear roadmap for the research project.
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
The methodology should be written in a clear and concise manner, and it should be based on established research practices and standards. It is important to provide enough detail so that the reader can understand how the research was conducted and evaluate the validity of the results.
Applications of Research Methodology
Here are some of the applications of research methodology:
- To identify the research problem: Research methodology is used to identify the research problem, which is the first step in conducting any research.
- To design the research: Research methodology helps in designing the research by selecting the appropriate research method, research design, and sampling technique.
- To collect data: Research methodology provides a systematic approach to collect data from primary and secondary sources.
- To analyze data: Research methodology helps in analyzing the collected data using various statistical and non-statistical techniques.
- To test hypotheses: Research methodology provides a framework for testing hypotheses and drawing conclusions based on the analysis of data.
- To generalize findings: Research methodology helps in generalizing the findings of the research to the target population.
- To develop theories : Research methodology is used to develop new theories and modify existing theories based on the findings of the research.
- To evaluate programs and policies : Research methodology is used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and policies by collecting data and analyzing it.
- To improve decision-making: Research methodology helps in making informed decisions by providing reliable and valid data.
Purpose of Research Methodology
Research methodology serves several important purposes, including:
- To guide the research process: Research methodology provides a systematic framework for conducting research. It helps researchers to plan their research, define their research questions, and select appropriate methods and techniques for collecting and analyzing data.
- To ensure research quality: Research methodology helps researchers to ensure that their research is rigorous, reliable, and valid. It provides guidelines for minimizing bias and error in data collection and analysis, and for ensuring that research findings are accurate and trustworthy.
- To replicate research: Research methodology provides a clear and detailed account of the research process, making it possible for other researchers to replicate the study and verify its findings.
- To advance knowledge: Research methodology enables researchers to generate new knowledge and to contribute to the body of knowledge in their field. It provides a means for testing hypotheses, exploring new ideas, and discovering new insights.
- To inform decision-making: Research methodology provides evidence-based information that can inform policy and decision-making in a variety of fields, including medicine, public health, education, and business.
Advantages of Research Methodology
Research methodology has several advantages that make it a valuable tool for conducting research in various fields. Here are some of the key advantages of research methodology:
- Systematic and structured approach : Research methodology provides a systematic and structured approach to conducting research, which ensures that the research is conducted in a rigorous and comprehensive manner.
- Objectivity : Research methodology aims to ensure objectivity in the research process, which means that the research findings are based on evidence and not influenced by personal bias or subjective opinions.
- Replicability : Research methodology ensures that research can be replicated by other researchers, which is essential for validating research findings and ensuring their accuracy.
- Reliability : Research methodology aims to ensure that the research findings are reliable, which means that they are consistent and can be depended upon.
- Validity : Research methodology ensures that the research findings are valid, which means that they accurately reflect the research question or hypothesis being tested.
- Efficiency : Research methodology provides a structured and efficient way of conducting research, which helps to save time and resources.
- Flexibility : Research methodology allows researchers to choose the most appropriate research methods and techniques based on the research question, data availability, and other relevant factors.
- Scope for innovation: Research methodology provides scope for innovation and creativity in designing research studies and developing new research techniques.
Research Methodology Vs Research Methods
About the author.
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

How to Write a Research Paper
- Smodin Editorial Team
- Updated: May 17, 2024
Most students hate writing research papers. The process can often feel long, tedious, and sometimes outright boring. Nevertheless, these assignments are vital to a student’s academic journey. Want to learn how to write a research paper that captures the depth of the subject and maintains the reader’s interest? If so, this guide is for you.
Today, we’ll show you how to assemble a well-organized research paper to help you make the grade. You can transform any topic into a compelling research paper with a thoughtful approach to your research and a persuasive argument.
In this guide, we’ll provide seven simple but practical tips to help demystify the process and guide you on your way. We’ll also explain how AI tools can expedite the research and writing process so you can focus on critical thinking.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear roadmap for tackling these essays. You will also learn how to tackle them quickly and efficiently. With time and dedication, you’ll soon master the art of research paper writing.
Ready to get started?
What Is a Research Paper?
A research paper is a comprehensive essay that gives a detailed analysis, interpretation, or argument based on your own independent research. In higher-level academic settings, it goes beyond a simple summarization and includes a deep inquiry into the topic or topics.
The term “research paper” is a broad term that can be applied to many different forms of academic writing. The goal is to combine your thoughts with the findings from peer-reviewed scholarly literature.
By the time your essay is done, you should have provided your reader with a new perspective or challenged existing findings. This demonstrates your mastery of the subject and contributes to ongoing scholarly debates.
7 Tips for Writing a Research Paper
Often, getting started is the most challenging part of a research paper. While the process can seem daunting, breaking it down into manageable steps can make it easier to manage. The following are seven tips for getting your ideas out of your head and onto the page.
1. Understand Your Assignment
It may sound simple, but the first step in writing a successful research paper is to read the assignment. Sit down, take a few moments of your time, and go through the instructions so you fully understand your assignment.
Misinterpreting the assignment can not only lead to a significant waste of time but also affect your grade. No matter how patient your teacher or professor may be, ignoring basic instructions is often inexcusable.
If you read the instructions and are still confused, ask for clarification before you start writing. If that’s impossible, you can use tools like Smodin’s AI chat to help. Smodin can help highlight critical requirements that you may overlook.
This initial investment ensures that all your future efforts will be focused and efficient. Remember, thinking is just as important as actually writing the essay, and it can also pave the wave for a smoother writing process.
2. Gather Research Materials
Now comes the fun part: doing the research. As you gather research materials, always use credible sources, such as academic journals or peer-reviewed papers. Only use search engines that filter for accredited sources and academic databases so you can ensure your information is reliable.
To optimize your time, you must learn to master the art of skimming. If a source seems relevant and valuable, save it and review it later. The last thing you want to do is waste time on material that won’t make it into the final paper.
To speed up the process even more, consider using Smodin’s AI summarizer . This tool can help summarize large texts, highlighting key information relevant to your topic. By systematically gathering and filing research materials early in the writing process, you build a strong foundation for your thesis.
3. Write Your Thesis
Creating a solid thesis statement is the most important thing you can do to bring structure and focus to your research paper. Your thesis should express the main point of your argument in one or two simple sentences. Remember, when you create your thesis, you’re setting the tone and direction for the entire paper.
Of course, you can’t just pull a winning thesis out of thin air. Start by brainstorming potential thesis ideas based on your preliminary research. And don’t overthink things; sometimes, the most straightforward ideas are often the best.
You want a thesis that is specific enough to be manageable within the scope of your paper but broad enough to allow for a unique discussion. Your thesis should challenge existing expectations and provide the reader with fresh insight into the topic. Use your thesis to hook the reader in the opening paragraph and keep them engaged until the very last word.
4. Write Your Outline
An outline is an often overlooked but essential tool for organizing your thoughts and structuring your paper. Many students skip the outline because it feels like doing double work, but a strong outline will save you work in the long run.
Here’s how to effectively structure your outline.
- Introduction: List your thesis statement and outline the main questions your essay will answer.
- Literature Review: Outline the key literature you plan to discuss and explain how it will relate to your thesis.
- Methodology: Explain the research methods you will use to gather and analyze the information.
- Discussion: Plan how you will interpret the results and their implications for your thesis.
- Conclusion: Summarize the content above to elucidate your thesis fully.
To further streamline this process, consider using Smodin’s Research Writer. This tool offers a feature that allows you to generate and tweak an outline to your liking based on the initial input you provide. You can adjust this outline to fit your research findings better and ensure that your paper remains well-organized and focused.
5. Write a Rough Draft
Once your outline is in place, you can begin the writing process. Remember, when you write a rough draft, it isn’t meant to be perfect. Instead, use it as a working document where you can experiment with and rearrange your arguments and evidence.
Don’t worry too much about grammar, style, or syntax as you write your rough draft. Focus on getting your ideas down on paper and flush out your thesis arguments. You can always refine and rearrange the content the next time around.
Follow the basic structure of your outline but with the freedom to explore different ways of expressing your thoughts. Smodin’s Essay Writer offers a powerful solution for those struggling with starting or structuring their drafts.
After you approve the outline, Smodin can generate an essay based on your initial inputs. This feature can help you quickly create a comprehensive draft, which you can then review and refine. You can even use the power of AI to create multiple rough drafts from which to choose.
6. Add or Subtract Supporting Evidence
Once you have a rough draft, but before you start the final revision, it’s time to do a little cleanup. In this phase, you need to review all your supporting evidence. You want to ensure that there is nothing redundant and that you haven’t overlooked any crucial details.
Many students struggle to make the required word count for an essay and resort to padding their writing with redundant statements. Instead of adding unnecessary content, focus on expanding your analysis to provide deeper insights.
A good essay, regardless of the topic or format, needs to be streamlined. It should convey clear, convincing, relevant information supporting your thesis. If you find some information doesn’t do that, consider tweaking your sources.
Include a variety of sources, including studies, data, and quotes from scholars or other experts. Remember, you’re not just strengthening your argument but demonstrating the depth of your research.
If you want comprehensive feedback on your essay without going to a writing center or pestering your professor, use Smodin. The AI Chat can look at your draft and offer suggestions for improvement.
7. Revise, Cite, and Submit
The final stages of crafting a research paper involve revision, citation, and final review. You must ensure your paper is polished, professionally presented, and plagiarism-free. Of course, integrating Smodin’s AI tools can significantly streamline this process and enhance the quality of your final submission.
Start by using Smodin’s Rewriter tool. This AI-powered feature can help rephrase and refine your draft to improve overall readability. If a specific section of your essay just “doesn’t sound right,” the AI can suggest alternative sentence structures and word choices.
Proper citation is a must for all academic papers. Thankfully, thanks to Smodin’s Research Paper app, this once tedious process is easier than ever. The AI ensures all sources are accurately cited according to the required style guide (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
Plagiarism Checker:
All students need to realize that accidental plagiarism can happen. That’s why using a Plagiarism Checker to scan your essay before you submit it is always useful. Smodin’s Plagiarism Checker can highlight areas of concern so you can adjust accordingly.
Final Submission
After revising, rephrasing, and ensuring all citations are in order, use Smodin’s AI Content Detector to give your paper one last review. This tool can help you analyze your paper’s overall quality and readability so you can make any final tweaks or improvements.
Mastering Research Papers
Mastering the art of the research paper cannot be overstated, whether you’re in high school, college, or postgraduate studies. You can confidently prepare your research paper for submission by leveraging the AI tools listed above.
Research papers help refine your abilities to think critically and write persuasively. The skills you develop here will serve you well beyond the walls of the classroom. Communicating complex ideas clearly and effectively is one of the most powerful tools you can possess.
With the advancements of AI tools like Smodin , writing a research paper has become more accessible than ever before. These technologies streamline the process of organizing, writing, and revising your work. Write with confidence, knowing your best work is yet to come!
- Florida State University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Special Collections & Archives
EDF 5519: The History of Higher Education
- Writing with Primary Sources
- Using Materials in SCA
- Recommended Resources in SCA
- University History in Brief
How to Analyze a Primary Source

FROM CARLETON COLLEGE HISTORY RESEARCH GUIDE
When you analyze a primary source, you are undertaking the most important job of the historian. There is no better way to understand events in the past than by examining the sources — whether journals, newspaper articles, letters, court case records, novels, artworks, music or autobiographies — that people from that period left behind.
Each historian, including you, will approach a source with a different set of experiences and skills, and will therefore interpret the document differently. Remember that there is no one right interpretation. However, if you do not do a careful and thorough job, you might arrive at a wrong interpretation.
In order to analyze a primary source you need information about two things: the document itself, and the era from which it comes. You can base your information about the time period on the readings you do in class and on lectures. On your own you need to think about the document itself. The following questions may be helpful to you as you begin to analyze the sources:
- Look at the physical nature of your source. This is particularly important and powerful if you are dealing with an original source (i.e., an actual old letter, rather than a transcribed and published version of the same letter). What can you learn from the form of the source? (Was it written on fancy paper in elegant handwriting, or on scrap-paper, scribbled in pencil?) What does this tell you?
- Think about the purpose of the source. What was the author’s message or argument? What was he/she trying to get across? Is the message explicit, or are there implicit messages as well?
- How does the author try to get the message across? What methods does he/she use?
- What do you know about the author? Race, sex, class, occupation, religion, age, region, political beliefs? Does any of this matter? How?
- Who constituted the intended audience? Was this source meant for one person’s eyes, or for the public? How does that affect the source?
- What can a careful reading of the text (even if it is an object) tell you? How does the language work? What are the important metaphors or symbols? What can the author’s choice of words tell you? What about the silences — what does the author choose NOT to talk about?
Now you can evaluate the source as historical evidence.
- Is it prescriptive — telling you what people thought should happen — or descriptive — telling you what people thought did happen?
- Does it describe ideology and/or behavior?
- Does it tell you about the beliefs/actions of the elite, or of “ordinary” people? From whose perspective?
- What historical questions can you answer using this source? What are the benefits of using this kind of source?
- What questions can this source NOT help you answer? What are the limitations of this type of source?
- If we have read other historians’ interpretations of this source or sources like this one, how does your analysis fit with theirs? In your opinion, does this source support or challenge their argument?
Remember, you cannot address each and every one of these questions in your presentation or in your paper, and I wouldn’t want you to. You need to be selective.
– Molly Ladd-Taylor, Annette Igra, Rachel Seidman, and others
Integrating Primary Sources into your Writing
While writing with primary sources can be intimidating, it is not very different from writing with secondary sources.
In all cases, incorporating quoted content or a description of a primary source should be in support of your overall argument. We are in support of using the "BEAM Model" to ensure your inclusion of a source is necessary. All sources should be either Background, Exhibit, Argument, or Method.
- Background: using a source to provide general information to explain the topic. For example, the use of a Wikipedia page on the Pledge of Allegiance to explain the relevant court cases and changes the Pledge has undergone.
- Exhibit: using a source as evidence or examples to analyze. For a literature paper, this would be a poem you are analyzing. For a history paper, a historical document you are analyzing. For a sociology paper, it might be the data from a study.
- Argument: using a source to engage its argument. For example, you might use an editorial from the New York Times on the value of higher education to refute in your own paper.
- This guide is from Hunter College Libraries' "How to Use a Source: The BEAM Method."
With primary sources, you will most likely be incorporating quotations from materials in the first three ways: Background, Exhibit, and Argument. Just like with a primary source, you will need to contextualize your quotations -- who is the writer? when was the source written? etc.
Primary sources can also be integrated into your writing by description of their physical properties. The text can not only be quoted but described: Is the handwriting scratchy? Nearly horizontal? Careful and considered calligraphy? The physical characteristics of a text object might serve as evidence for its intended use: As a small book, does this seem intended for silent and individual reading? Similarly, wear and tear (or lack thereof) on a book or manuscript may provide evidence of its treatment over the years since its creation, giving a sense of how the text might have been pored over or preserved.
Citing SCA Materials
Citations for rare or unique materials should include enough information to identify and locate the original work:
- title of work
- date of creation or publication
- collection name
- name and location of the repository or library unit
Optimally, a citation for rare and/or unpublished works will include other information to further identify and locate the original copy of the work, which may include:
- collection identifier
- folder name and/or number
- call number
- documentary or media format
- URL for a catalog entry, finding aid, or Digital Library object
Archives & Manuscripts
Preferred citation information is available from the ArchivesSpace database for archives and manuscripts collections. They generally follow this format:
Title of Item, Date of Item, Box and Folder Number, Title of Collection, Collection ID, Parent Unit, Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida. collection record URL
Example: Vita (Paul Dirac), 1984, Box: 15, Folder: 09. Paul A.M. Dirac Papers, MSS 1989-009. FSU Special Collections & Archives, Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida. http://purl.fcla.edu/fsu/MSS_1989-009
- << Previous: Using Materials in SCA
- Next: Recommended Resources in SCA >>
- Last Updated: May 21, 2024 2:44 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.fsu.edu/EDF5519
© 2022 Florida State University Libraries | 116 Honors Way | Tallahassee, FL 32306 | (850) 644-2706
How to Find Research Topics to Write About
So, you’ve got a research paper due, and the dread sets in – what to research about? We’ve all experienced that frustrating moment when finding a topic feels about as simple as finding a needle in a haystack.
But hold on! Before you check is essay pro legit enough to find someone to write your paper for you (tempting, I know!), take a deep breath. Finding a killer research topic doesn’t have to take weeks. It can actually be the spark that ignites your curiosity and leads you down a fascinating rabbit hole of discovery.
The key is knowing where to look for inspiration and how to narrow down those endless possibilities into a topic that’s manageable, meaningful, and maybe even a little bit exciting.
So, let’s come up with unconventional strategies, look for hidden sources of inspiration, and give you the tools to choose a topic that will give your research paper a head-start.
Source: https://www.pexels.com/photo/photo-of-a-woman-thinking-941555/
Look Beyond the Textbook
Sure, your course material is a good starting point for finding a research topic, but don’t let it be your only source of inspiration. Look around you – the world is full of fascinating questions just waiting to be explored.
What current events spark your interest? What social issues keep you up at night? Maybe there’s a scientific breakthrough that’s left you wanting to know more.
Don’t be afraid to let your curiosity guide you. Some of the most engaging research papers are born out of genuine interest and a desire to learn more about the world.
Another often-overlooked source of inspiration on what to research is your own life experiences. Have you ever faced a personal challenge or overcome an obstacle that could be relevant to others? Maybe you have a unique cultural background or a hobby that could be the basis for an intriguing research question.
Don’t undermine the potential of your own story to spark a meaningful topic.
Digg Deeper With Unconventional Sources
Now, let’s move beyond the obvious. While academic journals and textbooks are important resources, they’re not the only game in town.
Explore documentaries, podcasts, TED Talks, and even social media for potential research topic ideas. These sources often present complex issues in a more accessible way, making them a great way to spark your interest and notice new perspectives.
If you’re feeling stuck, try branching out into different fields of study. Maybe a sociology paper on the impact of social media on mental health or a history paper on the role of music in social movements could pique your interest.
Remember, research is about making connections, so don’t be afraid to get a little interdisciplinary with your topic choices.
Source: https://www.pexels.com/photo/box-with-brain-inscription-on-head-of-anonymous-woman-7203727/
Find Out What Makes a Good Research Paper Topic
So, you’ve got a whole bunch of potential research article topics swirling around in your head. Now what? It’s time to narrow it down and find the perfect fit.
A good topic should be several things:
- Interesting. You’re going to be spending a lot of time on this topic, so make sure it’s something you actually care about!
- Manageable. Choose a topic that’s narrow enough to be thoroughly researched within the scope of your assignment. Avoid topics that are too general or too niche.
- Relevant. Make sure your topic is in line with your course or field of study. If you’re unsure, talk to your professor for guidance.
- Original. While it’s okay to build on existing research, try to gauge a new angle or perspective on your topic.
If you still feel you can’t come up with the right topic, don’t hesitate to seek out help. Talk to your professor or librarian, or even consider consulting with one of the best coursework writing services to brainstorm ideas and get feedback on your choices.
Choosing a topic for a research paper is just the first step in the process. The real fun begins when you start diving into the research and getting new insights.
The Bottom Line
The journey of finding a research topic doesn’t have to be a dreaded chore. It can be an exciting opportunity to expand your knowledge and bring out new passions. Remember, there are no “easy research topics.” The best topics are the ones that ignite your curiosity and challenge you to think critically about the world around you.
So, feel free to get a little creative with your research topic choices. Whether you’re exploring a current event, a personal experience, or a complex social issue, the most important thing is to choose a topic that inspires you and makes you eager to dive into the research.
Learning how to find a research topic is an essential skill for any college student, and with the right approach, it can even be enjoyable! So, put on your explorer hat, embrace your curiosity, and let your research process begin.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Why writing by hand beats typing for thinking and learning
Jonathan Lambert

If you're like many digitally savvy Americans, it has likely been a while since you've spent much time writing by hand.
The laborious process of tracing out our thoughts, letter by letter, on the page is becoming a relic of the past in our screen-dominated world, where text messages and thumb-typed grocery lists have replaced handwritten letters and sticky notes. Electronic keyboards offer obvious efficiency benefits that have undoubtedly boosted our productivity — imagine having to write all your emails longhand.
To keep up, many schools are introducing computers as early as preschool, meaning some kids may learn the basics of typing before writing by hand.
But giving up this slower, more tactile way of expressing ourselves may come at a significant cost, according to a growing body of research that's uncovering the surprising cognitive benefits of taking pen to paper, or even stylus to iPad — for both children and adults.
Is this some kind of joke? A school facing shortages starts teaching standup comedy
In kids, studies show that tracing out ABCs, as opposed to typing them, leads to better and longer-lasting recognition and understanding of letters. Writing by hand also improves memory and recall of words, laying down the foundations of literacy and learning. In adults, taking notes by hand during a lecture, instead of typing, can lead to better conceptual understanding of material.
"There's actually some very important things going on during the embodied experience of writing by hand," says Ramesh Balasubramaniam , a neuroscientist at the University of California, Merced. "It has important cognitive benefits."
While those benefits have long been recognized by some (for instance, many authors, including Jennifer Egan and Neil Gaiman , draft their stories by hand to stoke creativity), scientists have only recently started investigating why writing by hand has these effects.
A slew of recent brain imaging research suggests handwriting's power stems from the relative complexity of the process and how it forces different brain systems to work together to reproduce the shapes of letters in our heads onto the page.
Your brain on handwriting
Both handwriting and typing involve moving our hands and fingers to create words on a page. But handwriting, it turns out, requires a lot more fine-tuned coordination between the motor and visual systems. This seems to more deeply engage the brain in ways that support learning.

Shots - Health News
Feeling artsy here's how making art helps your brain.
"Handwriting is probably among the most complex motor skills that the brain is capable of," says Marieke Longcamp , a cognitive neuroscientist at Aix-Marseille Université.
Gripping a pen nimbly enough to write is a complicated task, as it requires your brain to continuously monitor the pressure that each finger exerts on the pen. Then, your motor system has to delicately modify that pressure to re-create each letter of the words in your head on the page.
"Your fingers have to each do something different to produce a recognizable letter," says Sophia Vinci-Booher , an educational neuroscientist at Vanderbilt University. Adding to the complexity, your visual system must continuously process that letter as it's formed. With each stroke, your brain compares the unfolding script with mental models of the letters and words, making adjustments to fingers in real time to create the letters' shapes, says Vinci-Booher.
That's not true for typing.
To type "tap" your fingers don't have to trace out the form of the letters — they just make three relatively simple and uniform movements. In comparison, it takes a lot more brainpower, as well as cross-talk between brain areas, to write than type.
Recent brain imaging studies bolster this idea. A study published in January found that when students write by hand, brain areas involved in motor and visual information processing " sync up " with areas crucial to memory formation, firing at frequencies associated with learning.
"We don't see that [synchronized activity] in typewriting at all," says Audrey van der Meer , a psychologist and study co-author at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. She suggests that writing by hand is a neurobiologically richer process and that this richness may confer some cognitive benefits.
Other experts agree. "There seems to be something fundamental about engaging your body to produce these shapes," says Robert Wiley , a cognitive psychologist at the University of North Carolina, Greensboro. "It lets you make associations between your body and what you're seeing and hearing," he says, which might give the mind more footholds for accessing a given concept or idea.
Those extra footholds are especially important for learning in kids, but they may give adults a leg up too. Wiley and others worry that ditching handwriting for typing could have serious consequences for how we all learn and think.
What might be lost as handwriting wanes
The clearest consequence of screens and keyboards replacing pen and paper might be on kids' ability to learn the building blocks of literacy — letters.
"Letter recognition in early childhood is actually one of the best predictors of later reading and math attainment," says Vinci-Booher. Her work suggests the process of learning to write letters by hand is crucial for learning to read them.
"When kids write letters, they're just messy," she says. As kids practice writing "A," each iteration is different, and that variability helps solidify their conceptual understanding of the letter.
Research suggests kids learn to recognize letters better when seeing variable handwritten examples, compared with uniform typed examples.
This helps develop areas of the brain used during reading in older children and adults, Vinci-Booher found.
"This could be one of the ways that early experiences actually translate to long-term life outcomes," she says. "These visually demanding, fine motor actions bake in neural communication patterns that are really important for learning later on."
Ditching handwriting instruction could mean that those skills don't get developed as well, which could impair kids' ability to learn down the road.
"If young children are not receiving any handwriting training, which is very good brain stimulation, then their brains simply won't reach their full potential," says van der Meer. "It's scary to think of the potential consequences."
Many states are trying to avoid these risks by mandating cursive instruction. This year, California started requiring elementary school students to learn cursive , and similar bills are moving through state legislatures in several states, including Indiana, Kentucky, South Carolina and Wisconsin. (So far, evidence suggests that it's the writing by hand that matters, not whether it's print or cursive.)
Slowing down and processing information
For adults, one of the main benefits of writing by hand is that it simply forces us to slow down.
During a meeting or lecture, it's possible to type what you're hearing verbatim. But often, "you're not actually processing that information — you're just typing in the blind," says van der Meer. "If you take notes by hand, you can't write everything down," she says.
The relative slowness of the medium forces you to process the information, writing key words or phrases and using drawing or arrows to work through ideas, she says. "You make the information your own," she says, which helps it stick in the brain.
Such connections and integration are still possible when typing, but they need to be made more intentionally. And sometimes, efficiency wins out. "When you're writing a long essay, it's obviously much more practical to use a keyboard," says van der Meer.
Still, given our long history of using our hands to mark meaning in the world, some scientists worry about the more diffuse consequences of offloading our thinking to computers.
"We're foisting a lot of our knowledge, extending our cognition, to other devices, so it's only natural that we've started using these other agents to do our writing for us," says Balasubramaniam.
It's possible that this might free up our minds to do other kinds of hard thinking, he says. Or we might be sacrificing a fundamental process that's crucial for the kinds of immersive cognitive experiences that enable us to learn and think at our full potential.
Balasubramaniam stresses, however, that we don't have to ditch digital tools to harness the power of handwriting. So far, research suggests that scribbling with a stylus on a screen activates the same brain pathways as etching ink on paper. It's the movement that counts, he says, not its final form.
Jonathan Lambert is a Washington, D.C.-based freelance journalist who covers science, health and policy.
- handwriting
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Scientists use generative AI to answer complex questions in physics
Press contact :, media download.
*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."
Previous image Next image
When water freezes, it transitions from a liquid phase to a solid phase, resulting in a drastic change in properties like density and volume. Phase transitions in water are so common most of us probably don’t even think about them, but phase transitions in novel materials or complex physical systems are an important area of study.
To fully understand these systems, scientists must be able to recognize phases and detect the transitions between. But how to quantify phase changes in an unknown system is often unclear, especially when data are scarce.
Researchers from MIT and the University of Basel in Switzerland applied generative artificial intelligence models to this problem, developing a new machine-learning framework that can automatically map out phase diagrams for novel physical systems.
Their physics-informed machine-learning approach is more efficient than laborious, manual techniques which rely on theoretical expertise. Importantly, because their approach leverages generative models, it does not require huge, labeled training datasets used in other machine-learning techniques.
Such a framework could help scientists investigate the thermodynamic properties of novel materials or detect entanglement in quantum systems, for instance. Ultimately, this technique could make it possible for scientists to discover unknown phases of matter autonomously.
“If you have a new system with fully unknown properties, how would you choose which observable quantity to study? The hope, at least with data-driven tools, is that you could scan large new systems in an automated way, and it will point you to important changes in the system. This might be a tool in the pipeline of automated scientific discovery of new, exotic properties of phases,” says Frank Schäfer, a postdoc in the Julia Lab in the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) and co-author of a paper on this approach.
Joining Schäfer on the paper are first author Julian Arnold, a graduate student at the University of Basel; Alan Edelman, applied mathematics professor in the Department of Mathematics and leader of the Julia Lab; and senior author Christoph Bruder, professor in the Department of Physics at the University of Basel. The research is published today in Physical Review Letters.
Detecting phase transitions using AI
While water transitioning to ice might be among the most obvious examples of a phase change, more exotic phase changes, like when a material transitions from being a normal conductor to a superconductor, are of keen interest to scientists.
These transitions can be detected by identifying an “order parameter,” a quantity that is important and expected to change. For instance, water freezes and transitions to a solid phase (ice) when its temperature drops below 0 degrees Celsius. In this case, an appropriate order parameter could be defined in terms of the proportion of water molecules that are part of the crystalline lattice versus those that remain in a disordered state.
In the past, researchers have relied on physics expertise to build phase diagrams manually, drawing on theoretical understanding to know which order parameters are important. Not only is this tedious for complex systems, and perhaps impossible for unknown systems with new behaviors, but it also introduces human bias into the solution.
More recently, researchers have begun using machine learning to build discriminative classifiers that can solve this task by learning to classify a measurement statistic as coming from a particular phase of the physical system, the same way such models classify an image as a cat or dog.
The MIT researchers demonstrated how generative models can be used to solve this classification task much more efficiently, and in a physics-informed manner.
The Julia Programming Language , a popular language for scientific computing that is also used in MIT’s introductory linear algebra classes, offers many tools that make it invaluable for constructing such generative models, Schäfer adds.
Generative models, like those that underlie ChatGPT and Dall-E, typically work by estimating the probability distribution of some data, which they use to generate new data points that fit the distribution (such as new cat images that are similar to existing cat images).
However, when simulations of a physical system using tried-and-true scientific techniques are available, researchers get a model of its probability distribution for free. This distribution describes the measurement statistics of the physical system.
A more knowledgeable model
The MIT team’s insight is that this probability distribution also defines a generative model upon which a classifier can be constructed. They plug the generative model into standard statistical formulas to directly construct a classifier instead of learning it from samples, as was done with discriminative approaches.
“This is a really nice way of incorporating something you know about your physical system deep inside your machine-learning scheme. It goes far beyond just performing feature engineering on your data samples or simple inductive biases,” Schäfer says.
This generative classifier can determine what phase the system is in given some parameter, like temperature or pressure. And because the researchers directly approximate the probability distributions underlying measurements from the physical system, the classifier has system knowledge.
This enables their method to perform better than other machine-learning techniques. And because it can work automatically without the need for extensive training, their approach significantly enhances the computational efficiency of identifying phase transitions.
At the end of the day, similar to how one might ask ChatGPT to solve a math problem, the researchers can ask the generative classifier questions like “does this sample belong to phase I or phase II?” or “was this sample generated at high temperature or low temperature?”
Scientists could also use this approach to solve different binary classification tasks in physical systems, possibly to detect entanglement in quantum systems (Is the state entangled or not?) or determine whether theory A or B is best suited to solve a particular problem. They could also use this approach to better understand and improve large language models like ChatGPT by identifying how certain parameters should be tuned so the chatbot gives the best outputs.
In the future, the researchers also want to study theoretical guarantees regarding how many measurements they would need to effectively detect phase transitions and estimate the amount of computation that would require.
This work was funded, in part, by the Swiss National Science Foundation, the MIT-Switzerland Lockheed Martin Seed Fund, and MIT International Science and Technology Initiatives.
Share this news article on:
Press mentions.
Researchers at MIT and elsewhere have developed a new machine-learning model capable of “predicting a physical system’s phase or state,” report Kyle Wiggers and Devin Coldewey for TechCrunch .
Previous item Next item
Related Links
- Frank Schäfer
- Alan Edelman
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
- Department of Mathematics
- Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Related Topics
- Mathematics
- Computer science and technology
- Artificial intelligence
- Computer modeling
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL)
- Electrical Engineering & Computer Science (eecs)
Related Articles

Technique could efficiently solve partial differential equations for numerous applications
Computational model captures the elusive transition states of chemical reactions

Explained: Generative AI

From physics to generative AI: An AI model for advanced pattern generation
More mit news.

H2 underground
Read full story →

2024 MAD Design Fellows announced

School of Engineering first quarter 2024 awards

From NASA to MIT to Formlabs

An expansive approach to making new compounds

Q&A: A graduating student looks back on his MIT experience
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 3: Set your aims and objectives. Finally, the problem statement should frame how you intend to address the problem. Your goal here should not be to find a conclusive solution, but rather to propose more effective approaches to tackling or understanding it. The research aim is the overall purpose of your research.
Step 1: Understanding the Problem. The problem statement should provide a clear and concise background to the research problem you are investigating. Before starting your research, review the literature about the specific problem and find a gap to fill with your own research. Practical Research Problem Statement.
A research problem is a gap in existing knowledge, a contradiction in an established theory, or a real-world challenge that a researcher aims to address in their research. It is at the heart of any scientific inquiry, directing the trajectory of an investigation. The statement of a problem orients the reader to the importance of the topic, sets ...
A research problem can be theoretical in nature, focusing on an area of academic research that is lacking in some way. Alternatively, a research problem can be more applied in nature, focused on finding a practical solution to an established problem within an industry or an organisation. In other words, theoretical research problems are motivated by the desire to grow the overall body of ...
The purpose of the problem statement is to identify the issue that is a concern and focus it in a way that allows it to be studied in a systematic way. It defines the problem and proposes a way to research a solution, or demonstrates why further information is needed in order for a solution to become possible.
A research problem statement typically includes the following elements: 1. The research topic: The general area of interest or field of study that the research project addresses. 2. The specific problem or issue: A clear and concise statement of the problem or issue that the research project aims to address. 3.
A research problem is a definite or clear expression [statement] about an area of concern, a condition to be improved upon, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or within existing practice that points to a need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation.
Your problem statement in your research paper aims to: Define the gap: Clearly identify and articulate a specific gap or issue in the existing knowledge. Provide direction: Serve as a roadmap, guiding the course of your research and ensuring you remain focused. Establish relevance: Highlight the importance and significance of the problem in the ...
Feasibility: A research problem should be feasible in terms of the availability of data, resources, and research methods. It should be realistic and practical to conduct the study within the available time, budget, and resources. Novelty: A research problem should be novel or original in some way.
A Research Problem is Not a Thesis Statement. A thesis statement and a research problem are two different parts of the introduction section of your paper. The thesis statement succinctly describes in one or two sentences, usually in the last paragraph of the introduction, what position you have reached about a topic. It includes an assertion ...
A research problem statement is the descriptive statement which conveys the issue a researcher is trying to address through the study with the aim of informing the reader the context and significance of performing the study at hand. The research problem statement is crucial for researchers to focus on a particular component of a vast field of ...
We've covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are: To choose a research question and review the literature. To plan your paper structure and draft an outline. To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing.
Developing a 'good' research problem statement, therefore, involves systematic planning and setting time-based, realistic objectives. Your problem has to be achievable. You'll also need to apply feasible research methods based on an approach that best suits the research question. Your methods have to make sense.
Provide a background of the problem you wish to study. Explain why you have undertaken the study. Describes your research problem. Summarizes the existing knowledge related to your topic. Highlights the contribution that your research will make to your field. States your research question clearly. You can look up these resources to have a clear ...
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
A research problem is a specific issue or gap in existing knowledge that you aim to address in your research. You may choose to look for practical problems aimed at contributing to change, or theoretical problems aimed at expanding knowledge. Some research will do both of these things, but usually the research problem focuses on one or the other.
A research problem is a statement about an area of concern, a condition to be improved, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or in practice that points to the need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation. In some social science disciplines the research problem is typically posed in the form of a question.
How to Write Research Methodology. Writing a research methodology involves explaining the methods and techniques you used to conduct research, collect data, and analyze results. It's an essential section of any research paper or thesis, as it helps readers understand the validity and reliability of your findings. Here are the steps to write a ...
You can adjust this outline to fit your research findings better and ensure that your paper remains well-organized and focused. 5. Write a Rough Draft. Once your outline is in place, you can begin the writing process. Remember, when you write a rough draft, it isn't meant to be perfect.
FROM CARLETON COLLEGE HISTORY RESEARCH GUIDE. When you analyze a primary source, you are undertaking the most important job of the historian. There is no better way to understand events in the past than by examining the sources — whether journals, newspaper articles, letters, court case records, novels, artworks, music or autobiographies — that people from that period left behind.
Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist.
Generate structured outlines for your research paper introduction with Paperpal Copilot. Try it today - https://paperpal.com Struggling with the perfect int...
It sets the foundation for the entire research, guiding the researchers in formulating objectives, hypotheses, and the overall research design. Here are some steps to help you identify the research problem in a paper: Read the Introduction: The introduction of a research paper often contains a clear statement of the research problem.
The course will be highly beneficial for university students, teachers, PhD candidates, researchers and persons who are planning to have higher studies abroad with scholarships. This course will also demonstrate you one can utilize AI research tools such as ChatGPT, Jenni AI, Scite AI, Paperpal, Typeset etc. to accelerate the research process.
Choose a topic that's narrow enough to be thoroughly researched within the scope of your assignment. Avoid topics that are too general or too niche. Relevant. Make sure your topic is in line with your course or field of study. If you're unsure, talk to your professor for guidance. Original.
So far, research suggests that scribbling with a stylus on a screen activates the same brain pathways as etching ink on paper. It's the movement that counts, he says, not its final form.
Step 3: Formulate research questions. Next, based on the problem statement, you need to write one or more research questions. These target exactly what you want to find out. They might focus on describing, comparing, evaluating, or explaining the research problem. A strong research question should be specific enough that you can answer it ...
The research is published today in Physical Review Letters. Detecting phase transitions using AI. While water transitioning to ice might be among the most obvious examples of a phase change, more exotic phase changes, like when a material transitions from being a normal conductor to a superconductor, are of keen interest to scientists.