Need a business plan? Call now:
Talk to our experts:
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB1 Business Plan
- EB2 Visa Business Plan
- EB5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- UK Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- UK Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Planning
- Landlord Business Plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- eCommerce business plan
- Online Boutique Business Plan
- Daycare business plan
- Mobile Application Business Plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food Delivery Business Plan
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Buy Side Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Templates

Goals and Objectives for Business Plan with Examples
Published Nov.05, 2023
Updated Apr.23, 2024
By: Jakub Babkins
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 2
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Table of Content
Every business needs a clear vision of what it wants to achieve and how it plans to get there. A business plan is a document that outlines the goals and objectives of a business, as well as the strategies and actions to achieve them. A well-written business plan from business plan specialists can help a business attract investors, secure funding, and guide its growth.
Understanding Business Objectives
Business objectives are S pecific, M easurable, A chievable, R elevant, and T ime-bound (SMART) statements that describe what a business wants to accomplish in a given period. They are derived from the overall vision and mission of the business, and they support its strategic direction.
Business plan objectives can be categorized into different types, depending on their purpose and scope. Some common types of business objectives are:
- Financial objectives
- Operational objectives
- Marketing objectives
- Social objectives
For example, a sample of business goals and objectives for a business plan for a bakery could be:
- To increase its annual revenue by 20% in the next year.
- To reduce its production costs by 10% in the next six months.
- To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
- To improve its customer satisfaction rating by 15% in the next month.
The Significance of Business Objectives
Business objectives are important for several reasons. They help to:
- Clarify and direct the company and stakeholders
- Align the company’s efforts and resources to a common goal
- Motivate and inspire employees to perform better
- Measure and evaluate the company’s progress and performance
- Communicate the company’s value and advantage to customers and the market
For example, by setting a revenue objective, a bakery can focus on increasing its sales and marketing efforts, monitor its sales data and customer feedback, motivate its staff to deliver quality products and service, communicate its unique selling points and benefits to its customers, and adjust its pricing and product mix according to market demand.
Advantages of Outlining Business Objectives
Outlining business objectives is a crucial step in creating a business plan. It serves as a roadmap for the company’s growth and development. Outlining business objectives has several advantages, such as:
- Clarifies the company’s vision, direction, scope, and boundaries
- Break down the company’s goals into smaller tasks and milestones
- Assigns roles and responsibilities and delegates tasks
- Establishes standards and criteria for success and performance
- Anticipates risks and challenges and devises contingency plans
For example, by outlining its business objective for increasing the average revenue per customer in its business plan, a bakery can:
- Attract investors with its viable business plan for investors
- Secure funding from banks or others with its realistic financial plan
- Partner with businesses or organizations that complement or enhance its products or services
- Choose the best marketing, pricing, product, staff, location, etc. for its target market and customers
Setting Goals and Objectives for a Business Plan
Setting goals and objectives for a business plan is not a one-time task. It requires careful planning, research, analysis, and evaluation. To set effective goals and objectives for a business plan, one should follow some best practices, such as:
OPTION 1: Use the SMART framework. A SMART goal or objective is clear, quantifiable, realistic, aligned with the company’s mission and vision, and has a deadline. SMART stands for:
- Specific – The goal or objective should be clear, concise, and well-defined.
- Measurable – The goal or objective should be quantifiable or verifiable.
- Achievable – The goal or objective should be realistic and attainable.
- Relevant – The goal or objective should be aligned with the company’s vision, mission, and values.
- Time-bound – The goal or objective should have a deadline or timeframe.
For example, using the SMART criteria, a bakery can refine its business objective for increasing the average revenue per customer as follows:
- Specific – Increase revenue with new products and services from $5 to $5.50.
- Measurable – Track customer revenue monthly with sales reports.
- Achievable – Research the market, develop new products and services, and train staff to upsell and cross-sell.
- Relevant – Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, profitability and cash flow, and market competitiveness.
- Time-bound – Achieve this objective in six months, from January 1st to June 30th.
OPTION 2: Use the OKR framework. OKR stands for O bjectives and K ey R esults. An OKR is a goal-setting technique that links the company’s objectives with measurable outcomes. An objective is a qualitative statement of what the company wants to achieve. A key result is a quantitative metric that shows how the objective will be achieved.
OPTION 3: Use the SWOT analysis. SWOT stands for S trengths, W eaknesses, O pportunities, and T hreats. A SWOT analysis is a strategic tool that helps the company assess the internal and external factors that affect its goals and objectives.
- Strengths – Internal factors that give the company an advantage over others.
- Weaknesses – Internal factors that limit the company’s performance or growth.
- Opportunities – External factors that allow the company to improve or expand.
- Threats – External factors that pose a risk or challenge to the company.
For example, using these frameworks, a bakery might set the following goals and objectives for its SBA business plan :
Objective – To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
Key Results:
- Research gluten-free cake market demand and preferences by month-end.
- Create and test 10 gluten-free cake recipes by next month-end.
- Make and sell 100 gluten-free cakes weekly online or in-store by quarter-end.
SWOT Analysis:
- Expertise and experience in baking and cake decorating.
- Loyal and satisfied customer base.
- Strong online presence and reputation.
Weaknesses:
- Limited production capacity and equipment.
- High production costs and low-profit margins.
- Lack of knowledge and skills in gluten-free baking.
Opportunities:
- Growing demand and awareness for gluten-free products.
- Competitive advantage and differentiation in the market.
- Potential partnerships and collaborations with health-conscious customers and organizations.
- Increasing competition from other bakeries and gluten-free brands.
- Changing customer tastes and preferences.
- Regulatory and legal issues related to gluten-free labeling and certification.
Examples of Business Goals and Objectives
To illustrate how to write business goals and objectives for a business plan, let’s use a hypothetical example of a bakery business called Sweet Treats. Sweet Treats is a small bakery specializing in custom-made cakes, cupcakes, cookies, and other baked goods for various occasions.
Here are some examples of possible startup business goals and objectives for Sweet Treats:
Earning and Preserving Profitability
Profitability is the ability of a company to generate more revenue than expenses. It indicates the financial health and performance of the company. Profitability is essential for a business to sustain its operations, grow its market share, and reward its stakeholders.
Some possible objectives for earning and preserving profitability for Sweet Treats are:
- To increase the gross profit margin by 5% in the next quarter by reducing the cost of goods sold
- To achieve a net income of $100,000 in the current fiscal year by increasing sales and reducing overhead costs
Ensuring Consistent Cash Flow
Cash flow is the amount of money that flows in and out of a company. A company needs to have enough cash to cover its operating expenses, pay its debts, invest in its growth, and reward its shareholders.
Some possible objectives for ensuring consistent cash flow for Sweet Treats are:
- Increase monthly operating cash inflow by 15% by the end of the year by improving the efficiency and productivity of the business processes
- Increase the cash flow from investing activities by selling or disposing of non-performing or obsolete assets
Creating and Maintaining Efficiency
Efficiency is the ratio of output to input. It measures how well a company uses its resources to produce its products or services. Efficiency can help a business improve its quality, productivity, customer satisfaction, and profitability.
Some possible objectives for creating and maintaining efficiency for Sweet Treats are:
- To reduce the production time by 10% in the next month by implementing lean manufacturing techniques
- To increase the customer service response rate by 20% in the next week by using chatbots or automated systems
Winning and Keeping Clients
Clients are the people or organizations that buy or use the products or services of a company. They are the source of revenue and growth for a company. Therefore, winning and keeping clients is vital to generating steady revenue, increasing customer loyalty, and enhancing word-of-mouth marketing.
Some possible objectives for winning and keeping clients for Sweet Treats are:
- To acquire 100 new clients in the next quarter by launching a referral program or a promotional campaign
- To retain 90% of existing clients in the current year by offering loyalty rewards or satisfaction guarantees
Building a Recognizable Brand
A brand is the name, logo, design, or other features distinguishing a company from its competitors. It represents the identity, reputation, and value proposition of a company. Building a recognizable brand is crucial for attracting and retaining clients and creating a loyal fan base.
Some possible objectives for building a recognizable brand for Sweet Treats are:
- To increase brand awareness by 50% in the next six months by creating and distributing engaging content on social media platforms
- To improve brand image by 30% in the next year by participating in social causes or sponsoring events that align with the company’s values
Expanding and Nurturing an Audience with Marketing
An audience is a group of people interested in or following a company’s products or services. They can be potential or existing clients, fans, influencers, or partners. Expanding and nurturing an audience with marketing is essential for increasing a company’s visibility, reach, and engagement.
Some possible objectives for expanding and nurturing an audience with marketing for Sweet Treats are:
- To grow the email list by 1,000 subscribers in the next month by offering a free ebook or a webinar
- To nurture leads by sending them relevant and valuable information through email newsletters or blog posts
Strategizing for Expansion
Expansion is the process of increasing a company’s size, scope, or scale. It can involve entering new markets, launching new products or services, opening new locations, or forming new alliances. Strategizing for expansion is important for diversifying revenue streams, reaching new audiences, and gaining competitive advantages.
Some possible objectives for strategizing for expansion for Sweet Treats are:
- To launch a new product or service line by developing and testing prototypes
- To open a new branch or franchise by securing funding and hiring staff
Template for Business Objectives
A template for writing business objectives is a format or structure that can be used as a guide or reference for creating your objectives. A template for writing business objectives can help you to ensure that your objectives are SMART, clear, concise, and consistent.
To use this template, fill in the blanks with your information. Here is an example of how you can use this template:
Example of Business Objectives
Our business is a _____________ (type of business) that provides _____________ (products or services) to _____________ (target market). Our vision is to _____________ (vision statement) and our mission is to _____________ (mission statement).
Our long-term business goals and objectives for the next _____________ (time period) are:
S pecific: We want to _____________ (specific goal) by _____________ (specific action).
M easurable: We will measure our progress by _____________ (quantifiable indicator).
A chievable: We have _____________ (resources, capabilities, constraints) that will enable us to achieve this goal.
R elevant: This goal supports our vision and mission by _____________ (benefit or impact).
T ime-bound: We will complete this goal by _____________ (deadline).
Repeat this process for each goal and objective for your business plan.
How to Monitor Your Business Objectives?
After setting goals and objectives for your business plan, you should check them regularly to see if you are achieving them. Monitoring your business objectives can help you to:
- Track your progress and performance
- Identify and overcome any challenges
- Adjust your actions and strategies as needed
Some of the tools and methods that you can use to monitor your business objectives are:
- Dashboards – Show key data and metrics for your objectives with tools like Google Data Studio, Databox, or DashThis.
- Reports – Get detailed information and analysis for your objectives with tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, or SEMrush.
- Feedback – Learn from your customers and their needs and expectations with tools like SurveyMonkey, Typeform, or Google Forms.
Strategies for Realizing Business Objectives
To achieve your business objectives, you need more than setting and monitoring them. You need strategies and actions that support them. Strategies are the general methods to reach your objectives. Actions are the specific steps to implement your strategies.
Different objectives require different strategies and actions. Some common types are:
- Marketing strategies
- Operational strategies
- Financial strategies
- Human resource strategies
- Growth strategies
To implement effective strategies and actions, consider these factors:
- Alignment – They should match your vision, mission, values, goals, and objectives
- Feasibility – They should be possible with your capabilities, resources, and constraints
- Suitability – They should fit the context and needs of your business
How OGSCapital Can Help You Achieve Your Business Objectives?
We at OGSCapital can help you with your business plan and related documents. We have over 15 years of experience writing high-quality business plans for various industries and regions. We have a team of business plan experts who can assist you with market research, financial analysis, strategy formulation, and presentation design. We can customize your business plan to suit your needs and objectives, whether you need funding, launching, expanding, or entering a new market. We can also help you with pitch decks, executive summaries, feasibility studies, and grant proposals. Contact us today for a free quote and start working on your business plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the goals and objectives in business.
Goals and objectives in a business plan are the desired outcomes that a company works toward. To describe company goals and objectives for a business plan, start with your mission statement and then identify your strategic and operational objectives. To write company objectives, you must brainstorm, organize, prioritize, assign, track, and review them using the SMART framework and KPIs.
What are the examples of goals and objectives in a business plan?
Examples of goals and objectives in a business plan are: Goal: To increase revenue by 10% each year for the next five years. Objective: To launch a new product line and create a marketing campaign to reach new customers.
What are the 4 main objectives of a business?
The 4 main objectives of a business are economic, social, human, and organic. Economic objectives deal with financial performance, social objectives deal with social responsibility, human objectives deal with employee welfare, and organic objectives deal with business growth and development.
What are goals and objectives examples?
Setting goals and objectives for a business plan describes what a business or a team wants to achieve and how they will do it. For example: Goal: To provide excellent customer service. Objective: To increase customer satisfaction scores by 20% by the end of the quarter.
At OGSCapital, our business planning services offer expert guidance and support to create a realistic and actionable plan that aligns with your vision and mission. Get in touch to discuss further!
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Bowling Alley Business Plan Sample

Nightclub Business Plan (2024): A Comprehensive Guide

Rabbit Farming Business Plan

Beverages Business Plan

Private Schools Business Plan

Business Plan for a Lounge

Any questions? Get in Touch!
We have been mentioned in the press:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Search the site:

- Pricing Customers Get a Demo
- Platform Data Reporting Analytics Collaboration Security Integrations
- Solutions Strategic Planning Organizational Alignment Business Reporting Dashboards OKRs Project Management
- Industries Local Government Healthcare Banking & Finance Utilities & Energy Higher Education Enterprise

56 Strategic Objectives Examples to Inspire Your Company's Strategy

Ted Jackson
Ted is a Founder and Managing Partner of ClearPoint Strategy and leads the sales and marketing teams.
Boost your company's strategic alignment with these 56 examples of strategic objectives ready to implement.
Table of Contents
Strategic objectives are statements that indicate what is critical or important in your organizational strategy . In other words, they’re goals you’re trying to achieve in a certain period of time—typically 3-5 years. Your objectives link out to your measures and initiatives. Objectives are a key part of your Balanced Scorecard -- along with measures and initiatives.
This list of strategic objective examples should help you think through the various types of objectives that may work best in your organization. You’ll find all 56 of them categorized below by perspective and/or theme. Before we dive into the examples, let’s talk about how to choose the right ones for your organization. Once you have your list of objectives, you may want to consider choosing a software tool to help you track your progress.
ClearPoint Strategy offers a powerful platform designed to help you create, manage, and track your strategic objectives effectively, ensuring that your entire organization is aligned and focused. Our software offers intuitive tools that simplify the creation and management of strategic objectives, helping you monitor progress and ensure that your initiatives are on track.
Download your FREE 56 key Strategic Objective library for organizational success
Choosing the right strategic objectives.
Here’s some practical advice based on years of experience: Don’t put 56 objectives in your scorecard—that’s too many. You need to pick and choose. We recommend no more than 15 objectives maximum—you can read more about creating them here. But how do you know which objectives are right for your organization? It depends on your industry and your strategy.
Use this list of objectives to brainstorm what’s most important for your industry and your specific strategy, then build a set of objectives that best represent your organization.
Strategic Goals Based On Your Industry
What business are you in? If you’re operating in a fast-growing industry like IT, technical services, or construction, you should choose objectives that match your growth goals and include movement in a positive direction.
For example, those might include launching a new product or increasing gross revenue within the next year. If you’re in a slow-growing industry, like sugar manufacturing or coal-power production, choose company objectives that focus on protecting your assets and managing expenses, such as reducing administrative costs by a certain percentage.
Strategic Objectives For Municipalities
It’s not uncommon to hear that municipalities or agencies don’t really have a strategy, but that’s a myth. If you look more closely at individual cities, you’ll see that some are growing quickly...and some are not. Cities with strong growth have chosen strategic objectives based on their specific socioeconomic situation. Yes—virtually all municipalities have goals based on balancing the budget and improving safety.
But the most successful cities refine those high-level objectives. Does the city-planning portion of the budget need more focus than public utilities? Is street crime or retail crime more of a safety issue? Choosing objectives that function as answers to questions like these is the most strategic (and successful) approach for cities.
It’s also important to note that a municipality’s strategy must be specific to its economy and population, and it must be diverse. Goals cannot all be focused on a single source of revenue, such as tourism or manufacturing. For example, cities along the Gulf Coast have realized that when an oil spill occurs, a reliance on tourism is detrimental. They need a more resilient economy to build a healthy community.
In short, municipal objectives should be diverse enough to withstand economic and environmental shifts.
Claim your FREE 41-page Strategy Execution Toolkit for enhanced strategic performance
Strategic objectives for healthcare.
The healthcare industry is constantly changing. However, it’s crucial for healthcare organizations to continue to deliver effective, reliable care even as certain outside factors—medical practices, technology, and government regulations—evolve.
So, although healthcare organizations can’t always predict (or control) the future, strategic planning is the best way for them to set a course for excellence while taking into account possible changes that may occur in the years ahead.
Economic trends, government policies, and technological advancements can help provide context for healthcare objectives, but each organization needs to consider what it would like to accomplish strategically. You obviously want great health outcomes, but where do finances fit in? And what about your staff, skills, and technology?
For example, you may have an objective to optimize the use of real-time data to improve patient care but also have additional goals to develop a comprehensive employee wellness program or build trust in the community by improving your communications. Safety, quality, patient satisfaction, people, and finance are all areas of significance to consider.
Strategic Goals Based On Your Strategy
What’s your strategy within your industry? Two similar businesses in the same industry can have two very different strategies. Your strategy will determine the objectives you set as much as your industry. (Here are 6 expert tips on strategic planning to consider as you're going through the process.)
To further explain, here’s a business objectives example based on strategy. Think of two financial services companies: Goldman Sachs and E*TRADE. Both handle customer finances and investments, but (generally speaking) Goldman Sachs prioritizes high-touch, personal relationships, while E*TRADE values high-tech, self-service relationships. As a result, the two organizations undoubtedly have distinct objectives.
From a marketing perspective, Goldman Sachs might focus on referrals and connections, and E*TRADE on social media and customer service automation. Or from an HR perspective, Goldman Sachs could set objectives based on retention and client relationships, and E*TRADE on technical skills and product development.
Your business could have the same mission and purpose as another, but if it takes a different approach to achieve that purpose, you should have a unique set of strategic objectives.

56 Strategic Objective Examples
While you can certainly use these for inspiration, we don’t recommend simply duplicating them for your strategy without putting in some thought. Use this list of objectives to brainstorm what’s most important for your industry and your specific strategy. Then, build a set of objectives that best represents your organization.
Note: Because the below objectives reflect different strategies, we’ve provided a few ideas on how you can customize these examples in each definition.
Financial Objectives
Financial objectives are typically written as financial goals. When selecting and creating your financial objectives, consider what you’re trying to accomplish financially within the time span of your strategic plan. Examples of strategic goals for this perspective include:
- Grow shareholder value : The top goal of your organization may be to increase the value of your organization for your shareholders, stakeholders, or owners. Value can be defined in many ways, so this would need to be clearly defined.
- Grow earnings per share : This objective implies your organization is trying to increase its earnings or profits. For publicly traded companies, a common way to look at this is through “earnings per share.” This can be measured quarterly and/or annually.
- Increase revenue : Revenue represents growth in your organization, so increasing revenue is a sign of company health. You can make this more specific by defining revenue from a key area in your organization.
- Manage cost : On the other side of revenue is the costs or expenses in your business. As you grow (or shrink) you need to carefully manage cost—so this may be an important objective for you.
- Maintain appropriate financial leverage : Many organizations use debt—another word for financial leverage—as a key financial tool. There may be an optimal amount of debt you’d like to stay within.
- Ensure favorable bond ratings : For some organizations, bond ratings are a sign of healthy finances. This is a regularly occurring objective for a public sector scorecard.
- Balance the budget : A balanced budget reflects the discipline of good planning, budgeting, and management. It is also one that is typically seen in the public sector—or within divisions or departments of other organizations.
- Ensure financial sustainability : If your organization is in growth mode or has an uncertain economic environment, you need to be sure you remain financially stable. Sometimes this means seeking outside sources of revenue or managing costs that are appropriate to your operations.
- Maintain profitability : This is a solid top-level objective that shows balance between revenue and expenses. If your organization is investing in order to grow, you may look to an objective like this to govern how much you are able to invest.
- Diversify and grow revenue streams : Some organizations receive revenue from multiple sources or products and services. They set an objective to grow revenue in different areas to ensure that the organization is stable and not subject to risk associated with only one revenue stream.
Claim your FREE eBook on 68 effective financial KPIs you should use for better strategic insights
Customer objectives.
When looking at examples of a business’s customer objectives, you’ll see they are typically written like customer goals. Sometimes they are written in the form of a phrase or a statement that a customer would say when talking about your product or service.
- Best value for the cost : This means that your customers know they are not purchasing the most expensive product or service—or even the highest quality—but that they are getting the best deal . This may mean your customers are paying less than average and getting an average or above-average product.
- Broad product offering : This objective works if your strategy is to be able to offer the customer the best product in its class, regardless of price. In the hotel industry, for example, this could reflect the strategy of the Four Seasons or Ritz Carlton.
- Reliable products/services : If your organization takes pride in the reliability of your product or service, this objective—which reflects that you are targeting customers that also value this reliability—may be right for you. This could indicate the on-time reliability of an airline or the dependable reliability of a printer that generates high-quality output.
- Cross-sell more products : Some organizations—like banks or office product companies—focus on selling more products to the same customers. This strategy acknowledges that you already have the customer but can make money by selling them more.
- Increase share of market : This customer strategy focuses on selling to more customers, thus increasing the market share. For example, if your organization is a landscape company, you are likely trying to reach more households—or if your organization is a hospital, you likely want more of the local population to use your services.
- Increase share of wallet : This customer strategy focuses on gaining more purchases from the same customers. If you sell fertilizer, for example, you want each customer to purchase a larger percentage of their fertilizer spend with your organization rather than with your competitors.
- Partner with customers to provide solutions : This strategy reflects customer intimacy. As part of this strategy, you may deliver service-oriented solutions or have customers participate in research and development with your organization. Partnering comes at a cost but tends to foster more customer loyalty across your organization.
- Best service : This strategy indicates you want your customers to consider your organization easy to deal with. Customers may choose to work with you even if you have a product similar to your competitors—simply because your service is better.
- Understands my needs : This objective also reflects a customer intimacy strategy. The customer feels like you understand their needs, so they choose your organization's products and services because they are targeted for their specific problem or situation.
Discover ClearPoint's Strategic Plan Dashboard templates here
Internal process objectives.
The internal perspective is typically focused on processes that your organization must excel at. According to Michael Treacy and Fred Wiersema— who have written extensively on the topic —these examples of business strategy processes can be divided into three areas: innovation, customer intimacy, and operational excellence.
All of the objectives from the list below help measure innovation in a general sense. However, there are countless ways to innovate; your objectives should reflect your specific approach. Maybe you’re trying to hit a performance target with your product or improve the quality of a particular product or service, for example. Express your desired innovation goal in whatever way is best for you.
- Most innovative products/services : This objective is for organizations that pride themselves on constant and cutting-edge innovation. You would first need to define what you mean by “innovation” and how you’re innovating in each particular area.
- Differentiate the product : Your organization might use this objective if you are in an environment where the customer cannot tell the difference between your organization and another organization’s product. You are asking your organization to either develop new services around the product or new differentiating features of the product or service.
- Invest a certain amount in innovation : Sometimes organizations use an objective like this to drive investment in research and development or other innovative activities. This objective may be used in a strategy when you are signaling a shift in investments in the innovation category.
- Grow percentage of sales from new products : Similar to investing in innovation, this objective focuses on the outcome your organization is hoping to achieve. It forces you to constantly innovate, even on your most successful products.
- Improve or focus research and development (R&D) : This objective focuses on specific innovation. If you are an organization with multiple product lines, you might want to focus your innovation on one product line over another; calling out the specific direction can be quite helpful in your objective.
- Acquire new customers from innovative offerings : This objective focuses on the reason you put focus on innovation. For example, you may be innovating in order to enter a new market or attract customers you might not be able to reach with your current offerings.
See ClearPoint Strategy in action! Click here to watch a quick DEMO on the software
Customer service.
Creating customer service objectives is a way to ensure your organization continuously maintains focus on this crucial area. In addition to the objectives listed above, consider which aspects of customer service are most relevant to your organization. You may want to improve your customer chat functionality, or, if you sell a software product, improve your customer onboarding process. The smoother your internal processes, the happier your customers.
- Great customer service : Defining what great customer service means in your organization is a way to set the standard and communicate internally. For example, hone in on whether you want to provide one-touch resolution or proactive support, or whether you’re focused on phone support or on-site support.
- Improve customer service : When your organization has a problem with good customer service, you may want an objective to focus on improvement therein. The problem your company has is likely in a specific area, so this objective should be focused on that particular call center or the reactive support that you provide.
- Invest in customer management : This objective is typically used when your strategy is to focus more on your customer management processes than you have in the past.
- Partner with customers to design solutions : Some organizations focus on forming close partnerships with their clients. If your business is an architectural firm or a custom software developer company, this could be a good objective to ensure you are working with your customers to design critical solutions.
- Improve customer satisfaction : If customer satisfaction is critical in your company, this may be a good objective to hone in on. Because it’s generic, the definition for your organization needs to be more focused around particular areas of satisfaction you place focus on.
- Improve customer retention : If your organization wants to focus on retaining current customers, this objective may work for you. You’d likely want to set measures and projects around certain activities to help retain customers.
- Develop and use a customer database : This is a specific objective focused on implementing a large project like a customer relationship management (CRM) system, that could take years to implement.
Claim your FREE 108 healthcare KPI library to improve your organizational performance
Operational excellence.
Sometimes, objectives for operational excellence can be too vague, referring to “excellent” or “world-class” processes or “high-performing” teams. All of the above goals are specific and tied to various aspects of performance. And while you might be tempted to skip over operational excellence goals altogether, it’s important to invest time and resources in this area! Efficiency and cost-effectiveness are key to staying competitive, and achieving these objectives can have a positive impact on your company’s growth.
- Reduce cost by a certain amount annually : This objective focuses on reducing costs—typically costs within a product or service that is an offering (to make that particular product or service more effective). It could also focus on reducing overhead costs across your organization.
- Reduce waste by a certain amount : If your organization uses a lot of raw materials, a typical objective is to reduce waste from that process. This usually results in significant cost savings.
- Invest in Total Quality Management : Total Quality Management (TQM) reflects a process around quality improvement, which can mean doing things more efficiently or effectively. This objective is used in organizations that have implemented (or are implementing) TQM.
- Reduce error rates : This objective applies for organizations that have many repeatable processes. Sometimes this results in Six Sigma projects, and other times the result is just a focus on defining processes so that staff can adhere to these processes.
- Improve and maintain workplace safety : If your organization uses heavy equipment, chemicals, mechanical parts, or machinery, focusing on workplace safety is a good objective. Improving it can reduce costs and improve job satisfaction.
- Reduce energy usage per unit of production : If your organization uses a significant amount of energy, making a goal to reduce this can be an effective and important strategy.
- Capitalize on physical facilities : In retail organizations, this could mean focusing on an appropriate storefront location. Or it could mean finding underutilized assets and either using them or selling/leasing them to others for use.
- Streamline core business processes : Many complex organizations have very long, drawn-out processes that have developed over many years. If your organization is looking at these processes, this could be a key objective for you.
- Increase reliability of operations : If your organization has poor reliability, having an objective like this will encourage management to look at investments and changes in processes that could increase this reliability.
Claim your FREE eBook on 8 effective strategic planning templates here
Regulatory (optional).
If your organization is part of an industry where regulations apply, creating regulatory-related objectives not only helps you stay in compliance but can also help you grow. (Finding a better way to stay informed about new regulations could be an objective itself!) Goals in this area could apply to anything from increasing accountability to implementing risk management plans to streamlining compliance processes.
- Ensure compliance : In a regulated environment, there may be a lot of rules that you need to follow, even if they don’t seem strategic. They are often called “strategic objectives” to ensure no one cuts corners.
- Increase recycling : This is a self-explanatory objective, but can sometimes apply to all aspects of waste. Depending on the organization, there are compliance rules around making this happen.
- Improve reporting and transparency : Organizations just entering a regulatory environment or that are trying to change their business model to meet contract needs may find that they need to improve or change the way they report in order to do better cost accounting or just be more clear about their actions.
- Increase community outreach : For some organizations, it is important to be seen as part of the community. This is especially true for organizations that are either selling a necessity in the community or are creating any kind of negative externality (like pollution).
- Optimize control framework : If you’re a regulated organization in an incentive environment, you may need to make sure you have the proper controls in place to avoid one-off or systematic cheating.
Claim your FREE eBook on the Top 10 Business Strategy Best Practices for 2024
Learning & growth (l&g) objectives.
Learning and growth objectives focus on skills, culture, and organizational capacity. They support the employees responsible for carrying out your strategy, which makes this category of objectives extremely valuable. To make the most of these goals, first, take time to evaluate the specific capabilities required to deliver exceptional performance in your organization. Doing so will help you formulate more specific goals that will give your team the capabilities it needs to support your company’s growth—and improve employee satisfaction at the same time.
- Improve technical and analytical skills : With the increasing advance of computers and technical innovations affecting all industries, this is a common objective for some organizations. Specific technical skills—or a more specific definition—may be included in the objective name.
- Improve a certain skill : This is seen in a goal if an organization is either affected by a new competitive environment or is trying to address a new market. The particular skill would be specific to the organization. This is also seen in organizations with an aging workforce without a clear means to replace highly technical skills.
- Create a performance-focused culture : This objective can be used if your organization is trying to change its culture to one that focuses more on performance management or incentives. This objective shows up a lot in government and nonprofit organizations.
- Improve productivity with cross-functional teams : Large companies see synergies from working together but want to encourage staff to help with this. For example, a bank with multiple products or a multinational company with multiple lines of business may use this objective.
- Invest in tools to make staff more productive : If your organization has the right staff, but the staff does not have the right tools for the job, this may be a critical objective.
- Improve employee retention : This objective is common in learning and growth and may focus on skills, culture, pay, and the overall work environment.
- Attract and retain the best people : This is a good “beginner objective” if your organization is just starting to use the Balanced Scorecard. Ultimately, you’ll need a good plan regarding who you need to hire, how many hires you need, and what the biggest challenges with regard to retention are. You can then become more specific in this objective by addressing those challenges.
- Build high-performing teams : If teamwork is critical in your organization, consider this objective. It can be hard to measure, so you should think about whether you are encouraging teams or mandating teamwork .
- Maintain alignment across the organization : Some companies demand an extensive amount of alignment across the organization, which can be seen through having common objectives or common incentive programs where alignment is important.
- Develop leadership abilities and potential of the team : Many organizations realize that they are good at hiring people but not developing them into good leaders. If this is something your company wants to change, this objective is important.
If you have questions about which of these strategic objective examples may work for you, drop us a line. We’re happy to help.
Turn Strategic Objectives into Success with ClearPoint
Looking for strategic objective examples to inspire your company’s success? ClearPoint Strategy provides the ultimate tools to define, track, and achieve your strategic objectives. Our comprehensive software simplifies the process of setting clear goals, monitoring progress, and ensuring alignment across your organization.
Transform your strategic planning and drive impactful results— book a personalized demo with ClearPoint Strategy today and see how we can help you turn your objectives into achievements.
Book your FREE 1-on-1 DEMO with ClearPoint Strategy
Frequently asked questions, what are strategic objectives.
Strategic objectives are specific, measurable goals that an organization sets to achieve its long-term vision and mission. They guide the direction of the organization and provide a clear roadmap for achieving desired outcomes, aligning resources and efforts toward common goals.
How do you write strategic objectives?
To write strategic objectives:
- Define the Vision and Mission: Ensure your objectives align with the organization's overall vision and mission.
- Use the SMART Criteria: Make objectives Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage key stakeholders in the process to ensure alignment and commitment.
- Prioritize Goals: Identify and prioritize the most critical objectives that will drive the organization forward.
- Draft Clear Statements: Write concise and clear statements that specify what is to be achieved and by when.
What are some examples of strategic objectives?
Examples of strategic objectives include:
- Increase Market Share: Achieve a 15% market share in the next two years by expanding into new regions.
- Enhance Customer Satisfaction: Improve customer satisfaction scores by 20% over the next 12 months through improved service delivery.
- Boost Revenue: Increase annual revenue by 25% within the next three years through new product launches and market expansion.
- Improve Operational Efficiency: Reduce operational costs by 10% within the next 18 months by streamlining processes.
- Develop Talent: Implement a comprehensive training program to increase employee skills and retention rates by 15% over the next year.
What are the benefits of using strategic objectives?
The benefits of using strategic objectives include:
- Clear Direction: Provides a clear and focused direction for the organization’s efforts.
- Alignment: Ensures all departments and employees are working toward the same goals.
- Resource Allocation: Helps in the effective allocation of resources to priority areas.
- Performance Measurement: Allows for tracking progress and measuring success against defined targets.
- Motivation and Engagement: Enhances employee motivation and engagement by providing clear goals to strive for.
How can strategic objectives be used to improve business performance?
Strategic objectives can improve business performance by:
- Guiding Decision-Making: Providing a framework for making informed and consistent decisions.
- Fostering Innovation: Encouraging innovative approaches to achieve objectives and stay competitive.
- Enhancing Accountability: Holding individuals and teams accountable for achieving specific goals.
- Driving Continuous Improvement: Promoting ongoing evaluation and refinement of strategies and processes.
- Aligning Efforts: Ensuring that all organizational efforts are aligned with long-term goals, leading to cohesive and efficient operations.

Latest posts

The ClearPoint Strategy Success Framework: Aligning Organizations

The ClearPoint Strategy Success Framework: Organizing Strategy

Streamlining Strategic Planning with AI
Business growth
Business tips
Business objectives: How to set them (with 5 examples and a template)
As anyone who played rec league sports in the '90s might remember, being on a team for some reason required you to sell knockoff candy bars to raise funds. Every season, my biggest customer was always me. Some kids went door-to-door, some set up outside local businesses, some sent boxes to their parents' jobs—I just used my allowance to buy a few for myself.
Aside from initiative, what my approach lacked was a plan, a goal, and accountability. A lot to ask of an unmotivated nine-year-old, I know, but 100% required for anyone who runs an actual business.
Business objectives help companies avoid my pitfalls by laying the groundwork for all the above so they can pursue achievable growth.
Table of contents:
What are business objectives?
What you want the company to achieve
How you can measure success
Which players are involved in driving success
The timelines needed to plan, initiate, and implement steps
How, if successful, these actions can be integrated sustainably going forward
Business objectives vs. goals
Here's what that breakdown could have looked like for nine-year-old me selling candy for my little league team:
Business objective: I will increase my sales output by learning and implementing point-of-sale conversion frameworks. I'll measure success by comparing week-over-week sales growth to median sales across players on my baseball team.
Business goal: I will sell more candy bars than anyone on my team and earn the grand prize: a team party at Pizza Hut.
The benefits of setting business objectives
You might think it's good enough to continue working status quo toward your goals, but as the cliche goes, good enough usually isn't. Establishing and following defined, actionable steps through business objectives can:
Help establish clear roadmaps: You can translate your objectives into time-sensitive sequences to chart your path toward growth.
Set groundwork for culture: Clear objectives should reflect the culture you envision, and, in turn, they should help guide your team to foster it.
Influence talent acquisition: Once you know your objectives, you can use them to find the people with the specific skills and experiences needed to actualize them.
Encourage teamwork: People work together better when they know what they're working toward.
Establish accountability: By measuring progress, you can see where errors and inefficiencies come from.
Drive productivity: The endgame of an objective is to make individual team members and processes more effective.
How to set business objectives
Setting business objectives takes a thoughtful, top-to-bottom approach. At every level of your business—whether you're a massive candy corporation or one kid selling chocolate almond bars door-to-door—there are improvements to make, steps to take, and players with stakes (or in my case, bats) in the game.

1. Establish clear goals
You can't hit a home run without a fence, and you can't reach a goal without setting it. Before you start brainstorming your objectives, you need to know what your objectives will help you work toward.
Increase total revenue by 25% over the next two years
Reduce production costs by 10% by the end of the year
Provide health insurance for employees by next fiscal year
Grow design department to 10+ employees this year
Reach 100k Instagram followers ahead of new product launch
Implement full rebrand before new partnership announcement
Once you have these goals in place, you can establish individual objectives that position your company to reach them.
2. Set a baseline
Like a field manager before a game, you've got to set your baselines. (Very niche pun, I know.) With a definite goal in mind, the only way to know your progress is to know where you're starting from.
Analyzing your baselines could also help you recalibrate your goals. You may have decided abstractly that you want conversion rates to double in six months, but is that really possible? If your measurables show there's potentially a heavier lift involved than you expected, you can always roll back the goal performance or expand the timeline.
3. Involve players at all levels in the conversation
Too often, the most important people are left out of conversations about goals and objectives. The more levels of complexity and oversight, the more important it is to hear from everyone—yet the more likely it is that some will be excluded.
Let's say you want to reduce overhead by 5% over the next two years for your sporting goods manufacturing outfit. At a high level, your team finds you can reduce production costs by using cheaper materials for baseball gloves. A member of your sales team points out that the reduction in quality, which your brand is famous for, could lead to losses that offset those savings. Meanwhile, a factory representative points out that replacing outdated machines would be expensive initially but would increase efficiency, reduce defects, and cut maintenance costs, breaking even in four years.
By involving various teams at multiple levels, you find it's worth it to extend timelines from two to four years. Your overhead reduction may be lower than 5% by year two but should be much higher than that by year four based on these changes.
The takeaway from this pretty crude example is that it's helpful to make sure every team that touches anything related to your objective gets consulted. They should give valuable, practical input thanks to their boots- (or cleats-) on-the-ground experience.
4. Define measurable outcomes
An objective should be exactly that. Using KPIs (key performance indicators) to apply a level of objectivity to your action steps allows you to measure their progress and success over time and either adapt as you go along or stay the course.
How do you know if your specific objectives are leading to increased web traffic, or if that's just natural (or even incidental) growth? How do you know if your recruiting efforts lead to better candidates, or whether your employees are actually more satisfied? Here are a few examples of measurable outcomes to show proof:
Percentage change (15% overall increase in revenue)
Goal number (10,000 subscribers)
Success range (five to 10 new clients)
Clear change (new company name)
Executable action (weekly newsletter launch)
5. Outline a roadmap with a schedule
You've got your organizational goals defined, logged your baselines, sourced objectives from across your company, and know your metrics for defining success. Now it's time to set an actionable plan you can execute.
Your objectives roadmap should include all involved team members and departments and clear timelines for reaching milestones. Within your objectives, set action items with deadlines to stay on track, along with corresponding progress markers. For the objective of "increase lead conversion efficiency by 10%," that could look like:
May 15: Begin time logging
June 1: Register team members for productivity seminar
June 15: Integrate Trello for managing processes
June 15: Audit time log
August 1: Audit time log—goal efficiency increase of 5%
6. Integrate successful changes
You've successfully achieved your objectives—great! But as Yogi Berra famously said, "It ain't over till it's over," and it ain't over yet.
Don't let this win be a one-off accomplishment. Berra also said "You can observe a lot by just watching," and applying what you observed from this process will help you continue growing your company. Take what worked, and integrate it into your business processes for sustainable improvement. Then create new objectives, so you can continue the cycle.
Examples of business objectives and goals
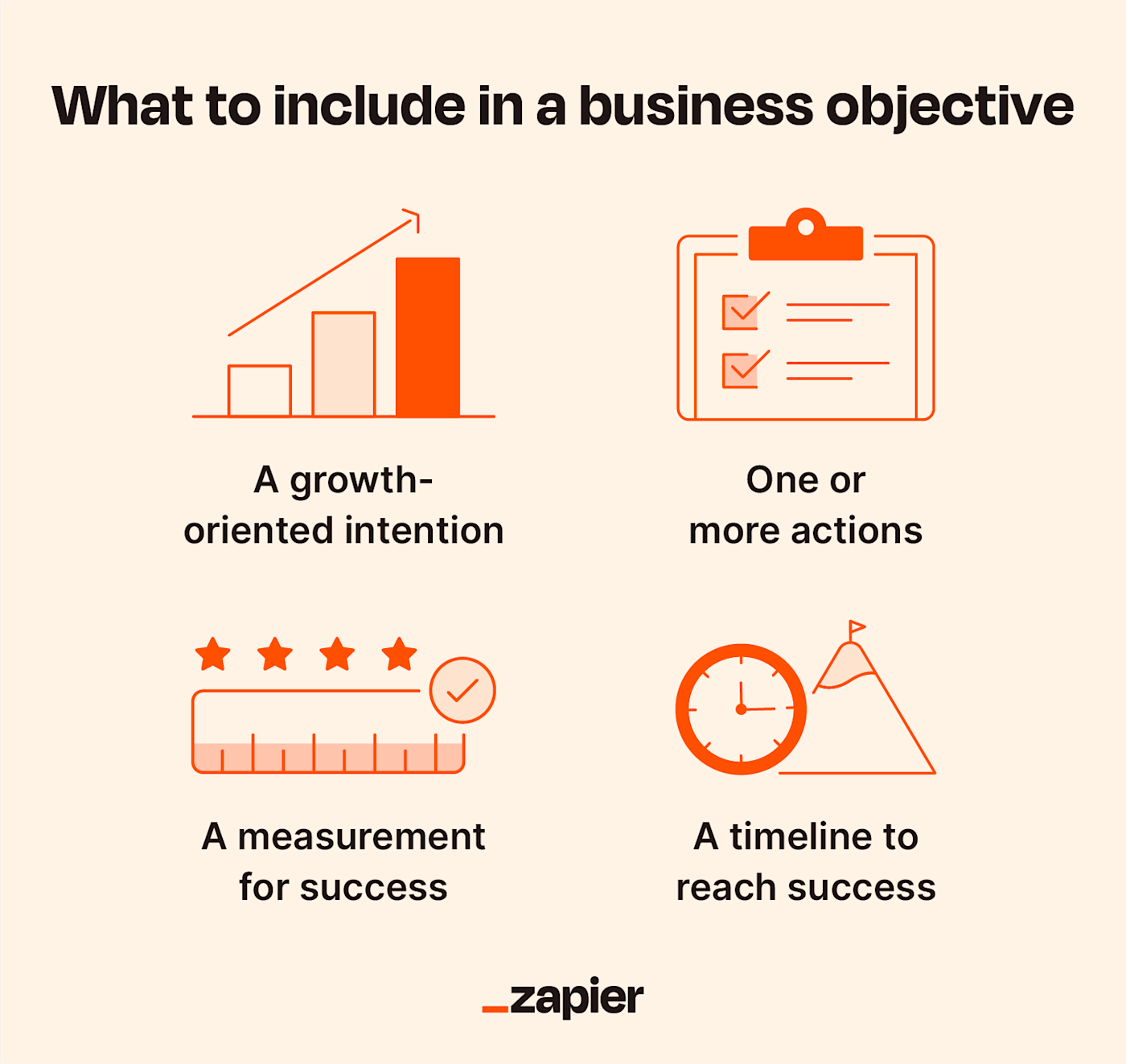
Business objectives aren't collated plans or complicated flowcharts—they're short, impactful statements that are easy to memorize and communicate. There are four basic components every business objective should have:
A growth-oriented intention (improve efficiency)
One or more actions (implement monthly training sessions)
A measurement for success (20% increase)
A timeline to reach success (by end of year)
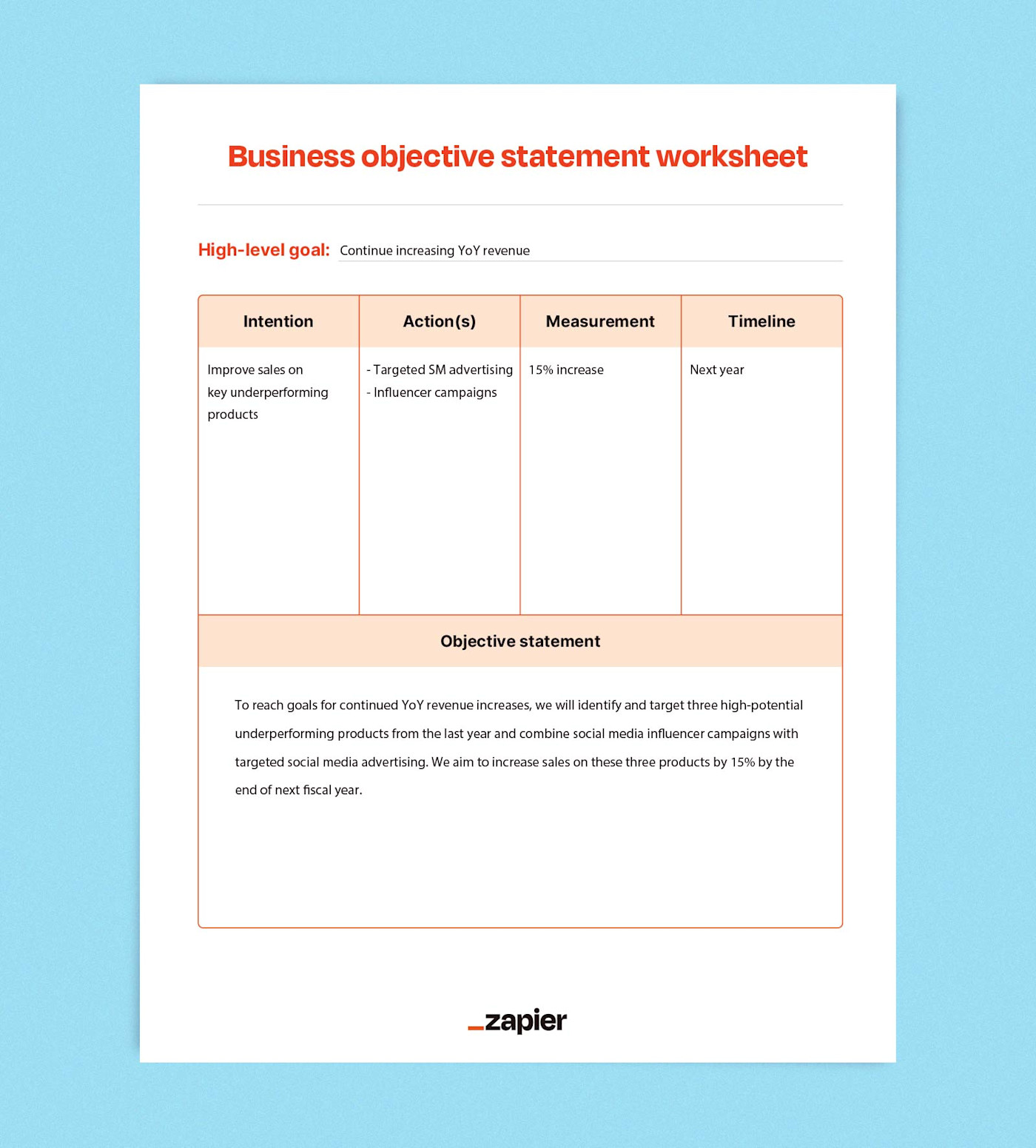
Our SaaS product's implementation team will grow to five during the next fiscal year. This will require us to submit a budget proposal by the end of the quarter and look into restructured growth tracks, new job posting templates, and revised role descriptions by the start of next fiscal year.
We will increase customer satisfaction for our mobile app product demonstrably by the end of the year by integrating a new AI chatbot feature. To measure the change in customer satisfaction, we will monitor ratings in the app store, specifically looking for decreases in rates of negative reviews by 5%-10% as well as increases in overall positive reviews by 5%-10%.
Each of our water filtration systems will achieve NSF certification ahead of the launch of our rebranding campaign. Our product team will establish a checklist of changes necessary for meeting certification requirements and communicate timelines to the marketing team.
HR will implement bi-annual performance reviews starting next year. Review timelines will be built into scheduling software, and HR will automate email reminders to managers to communicate to their teams.
Business objective template
Business objectives can be as simple as one action or as complex as a multi-year roadmap—but they should be able to fall into a clear, actionable framework.
Tips for achieving business objectives
Calling your shot to the left centerfield wall and hitting a ball over that wall are two different things—the same goes for setting an objective and actualizing it.
Start with clear, attainable goals: Objectives should position your business to reach broader growth goals, so start by establishing those.
Align decisions with objectives: Once you set objectives, they should inform other decisions. Decision-makers should think about how changes they make along the way affect their objectives' timelines and execution.
Listen to team members at all levels: Those most affected by organizational changes can be the ones with the least say in the matter. Great ideas and insights can come from any level—even if they're only tangentially related to an outcome.
What makes business objectives so useful is that they can help you build a plan with defined steps to reach obtainable growth goals. As (one more time) Yogi Berra also once said, "You've got to be very careful if you don't know where you are going, because you might not get there."
As you outline your objectives, here are some guides that can help you find KPIs and improvement opportunities:
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Bryce Emley
Currently based in Albuquerque, NM, Bryce Emley holds an MFA in Creative Writing from NC State and nearly a decade of writing and editing experience. His work has been published in magazines including The Atlantic, Boston Review, Salon, and Modern Farmer and has received a regional Emmy and awards from venues including Narrative, Wesleyan University, the Edward F. Albee Foundation, and the Pablo Neruda Prize. When he isn’t writing content, poetry, or creative nonfiction, he enjoys traveling, baking, playing music, reliving his barista days in his own kitchen, camping, and being bad at carpentry.
- Small business
- Sales & business development
Related articles

Project milestones for improved project management
Project milestones for improved project...

14 data visualization examples to captivate your audience
14 data visualization examples to captivate...

61 best businesses to start with $10K or less
61 best businesses to start with $10K or...
SWOT analysis: A how-to guide and template (that won't bore you to tears)
SWOT analysis: A how-to guide and template...
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Capacity planning
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- 65 strategic goals for your company (wi ...
65 strategic goals for your company (with examples)

Strategic goals are a critical part of your strategic plan. In order to achieve your long-term goals, you need a clear sense of where you want to go—and an easy way to share those goals with your team. In this article, we take a look at the difference between strategic goals and other goal setting methodologies, then offer 65 example metrics and strategic goals you can use to get started.
Goal-setting is a critical part of your business strategy. You want to make sure your team is cohesively moving in the right direction—and goals are a great way to do that.
But in order for goals to be effective, they need to be measurable. The important thing isn’t just to create goals, but to create strategic goals that help you accomplish your overall company mission.
In this article, we’ll walk you through when to set strategic goals—vs. other types of goals—and how to do so.
What is a strategic goal?
Because strategic goals are closely connected to strategic planning, they tend to be three to five year goals. But the most important part of setting a strategic goal is to identify where you want to go, and what goals you need to achieve to get there.
How strategic goals compare to other business processes
There are a lot of different strategy and goal setting frameworks you can use. Here’s how strategic goals differ from other types of goals.
Strategic goals vs. strategic planning
Strategic planning is the process of defining the direction your company wants to go in the next three to five years. A strategic plan includes longer term goals, strategic goals, and shorter-term goals that describe how you’ll achieve your strategic goals. The strategic planning process is typically run by decision-makers and stakeholders.
Part of defining your strategic plan is coming up with strategic goals. Your strategic plan should also include customer insights, a SWOT analysis , your company values , your organization’s competitive advantages, specific goals on a quarterly or yearly timeline, and a high-level project roadmap if you have one.
Strategic goals vs. strategic management
Strategic management is the organization and execution of business resources in order to achieve your company goals. These usually help you implement your overall organizational strategy.
Strategic goals, on the other hand, are generally three to five year objectives that tie closely to your strategic plan.
Think of strategic goals as the specific things you want to achieve in three to five years. These strategic goals are part of your strategic plan, which provides more context and direction for why your company wants to move in that direction. Your strategic plan fuels your strategic management process, which is how you’ll actually achieve those goals.
Strategic goals vs. strategic objectives
The difference between strategic goals and strategic objectives is somewhat subjective. In general, objectives tend to be more specific than goals—some people argue that objectives are always quantitative, while goals can be either qualitative or quantitative.
Whether you use the terminology strategic goals vs. objectives , it’s critical to make sure your goals are specific, measurable, and actionable.
Strategic goals vs. big hairy audacious goals (BHAGs)
Big Hairy Audacious Goals (BHAGs) are long-term goals that typically take between 10 and 25 years to complete. These are industry-defining goals, like Microsoft’s famous goal to put "a computer on every desk and in every home."
Not every organization has—or needs—BHAGs. Depending on your business strategy, a vision statement might be enough. Whether or not you set BHAGs, strategic goals are shorter-term goals that help you accomplish these bigger, ambitious goals.
Strategic goals vs. OKRs
OKRs , which stands for Objectives and Key Results, is a goal setting methodology developed by Andy Grove that follows a simple but flexible framework:
I will [objective] as measured by [key result] .
OKRs can span multiple years, but most commonly these are one to two year objectives that help your company accomplish your larger strategic plan. In a typical OKR structure, your OKRs feed into your broader strategic goals.
Strategic goals vs. KPIs
KPIs, or key performance indicators , are qualitative measures of how you’re progressing. Like OKRs, KPIs tend to be shorter in time frame than strategic goals. This is partially due to the fact that KPIs are nearly always quantitative. Achieving several long-term KPIs helps you achieve your broader three to five year strategic goals.
Strategic goals vs. business goals
Business goals are predetermined targets that organizations plan to achieve in a specific amount of time. Technically, strategic goals—along with BHAGs, OKRs, and KPIs—are a type of business goal.
65 example strategic metrics and goals
If you’ve never written a strategic goal before, it’s helpful to check out common goals. Though your strategic goals are unique to your strategic plan, use these examples as templates to create measurable, actionable goals with clear success metrics.
Set strategic goals that are:
Simply phrased
Easy to track
For more tips on what constitutes a good goal, read our article on how to write SMART goals .
Keep in mind that these goals should be achievable in three to five years. For shorter goals, consider setting OKRs or KPIs instead. For longer goals, check out vision statements and BHAGs .
Strategic goals: finance
Financial strategic goals typically center around a few different important financial metrics, including:
1. Increasing revenue
2. Attaining or maintaining profitability
3. Growing shareholder value
4. Diversifying your revenue streams
5. Becoming a financially sustainable company
6. Reducing production costs
7. Increasing profit margin
8. Setting revenue targets for new products
9. Reducing department-specific budgets
10. Influencing the percentage of local vs. international sales
Examples of financial strategic goals
These examples do not represent Asana’s goals, and are merely included here for educational purposes.
11. Increase total revenue by $10M in the next three years.
12. Reduce cost by 12% to become a profitable company by 2024.
13. Grow a specific product’s revenue to 30% of overall business revenue within the next five years.
14. Reduce marketing budget by 10% in the next three years.
15. Update our sales profile so 50% of our sales are international by 2026.
Strategic goals: customer-focused
Strategic goals that focus on your customers can help you break into a new market or further develop a trustworthy brand. These metrics can include:
16. Reducing customer churn
17. Measurably increasing customer satisfaction
18. Increasing the number of new customers
19. Increasing customer retention
20. Offering great customer value
21. Boosting customer outreach
22. Increasing customer conversion rates
23. Breaking into new customer segments
24. Increasing the number of returning customers
25. Decreasing the percentage of returned products
Examples of strategic goals focused on customer metrics
26. Increase net promoter score (NPS) by three points in the next year, and 10 points in the next five years.
27. Capture 23% market share by 2025.
28. Provide the best customer experience in the market—measured based on reaction time, customer sentiment, and brand tracking.
29. Increase customer retention by 3% every year.
30. Reduce the percentage of returned products to 2% by 2023.
Strategic goals: growth
On an organizational level, growth refers to how your company expands and develops. Growth metrics include:
31. Increasing market share
32. Breaking into new markets
33. Developing new products, features, or services
34. Increasing operational reliability and/or compliance
35. Increasing company velocity
36. Opening new locations
37. Building your brand on social media
38. Increasing website traffic
39. Acquiring a new company
Examples of strategic goals about growth
40. Open 12 new locations within the next four years.
41. Increase market share to 8% by 2026.
42. Reach 5M followers on social media (including Instagram and Twitter).
43. Increase web traffic to 300K visitors per year by 2024.
44. Start three new product streams by 2027.
Strategic goals: internal
You can also set strategic goals focusing on your internal company goals. Example employee-centric metrics can include:
45. Increasing employee retention
46. Adding new team members
47. Building a healthy organizational culture
48. Implementing a performance review cycle
49. Standardizing titles and/or levels
50. Improving cross-functional productivity
51. Spinning up a project management office (PMO) to standardize processes
52. Attracting the best talent
53. Building high-performing teams
54. Investing in personal and professional development
55. Reducing burnout and impostor syndrome
56. Building employee-focused training programs
57. Reducing employee turnover
58. Improving workplace safety
59. Building better facilities management
Examples of internal strategic goals
60. Add 20 new team members within the next four years.
61. Increase overall engagement scores by 7% based on yearly surveys.
62. Increase new hire referrals to 5,000 team members per year by 2026.
63. Develop and circulate new company values by 2023.
64. Implement a biannual performance review cycle within the next three years.
65. Attain maximum workplace safety score rating within the next three years.
How Asana uses work management to effectively manage goals
Learn how Asana's Head of Organizational Strategy helps teams set, track, and achieve their goals.
Achieve your goals with goal tracking technology
Once you develop your goals, you need a clear way to track, measure, and communicate those goals. Too often, teams set great goals and then don’t know how to track those goals over time.
Instead of letting your goals collect dust in a slide deck or spreadsheet somewhere, use goal tracking technology to connect your strategic goals to your team’s daily work. With Asana , you can track long-term goals, as well as the shorter-term objectives that feed into those goals.
Related resources

What's the difference between accuracy and precision?

How Asana streamlines strategic planning with work management
What is management by objectives (MBO)?

7 steps to complete a social media audit (with template)
Business Goals 101: How to Set, Track, and Achieve Your Organization’s Goals with Examples
By Kate Eby | November 7, 2022
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Learning how to set concrete, achievable business goals is critical to your organization’s success. We’ve consulted seasoned experts on how to successfully set and achieve short- and long-term business goals, with examples to help you get started.
Included on this page, you’ll find a list of the different types of business goals , the benefits and challenges of business goal-setting, and examples of short-term and long-term business goals. Plus, find expert tips and compare and contrast business goal-setting frameworks.
What Are Business Goals?
Business goals are the outcomes an organization aims to achieve. They can be broad and long term or specific and short term. Business leaders set goals in order to motivate teams, measure progress, and improve performance.

“Business goals are those that represent a company's overarching mission,” says David Bitton, Co-founder and CMO of DoorLoop . “These goals typically cover the entire business and are vast in scope. They are established so that employees may work toward a common goal. In essence, business goals specify the ‘what’ of a company's purpose and provide teams with a general course to pursue.”
For more resources and information on setting goals, try one of these free goal tracking and setting templates .
Business Goals vs. Business Objectives
Many professionals use the terms business goal and business objective interchangeably. Generally, a business goal is a broad, long-term outcome an organization works toward, while a business objective is a specific and measurable task, project, or initiative.
Think of business objectives as the steps an organization takes toward their broader, long-term goals. In some cases, a business objective might simply be a short-term goal. In most cases, business goals refer to outcomes, while business objectives refer to actionable tasks.
“Business objectives are clear and precise,” says Bitton. “When businesses set out to achieve their business goals, they do so by establishing quantifiable, simply defined, and trackable objectives. Business objectives lay out the ‘how’ in clear, doable steps that lead to the desired result.”
For more information and resources, see this article on the key differences between goals and objectives.
Common Frameworks for Writing Business Goals
Goal-setting frameworks can help you get the most out of your business goals. Common frameworks include SMART, OKR, MBO, BHAG, and KRA. Learning about these goal-setting tools can help you choose the right one for your company.
Here are the common frameworks for writing business goals with examples:
- SMART: SMART goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. This is probably the most popular method for setting goals. Ensuring that your goals meet SMART goal criteria is a tried and true way to increase your chances of success and make progress on even your most ambitious goals. Example SMART Goal: We will increase the revenue from our online store by 5 percent in three months by increasing our sign-up discount from 25 to 30 percent.
- OKR: Another popular approach is to set OKRs, or objectives and key results. In order to use OKRs , a team or individual selects an objective they would like to work toward. Then they select key results , or standardized measurements of success or progress. Example Objective: We aim to increase the sales revenue of our online store. Example Key Result: Make $200,000 in sales revenue from the online store in June.
- MBO: MBO, or management by objectives , is a collaborative goal-setting framework and management technique. When using MBO, managers work with employees to create specific, agreed-upon objectives and develop a plan to achieve them. This framework is excellent for ensuring that everyone is aligned on their goals. Example MBO: This quarter, we aim to decrease patient waiting times by 30 percent.
- BHAG: A BHAG, or a big hairy audacious goal , is an ambitious, possibly unattainable goal. While the idea of setting a BHAG might run contrary to a lot of advice about goal-setting, a BHAG can energize the team by giving everyone a shared purpose. These are best for long-term, visionary business goals. Example BHAG: We want to be the leading digital music service provider globally by 2030.
- KRA: KRAs, or key result areas , refer to a short list of goals that an individual, department, or organization can work toward. KRAs function like a rubric for general progress and to help ensure that the team’s efforts have an optimal impact on the overall health of the business. Example KRA: Increase high-quality sales leads per sales representative.
Use the table below to compare the pros and cons of each goal-setting framework to help you decide which framework will be most useful for your business goals.
| Framework | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, time-bound) | ||
| OKRs (objectives and key results) | ||
| MBOs (management by objectives) | ||
| BHAGs (big hairy audacious goals) | ||
| KRAs (key results areas) |
Types of Business Goals
A business goal is any goal that helps move an organization toward a desired result. There are many types of business goals, including process goals, development goals, innovation goals, and profitability goals.
Here are some common types of business goals:
- Growth: A growth goal is a goal relating to the size and scope of the company. A growth goal might involve increasing the number of employees, adding new verticals, opening new stores or offices, or generally expanding the impact or market share of a company.
- Process: A process goal , also called a day-to-day goal or an efficiency goal , is a goal to improve the everyday effectiveness of a team or company. A process goal might involve establishing or improving workflows or routines, delegating responsibilities, or improving team skills.
- Problem-Solving: Problem-solving goals address a specific challenge. Problem-solving goals might involve removing an inefficiency, changing policies to accommodate a new law or regulation, or reorienting after an unsuccessful project or initiative.
- Development: A development goal , also called an educational goal , is a goal to develop new skills or expertise, either for your team or for yourself. For example, development goals might include developing a new training module, learning a new coding language, or taking a continuing education class in your field.
- Innovation: An innovation goal is a goal to create new or more reliable products or services. Innovation goals might involve developing a new mobile app, redesigning an existing product, or restructuring to a new business model.
- Profitability: A profitability goal , also called a financial goal , is any goal to improve the financial prospects of a company. Profitability goals might involve increasing revenue, decreasing debt, or growing the company’s shareholder value.
- Sustainability: A s ustainability goal is a goal to either decrease your company’s negative impact on the environment or actively improve the environment through specific initiatives. For example, a sustainability goal might be to decrease a company’s carbon footprint, reduce energy use, or divest from environmentally irresponsible organizations and reinvest in sustainable ones.
- Marketing: A marketing goal , also called a brand goal , is a goal to increase a company’s influence and brand awareness in the market. A marketing goal might be to boost engagement across social media platforms or generate more higher-quality leads.
- Customer Relations: A customer relations goal is a goal to improve customer satisfaction with and trust in your product or services. A customer relations goal might be to decrease customer service wait times, improve customers’ self-reported satisfaction with your products or services, or increase customer loyalty.
- Company Culture: A company culture goal , also called a social goal , is a goal to improve the work environment of your company. A company culture goal might be to improve employee benefits; improve diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) across your organization; or create a greater sense of work-life balance among employees.
What Are Business Goal Examples?
Business goal examples are real or hypothetical business goal statements. A business goal example can use any goal-setting framework, such as SMART, OKR, or KRA. Teams and individuals use these examples to guide them in the goal-setting process.
For a comprehensive list of examples by industry and type, check out this collection of business goal examples .
What Are Short-Term Business Goals?
Short-term business goals are measurable objectives that can be completed within hours, days, weeks, or months. Many short-term business goals are smaller objectives that help a company make progress on a longer-term goal.
The first step in setting a short-term business goal is to clarify your long-term goals.

“My practice is to start with an aspirational vision that is the framework for my long-term goals and to compare that ‘better tomorrow’ with the realities of today,” says Morgan Roth, Chief Communication Strategy Officer at EveryLife Foundation for Rare Diseases . “Once that framework of three to five major goals is drafted and I have buy-in, I can think about how we get there. Those will be my short-term goals.”
Bitton recommends using the SMART framework for setting short-term business goals to ensure that your team has structure and that their goals are achievable. “Determine which objectives can be attained in a reasonable amount of time,” she adds. “This will help you stay motivated. Your organization may suffer if you try to squeeze years-long ambitions into a month-long project.”
Short-Term Business Goal Examples
Companies can use short-term business goals to increase profits, implement new policies or initiatives, or improve company culture. We’ve gathered some examples of short-term business goals to help you brainstorm your own goal ideas.
Here are three sample short-term business goals:
- Increase Your Market Share: When companies increase their market share, they increase the percentage of their target audience who chooses their product or service over competitors. This is a good short-term goal for companies that have long-term expansion goals. For example, a local retail business might want to draw new customers from the local community. The business sets a goal of increasing the average number of customers who enter its store from 500 per week to 600 per week within three months. It can meet this goal by launching a local advertising initiative, reducing prices, or expanding its presence on local social media groups. Small business owners can check out this comprehensive guide to learn more about setting productive goals for their small businesses.
- Reduce Paper Waste: All businesses produce waste, but company leaders can take actions to reduce or combat excessive waste. Reducing your company’s paper waste is a good short-term goal for companies that have long-term sustainability goals. For example, a large company’s corporate headquarters is currently producing an average of four pounds of paper waste per employee per day. They set a goal of decreasing this number to two pounds by the end of the current quarter. They can meet this goal by incentivizing or requiring electronic reporting and forms whenever possible.
- Increase Social Media Engagement: High social media engagement is essential for businesses that want to increase brand awareness or attract new customers. This is a good short-term goal for companies with long-term marketing or brand goals. For example, after reviewing a recent study, a natural cosmetics company learns that its target audience is 30 percent more likely to purchase products recommended to them by TikTok influencers, but the company’s social media team only posts sporadically on its TikTok. The company sets a goal of producing and posting two makeup tutorials on TikTok each week for the next three months.
What Are Long-Term Business Goals?
A l ong-term business goal is an ambitious desired outcome for your company that is broad in scope. Long-term business goals might be harder to measure or achieve. They provide a shared direction and motivation for team members.
“Long-term planning is increasingly difficult in our very complex and interconnected world,” says Roth. “Economically, politically, and culturally, we’re seeing sea changes in the way we live and work. Accordingly, it’s important to be thoughtful about long-term goal-setting, but not to the point where concerns stifle creativity and your ‘Big Ideas.’ A helpful strategy I employ is to avoid assumptions. Long-term planning should be based on what you know, not on what you assume will be true in some future state.”
Tip: You can turn most short-term goals into long-term goals by increasing their scope. For example, to turn the “increase market share” goal described above into a long-term goal, you might increase the target weekly customers from 600 to 2,000. This will likely take longer than a few months and might require expanding the store or opening new locations.
Long-Term Business Goal Examples
An organization can use long-term business goals to unify their vision, motivate workers, and prioritize short-term goals. We’ve gathered some examples of long-term business goals to guide you in setting goals for your business.
Here are three sample long-term business goals:
- Increase Total Sales: A common growth profitability goal is to increase sales. An up-and-coming software company might set a long-term goal of increasing their product sales by 75 percent over two years.
- Increase Employee Retention: Companies with high employee retention enjoy many benefits, such as decreased hiring costs, better brand reputation, and a highly skilled workforce. A large corporation with an employee retention rate of 80 percent might set a long-term goal of increasing that retention rate to 90 percent within five years.
- Develop a New Technology: Most companies in the IT sphere rely on innovation goals to stay competitive. A company might set a long-term goal of creating an entirely new AI technology within 10 years.
Challenges of Setting Business Goals
Although setting business goals has few downsides, teams can run into problems. For example, setting business goals that are too ambitious, inflexible, or not in line with the company vision can end up being counterproductive.
Here are some common challenges teams face when setting business goals:
- Having a Narrow Focus: One of the greatest benefits of setting business goals is how doing so can focus your team. That said, this can also be a drawback, as such focus on a single goal can narrow the team’s perspective and make people less able to adapt to change or recognize and seize unexpected opportunities.
- Being Overly Ambitious: It’s important to be ambitious, but some goals are simply too lofty. If a goal is impossible to hit, it can be demoralizing.
- Not Being Ambitious Enough: The opposite problem is when companies are too modest with their goal-setting. Goals should be realistic but challenging. Teams that prioritize the former while ignoring the latter will have problems with motivation and momentum.
- Facing Unexpected Obstacles: If something happens that suddenly derails progress toward a goal, it can be a huge blow to a company. Learn about project risk management to better manage uncertainty in your projects.
- Having Unclear Objectives: Goals that are vague or unquantifiable will not be as effective as clear, measurable goals. Use frameworks such as SMART goals or OKRs to make sure your goals are clear.
- Losing Motivation: Teams can lose sight of their goals over time, especially with long-term goals. Be sure to review and assess progress toward goals regularly to keep your long-term vision front of mind.
Why You Need Business Goals
Every business needs to set clear goals in order to succeed. Business goals provide direction, encourage focus, improve morale, and spur growth. We’ve gathered some common benefits of goal-setting for your business.
Here are some benefits you can expect from setting business goals:
- More Clarity: Business goals ensure that everyone is moving toward a determined end point. Companies with clear business goals have teams that agree on what is important and what everyone should be working toward.
- Increased Focus: Business goals encourage focus, which improves performance and increases productivity.
- Faster Growth: Business goals help companies expand and thrive. “Setting goals and objectives for your business will help you grow it more quickly,” says Bitton. “Your potential for growth increases as you consistently accomplish your goals and objectives.”
- Improved Morale: Everyone is happier when they are working toward a tangible goal. Companies with clear business goals have employees that are more motivated and fulfilled at work. Plus, measuring progress toward specific goals makes it easier to notice and acknowledge everyone’s successes.
- More Accountability: Having tangible goals means that everyone can see whether or not their work is effective at making progress toward those goals.
- Better Decision-Making: Business goals help teams prioritize tasks and make tough decisions. “You gain perspective on your entire business, which makes it easier for you to make smart decisions,” says Bitton. “You are forming a clear vision for the direction you want your business to go, which facilitates the efficient distribution of resources, the development of strategies, and the prioritization of tasks.”
Improve Your Goal-Setting with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
How to Write a Business Plan in 9 Steps (+ Template and Examples)
Every successful business has one thing in common, a good and well-executed business plan. A business plan is more than a document, it is a complete guide that outlines the goals your business wants to achieve, including its financial goals . It helps you analyze results, make strategic decisions, show your business operations and growth.
If you want to start a business or already have one and need to pitch it to investors for funding, writing a good business plan improves your chances of attracting financiers. As a startup, if you want to secure loans from financial institutions, part of the requirements involve submitting your business plan.
Writing a business plan does not have to be a complicated or time-consuming process. In this article, you will learn the step-by-step process for writing a successful business plan.
You will also learn what you need a business plan for, tips and strategies for writing a convincing business plan, business plan examples and templates that will save you tons of time, and the alternatives to the traditional business plan.
Let’s get started.
What Do You Need A Business Plan For?
Businesses create business plans for different purposes such as to secure funds, monitor business growth, measure your marketing strategies, and measure your business success.
1. Secure Funds
One of the primary reasons for writing a business plan is to secure funds, either from financial institutions/agencies or investors.
For you to effectively acquire funds, your business plan must contain the key elements of your business plan . For example, your business plan should include your growth plans, goals you want to achieve, and milestones you have recorded.
A business plan can also attract new business partners that are willing to contribute financially and intellectually. If you are writing a business plan to a bank, your project must show your traction , that is, the proof that you can pay back any loan borrowed.
Also, if you are writing to an investor, your plan must contain evidence that you can effectively utilize the funds you want them to invest in your business. Here, you are using your business plan to persuade a group or an individual that your business is a source of a good investment.
2. Monitor Business Growth
A business plan can help you track cash flows in your business. It steers your business to greater heights. A business plan capable of tracking business growth should contain:
- The business goals
- Methods to achieve the goals
- Time-frame for attaining those goals
A good business plan should guide you through every step in achieving your goals. It can also track the allocation of assets to every aspect of the business. You can tell when you are spending more than you should on a project.
You can compare a business plan to a written GPS. It helps you manage your business and hints at the right time to expand your business.
3. Measure Business Success
A business plan can help you measure your business success rate. Some small-scale businesses are thriving better than more prominent companies because of their track record of success.
Right from the onset of your business operation, set goals and work towards them. Write a plan to guide you through your procedures. Use your plan to measure how much you have achieved and how much is left to attain.
You can also weigh your success by monitoring the position of your brand relative to competitors. On the other hand, a business plan can also show you why you have not achieved a goal. It can tell if you have elapsed the time frame you set to attain a goal.
4. Document Your Marketing Strategies
You can use a business plan to document your marketing plans. Every business should have an effective marketing plan.
Competition mandates every business owner to go the extraordinary mile to remain relevant in the market. Your business plan should contain your marketing strategies that work. You can measure the success rate of your marketing plans.
In your business plan, your marketing strategy must answer the questions:
- How do you want to reach your target audience?
- How do you plan to retain your customers?
- What is/are your pricing plans?
- What is your budget for marketing?

How to Write a Business Plan Step-by-Step
1. create your executive summary.
The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans . Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.

Generally, there are nine sections in a business plan, the executive summary should condense essential ideas from the other eight sections.
A good executive summary should do the following:
- A Snapshot of Growth Potential. Briefly inform the reader about your company and why it will be successful)
- Contain your Mission Statement which explains what the main objective or focus of your business is.
- Product Description and Differentiation. Brief description of your products or services and why it is different from other solutions in the market.
- The Team. Basic information about your company’s leadership team and employees
- Business Concept. A solid description of what your business does.
- Target Market. The customers you plan to sell to.
- Marketing Strategy. Your plans on reaching and selling to your customers
- Current Financial State. Brief information about what revenue your business currently generates.
- Projected Financial State. Brief information about what you foresee your business revenue to be in the future.
The executive summary is the make-or-break section of your business plan. If your summary cannot in less than two pages cannot clearly describe how your business will solve a particular problem of your target audience and make a profit, your business plan is set on a faulty foundation.
Avoid using the executive summary to hype your business, instead, focus on helping the reader understand the what and how of your plan.
View the executive summary as an opportunity to introduce your vision for your company. You know your executive summary is powerful when it can answer these key questions:
- Who is your target audience?
- What sector or industry are you in?
- What are your products and services?
- What is the future of your industry?
- Is your company scaleable?
- Who are the owners and leaders of your company? What are their backgrounds and experience levels?
- What is the motivation for starting your company?
- What are the next steps?
Writing the executive summary last although it is the most important section of your business plan is an excellent idea. The reason why is because it is a high-level overview of your business plan. It is the section that determines whether potential investors and lenders will read further or not.
The executive summary can be a stand-alone document that covers everything in your business plan. It is not uncommon for investors to request only the executive summary when evaluating your business. If the information in the executive summary impresses them, they will ask for the complete business plan.
If you are writing your business plan for your planning purposes, you do not need to write the executive summary.
2. Add Your Company Overview
The company overview or description is the next section in your business plan after the executive summary. It describes what your business does.
Adding your company overview can be tricky especially when your business is still in the planning stages. Existing businesses can easily summarize their current operations but may encounter difficulties trying to explain what they plan to become.
Your company overview should contain the following:
- What products and services you will provide
- Geographical markets and locations your company have a presence
- What you need to run your business
- Who your target audience or customers are
- Who will service your customers
- Your company’s purpose, mission, and vision
- Information about your company’s founders
- Who the founders are
- Notable achievements of your company so far
When creating a company overview, you have to focus on three basics: identifying your industry, identifying your customer, and explaining the problem you solve.
If you are stuck when creating your company overview, try to answer some of these questions that pertain to you.
- Who are you targeting? (The answer is not everyone)
- What pain point does your product or service solve for your customers that they will be willing to spend money on resolving?
- How does your product or service overcome that pain point?
- Where is the location of your business?
- What products, equipment, and services do you need to run your business?
- How is your company’s product or service different from your competition in the eyes of your customers?
- How many employees do you need and what skills do you require them to have?
After answering some or all of these questions, you will get more than enough information you need to write your company overview or description section. When writing this section, describe what your company does for your customers.

The company description or overview section contains three elements: mission statement, history, and objectives.
- Mission Statement
The mission statement refers to the reason why your business or company is existing. It goes beyond what you do or sell, it is about the ‘why’. A good mission statement should be emotional and inspirational.
Your mission statement should follow the KISS rule (Keep It Simple, Stupid). For example, Shopify’s mission statement is “Make commerce better for everyone.”
When describing your company’s history, make it simple and avoid the temptation of tying it to a defensive narrative. Write it in the manner you would a profile. Your company’s history should include the following information:
- Founding Date
- Major Milestones
- Location(s)
- Flagship Products or Services
- Number of Employees
- Executive Leadership Roles
When you fill in this information, you use it to write one or two paragraphs about your company’s history.
Business Objectives
Your business objective must be SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.) Failure to clearly identify your business objectives does not inspire confidence and makes it hard for your team members to work towards a common purpose.
3. Perform Market and Competitive Analyses to Proof a Big Enough Business Opportunity
The third step in writing a business plan is the market and competitive analysis section. Every business, no matter the size, needs to perform comprehensive market and competitive analyses before it enters into a market.
Performing market and competitive analyses are critical for the success of your business. It helps you avoid entering the right market with the wrong product, or vice versa. Anyone reading your business plans, especially financiers and financial institutions will want to see proof that there is a big enough business opportunity you are targeting.
This section is where you describe the market and industry you want to operate in and show the big opportunities in the market that your business can leverage to make a profit. If you noticed any unique trends when doing your research, show them in this section.
Market analysis alone is not enough, you have to add competitive analysis to strengthen this section. There are already businesses in the industry or market, how do you plan to take a share of the market from them?
You have to clearly illustrate the competitive landscape in your business plan. Are there areas your competitors are doing well? Are there areas where they are not doing so well? Show it.
Make it clear in this section why you are moving into the industry and what weaknesses are present there that you plan to explain. How are your competitors going to react to your market entry? How do you plan to get customers? Do you plan on taking your competitors' competitors, tap into other sources for customers, or both?
Illustrate the competitive landscape as well. What are your competitors doing well and not so well?
Answering these questions and thoughts will aid your market and competitive analysis of the opportunities in your space. Depending on how sophisticated your industry is, or the expectations of your financiers, you may need to carry out a more comprehensive market and competitive analysis to prove that big business opportunity.
Instead of looking at the market and competitive analyses as one entity, separating them will make the research even more comprehensive.
Market Analysis
Market analysis, boarding speaking, refers to research a business carried out on its industry, market, and competitors. It helps businesses gain a good understanding of their target market and the outlook of their industry. Before starting a company, it is vital to carry out market research to find out if the market is viable.

The market analysis section is a key part of the business plan. It is the section where you identify who your best clients or customers are. You cannot omit this section, without it your business plan is incomplete.
A good market analysis will tell your readers how you fit into the existing market and what makes you stand out. This section requires in-depth research, it will probably be the most time-consuming part of the business plan to write.
- Market Research
To create a compelling market analysis that will win over investors and financial institutions, you have to carry out thorough market research . Your market research should be targeted at your primary target market for your products or services. Here is what you want to find out about your target market.
- Your target market’s needs or pain points
- The existing solutions for their pain points
- Geographic Location
- Demographics
The purpose of carrying out a marketing analysis is to get all the information you need to show that you have a solid and thorough understanding of your target audience.
Only after you have fully understood the people you plan to sell your products or services to, can you evaluate correctly if your target market will be interested in your products or services.
You can easily convince interested parties to invest in your business if you can show them you thoroughly understand the market and show them that there is a market for your products or services.
How to Quantify Your Target Market
One of the goals of your marketing research is to understand who your ideal customers are and their purchasing power. To quantify your target market, you have to determine the following:
- Your Potential Customers: They are the people you plan to target. For example, if you sell accounting software for small businesses , then anyone who runs an enterprise or large business is unlikely to be your customers. Also, individuals who do not have a business will most likely not be interested in your product.
- Total Households: If you are selling household products such as heating and air conditioning systems, determining the number of total households is more important than finding out the total population in the area you want to sell to. The logic is simple, people buy the product but it is the household that uses it.
- Median Income: You need to know the median income of your target market. If you target a market that cannot afford to buy your products and services, your business will not last long.
- Income by Demographics: If your potential customers belong to a certain age group or gender, determining income levels by demographics is necessary. For example, if you sell men's clothes, your target audience is men.
What Does a Good Market Analysis Entail?
Your business does not exist on its own, it can only flourish within an industry and alongside competitors. Market analysis takes into consideration your industry, target market, and competitors. Understanding these three entities will drastically improve your company’s chances of success.

You can view your market analysis as an examination of the market you want to break into and an education on the emerging trends and themes in that market. Good market analyses include the following:
- Industry Description. You find out about the history of your industry, the current and future market size, and who the largest players/companies are in your industry.
- Overview of Target Market. You research your target market and its characteristics. Who are you targeting? Note, it cannot be everyone, it has to be a specific group. You also have to find out all information possible about your customers that can help you understand how and why they make buying decisions.
- Size of Target Market: You need to know the size of your target market, how frequently they buy, and the expected quantity they buy so you do not risk overproducing and having lots of bad inventory. Researching the size of your target market will help you determine if it is big enough for sustained business or not.
- Growth Potential: Before picking a target market, you want to be sure there are lots of potential for future growth. You want to avoid going for an industry that is declining slowly or rapidly with almost zero growth potential.
- Market Share Potential: Does your business stand a good chance of taking a good share of the market?
- Market Pricing and Promotional Strategies: Your market analysis should give you an idea of the price point you can expect to charge for your products and services. Researching your target market will also give you ideas of pricing strategies you can implement to break into the market or to enjoy maximum profits.
- Potential Barriers to Entry: One of the biggest benefits of conducting market analysis is that it shows you every potential barrier to entry your business will likely encounter. It is a good idea to discuss potential barriers to entry such as changing technology. It informs readers of your business plan that you understand the market.
- Research on Competitors: You need to know the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors and how you can exploit them for the benefit of your business. Find patterns and trends among your competitors that make them successful, discover what works and what doesn’t, and see what you can do better.
The market analysis section is not just for talking about your target market, industry, and competitors. You also have to explain how your company can fill the hole you have identified in the market.
Here are some questions you can answer that can help you position your product or service in a positive light to your readers.
- Is your product or service of superior quality?
- What additional features do you offer that your competitors do not offer?
- Are you targeting a ‘new’ market?
Basically, your market analysis should include an analysis of what already exists in the market and an explanation of how your company fits into the market.
Competitive Analysis
In the competitive analysis section, y ou have to understand who your direct and indirect competitions are, and how successful they are in the marketplace. It is the section where you assess the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, the advantage(s) they possess in the market and show the unique features or qualities that make you different from your competitors.

Many businesses do market analysis and competitive analysis together. However, to fully understand what the competitive analysis entails, it is essential to separate it from the market analysis.
Competitive analysis for your business can also include analysis on how to overcome barriers to entry in your target market.
The primary goal of conducting a competitive analysis is to distinguish your business from your competitors. A strong competitive analysis is essential if you want to convince potential funding sources to invest in your business. You have to show potential investors and lenders that your business has what it takes to compete in the marketplace successfully.
Competitive analysis will s how you what the strengths of your competition are and what they are doing to maintain that advantage.
When doing your competitive research, you first have to identify your competitor and then get all the information you can about them. The idea of spending time to identify your competitor and learn everything about them may seem daunting but it is well worth it.
Find answers to the following questions after you have identified who your competitors are.
- What are your successful competitors doing?
- Why is what they are doing working?
- Can your business do it better?
- What are the weaknesses of your successful competitors?
- What are they not doing well?
- Can your business turn its weaknesses into strengths?
- How good is your competitors’ customer service?
- Where do your competitors invest in advertising?
- What sales and pricing strategies are they using?
- What marketing strategies are they using?
- What kind of press coverage do they get?
- What are their customers saying about your competitors (both the positive and negative)?
If your competitors have a website, it is a good idea to visit their websites for more competitors’ research. Check their “About Us” page for more information.

If you are presenting your business plan to investors, you need to clearly distinguish yourself from your competitors. Investors can easily tell when you have not properly researched your competitors.
Take time to think about what unique qualities or features set you apart from your competitors. If you do not have any direct competition offering your product to the market, it does not mean you leave out the competitor analysis section blank. Instead research on other companies that are providing a similar product, or whose product is solving the problem your product solves.
The next step is to create a table listing the top competitors you want to include in your business plan. Ensure you list your business as the last and on the right. What you just created is known as the competitor analysis table.
Direct vs Indirect Competition
You cannot know if your product or service will be a fit for your target market if you have not understood your business and the competitive landscape.
There is no market you want to target where you will not encounter competition, even if your product is innovative. Including competitive analysis in your business plan is essential.
If you are entering an established market, you need to explain how you plan to differentiate your products from the available options in the market. Also, include a list of few companies that you view as your direct competitors The competition you face in an established market is your direct competition.
In situations where you are entering a market with no direct competition, it does not mean there is no competition there. Consider your indirect competition that offers substitutes for the products or services you offer.
For example, if you sell an innovative SaaS product, let us say a project management software , a company offering time management software is your indirect competition.
There is an easy way to find out who your indirect competitors are in the absence of no direct competitors. You simply have to research how your potential customers are solving the problems that your product or service seeks to solve. That is your direct competition.
Factors that Differentiate Your Business from the Competition
There are three main factors that any business can use to differentiate itself from its competition. They are cost leadership, product differentiation, and market segmentation.
1. Cost Leadership
A strategy you can impose to maximize your profits and gain an edge over your competitors. It involves offering lower prices than what the majority of your competitors are offering.
A common practice among businesses looking to enter into a market where there are dominant players is to use free trials or pricing to attract as many customers as possible to their offer.
2. Product Differentiation
Your product or service should have a unique selling proposition (USP) that your competitors do not have or do not stress in their marketing.
Part of the marketing strategy should involve making your products unique and different from your competitors. It does not have to be different from your competitors, it can be the addition to a feature or benefit that your competitors do not currently have.
3. Market Segmentation
As a new business seeking to break into an industry, you will gain more success from focusing on a specific niche or target market, and not the whole industry.
If your competitors are focused on a general need or target market, you can differentiate yourself from them by having a small and hyper-targeted audience. For example, if your competitors are selling men’s clothes in their online stores , you can sell hoodies for men.
4. Define Your Business and Management Structure
The next step in your business plan is your business and management structure. It is the section where you describe the legal structure of your business and the team running it.
Your business is only as good as the management team that runs it, while the management team can only strive when there is a proper business and management structure in place.
If your company is a sole proprietor or a limited liability company (LLC), a general or limited partnership, or a C or an S corporation, state it clearly in this section.
Use an organizational chart to show the management structure in your business. Clearly show who is in charge of what area in your company. It is where you show how each key manager or team leader’s unique experience can contribute immensely to the success of your company. You can also opt to add the resumes and CVs of the key players in your company.
The business and management structure section should show who the owner is, and other owners of the businesses (if the business has other owners). For businesses or companies with multiple owners, include the percent ownership of the various owners and clearly show the extent of each others’ involvement in the company.
Investors want to know who is behind the company and the team running it to determine if it has the right management to achieve its set goals.
Management Team
The management team section is where you show that you have the right team in place to successfully execute the business operations and ideas. Take time to create the management structure for your business. Think about all the important roles and responsibilities that you need managers for to grow your business.
Include brief bios of each key team member and ensure you highlight only the relevant information that is needed. If your team members have background industry experience or have held top positions for other companies and achieved success while filling that role, highlight it in this section.

A common mistake that many startups make is assigning C-level titles such as (CMO and CEO) to everyone on their team. It is unrealistic for a small business to have those titles. While it may look good on paper for the ego of your team members, it can prevent investors from investing in your business.
Instead of building an unrealistic management structure that does not fit your business reality, it is best to allow business titles to grow as the business grows. Starting everyone at the top leaves no room for future change or growth, which is bad for productivity.
Your management team does not have to be complete before you start writing your business plan. You can have a complete business plan even when there are managerial positions that are empty and need filling.
If you have management gaps in your team, simply show the gaps and indicate you are searching for the right candidates for the role(s). Investors do not expect you to have a full management team when you are just starting your business.
Key Questions to Answer When Structuring Your Management Team
- Who are the key leaders?
- What experiences, skills, and educational backgrounds do you expect your key leaders to have?
- Do your key leaders have industry experience?
- What positions will they fill and what duties will they perform in those positions?
- What level of authority do the key leaders have and what are their responsibilities?
- What is the salary for the various management positions that will attract the ideal candidates?
Additional Tips for Writing the Management Structure Section
1. Avoid Adding ‘Ghost’ Names to Your Management Team
There is always that temptation to include a ‘ghost’ name to your management team to attract and influence investors to invest in your business. Although the presence of these celebrity management team members may attract the attention of investors, it can cause your business to lose any credibility if you get found out.
Seasoned investors will investigate further the members of your management team before committing fully to your business If they find out that the celebrity name used does not play any actual role in your business, they will not invest and may write you off as dishonest.
2. Focus on Credentials But Pay Extra Attention to the Roles
Investors want to know the experience that your key team members have to determine if they can successfully reach the company’s growth and financial goals.
While it is an excellent boost for your key management team to have the right credentials, you also want to pay extra attention to the roles they will play in your company.
Organizational Chart

Adding an organizational chart in this section of your business plan is not necessary, you can do it in your business plan’s appendix.
If you are exploring funding options, it is not uncommon to get asked for your organizational chart. The function of an organizational chart goes beyond raising money, you can also use it as a useful planning tool for your business.
An organizational chart can help you identify how best to structure your management team for maximum productivity and point you towards key roles you need to fill in the future.
You can use the organizational chart to show your company’s internal management structure such as the roles and responsibilities of your management team, and relationships that exist between them.
5. Describe Your Product and Service Offering
In your business plan, you have to describe what you sell or the service you plan to offer. It is the next step after defining your business and management structure. The products and services section is where you sell the benefits of your business.
Here you have to explain how your product or service will benefit your customers and describe your product lifecycle. It is also the section where you write down your plans for intellectual property like patent filings and copyrighting.
The research and development that you are undertaking for your product or service need to be explained in detail in this section. However, do not get too technical, sell the general idea and its benefits.
If you have any diagrams or intricate designs of your product or service, do not include them in the products and services section. Instead, leave them for the addendum page. Also, if you are leaving out diagrams or designs for the addendum, ensure you add this phrase “For more detail, visit the addendum Page #.”
Your product and service section in your business plan should include the following:
- A detailed explanation that clearly shows how your product or service works.
- The pricing model for your product or service.
- Your business’ sales and distribution strategy.
- The ideal customers that want your product or service.
- The benefits of your products and services.
- Reason(s) why your product or service is a better alternative to what your competitors are currently offering in the market.
- Plans for filling the orders you receive
- If you have current or pending patents, copyrights, and trademarks for your product or service, you can also discuss them in this section.
What to Focus On When Describing the Benefits, Lifecycle, and Production Process of Your Products or Services
In the products and services section, you have to distill the benefits, lifecycle, and production process of your products and services.
When describing the benefits of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Unique features
- Translating the unique features into benefits
- The emotional, psychological, and practical payoffs to attract customers
- Intellectual property rights or any patents
When describing the product life cycle of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Upsells, cross-sells, and down-sells
- Time between purchases
- Plans for research and development.
When describing the production process for your products or services, you need to think about the following:
- The creation of new or existing products and services.
- The sources for the raw materials or components you need for production.
- Assembling the products
- Maintaining quality control
- Supply-chain logistics (receiving the raw materials and delivering the finished products)
- The day-to-day management of the production processes, bookkeeping, and inventory.
Tips for Writing the Products or Services Section of Your Business Plan
1. Avoid Technical Descriptions and Industry Buzzwords
The products and services section of your business plan should clearly describe the products and services that your company provides. However, it is not a section to include technical jargons that anyone outside your industry will not understand.
A good practice is to remove highly detailed or technical descriptions in favor of simple terms. Industry buzzwords are not necessary, if there are simpler terms you can use, then use them. If you plan to use your business plan to source funds, making the product or service section so technical will do you no favors.
2. Describe How Your Products or Services Differ from Your Competitors
When potential investors look at your business plan, they want to know how the products and services you are offering differ from that of your competition. Differentiating your products or services from your competition in a way that makes your solution more attractive is critical.
If you are going the innovative path and there is no market currently for your product or service, you need to describe in this section why the market needs your product or service.
For example, overnight delivery was a niche business that only a few companies were participating in. Federal Express (FedEx) had to show in its business plan that there was a large opportunity for that service and they justified why the market needed that service.
3. Long or Short Products or Services Section
Should your products or services section be short? Does the long products or services section attract more investors?
There are no straightforward answers to these questions. Whether your products or services section should be long or relatively short depends on the nature of your business.
If your business is product-focused, then automatically you need to use more space to describe the details of your products. However, if the product your business sells is a commodity item that relies on competitive pricing or other pricing strategies, you do not have to use up so much space to provide significant details about the product.
Likewise, if you are selling a commodity that is available in numerous outlets, then you do not have to spend time on writing a long products or services section.
The key to the success of your business is most likely the effectiveness of your marketing strategies compared to your competitors. Use more space to address that section.
If you are creating a new product or service that the market does not know about, your products or services section can be lengthy. The reason why is because you need to explain everything about the product or service such as the nature of the product, its use case, and values.
A short products or services section for an innovative product or service will not give the readers enough information to properly evaluate your business.
4. Describe Your Relationships with Vendors or Suppliers
Your business will rely on vendors or suppliers to supply raw materials or the components needed to make your products. In your products and services section, describe your relationships with your vendors and suppliers fully.
Avoid the mistake of relying on only one supplier or vendor. If that supplier or vendor fails to supply or goes out of business, you can easily face supply problems and struggle to meet your demands. Plan to set up multiple vendor or supplier relationships for better business stability.
5. Your Primary Goal Is to Convince Your Readers
The primary goal of your business plan is to convince your readers that your business is viable and to create a guide for your business to follow. It applies to the products and services section.
When drafting this section, think like the reader. See your reader as someone who has no idea about your products and services. You are using the products and services section to provide the needed information to help your reader understand your products and services. As a result, you have to be clear and to the point.
While you want to educate your readers about your products or services, you also do not want to bore them with lots of technical details. Show your products and services and not your fancy choice of words.
Your products and services section should provide the answer to the “what” question for your business. You and your management team may run the business, but it is your products and services that are the lifeblood of the business.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing your Products and Services Section
Answering these questions can help you write your products and services section quickly and in a way that will appeal to your readers.
- Are your products existing on the market or are they still in the development stage?
- What is your timeline for adding new products and services to the market?
- What are the positives that make your products and services different from your competitors?
- Do your products and services have any competitive advantage that your competitors’ products and services do not currently have?
- Do your products or services have any competitive disadvantages that you need to overcome to compete with your competitors? If your answer is yes, state how you plan to overcome them,
- How much does it cost to produce your products or services? How much do you plan to sell it for?
- What is the price for your products and services compared to your competitors? Is pricing an issue?
- What are your operating costs and will it be low enough for you to compete with your competitors and still take home a reasonable profit margin?
- What is your plan for acquiring your products? Are you involved in the production of your products or services?
- Are you the manufacturer and produce all the components you need to create your products? Do you assemble your products by using components supplied by other manufacturers? Do you purchase your products directly from suppliers or wholesalers?
- Do you have a steady supply of products that you need to start your business? (If your business is yet to kick-off)
- How do you plan to distribute your products or services to the market?
You can also hint at the marketing or promotion plans you have for your products or services such as how you plan to build awareness or retain customers. The next section is where you can go fully into details about your business’s marketing and sales plan.
6. Show and Explain Your Marketing and Sales Plan
Providing great products and services is wonderful, but it means nothing if you do not have a marketing and sales plan to inform your customers about them. Your marketing and sales plan is critical to the success of your business.
The sales and marketing section is where you show and offer a detailed explanation of your marketing and sales plan and how you plan to execute it. It covers your pricing plan, proposed advertising and promotion activities, activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success, and the benefits of your products and services.
There are several ways you can approach your marketing and sales strategy. Ideally, your marketing and sales strategy has to fit the unique needs of your business.
In this section, you describe how the plans your business has for attracting and retaining customers, and the exact process for making a sale happen. It is essential to thoroughly describe your complete marketing and sales plans because you are still going to reference this section when you are making financial projections for your business.
Outline Your Business’ Unique Selling Proposition (USP)

The sales and marketing section is where you outline your business’s unique selling proposition (USP). When you are developing your unique selling proposition, think about the strongest reasons why people should buy from you over your competition. That reason(s) is most likely a good fit to serve as your unique selling proposition (USP).
Target Market and Target Audience
Plans on how to get your products or services to your target market and how to get your target audience to buy them go into this section. You also highlight the strengths of your business here, particularly what sets them apart from your competition.

Before you start writing your marketing and sales plan, you need to have properly defined your target audience and fleshed out your buyer persona. If you do not first understand the individual you are marketing to, your marketing and sales plan will lack any substance and easily fall.
Creating a Smart Marketing and Sales Plan
Marketing your products and services is an investment that requires you to spend money. Like any other investment, you have to generate a good return on investment (ROI) to justify using that marketing and sales plan. Good marketing and sales plans bring in high sales and profits to your company.
Avoid spending money on unproductive marketing channels. Do your research and find out the best marketing and sales plan that works best for your company.
Your marketing and sales plan can be broken into different parts: your positioning statement, pricing, promotion, packaging, advertising, public relations, content marketing, social media, and strategic alliances.
Your Positioning Statement
Your positioning statement is the first part of your marketing and sales plan. It refers to the way you present your company to your customers.
Are you the premium solution, the low-price solution, or are you the intermediary between the two extremes in the market? What do you offer that your competitors do not that can give you leverage in the market?
Before you start writing your positioning statement, you need to spend some time evaluating the current market conditions. Here are some questions that can help you to evaluate the market
- What are the unique features or benefits that you offer that your competitors lack?
- What are your customers’ primary needs and wants?
- Why should a customer choose you over your competition? How do you plan to differentiate yourself from the competition?
- How does your company’s solution compare with other solutions in the market?
After answering these questions, then you can start writing your positioning statement. Your positioning statement does not have to be in-depth or too long.
All you need to explain with your positioning statement are two focus areas. The first is the position of your company within the competitive landscape. The other focus area is the core value proposition that sets your company apart from other alternatives that your ideal customer might consider.
Here is a simple template you can use to develop a positioning statement.
For [description of target market] who [need of target market], [product or service] [how it meets the need]. Unlike [top competition], it [most essential distinguishing feature].
For example, let’s create the positioning statement for fictional accounting software and QuickBooks alternative , TBooks.
“For small business owners who need accounting services, TBooks is an accounting software that helps small businesses handle their small business bookkeeping basics quickly and easily. Unlike Wave, TBooks gives small businesses access to live sessions with top accountants.”
You can edit this positioning statement sample and fill it with your business details.
After writing your positioning statement, the next step is the pricing of your offerings. The overall positioning strategy you set in your positioning statement will often determine how you price your products or services.
Pricing is a powerful tool that sends a strong message to your customers. Failure to get your pricing strategy right can make or mar your business. If you are targeting a low-income audience, setting a premium price can result in low sales.
You can use pricing to communicate your positioning to your customers. For example, if you are offering a product at a premium price, you are sending a message to your customers that the product belongs to the premium category.
Basic Rules to Follow When Pricing Your Offering
Setting a price for your offering involves more than just putting a price tag on it. Deciding on the right pricing for your offering requires following some basic rules. They include covering your costs, primary and secondary profit center pricing, and matching the market rate.
- Covering Your Costs: The price you set for your products or service should be more than it costs you to produce and deliver them. Every business has the same goal, to make a profit. Depending on the strategy you want to use, there are exceptions to this rule. However, the vast majority of businesses follow this rule.
- Primary and Secondary Profit Center Pricing: When a company sets its price above the cost of production, it is making that product its primary profit center. A company can also decide not to make its initial price its primary profit center by selling below or at even with its production cost. It rather depends on the support product or even maintenance that is associated with the initial purchase to make its profit. The initial price thus became its secondary profit center.
- Matching the Market Rate: A good rule to follow when pricing your products or services is to match your pricing with consumer demand and expectations. If you price your products or services beyond the price your customer perceives as the ideal price range, you may end up with no customers. Pricing your products too low below what your customer perceives as the ideal price range may lead to them undervaluing your offering.
Pricing Strategy
Your pricing strategy influences the price of your offering. There are several pricing strategies available for you to choose from when examining the right pricing strategy for your business. They include cost-plus pricing, market-based pricing, value pricing, and more.

- Cost-plus Pricing: This strategy is one of the simplest and oldest pricing strategies. Here you consider the cost of producing a unit of your product and then add a profit to it to arrive at your market price. It is an effective pricing strategy for manufacturers because it helps them cover their initial costs. Another name for the cost-plus pricing strategy is the markup pricing strategy.
- Market-based Pricing: This pricing strategy analyses the market including competitors’ pricing and then sets a price based on what the market is expecting. With this pricing strategy, you can either set your price at the low-end or high-end of the market.
- Value Pricing: This pricing strategy involves setting a price based on the value you are providing to your customer. When adopting a value-based pricing strategy, you have to set a price that your customers are willing to pay. Service-based businesses such as small business insurance providers , luxury goods sellers, and the fashion industry use this pricing strategy.
After carefully sorting out your positioning statement and pricing, the next item to look at is your promotional strategy. Your promotional strategy explains how you plan on communicating with your customers and prospects.
As a business, you must measure all your costs, including the cost of your promotions. You also want to measure how much sales your promotions bring for your business to determine its usefulness. Promotional strategies or programs that do not lead to profit need to be removed.
There are different types of promotional strategies you can adopt for your business, they include advertising, public relations, and content marketing.
Advertising
Your business plan should include your advertising plan which can be found in the marketing and sales plan section. You need to include an overview of your advertising plans such as the areas you plan to spend money on to advertise your business and offers.
Ensure that you make it clear in this section if your business will be advertising online or using the more traditional offline media, or the combination of both online and offline media. You can also include the advertising medium you want to use to raise awareness about your business and offers.
Some common online advertising mediums you can use include social media ads, landing pages, sales pages, SEO, Pay-Per-Click, emails, Google Ads, and others. Some common traditional and offline advertising mediums include word of mouth, radios, direct mail, televisions, flyers, billboards, posters, and others.
A key component of your advertising strategy is how you plan to measure the effectiveness and success of your advertising campaign. There is no point in sticking with an advertising plan or medium that does not produce results for your business in the long run.
Public Relations
A great way to reach your customers is to get the media to cover your business or product. Publicity, especially good ones, should be a part of your marketing and sales plan. In this section, show your plans for getting prominent reviews of your product from reputable publications and sources.
Your business needs that exposure to grow. If public relations is a crucial part of your promotional strategy, provide details about your public relations plan here.
Content Marketing
Content marketing is a popular promotional strategy used by businesses to inform and attract their customers. It is about teaching and educating your prospects on various topics of interest in your niche, it does not just involve informing them about the benefits and features of the products and services you have,

Businesses publish content usually for free where they provide useful information, tips, and advice so that their target market can be made aware of the importance of their products and services. Content marketing strategies seek to nurture prospects into buyers over time by simply providing value.
Your company can create a blog where it will be publishing content for its target market. You will need to use the best website builder such as Wix and Squarespace and the best web hosting services such as Bluehost, Hostinger, and other Bluehost alternatives to create a functional blog or website.
If content marketing is a crucial part of your promotional strategy (as it should be), detail your plans under promotions.
Including high-quality images of the packaging of your product in your business plan is a lovely idea. You can add the images of the packaging of that product in the marketing and sales plan section. If you are not selling a product, then you do not need to include any worry about the physical packaging of your product.
When organizing the packaging section of your business plan, you can answer the following questions to make maximum use of this section.
- Is your choice of packaging consistent with your positioning strategy?
- What key value proposition does your packaging communicate? (It should reflect the key value proposition of your business)
- How does your packaging compare to that of your competitors?
Social Media
Your 21st-century business needs to have a good social media presence. Not having one is leaving out opportunities for growth and reaching out to your prospect.
You do not have to join the thousands of social media platforms out there. What you need to do is join the ones that your customers are active on and be active there.

Businesses use social media to provide information about their products such as promotions, discounts, the benefits of their products, and content on their blogs.
Social media is also a platform for engaging with your customers and getting feedback about your products or services. Make no mistake, more and more of your prospects are using social media channels to find more information about companies.
You need to consider the social media channels you want to prioritize your business (prioritize the ones your customers are active in) and your branding plans in this section.

Strategic Alliances
If your company plans to work closely with other companies as part of your sales and marketing plan, include it in this section. Prove details about those partnerships in your business plan if you have already established them.
Strategic alliances can be beneficial for all parties involved including your company. Working closely with another company in the form of a partnership can provide access to a different target market segment for your company.
The company you are partnering with may also gain access to your target market or simply offer a new product or service (that of your company) to its customers.
Mutually beneficial partnerships can cover the weaknesses of one company with the strength of another. You should consider strategic alliances with companies that sell complimentary products to yours. For example, if you provide printers, you can partner with a company that produces ink since the customers that buy printers from you will also need inks for printing.
Steps Involved in Creating a Marketing and Sales Plan
1. Focus on Your Target Market
Identify who your customers are, the market you want to target. Then determine the best ways to get your products or services to your potential customers.
2. Evaluate Your Competition
One of the goals of having a marketing plan is to distinguish yourself from your competition. You cannot stand out from them without first knowing them in and out.
You can know your competitors by gathering information about their products, pricing, service, and advertising campaigns.
These questions can help you know your competition.
- What makes your competition successful?
- What are their weaknesses?
- What are customers saying about your competition?
3. Consider Your Brand
Customers' perception of your brand has a strong impact on your sales. Your marketing and sales plan should seek to bolster the image of your brand. Before you start marketing your business, think about the message you want to pass across about your business and your products and services.
4. Focus on Benefits
The majority of your customers do not view your product in terms of features, what they want to know is the benefits and solutions your product offers. Think about the problems your product solves and the benefits it delivers, and use it to create the right sales and marketing message.
Your marketing plan should focus on what you want your customer to get instead of what you provide. Identify those benefits in your marketing and sales plan.
5. Focus on Differentiation
Your marketing and sales plan should look for a unique angle they can take that differentiates your business from the competition, even if the products offered are similar. Some good areas of differentiation you can use are your benefits, pricing, and features.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing Your Marketing and Sales Plan
- What is your company’s budget for sales and marketing campaigns?
- What key metrics will you use to determine if your marketing plans are successful?
- What are your alternatives if your initial marketing efforts do not succeed?
- Who are the sales representatives you need to promote your products or services?
- What are the marketing and sales channels you plan to use? How do you plan to get your products in front of your ideal customers?
- Where will you sell your products?
You may want to include samples of marketing materials you plan to use such as print ads, website descriptions, and social media ads. While it is not compulsory to include these samples, it can help you better communicate your marketing and sales plan and objectives.
The purpose of the marketing and sales section is to answer this question “How will you reach your customers?” If you cannot convincingly provide an answer to this question, you need to rework your marketing and sales section.
7. Clearly Show Your Funding Request
If you are writing your business plan to ask for funding from investors or financial institutions, the funding request section is where you will outline your funding requirements. The funding request section should answer the question ‘How much money will your business need in the near future (3 to 5 years)?’
A good funding request section will clearly outline and explain the amount of funding your business needs over the next five years. You need to know the amount of money your business needs to make an accurate funding request.
Also, when writing your funding request, provide details of how the funds will be used over the period. Specify if you want to use the funds to buy raw materials or machinery, pay salaries, pay for advertisements, and cover specific bills such as rent and electricity.
In addition to explaining what you want to use the funds requested for, you need to clearly state the projected return on investment (ROI) . Investors and creditors want to know if your business can generate profit for them if they put funds into it.
Ensure you do not inflate the figures and stay as realistic as possible. Investors and financial institutions you are seeking funds from will do their research before investing money in your business.
If you are not sure of an exact number to request from, you can use some range of numbers as rough estimates. Add a best-case scenario and a work-case scenario to your funding request. Also, include a description of your strategic future financial plans such as selling your business or paying off debts.
Funding Request: Debt or Equity?
When making your funding request, specify the type of funding you want. Do you want debt or equity? Draw out the terms that will be applicable for the funding, and the length of time the funding request will cover.
Case for Equity
If your new business has not yet started generating profits, you are most likely preparing to sell equity in your business to raise capital at the early stage. Equity here refers to ownership. In this case, you are selling a portion of your company to raise capital.
Although this method of raising capital for your business does not put your business in debt, keep in mind that an equity owner may expect to play a key role in company decisions even if he does not hold a major stake in the company.
Most equity sales for startups are usually private transactions . If you are making a funding request by offering equity in exchange for funding, let the investor know that they will be paid a dividend (a share of the company’s profit). Also, let the investor know the process for selling their equity in your business.
Case for Debt
You may decide not to offer equity in exchange for funds, instead, you make a funding request with the promise to pay back the money borrowed at the agreed time frame.
When making a funding request with an agreement to pay back, note that you will have to repay your creditors both the principal amount borrowed and the interest on it. Financial institutions offer this type of funding for businesses.
Large companies combine both equity and debt in their capital structure. When drafting your business plan, decide if you want to offer both or one over the other.
Before you sell equity in exchange for funding in your business, consider if you are willing to accept not being in total control of your business. Also, before you seek loans in your funding request section, ensure that the terms of repayment are favorable.
You should set a clear timeline in your funding request so that potential investors and creditors can know what you are expecting. Some investors and creditors may agree to your funding request and then delay payment for longer than 30 days, meanwhile, your business needs an immediate cash injection to operate efficiently.
Additional Tips for Writing the Funding Request Section of your Business Plan
The funding request section is not necessary for every business, it is only needed by businesses who plan to use their business plan to secure funding.
If you are adding the funding request section to your business plan, provide an itemized summary of how you plan to use the funds requested. Hiring a lawyer, accountant, or other professionals may be necessary for the proper development of this section.
You should also gather and use financial statements that add credibility and support to your funding requests. Ensure that the financial statements you use should include your projected financial data such as projected cash flows, forecast statements, and expenditure budgets.
If you are an existing business, include all historical financial statements such as cash flow statements, balance sheets and income statements .
Provide monthly and quarterly financial statements for a year. If your business has records that date back beyond the one-year mark, add the yearly statements of those years. These documents are for the appendix section of your business plan.
8. Detail Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projections
If you used the funding request section in your business plan, supplement it with a financial plan, metrics, and projections. This section paints a picture of the past performance of your business and then goes ahead to make an informed projection about its future.
The goal of this section is to convince readers that your business is going to be a financial success. It outlines your business plan to generate enough profit to repay the loan (with interest if applicable) and to generate a decent return on investment for investors.
If you have an existing business already in operation, use this section to demonstrate stability through finance. This section should include your cash flow statements, balance sheets, and income statements covering the last three to five years. If your business has some acceptable collateral that you can use to acquire loans, list it in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
Apart from current financial statements, this section should also contain a prospective financial outlook that spans the next five years. Include forecasted income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, and capital expenditure budget.
If your business is new and is not yet generating profit, use clear and realistic projections to show the potentials of your business.
When drafting this section, research industry norms and the performance of comparable businesses. Your financial projections should cover at least five years. State the logic behind your financial projections. Remember you can always make adjustments to this section as the variables change.
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section create a baseline which your business can either exceed or fail to reach. If your business fails to reach your projections in this section, you need to understand why it failed.
Investors and loan managers spend a lot of time going through the financial plan, metrics, and projection section compared to other parts of the business plan. Ensure you spend time creating credible financial analyses for your business in this section.
Many entrepreneurs find this section daunting to write. You do not need a business degree to create a solid financial forecast for your business. Business finances, especially for startups, are not as complicated as they seem. There are several online tools and templates that make writing this section so much easier.
Use Graphs and Charts
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section is a great place to use graphs and charts to tell the financial story of your business. Charts and images make it easier to communicate your finances.
Accuracy in this section is key, ensure you carefully analyze your past financial statements properly before making financial projects.
Address the Risk Factors and Show Realistic Financial Projections
Keep your financial plan, metrics, and projection realistic. It is okay to be optimistic in your financial projection, however, you have to justify it.
You should also address the various risk factors associated with your business in this section. Investors want to know the potential risks involved, show them. You should also show your plans for mitigating those risks.
What You Should In The Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection Section of Your Business Plan
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section of your business plan should have monthly sales and revenue forecasts for the first year. It should also include annual projections that cover 3 to 5 years.
A three-year projection is a basic requirement to have in your business plan. However, some investors may request a five-year forecast.
Your business plan should include the following financial statements: sales forecast, personnel plan, income statement, income statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, and an exit strategy.
1. Sales Forecast
Sales forecast refers to your projections about the number of sales your business is going to record over the next few years. It is typically broken into several rows, with each row assigned to a core product or service that your business is offering.
One common mistake people make in their business plan is to break down the sales forecast section into long details. A sales forecast should forecast the high-level details.
For example, if you are forecasting sales for a payroll software provider, you could break down your forecast into target market segments or subscription categories.

Your sales forecast section should also have a corresponding row for each sales row to cover the direct cost or Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). The objective of these rows is to show the expenses that your business incurs in making and delivering your product or service.
Note that your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) should only cover those direct costs incurred when making your products. Other indirect expenses such as insurance, salaries, payroll tax, and rent should not be included.
For example, the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) for a restaurant is the cost of ingredients while for a consulting company it will be the cost of paper and other presentation materials.

2. Personnel Plan
The personnel plan section is where you provide details about the payment plan for your employees. For a small business, you can easily list every position in your company and how much you plan to pay in the personnel plan.
However, for larger businesses, you have to break the personnel plan into functional groups such as sales and marketing.
The personnel plan will also include the cost of an employee beyond salary, commonly referred to as the employee burden. These costs include insurance, payroll taxes , and other essential costs incurred monthly as a result of having employees on your payroll.

3. Income Statement
The income statement section shows if your business is making a profit or taking a loss. Another name for the income statement is the profit and loss (P&L). It takes data from your sales forecast and personnel plan and adds other ongoing expenses you incur while running your business.

Every business plan should have an income statement. It subtracts your business expenses from its earnings to show if your business is generating profit or incurring losses.
The income statement has the following items: sales, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), gross margin, operating expenses, total operating expenses, operating income , total expenses, and net profit.
- Sales refer to the revenue your business generates from selling its products or services. Other names for sales are income or revenue.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) refers to the total cost of selling your products. Other names for COGS are direct costs or cost of sales. Manufacturing businesses use the Costs of Goods Manufactured (COGM) .
- Gross Margin is the figure you get when you subtract your COGS from your sales. In your income statement, you can express it as a percentage of total sales (Gross margin / Sales = Gross Margin Percent).
- Operating Expenses refer to all the expenses you incur from running your business. It exempts the COGS because it stands alone as a core part of your income statement. You also have to exclude taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Your operating expenses include salaries, marketing expenses, research and development (R&D) expenses, and other expenses.
- Total Operating Expenses refers to the sum of all your operating expenses including those exemptions named above under operating expenses.
- Operating Income refers to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. It is simply known as the acronym EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization). Calculating your operating income is simple, all you need to do is to subtract your COGS and total operating expenses from your sales.
- Total Expenses refer to the sum of your operating expenses and your business’ interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
- Net profit shows whether your business has made a profit or taken a loss during a given timeframe.
4. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the money you have in the bank at any given point. It is often confused with the income statement or the profit and loss statement. They are both different types of financial statements. The income statement calculates your profits and losses while the cash flow statement shows you how much you have in the bank.

5. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a financial statement that provides an overview of the financial health of your business. It contains information about the assets and liabilities of your company, and owner’s or shareholders’ equity.
You can get the net worth of your company by subtracting your company’s liabilities from its assets.

6. Exit Strategy
The exit strategy refers to a probable plan for selling your business either to the public in an IPO or to another company. It is the last thing you include in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
You can choose to omit the exit strategy from your business plan if you plan to maintain full ownership of your business and do not plan on seeking angel investment or virtual capitalist (VC) funding.
Investors may want to know what your exit plan is. They invest in your business to get a good return on investment.
Your exit strategy does not have to include long and boring details. Ensure you identify some interested parties who may be interested in buying the company if it becomes a success.

Key Questions to Answer with Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection
Your financial plan, metrics, and projection section helps investors, creditors, or your internal managers to understand what your expenses are, the amount of cash you need, and what it takes to make your company profitable. It also shows what you will be doing with any funding.
You do not need to show actual financial data if you do not have one. Adding forecasts and projections to your financial statements is added proof that your strategy is feasible and shows investors you have planned properly.
Here are some key questions to answer to help you develop this section.
- What is your sales forecast for the next year?
- When will your company achieve a positive cash flow?
- What are the core expenses you need to operate?
- How much money do you need upfront to operate or grow your company?
- How will you use the loans or investments?
9. Add an Appendix to Your Business Plan
Adding an appendix to your business plan is optional. It is a useful place to put any charts, tables, legal notes, definitions, permits, résumés, and other critical information that do not fit into other sections of your business plan.
The appendix section is where you would want to include details of a patent or patent-pending if you have one. You can always add illustrations or images of your products here. It is the last section of your business plan.
When writing your business plan, there are details you cut short or remove to prevent the entire section from becoming too lengthy. There are also details you want to include in the business plan but are not a good fit for any of the previous sections. You can add that additional information to the appendix section.
Businesses also use the appendix section to include supporting documents or other materials specially requested by investors or lenders.
You can include just about any information that supports the assumptions and statements you made in the business plan under the appendix. It is the one place in the business plan where unrelated data and information can coexist amicably.
If your appendix section is lengthy, try organizing it by adding a table of contents at the beginning of the appendix section. It is also advisable to group similar information to make it easier for the reader to access them.
A well-organized appendix section makes it easier to share your information clearly and concisely. Add footnotes throughout the rest of the business plan or make references in the plan to the documents in the appendix.
The appendix section is usually only necessary if you are seeking funding from investors or lenders, or hoping to attract partners.
People reading business plans do not want to spend time going through a heap of backup information, numbers, and charts. Keep these documents or information in the Appendix section in case the reader wants to dig deeper.
Common Items to Include in the Appendix Section of Your Business Plan
The appendix section includes documents that supplement or support the information or claims given in other sections of the business plans. Common items you can include in the appendix section include:
- Additional data about the process of manufacturing or creation
- Additional description of products or services such as product schematics
- Additional financial documents or projections
- Articles of incorporation and status
- Backup for market research or competitive analysis
- Bank statements
- Business registries
- Client testimonials (if your business is already running)
- Copies of insurances
- Credit histories (personal or/and business)
- Deeds and permits
- Equipment leases
- Examples of marketing and advertising collateral
- Industry associations and memberships
- Images of product
- Intellectual property
- Key customer contracts
- Legal documents and other contracts
- Letters of reference
- Links to references
- Market research data
- Organizational charts
- Photographs of potential facilities
- Professional licenses pertaining to your legal structure or type of business
- Purchase orders
- Resumes of the founder(s) and key managers
- State and federal identification numbers or codes
- Trademarks or patents’ registrations
Avoid using the appendix section as a place to dump any document or information you feel like adding. Only add documents or information that you support or increase the credibility of your business plan.
Tips and Strategies for Writing a Convincing Business Plan
To achieve a perfect business plan, you need to consider some key tips and strategies. These tips will raise the efficiency of your business plan above average.
1. Know Your Audience
When writing a business plan, you need to know your audience . Business owners write business plans for different reasons. Your business plan has to be specific. For example, you can write business plans to potential investors, banks, and even fellow board members of the company.
The audience you are writing to determines the structure of the business plan. As a business owner, you have to know your audience. Not everyone will be your audience. Knowing your audience will help you to narrow the scope of your business plan.
Consider what your audience wants to see in your projects, the likely questions they might ask, and what interests them.
- A business plan used to address a company's board members will center on its employment schemes, internal affairs, projects, stakeholders, etc.
- A business plan for financial institutions will talk about the size of your market and the chances for you to pay back any loans you demand.
- A business plan for investors will show proof that you can return the investment capital within a specific time. In addition, it discusses your financial projections, tractions, and market size.
2. Get Inspiration from People
Writing a business plan from scratch as an entrepreneur can be daunting. That is why you need the right inspiration to push you to write one. You can gain inspiration from the successful business plans of other businesses. Look at their business plans, the style they use, the structure of the project, etc.
To make your business plan easier to create, search companies related to your business to get an exact copy of what you need to create an effective business plan. You can also make references while citing examples in your business plans.
When drafting your business plan, get as much help from others as you possibly can. By getting inspiration from people, you can create something better than what they have.
3. Avoid Being Over Optimistic
Many business owners make use of strong adjectives to qualify their content. One of the big mistakes entrepreneurs make when preparing a business plan is promising too much.
The use of superlatives and over-optimistic claims can prepare the audience for more than you can offer. In the end, you disappoint the confidence they have in you.
In most cases, the best option is to be realistic with your claims and statistics. Most of the investors can sense a bit of incompetency from the overuse of superlatives. As a new entrepreneur, do not be tempted to over-promise to get the interests of investors.
The concept of entrepreneurship centers on risks, nothing is certain when you make future analyses. What separates the best is the ability to do careful research and work towards achieving that, not promising more than you can achieve.
To make an excellent first impression as an entrepreneur, replace superlatives with compelling data-driven content. In this way, you are more specific than someone promising a huge ROI from an investment.
4. Keep it Simple and Short
When writing business plans, ensure you keep them simple throughout. Irrespective of the purpose of the business plan, your goal is to convince the audience.
One way to achieve this goal is to make them understand your proposal. Therefore, it would be best if you avoid the use of complex grammar to express yourself. It would be a huge turn-off if the people you want to convince are not familiar with your use of words.
Another thing to note is the length of your business plan. It would be best if you made it as brief as possible.
You hardly see investors or agencies that read through an extremely long document. In that case, if your first few pages can’t convince them, then you have lost it. The more pages you write, the higher the chances of you derailing from the essential contents.
To ensure your business plan has a high conversion rate, you need to dispose of every unnecessary information. For example, if you have a strategy that you are not sure of, it would be best to leave it out of the plan.
5. Make an Outline and Follow Through
A perfect business plan must have touched every part needed to convince the audience. Business owners get easily tempted to concentrate more on their products than on other sections. Doing this can be detrimental to the efficiency of the business plan.
For example, imagine you talking about a product but omitting or providing very little information about the target audience. You will leave your clients confused.
To ensure that your business plan communicates your full business model to readers, you have to input all the necessary information in it. One of the best ways to achieve this is to design a structure and stick to it.
This structure is what guides you throughout the writing. To make your work easier, you can assign an estimated word count or page limit to every section to avoid making it too bulky for easy reading. As a guide, the necessary things your business plan must contain are:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Product or service description
- Target audience
- Market size
- Competition analysis
- Financial projections
Some specific businesses can include some other essential sections, but these are the key sections that must be in every business plan.
6. Ask a Professional to Proofread
When writing a business plan, you must tie all loose ends to get a perfect result. When you are done with writing, call a professional to go through the document for you. You are bound to make mistakes, and the way to correct them is to get external help.
You should get a professional in your field who can relate to every section of your business plan. It would be easier for the professional to notice the inner flaws in the document than an editor with no knowledge of your business.
In addition to getting a professional to proofread, get an editor to proofread and edit your document. The editor will help you identify grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and inappropriate writing styles.
Writing a business plan can be daunting, but you can surmount that obstacle and get the best out of it with these tips.
Business Plan Examples and Templates That’ll Save You Tons of Time
1. hubspot's one-page business plan.

The one-page business plan template by HubSpot is the perfect guide for businesses of any size, irrespective of their business strategy. Although the template is condensed into a page, your final business plan should not be a page long! The template is designed to ask helpful questions that can help you develop your business plan.
Hubspot’s one-page business plan template is divided into nine fields:
- Business opportunity
- Company description
- Industry analysis
- Target market
- Implementation timeline
- Marketing plan
- Financial summary
- Funding required
2. Bplan’s Free Business Plan Template

Bplans' free business plan template is investor-approved. It is a rich template used by prestigious educational institutions such as Babson College and Princeton University to teach entrepreneurs how to create a business plan.
The template has six sections: the executive summary, opportunity, execution, company, financial plan, and appendix. There is a step-by-step guide for writing every little detail in the business plan. Follow the instructions each step of the way and you will create a business plan that impresses investors or lenders easily.
3. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

HubSpot’s downloadable business plan template is a more comprehensive option compared to the one-page business template by HubSpot. This free and downloadable business plan template is designed for entrepreneurs.
The template is a comprehensive guide and checklist for business owners just starting their businesses. It tells you everything you need to fill in each section of the business plan and how to do it.
There are nine sections in this business plan template: an executive summary, company and business description, product and services line, market analysis, marketing plan, sales plan, legal notes, financial considerations, and appendix.
4. Business Plan by My Own Business Institute

My Own Business Institute (MOBI) which is a part of Santa Clara University's Center for Innovation and Entrepreneurship offers a free business plan template. You can either copy the free business template from the link provided above or download it as a Word document.
The comprehensive template consists of a whopping 15 sections.
- The Business Profile
- The Vision and the People
- Home-Based Business and Freelance Business Opportunities
- Organization
- Licenses and Permits
- Business Insurance
- Communication Tools
- Acquisitions
- Location and Leasing
- Accounting and Cash Flow
- Opening and Marketing
- Managing Employees
- Expanding and Handling Problems
There are lots of helpful tips on how to fill each section in the free business plan template by MOBI.
5. Score's Business Plan Template for Startups

Score is an American nonprofit organization that helps entrepreneurs build successful companies. This business plan template for startups by Score is available for free download. The business plan template asks a whooping 150 generic questions that help entrepreneurs from different fields to set up the perfect business plan.
The business plan template for startups contains clear instructions and worksheets, all you have to do is answer the questions and fill the worksheets.
There are nine sections in the business plan template: executive summary, company description, products and services, marketing plan, operational plan, management and organization, startup expenses and capitalization, financial plan, and appendices.
The ‘refining the plan’ resource contains instructions that help you modify your business plan to suit your specific needs, industry, and target audience. After you have completed Score’s business plan template, you can work with a SCORE mentor for expert advice in business planning.
6. Minimalist Architecture Business Plan Template by Venngage

The minimalist architecture business plan template is a simple template by Venngage that you can customize to suit your business needs .
There are five sections in the template: an executive summary, statement of problem, approach and methodology, qualifications, and schedule and benchmark. The business plan template has instructions that guide users on what to fill in each section.
7. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two free business plan templates, filled with practical real-life examples that you can model to create your business plan. Both free business plan templates are written by fictional business owners: Rebecca who owns a consulting firm, and Andrew who owns a toy company.
There are five sections in the two SBA’s free business plan templates.
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Service Line
- Marketing and Sales
8. The $100 Startup's One-Page Business Plan

The one-page business plan by the $100 startup is a simple business plan template for entrepreneurs who do not want to create a long and complicated plan . You can include more details in the appendices for funders who want more information beyond what you can put in the one-page business plan.
There are five sections in the one-page business plan such as overview, ka-ching, hustling, success, and obstacles or challenges or open questions. You can answer all the questions using one or two sentences.
9. PandaDoc’s Free Business Plan Template

The free business plan template by PandaDoc is a comprehensive 15-page document that describes the information you should include in every section.
There are 11 sections in PandaDoc’s free business plan template.
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Products and services
- Operations plan
- Management organization
- Financial plan
- Conclusion / Call to action
- Confidentiality statement
You have to sign up for its 14-day free trial to access the template. You will find different business plan templates on PandaDoc once you sign up (including templates for general businesses and specific businesses such as bakeries, startups, restaurants, salons, hotels, and coffee shops)
PandaDoc allows you to customize its business plan templates to fit the needs of your business. After editing the template, you can send it to interested parties and track opens and views through PandaDoc.
10. Invoiceberry Templates for Word, Open Office, Excel, or PPT

InvoiceBerry is a U.K based online invoicing and tracking platform that offers free business plan templates in .docx, .odt, .xlsx, and .pptx formats for freelancers and small businesses.
Before you can download the free business plan template, it will ask you to give it your email address. After you complete the little task, it will send the download link to your inbox for you to download. It also provides a business plan checklist in .xlsx file format that ensures you add the right information to the business plan.
Alternatives to the Traditional Business Plan
A business plan is very important in mapping out how one expects their business to grow over a set number of years, particularly when they need external investment in their business. However, many investors do not have the time to watch you present your business plan. It is a long and boring read.
Luckily, there are three alternatives to the traditional business plan (the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck). These alternatives are less laborious and easier and quicker to present to investors.
Business Model Canvas (BMC)
The business model canvas is a business tool used to present all the important components of setting up a business, such as customers, route to market, value proposition, and finance in a single sheet. It provides a very focused blueprint that defines your business initially which you can later expand on if needed.

The sheet is divided mainly into company, industry, and consumer models that are interconnected in how they find problems and proffer solutions.
Segments of the Business Model Canvas
The business model canvas was developed by founder Alexander Osterwalder to answer important business questions. It contains nine segments.

- Key Partners: Who will be occupying important executive positions in your business? What do they bring to the table? Will there be a third party involved with the company?
- Key Activities: What important activities will production entail? What activities will be carried out to ensure the smooth running of the company?
- The Product’s Value Propositions: What does your product do? How will it be different from other products?
- Customer Segments: What demography of consumers are you targeting? What are the habits of these consumers? Who are the MVPs of your target consumers?
- Customer Relationships: How will the team support and work with its customer base? How do you intend to build and maintain trust with the customer?
- Key Resources: What type of personnel and tools will be needed? What size of the budget will they need access to?
- Channels: How do you plan to create awareness of your products? How do you intend to transport your product to the customer?
- Cost Structure: What is the estimated cost of production? How much will distribution cost?
- Revenue Streams: For what value are customers willing to pay? How do they prefer to pay for the product? Are there any external revenues attached apart from the main source? How do the revenue streams contribute to the overall revenue?
Lean Canvas
The lean canvas is a problem-oriented alternative to the standard business model canvas. It was proposed by Ash Maurya, creator of Lean Stack as a development of the business model generation. It uses a more problem-focused approach and it majorly targets entrepreneurs and startup businesses.

Lean Canvas uses the same 9 blocks concept as the business model canvas, however, they have been modified slightly to suit the needs and purpose of a small startup. The key partners, key activities, customer relationships, and key resources are replaced by new segments which are:
- Problem: Simple and straightforward number of problems you have identified, ideally three.
- Solution: The solutions to each problem.
- Unfair Advantage: Something you possess that can't be easily bought or replicated.
- Key Metrics: Important numbers that will tell how your business is doing.
Startup Pitch Deck
While the business model canvas compresses into a factual sheet, startup pitch decks expand flamboyantly.
Pitch decks, through slides, convey your business plan, often through graphs and images used to emphasize estimations and observations in your presentation. Entrepreneurs often use pitch decks to fully convince their target audience of their plans before discussing funding arrangements.

Considering the likelihood of it being used in a small time frame, a good startup pitch deck should ideally contain 20 slides or less to have enough time to answer questions from the audience.
Unlike the standard and lean business model canvases, a pitch deck doesn't have a set template on how to present your business plan but there are still important components to it. These components often mirror those of the business model canvas except that they are in slide form and contain more details.

Using Airbnb (one of the most successful start-ups in recent history) for reference, the important components of a good slide are listed below.
- Cover/Introduction Slide: Here, you should include your company's name and mission statement. Your mission statement should be a very catchy tagline. Also, include personal information and contact details to provide an easy link for potential investors.
- Problem Slide: This slide requires you to create a connection with the audience or the investor that you are pitching. For example in their pitch, Airbnb summarized the most important problems it would solve in three brief points – pricing of hotels, disconnection from city culture, and connection problems for local bookings.
- Solution Slide: This slide includes your core value proposition. List simple and direct solutions to the problems you have mentioned
- Customer Analysis: Here you will provide information on the customers you will be offering your service to. The identity of your customers plays an important part in fundraising as well as the long-run viability of the business.
- Market Validation: Use competitive analysis to show numbers that prove the presence of a market for your product, industry behavior in the present and the long run, as well as the percentage of the market you aim to attract. It shows that you understand your competitors and customers and convinces investors of the opportunities presented in the market.
- Business Model: Your business model is the hook of your presentation. It may vary in complexity but it should generally include a pricing system informed by your market analysis. The goal of the slide is to confirm your business model is easy to implement.
- Marketing Strategy: This slide should summarize a few customer acquisition methods that you plan to use to grow the business.
- Competitive Advantage: What this slide will do is provide information on what will set you apart and make you a more attractive option to customers. It could be the possession of technology that is not widely known in the market.
- Team Slide: Here you will give a brief description of your team. Include your key management personnel here and their specific roles in the company. Include their educational background, job history, and skillsets. Also, talk about their accomplishments in their careers so far to build investors' confidence in members of your team.
- Traction Slide: This validates the company’s business model by showing growth through early sales and support. The slide aims to reduce any lingering fears in potential investors by showing realistic periodic milestones and profit margins. It can include current sales, growth, valuable customers, pre-orders, or data from surveys outlining current consumer interest.
- Funding Slide: This slide is popularly referred to as ‘the ask'. Here you will include important details like how much is needed to get your business off the ground and how the funding will be spent to help the company reach its goals.
- Appendix Slides: Your pitch deck appendix should always be included alongside a standard pitch presentation. It consists of additional slides you could not show in the pitch deck but you need to complement your presentation.
It is important to support your calculations with pictorial renditions. Infographics, such as pie charts or bar graphs, will be more effective in presenting the information than just listing numbers. For example, a six-month graph that shows rising profit margins will easily look more impressive than merely writing it.
Lastly, since a pitch deck is primarily used to secure meetings and you may be sharing your pitch with several investors, it is advisable to keep a separate public version that doesn't include financials. Only disclose the one with projections once you have secured a link with an investor.
Advantages of the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck over the Traditional Business Plan
- Time-Saving: Writing a detailed traditional business plan could take weeks or months. On the other hand, all three alternatives can be done in a few days or even one night of brainstorming if you have a comprehensive understanding of your business.
- Easier to Understand: Since the information presented is almost entirely factual, it puts focus on what is most important in running the business. They cut away the excess pages of fillers in a traditional business plan and allow investors to see what is driving the business and what is getting in the way.
- Easy to Update: Businesses typically present their business plans to many potential investors before they secure funding. What this means is that you may regularly have to amend your presentation to update statistics or adjust to audience-specific needs. For a traditional business plan, this could mean rewriting a whole section of your plan. For the three alternatives, updating is much easier because they are not voluminous.
- Guide for a More In-depth Business Plan: All three alternatives have the added benefit of being able to double as a sketch of your business plan if the need to create one arises in the future.
Business Plan FAQ
Business plans are important for any entrepreneur who is looking for a framework to run their company over some time or seeking external support. Although they are essential for new businesses, every company should ideally have a business plan to track their growth from time to time. They can be used by startups seeking investments or loans to convey their business ideas or an employee to convince his boss of the feasibility of starting a new project. They can also be used by companies seeking to recruit high-profile employee targets into key positions or trying to secure partnerships with other firms.
Business plans often vary depending on your target audience, the scope, and the goals for the plan. Startup plans are the most common among the different types of business plans. A start-up plan is used by a new business to present all the necessary information to help get the business up and running. They are usually used by entrepreneurs who are seeking funding from investors or bank loans. The established company alternative to a start-up plan is a feasibility plan. A feasibility plan is often used by an established company looking for new business opportunities. They are used to show the upsides of creating a new product for a consumer base. Because the audience is usually company people, it requires less company analysis. The third type of business plan is the lean business plan. A lean business plan is a brief, straight-to-the-point breakdown of your ideas and analysis for your business. It does not contain details of your proposal and can be written on one page. Finally, you have the what-if plan. As it implies, a what-if plan is a preparation for the worst-case scenario. You must always be prepared for the possibility of your original plan being rejected. A good what-if plan will serve as a good plan B to the original.
A good business plan has 10 key components. They include an executive plan, product analysis, desired customer base, company analysis, industry analysis, marketing strategy, sales strategy, financial projection, funding, and appendix. Executive Plan Your business should begin with your executive plan. An executive plan will provide early insight into what you are planning to achieve with your business. It should include your mission statement and highlight some of the important points which you will explain later. Product Analysis The next component of your business plan is your product analysis. A key part of this section is explaining the type of item or service you are going to offer as well as the market problems your product will solve. Desired Consumer Base Your product analysis should be supplemented with a detailed breakdown of your desired consumer base. Investors are always interested in knowing the economic power of your market as well as potential MVP customers. Company Analysis The next component of your business plan is your company analysis. Here, you explain how you want to run your business. It will include your operational strategy, an insight into the workforce needed to keep the company running, and important executive positions. It will also provide a calculation of expected operational costs. Industry Analysis A good business plan should also contain well laid out industry analysis. It is important to convince potential investors you know the companies you will be competing with, as well as your plans to gain an edge on the competition. Marketing Strategy Your business plan should also include your marketing strategy. This is how you intend to spread awareness of your product. It should include a detailed explanation of the company brand as well as your advertising methods. Sales Strategy Your sales strategy comes after the market strategy. Here you give an overview of your company's pricing strategy and how you aim to maximize profits. You can also explain how your prices will adapt to market behaviors. Financial Projection The financial projection is the next component of your business plan. It explains your company's expected running cost and revenue earned during the tenure of the business plan. Financial projection gives a clear idea of how your company will develop in the future. Funding The next component of your business plan is funding. You have to detail how much external investment you need to get your business idea off the ground here. Appendix The last component of your plan is the appendix. This is where you put licenses, graphs, or key information that does not fit in any of the other components.
The business model canvas is a business management tool used to quickly define your business idea and model. It is often used when investors need you to pitch your business idea during a brief window.
A pitch deck is similar to a business model canvas except that it makes use of slides in its presentation. A pitch is not primarily used to secure funding, rather its main purpose is to entice potential investors by selling a very optimistic outlook on the business.
Business plan competitions help you evaluate the strength of your business plan. By participating in business plan competitions, you are improving your experience. The experience provides you with a degree of validation while practicing important skills. The main motivation for entering into the competitions is often to secure funding by finishing in podium positions. There is also the chance that you may catch the eye of a casual observer outside of the competition. These competitions also provide good networking opportunities. You could meet mentors who will take a keen interest in guiding you in your business journey. You also have the opportunity to meet other entrepreneurs whose ideas can complement yours.
Exlore Further
- 12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
- 13 Sources of Business Finance For Companies & Sole Traders
- 5 Common Types of Business Structures (+ Pros & Cons)
- How to Buy a Business in 8 Steps (+ Due Diligence Checklist)
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
CEOs & Founders
Transform your hiring with charlie recruit.
Say hello to better, faster, fairer hiring with our new recruitment software add-on. Find out more.
The best business objective examples for success (from a CEO)
A business is defined by its mission, by its why . Business objectives are the goals you set for yourself, so that your organisation can make progress towards your mission.
I’ve been with Charlie since the very beginning as one of the original co-founders. I watched it grow from a small team cobbling together a product to an expanding business people are proud to work for.
How did we get there? By setting goals that were well-defined and aligned to what we wanted to achieve – that’s why I wanted to share with you some business objectives examples I’ve used over the year.
Why setting the right business objectives is important
When you’re a small business, you have to do the most that you can with what you have. You will always be lacking in something - money, software tools, talent, staff. You have to make the most out of what you’re given. Every choice matters.
Objectives help you make the best strategic decisions you can. They inspire your teams, get them working towards a common purpose, and turn challenges into potential opportunities for success.
Setting the right business objectives will guide you towards making the most out of your limited resources so your business can grow.
How to formulate effective business objectives
Creating business objectives that work is an art form. Many small business leaders (including myself) set our business objectives within a SMART framework: Specific, Measurable, Actionable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
- Specific : Clearly define what you want to achieve, and why. It gives you a clear direction
- Measurable : Can your progress be tracked, measured, and quantified? Set KPIs that tell you whether or not your strategies are working
- Achievable : It’s important to be ambitious, but your goals and objectives should be easily attainable
- Relevant : Having goals is fine and dandy, but how do they matter for the success of your business? Your objectives should align with your organisation’s values and long-term vision
- Time-bound : Your goals only matter if you make progress towards them. Setting a time frame for your goals
Find out how to set SMART goals in our complete guide on the topic.
Business objectives examples you can use
What kinds of business objectives should you set for yourself? How do you write your business objectives? I’d like to offer some examples of business objectives you might use yourself as a small business CEO.
Sales targets
Sales objectives focus on your business growth, whether that be through building your online presence or through diversification.
Example : Increase revenue by 5% month-over-month through new product lines and multi-channel digital marketing strategies.
Customer satisfaction
Your business is nothing without your customers. Customer satisfaction objectives help you improve the customer experience, build loyalty with your audience, and improve your brand reputation.
Example : Achieve a customer satisfaction score of 80% by improving support services and collecting regular customer feedback.
Market expansion
Are you thinking of expanding into a new geographical market? Use market expansion objectives to broaden your customer base and increase your business' market share.
Example : Expand into two new international markets by year's end, and establish a presence in two key cities.
Employee engagement
Are your employees motivated? Do they share your vision, and are they committed to your organisation? Setting engagement objectives can help keep it that way.
Example : Increase employee engagement scores by 25% by implementing a comprehensive wellness program and monthly team-building activities
Operational efficiency
Are there operations that can be optimized or improved? Set business objectives for operational efficiency to make them happen.
Example : Reduce operational costs by 15% through process optimization and adopting new technology solutions by the end of Q3.
Customer retention
Are your customers sticking around, or are they leaving? Can you figure out why? Use these business objectives to reduce your churn and improve your customer retention rates.
Example : Improve customer retention rates by 15% through a loyalty program and personalised customer service initiatives.
Charlie’s approach to setting objectives – our own example
At the beginning of each year, we set one objective that we want to accomplish. In 2023, that goal was We support a total of 3650 small businesses by the end of 2023 .
Once we have our objective, each team at Charlie has to come together and decide how we will work towards it together.
Each team sets their own internal SMART goals that contribute to the objective. The marketing team might set out to increase brand awareness by a certain amount. The sales team will set goals for customer acquisition.
Cycles and quests
Then, we use a Cycles and Quests model to keep each team working towards the primary objective.
Charlie divides the year into two 6-month Quests, where we focus on 3-4 company priorities. Each Quest consists of 4-week long “Cycles.”
We split up into smaller teams to work towards these business objectives for the coming Quest. Each time decide what tactics they will use to achieve those objectives to complete the Quest.
This way, we not only set ambitious goals, but we create a structured approach to achieving them.
How HR software helps you achieve your business objectives
A dedicated HR software tool can help you define your business objectives and come up with a plan for achieving them. The Charlie platform allows you to set and track goals so you can know what your team should focus on at any given time.
That ensures that everyone is contributing to the objectives. Individual team members can also set goals for themselves.
Your business objectives lead the way to your success
Having business objectives balances your short and long-term goals, keeps the organisation heading in the right direction, and helps you make the most out of whatever capital and manpower you have on hand.
It’s the new year. Take some time to reflect on your business processes. Are they based on SMART criteria?
If you need some guidance on setting appropriate business objectives, give Charlie a try to set both your business objectives and your personal goals.
How to develop an HR strategy for small businesses
Succession planning for businesses (with expert tips and free template), what is a cash flow forecast (tips and examples for small businesses and startups), try charlie for free.

25 Best Strategic Objectives Examples

What are Strategic Objectives Examples?
We've written extensively about how to go about creating good strategic objectives ( see this post ) - but sometimes, instead of a long blog article, all you need are a few examples of good strategic objectives to get your own creative juices flowing.
If you need broader help on writing a strategic plan, check out our complete guide . We've put together the following list - based on hundreds of successfully executed strategic plans from our very own cloud system Cascade .

We've grouped our examples of good strategic objectives into a series of broad categories (which we call Focus Areas ).
So without further ado, here's our list of strategic objective examples!
Strategic Objectives Examples
Focus area: financial growth.
- Grow gross revenue to $2m by 31st Dec 2022
- Increase net margin by 15% by 31st Jul 2023
- Reduce net costs by $900k by 1st Nov 2022
- Deliver 3 consecutive periods of monthly recurring revenue (MRR) of $50k by 1st Jul 2023
- Build $1m of reserve working capital by 31st Dec 2022
And here's an example of what not to write when creating good strategic objectives:
- Significantly increase profit in all business lines by 1st Nov 2022
The term 'significantly' is highly subjective - avoid where possible anything that can't be measured - there's really no excuse when it comes to financial goals!
Focus Area: Customer Satisfaction
- Deliver a customer survey overall satisfaction score of 90% by 1st Jul 2023
- Increase average customer product holding to 1.5 products per customer by 1st Jan 2023
- Lose fewer than 2 major accounts per year until 1st Dec 2022
- Win at least 1 industry award for customer service by 1st Jan 2023
- Attract 3 major customers in Asia Pacific by 30th Sept 2022
- Work with the customer service team to improve satisfaction by 1st Jan 2023
Apart from having no defined target as to what 'improve' means - strategic objectives need to be actual goals, rather than statements of intent!
Focus Area: Innovation/Product Growth
- Launch 3 new products by 31st Dec 2022
- Launch/transition to a cloud service model by 1st Jan 2023
- Establish 4 new major distribution partnerships by 1st Feb 2023
- Ensure that 30% of our approved projects are classed as 'Horizon 3: Blue Sky Thinking' by 1st Jan 2023
- Launch an innovation lab by 31st Dec 2022
And here's an example of what not to write when creating good strategic objectives:
- Become more competitive than our competitors by 1st Nov 2022
Strategic objectives need clearly defined start and end points - define your starting position, set a target increase (in percentage or absolute terms) then state that number as part of your goal.
Focus Area: People/Culture
- Reduce staff attrition to less than 10% per annum by 1st Jan 2023
- Launch a staff engagement/survey program by 1st Mar 2023
- Win a major employer award by 1st Jan 2023
- Implement a flexible working program by 1st Jul 2023
- Hire 3 additional product managers by 1st Feb 2023
- Improve our workplace culture by 1st Nov 2023
This is far too broad for an example of a good strategic objective and should instead by either part of your Vision or your Focus Areas. Break this down into several actionable goals!
Focus Area: Processes/Operations
- Reduce product return rate to less than 3% by 1st Jan 2023
- Implement a rigorous process of auditing our warehouses by 1st Nov 2023
- Increase sales efficiency to a 20% conversion rate through the use of a CRM by 1st Dec 2023
- Host a quarterly supplier forum with our top 20 suppliers by volume by 1st Jan 2023
- Implement a cloud-based strategy management platform by 15th Nov 2022
- Be more compliant as a business by 1st Mar 2023
Don't leave room for interpretation in your strategic objectives (unless you actively want to encourage discussion as part of the planning phase) - be specific about what you mean rather than using general words like 'compliance'.
What are your best strategic objective examples?
Hopefully, the above examples of good strategic objectives will help your own thinking in terms of what objectives to create for your next strategic plan.
So long as you keep your strategic objectives clear, concise, specific, and measurable - you won't go too far wrong!
Popular articles

6 Steps To Successful Strategy Execution & Best Practices
.png)
How To Create A Culture Of Strategy Execution
.png)
McKinsey GE Matrix: Importance & How To Use It (2024)
.png)
How To Be More Strategic: 7 Tips & Best Practices For Leaders
Your toolkit for strategy success.

6 examples of objectives for a small business plan
Table of Contents
1) Becoming and staying profitable
2) maintaining cash flow , 3) establishing and sustaining productivity , 4) attracting and retaining customers , 5) developing a memorable brand and marketing strategy, 6) planning for growth , track your business objectives and more with countingup.
Your new company’s business plan is a crucial part of your success, as it helps you set up your business and secure the necessary funding. A major part of this plan is your objectives or the outcomes you aim to reach. If you’re unsure where to start, this list of business objective examples can help.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- Becoming and staying profitable
- Maintaining cash flow
- Establishing and sustaining productivity
- Attracting and retaining customers
- Developing a memorable brand
- Reaching and growing an audience through marketing
- Planning for growth
One of the key objectives you may consider is establishing and maintaining profitability . In short, you’ll aim to earn more than you spend and pay off your startup costs. To do this, you’ll need to consider your business’s starting budget and how you’ll stick to it.
To create an objective around profitability, you’ll need to calculate how much you spend to start your business and how much you’ll have to spend regularly to run it. Knowing these numbers will help you determine the earnings you’ll need to become profitable. From there, you can factor in the pricing of your products or services and create sales goals .
For example, say you spend £2,000 on startup costs and expect to spend about £200 monthly to cover business expenses. To earn a profit, you’ll first need to earn back that £2,000 then make more than £200 monthly.
Once you know what you’ll need to earn to become profitable, you can create a realistic timeline to achieve it. If demand and sales forecasts suggest you could earn about £700 monthly, you may create a timeline of 5 months to become profitable.
We have created a free profit margin calculator tool which can help you work out your profit margins.
Maintaining cash flow is another financial objective you could include in your business plan. While profitability means you’ll make more money than you spend, cash flow is the cash running in and out of your business over a given time. This flow is crucial to your company’s success because you need available cash to cover business expenses .
When you complete services, clients may not pay out an invoice right away, meaning you won’t see the cash until they do. If you make enough sales but have low cash flow, you’ll struggle to run your business. So, create an achievable and measurable plan for how you’ll maintain the cash flow you need.
For example, if you spend £500 monthly, you’ll need to ensure you have at least that much available cash. On top of that, anticipate and save for unexpected or emergency expenses, such as broken equipment. To maintain your cash flow, you may want to prioritise cash payments, introduce a realistic deadline for invoices, or create a system to turn your profit to cash.
Aside from financial objectives, another example of objectives for a business plan is sustaining productivity . When you run a business, it can be overwhelming and challenging to stay on top of all the tasks you have to get done. But, if you aim to remain productive and create a clear plan as to how, you can better manage your to-do list.
For example, you may find project management tools that can help you track what you need to do and how to organise your priorities. You may also plan to outsource some aspects of your business eventually, such as investing in an accountant.
Other than planning how you’ll get things done, you may want to create an objective for developing and retaining a customer base. Here, you may outline your efforts to find leads and recruit customers. So, establish goals for how many customers you want to find in your business’s first month, quarter, or year. Your market research can help you understand demand and create realistic sales goals.
If you start a business that customers regularly need, like hairdressing, you may also want to create a strategy for how you’ll retain customers you earn. For example, you could introduce a loyalty program or prioritise customer service to build strong relationships.
Another example of objectives for a business plan is to develop a memorable brand and overall marketing strategy . Your brand is how you present your business to the public, including its unique tone and design. So, here you might research how to make a brand memorable and consider what colour scheme and style will best reach your target audience.
To measure your brand’s progress, you could hold focus groups on understanding what people think of your overall look. Then, surveys can help you grasp the reach of your reputation over time.
Aside from tracking the success of your brand strategy, you may want to consider your business’s marketing approach. For example, you might invest in paid advertising and use social media. You can measure the progress of this over time by using tools like Google Analytics to track your following and reach.
Finally, creating an objective for your company’s growth will help you understand and plan for where you want to go. For example, you may want to expand your services or open a second location for a shop. Whatever ideas you have for the future of your business, try to create a clear, measurable way of getting there, including a timeline. You may also want to include steps towards this goal and savings goals for growth.
To achieve and track your business plan objectives, you’ll need to organise your finances well. But, financial management can be stressful and time-consuming when you’re self-employed. That’s why thousands of business owners use the Countingup app to make their financial admin easier.
Countingup is the business account with built-in accounting software that allows you to manage all your financial data in one place. With the cash flow insights feature, you can confidently keep on top of your finances wherever you are. Plus, the app lets you track and manage what you spend on your business with automatic expense categorisation. This way, you can stick to your budget and plan to accomplish your objectives.

- Counting Up on Facebook
- Counting Up on Twitter
- Counting Up on LinkedIn
Related Resources
Business insurance from superscript.
We’re partnered with insurance experts, Superscript to provide you with small business insurance.
How to register a company in the UK
There are over five million companies registered in the UK and 500,000 new
How to set up a TikTok shop (2024)
TikTok can be an excellent platform for growing a business, big or small.
Best Side Hustle Ideas To Make Extra Money In 2024 (UK Edition)
Looking to start a new career? Or maybe you’re looking to embrace your
How to throw a launch party for a new business
So your business is all set up, what next? A launch party can
How to set sales goals
Want to make manageable and achievable sales goals for your business? Find out
10 key tips to starting a business in the UK
10 things you need to know before starting a business in the UK
How to set up your business: Sole trader or limited company
If you’ve just started a business, you’ll likely be faced with the early
How to register as a sole trader
Running a small business and considering whether to register as a sole trader?
How to open a Barclays business account
When starting a new business, one of the first things you need to
How to start a successful business during a recession
Starting a business during a recession may sound like madness, but some big
What is a mission statement (and how to write one)
When starting a small business, you’ll need a plan to get things up
- Newsletters
- Best Industries
- Business Plans
- Home-Based Business
- The UPS Store
- Customer Service
- Black in Business
- Your Next Move
- Female Founders
- Best Workplaces
- Company Culture
- Public Speaking
- HR/Benefits
- Productivity
- All the Hats
- Digital Transformation
- Artificial Intelligence
- Bringing Innovation to Market
- Cloud Computing
- Social Media
- Data Detectives
- Exit Interview
- Bootstrapping
- Crowdfunding
- Venture Capital
- Business Models
- Personal Finance
- Founder-Friendly Investors
- Upcoming Events
- Inc. 5000 Vision Conference
- Become a Sponsor
- Cox Business
- Verizon Business
- Branded Content
- Apply Inc. 5000 US
Inc. Premium

- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Overview and Objectives
The third in a comprehensive series to help you craft the perfect business plan for your startup.

This article is part of a series on how to write a great business plan .
Providing an overview of your business can be tricky, especially when you're still in the planning stages. If you already own an existing business, summarizing your current operation should be relatively easy; it can be a lot harder to explain what you plan to become .
So start by taking a step back.
Think about what products and services you will provide, how you will provide those items, what you need to have in order to provide those items, exactly who will provide those items... and most importantly, whom you will provide those items to.
Consider our bicycle rental business example. It's serves retail customers. It has an online component, but the core of the business is based on face-to-face transactions for bike rentals and support.
So you'll need a physical location, bikes, racks and tools and supporting equipment, and other brick-and-mortar related items. You'll need employees with a very particular set of skills to serve those customers, and you'll need an operating plan to guide your everyday activities.
Sound like a lot? It boils down to:
- What you will provide
- What you need to run your business
- Who will service your customers, and
- Who your customers are
In our example, defining the above is fairly simple. You know what you will provide to meet your customer's needs. You will of course need a certain quantity of bikes to service demand, but you will not need a number of different types of bikes. You need a retail location, furnished to meet the demands of your business. You need semi-skilled employees capable of sizing, customizing, and repairing bikes.
And you know your customers: Cycling enthusiasts.
In other businesses and industries answering the above questions can be more difficult. If you open a restaurant, what you plan to serve will in some ways determine your labor needs, the location you choose, the equipment you need to purchase... and most importantly will help define your customer. Changing any one element may change other elements; if you cannot afford to purchase expensive kitchen equipment, you may need to adapt your menu accordingly. If you hope to attract an upscale clientele, you may need to invest more in purchasing a prime location and creating an appealing ambience.
So where do you start? Focus on the basics first:
- Identify your industry: Retail, wholesale, service, manufacturing, etc. Clearly define your type of business.
- Identify your customer. You cannot market and sell to customers until you know who they are.
- Explain the problem you solve. Successful businesses create customer value by solving problems. In our rental example, one problem is cycling enthusiasts who don't--or can't--travel with bikes. Another problem is casual cyclists who can't--or choose not to--spend significant sums on their own bikes. The rental shop will solve that problem by offering a lower-cost and convenient alternative.
- Show how you will solve that problem. Our rental shop will offer better prices and enhanced services like remote deliveries, off-hours equipment returns, and online reservations.
If you are still stuck, try answering these questions. Some may pertain to you; others may not.
- Who is my average customer? Who am I targeting? (Unless you plan to open a grocery store, you should be unlikely to answer, "Everyone!")
- What problem do I solve for my customers?
- How will I solve that problem?
- Where will I fail to solve a customer problem... and what can I do to overcome that issue? (In our rental example, one problem is a potential lack of convenience; we will overcome that issue by offering online reservations, on-resort deliveries, and drive-up equipment returns.)
- Where will I locate my business?
- What products, services, and equipment do I need to run my business?
- What skills do my employees need, and how many do I need?
- How will I beat my competition?
- How can I differentiate myself from my competition in the eyes of my customers? (You can have a great plan to beat your competition but you also must win the perception battle among your customers. If customers don't feel you are different... then you aren't truly different. Perception is critical.)
Once you work through this list you will probably end up with a lot more detail than is necessary for your business plan. That is not a problem: Start summarizing the main points. For example, your Business Overview and Objectives section could start something like this:
History and Vision
Blue Mountain Cycle Rentals is a new retail venture that will be located at 321 Mountain Drive, directly adjacent to an extremely popular cycling destination. Our initial goal is to become the premier provider for bicycle rentals. We will then leverage our customer base and position in the market to offer new equipment sales as well as comprehensive maintenance and service, custom equipment fittings, and expert trail advice.
- Achieve the largest market share bicycle rentals in the area
- Generate a net income of $235,000 at the end of the second year of operation
- Minimize rental inventory replacement costs by maintaining a 7% attrition rate on existing equipment (industry average is 12%)
Keys to Success
- Provide high quality equipment, sourcing that equipment as inexpensively as possible through existing relationships with equipment manufacturers and other cycling shops
- Use signage to attract visitors traveling to the national forest, highlighting our cost and service advantage
- Create additional customer convenience factors to overcome a perceived lack of convenience for customers planning to ride roads and trails some distance away from our shop
- Develop customer incentive and loyalty programs to leverage customer relationships and create positive word of mouth
You could certainly include more detail in each section; this is simply a quick guide. And if you plan to develop a product or service, you should thoroughly describe the development process as well as the end result.
The key is to describe what you will do for your customers--if you can't, you won't have any customers.
Next time we'll look at another major component in a business plan: your Products and Services .
More in this series:
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Key Concepts
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: the Executive Summary
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Products and Services
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Market Opportunities
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Sales and Marketing
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Competitive Analysis
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Operations
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Management Team
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Financial Analysis
The Daily Digest for Entrepreneurs and Business Leaders
Privacy Policy
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- United Kingdom
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
Plan Your Business Plan Before you put pen to paper, find out how to assess your business's goals and objectives.
You've decided to write a business plan, and you're ready to get started. Congratulations. You've just greatly increased the chances that your business venture will succeed. But before you start drafting your plan, you need to--you guessed it--plan your draft.
One of the most important reasons to plan your plan is that you may be held accountable for the projections and proposals it contains. That's especially true if you use your plan to raise money to finance your company. Let's say you forecast opening four new locations in the second year of your retail operation. An investor may have a beef if, due to circumstances you could have foreseen, you only open two. A business plan can take on a life of its own, so thinking a little about what you want to include in your plan is no more than common prudence.
Second, as you'll soon learn if you haven't already, business plans can be complicated documents. As you draft your plan, you'll be making lots of decisions on serious matters, such as what strategy you'll pursue, as well as less important ones, like what color paper to print it on. Thinking about these decisions in advance is an important way to minimize the time you spend planning your business and maximize the time you spend generating income.
To sum up, planning your plan will help control your degree of accountability and reduce time-wasting indecision. To plan your plan, you'll first need to decide what your goals and objectives in business are. As part of that, you'll assess the business you've chosen to start, or are already running, to see what the chances are that it will actually achieve those ends. Finally, you'll take a look at common elements of most plans to get an idea of which ones you want to include and how each will be treated.
Determine Your Objectives Close your eyes. Imagine that the date is five years from now. Where do you want to be? Will you be running a business that hasn't increased significantly in size? Will you command a rapidly growing empire? Will you have already cashed out and be relaxing on a beach somewhere, enjoying your hard-won gains?
Answering these questions is an important part of building a successful business plan. In fact, without knowing where you're going, it's not really possible to plan at all.
Now is a good time to free-associate a little bit--to let your mind roam, exploring every avenue that you'd like your business to go down. Try writing a personal essay on your business goals. It could take the form of a letter to yourself, written from five years in the future, describing all you have accomplished and how it came about.
As you read such a document, you may make a surprising discovery, such as that you don't really want to own a large, fast-growing enterprise but would be content with a stable small business. Even if you don't learn anything new, though, getting a firm handle on your goals and objectives is a big help in deciding how you'll plan your business.
Goals and Objectives Checklist If you're having trouble deciding what your goals and objectives are, here are some questions to ask yourself:
- How determined am I to see this succeed?
- Am I willing to invest my own money and work long hours for no pay, sacrificing personal time and lifestyle, maybe for years?
- What's going to happen to me if this venture doesn't work out?
- If it does succeed, how many employees will this company eventually have?
- What will be its annual revenues in a year? Five years?
- What will be its market share in that time frame?
- Will it be a niche marketer, or will it sell a broad spectrum of good and services?
- What are my plans for geographic expansion? Local? National? Global?
- Am I going to be a hands-on manager, or will I delegate a large proportion of tasks to others?
- If I delegate, what sorts of tasks will I share? Sales? Technical? Others?
- How comfortable am I taking direction from others? Could I work with partners or investors who demand input into the company's management?
- Is it going to remain independent and privately owned, or will it eventually be acquired or go public?
Your Financing Goals
It doesn't necessarily take a lot of money to make a lot of money, but it does take some. That's especially true if, as part of examining your goals and objectives, you envision very rapid growth.
Energetic, optimistic entrepreneurs often tend to believe that sales growth will take care of everything, that they'll be able to fund their own growth by generating profits. However, this is rarely the case, for one simple reason: You usually have to pay your own suppliers before your customers pay you. This cash flow conundrum is the reason so many fast-growing companies have to seek bank financing or equity sales to finance their growth. They are literally growing faster than they can afford.
Start by asking yourself what kinds of financing you're likely to need--and what you'd be willing to accept. It's easy when you're short of cash, or expect to be short of cash, to take the attitude that almost any source of funding is just fine. But each kind of financing has different characteristics that you should take into consideration when planning your plan. These characteristics take three primary forms:
- First, there's the amount of control you'll have to surrender. An equal partner may, quite naturally, demand approximately equal control. Venture capitalists often demand significant input into management decisions by, for instance, placing one or more people on your board of directors. Angel investors may be very involved or not involved at all, depending on their personal style. Bankers, at the other end of the scale, are likely to offer no advice whatsoever as long as you make payments of principal and interest on time and are not in violation of any other terms of your loan.
- You should also consider the amount of money you're likely to need. Any amount less than several million dollars is too small to be considered for a standard initial public offering of stock, for example. Venture capital investors are most likely to invest amounts of $250,000 to $3 million. On the other hand, only the richest angel investor will be able to provide more than a few hundred thousand dollars, if that.
Almost any source of funds, from a bank to a factor, has some guidelines about the size of financing it prefers. Anticipating the size of your needs now will guide you in preparing your plan.
- The third consideration is cost. This can be measured in terms of interest rates and shares of ownership as well as in time, paperwork and plain old hassle.
How Will You Use Your Plan
Believe it or not, part of planning your plan is planning what you'll do with it. No, we haven't gone crazy--at least not yet. A business plan can be used for several things, from monitoring your company's progress toward goals to enticing key employees to join your firm. Deciding how you intend to use yours is an important part of preparing to write it.
Do you intend to use your plan to help you raise money? In that case, you'll have to focus very carefully on the executive summary, the management, and marketing and financial aspects. You'll need to have a clearly focused vision of how your company is going to make money. If you're looking for a bank loan, you'll need to stress your ability to generate sufficient cash flow to service loans. Equity investors, especially venture capitalists, must be shown how they can cash out of your company and generate a rate of return they'll find acceptable.
Do you intend to use your plan to attract talented employees? Then you'll want to emphasize such things as stock options and other aspects of compensation as well as location, work environment, corporate culture and opportunities for growth and advancement.
Do you anticipate showing your plan to suppliers to demonstrate that you're a worthy customer? A solid business plan may convince a supplier of some precious commodity to favor you over your rivals. It may also help you arrange supplier credit. You may want to stress your blue-ribbon customer list and spotless record of repaying trade debts in this plan.
Assessing Your Company's Potential
For most of us, unfortunately, our desires about where we would like to go aren't as important as our businesses' ability to take us there. Put another way, if you choose the wrong business, you're going nowhere.
Luckily, one of the most valuable uses of a business plan is to help you decide whether the venture you have your heart set on is really likely to fulfill your dreams. Many, many business ideas never make it past the planning stage because their would-be founders, as part of a logical and coherent planning process, test their assumptions and find them wanting.
Test your idea against at least two variables. First, financial, to make sure this business makes economic sense. Second, lifestyle, because who wants a successful business that they hate?
Answer the following questions to help you outline your company's potential. There are no wrong answers. The objective is simply to help you decide how well your proposed venture is likely to match up with your goals and objectives.
- What initial investment will the business require?
- How much control are you willing to relinquish to investors?
- When will the business turn a profit?
- When can investors, including you, expect a return on their money?
- What are the projected profits of the business over time?
- Will you be able to devote yourself full time to the business, financially?
- What kind of salary or profit distribution can you expect to take home?
- What are the chances the business will fail?
- What will happen if it does?
- Where are you going to live?
- What kind of work are you going to be doing?
- How many hours will you be working?
- Will you be able to take vacations?
- What happens if you get sick?
- Will you earn enough to maintain your lifestyle?
- Does your family understand and agree with the sacrifices you envision?
Sources: The Small Business Encyclopedia , Business Plans Made Easy, Start Your Own Business and Entrepreneur magazine.
Continue on to the next section of our Business Plan How-To >> Elements of a Business Plan
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- His Ex-Boss Issued Him a Cease-and-Desist Order . Neither Man Expected What Happened in a Parking Lot Next: 'I Bleed This Business. It's Cold-Blooded.'
- Lock 8 Evening Routines With Surprising Effects on Your Ability to Get Things Done
- Why Are Nvidia Earnings So Important? They Could Be a 'Market Mover,' Says Expert.
- Lock I Sent My Role Model a DM, Never Imagining She'd Respond — Then This Happened
- Lock This Couple's Weekend Side Hustle Began With a $50 Facebook Marketplace Purchase — Now It Earns Millions of Dollars a Year: 'You Don't Need Money to Start'
- Walmart and Burger King's New Partnership Is Poised to Give a Boost to Franchise Traffic
Most Popular Red Arrow
Why being a more generous leader will create a more successful business.
There is no time like the present to think more about others than oneself. Give generously in all you do: your time, energy, enthusiasm, caring and financial impact. Your company, clients, community and team will thank you.
These Are the Best Jobs for Every Personality Type, According to a New Report
You don't have to be an extrovert to find a job that aligns with your strengths.
63 Small Business Ideas to Start in 2024
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
What Is Elon Musk's New Master Plan For Tesla? Original Blueprint Disappears From Tesla's Website After 18 years
Tesla seems to have removed Musk's original master plan (and the follow-up) from its website.
Double Your Organic Traffic and Boost Your Sales With This SEO Guide for Ecommerce Businesses
Discover proven SEO tips to double organic traffic to your ecommerce business and drive more sales.
'Pressure Cooker': Why Millionaire Nvidia Employees Are Still Working Until 2 a.m.
In a new report, current and former Nvidia employees gave insight into the work culture at the chip-maker, including long hours, lots of yelling, and unbelievable bank accounts.
Successfully copied link
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
Business Plan Executive Summary Example & Template

Updated: Jun 3, 2024, 1:03pm

Table of Contents
Components of an executive summary, how to write an executive summary, example of an executive summary, frequently asked questions.
A business plan is a document that you create that outlines your company’s objectives and how you plan to meet those objectives. Every business plan has key sections such as management and marketing. It should also have an executive summary, which is a synopsis of each of the plan sections in a one- to two-page overview. This guide will help you create an executive summary for your business plan that is comprehensive while being concise.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
$0 + State Fee
On Formations' Website
The executive summary should mimic the sections found in the business plan . It is just a more concise way of stating what’s in the plan so that a reader can get a broad overview of what to expect.
State the company’s mission statement and provide a few sentences on what the company’s purpose is.
Company History and Management
This section describes the basics of where the company is located, how long it has been in operation, who is running it and what their level of experience is. Remember that this is a summary and that you’ll expand on management experience within the business plan itself. But the reader should know the basics of the company structure and who is running the company from this section.
Products or Services
This section tells the reader what the product or service of the company is. Every company does something. This is where you outline exactly what you do and how you solve a problem for the consumer.
This is an important section that summarizes how large the market is for the product or service. In the business plan, you’ll do a complete market analysis. Here, you will write the key takeaways that show that you have the potential to grow the business because there are consumers in the market for it.
Competitive Advantages
This is where you will summarize what makes you better than the competitors. Identify key strengths that will be reasons why consumers will choose you over another company.
Financial Projections
This is where you estimate the sales projections for the first years in business. At a minimum, you should have at least one year’s projections, but it may be better to have three to five years if you can project that far ahead.
Startup Financing Requirements
This states what it will cost to get the company launched and running. You may tackle this as a first-year requirement or if you have made further projections, look at two to three years of cost needs.
The executive summary is found at the start of the business plan, even though it is a summary of the plan. However, you should write the executive summary last. Writing the summary once you have done the work and written the business plan will be easier. After all, it is a summary of what is in the plan. Keep the executive summary limited to two pages so that it doesn’t take someone a long time to peruse what the summary says.
Start A Limited Liability Company Online Today with ZenBusiness
Click to get started.
It might be easier to write an executive summary if you know what to expect. Here is an example of an executive summary that you can use as a template.

Bottom Line
Writing an executive summary doesn’t need to be difficult if you’ve already done the work of writing the business plan itself. Take the elements from the plan and summarize each section. Point out key details that will make the reader want to learn more about the company and its financing needs.
How long is an executive summary?
An executive summary should be one to two pages and no more. This is just enough information to help the reader determine their overall interest in the company.
Does an executive summary have keywords?
The executive summary uses keywords to help sell the idea of the business. As such, there may be enumeration, causation and contrasting words.
How do I write a business plan?
If you have business partners, make sure to collaborate with them to ensure that the plan accurately reflects the goals of all parties involved. You can use our simple business plan template to get started.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best LLC Services
- Best Registered Agent Services
- Best Trademark Registration Services
- Top LegalZoom Competitors
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Plan Software
- ZenBusiness Review
- LegalZoom LLC Review
- Northwest Registered Agent Review
- Rocket Lawyer Review
- Inc. Authority Review
- Rocket Lawyer vs. LegalZoom
- Bizee Review (Formerly Incfile)
- Swyft Filings Review
- Harbor Compliance Review
- Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC
- LLC vs. Corporation
- LLC vs. S Corp
- LLP vs. LLC
- DBA vs. LLC
- LegalZoom vs. Incfile
- LegalZoom vs. ZenBusiness
- LegalZoom vs. Rocket Lawyer
- ZenBusiness vs. Incfile
- How To Start A Business
- How to Set Up an LLC
- How to Get a Business License
- LLC Operating Agreement Template
- 501(c)(3) Application Guide
- What is a Business License?
- What is an LLC?
- What is an S Corp?
- What is a C Corp?
- What is a DBA?
- What is a Sole Proprietorship?
- What is a Registered Agent?
- How to Dissolve an LLC
- How to File a DBA
- What Are Articles Of Incorporation?
- Types Of Business Ownership
Next Up In Business
- Best Online Legal Services
- How To Write A Business Plan
- Member-Managed LLC Vs. Manager-Managed LLC
- Starting An S-Corp
- LLC Vs. C Corp
- How Much Does It Cost To Start An LLC?


What Is SNMP? Simple Network Management Protocol Explained
What Is A Single-Member LLC? Definition, Pros And Cons
What Is Penetration Testing? Definition & Best Practices
What Is Network Access Control (NAC)?
What Is Network Segmentation?

How To Start A Business In Louisiana (2024 Guide)
Kimberlee Leonard has 22 years of experience as a freelance writer. Her work has been featured on US News and World Report, Business.com and Fit Small Business. She brings practical experience as a business owner and insurance agent to her role as a small business writer.
Cassie is a deputy editor collaborating with teams around the world while living in the beautiful hills of Kentucky. Focusing on bringing growth to small businesses, she is passionate about economic development and has held positions on the boards of directors of two non-profit organizations seeking to revitalize her former railroad town. Prior to joining the team at Forbes Advisor, Cassie was a content operations manager and copywriting manager.
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

9 Business Plan Examples to Inspire Your Own (2024)
Need support creating your business plan? Check out these business plan examples for inspiration and guidance.

Any aspiring entrepreneur researching how to start a business will likely be advised to write a business plan. But few resources provide business plan examples to really guide you through writing one of your own.
Here are some real-world and illustrative business plan examples to help you craft your business plan .
Business plan format: 9 examples
The business plan examples in this article follow this template:
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Market analysis
- Products and services
- Marketing plan
- Logistics and operations plan
- Financial plan
- Customer segmentation
1. Executive summary
Your executive summary is a page that gives a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. While it appears at the beginning, it’s easiest to write this section last, as there are details further in the report you’ll need to include here.
In this free business plan template , the executive summary is four paragraphs and takes a little over half a page. It clearly and efficiently communicates what the business does and what it plans to do, including its business model and target customers.

2. Company description
You might repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page , social media profile pages, or other properties that require a boilerplate description of your small business.
Soap brand ORRIS has a blurb on its About page that could easily be repurposed for the company description section of its business plan.

You can also go more in-depth with your company overview and include the following sections, like in this business plan example for Paw Print Post:
Business structure
This section outlines how you registered your business —as an LLC , sole proprietorship, corporation, or other business type : “Paw Print Post will operate as a sole proprietorship run by the owner, Jane Matthews.”
Nature of the business
“Paw Print Post sells unique, one-of-a-kind digitally printed cards that are customized with a pet’s unique paw prints.”
“Paw Print Post operates primarily in the pet industry and sells goods that could also be categorized as part of the greeting card industry.”
Background information
“Jane Matthews, the founder of Paw Print Post, has a long history in the pet industry and working with animals, and was recently trained as a graphic designer. She’s combining those two loves to capture a niche in the market: unique greeting cards customized with a pet’s paw prints, without needing to resort to the traditional (and messy) options of casting your pet’s prints in plaster or using pet-safe ink to have them stamp their ’signature.’”
Business objectives
“Jane will have Paw Print Post ready to launch at the Big Important Pet Expo in Toronto to get the word out among industry players and consumers alike. After two years in business, Jane aims to drive $150,000 in annual revenue from the sale of Paw Print Post’s signature greeting cards and to have expanded into two new product categories.”
“Jane Matthews is the sole full-time employee of Paw Print Post but hires contractors as needed to support her workflow and fill gaps in her skill set. Notably, Paw Print Post has a standing contract for five hours a week of virtual assistant support with Virtual Assistants Pro.”
Your mission statement may also make an appearance here. Passionfruit shares its mission statement on its company website, and it would also work well in its example business plan.

3. Market analysis
The market analysis consists of research about supply and demand , your target demographics, industry trends, and the competitive landscape. You might run a SWOT analysis and include that in your business plan.
Here’s an example SWOT analysis for an online tailored-shirt business:

You’ll also want to do a competitive analysis as part of the market research component of your business plan. This will tell you which businesses you’re up against and give you ideas on how to differentiate your brand. A broad competitive analysis might include:
- Target customers
- Unique value proposition , or what sets the products apart
- Sales pitch
- Price points for products
- Shipping policy
4. Products and services
This section of your business plan describes your offerings—which products and services do you sell to your customers? Here’s an example for Paw Print Post that explains its line of custom greeting cards, along with details on what makes its products unique.

5. Marketing plan
It’s always a good idea to develop a marketing plan before you launch your business. Your marketing plan shows how you’ll get the word out about your business, and it’s an essential component of your business plan as well.

The Paw Print Post focuses on four Ps: price, product, promotion, and place. However, you can take a different approach with your marketing plan. Maybe you can pull from your existing marketing strategy , or maybe you break it down by the different marketing channels. Whatever approach you take, your marketing plan should describe how you intend to promote your business and offerings to potential customers.
6. Logistics and operations plan
The Paw Print Post example considered suppliers, production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory. This includes any raw materials needed to produce the products.

7. Financial plan
The financial plan provides a breakdown of sales, revenue, profit, expenses, and other relevant financial metrics related to funding and profiting from your business.
Ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy’s financial plan breaks down predicted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.

It then dives deeper into the financials to include:
- Funding needs
- Projected profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
- Projected cash-flow statement
You can use a financial plan spreadsheet to build your own financial statements, including income statement, balance sheet, and cash-flow statement.

8. Customer segmentation
Customer segmentation means dividing your target market into groups based on specific characteristics. These characteristics can be demographics, psychographics, behavior, or geography. Your business plan will provide detailed information on each segment, like its size and growth potential, so you can show why they are valuable to your business.
Airsign , an eco-friendly vacuum cleaner company, faced the challenge of building a sustainable business model in the competitive home appliance market. They identified three key customer personas to target:
- Design-oriented urban dwellers
- Millennials moving to suburbs
- Older consumers seeking high-quality appliances
The company utilized Shopify’s customer segmentation tools to gain insights and take action to target them. Airsign created targeted segments for specific marketing initiatives.
Put your customer data to work with Shopify’s customer segmentation
Shopify’s built-in segmentation tools help you discover insights about your customers, build segments as targeted as your marketing plans with filters based on your customers’ demographic and behavioral data, and drive sales with timely and personalized emails.
9. Appendix
The appendix provides in-depth data, research, or documentation that supports the claims and projections made in the main business plan. It includes things like market research, finance, résumés, product specs, and legal documents.
Readers can access detailed info in the appendix, but the main plan stays focused and easy to read. Here’s an example from a fictional clothing brand called Bloom:
Appendix: Bloom Business Plan
Types of business plans, and what to include for each
This lean business plan is meant to be high level and easy to understand at a glance. You’ll want to include all of the same sections in one-page business plan, but make sure they’re truncated and summarized:
- Executive summary: truncated
- Market analysis: summarized
- Products and services: summarized
- Marketing plan: summarized
- Logistics and operations plan: summarized
- Financials: summarized
A startup business plan is for a new business. Typically, these plans are developed and shared to secure funding . As such, there’s a bigger focus on the financials, as well as on other sections that determine viability of your business idea—market research, for example:
- Market analysis: in-depth
- Financials: in-depth
Your internal business plan is meant to keep your team on the same page and aligned toward the same goal:
A strategic, or growth, business plan is a big-picture, long-term look at your business. As such, the forecasts tend to look further into the future, and growth and revenue goals may be higher. Essentially, you want to use all the sections you would in a normal business plan and build upon each:
- Market analysis: comprehensive outlook
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Marketing plan: comprehensive outlook
- Logistics and operations plan: comprehensive outlook
- Financials: comprehensive outlook
Feasibility
Your feasibility business plan is sort of a pre-business plan—many refer to it as simply a feasibility study. This plan essentially lays the groundwork and validates that it’s worth the effort to make a full business plan for your idea. As such, it’s mostly centered around research:
Nonprofit business plans are used to attract donors, grants, and partnerships. They focus on what their mission is, how they measure success, and how they get funded. You’ll want to include the following sections in addition to a traditional business plan:
- Organization description
- Need statement
- Programs and services
- Fundraising plan
- Partnerships and collaborations
- Impact measurement
Set yourself up for success as a business owner
Building a good business plan serves as a roadmap you can use for your ecommerce business at launch and as you reach each of your business goals. Business plans create accountability for entrepreneurs and synergy among teams, regardless of your business model .
Kickstart your ecommerce business and set yourself up for success with an intentional business planning process—and with the sample business plans above to guide your own path.
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- The 13 Best Dropshipping Suppliers in 2024
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- 25+ Ideas for Online Businesses To Start Now (2024)
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- How to Build a Business Website for Beginners
- 7 Inspiring Marketing Plan Examples (and How You Can Implement Them)
- 10 Ways to Write Product Descriptions That Persuade (2024)
- Get Guidance- 6 Business Plan Software to Help Write Your Future
- Business Valuation- Learn the Value of Your Business
Business plan examples FAQ
How do i write a simple business plan.
To write a simple business plan, begin with an executive summary that outlines your business and your plans. Follow this with sections detailing your company description, market analysis, organization and management structure, product or service, marketing and sales strategy, and financial projections. Each section should be concise and clearly illustrate your strategies and goals.
What is the best format to write a business plan?
The best business plan format presents your plan in a clear, organized manner, making it easier for potential investors to understand your business model and goals. Always begin with the executive summary and end with financial information or appendices for any additional data.
What are the 4 key elements of a business plan?
- Executive summary: A concise overview of the company’s mission, goals, target audience, and financial objectives.
- Business description: A description of the company’s purpose, operations, products and services, target markets, and competitive landscape.
- Market analysis: An analysis of the industry, market trends, potential customers, and competitors.
- Financial plan: A detailed description of the company’s financial forecasts and strategies.
What are the 3 main points of a business plan?
- Concept: Your concept should explain the purpose of your business and provide an overall summary of what you intend to accomplish.
- Contents: Your content should include details about the products and services you provide, your target market, and your competition.
- Cash flow: Your cash flow section should include information about your expected cash inflows and outflows, such as capital investments, operating costs, and revenue projections.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Aug 31, 2024
Aug 30, 2024
Aug 29, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
It's All You Boo
10 Business Goals and Objectives Examples to Help You Succeed
August 6, 2023 28 Comments
Want a list of business goals to help you get started? Looking for the most effective business goals and objectives examples to help you succeed?
What are smart business goals and objectives, and why do you need them?
We’ll answer that question and provide examples below. If you own a business, goals, and objectives are vital to your success.
They give your business goals, give direction, and purpose and help you stay focused on the essential things.
We’ll cover types of business goals, and then we’ll discuss 10 business goals and objectives examples to help you get started setting your own. And read on if you don’t know the difference between goals and objectives .
Types of Business Goals
There are many different types of business goals to consider, so read through these to help you develop appropriate goals for your situation.
#1. Startup Business Objectives Examples
A startup business will have different-term goals and objectives than established companies. For example, a startup company will need to set goals regarding finding investors and taking on debt to open. The objectives for reaching those goals will involve speaking to financial advisors and developing plans to acquire investor funding.
#2. Personal Business Goals Examples
It’s essential to have general business goals, but you also need to have personal goals related to your business. For example, maybe you’ve realized you’re not a good communicator.
You can have a goal setting for yourself to become better at talking to others, and your objectives may include working with a mentor. You could also join a Toastmasters group to learn and practice your communication skills.
If you’d like to set a goal for saving for retirement, make objectives for how much money you want to put away each month.
You can set term goals like short-term or long-term to meet your unique needs and business model, use a specific business strategy, or improve profit margins. But then, you’ll need to develop objectives to help you reach those goals.

#3. 5-Year Business Goals Examples
Sometimes, it’s easy to focus on quarterly goals and forget longer-term goals. Instead, make sure you spend some time focusing on where you want to be in five years and how you’re going to get there.
For example, you might want your business to double profits or shareholder value in five years. Then, you can set objectives to grow each month in a structured way to reach that long-term business goal.
Another example of a five-year business goal is to become debt-free . Once again, when you set big, long-term goals, you want to break them down into step-by-step goals and objectives. You want to make sure the data matches and this is a reasonable goal.
#4. Examples of Short- and Long-Term Goals for a Business
Short-term goals should fit into your long-term goals. Short-term goals should be the stair steps to reaching the top.
For example, increasing your market share might be a long-term goal, while reaching five new customers may be a short-term related goal.
Business Goals and Objectives Examples
One of the most important ways to become successful in business is to know where you’re going. Making a list of smart business goals forces you to be specific about success, and objectives give you the method of reaching those goals. But how do you write business goals and objectives?
The first step is to brainstorm and narrow down your ideas to align with your business plan . Next, write those goals out, develop objectives to reach them, and then share those goals with your team leaders.
What are some examples of business objectives? While your goals and objectives will vary to meet your business plan, we’ll share 10 business goals and objectives examples that are general enough for anyone to consider using.

Goal #1. Improve Employee Retention
Onboarding a new employee costs a lot of money. You have to pay for training time, including the time from both the trainer and the new employee.
Getting a new employee to independent productivity can take up to two months, and they won’t reach their prime performance until a couple of months after that.
If you can retain an employee, you’ll avoid losing profits by training new employees.
Objective: Communicate often
When you communicate with your employees frequently, they will feel comfortable sharing their frustrations with you. Then, you can problem-solve together to improve their enjoyment of their work. Sometimes, simply offering encouraging words can help retain employees, and other times you may need to shift assignments for a better fit.
Goal #2. Increase Profitability
The more profitable your business, the more options you have for growth, investment, and improvement. Everyone should have an increased profitability goal, but the objectives for reaching that goal will differ.
For example, some may need to cut spending , while others may need to spend more for increased profitability or increased sales.

Objective: Analyze advertising spending
By analyzing ad spending and return on investment, you’ll be able to pinpoint the best avenues to spend and where you should cut . Analytics is one of the most powerful tools for maximizing spending for the greatest rewards.
Goal #3. Decrease Debt
Debt is often a necessary part of life, but the less debt you have, the less profit you will lose to paying interest on that debt. On the other hand, sometimes taking on debt allows your business to grow in ways that exceed the interest on that debt, and that’s a sign that taking out that loan was a wise financial decision.
However, you should always seek to pay down debt , raise capital and increase market share so the next time you want to invest a large amount of money, you’ll have the assets to do so without a loan.
Objective: Get a business owner’s insurance policy
Part of your debt mitigation strategy should include a business owner’s policy for insurance. Without it, you could rapidly increase your debt with costs to defend yourself against lawsuits or pay for losses due to weather or fire damage.
Goal #4. Improve Customer Retention
Similar to how employee retention helps your bottom line, customer retention does as well. Acquiring a new customer costs more than keeping a customer. You’ll want to reach a larger audience to keep your business growing, but don’t forget to keep your current customers happy and coming back for more.

Objective: Start using customer surveys
There’s no better way to find out how satisfied your customers are than to hear directly from them. Customer surveys provide an avenue for direct responses from customers. You can learn what they tend to like and what tends to be bothersome.
Customers often ignore surveys unless offered an incentive, so you might want to consider offering a discount code for complete surveys or entering their name into a drawing for a prize. This is a simple, yet easy way to increase customer satisfaction.
Goal #5. Create A Better Product
You have a new product, and that’s why you have a business. Making your product as good as possible will improve your customer retention and their trust in your business .
Better products also have an internal benefit because when your employees see the value you place on improvement, they’ll feel more invested in their work.
Objective: Analyze weaknesses in the product and invite team members to develop solutions
Involvement from the team will help you develop the best solutions because of the different perspectives each team member has. Goals give everyone on the team understanding of what the end result should become.
Goal #6. Improve Customer Service
Customer service is one of the keys to customer retention. You’ll find that setting business goals often work together, and when you have success in one area, you’ll also experience success in other areas. Customer service is how your business deals with its customers. And it’s a critical component of customer satisfaction.
For example, if a customer has a bad experience with your product, their customer service engagement could make the difference between losing a customer or building loyalty. A customer service agent who remedies the problem will likely help the customer build trust with the company.

Objective: Host customer service training
You can’t expect your customer relations team members to act in a way that represents your brand unless you explain. These training sessions can help customer service employees to develop strategies and techniques for de-escalating situations and leading the customer to a place of fulfilled needs.
Goal #7. Hire Better New Employees
Ideally, every new employee will be a perfect fit and stay at your company until they retire. In reality, you’ll get a couple of people like that, and you’ll get a lot who wash out within a year.
If you want to improve employee retention, you’ll help yourself out by hiring better new employees in the first place.
Objective: Set new hire criteria
If you’ve been hiring new employees without knowing precisely what you’re looking for, you’ll tend to make more mistakes and hire people you shouldn’t.
Sometimes, an employee can be a great fit even if they don’t match every criterion you set so you can be flexible, but writing out the traits you need in new employees will help you focus on what’s most important.
Goal #8. Increase Employee Growth
If employees feel like they’re in a dead-end position, they’ll likely have decreased productivity and an increased desire to find work elsewhere.
An employee growth mindset allows employees to become more profitable and find more meaning in their work. If you have an employee capable of excellent leadership, you’re wasting their talent and reducing your profitability if you keep them in the lowest position.

Objective: Provide employees with avenues to display strengths
Not everyone has the same strengths, so there’s no single way to find employees’ strengths and help them grow. So instead, give all your employees different ways to grow each week and see where individuals thrive .
For example, one month, you may ask employees to present a training session and help them see who communicates well in a teaching setting. Another month, you may ask employees to look for ways to increase productivity, which will help you find those with analytical minds.
Goal #9. Improve Customer Engagement
When your customers engage with you, that means you’re on their minds. And then, when they need something you provide the solution for, they’ll turn to you because they know you.
Objective: Connect with customers on social media weekly
A social media strategy is a new technology that can help you connect with customers. If someone engages with your posts, make sure they feel appreciated. People like to know what they say or think matters, so don’t hold back.
Goal #10. Purchase A Storefront
A brick-and-mortar location isn’t appropriate or common for all businesses. For example, your business involves internet and software services, and all your employees work remotely. Therefore, you don’t need a physical storefront. However, if you’re renting a storefront, you may want to start looking into buying.
Objective: Reach out to lenders
The first step on a journey to purchase property is reaching out to lenders to develop more specific objectives to help you reach your property goals. For example, you may need to save for a down payment, or perhaps you’ll need to increase your credit score so you can qualify for better interest rates. You’ll know more about your next steps after taking the first step.

Business Plan Objectives Examples
While smart business goals and objectives examples sound similar to business plan objectives examples, they’re surprisingly different. Goals are specific things you want to attain, while a plan is your overarching way of running your business.
Perhaps a business plan could be to do direct marketing, and your goals and objectives could be to increase your customer base and reach out to five new individuals a week.
Another example of a business plan is an overview of what you provide, and objectives would designate ways to meet goals that fit into your business plan.
Get Your SMART Goals Worksheet
Ready to set these business goals and objectives examples? Sign up below to get your FREE SMART Goals Worksheet , form-fillable, and printable, and includes more examples to help you.

Sign up below for your FREE SMART Goals Worksheet + get weekly tips to help you slay your goals. Privacy Policy
What are good goals and objectives examples? Reasonable or smart goals and objectives will help your business plan be successful.
You can use our list of goals and objectives to help you get started, and then you can tweak them to serve your business best. So spend the time you need on organization and developing goals and objectives.

Are these business goals and objectives examples helpful?

More About Guest Contributor
Melanie Musson writes and researches for the insurance comparison site, ExpertInsuranceReviews.com . She is passionate about helping others succeed in their business goals and find the business insurance policy right for their situation.
Last Updated on July 18, 2024
Share or save for later!
It's All You Boo
Looking for something, trending topics.
Goal Setting • College Student Life • Get Motivated • Be More Productive • Change Your Mindset • Improve Your Mental Health • Develop Good Habits • Inspirational Quotes • Self-Love & Care • Organize Your Life • Be Your Own Boss • Manage Your Money
MY FAV TOOLS
Amazon storefront, slay your goals planner, positive mindset mantras, goal setting 101, #goalslayer program, conquer procrastination book 📘, pinterest courses + pin templates📌, want to connect, become an affiliate, pin with me, submit a guest post.
Get access to over 25 resources + weekly tips to help you slay your goals.
Privacy Policy.
BECOME A VIP
Get your FREE 10-Step Guide
+ weekly tips to help you slay your goals
Take the FREE Challenge
Sign up below to join us LIVE Weds, December 11th @ 8pm EST
+ get access to the replay
Sign up below to plan your personal goals for 2020.
+ get tips to help you slay your goals
Sign up below to join my FREE 7-Day Challenge!
Sign up below to start the FREE Masterclass.
Get your FREE Printable Workbook
Get your FREE Printable Checklist
Sign up below to join us LIVE Weds., March 6th @ 8pm EST
Sign up below to plan your online blog and business goals.
How To Write a Strategic Plan for Your Business

What to read next:
See how Quantive can help you achieve more of your strategy.
Strategic planning forms the foundation of effective strategy management. It's the crucial first step that sets the direction for your entire business, regardless of its size or industry. A well-crafted strategic plan does more than outline goals—it provides a roadmap for achieving them, aligning your team's efforts, and adapting to change. Whether you're steering a multinational corporation or managing a neighborhood café, mastering the art of strategic planning can significantly impact your business's trajectory. Let's explore how strategic planning initiates the strategic management process and lays the groundwork for long-term success.
What are the seven elements of a strategic plan?
A comprehensive strategic plan typically consists of seven key elements that work together to create a cohesive roadmap for your business. Let's explore each of these elements:
Vision
Your vision statement articulates what your organization aspires to achieve in the future. It's your long-term goal to provide a clear picture of where you want your business to be. A strong vision statement is inspirational and guides your strategic decision-making.
The mission statement is the driving force behind why your company exists. It defines who you serve, how you create value, and what sets you apart. A well-crafted mission statement should be concise, memorable, and aligned with your vision.
Values
Your core values are the fundamental beliefs that guide your company's behavior and decision-making process. They shape your organizational culture and influence how you interact with customers, employees, and stakeholders.
Goals
Goals are the measurable objectives that align with your business mission, vision, and values. These are typically your long-term ambitions, often set for a 3-5 year timeframe. They provide direction and focus for your entire organization.
Your strategy is the long-term plan for achieving your objectives. It's based on both internal and external factors, often informed by a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats). Your strategy maps out how you'll leverage your strengths, address weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate threats.
The approach outlines how you'll execute your strategy and achieve your objectives. It involves defining specific actions and initiatives. These are often your short-term objectives, breaking down long-term goals into smaller, measurable milestones to track progress and maintain momentum.
Tactics are the granular, short-term actions, programs, and activities that support your approach. They are the detailed steps and specific tasks that, when executed, help you achieve your objectives and, ultimately, your long-term goals.
By incorporating these seven elements into your strategic plan, you create a comprehensive framework that bridges the gap between your current state and your desired future. This strategic roadmap not only defines where you want to go but also outlines how you'll get there, ensuring that every aspect of your business is aligned towards achieving your vision.
What is an example of a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is your business's GPS, guiding you from where you are to where you want to be. It's a comprehensive document that outlines your goals, strategies, and the steps needed to achieve them.
Let's look at a real-world example to see what a strategic plan could look like in practice:
Imagine a mid-sized tech company aiming to become a market leader in cloud computing solutions.
Their strategic plan might include:
- Mission : To revolutionize business efficiency through innovative cloud solutions
- Vision: To be the go-to cloud service provider for small and medium enterprises by 2026
- Core values: Innovation, customer-centricity, collaboration
- SWOT analysis: Identifying strengths (cutting-edge technology), weaknesses (limited market presence), opportunities (growing demand for cloud services), and threats (intense competition)
- Long-term goals : Achieve 25% market share within five years
- Short-term objectives: Increase customer base by 50% in the next 12 months
- Action plans: Launch a targeted marketing campaign, develop new product features, and expand the sales team
This example demonstrates how a strategic plan provides a clear roadmap for achieving business objectives.
Specific examples of strategic plans for various sectors
Different sectors may emphasize different aspects of strategic planning . For instance:
- Healthcare: Focus on patient outcomes, technology integration, and regulatory compliance
- Education: Prioritize student achievement, faculty development, and funding strategies
- Non-profit: Emphasize mission alignment, donor engagement, and program effectiveness
Remember, the key is to adapt your strategic plan to your unique context and needs.
How do you make a strategic plan for a small business?
Strategic planning is essential for all business sizes, not just corporate giants. Small businesses, with their limited resources, can greatly benefit from a well-structured strategic plan. By prioritizing initiatives and allocating resources wisely, a strategic plan helps avoid costly mistakes and maximizes return on investment. It allows business owners to focus on impactful activities, adapt quickly to market changes, and ensure every effort contributes to long-term goals.
Even a simplified version of the seven strategic planning elements can provide a solid foundation for growth. The key is creating a plan that's both comprehensive and flexible. In the resource-constrained world of small business, a well-crafted strategic plan ensures that every resource is channeled effectively, promoting smart, strategic growth rather than just hard work.
Here's how a small business can create a strategic plan:
- Clarify your vision, mission, and values
- Conduct an environmental scan
- Define strategic priorities
- Develop goals and metrics
- Derive a strategic plan
- Write and communicate your strategic plan
- Implement, monitor, and revise
These steps provide a comprehensive framework for organizations to create, execute, and maintain an effective strategic plan.
For a more in-depth guide, check out this article on the strategic planning process .
Simplify the process using strategic frameworks and templates
Strategic frameworks and templates can be invaluable tools, especially for those new to the process or looking to streamline their approach. They provide structure and ensure you don't overlook critical components. Here are some examples of strategic frameworks and templates and their specific use cases:
- Use case: Ideal for small businesses or startups needing a concise overview.
- Example : A tech startup might use this to outline its product development roadmap, key market targets, and growth milestones for the next 12 months.
- Use case: Perfect for teams setting specific, measurable objectives.
- Example: A sales team could use this to set targets like “Increase quarterly revenue by 15% through expanding into two new market segments by Q3.”
- Use case: Valuable for businesses conducting a comprehensive situational analysis.
- Example: A retail company might use this to assess its e-commerce capabilities (strength), limited physical presence (weakness), emerging markets (opportunity), and increasing online competition (threat).
- Use case: Suited for larger organizations needing to align various departments.
- Example: A healthcare provider could use this to track patient satisfaction (customer), operational efficiency (internal processes), staff training (learning and growth), and cost management (financial) metrics.
- Use case: Useful for project managers or team leaders implementing specific strategies.
- Example: A marketing team might use this to outline steps for a product launch, including timelines for content creation, media outreach, and performance tracking.
By choosing the right framework for your specific needs, you can significantly simplify the strategic planning process and ensure all crucial elements are addressed. Remember, these templates are starting points - customize them to fit your unique business context and goals.
Want to streamline strategic planning?
Strategic planning is more than a business exercise — it's a commitment to your future success. Whether you're learning how to write a strategic plan for a department or figuring out how to write a strategy for a project, the principles remain the same: clarity, focus, and actionable steps.
Writing a strategic plan from scratch may seem daunting, but it doesn't have to be. Our strategic intelligence platform, Quantive StrategyAI , can help you create a strategic plan based on your current business circumstances, ways of working, and goals. Here's how:
- AI-Powered Insights: StrategyAI analyzes your business data, both structured and unstructured, to provide contextually relevant insights and guidance at every step.
- End-to-end Management: From strategy development to execution and evaluation, StrategyAI offers a comprehensive solution to manage your entire strategic process.
- Adaptive Approach: The platform adapts to your business context, inputs, and way of working, eliminating the need for you to adjust to a new system.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: With over 170 integrations, StrategyAI connects with your business data sources, ensuring your insights are always fresh and relevant.
- Always-On Strategy: StrategyAI enables a continuous, responsive, and connected approach to strategy, which is crucial for success in today's fast-paced business environment.
At Quantive, we specialize in turning complex business challenges into clear, effective strategies. Our AI-powered platform, combined with our team of experts, can guide you through the process, helping you create and execute a strategic plan that drives real results.
Quantive empowers modern organizations to turn their ambitions into reality through strategic agility. It's where strategy, teams, and data come together to drive effective decision-making, streamline execution, and maximize performance.
As your company navigates today’s competitive landscape, you need an Always-On Strategy to continuously bridge the gap between current and desired business outcomes. Quantive brings together the technology, expertise, and passion for transforming your strategy and playbooks from a static formulation to a feedback-driven engine for growth.
Whether you’re a fast-growing scale-up, a mid-market business looking to conquer, or a large enterprise looking for innovation, Quantive keeps you ahead – every step of the way. For more information, visit www.quantive.com .
Subscribe for our Newsletter
Financial modeling spreadsheets and templates in Excel & Google Sheets
- Your cart is empty.

Examples of Business Plans That Drive Success

A robust business plan is more than just a document; it’s a blueprint for success, guiding entrepreneurs through the complexities of building a thriving company. For instance, the early business plan of Starbucks outlined a strategy for turning a local coffee shop into a national phenomenon through an aggressive expansion and unique customer experience, which became key drivers of their widespread success. Similarly, Google’s initial business plan focused on improving the speed and accuracy of search results, emphasizing a user-friendly interface and algorithmic innovations, which helped them dominate the internet search industry.
These examples highlight the critical role a well-constructed business plan plays in setting the stage for a company’s success. A successful business plan not only details what the company plans to do but also articulates how it plans to outperform competitors by addressing a specific market need in a unique way. By studying such successful business plans, new entrepreneurs can learn how to craft plans that attract investors, guide internal operations, and achieve sustainable growth, turning visionary ideas into profitable realities.
The Importance of a Well-Structured Business Plan
The cornerstone of any successful business journey is often a comprehensive and well-structured business plan. Whether you are an entrepreneur seeking funding , an investor evaluating opportunities, or a finance professional advising clients, the importance of a meticulously crafted business plan cannot be overstated. A robust business plan not only acts as a roadmap for growth and sustainability but also fosters confidence among stakeholders, thereby driving success. In this article, we will delve deep into various examples of business plans that have led to flourishing enterprises, aiming to provide you with a collection of insightful templates and strategies.
A solid business plan plays several key roles in driving business success:
- Acts as a roadmap for growth and sustainability
- Fosters stakeholder confidence
- Serves as a basis for capital allocation decisions
The roles outlined above are critical in shaping the direction and viability of any business. Acting as a detailed strategic document, a business plan underpins sustainable growth, instills confidence among investors and stakeholders, and guides sound investment decisions.
Key Components of a Business Plan
To build an effective business plan, several components must be carefully structured. These components form the backbone of the plan, each contributing to its overall strength and functionality.
Strategic Goal Setting
Strategic goals provide clarity and focus, driving the business towards its long-term vision. Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound ( SMART ) goals ensures that each step taken is aligned with the overall objectives of the enterprise.
Market Analysis
Understanding the market landscape is crucial. Comprehensive market analysis offers insights into customer needs, competitor actions, and industry trends. This information is indispensable for positioning the business strategically and identifying competitive advantages.
Budget Planning
Effective budget planning entails creating a detailed financial blueprint that forecasts revenue, expenses, and profitability. It is essential for ensuring the sustainable financial health of the business, guiding operational decisions, and managing resources efficiently.
Feasibility Studies
Feasibility studies assess the practicality and potential success of a business idea. By evaluating market demand, economic factors, and operational challenges, these studies help in making informed decisions and mitigating risks.
Practical Examples of Business Plans
To illustrate how these components come together to form a robust business plan, let us explore a few real-world examples:
| Example | Key Components | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Tech Startup | Secured $5M in initial funding and surpassed growth targets in the first two years. | |
| E-commerce Platform | Expanded internationally, achieving a 35% increase in revenue from new markets. |
These examples illustrate how integrating strategic goal setting, market analysis, budget planning, and feasibility studies can lead to tangible business successes. By leveraging these elements, entrepreneurs and finance professionals alike can construct business plans that not only map out the path to success but also adapt flexibly to changing market conditions.
Understanding the importance of these components and seeing their application in real-world scenarios can significantly enhance your ability to create effective business plans. Let’s embark on this journey to understanding why a concrete business plan is indispensable and how real-world examples can guide you toward achieving your business objectives.
Creating a Business Plan for a Tech Startup
Creating a business plan for a tech startup involves addressing unique challenges and leveraging specific opportunities within the technology sector. A well-rounded business plan typically includes key components such as the executive summary, market analysis, marketing strategy, and financial plan. This was excellently demonstrated by TechInspire, a hypothetical startup focused on an innovative Software as a Service platform. Below, we provide a comprehensive breakdown of their approach.
Key Components
Executive summary.
TechInspire’s mission is to streamline project management for small to medium-sized enterprises through their Software as a Service product, aiming to offer a more efficient and effective tool tailored to this market segment’s needs.
A thorough analysis identified a growing demand for cloud-based solutions, with projections showing a 20% annual market growth rate, highlighting a rife opportunity for expansion and dominance.
Marketing Strategy
The strategy emphasized a multifaceted approach including digital marketing, partnerships with industry influencers, and a freemium pricing model designed to attract initial users and build a strong customer base swiftly.
Financial Plan
The financial plan outlined critical financial metrics such as break-even analysis, projected cash flow, and detailed funding requirements essential for scaling operations effectively and sustainably.
Key Data Points
To provide a quick snapshot of the most critical information in TechInspire’s business plan, refer to the table below, which outlines key data points like market growth rate and projected cash flow.
| Data Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Growth Rate | 20% annually |
| Projected Cash Flow | Positive cash flow by Year 2 |
| Break-even Point | Year 3 |
| Initial Funding Requirement | $500,000 |
This table highlights the actionable insights derived from the market analysis and financial projections, giving potential investors a clear picture of TechInspire’s financial health and growth prospects. By ensuring that critical data points are easily accessible, TechInspire enhances the business plan’s readability and impact.
Challenges and Unique Solutions
Tech startups face numerous challenges, but TechInspire’s business plan takes specific strategies to overcome these obstacles. Here is a breakdown of common challenges and TechInspire’s approach to addressing them:
- Technical Development: In the highly competitive tech sector, staying ahead with cutting-edge technology is crucial.
- Market Penetration: Gaining initial user traction can be difficult amidst numerous competing solutions.
- Resource Management: Efficiently managing limited resources to maximize growth and scalability.
TechInspire addresses these challenges with the following strategies:
- Investing in continuous development and hiring top-tier talent to maintain a technological edge.
- Implementing a freemium pricing model to attract users and build a community base quickly.
- Focusing on strategic partnerships and digital marketing to increase visibility and customer acquisition.
By understanding the specific challenges faced by tech startups and developing targeted solutions, TechInspire’s business plan demonstrates foresight and strategic planning. This ensures a more resilient and adaptive business model capable of navigating the dynamic tech landscape successfully.
The Importance of a Well-Developed Business Plan in the Retail Clothing Industry
In the competitive world of retail clothing, having a well-developed business plan is not just beneficial but essential. It can be the strategic difference between thriving in a crowded market and being forced to close shop. Consider the fictional case of FashionForward, a retail clothing store that meticulously crafted a detailed business plan to steer its operations and growth strategy toward success.
Key Components of FashionForward’s Business Plan
Each component of a business plan plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth functioning and strategic direction of the business. Below are the key sections of FashionForward’s plan, each introduced with a brief explanation.
FashionForward strives to become a leading brand in the retail sector by focusing on trendy, affordable, and eco-friendly clothing options that appeal to a growing segment of environmentally-conscious consumers.
The market analysis section includes
- Identification of target demographics
- In-depth competitor analysis
- Assessment of market trends, particularly the shift toward sustainable fashion
Understanding these elements helps FashionForward position itself appropriately and strategize its market entry effectively.
Operational Plan
The operational plan covers the nuts and bolts of running the business, including:
- Selected store locations
- Advanced inventory management system
- Strong relationships with suppliers
- Clear staffing requirements
These details ensure that operations run smoothly and efficiently, providing a seamless experience for customers.
Financial Projections
The financial projections provide a blueprint for potential profitability and include:
- Startup costs
- Sales forecasts
- Profit margins
- Break-even analysis
These projections are vital for attracting potential investors by demonstrating the financial viability of the business.
Comparing Industry Trends with FashionForward’s Market Positioning
FashionForward’s business plan also considers industry trends to ensure it remains competitive. The table below compares key industry trends with FashionForward’s market positioning and projected financial data.
| Industry Trend | FashionForward’s Strategy |
|---|---|
| Sustainability in Fashion | Eco-friendly materials and production processes |
| Increasing Online Sales | Robust e-commerce platform and digital marketing |
| Personalization | Customizable clothing options |
| Fast Fashion Demand | Quick turnaround from design to shelf |
By aligning its strategies with these industry trends, FashionForward is better positioned to capture market share and achieve long-term growth. Investors will be more inclined to fund a business that is responsive to current market conditions and consumer needs.
By thoroughly addressing each of these components, FashionForward’s business plan provides a robust foundation for not only launching but also sustaining and growing the business in a competitive retail market. The detailed planning in each component assures stakeholders of the business’s potential for success and profitability.
Consulting Firms and the Importance of Business Plans
Consulting firms rely heavily on their business plans to strategize growth and establish credibility. Consider Strategic Solutions, a mock consulting firm specializing in financial advisory services. Their business plan illustrates a well-rounded approach to capturing market share and delivering value to clients by offering unique services and differentiating themselves from competitors.
Key Components and Strategic Objectives
The following table outlines the key components of Strategic Solutions’ business plan and illustrates how each element supports the firm’s overarching strategic objectives.
| Component | Description | Strategic Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Summary | Provides bespoke financial advisory services tailored to mid-sized companies aiming for strategic growth. | Establishes credibility and outlines the value proposition to potential clients and investors. |
| Service Offerings | Detailed descriptions of core services such as financial planning, risk management, and investment advice. | Highlights specialized services that set Strategic Solutions apart from competitors. |
| Market Positioning | Outlines competitive advantages, market segments, and marketing strategies focused on brand authority and client acquisition. | Targets high-value clients through strategic positioning and effective marketing. |
| Financial Plan | Projected earnings, cost structures, and scalable models for service expansion and profitability. | Ensures financial sustainability and prepares for scalable growth. |
Each component of the business plan plays a pivotal role in ensuring that Strategic Solutions remains competitive in the financial advisory market. From the executive summary that sets the tone and credibility of the firm to the detailed financial plan that maps out future profitability, every facet is geared towards reinforcing the firm’s strategic objectives.
Key Tactics for Market Share and Brand Authority
In addition to a well-structured business plan, Strategic Solutions employs various tactics to capture market share and establish brand authority. The following bullet points outline these key tactics:
- Customized Service Packages: Tailoring services to meet the specific needs of mid-sized companies.
- Thought Leadership: Publishing white papers and conducting webinars to establish expertise in financial advisory services.
- Client Testimonials and Case Studies: Showcasing successful projects and satisfied clients to build trust and credibility.
- Partnerships and Alliances: Forming strategic alliances with other firms to expand service offerings and market reach.
- Digital Marketing Campaigns: Leveraging SEO, content marketing, and social media to enhance online presence and attract new clients.
These tactics allow Strategic Solutions to differentiate themselves in the competitive consulting landscape. By focusing on customized service packages and thought leadership, the firm attracts and retains high-value clients. Additionally, client testimonials and strategic partnerships further bolster their market position, while digital marketing campaigns ensure a broad reach and sustained online visibility.
Well-Structured Business Plans: The Foundation of Success
Well-structured business plans are fundamental to the success of any enterprise. By taking inspiration from diverse examples, whether it’s for a tech startup, a retail clothing business, or a consulting firm, entrepreneurs can glean valuable insights into effectively presenting their vision, strategies, and financial forecasts. Each element, from the executive summary to the financial plan, plays a crucial role in addressing stakeholder concerns and steering the business toward its goals. Below, we summarize the key takeaways from each example discussed in the article.
Key Takeaways from Business Plan Examples
Drawing from various business plan examples, here are the essential elements that contribute to a successful business plan:
- Executive Summary: Offers a concise overview of the business, including its mission, vision, and objectives. It should capture the reader’s interest and provide a snapshot of the overall plan.
- Market Analysis: Analyzes the target market, industry trends, and competitive landscape. Essential for demonstrating the demand for the product or service and how the business will meet this demand.
- Marketing Strategy: Details the methods for reaching and attracting customers, including advertising, sales tactics, and promotional activities. It should outline how the business will build its brand and gain market share.
- Financial Plan: Includes detailed financial projections, such as income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. This section should justify financial needs and illustrate the potential for profitability and growth.
Understanding these key elements are critical for anyone involved in business planning. The executive summary sets the stage and draws in stakeholders, while the market analysis provides the necessary context and justification for the venture. The marketing strategy outlines how the business will penetrate its market, and the financial plan offers concrete evidence of financial viability. Together, these components form a comprehensive picture that can persuade investors, guide strategic decisions, and keep the business on course for success.
The Elements of a Successful Business Plan
Here is a table summarizing the vital elements that ensure a business plan is robust and impactful:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Executive Summary | A brief overview that includes the mission, vision, and primary objectives of the business. |
| Market Analysis | An examination of the industry, target market, and competitors. Provides insights into the market demand and business potential. |
| Marketing Strategy | Plans for product or service promotion to attract and retain customers. Covers advertising, sales tactics, and promotional efforts. |
| Financial Plan | Financial projections including income statements, cash flow summaries, and balance sheets. Shows financial needs, potential profitability, and growth projections. |
This table serves as a quick reference to the vital elements of a well-structured business plan. Each component plays an irreplaceable role in painting a complete picture of the business’s pathway to success. By paying close attention to these elements, entrepreneurs, investors, and financial professionals can ensure their business planning is comprehensive and impactful.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, whether you are an aspiring entrepreneur, a seasoned investor, or a financial professional, understanding these examples of business plans can significantly bolster your planning process and pave the way for success. The relevance of structured plans in achieving business success cannot be overstated, as they provide a clear, detailed roadmap for navigating the complexities of business growth and development. A meticulously crafted business plan helps address stakeholder concerns and equips your enterprise with a guide to steer it toward its goals effectively.
What is the Significance of an Executive Summary in a Business Plan?
The executive summary is a pivotal section of your business plan, offering a brief yet comprehensive overview of your proposed venture. It encapsulates key elements like the business concept, market potential, financial highlights, and strategic goals. This section is particularly crucial because it usually is the first part that potential investors and stakeholders read, setting the tone for the entire document.
**Key Points to Include in an Executive Summary:**
- Business Concept: What your business does, its mission, and its vision.
- Market Potential: The size and characteristics of your target market.
- Financial Highlights: Summary of projections, including revenue and profit forecasts.
- Strategic Goals: Short-term and long-term objectives.
These key points serve as a snapshot that should entice potential investors and stakeholders to read further into your business plan. By clearly summarizing your business idea and its merits, you provide a compelling reason for readers to continue exploring the finer details.
How Detailed Should the Market Analysis Be in a Business Plan?
A well-executed market analysis is a cornerstone of a robust business plan. This section should demonstrate your deep understanding of the industry landscape, target market, and competitive environment. It is advisable to be as detailed and data-driven as possible.
**Elements to Include in Market Analysis:**
- Market Size: Quantitative data on your market’s size and potential.
- Growth Trends: Historical data and future projections for the market.
- Customer Segments: Detailed description of the primary customer groups.
- Competitor Analysis: Insights into key competitors, their strengths, and weaknesses.
An in-depth market analysis not only underscores your business’s growth potential but also builds confidence among stakeholders and investors. It shows that you have conducted rigorous research and are prepared to navigate the complexities of the market.
What Financial Projections are Essential in a Business Plan?
Financial projections are essential to providing an objective view of your business’s financial viability. This section should include comprehensive projections for income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets over a minimum period of three to five years.
**Essential Financial Projections:**
- Income Statements: Expected revenue, costs, and profits over the defined period.
- Cash Flow Statements: Forecasts of cash inflows and outflows.
- Balance Sheets: Snapshot of your business’s financial position at specific points in time.
Providing detailed financial projections allows potential investors to gauge the financial health of your business. Including the assumptions behind your projections—such as revenue growth rates, expense margins, and capital requirements—adds another layer of transparency and reliability.
Can a Business Plan Evolve Over Time?
Yes, a business plan is inherently a dynamic document that must evolve. Regular reviews and updates ensure that the plan remains aligned with current market conditions, business performance, and strategic goals.
**Reasons to Update Your Business Plan:**
- Market Changes: Adapt to new trends, technologies, or regulations.
- Business Performance: Modify based on actual performance versus projections.
- Strategy Adjustments: Realign objectives and strategies as needed.
A living business plan offers the flexibility to pivot or scale according to emerging opportunities and challenges. Consistent updates make sure your business stays on the right path toward achieving its goals.
Is Professional Help Necessary to Create a Business Plan?
Although you can create a business plan independently, seeking professional assistance can add substantial value. Experts in financial modeling, business consultancy, and market analysis bring specialized skills that can enhance both the credibility and depth of your plan.
**Advantages of Professional Help:**
- Expertise: Specialized knowledge to cover essential elements comprehensively.
- Credibility: A polished, expert-reviewed plan enhances investor confidence.
- Strategic Insights: Objective perspectives to guide your business strategy.
Engaging professionals not only elevates the quality of your business plan but also significantly increases its chances of attracting investors and guiding effective strategic decisions.

Online Clothing Store Financial Model Excel Template
Impress bankers and investors with a proven, solid Online Clothing Store Financial Projection Template. Five year online clothing store cash... read more
- Excel - Multi-User – $129.00 Version 1
- Excel - Single-User – $99.00 Version 1
- Free Demo – $0.00 Version 1

Clothing Store Financial Model Excel Template
Get Your Clothing Store Budget Template. Creates 5-year Pro-forma financial statements, and financial ratios in GAAP or IFRS formats on the fly. Five-... read more
- Excel - Multi-User – $129.00
- Excel - Single-User – $99.00
- Free Demo – $0.00

Bundle – Business Financial Forecasting Models
The purpose of this Bundle of Business Forecasting and Financial Models is to assist Business Owners and Consultants with a consistent approach to for... read more
- Template Bundle – $137.00 Version 1

Clothing Line Business Financial Model Excel Template
Clothing Line Budget Template Solid package of print-ready reports: P&L and Cash Flow statement, and a complete set of ratios. Shop Now Five-year ... read more

Fashion Marketplace Financial Model Excel Template
Shop Fashion Marketplace Pro-forma Template. Creates 5-year financial projection and financial ratios in GAAP or IFRS formats on the fly. Five-y... read more

Online Clothing Wholesaler – 5 Year Financial Model
Advanced Financial Model presenting a 5 Year Business Plan for an Online Clothing Wholesale company.
- Excel Financial Model – $89.00
- PDF Free Demo – $0.00

Tailor Financial Model Excel Template
Buy Tailor Financial Plan. Spend less time on Cash Flow forecasting and more time on your products. Generates 5-year tailor pro forma budget, pr... read more

Clothing Boutique Financial Model – Dynamic 10 Year Forecast
Financial Model providing a dynamic up to 10-year financial forecast for a startup or existing Clothing Boutique.
- Financial Model - Premium Version – $79.00
- Financial Model - Standard Version – $59.00

Retail Business Financial Model
The Retail Financial Plan is an all-inclusive financial planning template for the retail industry. Whether you have a large retail chain or just a sin... read more

Fashion Designer (Independent) – 5 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing a highly sophisticated 5-year financial plan for a startup Independent Fashion Designer Business.
- Financial Model - Standard Version – $89.00 Version 1
- Financial Model - Premium Version – $119.00 Version 1
- PDF Free Demo – $0.00 Version 1

Self-Service Laundromat Financial Model and Budget Control Template
The financial model for a self-service laundromat is a comprehensive tool that allows owners and investors in the industry to make informed decisions ... read more
- Excel Model – $60.00 Version 1
- PDF Demo – $0.00 Version 1

Laundromat Financial Model – 10 Year
This template allows the user to produce financial statements based on assumptions specific to the laundromat industry. Includes granular capex, opex,... read more
- Full Basic Version – $45.00 Version 1
- Advanced (3 loan types, sale leaseback toggle, more) – $99.00 Version 1

Ultra Fashion Revenue and DCF Valuation Model
In this model, we presented a completed revenue and DCF valuation model for an Ultra-Fashion project on a 5-year basis project.
- Full Excel Version – $65.00
- Free PDF Version – $0.00

Baby Clothes Store Financial Model Excel Template
Baby Clothes Store Financial Plan Excel - well-tested, robust and powerful Get you solid foundation to plan your business model. Shop Now Five-year Ba... read more

Clothing Manufacturing – Dynamic 10 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing a dynamic up to 10-year financial forecast for a startup or existing Clothing Manufacturing Company.
- Financial Model - Premium Version – $119.00
- Financial Model - Standard Version – $89.00

Tailoring Business Financial Model – Dynamic 10 Year Forecast
Financial model providing a dynamic 10-Year Financial Plan for a Tailoring Business.
- Standard Version – $69.00
- Premium Version – $89.00

Shoe Store Financial Model – Dynamic 10 Year Forecast
Financial Model providing a dynamic up to 10-year financial forecast for a startup or existing Shoe Store.

Bridal Shop Financial Model Excel Template
Bridal Shop Budget Template Enhance your pitches and impress potential investors with the expected financial metrics. Buy Now Five-year Bridal Shop p&... read more

Free Costing Sheet for Garments
Streamline your business operations with this Free Costing Sheet for Garments, designed to simplify your costing process and maximize profitability. T... read more
- Free Template – $0.00 Version 1
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Finding Investors
How Funding Works
Idea Validation Bootcamp
Pitch Deck Bootcamp
Pitching Investors
Product MVP
Product/MVP
Idea Validation
Customer Acquisition
Emotional Support
Top 4 Business Plan Examples
The Startups Team

Founders have to learn so many new skills when they're launching a startup, and writing a business plan is a big one. When you're writing your business plan for the first time, things can get… intimidating.
What do you include? What kind of wording should you use? What do you make sure not to include? Is a mid size business plan different than an enterprise plan or a scalable startup? Do I need to include financials like cash flow statements? What do investors want to see?
It's enough to make even a stalwart startup founder and management team throw in the towel before they've even begun.
Lucky for you — we've created a complete guide to writing your business plan . Check it out if you haven't already. (And if a link from there brought you here, just keep reading!) We'll share some business plan samples so you can get started writing your own professional business plan.
But, while it's nice to be guided step-by-step, it can also really help to have concrete examples when you're approaching creating something for the first time.
So, with that in mind, here are four sample business plans from the Startups community that we think really stand out from the crowd. We hope that these will serve as a startup business plan template and make it easier to write your own. At a minimum, these will provide some great business plan ideas whether you are writing traditional business plans for an established business or biz plans for an innovative new startup. While we would of course suggest you use our business plan creator, Bizplan.com, you can use these examples with any number of business plan apps or business plan software.
Click on the below links to see fully formatted versions or continue reading for the text-only version of Culina's.
LiveShopBuy

CULINA Executive Summary
Fast facts:.
Founded: 2013 Headquarters: San Francisco, CA Founder: Kent McClure Market Size: $12.5 billion Target Audience: Homeowners; property managers; insurance providers.
Quick Description:
Culina is a San Francisco-based IoT and home automation company. We design an advanced smart hub technology that enables users to interconnect and remotely monitor all of their cooking devices and kitchen appliances through a single user-friendly platform.
Our Mission:
To make homes smarter, more connected, and safer for families while helping them save money and conserve energy through the power of affordable, automated technology.
Our Vision:
To become the leading provider of IoT technology for kitchen appliances on a global scale with applications across both residential and commercial properties.
Company Synopsis:
Culina Tech is the next leading name in home automation and IoT. We're committed to leading the charge in creating the ultimate smart kitchen for homeowners all around the world. Our revolutionary Smart Plugs enable users to make any kitchen appliance or cooking device intelligent. Compatible with all existing brands that plug into standard two or three-prong wall outlets, Culina creates an entire network of Wi-Fi-connected kitchen devices. The Culina App allows users to remotely monitor the status of and control all devices connected to our Smart Plugs. Whether it's remotely turning on the coffee pot after getting out of bed, turning off the stove if it was accidentally left on via smartphone, or switching on the crockpot before getting home from work, Culina is purpose-built to deliver unrivaled convenience and peace of mind.
With the ability to set energy usage caps on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis, Culina helps homeowners stay within their monthly utility budget and save energy in the kitchen through more efficient use of the dishwasher, refrigerator, freezer, stove, and other common appliances.
When a device reaches its energy limit, Culina alerts users through their smartphone and is built with the ability to power down the device automatically if the user chooses. The App measures key usage metrics in real-time, allowing users to get an instant dashboard view of energy consumption as it occurs.
Our team has already finished the product development and design phase, with 3 prototype iterations completed, and we are now ready to begin mass manufacturing. We've also gained major traction among consumers and investors alike, with 10,000 pre-ordered units sold and $5 million in capital secured to date.
With this round of funding, our objective is to ramp up hardware manufacturing, improve software UX and UI, expand our sales and marketing efforts, and fulfill pre-orders in time for the 2017 holiday season. We are currently seeking a $15M Series B capital investment that will give us the financial flexibility to achieve these goals. On behalf of the entire Culina Tech team, we'd like to thank you for your time and interest in our company and this investment opportunity.
Funding Allocation:
⇾ 30% Manufacturing ⇾ 25% Sales & Marketing ⇾ 25% Key Hires ⇾ 20% Operational
Team Overview:
The kitchen is the heart of the home. It's a quintessential gathering place where families and friends come together to break bread, be merry, and make memories. But the kitchen is also where tragedy often strikes due to misuse of appliances. Kent McClure and his team set out to make the kitchen a safer and more energy-efficient place for the family after a tragic fire struck his own kitchen in late 2012. Thankfully, no lives were lost and everyone in his family made it out safe and sound, but Kent couldn't help but wonder “what if.”
With decades in the industrial design space, Kent knew he had the knowledge and the industry contacts to set out to improve upon home automation devices for the kitchen with a solution that not only made homes safer but also cut down on energy consumption and associated costs. In early 2013, Culina was born. Since that time, Kent and the Culina team have made it their mission to completely revolutionize the home automation and IoT space with innovative, AI-powered technology.
Kent McClure | Founder & CEO Kent is a Carnegie Mellon graduate with over 10 years of executive leadership experience in industrial design and engineering. He has a successful entrepreneurial history, founding a prior tech-based startup which he grew to $100 million in revenue, followed by an acquisition in 2010 and then IPO shortly after.
Sherri Carlson | COO Sherri earned her MBA from Harvard Business School. She oversees all of Culina's ongoing operations and procedures and is responsible for driving Culina to achieve and surpass sales, profitability, cash flow, and business goals and objectives.
Martin Frink | CTO Martin is a Stanford University alumnus with extensive technical expertise and over a decade of experience at venture-backed tech companies. He is responsible for Culina's technical vision, heading up all aspects of our technological development, strategic direction, development, and future growth.
Margaret Burns | CFO Margaret earned her degree in Financial Management from NYU. Prior to joining Culina, Margaret spent seven years as CFO for a publicly-traded mobile tech company headquartered in Silicon Valley. She currently manages Culina's financial risks and handles all financial planning, record-keeping, and reporting.

COMPANY OVERVIEW
Market opportunity.
An enormous need exists for dramatic reductions in energy consumption. Businesses alone consume 12-20% of the total US energy supply on food production, processing, manufacturing, distribution, and preparation.
On the residential side, the Energy Information Administration estimates that the average US household uses 11,280 kWh per year. Many homeowners are simply unaware of the large amount of energy consumed by many small household kitchen appliances:
Dishwasher: 133 watts Television: 1,200 to 2,400 watts Coffee Maker: 900 to 1,200 watts Washing Machine: 350 to 500 watts Toaster: 55 to 250 watts Window Fan: 800 to 1,400 watts
The majority of US households now spend roughly 35 percent of their energy consumption on appliances, electronics, and lighting.
Most homeowners don't think about the little details that can help save them money on their energy bill. The vast majority of people keep the refrigerator or freezer too cold, fail to make sure refrigerator door seals are airtight, neglect to regularly defrost fridges and freezers, overload their dishwashers, and keep dishwasher water temperature too hot. As a result, energy consumption remains high, and energy bills remain high.
Not only do kitchens represent a primary source of household energy consumption, but also a primary source of house fires. More fires start in the kitchen than in any other room in the home, and household cooking appliances frequently account for billions of dollars in fire-related insurance claims every year. The number one cause of house fires and house fire injuries is the stove.
✓ 46% of house fires caused by cooking equipment ✓ 62% of house fires caused by ranges or cooktops ✓ $4,000 average fire and smoke damage repair costs
Culina is actively solving both of these common challenges caused by cooking equipment simultaneously. Our technology provides homeowners with immediate, real-time insight into their energy consumption by aggregating data for all kitchen appliances connected to our Smart Plugs while also delivering the preventative intelligence necessary to reduce kitchen-related disasters.
Key Features and Benefits:
We designed our Culina Smart Plugs to work in tandem with an intuitive, user-friendly mobile application — allowing users to gain a much-needed technological upgrade to the most popular room in the house.
Easy Setup:
Culina Smart Plugs work with standard two and three-pronged appliances and cooking devices. Simply attach the Culina Smart Plug to the appliance's electrical, plug it into the wall, download the Culina app, connect, and configure.

Constantly Learning:
Powered by machine learning artificial intelligence, our Intelligent Culina Response System learns user habits every time someone uses an appliance connected to one of our Smart Plugs.
Multi-Threat Sensors:
Our state-of-the-art sensors detect a variety of potential threats to the kitchen — including sudden and unusual temperature fluctuations, poisonous gas and emissions, toxic smoke, and more. Homeowners receive alerts whenever unusual activity is in progress such as a stovetop being left on for too long or during an unusual time of day.
Remote Monitoring:
Users can monitor all information directly from an easy-to-navigate dashboard in real-time using the Culina App for iOS and Android. Users can check metrics such as fridge and freezer temperature, cook time, and usage data as it is being gathered.
Remote Appliance Control:
With the Culina App, users can control all connected appliances and devices. If our Smart Plug is attached to a crockpot, for example, a user can add the ingredients before they head to work, activate the crockpot remotely, and come home to a readymade meal waiting for them the moment they step through the front door.

Remote Shut-Off:
Not only does remote operation over appliances provide convenience, it also serves to prevent kitchen-related hazards. The Culina App includes auto shut-off capabilities allowing users to turn off appliances using their smartphone even when they're not at home. This is particularly useful in the event that users forget to turn off the oven or stove to prevent potential house fires.
Advanced Notifications:
In addition to notifying users if an appliance is left on by accident or if it detects a potential hazard, Culina also reminds users anytime regular maintenance is required.
Energy Consumption Data:
Users can also monitor energy consumption on a weekly basis right from the Culina App. By providing at-a-glance insight into whether energy use has gone up or down, users gain the ability to adjust their usage accordingly in order to conserve energy and ultimately save money in utility bills the long term.
Inter-operability:
Our cloud-based technology integrates with other popular platforms including Google's Nest and Lowe's Iris.
Cost-Saving Benefits:
Not only can users conserve money in energy consumption bills with Culina, but new insurance guidelines also provide significant discounts for homeowners who deploy smart technologies in their homes.
Pricing and revenue
Culina will initially monetize from hardware sales.
Our product will sell for $149 MSRP with approximately 40% profit margin. We will initially sell our product through popular e-commerce platforms and through our website — followed by brick-and-mortar outlets including Lowe's, Best Buy, Home Depot, and other major big box retailers.
Company Milestones:
With much of the heavy lifting already completed, Culina has laid the groundwork for rapid expansion going forward. Here's an overview of our accomplishments since first founding the company in 2013.
Consumer Validated:
Our first-generation product is market-ready and primed for commercial manufacturing. We have pre-sold 10,000 units, representing approximately $1,890,000 in pre-launch revenue. Our immediate customer base growing by the day and we have successfully proven that this is a product that consumers want and are enthusiastic about.
Investor-Backed:
We have secured a total of $5 million in funding from angel investors, founder capital, friends and family, and VCs.
Proprietary Technology:
We have applied for and have been granted a provisional patent for our Smart Plug technology.
Strategic Partnerships:
We are in the process of building relationships with notable industry leaders, influencers, and development teams in the home automation sector. We are also in advanced-stage partnership discussions with a number of major name insurance providers.
Press Mentions:
Culina has received coverage in many of today's most renowned tech and entrepreneurial publications, including The Wall Street Journal, The Huffington Post, TechCrunch, The Verge, WIRED, and Engadget, among others.
Manufacturing:
A US-based contract manufacturer has been secured and is ready to begin production with the capacity to produce around 50K units per month as we scale.

Future Development
Our initial focus on the consumer space with our launch product is just the first step in our long-term roadmap to growth. In order to capture a larger market share and continue scaling the company exponentially, we are planning on rolling out a B2B model in the future. This will provide Culina with new revenue streams and will offer a valuable, tech-driven solution for businesses.
Commercial Kitchens:
Commercial kitchens consume a huge amount of energy — roughly 2.5 times more per square foot than any other commercial space, according to the EPA.
The Foodservice Consultants Society International (FCSI) estimates commercial kitchen equipment is often only 50% efficient. The challenge with reducing energy consumption in commercial kitchens is that it's neither practical nor affordable to replace all kitchen equipment or redesign entire workspaces.
In an effort to reduce CO2 emissions, some governments are offering incentives to businesses that can cut back on their carbon footprint. In the UK, Enhanced Capital Allowances allow businesses to benefit from 100% tax relief on their qualifying capital expenditure on energy-saving equipment. This can provide a cash flow boost and an incentive to invest in energy-saving equipment which normally carries a price premium compared to less efficient alternatives.
Our 2nd generation product will represent a revenue-generating and energy-saving solution for commercial kitchens where equipment is frequently selected based on low capital cost with little regard to whole life-cycle cost and the resulting negative energy consumption.
Built on cloud computing, machine-to-machine communication, and information-gathering sensors, the Internet of Things market is rapidly making more and more commonplace devices “smarter.” Factor in the increasing prevalence of smartphones and tablets, and home automation and IoT products are now becoming much easier to use and significantly more affordable than they have ever been before.
What was once only reserved for the wealthy and tech-savvy, everyday consumers now have direct access to and can take advantage of a growing number of home automation devices. The evolution of the Internet of Things has enabled consumers to digitally connect and remotely control everything from their door locks to their thermostat to their garage opener and essentially everything else in between. Evidence of the enormous impact home automation tech has had in the consumer space can be seen in the enormous adoption of products like Nest and Amazon Echo.
The home automation market and Internet of Things (IoT) space is a thriving industry with growth expected to exceed $50 billion by 2020. This represents an estimated 300% increase from today's market of $12.5 billion. Around 8.4 billion connected devices will be installed globally by the end of 2017, representing a +31% increase in just one year. Around 63% of these devices will be used by consumers, with the remainder deployed by businesses.
Culina is perfectly positioned to capitalize on a major multi-billion dollar market opportunity to provide greater protection, actionable intelligence, lower energy consumption, and more cost savings to the millions of homes in the US.

Target Audience
We are directly targeting three specific target populations for our product:
Homeowners:
Homeowners are our end users and will benefit the most from our product. For homeowners, Culina represents safety, peace of mind, increased convenience, and an economically-wise investment that pays for itself over time.
Residential Property Managers:
Including apartment complexes and student housing owners. Culina offers increased owner ROI, occupant satisfaction, and significantly lower operational and maintenance costs.
Insurance Companies:
By reducing home fires caused by unattended cooking and the resulting billions of dollars in related insurance claims filed every year. Insurance companies can also leverage our technology to adjust homeowners insurance policy pricing.
Marketing Strategy
Culina has carefully developed a diverse marketing plan intended to keep our brand in the hearts and minds of our existing and prospective customers, enabling us to continue expanding our reach and grow our business. Between our massive social network followings and email database contacts, we regularly communicate directly with over 100,000 consumers.
SEO & Social:
We will drive traffic and conversions to our website using social media marketing via Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Instagram, Snapchat, YouTube, and others. We are also exploring SEO and SEM.
Content Marketing:
We consistently release marketing content through our blog that aims to educate our audience about the value that our product provides. Our content marketing efforts aim to influence and persuade readers without having to rely solely on conventional direct selling tactics.
Influencer Marketing:
We will launch an initiative to guest blog articles and features in IoT, home automation, and startup tech publications like TechCrunch, Wired, VentureBeat, and other outlets in our industry.

Competitive Landscape
Primary competitors for Culina include other companies that are currently operating in the home automation and Internet of Things space, such as Nest Labs, Amazon Echo, and Wallflower Labs.
Leading home automation company Nest introduced its first product, Nest Learning Thermostat, in 2011. The company was founded in 2010 by former Apple engineers Tony Fadell and Matt Rogers and is headquartered in Palo Alto, California. Nest was acquired by Google on January 14, 2014, by Google for $3.2 billion and still operates under its own brand identity.
Nest Labs designs programmable, self-learning, sensor-driven, Wi-Fi-enabled thermostats, smoke detectors, and other security systems.
The 3rd generation Nest Thermostat prices at $249; Nest Indoor and Outdoor Cams are $199; and their Smoke & CO Alarm retails for $99.
Key Weaknesses:
After Nest's acquisition, the company has underperformed in sales and fallen below the expectations that Google set for them when it purchased the startup.
Amazon Echo
Amazon Echo, also known as Alexa, is a voice command device powered by artificial intelligence and designed by mega online retailer Amazon.com. The smart home hub was initially released in November 2014.
Alexa is a voice-activated virtual assistant housed within the Echo smart speaker. Users simply say her name and then ask a question or give a command.
The Amazon Echo retails for $99 for Amazon Prime members and $170 for everyone else.
However, some users have noted the uneven sound quality and limited “skills” capabilities. Users can also only interact and communicate with Alexa in English and German.
Founded December 1, 2013, Wallflower Labs is a Charleston, MA-based startup that designs an internet-connected smart plug that works with any freestanding plug-in electric stove. The company's founder previously founded Yap — a speech recognition technology that was acquired by Amazon in 2011 to help develop Alexa. The startup has raised a total of $2.5 million from three rounds of equity funding to date, with the most recent funding reported at $1.5 million via a convertible note on August 30, 2016.
The smart plug sounds an alarm and alerts homeowners via smartphone when the stove is turned on, someone forgets to turn it off, when a cooking time expires, or the smoke alarm activates.
Because Wallflower Labs are still in the pre-launch phase, the company has not yet publicly released consumer pricing information.
Unlike Culina, which connects with all smart appliances and cooking devices in the kitchen, Wallflower Labs is solely focused on monitoring stove usage.
How Culina Measures Up:
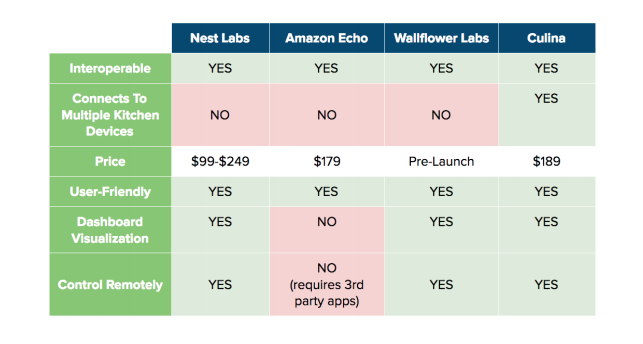
Differentiating Factors
Culina maintains a unique competitive advantage over other existing home automation and IoT products in several categories. Our biggest differentiators include:
Diverse Product Capabilities
Culina makes it possible to gain an across-the-board view from an entire network of interconnected devices. Whether they're connected to the refrigerator, gas or electric-powered stove, microwave, or dishwasher, our Smart Plugs can deliver insight into everything from smoke and gas detection, to temperature changes, and usage metrics — regardless of the brand and through a single, user-friendly app.
User-Friendly
Our technology is easy to use and doesn't require any technical-savvy. Setup and configuration are simple, users are able to be up and running out of the box in approximately 10 minutes, and software updates are deployed over the air.
Affordability
Culina is priced below our competitors' products while delivering superior functionality and value. This will be an essential factor in helping us continue to gain market share nationally.
Team Strength Our team is comprised of industry veterans who bring decades of experience to the table across industrial design, mobile tech, cloud-based technology, artificial intelligence, and more.
Our leadership team has a history of starting and leading companies to successful exits and has established valuable relationships with industry leaders along the way that will help us strategically position Culina as a market innovator in the days ahead.
Investment Opportunity
Culina is currently seeking a total of $15M in Series B equity financing to fuel the next stage of company growth — including manufacturing, pre-order fulfillment, ongoing development of our platform, and marketing efforts in order to continue expanding the Culina brand. Any remaining funds will be allocated as operating capital.
Why Invest in Culina? With Culina, investors have the opportunity to get in on the ground floor with a company that's positioned to grow into a leading innovator in the home automation and IoT space.
With Culina, we've tapped into something truly extraordinary that's being celebrated by both early adopters and investors alike. With 10,000 units pre-sold and $1.89M in pre-launch revenue , we've already successfully demonstrated validation in the consumer space. With over $5 million in funding secured across several financing rounds, we've already proven that investors believe in our company, our mission, and our ability to succeed.
We've also established a scalable business model and robust product pipeline that will prime us for widespread expansion in the days ahead. We're now seeking investors who share our passion and commitment to pushing the boundaries of what home automation can be and do through nextgen technology.
We're looking forward to working with you in accelerating Culina's growth to become a dominant player in the booming global home automation and IoT industry.

In Conclusion
We hope these business plan examples will get you started on the right path in getting your business idea into a full-on company. Keep in mind that these startup business plan examples are not a uniform guide for every business, and some information may vary. You may need a 5-year business plan template, or perhaps just some business plan examples for students. Make sure to remember this as you start writing your business plan, and comment below to let us know if these examples of business plans for startups were helpful in your startup journey.
For more helpful founder information: check out our podcast! The No BS version of startup life you've been looking for: Startup Therapy .
Afreen Zaheer
The examples were really helpful. It always makes such a difference actually seeing an example in action to help get a clearer picture of the overall objective.
Sarah Humphreys
The documents should be working now! Our apologies for the inconvenience.
Louisa Nicholson
Can't open the documents...
Upgrade to join the discussion.
What are business goals? Types and examples
As a manager or business leader , you may be wondering how to help lead your company in the right direction. Business goals help to set up a company for success. With long- and short-term goals, you can plan strategic actions and stay focused. By reading this guide, you'll learn about various types of business goals and objectives and how to set them. Here's what we'll cover:
- What are business goals?
- Types of business goals you may set as a manager
- How to set business goals as a manager
- Examples of business goals companies typically set
Adjusting business goals
What are business goals .
Business goals are broad targets a company wants to achieve over a set period. They shape business strategy and guide decision-making. They provide direction on how to align resources and efforts. Although many people use the terms "goals" and "objectives" interchangeably, they differ. In Singapore’s business landscape, clear business goals are important for planning and resource allocation. Objectives are measurable actions to get closer to your long-term business goals.
Types of business goals you may set as a manager
Explore the different business goals you can set for your team or company:
Short-term vs long-term business goals
Short-term business goals are measurable objectives you want the team to achieve in a few days, weeks, or months. They provide motivation and a sense of achievement as you reach each goal quickly. Here are some short-term business goals examples:
- Increase traffic on the company's blog by 20% by the end of the month.
- Hire five new sales representatives over the next three months.
- Create two social media posts per week.
A business's long-term goals are ambitious outcomes that aim further into the future, usually many months or years. Measuring the progress of these business goals may be harder. And they may take longer to achieve. But they provide shared direction and motivation for team members. A company may use a long-term goal as a vision or mission statement.
Here are some long-term business goal examples:
- Increase the company's market share to 35% in the next 10 years.
- Set up eight offices in the APAC region within 10 years.
- Increase employee retention to 85% in the next five years.
Long-term business goals may only provide a general course, not specific steps to take. Short-term goals provide step-by-step directions on how to reach your target. Many business leaders break down long-term business goals into several short-term goals. This can make them more achievable. Think of short-term business goals as building blocks towards larger goals.
It's important to balance short-term achievements with long-term vision to succeed. The company needs a long-term business goal to understand its destination. A long-term vision reminds team members of their end goal and motivates them to work towards it. Short-term goals help you understand what you need to do to achieve the long-term vision.
Financial goals
Financial or economic, goals are specific monetary targets a company wants to achieve. These goals can relate to the company's profit margin, cost reduction, investments, or economic stability. Financial business goals help you properly estimate and create budgets. With clear business objectives and measurable benchmarks, you can better manage the company's finances. Prioritising its spending can help the company achieve financial success.
Financial business goals are often measurable and focus on long-term success. These goals also vary based on which lifecycle stage the business is in. For example, a company may be in the start-up stage. Its economic goals may focus on getting funding from investors to buy equipment, rent office space, and hire employees. For mature organisations, financial business goals may centre on investing in new technologies and emerging markets.
In this digital age, you can use various financial planning tools and apps to simplify the financial goal-setting process. These tools can help with budgeting, investment management, and even tax preparation.
Non-financial goals
Examples of non-financial business goals include brand reputation, customer loyalty, employee training and development, and community involvement. These goals may help the company improve its image and stay in business for a long time. They also confirm that the company considers the well-being of its employees, customers, and the community. Companies that update employees' skills and relevant education may benefit from increased productivity. Improving brand perception can help attract and retain top-quality workers.
Businesses emphasise non-financial goals like corporate social responsibility (CSR) to enhance brand perception and attract top talent. Initiatives such as sponsoring charity events or promoting employee volunteerism contribute to community welfare, fostering a positive corporate image essential for sustained growth.
How to set business goals as a manager

The process of setting business goals may start with a review of past goals. It can also include an assessment of the current state of the organisation. It may involve working with a team and getting feedback and input. This helps you craft specific business goals and clear action plans.
SMART goals
SMART is a popular goal-setting framework. You can use it to define your business goals and ensure they're actionable. It also helps you set goals in an organised and structured way. SMART stands for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. SMART goals provide clear steps to take and help you stay on track while working towards your business objectives.
When setting a SMART goal, focus on a specific business goal. Use some kind of metric, such as a percentage, to measure progress and decide if you're on track to reach your business goals.
Ensure the goal is achievable. This helps motivate you even if the task is difficult. A relevant business goal helps you rank tasks and align them with the business plan. Finally, set a deadline to ensure timely progress on the goal. Here are some examples of SMART goals:
- Increase customer retention rate by 25% within one year.
- Increase revenue from the online store by 10% in the next six months.
- Acquire 10 new clients within the next three months.
One common mistake business leaders make is setting unrealistic goals. These are overly ambitious or lack a reasonable deadline. Be realistic about your team's abilities, the company's resources, and time constraints. Break down the large business goal into smaller, more manageable tasks to stay motivated.
Another error is neglecting to have a structured execution plan. Overcome this issue by assigning a project lead accountable for the tasks.
Alignment with vision and mission
It's essential to align business goals with the company's vision and mission. The company's vision reflects its purpose, so managers should tailor goals towards fulfilling it. To ensure alignment, reflect on the company's values and ask yourself how each goal is connected to the vision and mission. There is no clear direction when there's a misalignment between goals, vision, and mission. This can create confusion and a fall in motivation levels among employees.
A great example of a company that aligns its goals with its vision and mission is Amazon . The vision and mission of Amazon is "to be Earth's most customer-centric company, Earth's best employer, and Earth's safest place to work." Its goals and strategies start with the customer and work backwards.
Amazon is responsive to the customers' changing needs and wants, which has boosted customer satisfaction and increased loyalty. It's constantly innovating to improve user experience by giving personalised recommendations. Its huge selection of products, hassle-free return policy, and efficient customer service show its commitment to being a customer-centric company.
Examples of business goals companies typically set
Explore these examples of business goals :
Profit maximisation
A profit maximisation business goal is a company seeking to make the highest profit possible. This may mean extending the store's operating hours, expanding product offerings, or increasing employee productivity. It's important not to compromise on ethics when trying to increase profits. For example, reducing costs by using cheap, low-quality materials or overworking and underpaying employees is unethical.
Here are some steps you can take to set profit maximisation goals:
- Assess and reduce your operating costs.
- Adjust pricing.
- Increase customer lifetime value.
- Cross-sell products.
- Lower overhead costs.
- Motivate employees.
- Sustainable development
This business objective means using environmentally friendly and ethical practices. Companies may integrate sustainability into business models and strategies. For example, they may reduce waste production at factories. The PwC's Global Investor Survey 2023 found that most investors agree on the importance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues. 75% said that companies' management of sustainability-related matters is important in their investment decisions.
Singaporean companies such as Sembcorp Industries, Kawarin Enterprise, and Containers Printers are actively working to reduce carbon emissions and embrace a low-carbon future. Singapore businesses can enhance their competitiveness in today's dynamic market by pivoting towards green initiatives. This strategic shift opens new revenue streams and plays a crucial role in advancing a sustainable, low-carbon future for all.
You can explore areas such as energy efficiency or plastic usage to set a sustainable development goal. Set specific targets and devise ways to achieve them. For example, switching to LED lights makes the workplace more energy efficient.
Increased revenue
To increase company revenue, you can add products or services, new payment forms, or offer subscriptions. Innovation plays a key role in increasing revenue. It lets companies identify untapped markets, create new products and services, and apply technology.
Companies can also look at ways to improve online or in-person customer experience. Positive and consistent interactions can lead to brand loyalty; 86% of consumers would be willing to pay more for a better customer experience .
The Humble Food Company faced a 95% drop in revenue due to the COVID-19 pandemic. With a digitised point-of-sale (POS) solution, they optimised their workforce and costs. Specifically, their loyalty program using the POS cashback function led to an increase in sales.
Improved customer satisfaction
This represents how content and fulfilled customers are when they interact with products and services. You can measure customer satisfaction using metrics such as customer satisfaction score, customer effort score, net promoter score, and churn rate. When customers are happy, they tend to be loyal and may also serve as brand ambassadors. They're likely to share their positive experiences with others and drive word-of-mouth referrals. This can lead to an improvement in business performance.
To improve customer satisfaction, understand customer needs through market research. You can also gather feedback. Keep product quality consistently high by implementing strict quality control measures. Communicate effectively and regularly with customers. Let them know about new product launches and any updates or disruptions.
Business process optimisation

Process optimisation enhances efficiency by identifying bottlenecks and redundancies in the workflow. It helps you improve the quality of products and services. It can also boost profitability and promote innovation. All these factors contribute to achieving your business goals.
Explore process improvement methods and tool improvement-tools/s to optimise business operations. These include business process automation, business process management, Six Sigma, root cause analysis, and process diagrams. You can also use technology to automate repetitive tasks. This can free up employees' time for more important work. Employ data analytics to identify areas of improvement within business processes.
For example, Singapore Airports began using the Lean Six Sigma methodology to improve passenger flow through the airport. It applied this process optimisation to its terminal operations, security screening, and customer experience management. This improved wayfinding, reduced queue time and congestion, and enhanced maintenance. The company achieved its target. The average queue time at immigration was 10 minutes for departure and 15 minutes at arrival 90% of the time.
Assessing your business goals
Regularly assess the company's strategic goals to ensure you're on track to achieving them. You can use a scoreboard as a visual tool to keep track of your actions. Decide what data to track and design it in a way that's easy to understand at a glance. Update it often for motivation.
You can also gather feedback from team members to assess business goals. For example, they may tell you that the timeline wasn't realistic, as certain tasks took longer to complete. Learn from the issues employees raise and adjust strategies based on assessment outcomes.
Here are two ways to adjust your business goals:
Responding to market changes
Business goals should be dynamic instead of static, as the market is constantly changing. Set and adjust business goals according to the latest market trends. Seek customer feedback to get early signals of changing preferences or emerging needs. Engage with customers through surveys and social media platforms to gain insight into the evolving market.
For example, more customers may request sugar-free options. This may suggest that the broader market is moving towards health consciousness.
Use Agile methods in your product development process; they're flexible and allow you to deliver your product faster. Use Scrum, Kanban, or Lean frameworks and tools such as sprints, backlogs, and user stories to improve and speed up your product development process.
Companies like Yellow Pages effectively responded to digital and social media growth by digitising their entire business. They moved from being a print-based offering to providing an online directory for businesses. Another example would be the toy manufacturer Lego, which faced serious financial difficulties due to changing consumer preferences and low sales. It restructured its operations, streamlined its supply chains, and refocused its product lines. It also introduced the Lego Movie, which helped to boost its brand image and increase sales.
Continuous improvement
Continuous improvement means reviewing the company's performance and upgrading its products, processes, and strategies. It's about reaching a business goal. This can happen over time through incremental changes or, at once, through a breakthrough improvement.
You can foster a culture of continuous improvement. Do this by allowing employees to identify solutions and change their work areas within agreed guidelines. Create channels to get employee suggestions and feedback, and have a system to evaluate and implement their ideas.
Empower employees to take ownership, train them, and recognise and reward their efforts. You'll help create a supportive environment where they can experiment and grow. This can bring about positive changes in the organisation and contribute to reaching business goals.
Business goals are essential to set the direction of a company. They help you devise strategies and stay focused. Set various goals to ensure you're covering all aspects of the company's operations. For example, these can include cutting operational costs and increasing employee satisfaction.
Use the SMART framework to define your business goals and ensure they're achievable. Measure progress and use it to adjust the goals along the way. Also, market trends and employee and customer feedback should be considered.
Here are answers to common questions about business goals:
- What are some common challenges in setting and achieving business goals? One common challenge is that the goals lack clarity. When the team doesn't have a firm understanding of the goals, they're unable to plan specific actions to achieve them. This can cause confusion, frustration, and low motivation, which are common issues faced by businesses in Singapore striving for growth and efficiency. Another challenge is that the goals may be unrealistic in terms of the size of the accomplishment and the time period.
- How to set effective business goals as a manager? The first step is to assess the current state of the business through a framework, such as SWOT. After identifying the company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats, you can decide what needs to be improved. Get external and internal feedback to gain valuable insights. You can then use the SMART framework to set specific and time-bound goals. Finally, think about measuring progress and using existing metrics or creating new ones.
- How to communicate business goals to my colleagues? Share the business goals clearly and concisely. Avoid using jargon and buzzwords. Assign each team member with specific roles and responsibilities. Emphasise how the efforts of each individual will contribute to achieving the company's broader objectives. Use different internal channels to communicate the goals, such as newsletters, digital signage, and corporate screensavers. Repetitive messaging in various formats can help with message retention.
- How can I react to market changes as a manager? First, foster a culture of adaptability so that employees will embrace changes and be more resilient. Conduct market analysis regularly to identify emerging trends and customer preferences specific to Singapore. This can help you anticipate market changes and make informed decisions. Adopt an agile organisational structure to respond to the Singaporean market changes quickly. Encourage experimentation and innovation to develop agility and flexibility in the team. This can help the team to seize opportunities and lessen any negative impacts of market changes.
- How can I adjust my company's business goals? Monitor and measure the progress constantly and track KPIs to evaluate the results. Adjust the scope, timeline, or indicators of your goals depending on the progress and market changes. You may even add or remove some goals. Be open to new ideas and innovations and incorporate them into the goals. When modifying business goals, ensure they align with the company's mission and vision. Be transparent, communicate the changes to your team and stakeholders, and get their feedback and support.
- What are the benefits of setting long-term business objectives? Setting long-term business objectives gives you a clear target to work towards and motivates and inspires employees, especially during challenging times. They help you prioritise tasks, allocate resources effectively, measure progress over time, and celebrate achievements.
- Are there any tools or software to help with tracking business goals? Yes. Here's a list of tools you can use: -Asana -Trello -Engagedly -Friday -15Five -Jira -Goalscape -Lattice -PerformYard -Performance Pro
- How often should I review and adjust my business goals? It's advisable to review your business goals every quarter to make sure the goals are relevant to the Singaporean market. In Singapore, business conditions can change rapidly; therefore, reviewing your goals regularly also helps you track progress and determine if the goals are realistic.
- What strategies can I use to align my business goals with my company's mission? Clearly articulate the company's mission and values so that all team members know the purpose of the organisation and its principles. Refer to the overarching purpose and principles to guide the goal-setting process. Always ask "why" to ensure the goals reflect the company's mission and values.
Top search terms
Popular on jobstreet, explore related topics, subscribe to career advice.

- Get started
Top 10 Employee Development Plan Examples to Help Your Team Grow
Discover the top 10 employee development plan examples to help your team grow and drive your business to the heights of success.
.webp)
Investing in your employees’ transformation from average to exceptional is like building a valuable asset for your company. That's the reason an employee development plan is essential to create an environment where every member feels valued and motivated, resulting in working hard for your company's success.
Research reveals that 76% of employees prefer to stay in a company that frequently provides training for their growth. Considering the need, 47% of companies invest in career mentoring and coaching to boost employee retention. So, an employee development plan is a winning formula if you want to stay ahead of the curve. In this article, we will explore the top 10 employee development plan examples that will help you build a valuable workforce.
What is an Employee Development Plan?
The employee development plan is a roadmap designed to help employees grow professionally within the organization. These live documents, created collectively by employees and line managers, outline actionable steps, business goals, and milestones for growth.
This comprehensive growth plan encompasses various development programs, mentorships, and assignments that challenge individuals, push them to think outside the box, and enhance their capabilities. It also boosts employee critical thinking and fosters problem-solving skills.
The employee development plan benefits both employees and employers. Employees have clear goals and resources that will help them excel in their professional careers. Meanwhile, employers have a tangible way to support their team and equip them with the resources needed to reach their full potential and, in turn, work hard for the company's success.
Why is an Employee Development Plan Important?
According to the LinkedIn Global Talent Trends Report, 59% of employees listed professional development opportunities as a top area where organizations should invest in improving company culture. This shows that an employee development plan is more of a necessity to evolve and retain top talent in this competitive world.
Here are some more benefits of an employee career development plan:
1. Professional Development
A strong employee development plan helps employees in their professional careers, preventing learning stagnation that often comes during jobs. According to a Gallup report, 59% of millennials find growth opportunities at work highly critical, showing that skill development is more important for employees than ever.
2. Higher Employee Retention Rate
If employees feel that there's no growth opportunity in a job, they become demotivated and start looking for new challenges outside that fulfill their purpose. A survey reveals that lack of opportunities accounts for 37.1% of employee departures.
3. Enhanced Job Satisfaction
Employees who see a lot of growth potential in their jobs are more satisfied and committed to their company.
4. Increased Productivity
Employee development plans are not only for the benefit of employees but also for the organization's success. When equipped with top-level skills and knowledge, employees will perform better and be more productive.
5. Improving Business Performance
Providing development opportunities to your current employees is far better and cheaper than hiring new people every other day. Continuous learning and upskilling help build a strong team that actively participates in your company's success. Reports reveal that 66% of employers have seen higher ROI within one year of investing in upskilling their workforce.

Source: LinkedIn Talent Solutions
Top 10 Employee Development Plan Examples
A tailored employee development plan is crucial to meet the organization's unique needs. This approach addresses the various aspects of professional growth to create a skilled and valuable team. Here are the top 10 employee development plan examples to help your team grow:
1. Skill-based Employee Development Plan Examples
A skill-based development plan focuses on enhancing employees’ technical and soft skills. Examples of skill-based employee development plans include learning new software, improving communication skills, problem-solving skills, time management, and project management. These can be done through certification programs, hands-on training, or workshops led by experts.
With a detailed development plan for skill enhancement, employees feel a sense of satisfaction and confidence to meet new challenges. Furthermore, interacting with colleagues from different departments can help them exchange ideas, best practices, and insights, leading to a collaborative workforce.
2. Leadership Skills Development Plan
A key goal of a leadership development plan is to spot top and skilled talent and prepare them for future leadership roles within the organization. According to a Gartner survey, 60% of HR executives prioritize building leadership and management competencies for their company.
Employee development plan examples in leadership include team building, emotional intelligence, conflict resolution, and communication. These plans are implemented via seminars, workshops, coaching sessions, and mentorships under already skilled individuals. While training and knowledge are essential, hands-on practice helps grow your leadership skills.

Source: Gartner.
3. Goal-Based Employee Development Plan Examples
A goal-based development plan empowers employees to set and meet certain milestones, objectives, and key results (OKRs).
It begins with identifying long-term goals, which are then broken down into smaller ones. Then, small goals are turned into individual objectives and key results. Next, employees are given to-do lists and resources to reach their goals.
Goal-based employee development plan examples encompass task prioritization, multitasking, deadline management, and productivity. Conduct seminars or some one-on-one effective training programs to help your employees excel at these tasks. Above all, collaboration between managers and employees is vital for the success of a development plan.
4. Performance-Based Employee Development Plan Examples
A performance-based development plan focuses on improving employees' existing skills that directly influence their performance. To achieve this, incorporate workshops, seminars, professional conferences, certification programs, and mentorships to help your employees develop expertise.
Regular feedback for performance is imperative to helping employees enhance their skills. For instance, if a sales manager struggles with communication, a development strategy should be devised to close this gap. According to a survey, 83% of employees appreciate receiving feedback from their managers to improve their work performance.

Source: TRUELIST
5. Individual Employee Development Plan Examples (IDPs)
An Individual development plan is tailored to meet each employee’s needs, skills, and interests. It outlines a personalized roadmap for career advancement through courses, specific training programs, mentorship opportunities, and e-learning development services . Individual development plans enhance employee retention, engagement, and business performance and empower them to work confidently.
6. Ad Hoc Employee Development Plan Examples
An ad hoc growth plan is suitable for employees who want to learn unique skills and pursue degrees or certifications to increase their competitive advantage in career roles. This development plan is tailored to each employee's needs, improving job performance, satisfaction, and better career prospects. For example, an employee aspiring to take a degree in leadership while continuing his job can achieve this only through an ad hoc development plan.
By offering such plans, companies showcase their interest in their employees' growth, gaining long-term benefits in the form of employee retention and commitment to the company.
7. Cross-Functional Employee Development Plan Examples
A cross-functional employee development plan brings people from different departments together, allowing them to broaden their perspectives and experience. It's especially helpful to potential executives, as it gives them insights about what skills they need for career advancement. Creating this development plan involves coordinating with colleagues, rotations in different departments, organizing projects, and brainstorming sessions.
To evaluate what employees have learned, utilize assessment tools and take quizzes to better understand their performance. Assessing performance is not difficult with Coursebox.ai . You can use an AI quiz generator to create quizzes, and even your learners can get instant feedback based on your set criteria.
8. Objective-Based Employee Development Plan Examples
An objective-based development plan is based on the specific goals of the team and is aligned with the company's objectives. The team manager understands job goals or objectives and what employees are expected to do. Then, after identifying areas that need improvement, the manager creates a development plan for employees. By doing so, employees feel more motivated and empowered.
9. Succession Development Plan
A succession growth plan involves helping employees advance to higher positions within the organization. This development strategy is about identifying skilled members for future critical roles. To achieve this, take a holistic view of your organization's goals, ensuring you have talent available in the coming months or years.
According to a SHRM report , only 21% of HR professionals have a formal succession plan, while 24% have an informal one. Neglecting proper succession plans can damage the company's reputation and instill confusion and uncertainty among employees. A global survey showed that 53% of companies didn't have CEO succession plans, leading to significant disruption.

Source: HBR
10. Skill Gap-Focused Employee Development Plan Examples
According to the McKinsey Report, 87% of companies know they have a skill gap or will have one in the coming years. That's why companies must work on filling these gaps through tailored skill gap-focused development plans.
It involves identifying areas your organization lacks and skills needed to meet future challenges. After that, create a plan to upskill your team to improve their performance. To make it successful, educate employees on the purpose of the training and how it's going to help them in the future.

Source: Mckinsey
4-Step Employee Development Plan Framework
Creating a practical employee development plan needs a lot of planning. The key to it is setting SMART learning objectives (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, time-bound) that align with the company's goals. Here is a four-step framework to help your employees:
Step 1: Analyze Goals and Conduct a Thorough Self-assessment
The first, and most crucial, step is to analyze the goals and objectives of the company. Then, identify which skills are required in the future. Next comes the main part, where you assess employees’ skills, determine which areas need improvement, and start working on staff development ideas.
Step 2: Collaborate on Goal-setting
Collaboration between managers and employees is the key to creating a proper development plan. In fact, working on a goal setting collectively gets them on the same page. Employees feel a sense of ownership and are motivated to fulfill the goals they help in setting. On the other hand, managers get to know what it takes to achieve goals and support employees in reaching those goals.
Step 3: Identify Development Activities
Once the goals are set, the next step is identifying the necessary resources to help employees reach them. This may include certifications, diplomas, or degrees to help them achieve higher positions.
You can also consider connecting them to a senior mentor for one-on-one training or enrolling them in mentorship programs. Apart from these, consider online workshops, webinars, and online e-learning courses to turn their goals into reality.
Step 4: Monitor Progress and Review
When employees have started learning, the next step is to monitor their progress alongside. The best way is to utilize learning management systems like Coursebox to create, manage, and track online learning and improvement. You can also review where they stand through assessments and automatically issue achievement certificates.
Conclusion
Thus, a solid employee development plan is a win-win for both employees and managers. Managers get a highly skilled team, while employees excel in their career goals. But that's only possible when a company provides suitable resources, such as an environment, and learning platforms like Coursebox AI , to help its employees reach their full potential.
Coursebox AI is an all-in-one learning platform that can transform your team's learning experience into a super smooth and enjoyable one. You also don't need to worry about assessment, as it helps create quizzes and questionnaires instantly without any hassle.
Your company's future is in your hands; let Coursebox be your ally!
How to write a development plan for employees?
To write an employee development plan, first, you need to identify your organization's development plans or goals. After this, assess employees’ skills and check what’s lacking and needs attention. This leads to creating an individual development plan aligned with employees and the company's mutual interests.
What are your development plan examples?
Development plan of any company varies based on their preference and goals. At Coursebox.ai, our development plan examples include providing companies with e-learning development services, course creation using AI, quizzes and video generation and AI assessment.
What should we write in our development plan?
In a personal development plan, only you are responsible for your decisions, so accountability from your end is important to reaching your goals. First thing first—set your goals and prioritize them based on your needs. Set deadlines for yourself to reach them, keeping in mind all the distractions or threats you encounter along the way. Keep learning and improving your skills side by side and track your progress.
CMO at Coursebox AI
Latest articles

What is Skill-Based Training & How to Implement it
.webp)
What Are Learning Paths? (Examples Included)

Market Research Plan

In 1970, food and drink sales of the US restaurant industry reached only 42.8 billion US dollars, which is way behind the 745.61 billion US dollar sales of 2015. According to the statistic posted in statista, this number should grow in the next few years. In fact, the website reported that from the 2015’s over 14 million employees of the restaurant industry, it should increase up to 16 million in 2026. However, as a result of this growth, there will be possibilities that the market will be saturated and more competitive. Thus, as a business owner, you will need to gear up and gain an edge to stand out in the market. By conducting market research for a restaurant, you can prepare your business to become more competitive and strategic, which will ensure its success.
What Do You Need to Know About Market Research?
Market research is an essential component of a business plan which aims to get information concerning the target market of a business. Through this study, you will determine the chances of a proposed service or new product to survive in the market. As part of market research, you need to develop a research plan.
What is Market Research Plan?
In general, market research plan is the foundation of a detailed research proposal . This document contains the initial thoughts about the research project that you are planning to take place logically and concisely, which is a crucial content of market research. Simply put, by obtaining a market research plan, you can thoroughly examine how your product or service will proceed in a specific domain.
2+ Market Research Plan Examples
Conducting market research will give significant benefits to your business. However, to materialize it, you may need to ensure that you build your market research plan correctly. Below is a list of the market research plan samples and templates that you can use as a guide.
1. Market Research Plan Template

- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
Size: 19 KB
2. Sample Market Research Plan Example
Size: 68 KB
3. Basic Market Research Plan Example
Size: 151 KB
4. Market Research Business Plan Example

Size: 600 KB
How to Develop a Strong Market Research Project Plan?
Now that you know how a marketing research plan should look, make a secure market research plan by following the steps below:
1. Set Goals and Objectives
What do you want to attain with your research? Your goals and objectives should answer that question. You can start by forming a general marketing goal . You will, then, make it more specific. This goal will help you focus and direct the entire research process to make the best data-driven marketing decisions. To determine the most critical issue, you may conduct qualitative research . This research methodology ensures that you address the issue that really requires an urgent solution.
2. Determine Your Target Respondents and Appropriate Distribution Method
In this step, you will identify the right people to get the information that you need to create the right decision for your marketing goals. After that, list down the best possible ways for the data gathering. For example, your target market is veterans. You may want to use more appropriate channels such as direct mails, phone, or personal interview. Once you have chosen the most appropriate data collection method, create an outline that will allow your team to get the most relevant information from your target market or audience.
4. Brainstorm for the Right Questions
In deciding the right questions for your marketing research, it is crucial to keep your study goals in mind. Only include items that are relevant to the study to come up with the best business decisions. Asking the wrong questions may lead to inadequate conclusions. Data-driven solutions mostly obtained through quantitative research questions. You can still use qualitative research questions but make it minimal to avoid making the respondents bored and held up, which can lead to survey abandonment. As much as possible, make your survey short and answerable in less than 5 minutes. Otherwise, you may want to find an alternative option in getting the desired data. Also, it would help if you will consider other factors in building the right questions. Refrain from asking sensitive, personal, and offensive questions. To do it, research your target audience.
5. Analyze the Data
Start this step by cleaning your survey data. To do it, filter out any low-quality responses. These items can affect your decision-making negatively. Basing on the set standards, remove the outlier responses. To do that, determine if the respondents answered in the desired format. If not, especially if it has become a trend, disqualify the question or conduct another data-gathering or investigation for this question. In this process, you will also find out if the answers of the participants are contributing to your research goals. At the end of this stage, you will, then, share your findings. To effectively show your results, you can use data visualization methods such as charts, graphs, and infographics.
6. Create a Data-Driven Marketing Decisions
Now that you have the necessary market research data, you can come up with a data-driven decision. Whether you are running a pharmaceutical firm or a corporal business such as Coca Cola, you can develop a new marketing campaign and other relevant business actions without unnecessary worries since you have directly reached out to your target market.
In a market that is becoming more competitive, creating a market research plan for a new product of your business can give you an advantage and an edge over your opponents. This type of method will also save your time, effort, and money because it allows you to determine the proper actions that you can take towards the corporate goals in terms of marketing and other relevant sectors.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.
Once only the responsibility of sustainability managers, ESG performance and sustainability are today considered key areas of strategic focus for organizations, often reflected in Sustainability Action Plans developed by organizations.
Looming investor pressure, consumer awareness and the understanding that sustainability is an important tenet in risk management and corporate governance has seen responsibilities shift and awareness ripple across both departments and management levels. The tidal shift has been embraced by organizations as they champion decarbonization. It presents ever-growing opportunities for innovation and increased investments towards green technologies, which ultimately accelerate sustainability.
Much like operational plans are developed to future-proof an organization’s success, so too are Sustainability Action Plans in helping to achieve a low-carbon business fit for the future. In this article, we lay out practical guidance on how to create a Sustainability Action Plan along with recommended inclusions and structure. We also provide a free Sustainability Action Plan template for download to support your sustainability and environmental, social and governance (ESG) goals.
What is a Sustainability Action Plan?
A Sustainability Action Plan is created by an organization to detail how it will achieve sustainability goals over time, particularly if ambitious targets have been set, such as achieving net zero by a specific time frame. It is usually a static document that details a two to five-year timeline of objectives, although this period is at the organization’s discretion.
Its purpose is to embed ESG and sustainability across an organization, within all business operations. The path to a Sustainability Action Plan typically starts with a vision at an executive level, with the Sustainability Action Plan serving as the detailed strategy of how the vision will be achieved.
To complement the Sustainability Action Plan, organizations often release annual Sustainability Reports that detail the organization’s progress against the objectives. Together, Sustainability Action Plans and Sustainability Reports function as an important communications tool for organizations to illustrate their sustainability journey to a wide audience of stakeholders.
Sustainability Action Plans are not mandatory, rather, they are an initiative of an organization who wishes to make a positive impact on their sustainability performance.
In addition to planning and internal reporting, many organizations disclose their sustainability performance via various ESG reporting frameworks. In some instances, the data collected for the production of a Sustainability Action Plan can be used to support the reporting requirements of frameworks such as GRI, GRESB and SASB.
And vice-versa, organizations reporting detailed information to ESG reporting frameworks may export some of those responses to their Sustainability Action Plans to illustrate how they are performing against their goals.
This task is made easy with Envizi’s ESG Reporting Frameworks module which allows organizations to collate responses for both external and internal reporting frameworks in one place. In addition to collating responses, the module includes functionality to extract responses for use in documentation such as a Sustainability Action Plan.
Who needs a Sustainability Action Plan?
Organizations of all sizes can make steps towards making their business operations more sustainable and positively contributing to their community and environment. Smaller organizations should consider the resource requirements of developing a comprehensive Sustainability Action Plan and achieving those objectives over time.
For larger organizations, a comprehensive Sustainability Action Plan is ideal for outlining the long-term vision and plans to satisfy investor requirements, to change consumer attitudes and to take advantage of opportunities. This is especially the case once pledges have been made, as the next stage in the process is to work out exactly how the organization will achieve those pledges.
How to create a Sustainability Action Plan
A Sustainability Action Plan requires dedicated commitment across all levels of an organization, and it can be transformational as it requires a top-down approach with cultural change, realignment of values and leadership endorsement. As a result, there are several considerations to take into account when developing a plan.
The consultation process and stakeholder engagement
Much like corporate annual reports require the input of an executive team, the Board, finance department and other internal departments, so too does the process of creating a Sustainability Action Plan.
It requires extensive consultation across the executive and leadership levels, committees and even the community (depending on the sector and type of organization) to establish targets and accountabilities. At the center of the consultation process is an organization’s Sustainability Manager. In many organizations, the person in this role is responsible for developing both the business cases and doing the work to support the implementation and management of programs within organizations to deliver on their objectives.
Whether the organization has a Sustainability Manager or not, they may also choose to use the services of a sustainability consulting firm to guide them on the process and support their objectives.
Other examples of stakeholders involved in the consultation and implementation process may include:
| Committees or subcommittees established | Environmental Stewardship Committee | Provides viewpoints from various parts of the organization and sometimes the wider community in relation to how certain initiatives are likely to impact or benefit the group. |
| Finance | Chief Financial Officer | Provides financial forecasting and advises on necessary budget to implement the requires actions to achieve objectives in the Sustainability Action Plan. They play a key role in advocating for the organization’s sustainable financial success and understanding the cost-benefit of implementing energy-saving measures. |
| Operations | Facilities Manager | Advises on shared services and utilities such as telecommunications, water and electricity and holds the relationship with these suppliers should any changes need to be made. |
| Procurement | Procurement Operations Manager | Manages an organization’s supply chain and can therefore advise on partners and practices and establish SLAs in line with the Sustainability Action Plan. Ensures suppliers of goods and services to the organization reflect any objectives of the organization’s sustainability commitment. |
| Risk and compliance | Chief Legal and Risk Officer | Assists with due diligence process for suppliers and advises on reputational and regulatory risks when progressing through the Sustainability Action Plan. |
| Energy and utilities | Energy Manager | Advises on the current state of energy efficiency for the organization and other conservation and energy efficiency measures the organization can take to achieve its objectives. |
Scroll to view full table
Establishing benchmarks
The Sustainability Action Plan will involve setting outcomes, actions and targets. Therefore it’s important that an organization understands its current ESG performance with accurate data to inform future benchmarks. Using an ESG and sustainability reporting software platform such as Envizi can simplify emissions calculations and automate the collection of energy consumption data, which will be required when reporting on the progress of the plan.
What is included in a Sustainability Action Plan?
Inclusions in a Sustainability Action Plan can vary depending on the type of organization, its size, and the sector it operates in. For example, a start-up or an independent education center such as a school may choose to focus on smaller initiatives to start implementing changes at the business.
Examples of achievable initiatives at this level could include:
- Using water tanks
- Gardening, such as a vegetable garden
- Recycling system
- Turning off lights when not in use
- Using energy-saving bulbs
- Implementing a printing policy
Larger organizations with ambitious goals and extensive resources could include initiatives such as:
Councils and municipalities
- Reducing Scope 3 emissions from suppliers
- Implementing a mass tree planting scheme
- Providing a community shuttle bus
- Introducing cycle routes
- Installing LED lighting
Property developers and organizations
- Optimizing HVAC equipment performance
- Using local labor and materials
- Incorporating water and waste reuse strategies
- Ensuring sustainability is part of client consultation and scoping
- Incentivizing staff remote-work opportunities
Manufacturing
- Reducing GHG emissions in the upstream supply chain
- Reducing power usage in data centers
- Investing in renewable energy sources
- Electrifying the transport fleet
- Upgrading energy-intensive equipment
Commercial real estate
- Developing a demand-side energy management strategy
- Minimizing waste
- Implementing renewable energy
- Improving GRESB score
- Implementing end-of-trip facilities
Structure of a Sustainability Action Plan
Whilst the structure, inclusions and scale of a Sustainability Action Plan are at the organization’s discretion and stem from the initial consultation process, there are a few inclusions we recommend to ensure a Sustainability Action Plan which reflects an organization’s commitment to sustainability:
Sustainability values
Background on the organization’s view of sustainability and its core values which motivate the development of the Sustainability Action Plan.
Executive message
Endorsement at the C-Level usually from the CEO, outlining the organization’s commitment to sustainability.
Mandatory frameworks
If the organization operates within a sector which legislates reporting to a framework, this section would outline the requirements of that legislation or policy to provide stakeholders with context around the motivations for the Sustainability Action Plan.
Consultation process
Outlines how stakeholders participated in the development of the Sustainability Action Plan (such as workshops and forums), and which stakeholders were involved.
Methodology and review process
Outlines how the targets will be measured and progress monitored, which could include how regularly a Steering Committee or other key stakeholders will be updated. A Sustainability Report could be one of the vehicles for communicating this progress.
These are broad outcomes that steer the detailed actions and targets in the Sustainability Action Plan. Examples of outcomes could be “Decrease energy usage by 2025” or “Educate stakeholders.”
- Secondary outcomes These could be complementary outcomes which help to group actions within the broader outcome. Examples of secondary outcomes could be “Transport” or “Energy and emissions.”
- Action The tangible actions that will be undertaken to achieve a specific target within that secondary outcome, and broader outcome. Examples of actions could be “Replace inefficient HVAC systems” or “Develop recycling policy.”
- Target Specific KPIs placed against the actions to ensure progress is made. Examples of targets could be “100% of older HVAC systems replaced” or “75% increase in electronics diverted to e-waste programs.”
- Responsibility Assigning champions to action the targets could include listing departments or position titles.
- Timeframe Assigning specific months or quarterly timeframes ensures that targets can be realistically achieved.
The structure of a Sustainability Action Plan varies widely, and care should be taken to ensure that the inclusions of the plan, including the targets, are achievable for the organization.
Download template
Build your sustainability data foundation, streamline reporting and accelerate decarbonization with the IBM Envizi ESG Suite

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Economic Business Objective: Also called financial objectives, economic objectives relate to the financial health and growth of the company. These objectives can involve profits, revenue, costs, cash flow, sustainable growth, debt management, and investments. Example: Reduce spending on paid advertisements by 20 percent.
Social objectives. For example, a sample of business goals and objectives for a business plan for a bakery could be: To increase its annual revenue by 20% in the next year. To reduce its production costs by 10% in the next six months. To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
8. Critical success factors: Clarify the high-level goals you need to achieve in order to achieve your strategic goals. 9. Strategic management: Execute against your strategic plan in order to achieve your company goals. 10. Business goals: Set predetermined targets to achieve in a set period of time. 11.
Related: 26 of the Best Survey Software. 3. Organize. Noticing patterns in the information you brainstorm and gather from employees can help you write meaningful business objectives. For example, if many of your ideas relate to revenue, it might reveal that you prioritize profits.
Driving Continuous Improvement: Promoting ongoing evaluation and refinement of strategies and processes. Aligning Efforts: Ensuring that all organizational efforts are aligned with long-term goals, leading to cohesive and efficient operations. Discover 56 strategic objectives examples to inspire your company's strategy.
Business objective examples. Now you have a basic understanding of how to set business objectives for your business plan. Here are four examples of business objectives in different categories. Example #1: Customer service business objective. Our business will reduce customer complaints by 25% this year. To accomplish this goal, we will hire ...
Business objectives vs. goals. Where a business objective is an actionable step taken to make improvements toward growth, a business goal is the specific high-level growth an objective helps a company reach. Business objectives are often used interchangeably with business goals, but an objective is in service of a goal.
Strategic goals vs. business goals. Business goals are predetermined targets that organizations plan to achieve in a specific amount of time. Technically, strategic goals—along with BHAGs, OKRs, and KPIs—are a type of business goal. Read: OKR vs. KPI: Which goal-setting framework is better? 65 example strategic metrics and goals
Growth objectives aim to expand the business and increase market share. They often involve expanding into new markets, developing new products or services, or increasing production capacity. For example, a growth objective could be to increase the company's presence in the European market by opening new retail locations in major cities across ...
Many professionals use the terms business goal and business objective interchangeably. Generally, a business goal is a broad, long-term outcome an organization works toward, while a business objective is a specific and measurable task, project, or initiative.. Think of business objectives as the steps an organization takes toward their broader, long-term goals.
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
To improve brand and reputation. To grow production size to meet demand. 4. Social objectives. Social business objectives are created to help or give back to society in some way. Businesses often set social goals: To ensure better quality products for customers.
Customer satisfaction. Your business is nothing without your customers. Customer satisfaction objectives help you improve the customer experience, build loyalty with your audience, and improve your brand reputation. Example: Achieve a customer satisfaction score of 80% by improving support services and collecting regular customer feedback.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Focus Area: Financial Growth. Grow gross revenue to $2m by 31st Dec 2022. Increase net margin by 15% by 31st Jul 2023. Reduce net costs by $900k by 1st Nov 2022. Deliver 3 consecutive periods of monthly recurring revenue (MRR) of $50k by 1st Jul 2023. Build $1m of reserve working capital by 31st Dec 2022. And here's an example of what not to ...
Your new company's business plan is a crucial part of your success, as it helps you set up your business and secure the necessary funding. A major part of this plan is your objectives or the outcomes you aim to reach. If you're unsure where to start, this list of business objective examples can help. In this guide, you'll learn:
Some of the reasons why setting objectives is important for businesses include: encouraging growth. motivating and focusing staff. encouraging collaboration and teamwork. supporting relationships between employees. strengthening certain areas of the business. providing structure. increasing the company's market share.
Focus on the basics first: Identify your industry: Retail, wholesale, service, manufacturing, etc. Clearly define your type of business. Identify your customer. You cannot market and sell to ...
To plan your plan, you'll first need to decide what your goals and objectives in business are. As part of that, you'll assess the business you've chosen to start, or are already running, to see ...
Table of Contents. A business plan is a document that you create that outlines your company's objectives and how you plan to meet those objectives. Every business plan has key sections such as ...
5. Marketing plan. It's always a good idea to develop a marketing plan before you launch your business. Your marketing plan shows how you'll get the word out about your business, and it's an essential component of your business plan as well. The Paw Print Post focuses on four Ps: price, product, promotion, and place.
For example, one month, you may ask employees to present a training session and help them see who communicates well in a teaching setting. Another month, you may ask employees to look for ways to increase productivity, which will help you find those with analytical minds. Goal #9. Improve Customer Engagement.
The key is to have an effective marketing plan going in, setting realistic but challenging goals, and identifying the baby steps needed to get you there. The best long-term business goals include: Increasing sales. Building brand recognition. Creating a stellar reputation. Growing social media following.
Short-term objectives: Increase customer base by 50% in the next 12 months; Action plans: Launch a targeted marketing campaign, develop new product features, and expand the sales team; This example demonstrates how a strategic plan provides a clear roadmap for achieving business objectives. Specific examples of strategic plans for various sectors
Key Takeaways from Business Plan Examples. Drawing from various business plan examples, here are the essential elements that contribute to a successful business plan: Executive Summary: Offers a concise overview of the business, including its mission, vision, and objectives. It should capture the reader's interest and provide a snapshot of ...
Our Complete Business Planning Guide includes concrete business plan examples and samples to help you get started. ... With this round of funding, our objective is to ramp up hardware manufacturing, improve software UX and UI, expand our sales and marketing efforts, and fulfill pre-orders in time for the 2017 holiday season. ...
Examples of business goals companies typically set Explore these examples of business goals: Profit maximisation . A profit maximisation business goal is a company seeking to make the highest profit possible. This may mean extending the store's operating hours, expanding product offerings, or increasing employee productivity.
These live documents, created collectively by employees and line managers, outline actionable steps, business goals, and milestones for growth. ... Objective-Based Employee Development Plan Examples An objective-based development plan is based on the specific goals of the team and is aligned with the company's objectives. The team manager ...
2+ Market Research Plan Examples. Conducting market research will give significant benefits to your business. However, to materialize it, you may need to ensure that you build your market research plan correctly. Below is a list of the market research plan samples and templates that you can use as a guide. 1. Market Research Plan Template
Smaller organizations should consider the resource requirements of developing a comprehensive Sustainability Action Plan and achieving those objectives over time. ... education center such as a school may choose to focus on smaller initiatives to start implementing changes at the business. Examples of achievable initiatives at this level could ...