
13 Different Types of Hypothesis

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
There are 13 different types of hypothesis. These include simple, complex, null, alternative, composite, directional, non-directional, logical, empirical, statistical, associative, exact, and inexact.
A hypothesis can be categorized into one or more of these types. However, some are mutually exclusive and opposites. Simple and complex hypotheses are mutually exclusive, as are direction and non-direction, and null and alternative hypotheses.
Below I explain each hypothesis in simple terms for absolute beginners. These definitions may be too simple for some, but they’re designed to be clear introductions to the terms to help people wrap their heads around the concepts early on in their education about research methods .
Types of Hypothesis
Before you Proceed: Dependent vs Independent Variables
A research study and its hypotheses generally examine the relationships between independent and dependent variables – so you need to know these two concepts:
- The independent variable is the variable that is causing a change.
- The dependent variable is the variable the is affected by the change. This is the variable being tested.
Read my full article on dependent vs independent variables for more examples.
Example: Eating carrots (independent variable) improves eyesight (dependent variable).
1. Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a hypothesis that predicts a correlation between two test variables: an independent and a dependent variable.
This is the easiest and most straightforward type of hypothesis. You simply need to state an expected correlation between the dependant variable and the independent variable.
You do not need to predict causation (see: directional hypothesis). All you would need to do is prove that the two variables are linked.
Simple Hypothesis Examples
2. complex hypothesis.
A complex hypothesis is a hypothesis that contains multiple variables, making the hypothesis more specific but also harder to prove.
You can have multiple independent and dependant variables in this hypothesis.
Complex Hypothesis Example
In the above example, we have multiple independent and dependent variables:
- Independent variables: Age and weight.
- Dependent variables: diabetes and heart disease.
Because there are multiple variables, this study is a lot more complex than a simple hypothesis. It quickly gets much more difficult to prove these hypotheses. This is why undergraduate and first-time researchers are usually encouraged to use simple hypotheses.
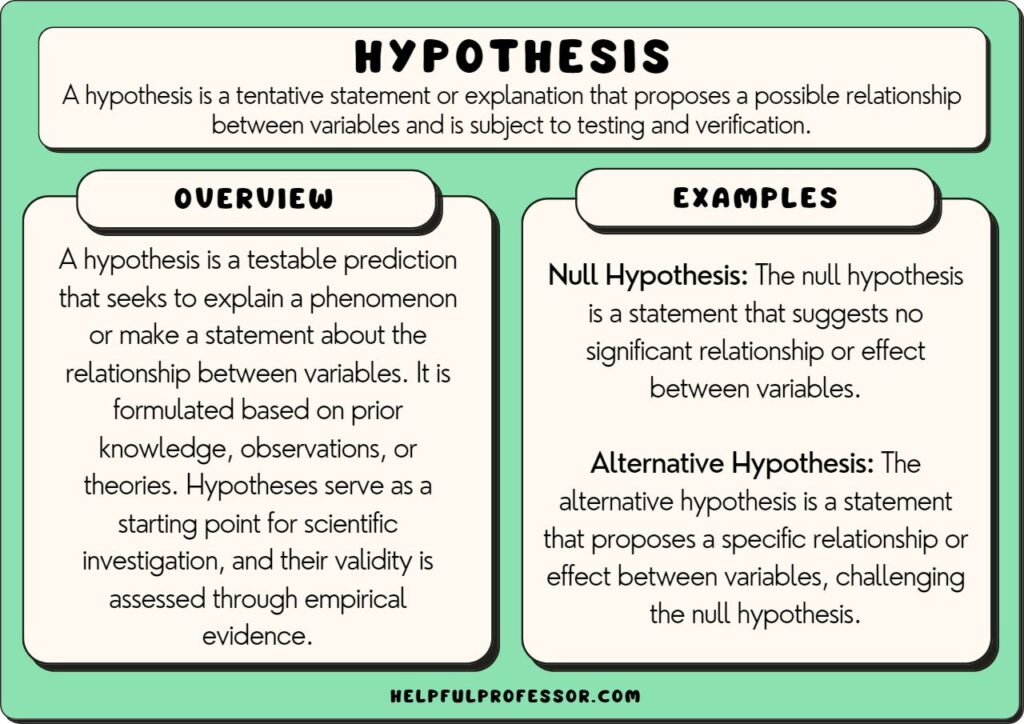
3. Null Hypothesis
A null hypothesis will predict that there will be no significant relationship between the two test variables.
For example, you can say that “The study will show that there is no correlation between marriage and happiness.”
A good way to think about a null hypothesis is to think of it in the same way as “innocent until proven guilty”[1]. Unless you can come up with evidence otherwise, your null hypothesis will stand.
A null hypothesis may also highlight that a correlation will be inconclusive . This means that you can predict that the study will not be able to confirm your results one way or the other. For example, you can say “It is predicted that the study will be unable to confirm a correlation between the two variables due to foreseeable interference by a third variable .”
Beware that an inconclusive null hypothesis may be questioned by your teacher. Why would you conduct a test that you predict will not provide a clear result? Perhaps you should take a closer look at your methodology and re-examine it. Nevertheless, inconclusive null hypotheses can sometimes have merit.
Null Hypothesis Examples
4. alternative hypothesis.
An alternative hypothesis is a hypothesis that is anything other than the null hypothesis. It will disprove the null hypothesis.
We use the symbol H A or H 1 to denote an alternative hypothesis.
The null and alternative hypotheses are usually used together. We will say the null hypothesis is the case where a relationship between two variables is non-existent. The alternative hypothesis is the case where there is a relationship between those two variables.
The following statement is always true: H 0 ≠ H A .
Let’s take the example of the hypothesis: “Does eating oatmeal before an exam impact test scores?”
We can have two hypotheses here:
- Null hypothesis (H 0 ): “Eating oatmeal before an exam does not impact test scores.”
- Alternative hypothesis (H A ): “Eating oatmeal before an exam does impact test scores.”
For the alternative hypothesis to be true, all we have to do is disprove the null hypothesis for the alternative hypothesis to be true. We do not need an exact prediction of how much oatmeal will impact the test scores or even if the impact is positive or negative. So long as the null hypothesis is proven to be false, then the alternative hypothesis is proven to be true.
5. Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis is a hypothesis that does not predict the exact parameters, distribution, or range of the dependent variable.
Often, we would predict an exact outcome. For example: “23 year old men are on average 189cm tall.” Here, we are giving an exact parameter. So, the hypothesis is not composite.
But, often, we cannot exactly hypothesize something. We assume that something will happen, but we’re not exactly sure what. In these cases, we might say: “23 year old men are not on average 189cm tall.”
We haven’t set a distribution range or exact parameters of the average height of 23 year old men. So, we’ve introduced a composite hypothesis as opposed to an exact hypothesis.
Generally, an alternative hypothesis (discussed above) is composite because it is defined as anything except the null hypothesis. This ‘anything except’ does not define parameters or distribution, and therefore it’s an example of a composite hypothesis.
6. Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis makes a prediction about the positivity or negativity of the effect of an intervention prior to the test being conducted.
Instead of being agnostic about whether the effect will be positive or negative, it nominates the effect’s directionality.
We often call this a one-tailed hypothesis (in contrast to a two-tailed or non-directional hypothesis) because, looking at a distribution graph, we’re hypothesizing that the results will lean toward one particular tail on the graph – either the positive or negative.
Directional Hypothesis Examples
7. non-directional hypothesis.
A non-directional hypothesis does not specify the predicted direction (e.g. positivity or negativity) of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable.
These hypotheses predict an effect, but stop short of saying what that effect will be.
A non-directional hypothesis is similar to composite and alternative hypotheses. All three types of hypothesis tend to make predictions without defining a direction. In a composite hypothesis, a specific prediction is not made (although a general direction may be indicated, so the overlap is not complete). For an alternative hypothesis, you often predict that the even will be anything but the null hypothesis, which means it could be more or less than H 0 (or in other words, non-directional).
Let’s turn the above directional hypotheses into non-directional hypotheses.
Non-Directional Hypothesis Examples
8. logical hypothesis.
A logical hypothesis is a hypothesis that cannot be tested, but has some logical basis underpinning our assumptions.
These are most commonly used in philosophy because philosophical questions are often untestable and therefore we must rely on our logic to formulate logical theories.
Usually, we would want to turn a logical hypothesis into an empirical one through testing if we got the chance. Unfortunately, we don’t always have this opportunity because the test is too complex, expensive, or simply unrealistic.
Here are some examples:
- Before the 1980s, it was hypothesized that the Titanic came to its resting place at 41° N and 49° W, based on the time the ship sank and the ship’s presumed path across the Atlantic Ocean. However, due to the depth of the ocean, it was impossible to test. Thus, the hypothesis was simply a logical hypothesis.
- Dinosaurs closely related to Aligators probably had green scales because Aligators have green scales. However, as they are all extinct, we can only rely on logic and not empirical data.
9. Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is the opposite of a logical hypothesis. It is a hypothesis that is currently being tested using scientific analysis. We can also call this a ‘working hypothesis’.
We can to separate research into two types: theoretical and empirical. Theoretical research relies on logic and thought experiments. Empirical research relies on tests that can be verified by observation and measurement.
So, an empirical hypothesis is a hypothesis that can and will be tested.
- Raising the wage of restaurant servers increases staff retention.
- Adding 1 lb of corn per day to cows’ diets decreases their lifespan.
- Mushrooms grow faster at 22 degrees Celsius than 27 degrees Celsius.
Each of the above hypotheses can be tested, making them empirical rather than just logical (aka theoretical).
10. Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis utilizes representative statistical models to draw conclusions about broader populations.
It requires the use of datasets or carefully selected representative samples so that statistical inference can be drawn across a larger dataset.
This type of research is necessary when it is impossible to assess every single possible case. Imagine, for example, if you wanted to determine if men are taller than women. You would be unable to measure the height of every man and woman on the planet. But, by conducting sufficient random samples, you would be able to predict with high probability that the results of your study would remain stable across the whole population.
You would be right in guessing that almost all quantitative research studies conducted in academic settings today involve statistical hypotheses.
Statistical Hypothesis Examples
- Human Sex Ratio. The most famous statistical hypothesis example is that of John Arbuthnot’s sex at birth case study in 1710. Arbuthnot used birth data to determine with high statistical probability that there are more male births than female births. He called this divine providence, and to this day, his findings remain true: more men are born than women.
- Lady Testing Tea. A 1935 study by Ronald Fisher involved testing a woman who believed she could tell whether milk was added before or after water to a cup of tea. Fisher gave her 4 cups in which one randomly had milk placed before the tea. He repeated the test 8 times. The lady was correct each time. Fisher found that she had a 1 in 70 chance of getting all 8 test correct, which is a statistically significant result.
11. Associative Hypothesis
An associative hypothesis predicts that two variables are linked but does not explore whether one variable directly impacts upon the other variable.
We commonly refer to this as “ correlation does not mean causation ”. Just because there are a lot of sick people in a hospital, it doesn’t mean that the hospital made the people sick. There is something going on there that’s causing the issue (sick people are flocking to the hospital).
So, in an associative hypothesis, you note correlation between an independent and dependent variable but do not make a prediction about how the two interact. You stop short of saying one thing causes another thing.

Associative Hypothesis Examples
- Sick people in hospital. You could conduct a study hypothesizing that hospitals have more sick people in them than other institutions in society. However, you don’t hypothesize that the hospitals caused the sickness.
- Lice make you healthy. In the Middle Ages, it was observed that sick people didn’t tend to have lice in their hair. The inaccurate conclusion was that lice was not only a sign of health, but that they made people healthy. In reality, there was an association here, but not causation. The fact was that lice were sensitive to body temperature and fled bodies that had fevers.
12. Causal Hypothesis
A causal hypothesis predicts that two variables are not only associated, but that changes in one variable will cause changes in another.
A causal hypothesis is harder to prove than an associative hypothesis because the cause needs to be definitively proven. This will often require repeating tests in controlled environments with the researchers making manipulations to the independent variable, or the use of control groups and placebo effects .
If we were to take the above example of lice in the hair of sick people, researchers would have to put lice in sick people’s hair and see if it made those people healthier. Researchers would likely observe that the lice would flee the hair, but the sickness would remain, leading to a finding of association but not causation.
Causal Hypothesis Examples
13. exact vs. inexact hypothesis.
For brevity’s sake, I have paired these two hypotheses into the one point. The reality is that we’ve already seen both of these types of hypotheses at play already.
An exact hypothesis (also known as a point hypothesis) specifies a specific prediction whereas an inexact hypothesis assumes a range of possible values without giving an exact outcome. As Helwig [2] argues:
“An “exact” hypothesis specifies the exact value(s) of the parameter(s) of interest, whereas an “inexact” hypothesis specifies a range of possible values for the parameter(s) of interest.”
Generally, a null hypothesis is an exact hypothesis whereas alternative, composite, directional, and non-directional hypotheses are all inexact.
See Next: 15 Hypothesis Examples
This is introductory information that is basic and indeed quite simplified for absolute beginners. It’s worth doing further independent research to get deeper knowledge of research methods and how to conduct an effective research study. And if you’re in education studies, don’t miss out on my list of the best education studies dissertation ideas .
[1] https://jnnp.bmj.com/content/91/6/571.abstract
[2] http://users.stat.umn.edu/~helwig/notes/SignificanceTesting.pdf

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
2 thoughts on “13 Different Types of Hypothesis”
Wow! This introductionary materials are very helpful. I teach the begginers in research for the first time in my career. The given tips and materials are very helpful. Chris, thank you so much! Excellent materials!

You’re more than welcome! If you want a pdf version of this article to provide for your students to use as a weekly reading on in-class discussion prompt for seminars, just drop me an email in the Contact form and I’ll get one sent out to you.
When I’ve taught this seminar, I’ve put my students into groups, cut these definitions into strips, and handed them out to the groups. Then I get them to try to come up with hypotheses that fit into each ‘type’. You can either just rotate hypothesis types so they get a chance at creating a hypothesis of each type, or get them to “teach” their hypothesis type and examples to the class at the end of the seminar.
Cheers, Chris
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Research Hypothesis In Psychology: Types, & Examples
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A research hypothesis, in its plural form “hypotheses,” is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method .
Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding
Some key points about hypotheses:
- A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
- It is stated in clear, precise terms before any data collection or analysis occurs. This makes the hypothesis testable.
- A hypothesis must be falsifiable. It should be possible, even if unlikely in practice, to collect data that disconfirms rather than supports the hypothesis.
- Hypotheses guide research. Scientists design studies to explicitly evaluate hypotheses about how nature works.
- For a hypothesis to be valid, it must be testable against empirical evidence. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
- Hypotheses are informed by background knowledge and observation, but go beyond what is already known to propose an explanation of how or why something occurs.
Predictions typically arise from a thorough knowledge of the research literature, curiosity about real-world problems or implications, and integrating this to advance theory. They build on existing literature while providing new insight.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Alternative hypothesis.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative or experimental hypothesis in experimental research.
It typically suggests a potential relationship between two key variables: the independent variable, which the researcher manipulates, and the dependent variable, which is measured based on those changes.
The alternative hypothesis states a relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable affects the other).
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses:
- Important hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested empirically. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
In summary, a hypothesis is a precise, testable statement of what researchers expect to happen in a study and why. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and are significant in supporting the theory being investigated.
The alternative hypothesis can be directional, indicating a specific direction of the effect, or non-directional, suggesting a difference without specifying its nature. It’s what researchers aim to support or demonstrate through their study.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable.
It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The null hypothesis, positing no effect or relationship, is a foundational contrast to the research hypothesis in scientific inquiry. It establishes a baseline for statistical testing, promoting objectivity by initiating research from a neutral stance.
Many statistical methods are tailored to test the null hypothesis, determining the likelihood of observed results if no true effect exists.
This dual-hypothesis approach provides clarity, ensuring that research intentions are explicit, and fosters consistency across scientific studies, enhancing the standardization and interpretability of research outcomes.
Nondirectional Hypothesis
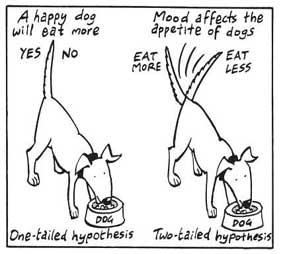
A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of this relationship.
It merely indicates that a change or effect will occur without predicting which group will have higher or lower values.
For example, “There is a difference in performance between Group A and Group B” is a non-directional hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional (one-tailed) hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It predicts in which direction the change will take place. (i.e., greater, smaller, less, more)
It specifies whether one variable is greater, lesser, or different from another, rather than just indicating that there’s a difference without specifying its nature.
For example, “Exercise increases weight loss” is a directional hypothesis.
Falsifiability
The Falsification Principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory or hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable and irrefutable.
Falsifiability emphasizes that scientific claims shouldn’t just be confirmable but should also have the potential to be proven wrong.
It means that there should exist some potential evidence or experiment that could prove the proposition false.
However many confirming instances exist for a theory, it only takes one counter observation to falsify it. For example, the hypothesis that “all swans are white,” can be falsified by observing a black swan.
For Popper, science should attempt to disprove a theory rather than attempt to continually provide evidence to support a research hypothesis.
Can a Hypothesis be Proven?
Hypotheses make probabilistic predictions. They state the expected outcome if a particular relationship exists. However, a study result supporting a hypothesis does not definitively prove it is true.
All studies have limitations. There may be unknown confounding factors or issues that limit the certainty of conclusions. Additional studies may yield different results.
In science, hypotheses can realistically only be supported with some degree of confidence, not proven. The process of science is to incrementally accumulate evidence for and against hypothesized relationships in an ongoing pursuit of better models and explanations that best fit the empirical data. But hypotheses remain open to revision and rejection if that is where the evidence leads.
- Disproving a hypothesis is definitive. Solid disconfirmatory evidence will falsify a hypothesis and require altering or discarding it based on the evidence.
- However, confirming evidence is always open to revision. Other explanations may account for the same results, and additional or contradictory evidence may emerge over time.
We can never 100% prove the alternative hypothesis. Instead, we see if we can disprove, or reject the null hypothesis.
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct but does support the alternative/experimental hypothesis.
Upon analysis of the results, an alternative hypothesis can be rejected or supported, but it can never be proven to be correct. We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist which could refute a theory.
How to Write a Hypothesis
- Identify variables . The researcher manipulates the independent variable and the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
- Operationalized the variables being investigated . Operationalization of a hypothesis refers to the process of making the variables physically measurable or testable, e.g. if you are about to study aggression, you might count the number of punches given by participants.
- Decide on a direction for your prediction . If there is evidence in the literature to support a specific effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a directional (one-tailed) hypothesis. If there are limited or ambiguous findings in the literature regarding the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.
- Make it Testable : Ensure your hypothesis can be tested through experimentation or observation. It should be possible to prove it false (principle of falsifiability).
- Clear & concise language . A strong hypothesis is concise (typically one to two sentences long), and formulated using clear and straightforward language, ensuring it’s easily understood and testable.
Consider a hypothesis many teachers might subscribe to: students work better on Monday morning than on Friday afternoon (IV=Day, DV= Standard of work).
Now, if we decide to study this by giving the same group of students a lesson on a Monday morning and a Friday afternoon and then measuring their immediate recall of the material covered in each session, we would end up with the following:
- The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
- The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors.
More Examples
- Memory : Participants exposed to classical music during study sessions will recall more items from a list than those who studied in silence.
- Social Psychology : Individuals who frequently engage in social media use will report higher levels of perceived social isolation compared to those who use it infrequently.
- Developmental Psychology : Children who engage in regular imaginative play have better problem-solving skills than those who don’t.
- Clinical Psychology : Cognitive-behavioral therapy will be more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety over a 6-month period compared to traditional talk therapy.
- Cognitive Psychology : Individuals who multitask between various electronic devices will have shorter attention spans on focused tasks than those who single-task.
- Health Psychology : Patients who practice mindfulness meditation will experience lower levels of chronic pain compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Organizational Psychology : Employees in open-plan offices will report higher levels of stress than those in private offices.
- Behavioral Psychology : Rats rewarded with food after pressing a lever will press it more frequently than rats who receive no reward.

IMAGES
VIDEO