- Polynomials Class 9 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 2

Last Updated on August 9, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 9 maths. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 9 maths. In this article, you will find case study questions for CBSE Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials. It is a part of Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 9 Maths Series.
| Polynomials | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Competency Based Questions | |
| CBSE | |
| 9 | |
| Maths | |
| Class 9 Studying Students | |
| Yes | |
| Mentioned | |
Table of Contents

Case Study Questions on Polynomials
In the current scenario, people use such door whose top half part is made of glass and bottom half part is wooden.

The glass portion of the door is having length and width in the ratio of 5 : 3. The wooden frame around the glass portion adds 11 inches to the total width and 14 inches to the total length. Consider the length of the glass portion as 5 x inches:
On the basis of the above information, solve the following questions:
Q. 1. Find the total length of the glass portion of the door (in inches) is represented in terms of x .
Q. 2. Find the total width of the glass portion of the door (in inches).
Q. 3. Write the polynomial representation of the area top half part of the door.
Q. 4. Find the zeroes of the polynomial representing the area.
1. The total length of the glass portion in the door is represented by $(5 x+14)$ inches. 2. The total width of the glass portion in the door is $(3 x+11)$ inches. 3. The area of top half part of the door $$ \begin{aligned} & =\text { length } \times \text { width } \\ & =(5 x+14)(3 x+11) \\ =& 15 x^2+55 x+42 x+154 \\ & =15 x^2+97 x+154 \end{aligned} $$ 4. We have area, $p(x)=(5 x+14)(3 x+11)$ For finding zeroes, put $p(x)=0$ \begin{array}{ll} \therefore(5 x+14) (3 x+11)=0 \\ \Rightarrow (5 x+14)=0 \text { or }(3 x+11)=0 \\ \Rightarrow x=\frac{-14}{5} \text { or } x=\frac{-11}{3} \end{array}
Algebraic Identities
Algebraic equations that are true for all values of variables occurring in it. Some useful algebraic identities are:
(i) $(x+y)^2=x^2+2 x y+y^2$ (ii) $(x-y)^2=x^2-2 x y+y^2$ (iii) $x^2-y^2=(x+y)(x-y)$ (iv) $(x+a)(x+b)=x^2+(a+b) x+a b$ (v) $(x+y+z)^2$ =$x^2+y^2+z^2+2 x y+2 y z+2 z x$ (vi) $(x+y)^3$ =$x^3+y^3+3 x y(x+y)$ =$x^3+y^3+3 x^2 y+3 x y^2$ (vii) $(x-y)^3$ =$x^3-y^3-3 x y(x-y)$ =$x^3-y^3-3 x^2 y+3 x y^2$ (viii) $x^3+y^3$ =$(x+y)\left(x^2-x y+y^2\right)$ =$(x+y)^3-3 x y(x+y)$ (ix) $x^3-y^3$ =$(x-y)\left(x^2+x y+y^2\right)$ =$(x-y)^3+3 x y(x-y)$ (x) $\left(x^3+y^3+z^3-3 x y z\right)$ $=\left(x+y+z)(x^2+y^2+z^2-x y-y z-z x\right)$ Note: If $x+y+z=0$, then $x^3+y^3+z^3=3 x y z$
- Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 9 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 4
Coordinate Geometry Class 9 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 3
Number systems class 9 case study questions maths chapter 1, topics from which case study questions may be asked.
- Definition of a polynomial in one variable, with examples and counter examples.
- Coefficients of a polynomial
- Terms of a polynomial and zero polynomial.
- Degree of a polynomial.
- Constant, linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials.
- Monomials, binomials, trinomials.
- Factors and multiples.
- Zeros of a polynomial.
- Remainder Theorem with examples.
Linear polynomial can be monomial or binomial. Quadratic polynomial can be monomial, binomial or trinomial. The degree of a zero polynomial is not defined.
Case study questions from the above given topic may be asked.
Download Customised White Label Study Materials in MS Word Format
We are providing teaching resources to teachers and coaching institute looking for customised study materials in MS word format. Our High-quality editable study material which is prepared by the expert faculties are Highly useful for Teachers, Mentors, Tutors, Faculties, Coaching Institutes, Coaching Experts, Tuition Centers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Polynomials Case Study
Q1: what are polynomials in mathematics.
A1: Polynomials are algebraic expressions that consist of variables and coefficients, connected by addition, subtraction, and multiplication. They can have multiple terms, and the degree of a polynomial is determined by the highest power of the variable in the expression.
Q2: H ow many types of polynomials are there?
A2: Polynomials are classified based on the number of terms they have: Monomial: A polynomial with just one term. Binomial: A polynomial with two terms. Trinomial: A polynomial with three terms Multinomial: A polynomial with more than three terms
Q3: What is the degree of a polynomial?
A3: The degree of a polynomial is the highest power of the variable in the polynomial.
Q4: What are the key concepts covered in Chapter 1 of CBSE Class 9 Maths regarding polynomials?
A4: Chapter 2 of CBSE Class 9 Maths covers concepts such as understanding polynomials and its types. (i) Types of polynomials (ii) Terms and coefficient of polynomials (iii) Zeroes of a polynomial (iv) Division algorithm (v) Remainder theorem (vi) Factor theorem (vii) Factorisation of quadratic polynomial
Q5: What is the difference between a polynomial and a non-polynomial expression?
A5: A polynomial expression consists of variables with non-negative integer exponents and real coefficients, combined using addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Non-polynomial expressions may include variables with negative exponents, fractional exponents, or other operations like division by variables or roots
Q6: What are the common mistakes to avoid when working with polynomials?
A6: Common mistakes include: Misidentifying the degree of the polynomial. Incorrectly applying the distributive property when multiplying polynomials. Forgetting to arrange the polynomial terms in standard form (descending order of exponents). Overlooking the signs while combining like terms. Misapplying the rules of exponents.
Q7: Are there any online resources or tools available for practicing polynomials case study questions?
A7: We provide case study questions for CBSE Class 9 Maths on our website. Students can visit the website and practice sufficient case study questions and prepare for their exams. If you need more case study questions, then you can visit Physics Gurukul website. they are having a large collection of case study questions for all classes.
Q8: What are the important keywords for CBSE Class 9 Maths Polynomials?
A8: List of important keywords given below – Algebraic Expression: Any expression that contains constants and variables, connected by some or all of the operations +, -, x, ÷. Polynomials: An algebraic expression in which the variables involved have only non-negative integral powers. Polynomials in one Variable: An algebraic expression which consist of only one type of variables in the entire expression. Degree of Polynomial: Highest power of a variable in the polynomial. Constant Polynomial: Polynomial of zero degree. Zero Polynomials: A polynomial consisting of one term, namely zero. Zeroes of a Polynomial: Let p(x) be a polynomial in one variable and ‘a’ be a real number such that the value of polynomial at x=a is zero i.e., p(a) = 0, then ‘a’ is said to be a zero polynomial of p(x). Remainder Theorem: Let p(x) be a polynomial having degree 1 or more than 1 and let ‘a’ be any real number. If p(x) is divided by (x-a), then remainder is p(a).

Related Posts


Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Last modified on: 2 years ago
- Reading Time: 3 Minutes
Case Study Questions
Question 1:
On one day, principal of a particular school visited the classroom. Class teacher was teaching the concept of polynomial to students. He was very much impressed by her way of teaching. To check, whether the students also understand the concept taught by her or not, he asked various questions to students. Some of them are given below. Answer them.
(i) Which one of the following is not a polynomial? (a) 4x 2 + 2x – 1 (b) y+ (3/y) (c) x 3 – 1 (d) y 2 + 5y + 1
(ii) The polynomial of the type ax 2 + bx + c, a = 0 is called (a) Linear polynomial (b) Quadratic polynomial (c) Cubic polynomial (d) Biquadratic polynomial
(iii) The value of k, if (x – 1) is a factor of 4x 3 + 3x 2 – 4x + k, is (a) 1 (b) –2 (c) –3 (d) 3
(iv) If x + 2 is the factor of x 3 – 2ax 2 + 16, then value of a is (a) –7 (b) 1 (c) –1 (d) 7
(v) The number of zeroes of the polynomial x 2 + 4x + 2 is (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4

Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
CBSE Expert
CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions PDF Download
Download Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams 2023-24. These Case Study and Passage Based questions are published by the experts of CBSE Experts for the students of CBSE Class 9 so that they can score 100% in Exams.

Case study questions play a pivotal role in enhancing students’ problem-solving skills. By presenting real-life scenarios, these questions encourage students to think beyond textbook formulas and apply mathematical concepts to practical situations. This approach not only strengthens their understanding of mathematical concepts but also develops their analytical thinking abilities.
Table of Contents
CBSE Class 9th MATHS: Chapterwise Case Study Questions
Inboard exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. For Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions, there would be 5 case-based sub-part questions, wherein a student has to attempt 4 sub-part questions.

Chapterwise Case Study Questions of Class 9 Maths
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Number System
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Lines and Angles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Triangles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Circles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Constructions
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Heron’s Formula
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Surface Area and Volumes
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Statistics
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Probability
Checkout: Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
And for mathematical calculations, tap Math Calculators which are freely proposed to make use of by calculator-online.net
The above Class 9 Maths Case Study Question s will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions have been developed by experienced teachers of cbseexpert.com for the benefit of Class 10 students.
Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2023-24
UNIT I: NUMBER SYSTEMS
1. REAL NUMBERS (18 Periods)
1. Review of representation of natural numbers, integers, and rational numbers on the number line. Rational numbers as recurring/ terminating decimals. Operations on real numbers.
2. Examples of non-recurring/non-terminating decimals. Existence of non-rational numbers (irrational numbers) such as √2, √3 and their representation on the number line. Explaining that every real number is represented by a unique point on the number line and conversely, viz. every point on the number line represents a unique real number.
3. Definition of nth root of a real number.
4. Rationalization (with precise meaning) of real numbers of the type

(and their combinations) where x and y are natural number and a and b are integers.
5. Recall of laws of exponents with integral powers. Rational exponents with positive real bases (to be done by particular cases, allowing learner to arrive at the general laws.)
UNIT II: ALGEBRA
1. POLYNOMIALS (26 Periods)
Definition of a polynomial in one variable, with examples and counter examples. Coefficients of a polynomial, terms of a polynomial and zero polynomial. Degree of a polynomial. Constant, linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials. Monomials, binomials, trinomials. Factors and multiples. Zeros of a polynomial. Motivate and State the Remainder Theorem with examples. Statement and proof of the Factor Theorem. Factorization of ax2 + bx + c, a ≠ 0 where a, b and c are real numbers, and of cubic polynomials using the Factor Theorem. Recall of algebraic expressions and identities. Verification of identities:
RELATED STORIES
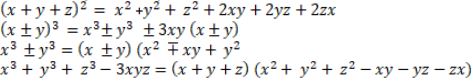
and their use in factorization of polynomials.
2. LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES (16 Periods)
Recall of linear equations in one variable. Introduction to the equation in two variables. Focus on linear equations of the type ax + by + c=0.Explain that a linear equation in two variables has infinitely many solutions and justify their being written as ordered pairs of real numbers, plotting them and showing that they lie on a line.
UNIT III: COORDINATE GEOMETRY COORDINATE GEOMETRY (7 Periods)
The Cartesian plane, coordinates of a point, names and terms associated with the coordinate plane, notations.
UNIT IV: GEOMETRY
1. INTRODUCTION TO EUCLID’S GEOMETRY (7 Periods)
History – Geometry in India and Euclid’s geometry. Euclid’s method of formalizing observed phenomenon into rigorous Mathematics with definitions, common/obvious notions, axioms/postulates and theorems. The five postulates of Euclid. Showing the relationship between axiom and theorem, for example: (Axiom)
1. Given two distinct points, there exists one and only one line through them. (Theorem)
2. (Prove) Two distinct lines cannot have more than one point in common.
2. LINES AND ANGLES (15 Periods)
1. (Motivate) If a ray stands on a line, then the sum of the two adjacent angles so formed is 180O and the converse.
2. (Prove) If two lines intersect, vertically opposite angles are equal.
3. (Motivate) Lines which are parallel to a given line are parallel.
3. TRIANGLES (22 Periods)
1. (Motivate) Two triangles are congruent if any two sides and the included angle of one triangle is equal to any two sides and the included angle of the other triangle (SAS Congruence).
2. (Prove) Two triangles are congruent if any two angles and the included side of one triangle is equal to any two angles and the included side of the other triangle (ASA Congruence).
3. (Motivate) Two triangles are congruent if the three sides of one triangle are equal to three sides of the other triangle (SSS Congruence).
4. (Motivate) Two right triangles are congruent if the hypotenuse and a side of one triangle are equal (respectively) to the hypotenuse and a side of the other triangle. (RHS Congruence)
5. (Prove) The angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal.
6. (Motivate) The sides opposite to equal angles of a triangle are equal.
4. QUADRILATERALS (13 Periods)
1. (Prove) The diagonal divides a parallelogram into two congruent triangles.
2. (Motivate) In a parallelogram opposite sides are equal, and conversely.
3. (Motivate) In a parallelogram opposite angles are equal, and conversely.
4. (Motivate) A quadrilateral is a parallelogram if a pair of its opposite sides is parallel and equal.
5. (Motivate) In a parallelogram, the diagonals bisect each other and conversely.
6. (Motivate) In a triangle, the line segment joining the mid points of any two sides is parallel to the third side and in half of it and (motivate) its converse.
5. CIRCLES (17 Periods)
1. (Prove) Equal chords of a circle subtend equal angles at the center and (motivate) its converse.
2. (Motivate) The perpendicular from the center of a circle to a chord bisects the chord and conversely, the line drawn through the center of a circle to bisect a chord is perpendicular to the chord.
3. (Motivate) Equal chords of a circle (or of congruent circles) are equidistant from the center (or their respective centers) and conversely.
4. (Prove) The angle subtended by an arc at the center is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle.
5. (Motivate) Angles in the same segment of a circle are equal.
6. (Motivate) If a line segment joining two points subtends equal angle at two other points lying on the same side of the line containing the segment, the four points lie on a circle.
7. (Motivate) The sum of either of the pair of the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180° and its converse.
UNIT V: MENSURATION 1.
1. AREAS (5 Periods)
Area of a triangle using Heron’s formula (without proof)
2. SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES (17 Periods)
Surface areas and volumes of spheres (including hemispheres) and right circular cones.
UNIT VI: STATISTICS & PROBABILITY
STATISTICS (15 Periods)
Bar graphs, histograms (with varying base lengths), and frequency polygons.
To crack case study questions, Class 9 Mathematics students need to apply their mathematical knowledge to real-life situations. They should first read the question carefully and identify the key information. They should then identify the relevant mathematical concepts that can be applied to solve the question. Once they have done this, they can start solving the Class 9 Mathematics case study question.
Benefits of Practicing CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions
Regular practice of CBSE Class 9 Maths case study questions offers several benefits to students. Some of the key advantages include:
- Deeper Understanding : Case study questions foster a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts by connecting them to real-world scenarios. This improves retention and comprehension.
- Practical Application : Students learn to apply mathematical concepts to practical situations, preparing them for real-life problem-solving beyond the classroom.
- Critical Thinking : Case study questions require students to think critically, analyze data, and devise appropriate solutions. This nurtures their critical thinking abilities, which are valuable in various academic and professional domains.
- Exam Readiness : By practicing case study questions, students become familiar with the question format and gain confidence in their problem-solving abilities. This enhances their readiness for CBSE Class 9 Maths exams.
- Holistic Development: Solving case study questions cultivates not only mathematical skills but also essential life skills like analytical thinking, decision-making, and effective communication.
Tips to Solve CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions Effectively
Solving case study questions can be challenging, but with the right approach, you can excel. Here are some tips to enhance your problem-solving skills:
- Read the case study thoroughly and understand the problem statement before attempting to solve it.
- Identify the relevant data and extract the necessary information for your solution.
- Break down complex problems into smaller, manageable parts to simplify the solution process.
- Apply the appropriate mathematical concepts and formulas, ensuring a solid understanding of their principles.
- Clearly communicate your solution approach, including the steps followed, calculations made, and reasoning behind your choices.
- Practice regularly to familiarize yourself with different types of case study questions and enhance your problem-solving speed.Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions
Remember, solving case study questions is not just about finding the correct answer but also about demonstrating a logical and systematic approach. Now, let’s explore some resources that can aid your preparation for CBSE Class 9 Maths case study questions.
Q1. Are case study questions included in the Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions syllabus?
Yes, case study questions are an integral part of the CBSE Class 9 Maths syllabus. They are designed to enhance problem-solving skills and encourage the application of mathematical concepts to real-life scenarios.
Q2. How can solving case study questions benefit students ?
Solving case study questions enhances students’ problem-solving skills, analytical thinking, and decision-making abilities. It also bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, making mathematics more relevant and engaging.
Q3. How do case study questions help in exam preparation?
Case study questions help in exam preparation by familiarizing students with the question format, improving analytical thinking skills, and developing a systematic approach to problem-solving. Regular practice of case study questions enhances exam readiness and boosts confidence in solving such questions.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
CBSE Class 9th Maths 2023 : 30 Most Important Case Study Questions with Answers; Download PDF

SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
CBSE Class 9 Maths exam 2022-23 will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. CBSE Class 9 Maths Question Bank on Case Studies given in this article can be very helpful in understanding the new format of questions.
Each question has five sub-questions, each followed by four options and one correct answer. Students can easily download these questions in PDF format and refer to them for exam preparation.
| Case Study Questions - 1 | |
| Case Study Questions - 2 | |
| Case Study Questions - 3 | |
| Case Study Questions - 4 | |
| Case Study Questions - 5 | |
| Case Study Questions - 6 | |
| Case Study Questions - 7 | |
| Case Study Questions - 8 | |
| Case Study Questions - 9 | |
| Case Study Questions - 10 | |
| Case Study Questions - 11 | |
| Case Study Questions - 12 | |
| Case Study Questions - 13 | |
| Case Study Questions - 14 | |
| Case Study Questions - 15 | |
| Case Study Questions - 16 | |
| Case Study Questions - 17 | |
| Case Study Questions - 18 | |
| Case Study Questions - 19 | |
| Case Study Questions - 20 | |
| Case Study Questions - 21 | |
| Case Study Questions - 22 | |
| Case Study Questions - 23 | |
| Case Study Questions - 24 | |
| Case Study Questions - 25 | |
| Case Study Questions - 26 | |
| Case Study Questions - 27 | |
| Case Study Questions - 28 | |
| Case Study Questions - 29 | |
| Case Study Questions - 30 |
CBSE Class 9 All Students can also Download here Class 9 Other Study Materials in PDF Format.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences
- CBSE Class 9th 2023-24 : Science Practical Syllabus; Download PDF 19 April, 2023, 4:52 pm
- CBSE Class 9 Maths Practice Book 2023 (Released By CBSE) 23 March, 2023, 6:16 pm
- CBSE Class 9 Science Practice Book 2023 (Released By CBSE) 23 March, 2023, 5:56 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Maths 2023 : 30 Most Important Case Study Questions with Answers; Download PDF 10 February, 2023, 6:20 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Maths 2023 : Important Assertion Reason Question with Solution Download Pdf 9 February, 2023, 12:16 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Exam 2023 : Social Science Most Important Short Notes; Download PDF 16 January, 2023, 4:29 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Mathematics 2023 : Most Important Short Notes with Solutions 27 December, 2022, 6:05 pm
- CBSE Class 9th English 2023 : Chapter-wise Competency-Based Test Items with Answer; Download PDF 21 December, 2022, 5:16 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Science 2023 : Chapter-wise Competency-Based Test Items with Answers; Download PDF 20 December, 2022, 5:37 pm

CBSE Class 9th 2023-24 : Science Practical Syllabus; Download PDF

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Are you preparing for your Class 9 Maths board exams and looking for an effective study resource? Well, you’re in luck! In this article, we will provide you with a collection of Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths specifically designed to help you excel in your exams. These questions are carefully curated to cover various mathematical concepts and problem-solving techniques. So, let’s dive in and explore these valuable resources that will enhance your preparation and boost your confidence.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

CBSE Class 9 Maths Board Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. The CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful to understand the new format of questions. Share this link with your friends.
If you want to want to prepare all the tough, tricky & difficult questions for your upcoming exams, this is where you should hang out. CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 will provide you with detailed, latest, comprehensive & confidence-inspiring solutions to the maximum number of Case Study Questions covering all the topics from your NCERT Text Books !
Table of Contents
CBSE Class 9th – MATHS: Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution
Case study questions are a form of examination where students are presented with real-life scenarios that require the application of mathematical concepts to arrive at a solution. These questions are designed to assess students’ problem-solving abilities, critical thinking skills, and understanding of mathematical concepts in practical contexts.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths
Case study questions play a crucial role in the field of mathematics education. They provide students with an opportunity to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, thereby enhancing their comprehension of mathematical concepts. By engaging with case study questions, students develop the ability to analyze complex problems, make connections between different mathematical concepts, and formulate effective problem-solving strategies.
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Number System
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Lines and Angles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Triangles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Quadilaterals
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Circles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Constructions
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Heron’s Formula
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Surface Area and Volumes
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Statistics
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Probability
The above Case studies for Class 9 Mathematics will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of schools.studyrate.in for benefit of Class 10 students.
- Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
- Class 9 Social Science Case Study Questions
How to Approach Case Study Questions
When tackling case study questions, it is essential to adopt a systematic approach. Here are some steps to help you approach and solve these types of questions effectively:
- Read the case study carefully: Understand the given scenario and identify the key information.
- Identify the mathematical concepts involved: Determine the relevant mathematical concepts and formulas applicable to the problem.
- Formulate a plan: Devise a plan or strategy to solve the problem based on the given information and mathematical concepts.
- Solve the problem step by step: Apply the chosen approach and perform calculations or manipulations to arrive at the solution.
- Verify and interpret the results: Ensure the solution aligns with the initial problem and interpret the findings in the context of the case study.
Tips for Solving Case Study Questions
Here are some valuable tips to help you effectively solve case study questions:
- Read the question thoroughly and underline or highlight important information.
- Break down the problem into smaller, manageable parts.
- Visualize the problem using diagrams or charts if applicable.
- Use appropriate mathematical formulas and concepts to solve the problem.
- Show all the steps of your calculations to ensure clarity.
- Check your final answer and review the solution for accuracy and relevance to the case study.
Benefits of Practicing Case Study Questions
Practicing case study questions offers several benefits that can significantly contribute to your mathematical proficiency:
- Enhances critical thinking skills
- Improves problem-solving abilities
- Deepens understanding of mathematical concepts
- Develops analytical reasoning
- Prepares you for real-life applications of mathematics
- Boosts confidence in approaching complex mathematical problems
Case study questions offer a unique opportunity to apply mathematical knowledge in practical scenarios. By practicing these questions, you can enhance your problem-solving abilities, develop a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts, and boost your confidence for the Class 9 Maths board exams. Remember to approach each question systematically, apply the relevant concepts, and review your solutions for accuracy. Access the PDF resource provided to access a wealth of case study questions and further elevate your preparation.
Q1: Can case study questions help me score better in my Class 9 Maths exams?
Yes, practicing case study questions can significantly improve your problem-solving skills and boost your performance in exams. These questions offer a practical approach to understanding mathematical concepts and their real-life applications.
Q2: Are the case study questions in the PDF resource relevant to the Class 9 Maths syllabus?
Absolutely! The PDF resource contains case study questions that align with the Class 9 Maths syllabus. They cover various topics and concepts included in the curriculum, ensuring comprehensive preparation.
Q3: Are the solutions provided for the case study questions in the PDF resource?
Yes, the PDF resource includes solutions for each case study question. You can refer to these solutions to validate your answers and gain a better understanding of the problem-solving process.
You Might Also Like
Ncert science book class 9 in hindi medium | विज्ञान की पुस्तक कक्षा 9 हिंदी, mcq questions of class 9 maths chapter 7 triangles with answers, class 9 mcq questions for chapter 4 structure of the atom with answers, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
myCBSEguide
- Mathematics
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics...
CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you’re looking for a comprehensive and reliable study resource and case study questions for class 9 CBSE, myCBSEguide is the perfect door to enter. With over 10,000 study notes, solved sample papers and practice questions, it’s got everything you need to ace your exams. Plus, it’s updated regularly to keep you aligned with the latest CBSE syllabus . So why wait? Start your journey to success with myCBSEguide today!
Significance of Mathematics in Class 9
Mathematics is an important subject for students of all ages. It helps students to develop problem-solving and critical-thinking skills, and to think logically and creatively. In addition, mathematics is essential for understanding and using many other subjects, such as science, engineering, and finance.
CBSE Class 9 is an important year for students, as it is the foundation year for the Class 10 board exams. In Class 9, students learn many important concepts in mathematics that will help them to succeed in their board exams and in their future studies. Therefore, it is essential for students to understand and master the concepts taught in Class 9 Mathematics .
Case studies in Class 9 Mathematics
A case study in mathematics is a detailed analysis of a particular mathematical problem or situation. Case studies are often used to examine the relationship between theory and practice, and to explore the connections between different areas of mathematics. Often, a case study will focus on a single problem or situation and will use a variety of methods to examine it. These methods may include algebraic, geometric, and/or statistical analysis.
Example of Case study questions in Class 9 Mathematics
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has included case study questions in the Class 9 Mathematics paper. This means that Class 9 Mathematics students will have to solve questions based on real-life scenarios. This is a departure from the usual theoretical questions that are asked in Class 9 Mathematics exams.
The following are some examples of case study questions from Class 9 Mathematics:
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 1
There is a square park ABCD in the middle of Saket colony in Delhi. Four children Deepak, Ashok, Arjun and Deepa went to play with their balls. The colour of the ball of Ashok, Deepak, Arjun and Deepa are red, blue, yellow and green respectively. All four children roll their ball from centre point O in the direction of XOY, X’OY, X’OY’ and XOY’ . Their balls stopped as shown in the above image.
Answer the following questions:
Answer Key:
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 2
- Now he told Raju to draw another line CD as in the figure
- The teacher told Ajay to mark ∠ AOD as 2z
- Suraj was told to mark ∠ AOC as 4y
- Clive Made and angle ∠ COE = 60°
- Peter marked ∠ BOE and ∠ BOD as y and x respectively
Now answer the following questions:
- 2y + z = 90°
- 2y + z = 180°
- 4y + 2z = 120°
- (a) 2y + z = 90°
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 3
- (a) 31.6 m²
- (c) 513.3 m³
- (b) 422.4 m²
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 4
How to Answer Class 9 Mathematics Case study questions
To crack case study questions, Class 9 Mathematics students need to apply their mathematical knowledge to real-life situations. They should first read the question carefully and identify the key information. They should then identify the relevant mathematical concepts that can be applied to solve the question. Once they have done this, they can start solving the Class 9 Mathematics case study question.
Students need to be careful while solving the Class 9 Mathematics case study questions. They should not make any assumptions and should always check their answers. If they are stuck on a question, they should take a break and come back to it later. With some practice, the Class 9 Mathematics students will be able to crack case study questions with ease.
Class 9 Mathematics Curriculum at Glance
At the secondary level, the curriculum focuses on improving students’ ability to use Mathematics to solve real-world problems and to study the subject as a separate discipline. Students are expected to learn how to solve issues using algebraic approaches and how to apply their understanding of simple trigonometry to height and distance problems. Experimenting with numbers and geometric forms, making hypotheses, and validating them with more observations are all part of Math learning at this level.
The suggested curriculum covers number systems, algebra, geometry, trigonometry, mensuration, statistics, graphing, and coordinate geometry, among other topics. Math should be taught through activities that include the use of concrete materials, models, patterns, charts, photographs, posters, and other visual aids.
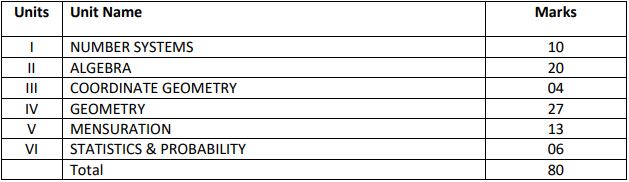
CBSE Class 9 Mathematics (Code No. 041)
| I | NUMBER SYSTEMS | 10 |
| II | ALGEBRA | 20 |
| III | COORDINATE GEOMETRY | 04 |
| IV | GEOMETRY | 27 |
| V | MENSURATION | 13 |
| VI | STATISTICS & PROBABILITY | 06 |
Class 9 Mathematics question paper design
The CBSE Class 9 mathematics question paper design is intended to measure students’ grasp of the subject’s fundamental ideas. The paper will put their problem-solving and analytical skills to the test. Class 9 mathematics students are advised to go through the question paper pattern thoroughly before they start preparing for their examinations. This will help them understand the paper better and enable them to score maximum marks. Refer to the given Class 9 Mathematics question paper design.
QUESTION PAPER DESIGN (CLASS 9 MATHEMATICS)
| 1. | Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas | 43 | 54 |
| 2. | Solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. | 19 | 24 |
| 3. | Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations Present and defend opinions by making judgments about information, validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria. Compile information together in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions | 18 | 22 |
| 80 | 100 |
myCBSEguide: Blessing in disguise
Class 9 is an important milestone in a student’s life. It is the last year of high school and the last chance to score well in the CBSE board exams. myCBSEguide is the perfect platform for students to get started on their preparations for Class 9 Mathematics. myCBSEguide provides comprehensive study material for all subjects, including practice questions, sample papers, case study questions and mock tests. It also offers tips and tricks on how to score well in exams. myCBSEguide is the perfect door to enter for class 9 CBSE preparations.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
16 thoughts on “CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Case Study Questions”
This method is not easy for me
aarti and rashika are two classmates. due to exams approaching in some days both decided to study together. during revision hour both find difficulties and they solved each other’s problems. aarti explains simplification of 2+ ?2 by rationalising the denominator and rashika explains 4+ ?2 simplification of (v10-?5)(v10+ ?5) by using the identity (a – b)(a+b). based on above information, answer the following questions: 1) what is the rationalising factor of the denominator of 2+ ?2 a) 2-?2 b) 2?2 c) 2+ ?2 by rationalising the denominator of aarti got the answer d) a) 4+3?2 b) 3+?2 c) 3-?2 4+ ?2 2+ ?2 d) 2-?3 the identity applied to solve (?10-?5) (v10+ ?5) is a) (a+b)(a – b) = (a – b)² c) (a – b)(a+b) = a² – b² d) (a-b)(a+b)=2(a² + b²) ii) b) (a+b)(a – b) = (a + b
MATHS PAAGAL HAI
All questions was easy but search ? hard questions. These questions was not comparable with cbse. It was totally wastage of time.
Where is search ? bar
maths is love
Can I have more questions without downloading the app.
I love math
Hello l am Devanshu chahal and l am an entorpinior. I am started my card bord business and remanded all the existing things this all possible by math now my business is 120 crore and my business profit is 25 crore in a month. l find the worker team because my business is going well Thanks
I am Riddhi Shrivastava… These questions was very good.. That’s it.. ..
For challenging Mathematics Case Study Questions, seeking a writing elite service can significantly aid your research. These services provide expert guidance, ensuring your case study is well-researched, accurately analyzed, and professionally written. With their assistance, you can tackle complex mathematical problems with confidence, leading to high-quality academic work that meets rigorous standards.
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Not Able To Find Desired Paper or Worksheet SEARCH
Find papers & worksheets search, class 9 polynomials case study questions - podar international.
- Mathematics
- (0) Comments
- 26 Downloads

Related Papers
Click to view more related papers, display_name = "class 11" && $paper->display_name = "class 12") { // echo $paper->display_name." questions papers and worksheets"; } //else { // echo $paper->display_name." sample papers and previous year papers"; //} //>, cbse class 9 maths chapter wise important questions - free pdf download.
CBSE Important Questions for Class 9 Maths are available in Printable format for Free Download.Here you may find NCERT Important Questions and Extra Questions for Class 9 Mathematics chapter wise with answers also. These questions will act as chapter wise test papers for Class 9 Mathematics. These Important Questions for Class 9 Mathematics are as per latest NCERT and CBSE Pattern syllabus and assure great success in achieving high score in Board Examinations
Total Papers :
| Class 9 Maths Marks Distribution | |
|---|---|
| Units | Marks |
| Number Systems | 08 |
| Algebra | 17 |
| Coordinate Geometry | 04 |
| Geometry | 28 |
| Mensuration | 13 |
| Statistics & Probability | 10 |
| Total | 80 |
| Internal Assessment | 20 |
| Grand Total | 100 |
Maths Topics to be covered for Class 9
- Real Numbers
- Polynomials
- Coordinate Geometry
- Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Introduction to Euclid's Geometry
- Lines and Angles
- Heron’s Formula
- Probability
- Quadrilaterals
- Area of Parallelogram and Triangles
- Constructions
- Surface Areas and Volumes
Structure of CBSE Maths Sample Paper for Class 9 is
| Type of Question | Marks per Question | Total No. of Questions | Total Marks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Objective Type Questions | 1 | 20 | 20 |
| Short Answer Type Questions - I | 2 | 6 | 12 |
| Short Answer Type Questions - II | 3 | 8 | 24 |
| Long Answer Type Questions | 4 | 6 | 24 |
| Total | 40 | 80 | |
For Preparation of exams students can also check out other resource material
CBSE Class 9 Maths Sample Papers
CBSE Class 9 Maths Worksheets
CBSE Class 9 Maths Question Papers
CBSE Class 9 Maths Test Papers
CBSE Class 9 Maths Revision Notes
Question Bank of Other Subjects of Class 9
Importance of Question Bank for Exam Preparation?
There are many ways to ascertain whether a student has understood the important points and topics of a particular chapter and is he or she well prepared for exams and tests of that particular chapter. Apart from reference books and notes, Question Banks are very effective study materials for exam preparation. When a student tries to attempt and solve all the important questions of any particular subject , it becomes very easy to gauge how much well the topics have been understood and what kind of questions are asked in exams related to that chapter.. Some of the other advantaging factors of Question Banks are as follows
- Since Important questions included in question bank are collections of questions that were asked in previous exams and tests thus when a student tries to attempt them they get a complete idea about what type of questions are usually asked and whether they have learned the topics well enough. This gives them an edge to prepare well for the exam.Students get the clear idea whether the questions framed from any particular chapter are mostly either short or long answer type questions or multiple choice based and also marks weightage of any particular chapter in final exams.
- CBSE Question Banks are great tools to help in analysis for Exams. As it has a collection of important questions that were asked previously in exams thereby it covers every question from most of the important topics. Thus solving questions from the question bank helps students in analysing their preparation levels for the exam. However the practice should be done in a way that first the set of questions on any particular chapter are solved and then solutions should be consulted to get an analysis of their strong and weak points. This ensures that they are more clear about what to answer and what can be avoided on the day of the exam.
- Solving a lot of different types of important questions gives students a clear idea of what are the main important topics of any particular chapter that needs to focussed on from examination perspective and should be emphasised on for revision before attempting the final paper. So attempting most frequently asked questions and important questions helps students to prepare well for almost everything in that subject.
- Although students cover up all the chapters included in the course syllabus by the end of the session, sometimes revision becomes a time consuming and difficult process. Thus, practicing important questions from Question Bank allows students to check the preparation status of each and every small topic in a chapter. Doing that ensures quick and easy insight into all the important questions and topics in each and every individual. Solving the important questions also acts as the revision process.
Question Bank of Other Classes
To Prepare better for CBSE paperclass; ?> " title="Download Free CBSE Papers">Ribblu.com brings to you all the previous years papers & worksheets of subject; ?//> for CBSE paperclass; ?>. This CBSE paper and worksheet can be instrumental in students achieving maximum marks in their exams. These Papers and worksheets help students gain confidence and make them ready to face their school examinations. These Papers and worksheets school wise, covers important concepts from an examination perspective. Students and parents can download all the available papers & worksheets directly in the form of PDF. One can use these papers and worksheets to get extensive practice and familiarise themselves with the format of the question paper.
You can help other users
Be the first to write comment .
Upload papers and the more your paper get downloaded the more you earn the points
You may send papers on email [email protected] along with userid
- Downloaded by: Adhyay Vlogs
- Downloaded by: Pintu Singh
Rules and regulations for uploads
| 1. | The uploaded material should be original and not duplicated. |
| 2. | It should be clear, legible and genuine. The file type should be pdf for multiple pages and jpg is allowed only for single page document. Use apps like “cam scanner” for mobile capture, crop and edit photos and save it as pdf. One file should be complete in all aspects like one full question paper, Notes of a complete topic. File name should be self explanatory (eg. CBSE 10th 2012 hindi question paper by – ‘Name of the uploader’) |
| 3. | No copyright violations allowed. |
| 4. | Points and coupons will be given at the sole discretion of Ribblu. |
| 5. | Ribblu admin has the power to reject, remove, alter, approve, accept any material that is uploaded by the user without consent of owner. |
Write your comment
Report this paper, how to earn points.
Upload Papers / Worksheets and Earn 50 Points.
The uploaded material should be original paper or worksheet of any school. Check out some videos on how to upload papers on ribblu
Rate & Review your school and Earn 25 Points.
Review any school that you may be knowing and once your review is approved, you will be credited with 25 points.
Answer on question posted on JustAsk and earn 15 points.
JustAsk is a platform where you can help others to find answers of any question. Share your Knowledge. Answer questions and once approved you will earn 15 points
Complete your profile and earn upto 25 Points.
Edit and complete your user profile and earn points. The more details you submit, the more points you will earn.
Download Ribblu Mobile App and you will (Earn 20 Points) (one time only)
CBSE Schools
- CBSE Schools In Delhi
- CBSE Schools In Noida
- CBSE Schools In Greater Noida
- CBSE Schools In Faridabad
- CBSE Schools In Ghaziabad
- CBSE Schools In Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools In Mumbai
- CBSE Schools In Pune
- CBSE Schools In Bangalore
- CBSE Schools In Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools In Kolkata
- CBSE Schools In Chennai
- CBSE Schools In Patna
- CBSE Schools In Meerut
- CBSE Schools In Kanpur
- CBSE Schools In Indore
- CBSE Schools In Ludhiana
- CBSE Schools In Dehradun
Top Schools
- Schools In Delhi
- Schools In Noida
- Schools In Greater Noida
- Schools In Faridabad
- Schools In Ghaziabad
- Schools In Gurgaon
- Schools In Mumbai
- Schools In Pune
- Schools In Bangalore
- Schools In Hyderabad
- Schools In Kolkata
- Schools In Chennai
- Schools In Patna
- Schools In Meerut
- Schools In Kanpur
- Schools In Indore
- Schools In Ludhiana
- Schools In Dehradun
Other Schools
- Pre Nursery Schools In Noida
- Day Boarding Schools In Noida
- Pre Nursery Schools In Gurgaon
- Pre Nursery Schools In Delhi
- Play Schools In Delhi
- Day Boarding Schools In Delhi
CBSE Papers
- CBSE Class 1 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 2 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 3 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 4 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 5 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 6 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 7 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 8 Sample Papers
Paper Categories
- Question Bank
- Question Papers
- Revision Notes
- Sample Papers
- Test Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 11 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials are provided here. Our NCERT Maths solutions contain all the questions of the NCERT textbook that are solved and explained beautifully. Here you will get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 all exercises Exercise in one place. These solutions are prepared by the subject experts and as per the latest NCERT syllabus and guidelines. CBSE Class 9 Students who wish to score good marks in the maths exam must practice these questions regularly.
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials NCERT Solutions
Below we have provided the solutions of each exercise of the chapter. Go through the links to access the solutions of exercises you want. You should also check out our NCERT Class 9 Solutions for other subjects to score good marks in the exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.3

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.4

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.5

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials – Topic Discussion
Below we have listed the topics that have been discussed in this chapter. As this is one of the important topics in maths, It comes under the unit – Algebra which has a weightage of 20 marks in class 9 maths board exams.
- Polynomials in one Variable – Discussion of Linear, Quadratic and Cubic Polynomial.
- Zeroes of a Polynomial
- Real Numbers and their Decimal Expansions
- Representing Real Numbers on the Number Line Operations on Real Numbers
- Laws of Exponents for Real Numbers.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.1 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths . Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.1.
- Polynomials
- Introduction
- Polynomials In One Variable
- Zeroes Of A Polynomial
- Remainder Theorem
- Factorisation Of Polynomials
- Algebraic Identities
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.1
Ex 2.1 Class 9 Maths Question 1. Which of the following expressions are polynomials in one variable and which are not? State reasons for your answer. (i) 4x 2 – 3x + 7 (ii) y 2 + √2 (iii) 3 √t + t√2 (iv) y+ \(\frac { 2 }{ y }\) (v) x 10 + y 3 +t 50 Solution: (i) We have 4x 2 – 3x + 7 = 4x 2 – 3x + 7x 0 It is a polynomial in one variable i.e., x because each exponent of x is a whole number.
(ii) We have y 2 + √2 = y 2 + √2y 0 It is a polynomial in one variable i.e., y because each exponent of y is a whole number.
(iii) We have 3 √t + t√2 = 3 √t 1/2 + √2.t It is not a polynomial, because one of the exponents of t is \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\), which is not a whole number.
(iv) We have y + \(y+\frac { 2 }{ y }\) = y + 2.y -1 It is not a polynomial, because one of the exponents of y is -1, which is not a whole number.
(v) We have x 10 + y 3 + t 50 Here, exponent of every variable is a whole number, but x 10 + y 3 + t 50 is a polynomial in x, y and t, i.e., in three variables. So, it is not a polynomial in one variable.
Ex 2.1 Class 9 Maths Question 2. Write the coefficients of x 2 in each of the following (i) 2 + x 2 + x (ii) 2 – x 2 + x 3 (iii) \(\frac { \pi }{ 2 }\) x 2 + x (iv) √2 x – 1 Solution: (i) The given polynomial is 2 + x 2 + x. The coefficient of x 2 is 1. (ii) The given polynomial is 2 – x 2 + x 3 . The coefficient of x 2 is -1. (iii) The given polynomial is \(\frac { \pi }{ 2 } { x }^{ 2 }\) + x. The coefficient of x 2 is \(\frac { \pi }{ 2 }\). (iv) The given polynomial is √2 x – 1. The coefficient of x 2 is 0.
Ex 2.1 Class 9 Maths Question 3. Give one example each of a binomial of degree 35, and of a monomial of degree 100. Solution: (i) Abmomial of degree 35 can be 3x 35 -4. (ii) A monomial of degree 100 can be √2y 100 .
Ex 2.1 Class 9 Maths Question 4. Write the degree of each of the following polynomials. (i) 5x 3 +4x 2 + 7x (ii) 4 – y 2 (iii) 5t – √7 (iv) 3 Solution: (i) The given polynomial is 5x 3 + 4x 2 + 7x. The highest power of the variable x is 3. So, the degree of the polynomial is 3. (ii) The given polynomial is 4- y 2 . The highest power of the variable y is 2. So, the degree of the polynomial is 2. (iii) The given polynomial is 5t – √7 . The highest power of variable t is 1. So, the degree of the polynomial is 1. (iv) Since, 3 = 3x° [∵ x°=1] So, the degree of the polynomial is 0.
Ex 2.1 Class 9 Maths Question 5. Classify the following as linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials. (i) x 2 + x (ii) x – x 3 (iii) y + y 2 +4 (iv) 1 + x (v) 3t (vi) r 2 (vii) 7x 3 Solution: (i) The degree of x 2 + x is 2. So, it is a quadratic polynomial. (ii) The degree of x – x 3 is 3. So, it is a cubic polynomial. (iii) The degree of y + y 2 + 4 is 2. So, it is a quadratic polynomial. (iv) The degree of 1 + x is 1. So, it is a linear polynomial. (v) The degree of 3t is 1. So, it is a linear polynomial. (vi) The degree of r 2 is 2. So, it is a quadratic polynomial. (vii) The degree of 7x 3 is 3. So, it is a cubic polynomial.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials (बहुपद) (Hindi Medium) Ex 2.1

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.2
Question 1. Find the value of the polynomial 5x – 4x 2 + 3 at (i) x = 0 (ii) x = – 1 (iii) x = 2 Solution: 1et p(x) = 5x – 4x 2 + 3 (i) p(0) = 5(0) – 4(0) 2 + 3 = 0 – 0 + 3 = 3 Thus, the value of 5x – 4x 2 + 3 at x = 0 is 3. (ii) p(-1) = 5(-1) – 4(-1) 2 + 3 = – 5x – 4x 2 + 3 = -9 + 3 = -6 Thus, the value of 5x – 4x 2 + 3 at x = -1 is -6. (iii) p(2) = 5(2) – 4(2) 2 + 3 = 10 – 4(4) + 3 = 10 – 16 + 3 = -3 Thus, the value of 5x – 4x 2 + 3 at x = 2 is – 3.
Question 2. Find p (0), p (1) and p (2) for each of the following polynomials. (i) p(y) = y 2 – y +1 (ii) p (t) = 2 +1 + 2t 2 -t 3 (iii) P (x) = x 3 (iv) p (x) = (x-1) (x+1) Solution: (i) Given that p(y) = y 2 – y + 1. ∴ P(0) = (0) 2 – 0 + 1 = 0 – 0 + 1 = 1 p(1) = (1) 2 – 1 + 1 = 1 – 1 + 1 = 1 p(2) = (2) 2 – 2 + 1 = 4 – 2 + 1 = 3 (ii) Given that p(t) = 2 + t + 2t 2 – t 3 ∴p(0) = 2 + 0 + 2(0) 2 – (0) 3 = 2 + 0 + 0 – 0=2 P(1) = 2 + 1 + 2(1) 2 – (1) 3 = 2 + 1 + 2 – 1 = 4 p( 2) = 2 + 2 + 2(2) 2 – (2) 3 = 2 + 2 + 8 – 8 = 4 (iii) Given that p(x) = x 3 ∴ p(0) = (0) 3 = 0, p(1) = (1) 3 = 1 p(2) = (2) 3 = 8 (iv) Given that p(x) = (x – 1)(x + 1) ∴ p(0) = (0 – 1)(0 + 1) = (-1)(1) = -1 p(1) = (1 – 1)(1 +1) = (0)(2) = 0 P(2) = (2 – 1)(2 + 1) = (1)(3) = 3
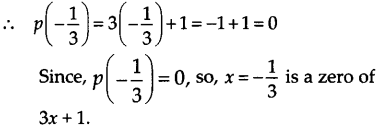
(iv) We have, p(x) = (x + 1)(x – 2) ∴ p(-1) = (-1 +1) (-1 – 2) = (0)(- 3) = 0 Since, p(-1) = 0, so, x = -1 is a zero of (x + 1)(x – 2). Also, p( 2) = (2 + 1)(2 – 2) = (3)(0) = 0 Since, p(2) = 0, so, x = 2 is also a zero of (x + 1)(x – 2).
(v) We have, p(x) = x 2 ∴ p(o) = (0) 2 = 0 Since, p(0) = 0, so, x = 0 is a zero of x 2 .
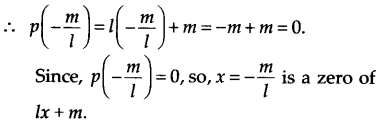
(viii) We have, p(x) = 2x + 1 ∴ \(p(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } )\quad =\quad 2(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } )+1=\quad 1+1\quad =\quad 2\) Since, \(p(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } )\) ≠ 0, so, x = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) is not a zero of 2x + 1.
Question 4. Find the zero of the polynomial in each of the following cases (i) p(x)=x+5 (ii) p (x) = x – 5 (iii) p (x) = 2x + 5 (iv) p (x) = 3x – 2 (v) p (x) = 3x (vi) p (x)= ax, a≠0 (vii) p (x) = cx + d, c ≠ 0 where c and d are real numbers. Solution: (i) We have, p(x) = x + 5. Since, p(x) = 0 ⇒ x + 5 = 0 ⇒ x = -5. Thus, zero of x + 5 is -5.
(ii) We have, p(x) = x – 5. Since, p(x) = 0 ⇒ x – 5 = 0 ⇒ x = -5 Thus, zero of x – 5 is 5.
(iii) We have, p(x) = 2x + 5. Since, p(x) = 0 ⇒ 2x + 5 =0 ⇒ 2x = -5 ⇒ x = \(\frac { -5 }{ 2 }\) Thus, zero of 2x + 5 is \(\frac { -5 }{ 2 }\) .
(iv) We have, p(x) = 3x – 2. Since, p(x) = 0 ⇒ 3x – 2 = 0 ⇒ 3x = 2 ⇒ x = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) Thus, zero of 3x – 2 is \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
(v) We have, p(x) = 3x. Since, p(x) = 0 ⇒ 3x = 0 ⇒ x = 0 Thus, zero of 3x is 0.
(vi) We have, p(x) = ax, a ≠ 0. Since, p(x) = 0 => ax = 0 => x-0 Thus, zero of ax is 0.
(vii) We have, p(x) = cx + d. Since, p(x) = 0 ⇒ cx + d = 0 ⇒ cx = -d ⇒ \( x =-\frac { d }{ c }\) Thus, zero of cx + d is \(-\frac { d }{ c }\)
NCERT So1utions for C1ass 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.3
Question 1. Find the remainder when x 3 + 3x 2 + 3x + 1 is divided by (i) x + 1 (ii) x – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (iii) x (iv) x + π (v) 5 + 2x Solution: Let p(x) = x 3 + 3x 2 + 3x +1 (i) The zero of x + 1 is -1. ∴ p(-1) = (-1)3 + 3(-1)2 + 3(-1) +1 = -1 + 3- 3 + 1 = 0 Thus, the required remainder = 0
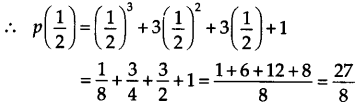
(iii) The zero of x is 0. ∴ p(0) = (0) 3 + 3(0) 2 + 3(0) + 1 = 0 + 0 + 0 + 1 = 1 Thus, the required remainder = 1.
(iv) The zero of x + π is -π. p(-π) = (-π) 3 + 3(- π) 2 2 + 3(- π) +1 = -π 3 + 3π 2 + (-3π) + 1 = – π 3 + 3π 2 – 3π +1 Thus, the required remainder is -π 3 + 3π 2 – 3π+1.
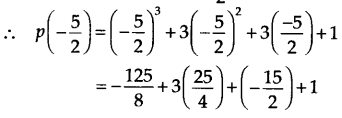
Question 2. Find the remainder when x 3 – ax 2 + 6x – a is divided by x – a. Solution: We have, p(x) = x 3 – ax 2 + 6x – a and zero of x – a is a. ∴ p(a) = (a) 3 – a(a) 2 + 6(a) – a = a 3 – a 3 + 6a – a = 5a Thus, the required remainder is 5a.
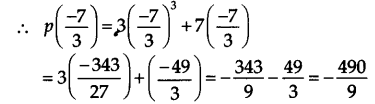
NCERT So1utions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.4
Question 1. Determine which of the following polynomials has (x +1) a factor. (i) x 3 +x 2 +x +1 (ii) x 4 + x 3 + x 2 + x + 1 (iii) x 4 + 3x 3 + 3x 2 + x + 1 (iv) x 3 – x 2 – (2 +√2 )x + √2 Solution: The zero of x + 1 is -1. (i) Let p (x) = x 3 + x 2 + x + 1 ∴ p (-1) = (-1) 3 + (-1) 2 + (-1) + 1 . = -1 + 1 – 1 + 1 ⇒ p (- 1) = 0 So, (x+ 1) is a factor of x 3 + x 2 + x + 1.
(ii) Let p (x) = x 4 + x 3 + x 2 + x + 1 ∴ P(-1) = (-1) 4 + (-1) 3 + (-1) 2 + (-1)+1 = 1 – 1 + 1 – 1 + 1 ⇒ P (-1) ≠ 1 So, (x + 1) is not a factor of x 4 + x 3 + x 2 + x+ 1.
(iii) Let p (x) = x 4 + 3x 3 + 3x 2 + x + 1 . ∴ p (-1)= (-1) 4 + 3 (-1) 3 + 3 (-1) 2 + (- 1) + 1 = 1 – 3 + 3 – 1 + 1 = 1 ⇒ p (-1) ≠ 0 So, (x + 1) is not a factor of x 4 + 3x 3 + 3x 2 + x+ 1.
(iv) Let p (x) = x 3 – x 2 – (2 + √2) x + √2 ∴ p (- 1) =(- 1)3- (-1)2 – (2 + √2)(-1) + √2 = -1 – 1 + 2 + √2 + √2 = 2√2 ⇒ p (-1) ≠ 0 So, (x + 1) is not a factor of x 3 – x 2 – (2 + √2) x + √2.
Question 2. Use the Factor Theorem to determine whether g (x) is a factor of p (x) in each of the following cases (i) p (x)= 2x 3 + x 2 – 2x – 1, g (x) = x + 1 (ii) p(x)= x 3 + 3x 2 + 3x + 1, g (x) = x + 2 (iii) p (x) = x 3 – 4x 2 + x + 6, g (x) = x – 3 Solution: (i) We have, p (x)= 2x 3 + x 2 – 2x – 1 and g (x) = x + 1 ∴ p(-1) = 2(-1) 3 + (-1) 2 – 2(-1) – 1 = 2(-1) + 1 + 2 – 1 = -2 + 1 + 2 -1 = 0 ⇒ p(-1) = 0, so g(x) is a factor of p(x).
(ii) We have, p(x) x 3 + 3x 2 + 3x + 1 and g(x) = x + 2 ∴ p(-2) = (-2) 3 + 3(-2) 2 + 3(-2) + 1 = -8 + 12 – 6 + 1 = -14 + 13 = -1 ⇒ p(-2) ≠ 0, so g(x) is not a factor of p(x).
(iii) We have, = x 3 – 4x 2 + x + 6 and g (x) = x – 3 ∴ p(3) = (3) 3 – 4(3) 2 + 3 + 6 = 27 – 4(9) + 3 + 6 = 27 – 36 + 3 + 6 = 0 ⇒ p(3) = 0, so g(x) is a factor of p(x).
Question 3. Find the value of k, if x – 1 is a factor of p (x) in each of the following cases (i) p (x) = x 2 + x + k (ii) p (x) = 2x 2 + kx + √2 (iii) p (x) = kx 2 – √2 x + 1 (iv) p (x) = kx 2 – 3x + k Solution: For (x – 1) to be a factor of p(x), p(1) should be equal to 0.
(i) Here, p(x) = x 2 + x + k Since, p(1) = (1) 2 +1 + k ⇒ p(1) = k + 2 = 0 ⇒ k = -2.
(ii) Here, p (x) = 2x 2 + kx + √2 Since, p(1) = 2(1) 2 + k(1) + √2 = 2 + k + √2 =0 k = -2 – √2 = -(2 + √2)
(iii) Here, p (x) = kx 2 – √2 x + 1 Since, p(1) = k(1) 2 – (1) + 1 = k – √2 + 1 = 0 ⇒ k = √2 -1
(iv) Here, p(x) = kx 2 – 3x + k p(1) = k(1) 2 – 3(1) + k = k – 3 + k = 2k – 3 = 0 ⇒ k = \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)
Question 4. Factorise (i) 12x 2 – 7x +1 (ii) 2x 2 + 7x + 3 (iii) 6x 2 + 5x – 6 (iv) 3x 2 – x – 4 Solution: (i) We have, 12x 2 – 7x + 1 = 12x 2 – 4x- 3x + 1 = 4x (3x – 1 ) -1 (3x – 1) = (3x -1) (4x -1) Thus, 12x 2 -7x + 3 = (2x – 1) (x + 3)
(ii) We have, 2x 2 + 7x + 3 = 2x 2 + x + 6x + 3 = x(2x + 1) + 3(2x + 1) = (2x + 1)(x + 3) Thus, 2×2 + 7x + 3 = (2x + 1)(x + 3)
(iii) We have, 6x 2 + 5x – 6 = 6x 2 + 9x – 4x – 6 = 3x(2x + 3) – 2(2x + 3) = (2x + 3)(3x – 2) Thus, 6x 2 + 5x – 6 = (2x + 3)(3x – 2)
(iv) We have, 3x 2 – x – 4 = 3x 2 – 4x + 3x – 4 = x(3x – 4) + 1(3x – 4) = (3x – 4)(x + 1) Thus, 3x 2 – x – 4 = (3x – 4)(x + 1)
Question 5. Factorise (i) x 3 – 2x 2 – x + 2 (ii) x 3 – 3x 2 – 9x – 5 (iii) x 3 + 13x 2 + 32x + 20 (iv) 2y 3 + y 2 – 2y – 1 Solution: (i) We have, x 3 – 2x 2 – x + 2 Rearranging the terms, we have x 3 – x – 2x 2 + 2 = x(x 2 – 1) – 2(x 2 -1) = (x 2 – 1)(x – 2) = [(x) 2 – (1) 2 ](x – 2) = (x – 1)(x + 1)(x – 2) [∵ (a 2 – b 2 ) = (a + b)(a-b)] Thus, x 3 – 2x 2 – x + 2 = (x – 1)(x + 1)(x – 2)
(ii) We have, x 3 – 3x 2 – 9x – 5 = x 3 + x 2 – 4x 2 – 4x – 5x – 5 , = x 2 (x + 1) – 4x(x + 1) – 5(x + 1) = (x + 1)(x 2 – 4x – 5) = (x + 1)(x 2 – 5x + x – 5) = (x + 1)[x(x – 5) + 1(x – 5)] = (x + 1)(x – 5)(x + 1) Thus, x 3 – 3x 2 – 9x – 5 = (x + 1)(x – 5)(x +1)
(iii) We have, x 3 + 13x 2 + 32x + 20 = x 3 + x 2 + 12x 2 + 12x + 20x + 20 = x 2 (x + 1) + 12x(x +1) + 20(x + 1) = (x + 1)(x 2 + 12x + 20) = (x + 1)(x 2 + 2x + 10x + 20) = (x + 1)[x(x + 2) + 10(x + 2)] = (x + 1)(x + 2)(x + 10) Thus, x 3 + 13x 2 + 32x + 20 = (x + 1)(x + 2)(x + 10)
(iv) We have, 2y 3 + y 2 – 2y – 1 = 2y 3 – 2y 2 + 3y 2 – 3y + y – 1 = 2y 2 (y – 1) + 3y(y – 1) + 1(y – 1) = (y – 1)(2y 2 + 3y + 1) = (y – 1)(2y 2 + 2y + y + 1) = (y – 1)[2y(y + 1) + 1(y + 1)] = (y – 1)(y + 1)(2y + 1) Thus, 2y 3 + y 2 – 2y – 1 = (y – 1)(y + 1)(2y +1)
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.5
Question 1. Use suitable identities to find the following products (i) (x + 4)(x + 10) (ii) (x+8) (x -10) (iii) (3x + 4) (3x – 5) (iv) (y 2 + \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)) (y 2 – \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)) (v) (3 – 2x) (3 + 2x) Solution: (i) We have, (x+ 4) (x + 10) Using identity, (x+ a) (x+ b) = x 2 + (a + b) x+ ab. We have, (x + 4) (x + 10) = x 2 +(4 + 10) x + (4 x 10) = x 2 + 14x+40
(ii) We have, (x+ 8) (x -10) Using identity, (x + a) (x + b) = x 2 + (a + b) x + ab We have, (x + 8) (x – 10) = x 2 + [8 + (-10)] x + (8) (- 10) = x 2 – 2x – 80
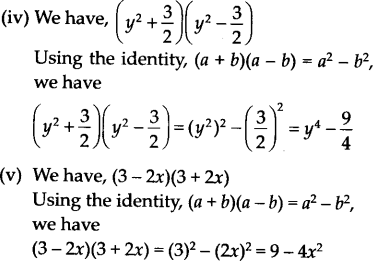
Question 2. Evaluate the following products without multiplying directly (i) 103 x 107 (ii) 95 x 96 (iii) 104 x 96 Solution: (i)We have, 103 x 107 = (100 + 3) (100 + 7) = ( 100) 2 + (3 + 7) (100)+ (3 x 7) [Using (x + a)(x + b) = x 2 + (a + b)x + ab] = 10000 + (10) x 100 + 21 = 10000 + 1000 + 21=11021
(ii) We have, 95 x 96 = (100 – 5) (100 – 4) = ( 100) 2 + [(- 5) + (- 4)] 100 + (- 5 x – 4) [Using (x + a)(x + b) = x 2 + (a + b)x + ab] = 10000 + (-9) + 20 = 9120 = 10000 + (-900) + 20 = 9120
(iii) We have 104 x 96 = (100 + 4) (100 – 4) = (100) 2 -4 2 [Using (a + b)(a -b) = a 2 – b 2 ] = 10000 – 16 = 9984
Question 3. Factorise the following using appropriate identities (i) 9x 2 + 6xy + y 2 (ii) 4y 2 -4y + 1 (iii) x 2 – \(\frac { { y }^{ 2 } }{ 100 }\) Solution: (i) We have, 9x 2 + 6xy + y 2 = (3x) 2 + 2(3x)(y) + (y) 2 = (3x + y) 2 [Using a 2 + 2ab + b 2 = (a + b) 2 ] = (3x + y)(3x + y)
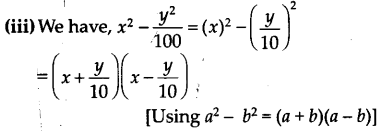
Question 4. Expand each of the following, using suitable identity (i) (x+2y+ 4z) 2 (ii) (2x – y + z) 2 (iii) (- 2x + 3y + 2z) 2 (iv) (3a -7b – c) z (v) (- 2x + 5y – 3z) 2 (vi) [ \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)a –\(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)b + 1] 2 Solution: We know that (x + y + z) 2 = x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2xy + 2yz + 2zx
(i) (x + 2y + 4z) 2 = x 2 + (2y) 2 + (4z) 2 + 2 (x) (2y) + 2 (2y) (4z) + 2(4z) (x) = x 2 + 4y 2 + 16z 2 + 4xy + 16yz + 8 zx
(ii) (2x – y + z) 2 = (2x) 2 + (- y) 2 + z 2 + 2 (2x) (- y)+ 2 (- y) (z) + 2 (z) (2x) = 4x 2 + y 2 + z 2 – 4xy – 2yz + 4zx
(iii) (- 2x + 3y + 2z) 2 = (- 2x) 2 + (3y) 2 + (2z) 2 + 2 (- 2x) (3y)+ 2 (3y) (2z) + 2 (2z) (- 2x) = 4x 2 + 9y 2 + 4z 2 – 12xy + 12yz – 8zx
(iv) (3a -7b- c) 2 = (3a) 2 + (- 7b) 2 + (- c) 2 + 2 (3a) (- 7b) + 2 (- 7b) (- c) + 2 (- c) (3a) = 9a 2 + 49b 2 + c 2 – 42ab + 14bc – 6ac
(v)(- 2x + 5y- 3z) 2 = (- 2x) 2 + (5y) 2 + (- 3z) 2 + 2 (- 2x) (5y) + 2 (5y) (- 3z) + 2 (- 3z) (- 2x) = 4x 2 + 25y 2 + 9z 2 – 20xy – 30yz + 12zx
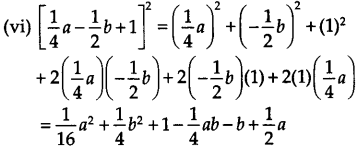
Question 5. Factorise (i) 4 x 2 + 9y 2 + 16z 2 + 12xy – 24yz – 16xz (ii) 2x 2 + y 2 + 8z 2 – 2√2xy + 4√2yz – 8xz Solution: (i) 4x 2 + 9y 2 + 16z 2 + 12xy – 24yz – 16xz = (2x) 2 + (3y) 2 + (- 4z) 2 + 2 (2x) (3y) + 2 (3y) (- 4z) + 2 (- 4z) (2x) = (2x + 3y – 4z) 2 = (2x + 3y + 4z) (2x + 3y – 4z)
(ii) 2x 2 + y 2 + 8z 2 – 2√2xy + 4√2yz – 8xz = (- √2x) 2 + (y) 2 + (2 √2z) 2 y + 2(- √2x) (y)+ 2 (y) (2√2z) + 2 (2√2z) (- √2x) = (- √2x + y + 2 √2z) 2 = (- √2x + y + 2 √2z) (- √2x + y + 2 √2z)

(i) (2x + 1) 3 = (2x) 3 + (1) 3 + 3(2x)(1)(2x + 1) [By (1)] = 8x 3 + 1 + 6x(2x + 1) = 8x 3 + 12x 2 + 6x + 1
(ii) (2a – 3b) 3 = (2a) 3 – (3b) 3 – 3(2a)(3b)(2a – 3b) [By (2)] = 8a 3 – 27b 3 – 18ab(2a – 3b) = 8a 3 – 27b 3 – 36a 2 b + 54ab 2
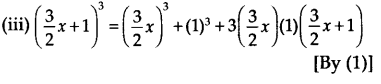
Question 7. Evaluate the following using suitable identities (i) (99) 3 (ii) (102) 3 (iii) (998) 3 Solution: (i) We have, 99 = (100 -1) ∴ 99 3 = (100 – 1) 3 = (100) 3 – 1 3 – 3(100)(1)(100 -1) [Using (a – b) 3 = a 3 – b 3 – 3ab (a – b)] = 1000000 – 1 – 300(100 – 1) = 1000000 -1 – 30000 + 300 = 1000300 – 30001 = 970299
(ii) We have, 102 =100 + 2 ∴ 102 3 = (100 + 2) 3 = (100) 3 + (2) 3 + 3(100)(2)(100 + 2) [Using (a + b) 3 = a 3 + b 3 + 3ab (a + b)] = 1000000 + 8 + 600(100 + 2) = 1000000 + 8 + 60000 + 1200 = 1061208
(iii) We have, 998 = 1000 – 2 ∴ (998) 3 = (1000-2) 3 = (1000) 3 – (2) 3 – 3(1000)(2)(1000 – 2) [Using (a – b) 3 = a 3 – b 3 – 3ab (a – b)] = 1000000000 – 8 – 6000(1000 – 2) = 1000000000 – 8 – 6000000 +12000 = 994011992
(ii) 8a 3 – b 3 – 12o 2 b + 6ab 2 = (2a) 3 – (b) 3 – 3(2a)(b)(2a – b) = (2a – b) 3 [Using a 3 + b 3 + 3 ab(a + b) = (a + b) 3 ] = (2a – b) (2a – b) (2a – b)
(iii) 27 – 125a 3 – 135a + 225a 2 = (3) 3 – (5a) 3 – 3(3)(5a)(3 – 5a) = (3 – 5a) 3 [Using a 3 + b 3 + 3 ab(a + b) = (a + b) 3 ] = (3 – 5a) (3 – 5a) (3 – 5a)
(iv) 64a 3 -27b 3 -144a 2 b + 108ab 2 = (4a) 3 – (3b) 3 – 3(4a)(3b)(4a – 3b) = (4a – 3b) 3 [Using a 3 – b 3 – 3 ab(a – b) = (a – b) 3 ] = (4a – 3b)(4a – 3b)(4a – 3b)
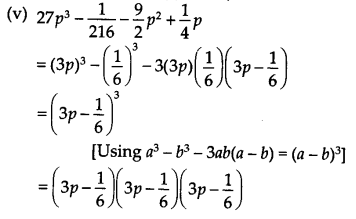
Question 9. Verify (i) x 3 + y 3 = (x + y)-(x 2 – xy + y 2 ) (ii) x 3 – y 3 = (x – y) (x 2 + xy + y 2 ) Solution: (i) ∵ (x + y) 3 = x 3 + y 3 + 3xy(x + y) ⇒ (x + y) 3 – 3(x + y)(xy) = x 3 + y 3 ⇒ (x + y)[(x + y)2-3xy] = x 3 + y 3 ⇒ (x + y)(x 2 + y 2 – xy) = x 3 + y 3 Hence, verified.
(ii) ∵ (x – y) 3 = x 3 – y 3 – 3xy(x – y) ⇒ (x – y) 3 + 3xy(x – y) = x 3 – y 3 ⇒ (x – y)[(x – y) 2 + 3xy)] = x 3 – y 3 ⇒ (x – y)(x 2 + y 2 + xy) = x 3 – y 3 Hence, verified.
Question 10. Factorise each of the following (i) 27y 3 + 125z 3 (ii) 64m 3 – 343n 3 [Hint See question 9] Solution: (i) We know that x 3 + y 3 = (x + y)(x 2 – xy + y 2 ) We have, 27y 3 + 125z 3 = (3y) 3 + (5z) 3 = (3y + 5z)[(3y) 2 – (3y)(5z) + (5z) 2 ] = (3y + 5z)(9y 2 – 15yz + 25z 2 )
(ii) We know that x 3 – y 3 = (x – y)(x 2 + xy + y 2 ) We have, 64m 3 – 343n 3 = (4m) 3 – (7n) 3 = (4m – 7n)[(4m) 2 + (4m)(7n) + (7n) 2 ] = (4m – 7n)(16m 2 + 28mn + 49n 2 )
Question 11. Factorise 27x 3 +y 3 +z 3 -9xyz. Solution: We have, 27x 3 + y 3 + z 3 – 9xyz = (3x) 3 + (y) 3 + (z) 3 – 3(3x)(y)(z) Using the identity, x 3 + y 3 + z 3 – 3xyz = (x + y + z)(x 2 + y 2 + z 2 – xy – yz – zx) We have, (3x) 3 + (y) 3 + (z) 3 – 3(3x)(y)(z) = (3x + y + z)[(3x) 3 + y 3 + z 3 – (3x × y) – (y × 2) – (z × 3x)] = (3x + y + z)(9x 2 + y 2 + z 2 – 3xy – yz – 3zx)
Question 12. Verify that x 3 +y 3 +z 3 – 3xyz = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (x + y+z)[(x-y) 2 + (y – z) 2 +(z – x) 2 ] Solution: R.H.S = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)(x + y + z)[(x – y) 2 +(y – z) 2 +(z – x) 2 ] = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (x + y + 2)[(x 2 + y 2 – 2xy) + (y 2 + z 2 – 2yz) + (z 2 + x 2 – 2zx)] = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (x + y + 2)(x 2 + y 2 + y 2 + z 2 + z 2 + x 2 – 2xy – 2yz – 2zx) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (x + y + z)[2(x 2 + y 2 + z 2 – xy – yz – zx)] = 2 x \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x (x + y + z)(x 2 + y 2 + z 2 – xy – yz – zx) = (x + y + z)(x 2 + y 2 + z 2 – xy – yz – zx) = x 3 + y 3 + z 3 – 3xyz = L.H.S. Hence, verified.
Question 13. If x + y + z = 0, show that x 3 + y 3 + z 3 = 3 xyz. Solution: Since, x + y + z = 0 ⇒ x + y = -z (x + y) 3 = (-z) 3 ⇒ x 3 + y 3 + 3xy(x + y) = -z 3 ⇒ x 3 + y 3 + 3xy(-z) = -z 3 [∵ x + y = -z] ⇒ x 3 + y 3 – 3xyz = -z 3 ⇒ x 3 + y 3 + z 3 = 3xyz Hence, if x + y + z = 0, then x 3 + y 3 + z 3 = 3xyz
Question 14. Without actually calculating the cubes, find the value of each of the following (i) (- 12) 3 + (7) 3 + (5) 3 (ii) (28) 3 + (- 15) 3 + (- 13) 3 Solution: (i) We have, (-12) 3 + (7) 3 + (5) 3 Let x = -12, y = 7 and z = 5. Then, x + y + z = -12 + 7 + 5 = 0 We know that if x + y + z = 0, then, x 3 + y 3 + z 3 = 3xyz ∴ (-12) 3 + (7) 3 + (5) 3 = 3[(-12)(7)(5)] = 3[-420] = -1260
(ii) We have, (28) 3 + (-15) 3 + (-13) 3 Let x = 28, y = -15 and z = -13. Then, x + y + z = 28 – 15 – 13 = 0 We know that if x + y + z = 0, then x 3 + y 3 + z 3 = 3xyz ∴ (28) 3 + (-15) 3 + (-13) 3 = 3(28)(-15)(-13) = 3(5460) = 16380
Question 15. Give possible expressions for the length and breadth of each of the following rectangles, in which their areas are given (i) Area 25a 2 – 35a + 12 (ii) Area 35y 2 + 13y – 12 Solution: Area of a rectangle = (Length) x (Breadth) (i) 25a 2 – 35a + 12 = 25a 2 – 20a – 15a + 12 = 5a(5a – 4) – 3(5a – 4) = (5a – 4)(5a – 3) Thus, the possible length and breadth are (5a – 3) and (5a – 4).
(ii) 35y 2 + 13y -12 = 35y 2 + 28y – 15y -12 = 7y(5y + 4) – 3(5y + 4) = (5 y + 4)(7y – 3) Thus, the possible length and breadth are (7y – 3) and (5y + 4).
Question 16. What are the possible expressions for the dimensions of the cuboids whose volumes are given below? (i) Volume 3x 2 – 12x (ii) Volume 12ky 2 + 8ky – 20k Solution: Volume of a cuboid = (Length) x (Breadth) x (Height) (i) We have, 3x 2 – 12x = 3(x 2 – 4x) = 3 x x x (x – 4) ∴ The possible dimensions of the cuboid are 3, x and (x – 4).
(ii) We have, 12ky 2 + 8ky – 20k = 4[3ky 2 + 2ky – 5k] = 4[k(3y 2 + 2y – 5)] = 4 x k x (3y 2 + 2y – 5) = 4k[3y 2 – 3y + 5y – 5] = 4k[3y(y – 1) + 5(y – 1)] = 4k[(3y + 5) x (y – 1)] = 4k x (3y + 5) x (y – 1) Thus, the possible dimensions of the cuboid are 4k, (3y + 5) and (y -1).
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths
- Chapter 1 Number systems
- Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry
- Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Chapter 5 Introduction to Euclid Geometry
- Chapter 6 Lines and Angles
- Chapter 7 Triangles
- Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals
- Chapter 9 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
- Chapter 10 Circles
- Chapter 11 Constructions
- Chapter 12 Heron’s Formula
- Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes
- Chapter 14 Statistics
- Chapter 15 Probability
- Class 9 Maths (Download PDF)
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.1, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.1, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources

(Education-Your Door To The Future)
CBSE Class 9 Maths Most Important Case Study Based Questions With Solution
Cbse class 9 mathematics case study questions.
In this post I have provided CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Study Based Questions With Solution. These questions are very important for those students who are preparing for their final class 9 maths exam.

All these questions provided in this article are with solution which will help students for solving the problems. Dear students need to practice all these questions carefully with the help of given solutions.
As you know CBSE Class 9 Maths exam will have a set of cased study based questions in the form of MCQs. CBSE Class 9 Maths Question Bank given in this article can be very helpful in understanding the new format of questions for new session.
All Of You Can Also Read
Case studies in class 9 mathematics.
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has included case study based questions in the Class 9 Mathematics paper in current session. According to new pattern CBSE Class 9 Mathematics students will have to solve case based questions. This is a departure from the usual theoretical conceptual questions that are asked in Class 9 Maths exam in this year.
Each question provided in this post has five sub-questions, each followed by four options and one correct answer. All CBSE Class 9th Maths Students can easily download these questions in PDF form with the help of given download Links and refer for exam preparation.
There is many more free study materials are available at Maths And Physics With Pandey Sir website. For many more books and free study material all of you can visit at this website.
Given Below Are CBSE Class 9th Maths Case Based Questions With Their Respective Download Links.
| Case-based Questions – 1 | |
| Case-based Questions – 2 | |
| Case-based Questions – 3 | |
| Case-based Questions – 4 | |
| Case-based Questions – 5 | |
| Case-based Questions – 6 | |
| Case-based Questions – 7 | |
| Case-based Questions – 8 | |
| Case-based Questions – 9 | |
| Case-based Questions – 10 | |
| Case-based Questions – 11 | |
| Case-based Questions – 12 | |
| Case-based Questions – 13 | |
| Case-based Questions – 14 | |
| Case-based Questions – 15 | |
| Case-based Questions – 16 | |
| Case-based Questions – 17 | |
| Case-based Questions – 18 | |
| Case-based Questions – 19 | |
| Case-based Questions – 20 | |
| Case-based Questions – 21 | |
| Case-based Questions – 22 | |
| Case-based Questions – 23 | |
| Case-based Questions – 24 | |
| Case-based Questions – 25 | |
| Case-based Questions – 26 | |
| Case-based Questions – 27 | |
| Case-based Questions – 28 | |
| Case-based Questions – 29 | |
| Case-based Questions – 30 |
Experience Teachmint X - AI driven Interactive Flat Panels and Smart Boards

More from SRINIVAS EDLA
Recommended content, learn from anywhere on any device.
Top Leader by G2
Top Performer by SourceForge
Top Leader by SoftwareSuggest
Ranked Amongst Top 25 Companies by LinkedIn
ISO27001 Certified
Most Preferred Workplace
We use cookies to enhance site navigation and analyse usage, read our Privacy Policy for more.
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 9
- NCERT 9 Maths
- Chapter 2: Polynomial
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
Ncert solutions class 9 maths chapter 2 – polynomials free pdf download.
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials are provided here. BYJU’S expert faculty create these NCERT Solutions to help students in preparation for their exams. BYJU’S provides NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths which will help students to solve problems easily. They give a detailed and stepwise explanation of each answer to the problems given in the exercises in the NCERT textbook for Class 9.
Download Exclusively Curated Chapter Notes for Class 9 Maths Chapter – 2 Polynomials
Download most important questions for class 9 maths chapter – 2 polynomials.
In NCERT Solutions for Class 9, students are introduced to many important topics that will be helpful for those who wish to pursue Mathematics as a subject in higher studies. NCERT Solutions help students to prepare for their upcoming exams by covering the updated CBSE syllabus for 2023-24 and its guidelines.
- Chapter 1: Number System
- Chapter 2: Polynomials
- Chapter 3: Coordinate Geometry
- Chapter 4: Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Chapter 5: Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry
- Chapter 6: Lines and Angles
- Chapter 7: Triangles
- Chapter 8: Quadrilaterals
- Chapter 9: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
- Chapter 10: Circles
- Chapter 11: Constructions
- Chapter 12: Heron’s Formula
- Chapter 13: Surface Areas and Volumes
- Chapter 14: Statistics
NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Topics
As this is one of the important Chapters in Class 9 Maths, it comes under the unit – Algebra and has a weightage of 12 marks in the Class 9 Maths CBSE examination. This chapter talks about:
- Polynomials in One Variable
- Zeroes of a Polynomial
- Remainder Theorem
- Factorisation of Polynomials
- Algebraic Identities
Students can refer to the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 while solving exercise problems and preparing for their Class 9 Maths exams.
NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 – Polynomials Summary
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials is the second chapter of Class 9 Maths. Polynomials are introduced and discussed in detail here. The chapter discusses Polynomials and their applications. The introduction of the chapter includes whole numbers, integers, and rational numbers.
The chapter starts with the introduction of Polynomials in section 2.1, followed by two very important topics in sections 2.2 and 2.3
- Polynomials in one Variable – Discussion of Linear, Quadratic and Cubic Polynomial.
- Zeroes of a Polynomial – A zero of a polynomial need not be zero and can have more than one zero.
- Real Numbers and their Decimal Expansions – Here, you study the decimal expansions of real numbers and see whether they can help in distinguishing between rational and irrational numbers.
Next, it discusses the following topics:
- Representing Real Numbers on the Number Line – In this, the solutions for 2 problems in Exercise 2.4.
- Operations on Real Numbers – Here, you explore some of the operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division on irrational numbers.
- Laws of Exponents for Real Numbers – Use these laws of exponents to solve the questions.
Key Advantages of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 – Polynomials
- These NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths help you solve and revise the updated CBSE syllabus of Class 9 for 2023-24.
- After going through the stepwise solutions given by our subject expert teachers, you will be able to score more marks.
- It follows NCERT guidelines which help in preparing the students accordingly.
- It contains all the important questions from the examination point of view.
- It helps in scoring well in Class 10 CBSE Maths exams.
To learn the NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials offline, click on the below link:
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 – Polynomials
carouselExampleControls111

Previous Next
List of Exercises in Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials contains 5 exercises. Based on the concept of polynomials, each exercise provides a number of questions. Click on the below links to access the exercise-wise NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 polynomials.
Exercise 2.1 Solutions 5 Questions
Exercise 2.2 Solutions 4 Questions
Exercise 2.3 Solutions 3 Questions
Exercise 2.4 Solutions 5 Questions
Exercise 2.5 Solutions 16 Questions
Access Answers of NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 – Polynomials
Exercise 2.1 page: 32.
1. Which of the following expressions are polynomials in one variable, and which are not? State reasons for your answer.
(i) 4x 2 –3x+7
The equation 4x 2 –3x+7 can be written as 4x 2 –3x 1 +7x 0
Since x is the only variable in the given equation and the powers of x (i.e. 2, 1 and 0) are whole numbers, we can say that the expression 4x 2 –3x+7 is a polynomial in one variable.
(ii) y 2 +√2
The equation y 2 + √2 can be written as y 2 + √ 2y 0
Since y is the only variable in the given equation and the powers of y (i.e., 2 and 0) are whole numbers, we can say that the expression y 2 + √ 2 is a polynomial in one variable.
(iii) 3√t+t√2
The equation 3√t+t√2 can be written as 3t 1/2 +√2t
Though t is the only variable in the given equation, the power of t (i.e., 1/2) is not a whole number. Hence, we can say that the expression 3√t+t√2 is not a polynomial in one variable.
The equation y+2/y can be written as y+2y -1
Though y is the only variable in the given equation, the power of y (i.e., -1) is not a whole number. Hence, we can say that the expression y+2/y is not a polynomial in one variable.
(v) x 10 +y 3 +t 50
Here, in the equation x 10 +y 3 +t 50
Though the powers, 10, 3, 50, are whole numbers, there are 3 variables used in the expression
x 10 +y 3 +t 50 . Hence, it is not a polynomial in one variable.
2. Write the coefficients of x 2 in each of the following:
(i) 2+x 2 +x
The equation 2+x 2 +x can be written as 2+(1)x 2 +x
We know that the coefficient is the number which multiplies the variable.
Here, the number that multiplies the variable x 2 is 1
Hence, the coefficient of x 2 in 2+x 2 +x is 1.
(ii) 2–x 2 +x 3
The equation 2–x 2 +x 3 can be written as 2+(–1)x 2 +x 3
We know that the coefficient is the number (along with its sign, i.e. – or +) which multiplies the variable.
Here, the number that multiplies the variable x 2 is -1
Hence, the coefficient of x 2 in 2–x 2 +x 3 is -1.
(iii) ( π /2)x 2 +x
The equation (π/2)x 2 +x can be written as (π/2)x 2 + x
Here, the number that multiplies the variable x 2 is π/2.
Hence, the coefficient of x 2 in (π/2)x 2 +x is π/2.
Here, the number that multiplies the variable x 2 is 0
Hence, the coefficient of x 2 in √2x-1 is 0.
3. Give one example each of a binomial of degree 35, and of a monomial of degree 100.
Binomial of degree 35: A polynomial having two terms and the highest degree 35 is called a binomial of degree 35.
For example, 3x 35 +5
Monomial of degree 100: A polynomial having one term and the highest degree 100 is called a monomial of degree 100.
For example, 4x 100
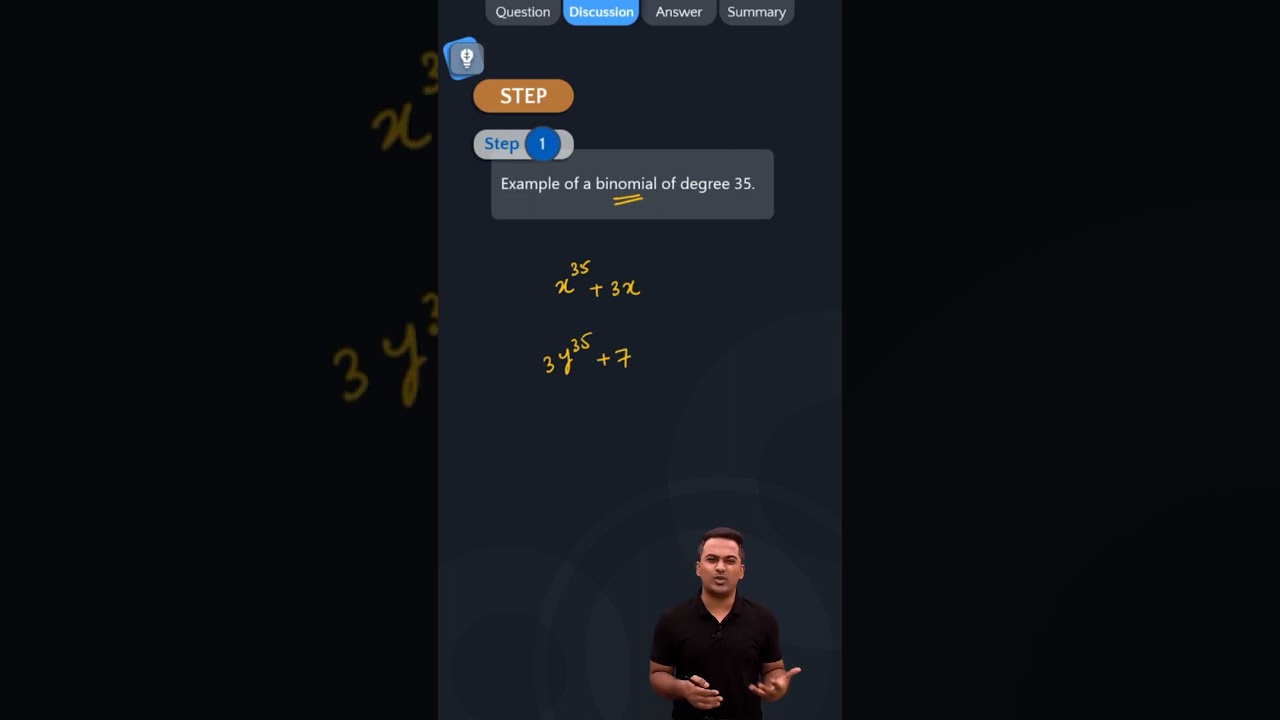
4. Write the degree of each of the following polynomials:
(i) 5x 3 +4x 2 +7x
The highest power of the variable in a polynomial is the degree of the polynomial.
Here, 5x 3 +4x 2 +7x = 5x 3 +4x 2 +7x 1
The powers of the variable x are: 3, 2, 1
The degree of 5x 3 +4x 2 +7x is 3, as 3 is the highest power of x in the equation.
Here, in 4–y 2 ,
The power of the variable y is 2
The degree of 4–y 2 is 2, as 2 is the highest power of y in the equation.
(iii) 5t–√7
Here, in 5t –√7
The power of the variable t is: 1
The degree of 5t –√7 is 1, as 1 is the highest power of y in the equation.
Here, 3 = 3×1 = 3× x 0
The power of the variable here is: 0
Hence, the degree of 3 is 0.
5. Classify the following as linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials:
We know that,
Linear polynomial: A polynomial of degree one is called a linear polynomial.
Quadratic polynomial: A polynomial of degree two is called a quadratic polynomial.
Cubic polynomial: A polynomial of degree three is called a cubic polynomial.
The highest power of x 2 +x is 2
The degree is 2
Hence, x 2 +x is a quadratic polynomial
The highest power of x–x 3 is 3
The degree is 3
Hence, x–x 3 is a cubic polynomial
(iii) y+y 2 +4
The highest power of y+y 2 +4 is 2
Hence, y+y 2 +4 is a quadratic polynomial
The highest power of 1+x is 1
The degree is 1
Hence, 1+x is a linear polynomial.
The highest power of 3t is 1
Hence, 3t is a linear polynomial.
The highest power of r 2 is 2
Hence, r 2 is a quadratic polynomial.
The highest power of 7x 3 is 3
Hence, 7x 3 is a cubic polynomial.
Exercise 2.2 Page: 34
1. Find the value of the polynomial (x)=5x−4x 2 +3.
(ii) x = – 1
(iii) x = 2
Let f(x) = 5x−4x 2 +3
(i) When x = 0
f(0) = 5(0)-4(0) 2 +3
(ii) When x = -1
f(x) = 5x−4x 2 +3
f(−1) = 5(−1)−4(−1) 2 +3
(iii) When x = 2
f(2) = 5(2)−4(2) 2 +3
2. Find p(0), p(1) and p(2) for each of the following polynomials:
(i) p(y)=y 2 −y+1
p(y) = y 2 –y+1
∴ p(0) = (0) 2 −(0)+1 = 1
p(1) = (1) 2 –(1)+1 = 1
p(2) = (2) 2 –(2)+1 = 3
(ii) p(t)=2+t+2t 2 −t 3
p(t) = 2+t+2t 2 −t 3
∴ p(0) = 2+0+2(0) 2 –(0) 3 = 2
p(1) = 2+1+2(1) 2 –(1) 3 =2+1+2–1 = 4
p(2) = 2+2+2(2) 2 –(2) 3 =2+2+8–8 = 4
(iii) p(x)=x 3
∴ p(0) = (0) 3 = 0
p(1) = (1) 3 = 1
p(2) = (2) 3 = 8
(iv) P(x) = (x−1)(x+1)
p(x) = (x–1)(x+1)
∴ p(0) = (0–1)(0+1) = (−1)(1) = –1
p(1) = (1–1)(1+1) = 0(2) = 0
p(2) = (2–1)(2+1) = 1(3) = 3
3. Verify whether the following are zeroes of the polynomial indicated against them.
(i) p(x)=3x+1, x = −1/3
For, x = -1/3, p(x) = 3x+1
∴ p(−1/3) = 3(-1/3)+1 = −1+1 = 0
∴ -1/3 is a zero of p(x).
(ii) p(x) = 5x–π, x = 4/5
For, x = 4/5, p(x) = 5x–π
∴ p(4/5) = 5(4/5)- π = 4-π
∴ 4/5 is not a zero of p(x).
(iii) p(x) = x 2 −1, x = 1, −1
For, x = 1, −1;
p(x) = x 2 −1
∴ p(1)=1 2 −1=1−1 = 0
p(−1)=(-1) 2 −1 = 1−1 = 0
∴ 1, −1 are zeros of p(x).
(iv) p(x) = (x+1)(x–2), x =−1, 2
For, x = −1,2;
p(x) = (x+1)(x–2)
∴ p(−1) = (−1+1)(−1–2)
= (0)(−3) = 0
p(2) = (2+1)(2–2) = (3)(0) = 0
∴ −1, 2 are zeros of p(x).
(v) p(x) = x 2 , x = 0
For, x = 0 p(x) = x 2
p(0) = 0 2 = 0
∴ 0 is a zero of p(x).
(vi) p(x) = lx +m, x = −m/ l
For, x = -m/ l ; p(x) = l x+m
∴ p(-m/ l) = l (-m/ l )+m = −m+m = 0
∴ -m/ l is a zero of p(x).
(vii) p(x) = 3x 2 −1, x = -1/√3 , 2/√3
For, x = -1/√3 , 2/√3 ; p(x) = 3x 2 −1
∴ p(-1/√3) = 3(-1/√3) 2 -1 = 3(1/3)-1 = 1-1 = 0
∴ p(2/√3 ) = 3(2/√3) 2 -1 = 3(4/3)-1 = 4−1 = 3 ≠ 0
∴ -1/√3 is a zero of p(x), but 2/√3 is not a zero of p(x).
(viii) p(x) =2x+1, x = 1/2
For, x = 1/2 p(x) = 2x+1
∴ p(1/2) = 2(1/2)+1 = 1+1 = 2≠0
∴ 1/2 is not a zero of p(x).
4. Find the zero of the polynomials in each of the following cases:
(i) p(x) = x+5
∴ -5 is a zero polynomial of the polynomial p(x).
(ii) p(x) = x–5
∴ 5 is a zero polynomial of the polynomial p(x).
(iii) p(x) = 2x+5
p(x) = 2x+5
∴x = -5/2 is a zero polynomial of the polynomial p(x).
(iv) p(x) = 3x–2
p(x) = 3x–2
∴ x = 2/3 is a zero polynomial of the polynomial p(x).
(v) p(x) = 3x
∴ 0 is a zero polynomial of the polynomial p(x).
(vi) p(x) = ax, a≠0
∴ x = 0 is a zero polynomial of the polynomial p(x).
(vii) p(x) = cx+d, c ≠ 0, c, d are real numbers.
p(x) = cx + d
∴ x = -d/c is a zero polynomial of the polynomial p(x).
Exercise 2.3 Page: 40
1. Find the remainder when x 3 +3x 2 +3x+1 is divided by
∴ Remainder:
p(−1) = (−1) 3 +3(−1) 2 +3(−1)+1
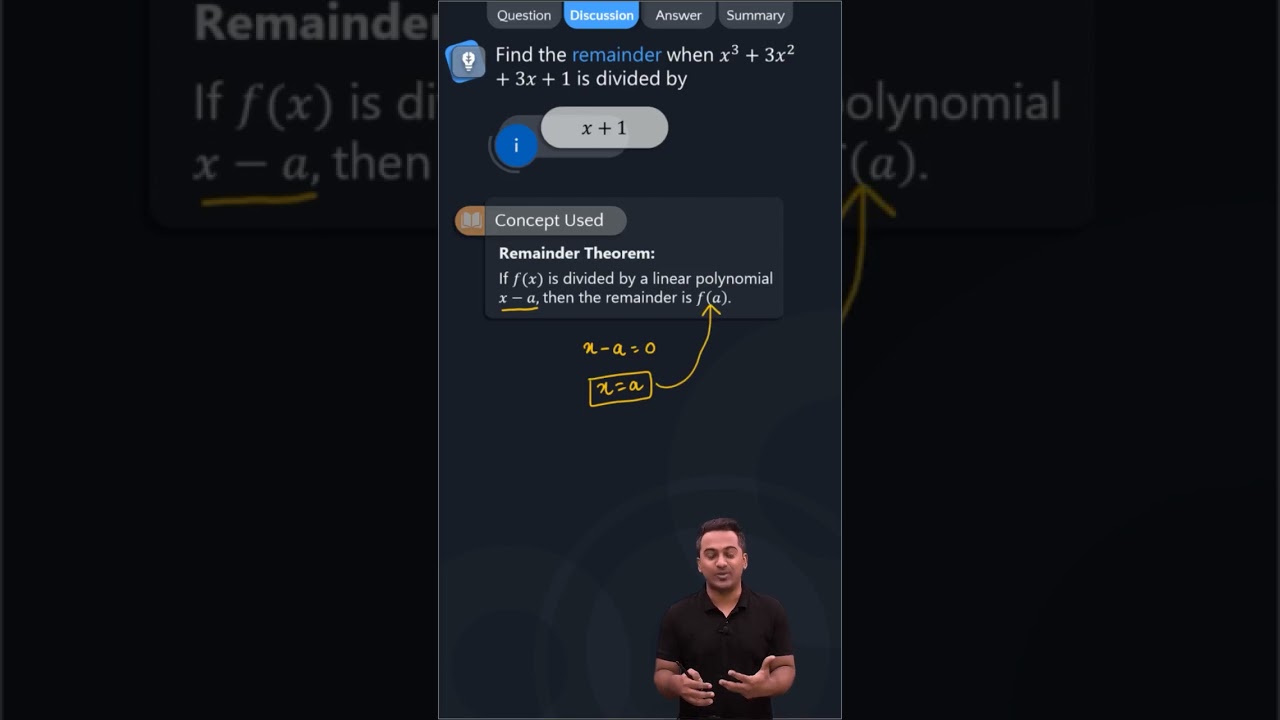
p(1/2) = (1/2) 3 +3(1/2) 2 +3(1/2)+1
= (1/8)+(3/4)+(3/2)+1
p(0) = (0) 3 +3(0) 2 +3(0)+1
p(0) = (−π) 3 +3(−π) 2 +3(−π)+1
= −π 3 +3π 2 −3π+1
(-5/2) 3 +3(-5/2) 2 +3(-5/2)+1 = (-125/8)+(75/4)-(15/2)+1
2. Find the remainder when x 3 −ax 2 +6x−a is divided by x-a.
Let p(x) = x 3 −ax 2 +6x−a
p(a) = (a) 3 −a(a 2 )+6(a)−a
= a 3 −a 3 +6a−a = 5a
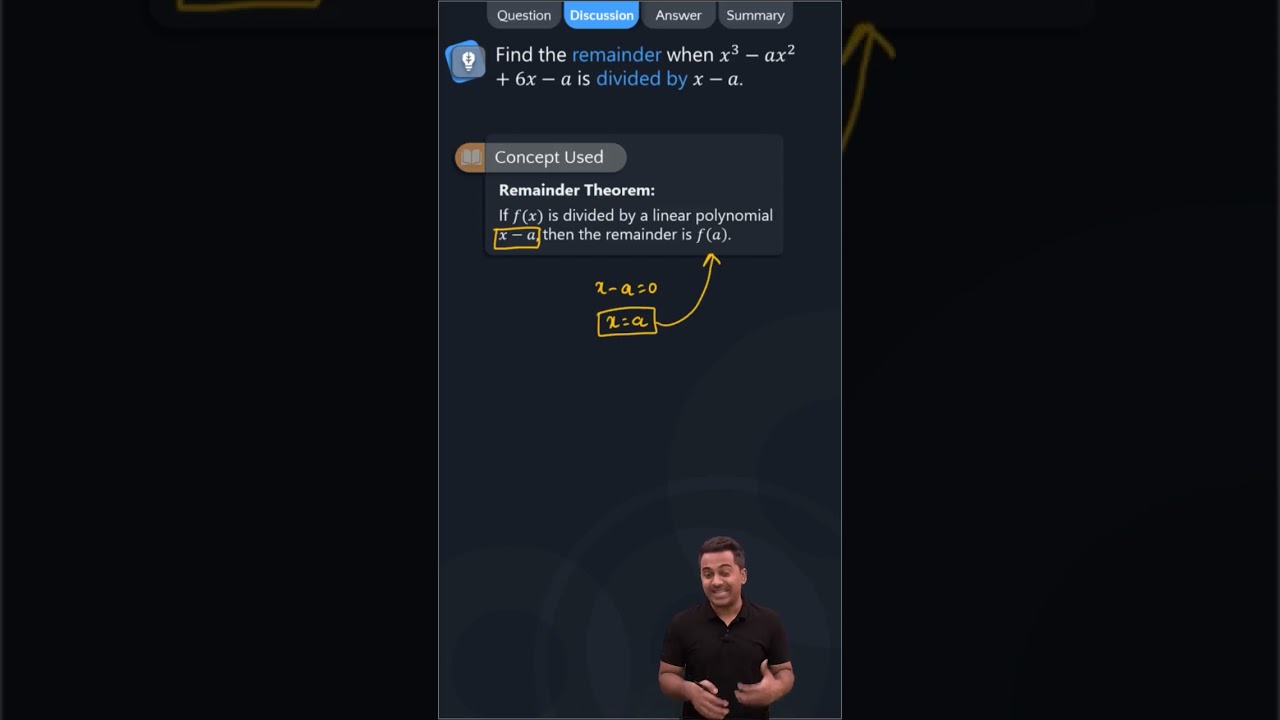
3. Check whether 7+3x is a factor of 3x 3 +7x.
3(-7/3) 3 +7(-7/3) = -(343/9)+(-49/3)
= (-343-(49)3)/9
= (-343-147)/9
= -490/9 ≠ 0
∴ 7+3x is not a factor of 3x 3 +7x
Exercise 2.4 Page: 43
1. Determine which of the following polynomials has (x + 1) a factor:
(i) x 3 +x 2 +x+1
Let p(x) = x 3 +x 2 +x+1
p(−1) = (−1) 3 +(−1) 2 +(−1)+1
∴ By factor theorem, x+1 is a factor of x 3 +x 2 +x+1
(ii) x 4 +x 3 +x 2 +x+1
Let p(x)= x 4 +x 3 +x 2 +x+1
p(−1) = (−1) 4 +(−1) 3 +(−1) 2 +(−1)+1
= 1−1+1−1+1
∴ By factor theorem, x+1 is not a factor of x 4 + x 3 + x 2 + x + 1
(iii) x 4 +3x 3 +3x 2 +x+1
Let p(x)= x 4 +3x 3 +3x 2 +x+1
The zero of x+1 is -1.
p(−1)=(−1) 4 +3(−1) 3 +3(−1) 2 +(−1)+1
∴ By factor theorem, x+1 is not a factor of x 4 +3x 3 +3x 2 +x+1
(iv) x 3 – x 2 – (2+√2)x +√2
Let p(x) = x 3 –x 2 –(2+√2)x +√2
p(−1) = (-1) 3 –(-1) 2 –(2+√2)(-1) + √2 = −1−1+2+√2+√2
∴ By factor theorem, x+1 is not a factor of x 3 –x 2 –(2+√2)x +√2
2. Use the Factor Theorem to determine whether g(x) is a factor of p(x) in each of the following cases:
(i) p(x) = 2x 3 +x 2 –2x–1, g(x) = x+1
p(x) = 2x 3 +x 2 –2x–1, g(x) = x+1
∴ Zero of g(x) is -1.
p(−1) = 2(−1) 3 +(−1) 2 –2(−1)–1
∴ By factor theorem, g(x) is a factor of p(x).
(ii) p(x)=x 3 +3x 2 +3x+1, g(x) = x+2
p(x) = x 3 +3x 2 +3x+1, g(x) = x+2
∴ Zero of g(x) is -2.
p(−2) = (−2) 3 +3(−2) 2 +3(−2)+1
= −8+12−6+1
∴ By factor theorem, g(x) is not a factor of p(x).
(iii) p(x)=x 3 –4x 2 +x+6, g(x) = x–3
p(x) = x 3 –4x 2 +x+6, g(x) = x -3
∴ Zero of g(x) is 3.
p(3) = (3) 3 −4(3) 2 +(3)+6
= 27−36+3+6
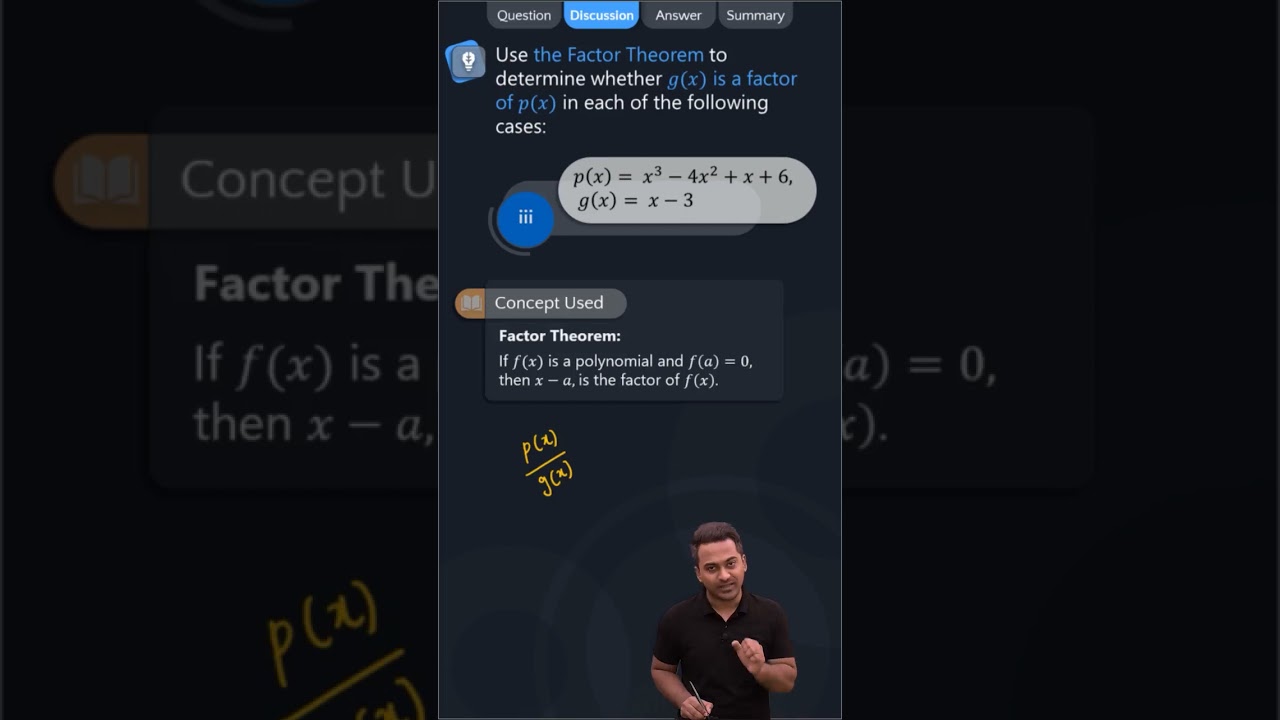
3. Find the value of k, if x–1 is a factor of p(x) in each of the following cases:
(i) p(x) = x 2 +x+k
If x-1 is a factor of p(x), then p(1) = 0
By Factor Theorem
⇒ (1) 2 +(1)+k = 0
⇒ 1+1+k = 0
(ii) p(x) = 2x 2 +kx+ √2
⇒ 2(1) 2 +k(1)+√2 = 0
⇒ 2+k+√2 = 0
⇒ k = −(2+√2)
(iii) p(x) = kx 2 – √ 2x+1
If x-1 is a factor of p(x), then p(1)=0
⇒ k(1) 2 -√2(1)+1=0
(iv) p(x)=kx 2 –3x+k
⇒ k(1) 2 –3(1)+k = 0
⇒ k−3+k = 0
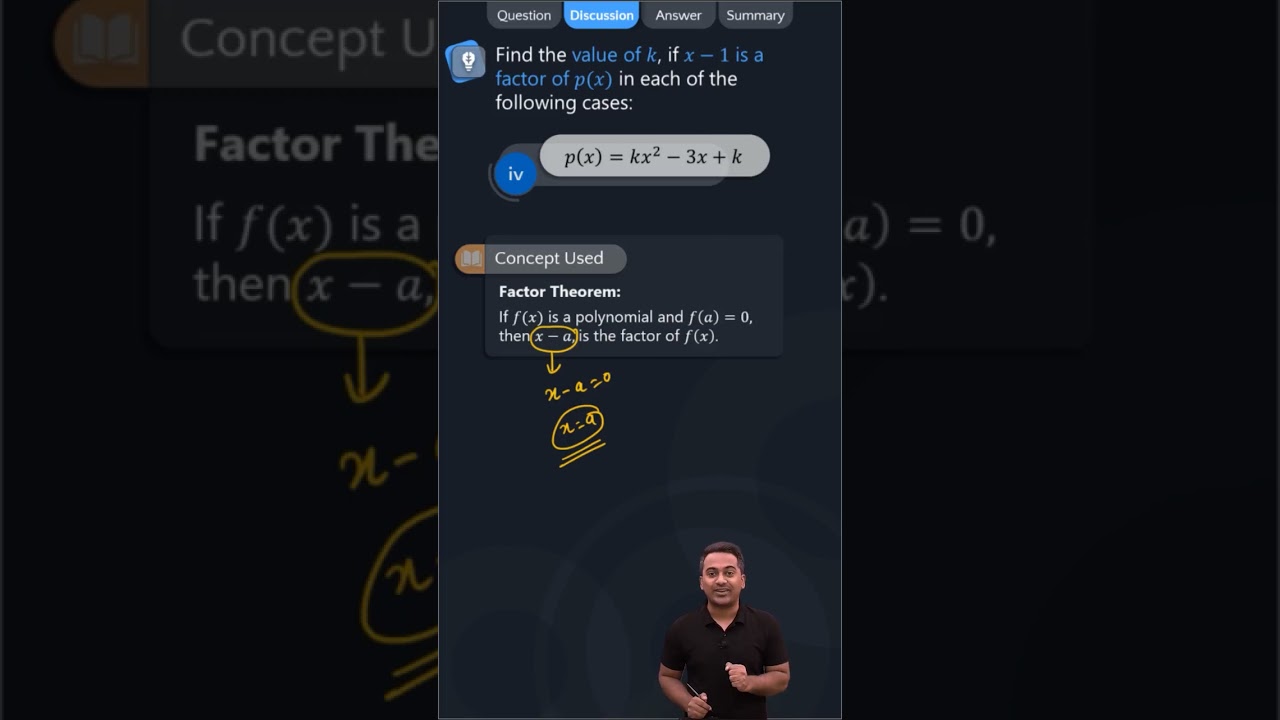
4. Factorise:
(i) 12x 2 –7x+1
Using the splitting the middle term method,
We have to find a number whose sum = -7 and product =1×12 = 12
12x 2 –7x+1= 12x 2 -4x-3x+1
= 4x(3x-1)-1(3x-1)
= (4x-1)(3x-1)
(ii) 2x 2 +7x+3
We have to find a number whose sum = 7 and product = 2×3 = 6
2x 2 +7x+3 = 2x 2 +6x+1x+3
= 2x (x+3)+1(x+3)
= (2x+1)(x+3)
(iii) 6x 2 +5x-6
We have to find a number whose sum = 5 and product = 6×-6 = -36
6x 2 +5x-6 = 6x 2 +9x–4x–6
= 3x(2x+3)–2(2x+3)
= (2x+3)(3x–2)
(iv) 3x 2 –x–4
We have to find a number whose sum = -1 and product = 3×-4 = -12
3x 2 –x–4 = 3x 2 –4x+3x–4
= x(3x–4)+1(3x–4)
= (3x–4)(x+1)
5. Factorise:
(i) x 3 –2x 2 –x+2
Let p(x) = x 3 –2x 2 –x+2
Factors of 2 are ±1 and ± 2
p(x) = x 3 –2x 2 –x+2
p(−1) = (−1) 3 –2(−1) 2 –(−1)+2
Therefore, (x+1) is the factor of p(x)
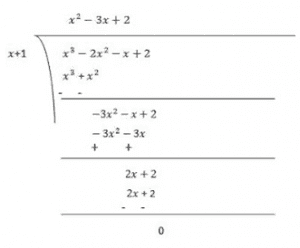
Now, Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
(x+1)(x 2 –3x+2) = (x+1)(x 2 –x–2x+2)
= (x+1)(x(x−1)−2(x−1))
= (x+1)(x−1)(x-2)
(ii) x 3 –3x 2 –9x–5
Let p(x) = x 3 –3x 2 –9x–5
Factors of 5 are ±1 and ±5
By the trial method, we find that
So, (x-5) is factor of p(x)
p(x) = x 3 –3x 2 –9x–5
p(5) = (5) 3 –3(5) 2 –9(5)–5
= 125−75−45−5
Therefore, (x-5) is the factor of p(x)
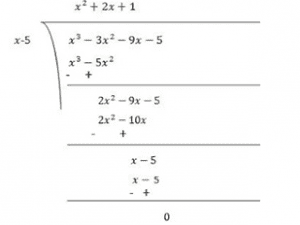
(x−5)(x 2 +2x+1) = (x−5)(x 2 +x+x+1)
= (x−5)(x(x+1)+1(x+1))
= (x−5)(x+1)(x+1)
(iii) x 3 +13x 2 +32x+20
Let p(x) = x 3 +13x 2 +32x+20
Factors of 20 are ±1, ±2, ±4, ±5, ±10 and ±20
So, (x+1) is factor of p(x)
p(x)= x 3 +13x 2 +32x+20
p(-1) = (−1) 3 +13(−1) 2 +32(−1)+20
= −1+13−32+20
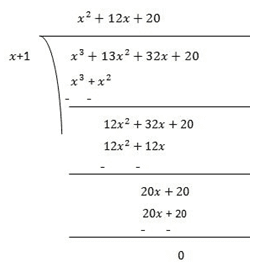
Now, Dividend = Divisor × Quotient +Remainder
(x+1)(x 2 +12x+20) = (x+1)(x 2 +2x+10x+20)
= (x+1)x(x+2)+10(x+2)
= (x+1)(x+2)(x+10)
(iv) 2y 3 +y 2 –2y–1
Let p(y) = 2y 3 +y 2 –2y–1
Factors = 2×(−1)= -2 are ±1 and ±2
So, (y-1) is factor of p(y)
p(y) = 2y 3 +y 2 –2y–1
p(1) = 2(1) 3 +(1) 2 –2(1)–1
Therefore, (y-1) is the factor of p(y)
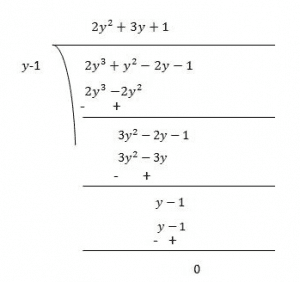
Now, Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
(y−1)(2y 2 +3y+1) = (y−1)(2y 2 +2y+y+1)
= (y−1)(2y(y+1)+1(y+1))
= (y−1)(2y+1)(y+1)
Exercise 2.5 Page: 48
1. Use suitable identities to find the following products:
(i) (x+4)(x +10)
Using the identity, (x+a)(x+b) = x 2 +(a+b)x+ab
(x+4)(x+10) = x 2 +(4+10)x+(4×10)
= x 2 +14x+40
(ii) (x+8)(x –10)
(x+8)(x−10) = x 2 +(8+(−10))x+(8×(−10))
= x 2 +(8−10)x–80
= x 2 −2x−80
(iii) (3x+4)(3x–5)
(3x+4)(3x−5) = (3x) 2 +[4+(−5)]3x+4×(−5)
= 9x 2 +3x(4–5)–20
= 9x 2 –3x–20
(iv) (y 2 +3/2)(y 2 -3/2)
Using the identity, (x+y)(x–y) = x 2 –y 2
(y 2 +3/2)(y 2 –3/2) = (y 2 ) 2 –(3/2) 2
2. Evaluate the following products without multiplying directly:
(i) 103×107
103×107= (100+3)×(100+7)
Using identity, [(x+a)(x+b) = x 2 +(a+b)x+ab
Here, x = 100
We get, 103×107 = (100+3)×(100+7)
= (100) 2 +(3+7)100+(3×7)
= 10000+1000+21
(ii) 95×96
95×96 = (100-5)×(100-4)
Using identity, [(x-a)(x-b) = x 2 -(a+b)x+ab
We get, 95×96 = (100-5)×(100-4)
= (100) 2 +100(-5+(-4))+(-5×-4)
= 10000-900+20
(iii) 104×96
104×96 = (100+4)×(100–4)
Here, a = 100
We get, 104×96 = (100+4)×(100–4)
= (100) 2 –(4) 2
3. Factorise the following using appropriate identities:
(i) 9x 2 +6xy+y 2
9x 2 +6xy+y 2 = (3x) 2 +(2×3x×y)+y 2
Using identity, x 2 +2xy+y 2 = (x+y) 2
Here, x = 3x
= (3x+y)(3x+y)
(ii) 4y 2 −4y+1
4y 2 −4y+1 = (2y) 2 –(2×2y×1)+1
Using identity, x 2 – 2xy + y 2 = (x – y) 2
Here, x = 2y
4y 2 −4y+1 = (2y) 2 –(2×2y×1)+1 2
= (2y–1)(2y–1)
(iii) x 2 –y 2 /100
x 2 –y 2 /100 = x 2 –(y/10) 2
Using identity, x 2 -y 2 = (x-y)(x+y)
Here, x = x
= (x–y/10)(x+y/10)
4. Expand each of the following using suitable identities:
(i) (x+2y+4z) 2
(ii) (2x−y+z) 2
(iii) (−2x+3y+2z) 2
(iv) (3a –7b–c) 2
(v) (–2x+5y–3z) 2
(vi) ((1/4)a-(1/2)b +1) 2
Using identity, (x+y+z) 2 = x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +2xy+2yz+2zx
(x+2y+4z) 2 = x 2 +(2y) 2 +(4z) 2 +(2×x×2y)+(2×2y×4z)+(2×4z×x)
= x 2 +4y 2 +16z 2 +4xy+16yz+8xz
(ii) (2x−y+z) 2
Here, x = 2x
(2x−y+z) 2 = (2x) 2 +(−y) 2 +z 2 +(2×2x×−y)+(2×−y×z)+(2×z×2x)
= 4x 2 +y 2 +z 2 –4xy–2yz+4xz
Here, x = −2x
(−2x+3y+2z) 2 = (−2x) 2 +(3y) 2 +(2z) 2 +(2×−2x×3y)+(2×3y×2z)+(2×2z×−2x)
= 4x 2 +9y 2 +4z 2 –12xy+12yz–8xz
Using identity (x+y+z) 2 = x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +2xy+2yz+2zx
Here, x = 3a
(3a –7b– c) 2 = (3a) 2 +(– 7b) 2 +(– c) 2 +(2×3a ×– 7b)+(2×– 7b ×– c)+(2×– c ×3a)
= 9a 2 + 49b 2 + c 2 – 42ab+14bc–6ca
Here, x = –2x
(–2x+5y–3z) 2 = (–2x) 2 +(5y) 2 +(–3z) 2 +(2×–2x × 5y)+(2× 5y×– 3z)+(2×–3z ×–2x)
= 4x 2 +25y 2 +9z 2 – 20xy–30yz+12zx
(vi) ((1/4)a-(1/2)b+1) 2
Here, x = (1/4)a
y = (-1/2)b
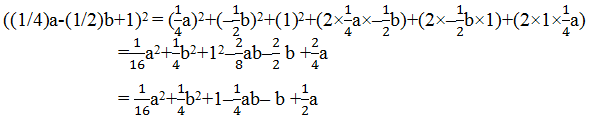
(i) 4x 2 +9y 2 +16z 2 +12xy–24yz–16xz
(ii) 2x 2 +y 2 +8z 2 –2√2xy+4√2yz–8xz
We can say that, x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +2xy+2yz+2zx = (x+y+z) 2
4x 2 +9y 2 +16z 2 +12xy–24yz–16xz = (2x) 2 +(3y) 2 +(−4z) 2 +(2×2x×3y)+(2×3y×−4z)+(2×−4z×2x)
= (2x+3y–4z) 2
= (2x+3y–4z)(2x+3y–4z)
Using identity, (x +y+z) 2 = x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +2xy+2yz+2zx
2x 2 +y 2 +8z 2 –2√2xy+4√2yz–8xz
= (-√2x) 2 +(y) 2 +(2√2z) 2 +(2×-√2x×y)+(2×y×2√2z)+(2×2√2×−√2x)
= (−√2x+y+2√2z) 2
= (−√2x+y+2√2z)(−√2x+y+2√2z)
6. Write the following cubes in expanded form:
(i) (2x+1) 3
(ii) (2a−3b) 3
(iii) ((3/2)x+1) 3
(iv) (x−(2/3)y) 3
Using identity,(x+y) 3 = x 3 +y 3 +3xy(x+y)
(2x+1) 3 = (2x) 3 +1 3 +(3×2x×1)(2x+1)
= 8x 3 +1+6x(2x+1)
= 8x 3 +12x 2 +6x+1
Using identity,(x–y) 3 = x 3 –y 3 –3xy(x–y)
(2a−3b) 3 = (2a) 3 −(3b) 3 –(3×2a×3b)(2a–3b)
= 8a 3 –27b 3 –18ab(2a–3b)
= 8a 3 –27b 3 –36a 2 b+54ab 2
((3/2)x+1) 3 =((3/2)x) 3 +1 3 +(3×(3/2)x×1)((3/2)x +1)
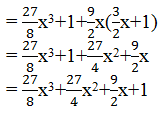
(iv) (x−(2/3)y) 3
Using identity, (x –y) 3 = x 3 –y 3 –3xy(x–y)
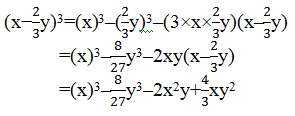
7. Evaluate the following using suitable identities:
(ii) (102) 3
(iii) (998) 3
We can write 99 as 100–1
(99) 3 = (100–1) 3
= (100) 3 –1 3 –(3×100×1)(100–1)
= 1000000 –1–300(100 – 1)
= 1000000–1–30000+300
We can write 102 as 100+2
(100+2) 3 =(100) 3 +2 3 +(3×100×2)(100+2)
= 1000000 + 8 + 600(100 + 2)
= 1000000 + 8 + 60000 + 1200
We can write 99 as 1000–2
(998) 3 =(1000–2) 3
=(1000) 3 –2 3 –(3×1000×2)(1000–2)
= 1000000000–8–6000(1000– 2)
= 1000000000–8- 6000000+12000
= 994011992
8. Factorise each of the following:
(i) 8a 3 +b 3 +12a 2 b+6ab 2
(ii) 8a 3 –b 3 –12a 2 b+6ab 2
(iii) 27–125a 3 –135a +225a 2
(iv) 64a 3 –27b 3 –144a 2 b+108ab 2
(v) 27p 3 –(1/216)−(9/2) p 2 +(1/4)p
The expression, 8a 3 +b 3 +12a 2 b+6ab 2 can be written as (2a) 3 +b 3 +3(2a) 2 b+3(2a)(b) 2
8a 3 +b 3 +12a 2 b+6ab 2 = (2a) 3 +b 3 +3(2a) 2 b+3(2a)(b) 2
= (2a+b)(2a+b)(2a+b)
Here, the identity, (x +y) 3 = x 3 +y 3 +3xy(x+y) is used.
The expression, 8a 3 –b 3 −12a 2 b+6ab 2 can be written as (2a) 3 –b 3 –3(2a) 2 b+3(2a)(b) 2
8a 3 –b 3 −12a 2 b+6ab 2 = (2a) 3 –b 3 –3(2a) 2 b+3(2a)(b) 2
= (2a–b)(2a–b)(2a–b)
Here, the identity,(x–y) 3 = x 3 –y 3 –3xy(x–y) is used.
(iii) 27–125a 3 –135a+225a 2
The expression, 27–125a 3 –135a +225a 2 can be written as 3 3 –(5a) 3 –3(3) 2 (5a)+3(3)(5a) 2
27–125a 3 –135a+225a 2 = 3 3 –(5a) 3 –3(3) 2 (5a)+3(3)(5a) 2
= (3–5a)(3–5a)(3–5a)
Here, the identity, (x–y) 3 = x 3 –y 3 -3xy(x–y) is used.
The expression, 64a 3 –27b 3 –144a 2 b+108ab 2 can be written as (4a) 3 –(3b) 3 –3(4a) 2 (3b)+3(4a)(3b) 2
64a 3 –27b 3 –144a 2 b+108ab 2 = (4a) 3 –(3b) 3 –3(4a) 2 (3b)+3(4a)(3b) 2
=(4a–3b)(4a–3b)(4a–3b)
Here, the identity, (x – y) 3 = x 3 – y 3 – 3xy(x – y) is used.
(v) 27p 3 – (1/216)−(9/2) p 2 +(1/4)p
The expression, 27p 3 –(1/216)−(9/2) p 2 +(1/4)p can be written as
(3p) 3 –(1/6) 3 −(9/2) p 2 +(1/4)p = (3p) 3 –(1/6) 3 −3(3p)(1/6)(3p – 1/6)
Using (x – y) 3 = x 3 – y 3 – 3xy (x – y)
27p 3 –(1/216)−(9/2) p 2 +(1/4)p = (3p) 3 –(1/6) 3 −3(3p)(1/6)(3p – 1/6)
Taking x = 3p and y = 1/6
= (3p–1/6) 3
= (3p–1/6)(3p–1/6)(3p–1/6)
(i) x 3 +y 3 = (x+y)(x 2 –xy+y 2 )
(ii) x 3 –y 3 = (x–y)(x 2 +xy+y 2 )
We know that, (x+y) 3 = x 3 +y 3 +3xy(x+y)
⇒ x 3 +y 3 = (x+y) 3 –3xy(x+y)
⇒ x 3 +y 3 = (x+y)(x 2 +y 2 –xy)
(ii) x 3 –y 3 = (x–y)(x 2 +xy+y 2 )
We know that, (x–y) 3 = x 3 –y 3 –3xy(x–y)
⇒ x 3 −y 3 = (x–y) 3 +3xy(x–y)
⇒ x 3 +y 3 = (x–y)(x 2 +y 2 +xy)
10. Factorise each of the following:
(i) 27y 3 +125z 3
(ii) 64m 3 –343n 3
The expression, 27y 3 +125z 3 can be written as (3y) 3 +(5z) 3
27y 3 +125z 3 = (3y) 3 +(5z) 3
We know that, x 3 +y 3 = (x+y)(x 2 –xy+y 2 )
= (3y+5z)(9y 2 –15yz+25z 2 )
The expression, 64m 3 –343n 3 can be written as (4m) 3 –(7n) 3
64m 3 –343n 3 = (4m) 3 –(7n) 3
We know that, x 3 –y 3 = (x–y)(x 2 +xy+y 2 )
= (4m-7n)(16m 2 +28mn+49n 2 )
11. Factorise: 27x 3 +y 3 +z 3 –9xyz.
The expression 27x 3 +y 3 +z 3 –9xyz can be written as (3x) 3 +y 3 +z 3 –3(3x)(y)(z)
27x 3 +y 3 +z 3 –9xyz = (3x) 3 +y 3 +z 3 –3(3x)(y)(z)
We know that, x 3 +y 3 +z 3 –3xyz = (x+y+z)(x 2 +y 2 +z 2 –xy –yz–zx)
= (3x+y+z)(9x 2 +y 2 +z 2 –3xy–yz–3xz)
12. Verify that:
x 3 +y 3 +z 3 –3xyz = (1/2) (x+y+z)[(x–y) 2 +(y–z) 2 +(z–x) 2 ]
x 3 +y 3 +z 3 −3xyz = (x+y+z)(x 2 +y 2 +z 2 –xy–yz–xz)
= (1/2)(x+y+z)(2x 2 +2y 2 +2z 2 –2xy–2yz–2xz)
13. If x+y+z = 0, show that x 3 +y 3 +z 3 = 3xyz.
x 3 +y 3 +z 3 -3xyz = (x +y+z)(x 2 +y 2 +z 2 –xy–yz–xz)
Now, according to the question, let (x+y+z) = 0,
Then, x 3 +y 3 +z 3 -3xyz = (0)(x 2 +y 2 +z 2 –xy–yz–xz)
⇒ x 3 +y 3 +z 3 –3xyz = 0
⇒ x 3 +y 3 +z 3 = 3xyz
Hence Proved
14. Without actually calculating the cubes, find the value of each of the following:
(i) (−12) 3 +(7) 3 +(5) 3
(ii) (28) 3 +(−15) 3 +(−13) 3
Let a = −12
We know that if x+y+z = 0, then x 3 +y 3 +z 3 =3xyz.
Here, −12+7+5=0
(−12) 3 +(7) 3 +(5) 3 = 3xyz
= 3×-12×7×5
(28) 3 +(−15) 3 +(−13) 3
We know that if x+y+z = 0, then x 3 +y 3 +z 3 = 3xyz.
Here, x+y+z = 28–15–13 = 0
(28) 3 +(−15) 3 +(−13) 3 = 3xyz
= 0+3(28)(−15)(−13)
15. Give possible expressions for the length and breadth of each of the following rectangles, in which their areas are given:
(i) Area: 25a 2 –35a+12
(ii) Area: 35y 2 +13y–12
We have to find a number whose sum = -35 and product =25×12 = 300
25a 2 –35a+12 = 25a 2 –15a−20a+12
= 5a(5a–3)–4(5a–3)
= (5a–4)(5a–3)
Possible expression for length = 5a–4
Possible expression for breadth = 5a –3
We have to find a number whose sum = 13 and product = 35×-12 = 420
35y 2 +13y–12 = 35y 2 –15y+28y–12
= 5y(7y–3)+4(7y–3)
= (5y+4)(7y–3)
Possible expression for length = (5y+4)
Possible expression for breadth = (7y–3)
16. What are the possible expressions for the dimensions of the cuboids whose volumes are given below?
(i) Volume: 3x 2 –12x
(ii) Volume: 12ky 2 +8ky–20k
3x 2 –12x can be written as 3x(x–4) by taking 3x out of both the terms.
Possible expression for length = 3
Possible expression for breadth = x
Possible expression for height = (x–4)
12ky 2 +8ky–20k can be written as 4k(3y 2 +2y–5) by taking 4k out of both the terms.
12ky 2 +8ky–20k = 4k(3y 2 +2y–5)
= 4k(3y 2 +5y–3y–5)
= 4k(3y+5)(y–1)
Possible expression for length = 4k
Possible expression for breadth = (3y +5)
Possible expression for height = (y -1)
Disclaimer:
Dropped Topics – 2.4 Remainder theorem.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2
How many exercises are present in ncert solutions for class 9 maths chapter 2, why should i opt for ncert solutions for class 9 maths chapter 2, are ncert solutions for class 9 maths chapter 2 difficult to learn, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Thanks a lot byjus It makes my homework easy😄
Thanks a lot byjus. It helped me for studying easily. 😀
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Case Based Questions Test: Polynomials - 1 - Class 9 MCQ
15 questions mcq test - case based questions test: polynomials - 1, direction: read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same: the below picture are few natural examples of parabolic shape which is represented by a quadratic polynomial. a parabolic arch is an arch in the shape of a parabola. in structures, their curve represents an efficient method of load, and so can be found in bridges and in architecture in a variety of forms. if the sum of the roots is –p and product of the roots is then the quadratic polynomial is.
x2 - (Sum of roots)x + Product of roots
Putting values
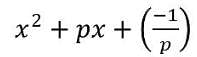
We can multiply any constant to this polynomial
So, required quadratic polynomial is
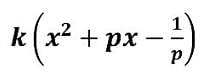
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same: The below picture are few natural examples of parabolic shape which is represented by a quadratic polynomial. A parabolic arch is an arch in the shape of a parabola. In structures, their curve represents an efficient method of load, and so can be found in bridges and in architecture in a variety of forms. If the roots of the quadratic polynomial are equal, where the discriminant D = b 2 – 4ac, then
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same: The below picture are few natural examples of parabolic shape which is represented by a quadratic polynomial. A parabolic arch is an arch in the shape of a parabola. In structures, their curve represents an efficient method of load, and so can be found in bridges and in architecture in a variety of forms. The graph of x 2 + 1 = 0
- A. Intersects x-axis at two distinct points.
- B. Touches x-axis at a point.
- C. Neither touches nor intersects x-axis.
- D. Either touches or intersects x-axis.
y = x 2 + 1
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same: The below picture are few natural examples of parabolic shape which is represented by a quadratic polynomial. A parabolic arch is an arch in the shape of a parabola. In structures, their curve represents an efficient method of load, and so can be found in bridges and in architecture in a variety of forms.

In the standard form of quadratic polynomial, ax 2 + bx, c, a, b and c are
All are real numbers.
All are rational numbers.
‘a’ is a non zero real number and b and c are any real numbers.
All are integers.
It can be written in the standard form ax2 + bx + c , where x is a variable, a, b, c are constants (numbers) and a = 0. The constants a, b, c are called the coefficients of the polynomial. A quadratic polynomial ax 2 + bx + c is called sometimes a quadratic trinomial.
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
The below picture are few natural examples of parabolic shape which is represented by a quadratic polynomial. A parabolic arch is an arch in the shape of a parabola. In structures, their curve represents an efficient method of load, and so can be found in bridges and in architecture in a variety of forms.

If α are 1/α the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial 2x 2 – x + 8k, then k is

Product of zeroes = c/a = 8k/2
So, 8k/2 = 1
Basketball and soccer are played with a spherical ball. Even though an athlete dribbles the ball in both sports, a basketball player uses his hands and a soccer player uses his feet. Usually, soccer is played outdoors on a large field and basketball is played indoor on a court made out of wood. The projectile (path traced) of soccer ball and basketball are in the form of parabola representing quadratic polynomial.
What will be the expression of the polynomial?
- A. x 3 + 2x 2 – 5x – 6
- B. x 3 + 2x 2 – 5x – 6
- C. x 3 + 2x 2 + 5x – 6
- D. x 3 + 2x 2 + 5x + 6
Hence, the expression is (x + 3)(x + 1)(x – 2)
= [x 2 + x + 3x + 3](x – 2)
= x 3 + 4x 2 + 3x – 2x 2 – 8x – 6
= x 3 + 2x 2 – 5x – 6
The graph of parabola opens upwards, if _______
The three zeroes in the above shown graph are
2, 3, –1
–2, 3, 1
–3, –1, 2
–2, –3, –1
Zeroes are the values of x where graph intersects the x-axis
∴ Zeroes are -3, -1 and 2
The shape of the path traced shown is
- D. Parabola
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same: Basketball and soccer are played with a spherical ball. Even though an athlete dribbles the ball in both sports, a basketball player uses his hands and a soccer player uses his feet. Usually, soccer is played outdoors on a large field and basketball is played indoor on a court made out of wood. The projectile (path traced) of soccer ball and basketball are in the form of parabola representing quadratic polynomial.
In the above graph, how many zeroes are there for the polynomial?
The number of zeroes of polynomial is the number of times the curve intersects the x-axis, i.e. attains the value 0. Here, the polynomial meets the x-axis at 3 points. So, number of zeroes = 3.
If the product of the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial p(x) = ax 2 – 6x – 6 is 4, then the value of a is:
p(x) = ax 2 – 6x – 6
Let α and β be the zeroes of the given polynomial, then
i.e., 4 = -6/a
Since the graph does not intersect the X-axis, therefore it has no zero.
If a and b are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial p(x) = 4x 2 + 5x + 1, then the product of zeroes is:
∴ αβ = c/a = 1/4.
If a linear polynomial is 2x + 3, then the zero of 2x + 3 is:
Let p(x) = 2x + 3
For a zero of p(x), 2x + 3 = 0
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial x 2 – 5x + k such that α – β = 1, then the value of k is:
and αβ = k/1 = k
Also given, α – β = 1
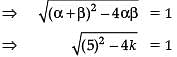
⇒ 25 – 4k = 1(Squaring both sides)
⇒ – 4k = 1 – 25 = – 24
Top Courses for Class 9

Important Questions for Case Based Questions Test: Polynomials - 1
Case based questions test: polynomials - 1 mcqs with answers, online tests for case based questions test: polynomials - 1.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
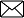
Forgot Password

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
Ncert solutions for class 9 maths chapter 2 polynomials| pdf download.

- Exercise 2.1 Chapter 2 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 2.2 Chapter 2 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 2.3 Chapter 2 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 2.4 Chapter 2 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 2.5 Chapter 2 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapters:
How can I download Chapter 2 Polynomials Class 9 NCERT Solutions PDF
What do you mean by algebraic expressions, what is the coefficient of a zero polynomial, what is biquadratic polynomial, contact form.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions of Chapter 2: Polynomials serve as a valuable resource for students seeking to enhance their understanding of polynomial concepts and problem-solving skills. By practicing these case studies, students can strengthen their grasp of polynomials and their applications in real-life scenarios.
Case Study Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Case Study 1. Ankur and Ranjan start a new business together. The amount invested by both partners together is given by the polynomial p (x) = 4x 2 + 12x + 5, which is the product of their individual shares. Coefficient of x2 in the given polynomial is.
The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 9 maths. In this article, you will find case study questions for CBSE Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials. It is a part of Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 9 Maths Series.
Case Study Questions Question 1: On one day, principal of a particular school visited the classroom. Class teacher was teaching the concept of polynomial to students. He was very much impressed by her way of teaching. To check, whether the students also understand the concept taught by her or not, he asked variousquestions to students. … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 9 ...
Download Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions for Class 9 Mathematics to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams 2023-24. These Case Study and Passage Based questions are published by the experts of CBSE Experts for the students of CBSE Class 9 so that they can score 100% in Exams.
CBSE Class 9th Maths 2023 : 30 Most Important Case Study Questions with Answers; Download PDF CBSE Class 9 Maths exam 2022-23 will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. CBSE Class 9 Maths Question Bank on Case Studies given in this article can be very helpful in understanding the new format of questions.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths are a type of assessment where students are given a real-world scenario or situation and they need to apply mathematical concepts to solve the problem. These types of questions help students to develop their problem-solving skills and apply their knowledge of mathematics to real-life situations.
Are you preparing for your Class 9 Maths board exams and looking for an effective study resource? Well, you're in luck! In this article, we will provide you with a collection of Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths specifically designed to help you excel in your exams. These questions are carefully curated to cover various mathematical concepts and problem-solving techniques. So, let's ...
practice metarial maths 9th class subject: mathematics std: ix practice paper case study questions ch polynomials attempt all questions no. case study school of
Case studies in Class 9 Mathematics A case study in mathematics is a detailed analysis of a particular mathematical problem or situation. Case studies are often used to examine the relationship between theory and practice, and to explore the connections between different areas of mathematics. Often, a case study will focus on a single problem or situation and will use a variety of methods to ...
TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 9 Maths Polynomials chapter. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem-solving skills with expert advice.
Important Polynomials Questions For Class 9- Chapter 2 (With Solutions) Some important questions from polynomials are given below with solutions. These questions will help the 9th class students to get acquainted with a wide variety of questions and develop the confidence to solve polynomial questions more efficiently. 1.
Download PDF of Class 9 Polynomials Case Study Questions - Podar International. Practice CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Important Questions Chapter Wise, MCQ's, Extra Questions for Exams.
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials NCERT Solutions Below we have provided the solutions of each exercise of the chapter. Go through the links to access the solutions of exercises you want. You should also check out our NCERT Class 9 Solutions for other subjects to score good marks in the exams.
Case study based questions class 9 | case study based on Polynomials class 9| cbse class 9 Maths SHARMA TUTORIAL 30.8K subscribers 104 11K views 1 year ago Class 9 Maths || Case Study Based Questions
Key Topics Covered: Case Study Questions Polynomial Class 9 Maths Exam 2023-24 Problem-Solving Techniques Whether you're a student looking to excel in your math exam or a teacher seeking effective ...
Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials solved by Expert Teachers as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. Class 9 Chapter 2 Polynomials Exercise Questions with Solutions to help you to revise complete Syllabus and Score More marks.
Case Studies In Class 9 Mathematics The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has included case study based questions in the Class 9 Mathematics paper in current session. According to new pattern CBSE Class 9 Mathematics students will have to solve case based questions. This is a departure from the usual theoretical conceptual questions that are asked in Class 9 Maths exam in this year.
9. POLYNOMIALS.pdf class-9th Mathematics 0 Likes 49 Views SRINIVAS EDLA Sep 18, 2022 Study Material
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 has 5 exercises. The topics discussed in these exercises are polynomials in one variable, zeros of polynomials, real numbers and their decimal expansions, representing real numbers on the number line and operations on real numbers laws of exponents for real numbers.
Case Based Questions Test: Polynomials - 1 for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Case Based Questions Test: Polynomials - 1 questions and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus.The Case Based Questions Test: Polynomials - 1 MCQs are made for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online ...
Chapter 2 Polynomials Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF download is very useful in understanding the basic concepts embedded in the chapter. It is very essential to solve every question before moving further to any other supplementary books.
The crime took place on the night of 9 August, when the woman, who was a junior doctor at the city's RG Kar Medical College, had gone to a seminar room to rest after a gruelling 36-hour shift.