
Home > Blog > Tips for Online Students > Dissertation vs Thesis: The Differences that Matter
Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students

Dissertation vs Thesis: The Differences that Matter
Updated: June 19, 2024
Published: April 26, 2020

As a graduate student, you will have many different types of challenging coursework and assignments. However, the biggest project that you’ll work on when earning your master’s or doctoral degree will be your thesis or dissertation . The differences between a dissertation vs thesis are plenty. That’s because each of these pieces of writing happen at different times in one’s educational journey.
Let’s break down what a dissertation and thesis are so that you have a strong handle on what’s expected. For both a thesis and a dissertation, there is an obvious fluency and understanding of the subject one studies.
Let’s take a look at their similarities and differences.
Photo by Glenn Carstens-Peters on Unsplash
What is a dissertation.
When you enter a doctoral program to earn a PhD, you will learn a lot about how to conduct your own research. At the culmination of your degree program, you’ll produce a dissertation.
A dissertation is a lengthy piece of written work that includes original research or expanded research on a new or existing topic. As the doctoral student, you get to choose what you want to explore and write about within your field of study.
What is a Thesis?
A thesis is also a scholarly piece of writing, but it is for those who are graduating from a master’s program. A thesis allows students to showcase their knowledge and expertise within the subject matter they have been studying.
Main Differences Between a Thesis vs. Dissertation
The biggest difference between a thesis and a dissertation is that a thesis is based on existing research.
On the other hand, a dissertation will more than likely require the doctoral student to conduct their own research and then perform analysis. The other big difference is that a thesis is for master’s students and the dissertation is for PhD students.
Structural Differences Between a Thesis and a Dissertation
Structurally, the two pieces of written analysis have many differences.
- A thesis is at least 100 pages in length
- A dissertation is 2-3x that in length
- A thesis expands upon and analyzes existing research
- A dissertation’s content is mostly attributed to the student as the author
Research Content and Oral Presentation
Once completed, some programs require students to orally present their thesis and dissertation to a panel of faculty members.
Typically, a dissertation oral presentation can take several hours. On the other hand, a thesis only takes about an hour to present and answer questions.
Let’s look at how the two scholarly works are similar and different:
Similarities:
- Each is considered a final project and required to graduate
- Both require immense understanding of the material
- Written skills are key to complete both
- Neither can be plagiarized
- Both are used to defend an argument
- Both require analytical skills
- You will have to draft, rewrite, and edit both pieces of writing
- For both, it is useful to have another person look over before submission
- Both papers are given deadlines
Differences:
- A dissertation is longer than a thesis
- A dissertation requires new research
- A dissertation requires a hypothesis that is then proven
- A thesis chooses a stance on an existing idea and defends it with analysis
- A dissertation has a longer oral presentation component
The Differences in Context: Location Matters
The united states.
In the US, everything that was previously listed is how schools differentiate between a thesis and a dissertation. A thesis is performed by master’s students, and a dissertation is written by PhD candidates.
In Europe, the distinction between a thesis and dissertation becomes a little more cloudy. That’s because PhD programs may require a doctoral thesis to graduate. Then, as a part of a broader post-graduate research project, students may complete a dissertation.
Photo by Russ Ward on Unsplash
The purpose behind written research.
Each piece of writing is an opportunity for a student to demonstrate his or her ability to think critically, express their opinions in writing, and present their findings in front of their department.
Graduate degrees take a lot of time, energy, and hard work to complete. When it comes to writing such lengthy and informative pieces, there is a lot of time management that is involved. The purpose of both a thesis and a dissertation are written proof that you understand and have mastered the subject matter of your degree.
Degree Types
A doctoral degree, or PhD, is the highest degree that one can earn. In most cases, students follow the following path to achieve this level of education: Earn a bachelor’s degree, then a master’s, and then a PhD. While not every job title requires this deep educational knowledge, the salaries that come along with each level of higher education increase accordingly.
Earning Your Degree
Whether you are currently a prospective student considering earning your higher education degree or a student enrolled in a master’s or doctoral program, you know the benefits of education.
However, for some, earning a traditional degree on-campus doesn’t make sense. This could be because of the financial challenges, familial obligations, accessibility, or any other number of reasons.
For students who are seeking their higher education degrees but need a flexible, affordable, and quality alternative to traditional college, take a look at the programs that the University of the People has to offer.
University of the People is an entirely online, US accredited and tuition-free institution dedicated to higher education. You can earn your Master’s in Business Administration or your Master’s in Education . Not to mention, there are a handful of associate’s and bachelor’s degree programs to choose from as well.
If you want to learn more, get in touch with us !
The Bottom Line
Regardless of where and when you earn your master’s or doctoral degree, you will likely have to complete a thesis or dissertation. The main difference between a thesis and dissertation is the level at which you complete them. A thesis is for a master’s degree, and a dissertation is for a doctoral degree.
Don’t be overwhelmed by the prospect of having to research and write so much. Your educational journey has prepared you with the right time management skills and writing skills to make this feat achievable!
In this article
At UoPeople, our blog writers are thinkers, researchers, and experts dedicated to curating articles relevant to our mission: making higher education accessible to everyone. Read More
Frequently asked questions
What is the difference between a dissertation and a thesis.
The words ‘ dissertation ’ and ‘thesis’ both refer to a large written research project undertaken to complete a degree, but they are used differently depending on the country:
- In the UK, you write a dissertation at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a thesis to complete a PhD.
- In the US, it’s the other way around: you may write a thesis at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a dissertation to complete a PhD.
Frequently asked questions: Knowledge Base
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research. Developing your methodology involves studying the research methods used in your field and the theories or principles that underpin them, in order to choose the approach that best matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyse data (e.g. interviews, experiments , surveys , statistical tests ).
In a dissertation or scientific paper, the methodology chapter or methods section comes after the introduction and before the results , discussion and conclusion .
Depending on the length and type of document, you might also include a literature review or theoretical framework before the methodology.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something:
- Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions).
- Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure).
If you are doing experimental research , you also have to consider the internal and external validity of your experiment.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Harvard referencing uses an author–date system. Sources are cited by the author’s last name and the publication year in brackets. Each Harvard in-text citation corresponds to an entry in the alphabetised reference list at the end of the paper.
Vancouver referencing uses a numerical system. Sources are cited by a number in parentheses or superscript. Each number corresponds to a full reference at the end of the paper.
| Harvard style | Vancouver style | |
|---|---|---|
| In-text citation | Each referencing style has different rules (Pears and Shields, 2019). | Each referencing style has different rules (1). |
| Reference list | Pears, R. and Shields, G. (2019). . 11th edn. London: MacMillan. | 1. Pears R, Shields G. Cite them right: The essential referencing guide. 11th ed. London: MacMillan; 2019. |
A Harvard in-text citation should appear in brackets every time you quote, paraphrase, or refer to information from a source.
The citation can appear immediately after the quotation or paraphrase, or at the end of the sentence. If you’re quoting, place the citation outside of the quotation marks but before any other punctuation like a comma or full stop.
In Harvard referencing, up to three author names are included in an in-text citation or reference list entry. When there are four or more authors, include only the first, followed by ‘ et al. ’
| In-text citation | Reference list | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 author | (Smith, 2014) | Smith, T. (2014) … |
| 2 authors | (Smith and Jones, 2014) | Smith, T. and Jones, F. (2014) … |
| 3 authors | (Smith, Jones and Davies, 2014) | Smith, T., Jones, F. and Davies, S. (2014) … |
| 4+ authors | (Smith , 2014) | Smith, T. (2014) … |
A bibliography should always contain every source you cited in your text. Sometimes a bibliography also contains other sources that you used in your research, but did not cite in the text.
MHRA doesn’t specify a rule about this, so check with your supervisor to find out exactly what should be included in your bibliography.
Footnote numbers should appear in superscript (e.g. 11 ). You can use the ‘Insert footnote’ button in Word to do this automatically; it’s in the ‘References’ tab at the top.
Footnotes always appear after the quote or paraphrase they relate to. MHRA generally recommends placing footnote numbers at the end of the sentence, immediately after any closing punctuation, like this. 12
In situations where this might be awkward or misleading, such as a long sentence containing multiple quotations, footnotes can also be placed at the end of a clause mid-sentence, like this; 13 note that they still come after any punctuation.
When a source has two or three authors, name all of them in your MHRA references . When there are four or more, use only the first name, followed by ‘and others’:
| Number of authors | Footnote example | Bibliography example |
|---|---|---|
| 1 author | David Smith | Smith, David |
| 2 authors | David Smith and Hugh Jones | Smith, David, and Hugh Jones |
| 3 authors | David Smith, Hugh Jones and Emily Wright | Smith, David, Hugh Jones and Emily Wright |
| 4+ authors | David Smith and others | Smith, David, and others |
Note that in the bibliography, only the author listed first has their name inverted. The names of additional authors and those of translators or editors are written normally.
A citation should appear wherever you use information or ideas from a source, whether by quoting or paraphrasing its content.
In Vancouver style , you have some flexibility about where the citation number appears in the sentence – usually directly after mentioning the author’s name is best, but simply placing it at the end of the sentence is an acceptable alternative, as long as it’s clear what it relates to.
In Vancouver style , when you refer to a source with multiple authors in your text, you should only name the first author followed by ‘et al.’. This applies even when there are only two authors.
In your reference list, include up to six authors. For sources with seven or more authors, list the first six followed by ‘et al.’.
The main difference is in terms of scale – a dissertation is usually much longer than the other essays you complete during your degree.
Another key difference is that you are given much more independence when working on a dissertation. You choose your own dissertation topic , and you have to conduct the research and write the dissertation yourself (with some assistance from your supervisor).
Dissertation word counts vary widely across different fields, institutions, and levels of education:
- An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000–15,000 words
- A master’s dissertation is typically 12,000–50,000 words
- A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000–100,000 words
However, none of these are strict guidelines – your word count may be lower or higher than the numbers stated here. Always check the guidelines provided by your university to determine how long your own dissertation should be.
At the bachelor’s and master’s levels, the dissertation is usually the main focus of your final year. You might work on it (alongside other classes) for the entirety of the final year, or for the last six months. This includes formulating an idea, doing the research, and writing up.
A PhD thesis takes a longer time, as the thesis is the main focus of the degree. A PhD thesis might be being formulated and worked on for the whole four years of the degree program. The writing process alone can take around 18 months.
References should be included in your text whenever you use words, ideas, or information from a source. A source can be anything from a book or journal article to a website or YouTube video.
If you don’t acknowledge your sources, you can get in trouble for plagiarism .
Your university should tell you which referencing style to follow. If you’re unsure, check with a supervisor. Commonly used styles include:
- Harvard referencing , the most commonly used style in UK universities.
- MHRA , used in humanities subjects.
- APA , used in the social sciences.
- Vancouver , used in biomedicine.
- OSCOLA , used in law.
Your university may have its own referencing style guide.
If you are allowed to choose which style to follow, we recommend Harvard referencing, as it is a straightforward and widely used style.
To avoid plagiarism , always include a reference when you use words, ideas or information from a source. This shows that you are not trying to pass the work of others off as your own.
You must also properly quote or paraphrase the source. If you’re not sure whether you’ve done this correctly, you can use the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker to find and correct any mistakes.
In Harvard style , when you quote directly from a source that includes page numbers, your in-text citation must include a page number. For example: (Smith, 2014, p. 33).
You can also include page numbers to point the reader towards a passage that you paraphrased . If you refer to the general ideas or findings of the source as a whole, you don’t need to include a page number.
When you want to use a quote but can’t access the original source, you can cite it indirectly. In the in-text citation , first mention the source you want to refer to, and then the source in which you found it. For example:
It’s advisable to avoid indirect citations wherever possible, because they suggest you don’t have full knowledge of the sources you’re citing. Only use an indirect citation if you can’t reasonably gain access to the original source.
In Harvard style referencing , to distinguish between two sources by the same author that were published in the same year, you add a different letter after the year for each source:
- (Smith, 2019a)
- (Smith, 2019b)
Add ‘a’ to the first one you cite, ‘b’ to the second, and so on. Do the same in your bibliography or reference list .
To create a hanging indent for your bibliography or reference list :
- Highlight all the entries
- Click on the arrow in the bottom-right corner of the ‘Paragraph’ tab in the top menu.
- In the pop-up window, under ‘Special’ in the ‘Indentation’ section, use the drop-down menu to select ‘Hanging’.
- Then close the window with ‘OK’.
Though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there is a difference in meaning:
- A reference list only includes sources cited in the text – every entry corresponds to an in-text citation .
- A bibliography also includes other sources which were consulted during the research but not cited.
It’s important to assess the reliability of information found online. Look for sources from established publications and institutions with expertise (e.g. peer-reviewed journals and government agencies).
The CRAAP test (currency, relevance, authority, accuracy, purpose) can aid you in assessing sources, as can our list of credible sources . You should generally avoid citing websites like Wikipedia that can be edited by anyone – instead, look for the original source of the information in the “References” section.
You can generally omit page numbers in your in-text citations of online sources which don’t have them. But when you quote or paraphrase a specific passage from a particularly long online source, it’s useful to find an alternate location marker.
For text-based sources, you can use paragraph numbers (e.g. ‘para. 4’) or headings (e.g. ‘under “Methodology”’). With video or audio sources, use a timestamp (e.g. ‘10:15’).
In the acknowledgements of your thesis or dissertation, you should first thank those who helped you academically or professionally, such as your supervisor, funders, and other academics.
Then you can include personal thanks to friends, family members, or anyone else who supported you during the process.
Yes, it’s important to thank your supervisor(s) in the acknowledgements section of your thesis or dissertation .
Even if you feel your supervisor did not contribute greatly to the final product, you still should acknowledge them, if only for a very brief thank you. If you do not include your supervisor, it may be seen as a snub.
The acknowledgements are generally included at the very beginning of your thesis or dissertation, directly after the title page and before the abstract .
In a thesis or dissertation, the acknowledgements should usually be no longer than one page. There is no minimum length.
You may acknowledge God in your thesis or dissertation acknowledgements , but be sure to follow academic convention by also thanking the relevant members of academia, as well as family, colleagues, and friends who helped you.
All level 1 and 2 headings should be included in your table of contents . That means the titles of your chapters and the main sections within them.
The contents should also include all appendices and the lists of tables and figures, if applicable, as well as your reference list .
Do not include the acknowledgements or abstract in the table of contents.
To automatically insert a table of contents in Microsoft Word, follow these steps:
- Apply heading styles throughout the document.
- In the references section in the ribbon, locate the Table of Contents group.
- Click the arrow next to the Table of Contents icon and select Custom Table of Contents.
- Select which levels of headings you would like to include in the table of contents.
Make sure to update your table of contents if you move text or change headings. To update, simply right click and select Update Field.
The table of contents in a thesis or dissertation always goes between your abstract and your introduction.
An abbreviation is a shortened version of an existing word, such as Dr for Doctor. In contrast, an acronym uses the first letter of each word to create a wholly new word, such as UNESCO (an acronym for the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization).
Your dissertation sometimes contains a list of abbreviations .
As a rule of thumb, write the explanation in full the first time you use an acronym or abbreviation. You can then proceed with the shortened version. However, if the abbreviation is very common (like UK or PC), then you can just use the abbreviated version straight away.
Be sure to add each abbreviation in your list of abbreviations !
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation, you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimising confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
A list of abbreviations is a list of all the abbreviations you used in your thesis or dissertation. It should appear at the beginning of your document, immediately after your table of contents . It should always be in alphabetical order.
Fishbone diagrams have a few different names that are used interchangeably, including herringbone diagram, cause-and-effect diagram, and Ishikawa diagram.
These are all ways to refer to the same thing– a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot solutions.
Fishbone diagrams (also called herringbone diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, and Ishikawa diagrams) are most popular in fields of quality management. They are also commonly used in nursing and healthcare, or as a brainstorming technique for students.
Some synonyms and near synonyms of among include:
- In the company of
- In the middle of
- Surrounded by
Some synonyms and near synonyms of between include:
- In the space separating
- In the time separating
In spite of is a preposition used to mean ‘ regardless of ‘, ‘notwithstanding’, or ‘even though’.
It’s always used in a subordinate clause to contrast with the information given in the main clause of a sentence (e.g., ‘Amy continued to watch TV, in spite of the time’).
Despite is a preposition used to mean ‘ regardless of ‘, ‘notwithstanding’, or ‘even though’.
It’s used in a subordinate clause to contrast with information given in the main clause of a sentence (e.g., ‘Despite the stress, Joe loves his job’).
‘Log in’ is a phrasal verb meaning ‘connect to an electronic device, system, or app’. The preposition ‘to’ is often used directly after the verb; ‘in’ and ‘to’ should be written as two separate words (e.g., ‘ log in to the app to update privacy settings’).
‘Log into’ is sometimes used instead of ‘log in to’, but this is generally considered incorrect (as is ‘login to’).
Some synonyms and near synonyms of ensure include:
- Make certain
Some synonyms and near synonyms of assure include:
Rest assured is an expression meaning ‘you can be certain’ (e.g., ‘Rest assured, I will find your cat’). ‘Assured’ is the adjectival form of the verb assure , meaning ‘convince’ or ‘persuade’.
Some synonyms and near synonyms for council include:
There are numerous synonyms and near synonyms for the two meanings of counsel :
| Direct | Direction |
| Guide | Guidance |
| Instruct | Instruction |
AI writing tools can be used to perform a variety of tasks.
Generative AI writing tools (like ChatGPT ) generate text based on human inputs and can be used for interactive learning, to provide feedback, or to generate research questions or outlines.
These tools can also be used to paraphrase or summarise text or to identify grammar and punctuation mistakes. Y ou can also use Scribbr’s free paraphrasing tool , summarising tool , and grammar checker , which are designed specifically for these purposes.
Using AI writing tools (like ChatGPT ) to write your essay is usually considered plagiarism and may result in penalisation, unless it is allowed by your university. Text generated by AI tools is based on existing texts and therefore cannot provide unique insights. Furthermore, these outputs sometimes contain factual inaccuracies or grammar mistakes.
However, AI writing tools can be used effectively as a source of feedback and inspiration for your writing (e.g., to generate research questions ). Other AI tools, like grammar checkers, can help identify and eliminate grammar and punctuation mistakes to enhance your writing.
The Scribbr Knowledge Base is a collection of free resources to help you succeed in academic research, writing, and citation. Every week, we publish helpful step-by-step guides, clear examples, simple templates, engaging videos, and more.
The Knowledge Base is for students at all levels. Whether you’re writing your first essay, working on your bachelor’s or master’s dissertation, or getting to grips with your PhD research, we’ve got you covered.
As well as the Knowledge Base, Scribbr provides many other tools and services to support you in academic writing and citation:
- Create your citations and manage your reference list with our free Reference Generators in APA and MLA style.
- Scan your paper for in-text citation errors and inconsistencies with our innovative APA Citation Checker .
- Avoid accidental plagiarism with our reliable Plagiarism Checker .
- Polish your writing and get feedback on structure and clarity with our Proofreading & Editing services .
Yes! We’re happy for educators to use our content, and we’ve even adapted some of our articles into ready-made lecture slides .
You are free to display, distribute, and adapt Scribbr materials in your classes or upload them in private learning environments like Blackboard. We only ask that you credit Scribbr for any content you use.
We’re always striving to improve the Knowledge Base. If you have an idea for a topic we should cover, or you notice a mistake in any of our articles, let us know by emailing [email protected] .
The consequences of plagiarism vary depending on the type of plagiarism and the context in which it occurs. For example, submitting a whole paper by someone else will have the most severe consequences, while accidental citation errors are considered less serious.
If you’re a student, then you might fail the course, be suspended or expelled, or be obligated to attend a workshop on plagiarism. It depends on whether it’s your first offence or you’ve done it before.
As an academic or professional, plagiarising seriously damages your reputation. You might also lose your research funding or your job, and you could even face legal consequences for copyright infringement.
Paraphrasing without crediting the original author is a form of plagiarism , because you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
However, paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you correctly reference the source . This means including an in-text referencing and a full reference , formatted according to your required citation style (e.g., Harvard , Vancouver ).
As well as referencing your source, make sure that any paraphrased text is completely rewritten in your own words.
Accidental plagiarism is one of the most common examples of plagiarism . Perhaps you forgot to cite a source, or paraphrased something a bit too closely. Maybe you can’t remember where you got an idea from, and aren’t totally sure if it’s original or not.
These all count as plagiarism, even though you didn’t do it on purpose. When in doubt, make sure you’re citing your sources . Also consider running your work through a plagiarism checker tool prior to submission, which work by using advanced database software to scan for matches between your text and existing texts.
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker takes less than 10 minutes and can help you turn in your paper with confidence.
The accuracy depends on the plagiarism checker you use. Per our in-depth research , Scribbr is the most accurate plagiarism checker. Many free plagiarism checkers fail to detect all plagiarism or falsely flag text as plagiarism.
Plagiarism checkers work by using advanced database software to scan for matches between your text and existing texts. Their accuracy is determined by two factors: the algorithm (which recognises the plagiarism) and the size of the database (with which your document is compared).
To avoid plagiarism when summarising an article or other source, follow these two rules:
- Write the summary entirely in your own words by paraphrasing the author’s ideas.
- Reference the source with an in-text citation and a full reference so your reader can easily find the original text.
Plagiarism can be detected by your professor or readers if the tone, formatting, or style of your text is different in different parts of your paper, or if they’re familiar with the plagiarised source.
Many universities also use plagiarism detection software like Turnitin’s, which compares your text to a large database of other sources, flagging any similarities that come up.
It can be easier than you think to commit plagiarism by accident. Consider using a plagiarism checker prior to submitting your essay to ensure you haven’t missed any citations.
Some examples of plagiarism include:
- Copying and pasting a Wikipedia article into the body of an assignment
- Quoting a source without including a citation
- Not paraphrasing a source properly (e.g. maintaining wording too close to the original)
- Forgetting to cite the source of an idea
The most surefire way to avoid plagiarism is to always cite your sources . When in doubt, cite!
Global plagiarism means taking an entire work written by someone else and passing it off as your own. This can include getting someone else to write an essay or assignment for you, or submitting a text you found online as your own work.
Global plagiarism is one of the most serious types of plagiarism because it involves deliberately and directly lying about the authorship of a work. It can have severe consequences for students and professionals alike.
Verbatim plagiarism means copying text from a source and pasting it directly into your own document without giving proper credit.
If the structure and the majority of the words are the same as in the original source, then you are committing verbatim plagiarism. This is the case even if you delete a few words or replace them with synonyms.
If you want to use an author’s exact words, you need to quote the original source by putting the copied text in quotation marks and including an in-text citation .
Patchwork plagiarism , also called mosaic plagiarism, means copying phrases, passages, or ideas from various existing sources and combining them to create a new text. This includes slightly rephrasing some of the content, while keeping many of the same words and the same structure as the original.
While this type of plagiarism is more insidious than simply copying and pasting directly from a source, plagiarism checkers like Turnitin’s can still easily detect it.
To avoid plagiarism in any form, remember to reference your sources .
Yes, reusing your own work without citation is considered self-plagiarism . This can range from resubmitting an entire assignment to reusing passages or data from something you’ve handed in previously.
Self-plagiarism often has the same consequences as other types of plagiarism . If you want to reuse content you wrote in the past, make sure to check your university’s policy or consult your professor.
If you are reusing content or data you used in a previous assignment, make sure to cite yourself. You can cite yourself the same way you would cite any other source: simply follow the directions for the citation style you are using.
Keep in mind that reusing prior content can be considered self-plagiarism , so make sure you ask your instructor or consult your university’s handbook prior to doing so.
Most institutions have an internal database of previously submitted student assignments. Turnitin can check for self-plagiarism by comparing your paper against this database. If you’ve reused parts of an assignment you already submitted, it will flag any similarities as potential plagiarism.
Online plagiarism checkers don’t have access to your institution’s database, so they can’t detect self-plagiarism of unpublished work. If you’re worried about accidentally self-plagiarising, you can use Scribbr’s Self-Plagiarism Checker to upload your unpublished documents and check them for similarities.
Plagiarism has serious consequences and can be illegal in certain scenarios.
While most of the time plagiarism in an undergraduate setting is not illegal, plagiarism or self-plagiarism in a professional academic setting can lead to legal action, including copyright infringement and fraud. Many scholarly journals do not allow you to submit the same work to more than one journal, and if you do not credit a coauthor, you could be legally defrauding them.
Even if you aren’t breaking the law, plagiarism can seriously impact your academic career. While the exact consequences of plagiarism vary by institution and severity, common consequences include a lower grade, automatically failing a course, academic suspension or probation, and even expulsion.
Self-plagiarism means recycling work that you’ve previously published or submitted as an assignment. It’s considered academic dishonesty to present something as brand new when you’ve already gotten credit and perhaps feedback for it in the past.
If you want to refer to ideas or data from previous work, be sure to cite yourself.
Academic integrity means being honest, ethical, and thorough in your academic work. To maintain academic integrity, you should avoid misleading your readers about any part of your research and refrain from offences like plagiarism and contract cheating, which are examples of academic misconduct.
Academic dishonesty refers to deceitful or misleading behavior in an academic setting. Academic dishonesty can occur intentionally or unintentionally, and it varies in severity.
It can encompass paying for a pre-written essay, cheating on an exam, or committing plagiarism . It can also include helping others cheat, copying a friend’s homework answers, or even pretending to be sick to miss an exam.
Academic dishonesty doesn’t just occur in a classroom setting, but also in research and other academic-adjacent fields.
Consequences of academic dishonesty depend on the severity of the offence and your institution’s policy. They can range from a warning for a first offence to a failing grade in a course to expulsion from your university.
For those in certain fields, such as nursing, engineering, or lab sciences, not learning fundamentals properly can directly impact the health and safety of others. For those working in academia or research, academic dishonesty impacts your professional reputation, leading others to doubt your future work.
Academic dishonesty can be intentional or unintentional, ranging from something as simple as claiming to have read something you didn’t to copying your neighbour’s answers on an exam.
You can commit academic dishonesty with the best of intentions, such as helping a friend cheat on a paper. Severe academic dishonesty can include buying a pre-written essay or the answers to a multiple-choice test, or falsifying a medical emergency to avoid taking a final exam.
Plagiarism means presenting someone else’s work as your own without giving proper credit to the original author. In academic writing, plagiarism involves using words, ideas, or information from a source without including a citation .
Plagiarism can have serious consequences , even when it’s done accidentally. To avoid plagiarism, it’s important to keep track of your sources and cite them correctly.
Common knowledge does not need to be cited. However, you should be extra careful when deciding what counts as common knowledge.
Common knowledge encompasses information that the average educated reader would accept as true without needing the extra validation of a source or citation.
Common knowledge should be widely known, undisputed, and easily verified. When in doubt, always cite your sources.
Most online plagiarism checkers only have access to public databases, whose software doesn’t allow you to compare two documents for plagiarism.
However, in addition to our Plagiarism Checker , Scribbr also offers an Self-Plagiarism Checker . This is an add-on tool that lets you compare your paper with unpublished or private documents. This way you can rest assured that you haven’t unintentionally plagiarised or self-plagiarised .
Compare two sources for plagiarism
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyse a large amount of readily available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how they are generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research project . It involves studying the methods used in your field and the theories or principles behind them, in order to develop an approach that matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyse data (e.g. experiments, surveys , and statistical tests ).
In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section .
In a longer or more complex research project, such as a thesis or dissertation , you will probably include a methodology section , where you explain your approach to answering the research questions and cite relevant sources to support your choice of methods.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organise your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organisation to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioural avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalise the variables that you want to measure.
Triangulation in research means using multiple datasets, methods, theories and/or investigators to address a research question. It’s a research strategy that can help you enhance the validity and credibility of your findings.
Triangulation is mainly used in qualitative research , but it’s also commonly applied in quantitative research . Mixed methods research always uses triangulation.
These are four of the most common mixed methods designs :
- Convergent parallel: Quantitative and qualitative data are collected at the same time and analysed separately. After both analyses are complete, compare your results to draw overall conclusions.
- Embedded: Quantitative and qualitative data are collected at the same time, but within a larger quantitative or qualitative design. One type of data is secondary to the other.
- Explanatory sequential: Quantitative data is collected and analysed first, followed by qualitative data. You can use this design if you think your qualitative data will explain and contextualise your quantitative findings.
- Exploratory sequential: Qualitative data is collected and analysed first, followed by quantitative data. You can use this design if you think the quantitative data will confirm or validate your qualitative findings.
An observational study could be a good fit for your research if your research question is based on things you observe. If you have ethical, logistical, or practical concerns that make an experimental design challenging, consider an observational study. Remember that in an observational study, it is critical that there be no interference or manipulation of the research subjects. Since it’s not an experiment, there are no control or treatment groups either.
The key difference between observational studies and experiments is that, done correctly, an observational study will never influence the responses or behaviours of participants. Experimental designs will have a treatment condition applied to at least a portion of participants.
Exploratory research explores the main aspects of a new or barely researched question.
Explanatory research explains the causes and effects of an already widely researched question.
Experimental designs are a set of procedures that you plan in order to examine the relationship between variables that interest you.
To design a successful experiment, first identify:
- A testable hypothesis
- One or more independent variables that you will manipulate
- One or more dependent variables that you will measure
When designing the experiment, first decide:
- How your variable(s) will be manipulated
- How you will control for any potential confounding or lurking variables
- How many subjects you will include
- How you will assign treatments to your subjects
There are four main types of triangulation :
- Data triangulation : Using data from different times, spaces, and people
- Investigator triangulation : Involving multiple researchers in collecting or analysing data
- Theory triangulation : Using varying theoretical perspectives in your research
- Methodological triangulation : Using different methodologies to approach the same topic
Triangulation can help:
- Reduce bias that comes from using a single method, theory, or investigator
- Enhance validity by approaching the same topic with different tools
- Establish credibility by giving you a complete picture of the research problem
But triangulation can also pose problems:
- It’s time-consuming and labour-intensive, often involving an interdisciplinary team.
- Your results may be inconsistent or even contradictory.
A confounding variable , also called a confounder or confounding factor, is a third variable in a study examining a potential cause-and-effect relationship.
A confounding variable is related to both the supposed cause and the supposed effect of the study. It can be difficult to separate the true effect of the independent variable from the effect of the confounding variable.
In your research design , it’s important to identify potential confounding variables and plan how you will reduce their impact.
In a between-subjects design , every participant experiences only one condition, and researchers assess group differences between participants in various conditions.
In a within-subjects design , each participant experiences all conditions, and researchers test the same participants repeatedly for differences between conditions.
The word ‘between’ means that you’re comparing different conditions between groups, while the word ‘within’ means you’re comparing different conditions within the same group.
A quasi-experiment is a type of research design that attempts to establish a cause-and-effect relationship. The main difference between this and a true experiment is that the groups are not randomly assigned.
In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different groups using randomisation. With this method, every member of the sample has a known or equal chance of being placed in a control group or an experimental group.
Quasi-experimental design is most useful in situations where it would be unethical or impractical to run a true experiment .
Quasi-experiments have lower internal validity than true experiments, but they often have higher external validity as they can use real-world interventions instead of artificial laboratory settings.
Within-subjects designs have many potential threats to internal validity , but they are also very statistically powerful .
Advantages:
- Only requires small samples
- Statistically powerful
- Removes the effects of individual differences on the outcomes
Disadvantages:
- Internal validity threats reduce the likelihood of establishing a direct relationship between variables
- Time-related effects, such as growth, can influence the outcomes
- Carryover effects mean that the specific order of different treatments affect the outcomes
Yes. Between-subjects and within-subjects designs can be combined in a single study when you have two or more independent variables (a factorial design). In a mixed factorial design, one variable is altered between subjects and another is altered within subjects.
In a factorial design, multiple independent variables are tested.
If you test two variables, each level of one independent variable is combined with each level of the other independent variable to create different conditions.
While a between-subjects design has fewer threats to internal validity , it also requires more participants for high statistical power than a within-subjects design .
- Prevents carryover effects of learning and fatigue.
- Shorter study duration.
- Needs larger samples for high power.
- Uses more resources to recruit participants, administer sessions, cover costs, etc.
- Individual differences may be an alternative explanation for results.
Samples are used to make inferences about populations . Samples are easier to collect data from because they are practical, cost-effective, convenient, and manageable.
Probability sampling means that every member of the target population has a known chance of being included in the sample.
Probability sampling methods include simple random sampling , systematic sampling , stratified sampling , and cluster sampling .
In non-probability sampling , the sample is selected based on non-random criteria, and not every member of the population has a chance of being included.
Common non-probability sampling methods include convenience sampling , voluntary response sampling, purposive sampling , snowball sampling , and quota sampling .
In multistage sampling , or multistage cluster sampling, you draw a sample from a population using smaller and smaller groups at each stage.
This method is often used to collect data from a large, geographically spread group of people in national surveys, for example. You take advantage of hierarchical groupings (e.g., from county to city to neighbourhood) to create a sample that’s less expensive and time-consuming to collect data from.
Sampling bias occurs when some members of a population are systematically more likely to be selected in a sample than others.
Simple random sampling is a type of probability sampling in which the researcher randomly selects a subset of participants from a population . Each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. Data are then collected from as large a percentage as possible of this random subset.
The American Community Survey is an example of simple random sampling . In order to collect detailed data on the population of the US, the Census Bureau officials randomly select 3.5 million households per year and use a variety of methods to convince them to fill out the survey.
If properly implemented, simple random sampling is usually the best sampling method for ensuring both internal and external validity . However, it can sometimes be impractical and expensive to implement, depending on the size of the population to be studied,
If you have a list of every member of the population and the ability to reach whichever members are selected, you can use simple random sampling.
Cluster sampling is more time- and cost-efficient than other probability sampling methods , particularly when it comes to large samples spread across a wide geographical area.
However, it provides less statistical certainty than other methods, such as simple random sampling , because it is difficult to ensure that your clusters properly represent the population as a whole.
There are three types of cluster sampling : single-stage, double-stage and multi-stage clustering. In all three types, you first divide the population into clusters, then randomly select clusters for use in your sample.
- In single-stage sampling , you collect data from every unit within the selected clusters.
- In double-stage sampling , you select a random sample of units from within the clusters.
- In multi-stage sampling , you repeat the procedure of randomly sampling elements from within the clusters until you have reached a manageable sample.
Cluster sampling is a probability sampling method in which you divide a population into clusters, such as districts or schools, and then randomly select some of these clusters as your sample.
The clusters should ideally each be mini-representations of the population as a whole.
In multistage sampling , you can use probability or non-probability sampling methods.
For a probability sample, you have to probability sampling at every stage. You can mix it up by using simple random sampling , systematic sampling , or stratified sampling to select units at different stages, depending on what is applicable and relevant to your study.
Multistage sampling can simplify data collection when you have large, geographically spread samples, and you can obtain a probability sample without a complete sampling frame.
But multistage sampling may not lead to a representative sample, and larger samples are needed for multistage samples to achieve the statistical properties of simple random samples .
In stratified sampling , researchers divide subjects into subgroups called strata based on characteristics that they share (e.g., race, gender, educational attainment).
Once divided, each subgroup is randomly sampled using another probability sampling method .
You should use stratified sampling when your sample can be divided into mutually exclusive and exhaustive subgroups that you believe will take on different mean values for the variable that you’re studying.
Using stratified sampling will allow you to obtain more precise (with lower variance ) statistical estimates of whatever you are trying to measure.
For example, say you want to investigate how income differs based on educational attainment, but you know that this relationship can vary based on race. Using stratified sampling, you can ensure you obtain a large enough sample from each racial group, allowing you to draw more precise conclusions.
Yes, you can create a stratified sample using multiple characteristics, but you must ensure that every participant in your study belongs to one and only one subgroup. In this case, you multiply the numbers of subgroups for each characteristic to get the total number of groups.
For example, if you were stratifying by location with three subgroups (urban, rural, or suburban) and marital status with five subgroups (single, divorced, widowed, married, or partnered), you would have 3 × 5 = 15 subgroups.
There are three key steps in systematic sampling :
- Define and list your population , ensuring that it is not ordered in a cyclical or periodic order.
- Decide on your sample size and calculate your interval, k , by dividing your population by your target sample size.
- Choose every k th member of the population as your sample.
Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method where researchers select members of the population at a regular interval – for example, by selecting every 15th person on a list of the population. If the population is in a random order, this can imitate the benefits of simple random sampling .
Populations are used when a research question requires data from every member of the population. This is usually only feasible when the population is small and easily accessible.
A statistic refers to measures about the sample , while a parameter refers to measures about the population .
A sampling error is the difference between a population parameter and a sample statistic .
There are eight threats to internal validity : history, maturation, instrumentation, testing, selection bias , regression to the mean, social interaction, and attrition .
Internal validity is the extent to which you can be confident that a cause-and-effect relationship established in a study cannot be explained by other factors.
Attrition bias is a threat to internal validity . In experiments, differential rates of attrition between treatment and control groups can skew results.
This bias can affect the relationship between your independent and dependent variables . It can make variables appear to be correlated when they are not, or vice versa.
The external validity of a study is the extent to which you can generalise your findings to different groups of people, situations, and measures.
The two types of external validity are population validity (whether you can generalise to other groups of people) and ecological validity (whether you can generalise to other situations and settings).
There are seven threats to external validity : selection bias , history, experimenter effect, Hawthorne effect , testing effect, aptitude-treatment, and situation effect.
Attrition bias can skew your sample so that your final sample differs significantly from your original sample. Your sample is biased because some groups from your population are underrepresented.
With a biased final sample, you may not be able to generalise your findings to the original population that you sampled from, so your external validity is compromised.
Construct validity is about how well a test measures the concept it was designed to evaluate. It’s one of four types of measurement validity , which includes construct validity, face validity , and criterion validity.
There are two subtypes of construct validity.
- Convergent validity : The extent to which your measure corresponds to measures of related constructs
- Discriminant validity: The extent to which your measure is unrelated or negatively related to measures of distinct constructs
When designing or evaluating a measure, construct validity helps you ensure you’re actually measuring the construct you’re interested in. If you don’t have construct validity, you may inadvertently measure unrelated or distinct constructs and lose precision in your research.
Construct validity is often considered the overarching type of measurement validity , because it covers all of the other types. You need to have face validity , content validity, and criterion validity to achieve construct validity.
Statistical analyses are often applied to test validity with data from your measures. You test convergent validity and discriminant validity with correlations to see if results from your test are positively or negatively related to those of other established tests.
You can also use regression analyses to assess whether your measure is actually predictive of outcomes that you expect it to predict theoretically. A regression analysis that supports your expectations strengthens your claim of construct validity .
Face validity is about whether a test appears to measure what it’s supposed to measure. This type of validity is concerned with whether a measure seems relevant and appropriate for what it’s assessing only on the surface.
Face validity is important because it’s a simple first step to measuring the overall validity of a test or technique. It’s a relatively intuitive, quick, and easy way to start checking whether a new measure seems useful at first glance.
Good face validity means that anyone who reviews your measure says that it seems to be measuring what it’s supposed to. With poor face validity, someone reviewing your measure may be left confused about what you’re measuring and why you’re using this method.
It’s often best to ask a variety of people to review your measurements. You can ask experts, such as other researchers, or laypeople, such as potential participants, to judge the face validity of tests.
While experts have a deep understanding of research methods , the people you’re studying can provide you with valuable insights you may have missed otherwise.
There are many different types of inductive reasoning that people use formally or informally.
Here are a few common types:
- Inductive generalisation : You use observations about a sample to come to a conclusion about the population it came from.
- Statistical generalisation: You use specific numbers about samples to make statements about populations.
- Causal reasoning: You make cause-and-effect links between different things.
- Sign reasoning: You make a conclusion about a correlational relationship between different things.
- Analogical reasoning: You make a conclusion about something based on its similarities to something else.
Inductive reasoning is a bottom-up approach, while deductive reasoning is top-down.
Inductive reasoning takes you from the specific to the general, while in deductive reasoning, you make inferences by going from general premises to specific conclusions.
In inductive research , you start by making observations or gathering data. Then, you take a broad scan of your data and search for patterns. Finally, you make general conclusions that you might incorporate into theories.
Inductive reasoning is a method of drawing conclusions by going from the specific to the general. It’s usually contrasted with deductive reasoning, where you proceed from general information to specific conclusions.
Inductive reasoning is also called inductive logic or bottom-up reasoning.
Deductive reasoning is a logical approach where you progress from general ideas to specific conclusions. It’s often contrasted with inductive reasoning , where you start with specific observations and form general conclusions.
Deductive reasoning is also called deductive logic.
Deductive reasoning is commonly used in scientific research, and it’s especially associated with quantitative research .
In research, you might have come across something called the hypothetico-deductive method . It’s the scientific method of testing hypotheses to check whether your predictions are substantiated by real-world data.
A dependent variable is what changes as a result of the independent variable manipulation in experiments . It’s what you’re interested in measuring, and it ‘depends’ on your independent variable.
In statistics, dependent variables are also called:
- Response variables (they respond to a change in another variable)
- Outcome variables (they represent the outcome you want to measure)
- Left-hand-side variables (they appear on the left-hand side of a regression equation)
An independent variable is the variable you manipulate, control, or vary in an experimental study to explore its effects. It’s called ‘independent’ because it’s not influenced by any other variables in the study.
Independent variables are also called:
- Explanatory variables (they explain an event or outcome)
- Predictor variables (they can be used to predict the value of a dependent variable)
- Right-hand-side variables (they appear on the right-hand side of a regression equation)
A correlation is usually tested for two variables at a time, but you can test correlations between three or more variables.
On graphs, the explanatory variable is conventionally placed on the x -axis, while the response variable is placed on the y -axis.
- If you have quantitative variables , use a scatterplot or a line graph.
- If your response variable is categorical, use a scatterplot or a line graph.
- If your explanatory variable is categorical, use a bar graph.
The term ‘ explanatory variable ‘ is sometimes preferred over ‘ independent variable ‘ because, in real-world contexts, independent variables are often influenced by other variables. This means they aren’t totally independent.
Multiple independent variables may also be correlated with each other, so ‘explanatory variables’ is a more appropriate term.
The difference between explanatory and response variables is simple:
- An explanatory variable is the expected cause, and it explains the results.
- A response variable is the expected effect, and it responds to other variables.
There are 4 main types of extraneous variables :
- Demand characteristics : Environmental cues that encourage participants to conform to researchers’ expectations
- Experimenter effects : Unintentional actions by researchers that influence study outcomes
- Situational variables : Eenvironmental variables that alter participants’ behaviours
- Participant variables : Any characteristic or aspect of a participant’s background that could affect study results
An extraneous variable is any variable that you’re not investigating that can potentially affect the dependent variable of your research study.
A confounding variable is a type of extraneous variable that not only affects the dependent variable, but is also related to the independent variable.
‘Controlling for a variable’ means measuring extraneous variables and accounting for them statistically to remove their effects on other variables.
Researchers often model control variable data along with independent and dependent variable data in regression analyses and ANCOVAs . That way, you can isolate the control variable’s effects from the relationship between the variables of interest.
Control variables help you establish a correlational or causal relationship between variables by enhancing internal validity .
If you don’t control relevant extraneous variables , they may influence the outcomes of your study, and you may not be able to demonstrate that your results are really an effect of your independent variable .
A control variable is any variable that’s held constant in a research study. It’s not a variable of interest in the study, but it’s controlled because it could influence the outcomes.
In statistics, ordinal and nominal variables are both considered categorical variables .
Even though ordinal data can sometimes be numerical, not all mathematical operations can be performed on them.
In scientific research, concepts are the abstract ideas or phenomena that are being studied (e.g., educational achievement). Variables are properties or characteristics of the concept (e.g., performance at school), while indicators are ways of measuring or quantifying variables (e.g., yearly grade reports).
The process of turning abstract concepts into measurable variables and indicators is called operationalisation .
There are several methods you can use to decrease the impact of confounding variables on your research: restriction, matching, statistical control, and randomisation.
In restriction , you restrict your sample by only including certain subjects that have the same values of potential confounding variables.
In matching , you match each of the subjects in your treatment group with a counterpart in the comparison group. The matched subjects have the same values on any potential confounding variables, and only differ in the independent variable .
In statistical control , you include potential confounders as variables in your regression .
In randomisation , you randomly assign the treatment (or independent variable) in your study to a sufficiently large number of subjects, which allows you to control for all potential confounding variables.
A confounding variable is closely related to both the independent and dependent variables in a study. An independent variable represents the supposed cause , while the dependent variable is the supposed effect . A confounding variable is a third variable that influences both the independent and dependent variables.
Failing to account for confounding variables can cause you to wrongly estimate the relationship between your independent and dependent variables.
To ensure the internal validity of your research, you must consider the impact of confounding variables. If you fail to account for them, you might over- or underestimate the causal relationship between your independent and dependent variables , or even find a causal relationship where none exists.
Yes, but including more than one of either type requires multiple research questions .
For example, if you are interested in the effect of a diet on health, you can use multiple measures of health: blood sugar, blood pressure, weight, pulse, and many more. Each of these is its own dependent variable with its own research question.
You could also choose to look at the effect of exercise levels as well as diet, or even the additional effect of the two combined. Each of these is a separate independent variable .
To ensure the internal validity of an experiment , you should only change one independent variable at a time.
No. The value of a dependent variable depends on an independent variable, so a variable cannot be both independent and dependent at the same time. It must be either the cause or the effect, not both.
You want to find out how blood sugar levels are affected by drinking diet cola and regular cola, so you conduct an experiment .
- The type of cola – diet or regular – is the independent variable .
- The level of blood sugar that you measure is the dependent variable – it changes depending on the type of cola.
Determining cause and effect is one of the most important parts of scientific research. It’s essential to know which is the cause – the independent variable – and which is the effect – the dependent variable.
Quantitative variables are any variables where the data represent amounts (e.g. height, weight, or age).
Categorical variables are any variables where the data represent groups. This includes rankings (e.g. finishing places in a race), classifications (e.g. brands of cereal), and binary outcomes (e.g. coin flips).
You need to know what type of variables you are working with to choose the right statistical test for your data and interpret your results .
Discrete and continuous variables are two types of quantitative variables :
- Discrete variables represent counts (e.g., the number of objects in a collection).
- Continuous variables represent measurable amounts (e.g., water volume or weight).
You can think of independent and dependent variables in terms of cause and effect: an independent variable is the variable you think is the cause , while a dependent variable is the effect .
In an experiment, you manipulate the independent variable and measure the outcome in the dependent variable. For example, in an experiment about the effect of nutrients on crop growth:
- The independent variable is the amount of nutrients added to the crop field.
- The dependent variable is the biomass of the crops at harvest time.
Defining your variables, and deciding how you will manipulate and measure them, is an important part of experimental design .
Including mediators and moderators in your research helps you go beyond studying a simple relationship between two variables for a fuller picture of the real world. They are important to consider when studying complex correlational or causal relationships.
Mediators are part of the causal pathway of an effect, and they tell you how or why an effect takes place. Moderators usually help you judge the external validity of your study by identifying the limitations of when the relationship between variables holds.
If something is a mediating variable :
- It’s caused by the independent variable
- It influences the dependent variable
- When it’s taken into account, the statistical correlation between the independent and dependent variables is higher than when it isn’t considered
A confounder is a third variable that affects variables of interest and makes them seem related when they are not. In contrast, a mediator is the mechanism of a relationship between two variables: it explains the process by which they are related.
A mediator variable explains the process through which two variables are related, while a moderator variable affects the strength and direction of that relationship.
When conducting research, collecting original data has significant advantages:
- You can tailor data collection to your specific research aims (e.g., understanding the needs of your consumers or user testing your website).
- You can control and standardise the process for high reliability and validity (e.g., choosing appropriate measurements and sampling methods ).
However, there are also some drawbacks: data collection can be time-consuming, labour-intensive, and expensive. In some cases, it’s more efficient to use secondary data that has already been collected by someone else, but the data might be less reliable.
A structured interview is a data collection method that relies on asking questions in a set order to collect data on a topic. They are often quantitative in nature. Structured interviews are best used when:
- You already have a very clear understanding of your topic. Perhaps significant research has already been conducted, or you have done some prior research yourself, but you already possess a baseline for designing strong structured questions.
- You are constrained in terms of time or resources and need to analyse your data quickly and efficiently
- Your research question depends on strong parity between participants, with environmental conditions held constant
More flexible interview options include semi-structured interviews , unstructured interviews , and focus groups .
The interviewer effect is a type of bias that emerges when a characteristic of an interviewer (race, age, gender identity, etc.) influences the responses given by the interviewee.
There is a risk of an interviewer effect in all types of interviews , but it can be mitigated by writing really high-quality interview questions.
A semi-structured interview is a blend of structured and unstructured types of interviews. Semi-structured interviews are best used when:
- You have prior interview experience. Spontaneous questions are deceptively challenging, and it’s easy to accidentally ask a leading question or make a participant uncomfortable.
- Your research question is exploratory in nature. Participant answers can guide future research questions and help you develop a more robust knowledge base for future research.
An unstructured interview is the most flexible type of interview, but it is not always the best fit for your research topic.
Unstructured interviews are best used when:
- You are an experienced interviewer and have a very strong background in your research topic, since it is challenging to ask spontaneous, colloquial questions
- Your research question is exploratory in nature. While you may have developed hypotheses, you are open to discovering new or shifting viewpoints through the interview process.
- You are seeking descriptive data, and are ready to ask questions that will deepen and contextualise your initial thoughts and hypotheses
- Your research depends on forming connections with your participants and making them feel comfortable revealing deeper emotions, lived experiences, or thoughts
The four most common types of interviews are:
- Structured interviews : The questions are predetermined in both topic and order.
- Semi-structured interviews : A few questions are predetermined, but other questions aren’t planned.
- Unstructured interviews : None of the questions are predetermined.
- Focus group interviews : The questions are presented to a group instead of one individual.
A focus group is a research method that brings together a small group of people to answer questions in a moderated setting. The group is chosen due to predefined demographic traits, and the questions are designed to shed light on a topic of interest. It is one of four types of interviews .
Social desirability bias is the tendency for interview participants to give responses that will be viewed favourably by the interviewer or other participants. It occurs in all types of interviews and surveys , but is most common in semi-structured interviews , unstructured interviews , and focus groups .
Social desirability bias can be mitigated by ensuring participants feel at ease and comfortable sharing their views. Make sure to pay attention to your own body language and any physical or verbal cues, such as nodding or widening your eyes.
This type of bias in research can also occur in observations if the participants know they’re being observed. They might alter their behaviour accordingly.
As a rule of thumb, questions related to thoughts, beliefs, and feelings work well in focus groups . Take your time formulating strong questions, paying special attention to phrasing. Be careful to avoid leading questions , which can bias your responses.
Overall, your focus group questions should be:
- Open-ended and flexible
- Impossible to answer with ‘yes’ or ‘no’ (questions that start with ‘why’ or ‘how’ are often best)
- Unambiguous, getting straight to the point while still stimulating discussion
- Unbiased and neutral
The third variable and directionality problems are two main reasons why correlation isn’t causation .
The third variable problem means that a confounding variable affects both variables to make them seem causally related when they are not.
The directionality problem is when two variables correlate and might actually have a causal relationship, but it’s impossible to conclude which variable causes changes in the other.
Controlled experiments establish causality, whereas correlational studies only show associations between variables.
- In an experimental design , you manipulate an independent variable and measure its effect on a dependent variable. Other variables are controlled so they can’t impact the results.
- In a correlational design , you measure variables without manipulating any of them. You can test whether your variables change together, but you can’t be sure that one variable caused a change in another.
In general, correlational research is high in external validity while experimental research is high in internal validity .
A correlation coefficient is a single number that describes the strength and direction of the relationship between your variables.
Different types of correlation coefficients might be appropriate for your data based on their levels of measurement and distributions . The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (Pearson’s r ) is commonly used to assess a linear relationship between two quantitative variables.
A correlational research design investigates relationships between two variables (or more) without the researcher controlling or manipulating any of them. It’s a non-experimental type of quantitative research .
A correlation reflects the strength and/or direction of the association between two or more variables.
- A positive correlation means that both variables change in the same direction.
- A negative correlation means that the variables change in opposite directions.
- A zero correlation means there’s no relationship between the variables.
Longitudinal studies can last anywhere from weeks to decades, although they tend to be at least a year long.
The 1970 British Cohort Study , which has collected data on the lives of 17,000 Brits since their births in 1970, is one well-known example of a longitudinal study .
Longitudinal studies are better to establish the correct sequence of events, identify changes over time, and provide insight into cause-and-effect relationships, but they also tend to be more expensive and time-consuming than other types of studies.
Longitudinal studies and cross-sectional studies are two different types of research design . In a cross-sectional study you collect data from a population at a specific point in time; in a longitudinal study you repeatedly collect data from the same sample over an extended period of time.
| Longitudinal study | Cross-sectional study |
|---|---|
| observations | Observations at a in time |
| Observes the multiple times | Observes (a ‘cross-section’) in the population |
| Follows in participants over time | Provides of society at a given point |
Cross-sectional studies cannot establish a cause-and-effect relationship or analyse behaviour over a period of time. To investigate cause and effect, you need to do a longitudinal study or an experimental study .
Cross-sectional studies are less expensive and time-consuming than many other types of study. They can provide useful insights into a population’s characteristics and identify correlations for further research.
Sometimes only cross-sectional data are available for analysis; other times your research question may only require a cross-sectional study to answer it.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess. It should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Individual Likert-type questions are generally considered ordinal data , because the items have clear rank order, but don’t have an even distribution.
Overall Likert scale scores are sometimes treated as interval data. These scores are considered to have directionality and even spacing between them.
The type of data determines what statistical tests you should use to analyse your data.
A Likert scale is a rating scale that quantitatively assesses opinions, attitudes, or behaviours. It is made up of four or more questions that measure a single attitude or trait when response scores are combined.
To use a Likert scale in a survey , you present participants with Likert-type questions or statements, and a continuum of items, usually with five or seven possible responses, to capture their degree of agreement.
A questionnaire is a data collection tool or instrument, while a survey is an overarching research method that involves collecting and analysing data from people using questionnaires.
A true experiment (aka a controlled experiment) always includes at least one control group that doesn’t receive the experimental treatment.
However, some experiments use a within-subjects design to test treatments without a control group. In these designs, you usually compare one group’s outcomes before and after a treatment (instead of comparing outcomes between different groups).
For strong internal validity , it’s usually best to include a control group if possible. Without a control group, it’s harder to be certain that the outcome was caused by the experimental treatment and not by other variables.
An experimental group, also known as a treatment group, receives the treatment whose effect researchers wish to study, whereas a control group does not. They should be identical in all other ways.
In a controlled experiment , all extraneous variables are held constant so that they can’t influence the results. Controlled experiments require:
- A control group that receives a standard treatment, a fake treatment, or no treatment
- Random assignment of participants to ensure the groups are equivalent
Depending on your study topic, there are various other methods of controlling variables .
Questionnaires can be self-administered or researcher-administered.
Self-administered questionnaires can be delivered online or in paper-and-pen formats, in person or by post. All questions are standardised so that all respondents receive the same questions with identical wording.
Researcher-administered questionnaires are interviews that take place by phone, in person, or online between researchers and respondents. You can gain deeper insights by clarifying questions for respondents or asking follow-up questions.
You can organise the questions logically, with a clear progression from simple to complex, or randomly between respondents. A logical flow helps respondents process the questionnaire easier and quicker, but it may lead to bias. Randomisation can minimise the bias from order effects.
Closed-ended, or restricted-choice, questions offer respondents a fixed set of choices to select from. These questions are easier to answer quickly.
Open-ended or long-form questions allow respondents to answer in their own words. Because there are no restrictions on their choices, respondents can answer in ways that researchers may not have otherwise considered.
Naturalistic observation is a qualitative research method where you record the behaviours of your research subjects in real-world settings. You avoid interfering or influencing anything in a naturalistic observation.
You can think of naturalistic observation as ‘people watching’ with a purpose.
Naturalistic observation is a valuable tool because of its flexibility, external validity , and suitability for topics that can’t be studied in a lab setting.
The downsides of naturalistic observation include its lack of scientific control , ethical considerations , and potential for bias from observers and subjects.
You can use several tactics to minimise observer bias .
- Use masking (blinding) to hide the purpose of your study from all observers.
- Triangulate your data with different data collection methods or sources.
- Use multiple observers and ensure inter-rater reliability.
- Train your observers to make sure data is consistently recorded between them.
- Standardise your observation procedures to make sure they are structured and clear.
The observer-expectancy effect occurs when researchers influence the results of their own study through interactions with participants.
Researchers’ own beliefs and expectations about the study results may unintentionally influence participants through demand characteristics .
Observer bias occurs when a researcher’s expectations, opinions, or prejudices influence what they perceive or record in a study. It usually affects studies when observers are aware of the research aims or hypotheses. This type of research bias is also called detection bias or ascertainment bias .
Data cleaning is necessary for valid and appropriate analyses. Dirty data contain inconsistencies or errors , but cleaning your data helps you minimise or resolve these.
Without data cleaning, you could end up with a Type I or II error in your conclusion. These types of erroneous conclusions can be practically significant with important consequences, because they lead to misplaced investments or missed opportunities.
Data cleaning involves spotting and resolving potential data inconsistencies or errors to improve your data quality. An error is any value (e.g., recorded weight) that doesn’t reflect the true value (e.g., actual weight) of something that’s being measured.
In this process, you review, analyse, detect, modify, or remove ‘dirty’ data to make your dataset ‘clean’. Data cleaning is also called data cleansing or data scrubbing.
Data cleaning takes place between data collection and data analyses. But you can use some methods even before collecting data.
For clean data, you should start by designing measures that collect valid data. Data validation at the time of data entry or collection helps you minimize the amount of data cleaning you’ll need to do.
After data collection, you can use data standardisation and data transformation to clean your data. You’ll also deal with any missing values, outliers, and duplicate values.
Clean data are valid, accurate, complete, consistent, unique, and uniform. Dirty data include inconsistencies and errors.
Dirty data can come from any part of the research process, including poor research design , inappropriate measurement materials, or flawed data entry.
Random assignment is used in experiments with a between-groups or independent measures design. In this research design, there’s usually a control group and one or more experimental groups. Random assignment helps ensure that the groups are comparable.
In general, you should always use random assignment in this type of experimental design when it is ethically possible and makes sense for your study topic.
Random selection, or random sampling , is a way of selecting members of a population for your study’s sample.
In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample into control and experimental groups.
Random sampling enhances the external validity or generalisability of your results, while random assignment improves the internal validity of your study.
To implement random assignment , assign a unique number to every member of your study’s sample .
Then, you can use a random number generator or a lottery method to randomly assign each number to a control or experimental group. You can also do so manually, by flipping a coin or rolling a die to randomly assign participants to groups.
Exploratory research is often used when the issue you’re studying is new or when the data collection process is challenging for some reason.
You can use exploratory research if you have a general idea or a specific question that you want to study but there is no preexisting knowledge or paradigm with which to study it.
Exploratory research is a methodology approach that explores research questions that have not previously been studied in depth. It is often used when the issue you’re studying is new, or the data collection process is challenging in some way.
Explanatory research is used to investigate how or why a phenomenon occurs. Therefore, this type of research is often one of the first stages in the research process , serving as a jumping-off point for future research.
Explanatory research is a research method used to investigate how or why something occurs when only a small amount of information is available pertaining to that topic. It can help you increase your understanding of a given topic.
Blinding means hiding who is assigned to the treatment group and who is assigned to the control group in an experiment .
Blinding is important to reduce bias (e.g., observer bias , demand characteristics ) and ensure a study’s internal validity .
If participants know whether they are in a control or treatment group , they may adjust their behaviour in ways that affect the outcome that researchers are trying to measure. If the people administering the treatment are aware of group assignment, they may treat participants differently and thus directly or indirectly influence the final results.
- In a single-blind study , only the participants are blinded.
- In a double-blind study , both participants and experimenters are blinded.
- In a triple-blind study , the assignment is hidden not only from participants and experimenters, but also from the researchers analysing the data.
Many academic fields use peer review , largely to determine whether a manuscript is suitable for publication. Peer review enhances the credibility of the published manuscript.
However, peer review is also common in non-academic settings. The United Nations, the European Union, and many individual nations use peer review to evaluate grant applications. It is also widely used in medical and health-related fields as a teaching or quality-of-care measure.
Peer assessment is often used in the classroom as a pedagogical tool. Both receiving feedback and providing it are thought to enhance the learning process, helping students think critically and collaboratively.
Peer review can stop obviously problematic, falsified, or otherwise untrustworthy research from being published. It also represents an excellent opportunity to get feedback from renowned experts in your field.
It acts as a first defence, helping you ensure your argument is clear and that there are no gaps, vague terms, or unanswered questions for readers who weren’t involved in the research process.
Peer-reviewed articles are considered a highly credible source due to this stringent process they go through before publication.
In general, the peer review process follows the following steps:
- First, the author submits the manuscript to the editor.
- Reject the manuscript and send it back to author, or
- Send it onward to the selected peer reviewer(s)
- Next, the peer review process occurs. The reviewer provides feedback, addressing any major or minor issues with the manuscript, and gives their advice regarding what edits should be made.
- Lastly, the edited manuscript is sent back to the author. They input the edits, and resubmit it to the editor for publication.
Peer review is a process of evaluating submissions to an academic journal. Utilising rigorous criteria, a panel of reviewers in the same subject area decide whether to accept each submission for publication.
For this reason, academic journals are often considered among the most credible sources you can use in a research project – provided that the journal itself is trustworthy and well regarded.
Anonymity means you don’t know who the participants are, while confidentiality means you know who they are but remove identifying information from your research report. Both are important ethical considerations .
You can only guarantee anonymity by not collecting any personally identifying information – for example, names, phone numbers, email addresses, IP addresses, physical characteristics, photos, or videos.
You can keep data confidential by using aggregate information in your research report, so that you only refer to groups of participants rather than individuals.
Research misconduct means making up or falsifying data, manipulating data analyses, or misrepresenting results in research reports. It’s a form of academic fraud.
These actions are committed intentionally and can have serious consequences; research misconduct is not a simple mistake or a point of disagreement but a serious ethical failure.
Research ethics matter for scientific integrity, human rights and dignity, and collaboration between science and society. These principles make sure that participation in studies is voluntary, informed, and safe.
Ethical considerations in research are a set of principles that guide your research designs and practices. These principles include voluntary participation, informed consent, anonymity, confidentiality, potential for harm, and results communication.
Scientists and researchers must always adhere to a certain code of conduct when collecting data from others .
These considerations protect the rights of research participants, enhance research validity , and maintain scientific integrity.
A systematic review is secondary research because it uses existing research. You don’t collect new data yourself.
The two main types of social desirability bias are:
- Self-deceptive enhancement (self-deception): The tendency to see oneself in a favorable light without realizing it.
- Impression managemen t (other-deception): The tendency to inflate one’s abilities or achievement in order to make a good impression on other people.
Demand characteristics are aspects of experiments that may give away the research objective to participants. Social desirability bias occurs when participants automatically try to respond in ways that make them seem likeable in a study, even if it means misrepresenting how they truly feel.
Participants may use demand characteristics to infer social norms or experimenter expectancies and act in socially desirable ways, so you should try to control for demand characteristics wherever possible.
Response bias refers to conditions or factors that take place during the process of responding to surveys, affecting the responses. One type of response bias is social desirability bias .
When your population is large in size, geographically dispersed, or difficult to contact, it’s necessary to use a sampling method .
This allows you to gather information from a smaller part of the population, i.e. the sample, and make accurate statements by using statistical analysis. A few sampling methods include simple random sampling , convenience sampling , and snowball sampling .
Stratified and cluster sampling may look similar, but bear in mind that groups created in cluster sampling are heterogeneous , so the individual characteristics in the cluster vary. In contrast, groups created in stratified sampling are homogeneous , as units share characteristics.
Relatedly, in cluster sampling you randomly select entire groups and include all units of each group in your sample. However, in stratified sampling, you select some units of all groups and include them in your sample. In this way, both methods can ensure that your sample is representative of the target population .
A sampling frame is a list of every member in the entire population . It is important that the sampling frame is as complete as possible, so that your sample accurately reflects your population.
Convenience sampling and quota sampling are both non-probability sampling methods. They both use non-random criteria like availability, geographical proximity, or expert knowledge to recruit study participants.
However, in convenience sampling, you continue to sample units or cases until you reach the required sample size.
In quota sampling, you first need to divide your population of interest into subgroups (strata) and estimate their proportions (quota) in the population. Then you can start your data collection , using convenience sampling to recruit participants, until the proportions in each subgroup coincide with the estimated proportions in the population.
Random sampling or probability sampling is based on random selection. This means that each unit has an equal chance (i.e., equal probability) of being included in the sample.
On the other hand, convenience sampling involves stopping people at random, which means that not everyone has an equal chance of being selected depending on the place, time, or day you are collecting your data.
Stratified sampling and quota sampling both involve dividing the population into subgroups and selecting units from each subgroup. The purpose in both cases is to select a representative sample and/or to allow comparisons between subgroups.
The main difference is that in stratified sampling, you draw a random sample from each subgroup ( probability sampling ). In quota sampling you select a predetermined number or proportion of units, in a non-random manner ( non-probability sampling ).
Snowball sampling is best used in the following cases:
- If there is no sampling frame available (e.g., people with a rare disease)
- If the population of interest is hard to access or locate (e.g., people experiencing homelessness)
- If the research focuses on a sensitive topic (e.g., extra-marital affairs)
Snowball sampling relies on the use of referrals. Here, the researcher recruits one or more initial participants, who then recruit the next ones.
Participants share similar characteristics and/or know each other. Because of this, not every member of the population has an equal chance of being included in the sample, giving rise to sampling bias .
Snowball sampling is a non-probability sampling method , where there is not an equal chance for every member of the population to be included in the sample .
This means that you cannot use inferential statistics and make generalisations – often the goal of quantitative research . As such, a snowball sample is not representative of the target population, and is usually a better fit for qualitative research .
Snowball sampling is a non-probability sampling method . Unlike probability sampling (which involves some form of random selection ), the initial individuals selected to be studied are the ones who recruit new participants.
Because not every member of the target population has an equal chance of being recruited into the sample, selection in snowball sampling is non-random.
Reproducibility and replicability are related terms.
- Reproducing research entails reanalysing the existing data in the same manner.
- Replicating (or repeating ) the research entails reconducting the entire analysis, including the collection of new data .
- A successful reproduction shows that the data analyses were conducted in a fair and honest manner.
- A successful replication shows that the reliability of the results is high.
The reproducibility and replicability of a study can be ensured by writing a transparent, detailed method section and using clear, unambiguous language.
Convergent validity and discriminant validity are both subtypes of construct validity . Together, they help you evaluate whether a test measures the concept it was designed to measure.
- Convergent validity indicates whether a test that is designed to measure a particular construct correlates with other tests that assess the same or similar construct.
- Discriminant validity indicates whether two tests that should not be highly related to each other are indeed not related
You need to assess both in order to demonstrate construct validity. Neither one alone is sufficient for establishing construct validity.
Construct validity has convergent and discriminant subtypes. They assist determine if a test measures the intended notion.
Content validity shows you how accurately a test or other measurement method taps into the various aspects of the specific construct you are researching.
In other words, it helps you answer the question: “does the test measure all aspects of the construct I want to measure?” If it does, then the test has high content validity.
The higher the content validity, the more accurate the measurement of the construct.
If the test fails to include parts of the construct, or irrelevant parts are included, the validity of the instrument is threatened, which brings your results into question.
Construct validity refers to how well a test measures the concept (or construct) it was designed to measure. Assessing construct validity is especially important when you’re researching concepts that can’t be quantified and/or are intangible, like introversion. To ensure construct validity your test should be based on known indicators of introversion ( operationalisation ).
On the other hand, content validity assesses how well the test represents all aspects of the construct. If some aspects are missing or irrelevant parts are included, the test has low content validity.
Face validity and content validity are similar in that they both evaluate how suitable the content of a test is. The difference is that face validity is subjective, and assesses content at surface level.
When a test has strong face validity, anyone would agree that the test’s questions appear to measure what they are intended to measure.
For example, looking at a 4th grade math test consisting of problems in which students have to add and multiply, most people would agree that it has strong face validity (i.e., it looks like a math test).
On the other hand, content validity evaluates how well a test represents all the aspects of a topic. Assessing content validity is more systematic and relies on expert evaluation. of each question, analysing whether each one covers the aspects that the test was designed to cover.
A 4th grade math test would have high content validity if it covered all the skills taught in that grade. Experts(in this case, math teachers), would have to evaluate the content validity by comparing the test to the learning objectives.
- Discriminant validity indicates whether two tests that should not be highly related to each other are indeed not related. This type of validity is also called divergent validity .
Criterion validity and construct validity are both types of measurement validity . In other words, they both show you how accurately a method measures something.
While construct validity is the degree to which a test or other measurement method measures what it claims to measure, criterion validity is the degree to which a test can predictively (in the future) or concurrently (in the present) measure something.
Construct validity is often considered the overarching type of measurement validity . You need to have face validity , content validity , and criterion validity in order to achieve construct validity.
Attrition refers to participants leaving a study. It always happens to some extent – for example, in randomised control trials for medical research.
Differential attrition occurs when attrition or dropout rates differ systematically between the intervention and the control group . As a result, the characteristics of the participants who drop out differ from the characteristics of those who stay in the study. Because of this, study results may be biased .
Criterion validity evaluates how well a test measures the outcome it was designed to measure. An outcome can be, for example, the onset of a disease.
Criterion validity consists of two subtypes depending on the time at which the two measures (the criterion and your test) are obtained:
- Concurrent validity is a validation strategy where the the scores of a test and the criterion are obtained at the same time
- Predictive validity is a validation strategy where the criterion variables are measured after the scores of the test
Validity tells you how accurately a method measures what it was designed to measure. There are 4 main types of validity :
- Construct validity : Does the test measure the construct it was designed to measure?
- Face validity : Does the test appear to be suitable for its objectives ?
- Content validity : Does the test cover all relevant parts of the construct it aims to measure.
- Criterion validity : Do the results accurately measure the concrete outcome they are designed to measure?
Convergent validity shows how much a measure of one construct aligns with other measures of the same or related constructs .
On the other hand, concurrent validity is about how a measure matches up to some known criterion or gold standard, which can be another measure.
Although both types of validity are established by calculating the association or correlation between a test score and another variable , they represent distinct validation methods.
The purpose of theory-testing mode is to find evidence in order to disprove, refine, or support a theory. As such, generalisability is not the aim of theory-testing mode.
Due to this, the priority of researchers in theory-testing mode is to eliminate alternative causes for relationships between variables . In other words, they prioritise internal validity over external validity , including ecological validity .
Inclusion and exclusion criteria are typically presented and discussed in the methodology section of your thesis or dissertation .
Inclusion and exclusion criteria are predominantly used in non-probability sampling . In purposive sampling and snowball sampling , restrictions apply as to who can be included in the sample .
Scope of research is determined at the beginning of your research process , prior to the data collection stage. Sometimes called “scope of study,” your scope delineates what will and will not be covered in your project. It helps you focus your work and your time, ensuring that you’ll be able to achieve your goals and outcomes.
Defining a scope can be very useful in any research project, from a research proposal to a thesis or dissertation . A scope is needed for all types of research: quantitative , qualitative , and mixed methods .
To define your scope of research, consider the following:
- Budget constraints or any specifics of grant funding
- Your proposed timeline and duration
- Specifics about your population of study, your proposed sample size , and the research methodology you’ll pursue
- Any inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Any anticipated control , extraneous , or confounding variables that could bias your research if not accounted for properly.
To make quantitative observations , you need to use instruments that are capable of measuring the quantity you want to observe. For example, you might use a ruler to measure the length of an object or a thermometer to measure its temperature.
Quantitative observations involve measuring or counting something and expressing the result in numerical form, while qualitative observations involve describing something in non-numerical terms, such as its appearance, texture, or color.
The Scribbr Reference Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Reference Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
To paraphrase effectively, don’t just take the original sentence and swap out some of the words for synonyms. Instead, try:
- Reformulating the sentence (e.g., change active to passive , or start from a different point)
- Combining information from multiple sentences into one
- Leaving out information from the original that isn’t relevant to your point
- Using synonyms where they don’t distort the meaning
The main point is to ensure you don’t just copy the structure of the original text, but instead reformulate the idea in your own words.
Plagiarism means using someone else’s words or ideas and passing them off as your own. Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas into your own words.
So when does paraphrasing count as plagiarism?
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if you don’t properly credit the original author.
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if your text is too close to the original wording (even if you cite the source). If you directly copy a sentence or phrase, you should quote it instead.
- Paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you put the author’s ideas completely into your own words and properly reference the source .
To present information from other sources in academic writing , it’s best to paraphrase in most cases. This shows that you’ve understood the ideas you’re discussing and incorporates them into your text smoothly.
It’s appropriate to quote when:
- Changing the phrasing would distort the meaning of the original text
- You want to discuss the author’s language choices (e.g., in literary analysis )
- You’re presenting a precise definition
- You’re looking in depth at a specific claim
A quote is an exact copy of someone else’s words, usually enclosed in quotation marks and credited to the original author or speaker.
Every time you quote a source , you must include a correctly formatted in-text citation . This looks slightly different depending on the citation style .
For example, a direct quote in APA is cited like this: ‘This is a quote’ (Streefkerk, 2020, p. 5).
Every in-text citation should also correspond to a full reference at the end of your paper.
In scientific subjects, the information itself is more important than how it was expressed, so quoting should generally be kept to a minimum. In the arts and humanities, however, well-chosen quotes are often essential to a good paper.
In social sciences, it varies. If your research is mainly quantitative , you won’t include many quotes, but if it’s more qualitative , you may need to quote from the data you collected .
As a general guideline, quotes should take up no more than 5–10% of your paper. If in doubt, check with your instructor or supervisor how much quoting is appropriate in your field.
If you’re quoting from a text that paraphrases or summarises other sources and cites them in parentheses , APA recommends retaining the citations as part of the quote:
- Smith states that ‘the literature on this topic (Jones, 2015; Sill, 2019; Paulson, 2020) shows no clear consensus’ (Smith, 2019, p. 4).
Footnote or endnote numbers that appear within quoted text should be omitted.
If you want to cite an indirect source (one you’ve only seen quoted in another source), either locate the original source or use the phrase ‘as cited in’ in your citation.
A block quote is a long quote formatted as a separate ‘block’ of text. Instead of using quotation marks , you place the quote on a new line, and indent the entire quote to mark it apart from your own words.
APA uses block quotes for quotes that are 40 words or longer.
A credible source should pass the CRAAP test and follow these guidelines:
- The information should be up to date and current.
- The author and publication should be a trusted authority on the subject you are researching.
- The sources the author cited should be easy to find, clear, and unbiased.
- For a web source, the URL and layout should signify that it is trustworthy.
Common examples of primary sources include interview transcripts , photographs, novels, paintings, films, historical documents, and official statistics.
Anything you directly analyze or use as first-hand evidence can be a primary source, including qualitative or quantitative data that you collected yourself.
Common examples of secondary sources include academic books, journal articles , reviews, essays , and textbooks.
Anything that summarizes, evaluates or interprets primary sources can be a secondary source. If a source gives you an overview of background information or presents another researcher’s ideas on your topic, it is probably a secondary source.
To determine if a source is primary or secondary, ask yourself:
- Was the source created by someone directly involved in the events you’re studying (primary), or by another researcher (secondary)?
- Does the source provide original information (primary), or does it summarize information from other sources (secondary)?
- Are you directly analyzing the source itself (primary), or only using it for background information (secondary)?
Some types of sources are nearly always primary: works of art and literature, raw statistical data, official documents and records, and personal communications (e.g. letters, interviews ). If you use one of these in your research, it is probably a primary source.
Primary sources are often considered the most credible in terms of providing evidence for your argument, as they give you direct evidence of what you are researching. However, it’s up to you to ensure the information they provide is reliable and accurate.
Always make sure to properly cite your sources to avoid plagiarism .
A fictional movie is usually a primary source. A documentary can be either primary or secondary depending on the context.
If you are directly analysing some aspect of the movie itself – for example, the cinematography, narrative techniques, or social context – the movie is a primary source.
If you use the movie for background information or analysis about your topic – for example, to learn about a historical event or a scientific discovery – the movie is a secondary source.
Whether it’s primary or secondary, always properly cite the movie in the citation style you are using. Learn how to create an MLA movie citation or an APA movie citation .
Articles in newspapers and magazines can be primary or secondary depending on the focus of your research.
In historical studies, old articles are used as primary sources that give direct evidence about the time period. In social and communication studies, articles are used as primary sources to analyse language and social relations (for example, by conducting content analysis or discourse analysis ).
If you are not analysing the article itself, but only using it for background information or facts about your topic, then the article is a secondary source.
In academic writing , there are three main situations where quoting is the best choice:
- To analyse the author’s language (e.g., in a literary analysis essay )
- To give evidence from primary sources
- To accurately present a precise definition or argument
Don’t overuse quotes; your own voice should be dominant. If you just want to provide information from a source, it’s usually better to paraphrase or summarise .
Your list of tables and figures should go directly after your table of contents in your thesis or dissertation.
Lists of figures and tables are often not required, and they aren’t particularly common. They specifically aren’t required for APA Style, though you should be careful to follow their other guidelines for figures and tables .
If you have many figures and tables in your thesis or dissertation, include one may help you stay organised. Your educational institution may require them, so be sure to check their guidelines.
Copyright information can usually be found wherever the table or figure was published. For example, for a diagram in a journal article , look on the journal’s website or the database where you found the article. Images found on sites like Flickr are listed with clear copyright information.
If you find that permission is required to reproduce the material, be sure to contact the author or publisher and ask for it.
A list of figures and tables compiles all of the figures and tables that you used in your thesis or dissertation and displays them with the page number where they can be found.
APA doesn’t require you to include a list of tables or a list of figures . However, it is advisable to do so if your text is long enough to feature a table of contents and it includes a lot of tables and/or figures .
A list of tables and list of figures appear (in that order) after your table of contents, and are presented in a similar way.
A glossary is a collection of words pertaining to a specific topic. In your thesis or dissertation, it’s a list of all terms you used that may not immediately be obvious to your reader. Your glossary only needs to include terms that your reader may not be familiar with, and is intended to enhance their understanding of your work.
Definitional terms often fall into the category of common knowledge , meaning that they don’t necessarily have to be cited. This guidance can apply to your thesis or dissertation glossary as well.
However, if you’d prefer to cite your sources , you can follow guidance for citing dictionary entries in MLA or APA style for your glossary.
A glossary is a collection of words pertaining to a specific topic. In your thesis or dissertation, it’s a list of all terms you used that may not immediately be obvious to your reader. In contrast, an index is a list of the contents of your work organised by page number.
Glossaries are not mandatory, but if you use a lot of technical or field-specific terms, it may improve readability to add one to your thesis or dissertation. Your educational institution may also require them, so be sure to check their specific guidelines.
A glossary is a collection of words pertaining to a specific topic. In your thesis or dissertation, it’s a list of all terms you used that may not immediately be obvious to your reader. In contrast, dictionaries are more general collections of words.
The title page of your thesis or dissertation should include your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date.
The title page of your thesis or dissertation goes first, before all other content or lists that you may choose to include.
Usually, no title page is needed in an MLA paper . A header is generally included at the top of the first page instead. The exceptions are when:
- Your instructor requires one, or
- Your paper is a group project
In those cases, you should use a title page instead of a header, listing the same information but on a separate page.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organise your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation, such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
While a theoretical framework describes the theoretical underpinnings of your work based on existing research, a conceptual framework allows you to draw your own conclusions, mapping out the variables you may use in your study and the interplay between them.
A literature review and a theoretical framework are not the same thing and cannot be used interchangeably. While a theoretical framework describes the theoretical underpinnings of your work, a literature review critically evaluates existing research relating to your topic. You’ll likely need both in your dissertation .
A theoretical framework can sometimes be integrated into a literature review chapter , but it can also be included as its own chapter or section in your dissertation . As a rule of thumb, if your research involves dealing with a lot of complex theories, it’s a good idea to include a separate theoretical framework chapter.
An abstract is a concise summary of an academic text (such as a journal article or dissertation ). It serves two main purposes:
- To help potential readers determine the relevance of your paper for their own research.
- To communicate your key findings to those who don’t have time to read the whole paper.
Abstracts are often indexed along with keywords on academic databases, so they make your work more easily findable. Since the abstract is the first thing any reader sees, it’s important that it clearly and accurately summarises the contents of your paper.
The abstract is the very last thing you write. You should only write it after your research is complete, so that you can accurately summarize the entirety of your thesis or paper.
Avoid citing sources in your abstract . There are two reasons for this:
- The abstract should focus on your original research, not on the work of others.
- The abstract should be self-contained and fully understandable without reference to other sources.
There are some circumstances where you might need to mention other sources in an abstract: for example, if your research responds directly to another study or focuses on the work of a single theorist. In general, though, don’t include citations unless absolutely necessary.
The abstract appears on its own page, after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents .
Results are usually written in the past tense , because they are describing the outcome of completed actions.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
A noun is a word that represents a person, thing, concept, or place (e.g., ‘John’, ‘house’, ‘affinity’, ‘river’). Most sentences contain at least one noun or pronoun .
Nouns are often, but not always, preceded by an article (‘the’, ‘a’, or ‘an’) and/or another determiner such as an adjective.
There are many ways to categorize nouns into various types, and the same noun can fall into multiple categories or even change types depending on context.
Some of the main types of nouns are:
- Common nouns and proper nouns
- Countable and uncountable nouns
- Concrete and abstract nouns
- Collective nouns
- Possessive nouns
- Attributive nouns
- Appositive nouns
- Generic nouns
Pronouns are words like ‘I’, ‘she’, and ‘they’ that are used in a similar way to nouns . They stand in for a noun that has already been mentioned or refer to yourself and other people.
Pronouns can function just like nouns as the head of a noun phrase and as the subject or object of a verb. However, pronouns change their forms (e.g., from ‘I’ to ‘me’) depending on the grammatical context they’re used in, whereas nouns usually don’t.
Common nouns are words for types of things, people, and places, such as ‘dog’, ‘professor’, and ‘city’. They are not capitalised and are typically used in combination with articles and other determiners.
Proper nouns are words for specific things, people, and places, such as ‘Max’, ‘Dr Prakash’, and ‘London’. They are always capitalised and usually aren’t combined with articles and other determiners.
A proper adjective is an adjective that was derived from a proper noun and is therefore capitalised .
Proper adjectives include words for nationalities, languages, and ethnicities (e.g., ‘Japanese’, ‘Inuit’, ‘French’) and words derived from people’s names (e.g., ‘Bayesian’, ‘Orwellian’).
The names of seasons (e.g., ‘spring’) are treated as common nouns in English and therefore not capitalised . People often assume they are proper nouns, but this is an error.
The names of days and months, however, are capitalised since they’re treated as proper nouns in English (e.g., ‘Wednesday’, ‘January’).
No, as a general rule, academic concepts, disciplines, theories, models, etc. are treated as common nouns , not proper nouns , and therefore not capitalised . For example, ‘five-factor model of personality’ or ‘analytic philosophy’.
However, proper nouns that appear within the name of an academic concept (such as the name of the inventor) are capitalised as usual. For example, ‘Darwin’s theory of evolution’ or ‘ Student’s t table ‘.
Collective nouns are most commonly treated as singular (e.g., ‘the herd is grazing’), but usage differs between US and UK English :
- In US English, it’s standard to treat all collective nouns as singular, even when they are plural in appearance (e.g., ‘The Rolling Stones is …’). Using the plural form is usually seen as incorrect.
- In UK English, collective nouns can be treated as singular or plural depending on context. It’s quite common to use the plural form, especially when the noun looks plural (e.g., ‘The Rolling Stones are …’).
The plural of “crisis” is “crises”. It’s a loanword from Latin and retains its original Latin plural noun form (similar to “analyses” and “bases”). It’s wrong to write “crisises”.
For example, you might write “Several crises destabilized the regime.”
Normally, the plural of “fish” is the same as the singular: “fish”. It’s one of a group of irregular plural nouns in English that are identical to the corresponding singular nouns (e.g., “moose”, “sheep”). For example, you might write “The fish scatter as the shark approaches.”
If you’re referring to several species of fish, though, the regular plural “fishes” is often used instead. For example, “The aquarium contains many different fishes , including trout and carp.”
The correct plural of “octopus” is “octopuses”.
People often write “octopi” instead because they assume that the plural noun is formed in the same way as Latin loanwords such as “fungus/fungi”. But “octopus” actually comes from Greek, where its original plural is “octopodes”. In English, it instead has the regular plural form “octopuses”.
For example, you might write “There are four octopuses in the aquarium.”
The plural of “moose” is the same as the singular: “moose”. It’s one of a group of plural nouns in English that are identical to the corresponding singular nouns. So it’s wrong to write “mooses”.
For example, you might write “There are several moose in the forest.”
Bias in research affects the validity and reliability of your findings, leading to false conclusions and a misinterpretation of the truth. This can have serious implications in areas like medical research where, for example, a new form of treatment may be evaluated.
Observer bias occurs when the researcher’s assumptions, views, or preconceptions influence what they see and record in a study, while actor–observer bias refers to situations where respondents attribute internal factors (e.g., bad character) to justify other’s behaviour and external factors (difficult circumstances) to justify the same behaviour in themselves.
Response bias is a general term used to describe a number of different conditions or factors that cue respondents to provide inaccurate or false answers during surveys or interviews . These factors range from the interviewer’s perceived social position or appearance to the the phrasing of questions in surveys.
Nonresponse bias occurs when the people who complete a survey are different from those who did not, in ways that are relevant to the research topic. Nonresponse can happen either because people are not willing or not able to participate.
In research, demand characteristics are cues that might indicate the aim of a study to participants. These cues can lead to participants changing their behaviors or responses based on what they think the research is about.
Demand characteristics are common problems in psychology experiments and other social science studies because they can bias your research findings.
Demand characteristics are a type of extraneous variable that can affect the outcomes of the study. They can invalidate studies by providing an alternative explanation for the results.
These cues may nudge participants to consciously or unconsciously change their responses, and they pose a threat to both internal and external validity . You can’t be sure that your independent variable manipulation worked, or that your findings can be applied to other people or settings.
You can control demand characteristics by taking a few precautions in your research design and materials.
Use these measures:
- Deception: Hide the purpose of the study from participants
- Between-groups design : Give each participant only one independent variable treatment
- Double-blind design : Conceal the assignment of groups from participants and yourself
- Implicit measures: Use indirect or hidden measurements for your variables
Some attrition is normal and to be expected in research. However, the type of attrition is important because systematic research bias can distort your findings. Attrition bias can lead to inaccurate results because it affects internal and/or external validity .
To avoid attrition bias , applying some of these measures can help you reduce participant dropout (attrition) by making it easy and appealing for participants to stay.
- Provide compensation (e.g., cash or gift cards) for attending every session
- Minimise the number of follow-ups as much as possible
- Make all follow-ups brief, flexible, and convenient for participants
- Send participants routine reminders to schedule follow-ups
- Recruit more participants than you need for your sample (oversample)
- Maintain detailed contact information so you can get in touch with participants even if they move
If you have a small amount of attrition bias , you can use a few statistical methods to try to make up for this research bias .
Multiple imputation involves using simulations to replace the missing data with likely values. Alternatively, you can use sample weighting to make up for the uneven balance of participants in your sample.
Placebos are used in medical research for new medication or therapies, called clinical trials. In these trials some people are given a placebo, while others are given the new medication being tested.
The purpose is to determine how effective the new medication is: if it benefits people beyond a predefined threshold as compared to the placebo, it’s considered effective.
Although there is no definite answer to what causes the placebo effect , researchers propose a number of explanations such as the power of suggestion, doctor-patient interaction, classical conditioning, etc.
Belief bias and confirmation bias are both types of cognitive bias that impact our judgment and decision-making.
Confirmation bias relates to how we perceive and judge evidence. We tend to seek out and prefer information that supports our preexisting beliefs, ignoring any information that contradicts those beliefs.
Belief bias describes the tendency to judge an argument based on how plausible the conclusion seems to us, rather than how much evidence is provided to support it during the course of the argument.
Positivity bias is phenomenon that occurs when a person judges individual members of a group positively, even when they have negative impressions or judgments of the group as a whole. Positivity bias is closely related to optimism bias , or the e xpectation that things will work out well, even if rationality suggests that problems are inevitable in life.
Perception bias is a problem because it prevents us from seeing situations or people objectively. Rather, our expectations, beliefs, or emotions interfere with how we interpret reality. This, in turn, can cause us to misjudge ourselves or others. For example, our prejudices can interfere with whether we perceive people’s faces as friendly or unfriendly.
There are many ways to categorize adjectives into various types. An adjective can fall into one or more of these categories depending on how it is used.
Some of the main types of adjectives are:
- Attributive adjectives
- Predicative adjectives
- Comparative adjectives
- Superlative adjectives
- Coordinate adjectives
- Appositive adjectives
- Compound adjectives
- Participial adjectives
- Proper adjectives
- Denominal adjectives
- Nominal adjectives
Cardinal numbers (e.g., one, two, three) can be placed before a noun to indicate quantity (e.g., one apple). While these are sometimes referred to as ‘numeral adjectives ‘, they are more accurately categorised as determiners or quantifiers.
Proper adjectives are adjectives formed from a proper noun (i.e., the name of a specific person, place, or thing) that are used to indicate origin. Like proper nouns, proper adjectives are always capitalised (e.g., Newtonian, Marxian, African).
The cost of proofreading depends on the type and length of text, the turnaround time, and the level of services required. Most proofreading companies charge per word or page, while freelancers sometimes charge an hourly rate.
For proofreading alone, which involves only basic corrections of typos and formatting mistakes, you might pay as little as £0.01 per word, but in many cases, your text will also require some level of editing , which costs slightly more.
It’s often possible to purchase combined proofreading and editing services and calculate the price in advance based on your requirements.
Then and than are two commonly confused words . In the context of ‘better than’, you use ‘than’ with an ‘a’.
- Julie is better than Jesse.
- I’d rather spend my time with you than with him.
- I understand Eoghan’s point of view better than Claudia’s.
Use to and used to are commonly confused words . In the case of ‘used to do’, the latter (with ‘d’) is correct, since you’re describing an action or state in the past.
- I used to do laundry once a week.
- They used to do each other’s hair.
- We used to do the dishes every day .
There are numerous synonyms and near synonyms for the various meanings of “ favour ”:
| Advocate | Adoration |
| Approve of | Appreciation |
| Endorse | Praise |
| Support | Respect |
There are numerous synonyms and near synonyms for the two meanings of “ favoured ”:
| Advocated | Adored |
| Approved of | Appreciated |
| Endorsed | Praised |
| Supported | Preferred |
No one (two words) is an indefinite pronoun meaning ‘nobody’. People sometimes mistakenly write ‘noone’, but this is incorrect and should be avoided. ‘No-one’, with a hyphen, is also acceptable in UK English .
Scribbr’s Free Grammar Checker can help make sure you’re using phrases like ‘no one’ correctly in your writing.
Nobody and no one are both indefinite pronouns meaning ‘no person’. They can be used interchangeably (e.g., ‘nobody is home’ means the same as ‘no one is home’).
Some synonyms and near synonyms of every time include:
- Without exception
‘Everytime’ is sometimes used to mean ‘each time’ or ‘whenever’. However, this is incorrect and should be avoided. The correct phrase is every time (two words).
Scribbr’s Grammar Checker can help make sure you’re using phrases like ‘every time’ correctly in your writing.
Yes, the conjunction because is a compound word , but one with a long history. It originates in Middle English from the preposition “bi” (“by”) and the noun “cause”. Over time, the open compound “bi cause” became the closed compound “because”, which we use today.
Though it’s spelled this way now, the verb “be” is not one of the words that makes up “because”.
Yes, today is a compound word , but a very old one. It wasn’t originally formed from the preposition “to” and the noun “day”; rather, it originates from their Old English equivalents, “tō” and “dæġe”.
In the past, it was sometimes written as a hyphenated compound: “to-day”. But the hyphen is no longer included; it’s always “today” now (“to day” is also wrong).
IEEE citation format is defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers and used in their publications.
It’s also a widely used citation style for students in technical fields like electrical and electronic engineering, computer science, telecommunications, and computer engineering.
An IEEE in-text citation consists of a number in brackets at the relevant point in the text, which points the reader to the right entry in the numbered reference list at the end of the paper. For example, ‘Smith [1] states that …’
A location marker such as a page number is also included within the brackets when needed: ‘Smith [1, p. 13] argues …’
The IEEE reference page consists of a list of references numbered in the order they were cited in the text. The title ‘References’ appears in bold at the top, either left-aligned or centered.
The numbers appear in square brackets on the left-hand side of the page. The reference entries are indented consistently to separate them from the numbers. Entries are single-spaced, with a normal paragraph break between them.
If you cite the same source more than once in your writing, use the same number for all of the IEEE in-text citations for that source, and only include it on the IEEE reference page once. The source is numbered based on the first time you cite it.
For example, the fourth source you cite in your paper is numbered [4]. If you cite it again later, you still cite it as [4]. You can cite different parts of the source each time by adding page numbers [4, p. 15].
A verb is a word that indicates a physical action (e.g., ‘drive’), a mental action (e.g., ‘think’) or a state of being (e.g., ‘exist’). Every sentence contains a verb.
Verbs are almost always used along with a noun or pronoun to describe what the noun or pronoun is doing.
There are many ways to categorize verbs into various types. A verb can fall into one or more of these categories depending on how it is used.
Some of the main types of verbs are:
- Regular verbs
- Irregular verbs
- Transitive verbs
- Intransitive verbs
- Dynamic verbs
- Stative verbs
- Linking verbs
- Auxiliary verbs
- Modal verbs
- Phrasal verbs
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding the suffix ‘-ed’ (e.g., ‘walked’).
Irregular verbs are verbs that form their simple past and past participles in some way other than by adding the suffix ‘-ed’ (e.g., ‘sat’).
The indefinite articles a and an are used to refer to a general or unspecified version of a noun (e.g., a house). Which indefinite article you use depends on the pronunciation of the word that follows it.
- A is used for words that begin with a consonant sound (e.g., a bear).
- An is used for words that begin with a vowel sound (e.g., an eagle).
Indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns . Like definite articles, they are a type of determiner .
Editing and proofreading are different steps in the process of revising a text.
Editing comes first, and can involve major changes to content, structure and language. The first stages of editing are often done by authors themselves, while a professional editor makes the final improvements to grammar and style (for example, by improving sentence structure and word choice ).
Proofreading is the final stage of checking a text before it is published or shared. It focuses on correcting minor errors and inconsistencies (for example, in punctuation and capitalization ). Proofreaders often also check for formatting issues, especially in print publishing.
Whether you’re publishing a blog, submitting a research paper , or even just writing an important email, there are a few techniques you can use to make sure it’s error-free:
- Take a break : Set your work aside for at least a few hours so that you can look at it with fresh eyes.
- Proofread a printout : Staring at a screen for too long can cause fatigue – sit down with a pen and paper to check the final version.
- Use digital shortcuts : Take note of any recurring mistakes (for example, misspelling a particular word, switching between US and UK English , or inconsistently capitalizing a term), and use Find and Replace to fix it throughout the document.
If you want to be confident that an important text is error-free, it might be worth choosing a professional proofreading service instead.
There are many different routes to becoming a professional proofreader or editor. The necessary qualifications depend on the field – to be an academic or scientific proofreader, for example, you will need at least a university degree in a relevant subject.
For most proofreading jobs, experience and demonstrated skills are more important than specific qualifications. Often your skills will be tested as part of the application process.
To learn practical proofreading skills, you can choose to take a course with a professional organisation such as the Society for Editors and Proofreaders . Alternatively, you can apply to companies that offer specialised on-the-job training programmes, such as the Scribbr Academy .
Though they’re pronounced the same, there’s a big difference in meaning between its and it’s .
- ‘The cat ate its food’.
- ‘It’s almost Christmas’.
Its and it’s are often confused, but its (without apostrophe) is the possessive form of ‘it’ (e.g., its tail, its argument, its wing). You use ‘its’ instead of ‘his’ and ‘her’ for neuter, inanimate nouns.
Then and than are two commonly confused words with different meanings and grammatical roles.
- Then (pronounced with a short ‘e’ sound) refers to time. It’s often an adverb , but it can also be used as a noun meaning ‘that time’ and as an adjective referring to a previous status.
- Than (pronounced with a short ‘a’ sound) is used for comparisons. Grammatically, it usually functions as a conjunction , but sometimes it’s a preposition .
| Examples: Then in a sentence | Examples: Than in a sentence |
|---|---|
| Mix the dry ingredients first, and add the wet ingredients. | Max is a better saxophonist you. |
| I was working as a teacher . | I usually like coaching a team more I like playing soccer myself. |
Use to and used to are commonly confused words . In the case of ‘used to be’, the latter (with ‘d’) is correct, since you’re describing an action or state in the past.
- I used to be the new coworker.
- There used to be 4 cookies left.
- We used to walk to school every day .
A grammar checker is a tool designed to automatically check your text for spelling errors, grammatical issues, punctuation mistakes , and problems with sentence structure . You can check out our analysis of the best free grammar checkers to learn more.
A paraphrasing tool edits your text more actively, changing things whether they were grammatically incorrect or not. It can paraphrase your sentences to make them more concise and readable or for other purposes. You can check out our analysis of the best free paraphrasing tools to learn more.
Some tools available online combine both functions. Others, such as QuillBot , have separate grammar checker and paraphrasing tools. Be aware of what exactly the tool you’re using does to avoid introducing unwanted changes.
Good grammar is the key to expressing yourself clearly and fluently, especially in professional communication and academic writing . Word processors, browsers, and email programs typically have built-in grammar checkers, but they’re quite limited in the kinds of problems they can fix.
If you want to go beyond detecting basic spelling errors, there are many online grammar checkers with more advanced functionality. They can often detect issues with punctuation , word choice, and sentence structure that more basic tools would miss.
Not all of these tools are reliable, though. You can check out our research into the best free grammar checkers to explore the options.
Our research indicates that the best free grammar checker available online is the QuillBot grammar checker .
We tested 10 of the most popular checkers with the same sample text (containing 20 grammatical errors) and found that QuillBot easily outperformed the competition, scoring 18 out of 20, a drastic improvement over the second-place score of 13 out of 20.
It even appeared to outperform the premium versions of other grammar checkers, despite being entirely free.
A teacher’s aide is a person who assists in teaching classes but is not a qualified teacher. Aide is a noun meaning ‘assistant’, so it will always refer to a person.
‘Teacher’s aid’ is incorrect.
A visual aid is an instructional device (e.g., a photo, a chart) that appeals to vision to help you understand written or spoken information. Aid is often placed after an attributive noun or adjective (like ‘visual’) that describes the type of help provided.
‘Visual aide’ is incorrect.
A job aid is an instructional tool (e.g., a checklist, a cheat sheet) that helps you work efficiently. Aid is a noun meaning ‘assistance’. It’s often placed after an adjective or attributive noun (like ‘job’) that describes the specific type of help provided.
‘Job aide’ is incorrect.
There are numerous synonyms for the various meanings of truly :
| Candidly | Completely | Accurately |
| Honestly | Really | Correctly |
| Openly | Totally | Exactly |
| Truthfully | Precisely |
Yours truly is a phrase used at the end of a formal letter or email. It can also be used (typically in a humorous way) as a pronoun to refer to oneself (e.g., ‘The dinner was cooked by yours truly ‘). The latter usage should be avoided in formal writing.
It’s formed by combining the second-person possessive pronoun ‘yours’ with the adverb ‘ truly ‘.
A pathetic fallacy can be a short phrase or a whole sentence and is often used in novels and poetry. Pathetic fallacies serve multiple purposes, such as:
- Conveying the emotional state of the characters or the narrator
- Creating an atmosphere or set the mood of a scene
- Foreshadowing events to come
- Giving texture and vividness to a piece of writing
- Communicating emotion to the reader in a subtle way, by describing the external world.
- Bringing inanimate objects to life so that they seem more relatable.
AMA citation format is a citation style designed by the American Medical Association. It’s frequently used in the field of medicine.
You may be told to use AMA style for your student papers. You will also have to follow this style if you’re submitting a paper to a journal published by the AMA.
An AMA in-text citation consists of the number of the relevant reference on your AMA reference page , written in superscript 1 at the point in the text where the source is used.
It may also include the page number or range of the relevant material in the source (e.g., the part you quoted 2(p46) ). Multiple sources can be cited at one point, presented as a range or list (with no spaces 3,5–9 ).
An AMA reference usually includes the author’s last name and initials, the title of the source, information about the publisher or the publication it’s contained in, and the publication date. The specific details included, and the formatting, depend on the source type.
References in AMA style are presented in numerical order (numbered by the order in which they were first cited in the text) on your reference page. A source that’s cited repeatedly in the text still only appears once on the reference page.
An AMA in-text citation just consists of the number of the relevant entry on your AMA reference page , written in superscript at the point in the text where the source is referred to.
You don’t need to mention the author of the source in your sentence, but you can do so if you want. It’s not an official part of the citation, but it can be useful as part of a signal phrase introducing the source.
On your AMA reference page , author names are written with the last name first, followed by the initial(s) of their first name and middle name if mentioned.
There’s a space between the last name and the initials, but no space or punctuation between the initials themselves. The names of multiple authors are separated by commas , and the whole list ends in a period, e.g., ‘Andreessen F, Smith PW, Gonzalez E’.
The names of up to six authors should be listed for each source on your AMA reference page , separated by commas . For a source with seven or more authors, you should list the first three followed by ‘ et al’ : ‘Isidore, Gilbert, Gunvor, et al’.
In the text, mentioning author names is optional (as they aren’t an official part of AMA in-text citations ). If you do mention them, though, you should use the first author’s name followed by ‘et al’ when there are three or more : ‘Isidore et al argue that …’
Note that according to AMA’s rather minimalistic punctuation guidelines, there’s no period after ‘et al’ unless it appears at the end of a sentence. This is different from most other styles, where there is normally a period.
Yes, you should normally include an access date in an AMA website citation (or when citing any source with a URL). This is because webpages can change their content over time, so it’s useful for the reader to know when you accessed the page.
When a publication or update date is provided on the page, you should include it in addition to the access date. The access date appears second in this case, e.g., ‘Published June 19, 2021. Accessed August 29, 2022.’
Don’t include an access date when citing a source with a DOI (such as in an AMA journal article citation ).
Some variables have fixed levels. For example, gender and ethnicity are always nominal level data because they cannot be ranked.
However, for other variables, you can choose the level of measurement . For example, income is a variable that can be recorded on an ordinal or a ratio scale:
- At an ordinal level , you could create 5 income groupings and code the incomes that fall within them from 1–5.
- At a ratio level , you would record exact numbers for income.
If you have a choice, the ratio level is always preferable because you can analyse data in more ways. The higher the level of measurement, the more precise your data is.
The level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyse your data.
Depending on the level of measurement , you can perform different descriptive statistics to get an overall summary of your data and inferential statistics to see if your results support or refute your hypothesis .
Levels of measurement tell you how precisely variables are recorded. There are 4 levels of measurement, which can be ranked from low to high:
- Nominal : the data can only be categorised.
- Ordinal : the data can be categorised and ranked.
- Interval : the data can be categorised and ranked, and evenly spaced.
- Ratio : the data can be categorised, ranked, evenly spaced and has a natural zero.
Statistical analysis is the main method for analyzing quantitative research data . It uses probabilities and models to test predictions about a population from sample data.
The null hypothesis is often abbreviated as H 0 . When the null hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an equality symbol (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
The alternative hypothesis is often abbreviated as H a or H 1 . When the alternative hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an inequality symbol (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >).
As the degrees of freedom increase, Student’s t distribution becomes less leptokurtic , meaning that the probability of extreme values decreases. The distribution becomes more and more similar to a standard normal distribution .
When there are only one or two degrees of freedom , the chi-square distribution is shaped like a backwards ‘J’. When there are three or more degrees of freedom, the distribution is shaped like a right-skewed hump. As the degrees of freedom increase, the hump becomes less right-skewed and the peak of the hump moves to the right. The distribution becomes more and more similar to a normal distribution .
‘Looking forward in hearing from you’ is an incorrect version of the phrase looking forward to hearing from you . The phrasal verb ‘looking forward to’ always needs the preposition ‘to’, not ‘in’.
- I am looking forward in hearing from you.
- I am looking forward to hearing from you.
Some synonyms and near synonyms for the expression looking forward to hearing from you include:
- Eagerly awaiting your response
- Hoping to hear from you soon
- It would be great to hear back from you
- Thanks in advance for your reply
People sometimes mistakenly write ‘looking forward to hear from you’, but this is incorrect. The correct phrase is looking forward to hearing from you .
The phrasal verb ‘look forward to’ is always followed by a direct object, the thing you’re looking forward to. As the direct object has to be a noun phrase , it should be the gerund ‘hearing’, not the verb ‘hear’.
- I’m looking forward to hear from you soon.
- I’m looking forward to hearing from you soon.
Traditionally, the sign-off Yours sincerely is used in an email message or letter when you are writing to someone you have interacted with before, not a complete stranger.
Yours faithfully is used instead when you are writing to someone you have had no previous correspondence with, especially if you greeted them as ‘ Dear Sir or Madam ’.
Just checking in is a standard phrase used to start an email (or other message) that’s intended to ask someone for a response or follow-up action in a friendly, informal way. However, it’s a cliché opening that can come across as passive-aggressive, so we recommend avoiding it in favor of a more direct opening like “We previously discussed …”
In a more personal context, you might encounter “just checking in” as part of a longer phrase such as “I’m just checking in to see how you’re doing”. In this case, it’s not asking the other person to do anything but rather asking about their well-being (emotional or physical) in a friendly way.
“Earliest convenience” is part of the phrase at your earliest convenience , meaning “as soon as you can”.
It’s typically used to end an email in a formal context by asking the recipient to do something when it’s convenient for them to do so.
ASAP is an abbreviation of the phrase “as soon as possible”.
It’s typically used to indicate a sense of urgency in highly informal contexts (e.g., “Let me know ASAP if you need me to drive you to the airport”).
“ASAP” should be avoided in more formal correspondence. Instead, use an alternative like at your earliest convenience .
Some synonyms and near synonyms of the verb compose (meaning “to make up”) are:
People increasingly use “comprise” as a synonym of “compose.” However, this is normally still seen as a mistake, and we recommend avoiding it in your academic writing . “Comprise” traditionally means “to be made up of,” not “to make up.”
Some synonyms and near synonyms of the verb comprise are:
- Be composed of
- Be made up of
People increasingly use “comprise” interchangeably with “compose,” meaning that they consider words like “compose,” “constitute,” and “form” to be synonymous with “comprise.” However, this is still normally regarded as an error, and we advise against using these words interchangeably in academic writing .
A fallacy is a mistaken belief, particularly one based on unsound arguments or one that lacks the evidence to support it. Common types of fallacy that may compromise the quality of your research are:
- Correlation/causation fallacy: Claiming that two events that occur together have a cause-and-effect relationship even though this can’t be proven
- Ecological fallacy : Making inferences about the nature of individuals based on aggregate data for the group
- The sunk cost fallacy : Following through on a project or decision because we have already invested time, effort, or money into it, even if the current costs outweigh the benefits
- The base-rate fallacy : Ignoring base-rate or statistically significant information, such as sample size or the relative frequency of an event, in favor of less relevant information e.g., pertaining to a single case, or a small number of cases
- The planning fallacy : Underestimating the time needed to complete a future task, even when we know that similar tasks in the past have taken longer than planned
The planning fallacy refers to people’s tendency to underestimate the resources needed to complete a future task, despite knowing that previous tasks have also taken longer than planned.
For example, people generally tend to underestimate the cost and time needed for construction projects. The planning fallacy occurs due to people’s tendency to overestimate the chances that positive events, such as a shortened timeline, will happen to them. This phenomenon is called optimism bias or positivity bias.
Although both red herring fallacy and straw man fallacy are logical fallacies or reasoning errors, they denote different attempts to “win” an argument. More specifically:
- A red herring fallacy refers to an attempt to change the subject and divert attention from the original issue. In other words, a seemingly solid but ultimately irrelevant argument is introduced into the discussion, either on purpose or by mistake.
- A straw man argument involves the deliberate distortion of another person’s argument. By oversimplifying or exaggerating it, the other party creates an easy-to-refute argument and then attacks it.
The red herring fallacy is a problem because it is flawed reasoning. It is a distraction device that causes people to become sidetracked from the main issue and draw wrong conclusions.
Although a red herring may have some kernel of truth, it is used as a distraction to keep our eyes on a different matter. As a result, it can cause us to accept and spread misleading information.
The sunk cost fallacy and escalation of commitment (or commitment bias ) are two closely related terms. However, there is a slight difference between them:
- Escalation of commitment (aka commitment bias ) is the tendency to be consistent with what we have already done or said we will do in the past, especially if we did so in public. In other words, it is an attempt to save face and appear consistent.
- Sunk cost fallacy is the tendency to stick with a decision or a plan even when it’s failing. Because we have already invested valuable time, money, or energy, quitting feels like these resources were wasted.
In other words, escalating commitment is a manifestation of the sunk cost fallacy: an irrational escalation of commitment frequently occurs when people refuse to accept that the resources they’ve already invested cannot be recovered. Instead, they insist on more spending to justify the initial investment (and the incurred losses).
When you are faced with a straw man argument , the best way to respond is to draw attention to the fallacy and ask your discussion partner to show how your original statement and their distorted version are the same. Since these are different, your partner will either have to admit that their argument is invalid or try to justify it by using more flawed reasoning, which you can then attack.
The straw man argument is a problem because it occurs when we fail to take an opposing point of view seriously. Instead, we intentionally misrepresent our opponent’s ideas and avoid genuinely engaging with them. Due to this, resorting to straw man fallacy lowers the standard of constructive debate.
A straw man argument is a distorted (and weaker) version of another person’s argument that can easily be refuted (e.g., when a teacher proposes that the class spend more time on math exercises, a parent complains that the teacher doesn’t care about reading and writing).
This is a straw man argument because it misrepresents the teacher’s position, which didn’t mention anything about cutting down on reading and writing. The straw man argument is also known as the straw man fallacy .
A slippery slope argument is not always a fallacy.
- When someone claims adopting a certain policy or taking a certain action will automatically lead to a series of other policies or actions also being taken, this is a slippery slope argument.
- If they don’t show a causal connection between the advocated policy and the consequent policies, then they commit a slippery slope fallacy .
There are a number of ways you can deal with slippery slope arguments especially when you suspect these are fallacious:
- Slippery slope arguments take advantage of the gray area between an initial action or decision and the possible next steps that might lead to the undesirable outcome. You can point out these missing steps and ask your partner to indicate what evidence exists to support the claimed relationship between two or more events.
- Ask yourself if each link in the chain of events or action is valid. Every proposition has to be true for the overall argument to work, so even if one link is irrational or not supported by evidence, then the argument collapses.
- Sometimes people commit a slippery slope fallacy unintentionally. In these instances, use an example that demonstrates the problem with slippery slope arguments in general (e.g., by using statements to reach a conclusion that is not necessarily relevant to the initial statement). By attacking the concept of slippery slope arguments you can show that they are often fallacious.
People sometimes confuse cognitive bias and logical fallacies because they both relate to flawed thinking. However, they are not the same:
- Cognitive bias is the tendency to make decisions or take action in an illogical way because of our values, memory, socialization, and other personal attributes. In other words, it refers to a fixed pattern of thinking rooted in the way our brain works.
- Logical fallacies relate to how we make claims and construct our arguments in the moment. They are statements that sound convincing at first but can be disproven through logical reasoning.
In other words, cognitive bias refers to an ongoing predisposition, while logical fallacy refers to mistakes of reasoning that occur in the moment.
An appeal to ignorance (ignorance here meaning lack of evidence) is a type of informal logical fallacy .
It asserts that something must be true because it hasn’t been proven false—or that something must be false because it has not yet been proven true.
For example, “unicorns exist because there is no evidence that they don’t.” The appeal to ignorance is also called the burden of proof fallacy .
An ad hominem (Latin for “to the person”) is a type of informal logical fallacy . Instead of arguing against a person’s position, an ad hominem argument attacks the person’s character or actions in an effort to discredit them.
This rhetorical strategy is fallacious because a person’s character, motive, education, or other personal trait is logically irrelevant to whether their argument is true or false.
Name-calling is common in ad hominem fallacy (e.g., “environmental activists are ineffective because they’re all lazy tree-huggers”).
Ad hominem is a persuasive technique where someone tries to undermine the opponent’s argument by personally attacking them.
In this way, one can redirect the discussion away from the main topic and to the opponent’s personality without engaging with their viewpoint. When the opponent’s personality is irrelevant to the discussion, we call it an ad hominem fallacy .
Ad hominem tu quoque (‘you too”) is an attempt to rebut a claim by attacking its proponent on the grounds that they uphold a double standard or that they don’t practice what they preach. For example, someone is telling you that you should drive slowly otherwise you’ll get a speeding ticket one of these days, and you reply “but you used to get them all the time!”
Argumentum ad hominem means “argument to the person” in Latin and it is commonly referred to as ad hominem argument or personal attack. Ad hominem arguments are used in debates to refute an argument by attacking the character of the person making it, instead of the logic or premise of the argument itself.
The opposite of the hasty generalization fallacy is called slothful induction fallacy or appeal to coincidence .
It is the tendency to deny a conclusion even though there is sufficient evidence that supports it. Slothful induction occurs due to our natural tendency to dismiss events or facts that do not align with our personal biases and expectations. For example, a researcher may try to explain away unexpected results by claiming it is just a coincidence.
To avoid a hasty generalization fallacy we need to ensure that the conclusions drawn are well-supported by the appropriate evidence. More specifically:
- In statistics , if we want to draw inferences about an entire population, we need to make sure that the sample is random and representative of the population . We can achieve that by using a probability sampling method , like simple random sampling or stratified sampling .
- In academic writing , use precise language and measured phases. Try to avoid making absolute claims, cite specific instances and examples without applying the findings to a larger group.
- As readers, we need to ask ourselves “does the writer demonstrate sufficient knowledge of the situation or phenomenon that would allow them to make a generalization?”
The hasty generalization fallacy and the anecdotal evidence fallacy are similar in that they both result in conclusions drawn from insufficient evidence. However, there is a difference between the two:
- The hasty generalization fallacy involves genuinely considering an example or case (i.e., the evidence comes first and then an incorrect conclusion is drawn from this).
- The anecdotal evidence fallacy (also known as “cherry-picking” ) is knowing in advance what conclusion we want to support, and then selecting the story (or a few stories) that support it. By overemphasizing anecdotal evidence that fits well with the point we are trying to make, we overlook evidence that would undermine our argument.
Although many sources use circular reasoning fallacy and begging the question interchangeably, others point out that there is a subtle difference between the two:
- Begging the question fallacy occurs when you assume that an argument is true in order to justify a conclusion. If something begs the question, what you are actually asking is, “Is the premise of that argument actually true?” For example, the statement “Snakes make great pets. That’s why we should get a snake” begs the question “are snakes really great pets?”
- Circular reasoning fallacy on the other hand, occurs when the evidence used to support a claim is just a repetition of the claim itself. For example, “People have free will because they can choose what to do.”
In other words, we could say begging the question is a form of circular reasoning.
Circular reasoning fallacy uses circular reasoning to support an argument. More specifically, the evidence used to support a claim is just a repetition of the claim itself. For example: “The President of the United States is a good leader (claim), because they are the leader of this country (supporting evidence)”.
An example of a non sequitur is the following statement:
“Giving up nuclear weapons weakened the United States’ military. Giving up nuclear weapons also weakened China. For this reason, it is wrong to try to outlaw firearms in the United States today.”
Clearly there is a step missing in this line of reasoning and the conclusion does not follow from the premise, resulting in a non sequitur fallacy .
The difference between the post hoc fallacy and the non sequitur fallacy is that post hoc fallacy infers a causal connection between two events where none exists, whereas the non sequitur fallacy infers a conclusion that lacks a logical connection to the premise.
In other words, a post hoc fallacy occurs when there is a lack of a cause-and-effect relationship, while a non sequitur fallacy occurs when there is a lack of logical connection.
An example of post hoc fallacy is the following line of reasoning:
“Yesterday I had ice cream, and today I have a terrible stomachache. I’m sure the ice cream caused this.”
Although it is possible that the ice cream had something to do with the stomachache, there is no proof to justify the conclusion other than the order of events. Therefore, this line of reasoning is fallacious.
Post hoc fallacy and hasty generalisation fallacy are similar in that they both involve jumping to conclusions. However, there is a difference between the two:
- Post hoc fallacy is assuming a cause and effect relationship between two events, simply because one happened after the other.
- Hasty generalisation fallacy is drawing a general conclusion from a small sample or little evidence.
In other words, post hoc fallacy involves a leap to a causal claim; hasty generalisation fallacy involves a leap to a general proposition.
The fallacy of composition is similar to and can be confused with the hasty generalization fallacy . However, there is a difference between the two:
- The fallacy of composition involves drawing an inference about the characteristics of a whole or group based on the characteristics of its individual members.
- The hasty generalization fallacy involves drawing an inference about a population or class of things on the basis of few atypical instances or a small sample of that population or thing.
In other words, the fallacy of composition is using an unwarranted assumption that we can infer something about a whole based on the characteristics of its parts, while the hasty generalization fallacy is using insufficient evidence to draw a conclusion.
The opposite of the fallacy of composition is the fallacy of division . In the fallacy of division, the assumption is that a characteristic which applies to a whole or a group must necessarily apply to the parts or individual members. For example, “Australians travel a lot. Gary is Australian, so he must travel a lot.”
Base rate fallacy can be avoided by following these steps:
- Avoid making an important decision in haste. When we are under pressure, we are more likely to resort to cognitive shortcuts like the availability heuristic and the representativeness heuristic . Due to this, we are more likely to factor in only current and vivid information, and ignore the actual probability of something happening (i.e., base rate).
- Take a long-term view on the decision or question at hand. Look for relevant statistical data, which can reveal long-term trends and give you the full picture.
- Talk to experts like professionals. They are more aware of probabilities related to specific decisions.
Suppose there is a population consisting of 90% psychologists and 10% engineers. Given that you know someone enjoyed physics at school, you may conclude that they are an engineer rather than a psychologist, even though you know that this person comes from a population consisting of far more psychologists than engineers.
When we ignore the rate of occurrence of some trait in a population (the base-rate information) we commit base rate fallacy .
Cost-benefit fallacy is a common error that occurs when allocating sources in project management. It is the fallacy of assuming that cost-benefit estimates are more or less accurate, when in fact they are highly inaccurate and biased. This means that cost-benefit analyses can be useful, but only after the cost-benefit fallacy has been acknowledged and corrected for. Cost-benefit fallacy is a type of base rate fallacy .
In advertising, the fallacy of equivocation is often used to create a pun. For example, a billboard company might advertise their billboards using a line like: “Looking for a sign? This is it!” The word sign has a literal meaning as billboard and a figurative one as a sign from God, the universe, etc.
Equivocation is a fallacy because it is a form of argumentation that is both misleading and logically unsound. When the meaning of a word or phrase shifts in the course of an argument, it causes confusion and also implies that the conclusion (which may be true) does not follow from the premise.
The fallacy of equivocation is an informal logical fallacy, meaning that the error lies in the content of the argument instead of the structure.
Fallacies of relevance are a group of fallacies that occur in arguments when the premises are logically irrelevant to the conclusion. Although at first there seems to be a connection between the premise and the conclusion, in reality fallacies of relevance use unrelated forms of appeal.
For example, the genetic fallacy makes an appeal to the source or origin of the claim in an attempt to assert or refute something.
The ad hominem fallacy and the genetic fallacy are closely related in that they are both fallacies of relevance. In other words, they both involve arguments that use evidence or examples that are not logically related to the argument at hand. However, there is a difference between the two:
- In the ad hominem fallacy , the goal is to discredit the argument by discrediting the person currently making the argument.
- In the genetic fallacy , the goal is to discredit the argument by discrediting the history or origin (i.e., genesis) of an argument.
False dilemma fallacy is also known as false dichotomy, false binary, and “either-or” fallacy. It is the fallacy of presenting only two choices, outcomes, or sides to an argument as the only possibilities, when more are available.
The false dilemma fallacy works in two ways:
- By presenting only two options as if these were the only ones available
- By presenting two options as mutually exclusive (i.e., only one option can be selected or can be true at a time)
In both cases, by using the false dilemma fallacy, one conceals alternative choices and doesn’t allow others to consider the full range of options. This is usually achieved through an“either-or” construction and polarised, divisive language (“you are either a friend or an enemy”).
The best way to avoid a false dilemma fallacy is to pause and reflect on two points:
- Are the options presented truly the only ones available ? It could be that another option has been deliberately omitted.
- Are the options mentioned mutually exclusive ? Perhaps all of the available options can be selected (or be true) at the same time, which shows that they aren’t mutually exclusive. Proving this is called “escaping between the horns of the dilemma.”
Begging the question fallacy is an argument in which you assume what you are trying to prove. In other words, your position and the justification of that position are the same, only slightly rephrased.
For example: “All freshmen should attend college orientation, because all college students should go to such an orientation.”
The complex question fallacy and begging the question fallacy are similar in that they are both based on assumptions. However, there is a difference between them:
- A complex question fallacy occurs when someone asks a question that presupposes the answer to another question that has not been established or accepted by the other person. For example, asking someone “Have you stopped cheating on tests?”, unless it has previously been established that the person is indeed cheating on tests, is a fallacy.
- Begging the question fallacy occurs when we assume the very thing as a premise that we’re trying to prove in our conclusion. In other words, the conclusion is used to support the premises, and the premises prove the validity of the conclusion. For example: “God exists because the Bible says so, and the Bible is true because it is the word of God.”
In other words, begging the question is about drawing a conclusion based on an assumption, while a complex question involves asking a question that presupposes the answer to a prior question.
“ No true Scotsman ” arguments aren’t always fallacious. When there is a generally accepted definition of who or what constitutes a group, it’s reasonable to use statements in the form of “no true Scotsman”.
For example, the statement that “no true pacifist would volunteer for military service” is not fallacious, since a pacifist is, by definition, someone who opposes war or violence as a means of settling disputes.
No true Scotsman arguments are fallacious because instead of logically refuting the counterexample, they simply assert that it doesn’t count. In other words, the counterexample is rejected for psychological, but not logical, reasons.
The appeal to purity or no true Scotsman fallacy is an attempt to defend a generalisation about a group from a counterexample by shifting the definition of the group in the middle of the argument. In this way, one can exclude the counterexample as not being “true”, “genuine”, or “pure” enough to be considered as part of the group in question.
To identify an appeal to authority fallacy , you can ask yourself the following questions:
- Is the authority cited really a qualified expert in this particular area under discussion? For example, someone who has formal education or years of experience can be an expert.
- Do experts disagree on this particular subject? If that is the case, then for almost any claim supported by one expert there will be a counterclaim that is supported by another expert. If there is no consensus, an appeal to authority is fallacious.
- Is the authority in question biased? If you suspect that an expert’s prejudice and bias could have influenced their views, then the expert is not reliable and an argument citing this expert will be fallacious.To identify an appeal to authority fallacy, you ask yourself whether the authority cited is a qualified expert in the particular area under discussion.
Appeal to authority is a fallacy when those who use it do not provide any justification to support their argument. Instead they cite someone famous who agrees with their viewpoint, but is not qualified to make reliable claims on the subject.
Appeal to authority fallacy is often convincing because of the effect authority figures have on us. When someone cites a famous person, a well-known scientist, a politician, etc. people tend to be distracted and often fail to critically examine whether the authority figure is indeed an expert in the area under discussion.
The ad populum fallacy is common in politics. One example is the following viewpoint: “The majority of our countrymen think we should have military operations overseas; therefore, it’s the right thing to do.”
This line of reasoning is fallacious, because popular acceptance of a belief or position does not amount to a justification of that belief. In other words, following the prevailing opinion without examining the underlying reasons is irrational.
The ad populum fallacy plays on our innate desire to fit in (known as “bandwagon effect”). If many people believe something, our common sense tells us that it must be true and we tend to accept it. However, in logic, the popularity of a proposition cannot serve as evidence of its truthfulness.
Ad populum (or appeal to popularity) fallacy and appeal to authority fallacy are similar in that they both conflate the validity of a belief with its popular acceptance among a specific group. However there is a key difference between the two:
- An ad populum fallacy tries to persuade others by claiming that something is true or right because a lot of people think so.
- An appeal to authority fallacy tries to persuade by claiming a group of experts believe something is true or right, therefore it must be so.
To identify a false cause fallacy , you need to carefully analyse the argument:
- When someone claims that one event directly causes another, ask if there is sufficient evidence to establish a cause-and-effect relationship.
- Ask if the claim is based merely on the chronological order or co-occurrence of the two events.
- Consider alternative possible explanations (are there other factors at play that could influence the outcome?).
By carefully analysing the reasoning, considering alternative explanations, and examining the evidence provided, you can identify a false cause fallacy and discern whether a causal claim is valid or flawed.
False cause fallacy examples include:
- Believing that wearing your lucky jersey will help your team win
- Thinking that everytime you wash your car, it rains
- Claiming that playing video games causes violent behavior
In each of these examples, we falsely assume that one event causes another without any proof.
The planning fallacy and procrastination are not the same thing. Although they both relate to time and task management, they describe different challenges:
- The planning fallacy describes our inability to correctly estimate how long a future task will take, mainly due to optimism bias and a strong focus on the best-case scenario.
- Procrastination refers to postponing a task, usually by focusing on less urgent or more enjoyable activities. This is due to psychological reasons, like fear of failure.
In other words, the planning fallacy refers to inaccurate predictions about the time we need to finish a task, while procrastination is a deliberate delay due to psychological factors.
A real-life example of the planning fallacy is the construction of the Sydney Opera House in Australia. When construction began in the late 1950s, it was initially estimated that it would be completed in four years at a cost of around $7 million.
Because the government wanted the construction to start before political opposition would stop it and while public opinion was still favorable, a number of design issues had not been carefully studied in advance. Due to this, several problems appeared immediately after the project commenced.
The construction process eventually stretched over 14 years, with the Opera House being completed in 1973 at a cost of over $100 million, significantly exceeding the initial estimates.
An example of appeal to pity fallacy is the following appeal by a student to their professor:
“Professor, please consider raising my grade. I had a terrible semester: my car broke down, my laptop got stolen, and my cat got sick.”
While these circumstances may be unfortunate, they are not directly related to the student’s academic performance.
While both the appeal to pity fallacy and red herring fallacy can serve as a distraction from the original discussion topic, they are distinct fallacies. More specifically:
- Appeal to pity fallacy attempts to evoke feelings of sympathy, pity, or guilt in an audience, so that they accept the speaker’s conclusion as truthful.
- Red herring fallacy attempts to introduce an irrelevant piece of information that diverts the audience’s attention to a different topic.
Both fallacies can be used as a tool of deception. However, they operate differently and serve distinct purposes in arguments.
Argumentum ad misericordiam (Latin for “argument from pity or misery”) is another name for appeal to pity fallacy . It occurs when someone evokes sympathy or guilt in an attempt to gain support for their claim, without providing any logical reasons to support the claim itself. Appeal to pity is a deceptive tactic of argumentation, playing on people’s emotions to sway their opinion.
Yes, it’s quite common to start a sentence with a preposition, and there’s no reason not to do so.
For example, the sentence “ To many, she was a hero” is perfectly grammatical. It could also be rephrased as “She was a hero to many”, but there’s no particular reason to do so. Both versions are fine.
Some people argue that you shouldn’t end a sentence with a preposition , but that “rule” can also be ignored, since it’s not supported by serious language authorities.
Yes, it’s fine to end a sentence with a preposition . The “rule” against doing so is overwhelmingly rejected by modern style guides and language authorities and is based on the rules of Latin grammar, not English.
Trying to avoid ending a sentence with a preposition often results in very unnatural phrasings. For example, turning “He knows what he’s talking about ” into “He knows about what he’s talking” or “He knows that about which he’s talking” is definitely not an improvement.
No, ChatGPT is not a credible source of factual information and can’t be cited for this purpose in academic writing . While it tries to provide accurate answers, it often gets things wrong because its responses are based on patterns, not facts and data.
Specifically, the CRAAP test for evaluating sources includes five criteria: currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose . ChatGPT fails to meet at least three of them:
- Currency: The dataset that ChatGPT was trained on only extends to 2021, making it slightly outdated.
- Authority: It’s just a language model and is not considered a trustworthy source of factual information.
- Accuracy: It bases its responses on patterns rather than evidence and is unable to cite its sources .
So you shouldn’t cite ChatGPT as a trustworthy source for a factual claim. You might still cite ChatGPT for other reasons – for example, if you’re writing a paper about AI language models, ChatGPT responses are a relevant primary source .
ChatGPT is an AI language model that was trained on a large body of text from a variety of sources (e.g., Wikipedia, books, news articles, scientific journals). The dataset only went up to 2021, meaning that it lacks information on more recent events.
It’s also important to understand that ChatGPT doesn’t access a database of facts to answer your questions. Instead, its responses are based on patterns that it saw in the training data.
So ChatGPT is not always trustworthy . It can usually answer general knowledge questions accurately, but it can easily give misleading answers on more specialist topics.
Another consequence of this way of generating responses is that ChatGPT usually can’t cite its sources accurately. It doesn’t really know what source it’s basing any specific claim on. It’s best to check any information you get from it against a credible source .
No, it is not possible to cite your sources with ChatGPT . You can ask it to create citations, but it isn’t designed for this task and tends to make up sources that don’t exist or present information in the wrong format. ChatGPT also cannot add citations to direct quotes in your text.
Instead, use a tool designed for this purpose, like the Scribbr Citation Generator .
But you can use ChatGPT for assignments in other ways, to provide inspiration, feedback, and general writing advice.
GPT stands for “generative pre-trained transformer”, which is a type of large language model: a neural network trained on a very large amount of text to produce convincing, human-like language outputs. The Chat part of the name just means “chat”: ChatGPT is a chatbot that you interact with by typing in text.
The technology behind ChatGPT is GPT-3.5 (in the free version) or GPT-4 (in the premium version). These are the names for the specific versions of the GPT model. GPT-4 is currently the most advanced model that OpenAI has created. It’s also the model used in Bing’s chatbot feature.
ChatGPT was created by OpenAI, an AI research company. It started as a nonprofit company in 2015 but became for-profit in 2019. Its CEO is Sam Altman, who also co-founded the company. OpenAI released ChatGPT as a free “research preview” in November 2022. Currently, it’s still available for free, although a more advanced premium version is available if you pay for it.
OpenAI is also known for developing DALL-E, an AI image generator that runs on similar technology to ChatGPT.
ChatGPT is owned by OpenAI, the company that developed and released it. OpenAI is a company dedicated to AI research. It started as a nonprofit company in 2015 but transitioned to for-profit in 2019. Its current CEO is Sam Altman, who also co-founded the company.
In terms of who owns the content generated by ChatGPT, OpenAI states that it will not claim copyright on this content , and the terms of use state that “you can use Content for any purpose, including commercial purposes such as sale or publication”. This means that you effectively own any content you generate with ChatGPT and can use it for your own purposes.
Be cautious about how you use ChatGPT content in an academic context. University policies on AI writing are still developing, so even if you “own” the content, you’re often not allowed to submit it as your own work according to your university or to publish it in a journal.
ChatGPT is a chatbot based on a large language model (LLM). These models are trained on huge datasets consisting of hundreds of billions of words of text, based on which the model learns to effectively predict natural responses to the prompts you enter.
ChatGPT was also refined through a process called reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), which involves “rewarding” the model for providing useful answers and discouraging inappropriate answers – encouraging it to make fewer mistakes.
Essentially, ChatGPT’s answers are based on predicting the most likely responses to your inputs based on its training data, with a reward system on top of this to incentivise it to give you the most helpful answers possible. It’s a bit like an incredibly advanced version of predictive text. This is also one of ChatGPT’s limitations : because its answers are based on probabilities, they’re not always trustworthy .
OpenAI may store ChatGPT conversations for the purposes of future training. Additionally, these conversations may be monitored by human AI trainers.
Users can choose not to have their chat history saved. Unsaved chats are not used to train future models and are permanently deleted from ChatGPT’s system after 30 days.
The official ChatGPT app is currently only available on iOS devices. If you don’t have an iOS device, only use the official OpenAI website to access the tool. This helps to eliminate the potential risk of downloading fraudulent or malicious software.
ChatGPT conversations are generally used to train future models and to resolve issues/bugs. These chats may be monitored by human AI trainers.
However, users can opt out of having their conversations used for training. In these instances, chats are monitored only for potential abuse.
Yes, using ChatGPT as a conversation partner is a great way to practice a language in an interactive way.
Try using a prompt like this one:
“Please be my Spanish conversation partner. Only speak to me in Spanish. Keep your answers short (maximum 50 words). Ask me questions. Let’s start the conversation with the following topic: [conversation topic].”
Yes, there are a variety of ways to use ChatGPT for language learning , including treating it as a conversation partner, asking it for translations, and using it to generate a curriculum or practice exercises.
AI detectors aim to identify the presence of AI-generated text (e.g., from ChatGPT ) in a piece of writing, but they can’t do so with complete accuracy. In our comparison of the best AI detectors , we found that the 10 tools we tested had an average accuracy of 60%. The best free tool had 68% accuracy, the best premium tool 84%.
Because of how AI detectors work , they can never guarantee 100% accuracy, and there is always at least a small risk of false positives (human text being marked as AI-generated). Therefore, these tools should not be relied upon to provide absolute proof that a text is or isn’t AI-generated. Rather, they can provide a good indication in combination with other evidence.
Tools called AI detectors are designed to label text as AI-generated or human. AI detectors work by looking for specific characteristics in the text, such as a low level of randomness in word choice and sentence length. These characteristics are typical of AI writing, allowing the detector to make a good guess at when text is AI-generated.
But these tools can’t guarantee 100% accuracy. Check out our comparison of the best AI detectors to learn more.
You can also manually watch for clues that a text is AI-generated – for example, a very different style from the writer’s usual voice or a generic, overly polite tone.
Our research into the best summary generators (aka summarisers or summarising tools) found that the best summariser available in 2023 is the one offered by QuillBot.
While many summarisers just pick out some sentences from the text, QuillBot generates original summaries that are creative, clear, accurate, and concise. It can summarise texts of up to 1,200 words for free, or up to 6,000 with a premium subscription.
Try the QuillBot summarizer for free
Deep learning requires a large dataset (e.g., images or text) to learn from. The more diverse and representative the data, the better the model will learn to recognise objects or make predictions. Only when the training data is sufficiently varied can the model make accurate predictions or recognise objects from new data.
Deep learning models can be biased in their predictions if the training data consist of biased information. For example, if a deep learning model used for screening job applicants has been trained with a dataset consisting primarily of white male applicants, it will consistently favour this specific population over others.
A good ChatGPT prompt (i.e., one that will get you the kinds of responses you want):
- Gives the tool a role to explain what type of answer you expect from it
- Is precisely formulated and gives enough context
- Is free from bias
- Has been tested and improved by experimenting with the tool
ChatGPT prompts are the textual inputs (e.g., questions, instructions) that you enter into ChatGPT to get responses.
ChatGPT predicts an appropriate response to the prompt you entered. In general, a more specific and carefully worded prompt will get you better responses.
Yes, ChatGPT is currently available for free. You have to sign up for a free account to use the tool, and you should be aware that your data may be collected to train future versions of the model.
To sign up and use the tool for free, go to this page and click “Sign up”. You can do so with your email or with a Google account.
A premium version of the tool called ChatGPT Plus is available as a monthly subscription. It currently costs £16 and gets you access to features like GPT-4 (a more advanced version of the language model). But it’s optional: you can use the tool completely free if you’re not interested in the extra features.
You can access ChatGPT by signing up for a free account:
- Follow this link to the ChatGPT website.
- Click on “Sign up” and fill in the necessary details (or use your Google account). It’s free to sign up and use the tool.
- Type a prompt into the chat box to get started!
A ChatGPT app is also available for iOS, and an Android app is planned for the future. The app works similarly to the website, and you log in with the same account for both.
According to OpenAI’s terms of use, users have the right to reproduce text generated by ChatGPT during conversations.
However, publishing ChatGPT outputs may have legal implications , such as copyright infringement.
Users should be aware of such issues and use ChatGPT outputs as a source of inspiration instead.
According to OpenAI’s terms of use, users have the right to use outputs from their own ChatGPT conversations for any purpose (including commercial publication).
However, users should be aware of the potential legal implications of publishing ChatGPT outputs. ChatGPT responses are not always unique: different users may receive the same response.
Furthermore, ChatGPT outputs may contain copyrighted material. Users may be liable if they reproduce such material.
ChatGPT can sometimes reproduce biases from its training data , since it draws on the text it has “seen” to create plausible responses to your prompts.
For example, users have shown that it sometimes makes sexist assumptions such as that a doctor mentioned in a prompt must be a man rather than a woman. Some have also pointed out political bias in terms of which political figures the tool is willing to write positively or negatively about and which requests it refuses.
The tool is unlikely to be consistently biased toward a particular perspective or against a particular group. Rather, its responses are based on its training data and on the way you phrase your ChatGPT prompts . It’s sensitive to phrasing, so asking it the same question in different ways will result in quite different answers.
Information extraction refers to the process of starting from unstructured sources (e.g., text documents written in ordinary English) and automatically extracting structured information (i.e., data in a clearly defined format that’s easily understood by computers). It’s an important concept in natural language processing (NLP) .
For example, you might think of using news articles full of celebrity gossip to automatically create a database of the relationships between the celebrities mentioned (e.g., married, dating, divorced, feuding). You would end up with data in a structured format, something like MarriageBetween(celebrity 1 ,celebrity 2 ,date) .
The challenge involves developing systems that can “understand” the text well enough to extract this kind of data from it.
Knowledge representation and reasoning (KRR) is the study of how to represent information about the world in a form that can be used by a computer system to solve and reason about complex problems. It is an important field of artificial intelligence (AI) research.
An example of a KRR application is a semantic network, a way of grouping words or concepts by how closely related they are and formally defining the relationships between them so that a machine can “understand” language in something like the way people do.
A related concept is information extraction , concerned with how to get structured information from unstructured sources.
Yes, you can use ChatGPT to summarise text . This can help you understand complex information more easily, summarise the central argument of your own paper, or clarify your research question.
You can also use Scribbr’s free text summariser , which is designed specifically for this purpose.
Yes, you can use ChatGPT to paraphrase text to help you express your ideas more clearly, explore different ways of phrasing your arguments, and avoid repetition.
However, it’s not specifically designed for this purpose. We recommend using a specialised tool like Scribbr’s free paraphrasing tool , which will provide a smoother user experience.
Yes, you use ChatGPT to help write your college essay by having it generate feedback on certain aspects of your work (consistency of tone, clarity of structure, etc.).
However, ChatGPT is not able to adequately judge qualities like vulnerability and authenticity. For this reason, it’s important to also ask for feedback from people who have experience with college essays and who know you well. Alternatively, you can get advice using Scribbr’s essay editing service .
No, having ChatGPT write your college essay can negatively impact your application in numerous ways. ChatGPT outputs are unoriginal and lack personal insight.
Furthermore, Passing off AI-generated text as your own work is considered academically dishonest . AI detectors may be used to detect this offense, and it’s highly unlikely that any university will accept you if you are caught submitting an AI-generated admission essay.
However, you can use ChatGPT to help write your college essay during the preparation and revision stages (e.g., for brainstorming ideas and generating feedback).
ChatGPT and other AI writing tools can have unethical uses. These include:
- Reproducing biases and false information
- Using ChatGPT to cheat in academic contexts
- Violating the privacy of others by inputting personal information
However, when used correctly, AI writing tools can be helpful resources for improving your academic writing and research skills. Some ways to use ChatGPT ethically include:
- Following your institution’s guidelines
- Critically evaluating outputs
- Being transparent about how you used the tool
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Chat with us
- Email [email protected]
- Call +44 (0)20 3917 4242
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our support team is here to help you daily via chat, WhatsApp, email, or phone between 9:00 a.m. to 11:00 p.m. CET.
Our APA experts default to APA 7 for editing and formatting. For the Citation Editing Service you are able to choose between APA 6 and 7.
Yes, if your document is longer than 20,000 words, you will get a sample of approximately 2,000 words. This sample edit gives you a first impression of the editor’s editing style and a chance to ask questions and give feedback.
How does the sample edit work?
You will receive the sample edit within 24 hours after placing your order. You then have 24 hours to let us know if you’re happy with the sample or if there’s something you would like the editor to do differently.
Read more about how the sample edit works
Yes, you can upload your document in sections.
We try our best to ensure that the same editor checks all the different sections of your document. When you upload a new file, our system recognizes you as a returning customer, and we immediately contact the editor who helped you before.
However, we cannot guarantee that the same editor will be available. Your chances are higher if
- You send us your text as soon as possible and
- You can be flexible about the deadline.
Please note that the shorter your deadline is, the lower the chance that your previous editor is not available.
If your previous editor isn’t available, then we will inform you immediately and look for another qualified editor. Fear not! Every Scribbr editor follows the Scribbr Improvement Model and will deliver high-quality work.
Yes, our editors also work during the weekends and holidays.
Because we have many editors available, we can check your document 24 hours per day and 7 days per week, all year round.
If you choose a 72 hour deadline and upload your document on a Thursday evening, you’ll have your thesis back by Sunday evening!
Yes! Our editors are all native speakers, and they have lots of experience editing texts written by ESL students. They will make sure your grammar is perfect and point out any sentences that are difficult to understand. They’ll also notice your most common mistakes, and give you personal feedback to improve your writing in English.
Every Scribbr order comes with our award-winning Proofreading & Editing service , which combines two important stages of the revision process.
For a more comprehensive edit, you can add a Structure Check or Clarity Check to your order. With these building blocks, you can customize the kind of feedback you receive.
You might be familiar with a different set of editing terms. To help you understand what you can expect at Scribbr, we created this table:
| Types of editing | Available at Scribbr? |
|---|---|
| | This is the “proofreading” in Scribbr’s standard service. It can only be selected in combination with editing. |
| | This is the “editing” in Scribbr’s standard service. It can only be selected in combination with proofreading. |
| | Select the Structure Check and Clarity Check to receive a comprehensive edit equivalent to a line edit. |
| | This kind of editing involves heavy rewriting and restructuring. Our editors cannot help with this. |
View an example
When you place an order, you can specify your field of study and we’ll match you with an editor who has familiarity with this area.
However, our editors are language specialists, not academic experts in your field. Your editor’s job is not to comment on the content of your dissertation, but to improve your language and help you express your ideas as clearly and fluently as possible.
This means that your editor will understand your text well enough to give feedback on its clarity, logic and structure, but not on the accuracy or originality of its content.
Good academic writing should be understandable to a non-expert reader, and we believe that academic editing is a discipline in itself. The research, ideas and arguments are all yours – we’re here to make sure they shine!
After your document has been edited, you will receive an email with a link to download the document.
The editor has made changes to your document using ‘Track Changes’ in Word. This means that you only have to accept or ignore the changes that are made in the text one by one.
It is also possible to accept all changes at once. However, we strongly advise you not to do so for the following reasons:
- You can learn a lot by looking at the mistakes you made.
- The editors don’t only change the text – they also place comments when sentences or sometimes even entire paragraphs are unclear. You should read through these comments and take into account your editor’s tips and suggestions.
- With a final read-through, you can make sure you’re 100% happy with your text before you submit!
You choose the turnaround time when ordering. We can return your dissertation within 24 hours , 3 days or 1 week . These timescales include weekends and holidays. As soon as you’ve paid, the deadline is set, and we guarantee to meet it! We’ll notify you by text and email when your editor has completed the job.
Very large orders might not be possible to complete in 24 hours. On average, our editors can complete around 13,000 words in a day while maintaining our high quality standards. If your order is longer than this and urgent, contact us to discuss possibilities.
Always leave yourself enough time to check through the document and accept the changes before your submission deadline.
Scribbr is specialised in editing study related documents. We check:
- Graduation projects
- Dissertations
- Admissions essays
- College essays
- Application essays
- Personal statements
- Process reports
- Reflections
- Internship reports
- Academic papers
- Research proposals
- Prospectuses
Calculate the costs
The fastest turnaround time is 24 hours.
You can upload your document at any time and choose between four deadlines:
At Scribbr, we promise to make every customer 100% happy with the service we offer. Our philosophy: Your complaint is always justified – no denial, no doubts.
Our customer support team is here to find the solution that helps you the most, whether that’s a free new edit or a refund for the service.
Yes, in the order process you can indicate your preference for American, British, or Australian English .
If you don’t choose one, your editor will follow the style of English you currently use. If your editor has any questions about this, we will contact you.

- Majors & Careers
- Online Grad School
- Preparing For Grad School
- Student Life
Dissertation vs Thesis: Your 2024 Guide

If you’ve been thinking about going to graduate school, you may be familiar with the application requirements, rigorous academic schedule, and thesis or dissertation you’ll be expected to complete. So, what exactly is the difference between a thesis and a dissertation? While there are similarities, there’s a clear difference between the two. In our guide, we compare dissertation vs thesis. Discover more about both – and what you can expect during your graduate program. Let’s get started!
- Table of Contents
What Is a Thesis?
A thesis is an academic paper or project that’s completed towards the end of a master’s degree program . It is typically completed as the capstone project , meaning it’s the final project required for a student to graduate.
Students need to select a narrow, specific topic within – or relating to – their field of study. Once they’ve selected a topic, students must conduct an in-depth review of existing research on their chosen subjects. The next step is to formulate an academic argument, an assertion they’ll need to support or prove with said research.
Therefore, a thesis is akin to an in-depth research paper. It’s comprised of research that essentially proves what a student has learned during their program.
What Is a Typical Thesis Structure?
A thesis generally follows a rigid structure that’s decided by the program, department, or university. Here is an example of a thesis structure:
- The Title Page
- Summary of Thesis Abstract
- Table of Maps and Figures
- The Thesis Body (Sometimes divided into chapters)
- The Results or Conclusion
Who Needs to Complete a Thesis?
Most master’s degree programs require students to complete a thesis. While some undergraduate programs may also require a thesis, these are generally shorter and narrower in scope.
Some programs will also require a master’s student to defend their thesis in front of a panel or committee.
What Is a Dissertation?
What is “the PhD paper” called? Some people refer to it as a PhD thesis, but it’s most commonly known as a dissertation in the US. Dissertations are the capstone project required at the tail end of a PhD program . It is almost always required, except for a select few one-year PhD programs .
Much like a thesis, dissertations are also academic papers that aim to prove a student’s expertise – while adding to the current body of knowledge – in their field. Thus, a student must look at existing research and conduct their own research .

Basically, it’s the magnum opus of a doctoral journey in the United States. A dissertation isn’t just a long research paper; it’s a beast of a project. It demands extensive research, originality, and the ability to make a meaningful contribution to your chosen field. Think of it as a research odyssey guided by a seasoned mentor. Once you’ve conquered this scholarly quest and defended your findings, you’ll proudly emerge with your hard-earned doctoral degree, a testament to your dedication and scholarly prowess.
A dissertation typically comes after a PhD student completes their required courses and passes their qualifying exams. In some programs, the dissertation process is embedded into the coursework. In such cases, students receive a jump start on their work, allowing them to potentially finish their program earlier.
What Does a Dissertation Do?
PhD candidates must present a new theory or hypothesis. Alternatively, they must present their research to question (or disprove) the existing accepted theory on their chosen subject. Students may choose to tackle their topic from a new angle or take their research in a different direction.
Most programs will require students to defend their dissertations. During the defense, candidates must be able to justify the methodology of their research and the results and interpretation of their findings. Defenses are typically oral presentations in front of a dissertation committee , where the students are asked questions or presented with challenges.
Although the defense may seem daunting, PhD students work closely with their advisors to prepare for their dissertations. Students receive feedback and advice to guide their dissertations in their chosen direction.
What Is the Typical Dissertation Structure?
Dissertations follow a rigid structure typically set by the program, department, or university. Here is an example format:
- The Acknowledgments Page
- The Abstract
- Introduction
- The Literature Review & Theoretical Framework
- The Methodology
- Findings/Results
- Discussions of the Findings, including analysis, interpretation, and applications
- The Conclusion
- List of References
- Any Appendices
What Is a Doctoral Thesis?
A doctoral thesis is a substantial piece of scholarly work that marks the pinnacle of a doctoral degree program, such as a PhD. Think of it as the academic grand finale. Its primary mission? To showcase the candidate’s mastery in their chosen field and their knack for delving deep into research.

In a nutshell, a doctoral thesis is a mammoth project that calls for originality. You’ve got to dig, investigate, gather data, crunch numbers, and present real data-supported findings. All this hard work usually happens under the watchful eye of a knowledgeable mentor. Once you’ve conquered this scholarly mountain and defended your thesis successfully, you’ll be proudly awarded your well-deserved doctoral degree. It’s the hallmark of your expertise and contribution to your field.
And how does a doctoral thesis differ from a dissertation? That’s mainly a geographic explanation. While they’re largely similar in scope and purpose, when comparing a doctoral thesis vs. a dissertation:
- A dissertation is the PhD capstone requirement in the US .
- A doctoral thesis is the PhD capstone requirement in Europe .
Related Reading: The Easiest PhDs
Dissertation vs. Thesis: The Similarities
In the master’s thesis vs dissertation discussion, there are plenty of similarities. Both are lengthy academic papers that require intense research and original writing. They’re also capstone projects which are completed at the tail end of their respective programs.
Students must work closely with their respective committees (e.g., faculty members, advisors, professionals) who provide feedback and guidance on their research, writing, and academic arguments. Both thesis and dissertation committees have a committee chair with whom the students work closely.
In some ways, the requirements for theses and dissertations are quite similar. They require a skillful defense of a student’s academic arguments. What’s more, both papers require critical thinking and good analytical reasoning, as well as in-depth expertise in the chosen field of study.
Students must also invest a significant amount of time into both projects while also being able to accept and action feedback on their work.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: The Differences
What are the differences between a PhD dissertation vs. thesis? The first and most distinct difference is the degree program requiring a PhD dissertation or thesis. A dissertation is typically the capstone project for a doctorate, while a thesis is the capstone project for a master’s degree program (or undergraduate program).
Candidates will have to defend their dissertation during an oral presentation in front of their committee. Only some master’s theses require this.
During a thesis, students typically conduct research by reviewing existing literature and knowledge on their chosen subject. During a dissertation, students must do their own research and prove their theory, concept, or hypothesis. They should also expect to develop a unique concept and defend it based on the practical and theoretical results achieved from their rigorous research.
Theses are also typically shorter (around 40 to 80 pages). Dissertations, however, are much longer (between 100 and 300 pages). Of course, the actual length of the paper may depend on the topic, program, department, or university.
Related Reading : PhD Candidate vs Student: What’s the Difference?
Dissertations and Theses: US vs. Europe
Whether you’re in the US or Europe, dissertations and theses are similar. However, European requirements and conventions differ slightly:
Doctoral Thesis
To ensure your PhD graduation, a dissertation is generally required. Doctoral theses in Europe are much like a PhD dissertation in the US : You must complete your own research and add to the existing body of knowledge in your field.
Master’s Dissertation
It may seem odd to require a dissertation for master’s degree programs, but in Europe, this is exactly what you’ll need. A master’s dissertation is a broader post-graduate program research project , though it’s most typically required for master’s programs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are a few of the most common questions we hear about the meaning of thesis vs. dissertation.
Is a Thesis and a Dissertation the Same?
Yes and no. In some ways, a dissertation and a thesis are the same. For example, both require original writing, critical skills, analytical thinking, plenty of research, and lots of academic effort. However, a thesis is more commonly reserved for master’s – and some undergraduate – programs. Dissertations are generally required by PhD programs in the United States.
Additionally, a thesis typically calls for heavy research and compilation of existing knowledge and literature on a subject. A dissertation requires candidates to conduct their own research to prove their own theory, concept, or hypothesis – adding to the existing body of knowledge in their chosen field of study.
How Long Is a Thesis vs. a Dissertation?
One of the primary differences between thesis and dissertation papers is their length. While a thesis might be anywhere from 40 to 80 pages long, a dissertation can easily run from 100 to 300. It’s important to note that these numbers depend on the specific program and university.
Does a PhD Require a Thesis or a Dissertation?
It all depends on where you are! While a US-based PhD requires you to complete a dissertation, a thesis (or “doctoral thesis”) is more commonly required for PhD candidates in Europe. In the US, a thesis is more commonly reserved for master’s degree programs and occasionally undergraduate programs. In Europe, a “master’s dissertation” is typically required for the completion of a master’s degree.
So, there you have it: an in-depth comparison of the dissertation vs. thesis academic requirements. Now that you know the primary similarities and differences between the two, it might become easier to decide your academic path. Just remember, you may be able to find a master’s program without a thesis or a doctorate without a dissertation requirement if you prefer. Good luck!
Are you ready to jump into your doctorate? Find out if you need a master’s degree to get a PhD .

Chriselle Sy
Chriselle has been a passionate professional content writer for over 10 years. She writes educational content for The Grad Cafe, Productivity Spot, The College Monk, and other digital publications. When she isn't busy writing, she spends her time streaming video games and learning new skills.
- Chriselle Sy https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/chriselle-sy/ When to Apply for Grad School: Easy Monthly Timeline [2025-2026]
- Chriselle Sy https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/chriselle-sy/ Best Laptop for Programming Students in 2024
- Chriselle Sy https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/chriselle-sy/ The Best Academic Planners for 2024/2025
- Chriselle Sy https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/chriselle-sy/ Graduate Certificate vs Degree: What’s the Difference? [2024 Guide]
This Week’s Top 5 Graduate Opportunities
These are the best states to start your tech career, related posts.

- How Many Grad Schools Should I Apply To?
![thesis and dissertation difference When to Apply for Grad School: The Simple Guide [2026/2027]](https://blog.thegradcafe.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/When-to-Apply-to-Grad-School-350x250.png)
- When to Apply for Grad School: Easy Monthly Timeline [2025-2026]

- 30+ Best Dorm Room Essentials for Guys in 2024

- Best Laptop for Programming Students in 2024

The Sassy Digital Assistant Revolutionizing Student Budgeting

The Best Academic Planners for 2024/2025

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
- Last Mile Education Fund Paves the Way for Tech Students, Offers Lifeline Grants

© 2024 TheGradCafe.com All rights reserved
- Partner With Us
- Results Search
- Submit Your Results
- Write For Us
- Home »
- Advice »
What is the Difference Between a Dissertation and a Thesis?
Find your perfect postgrad program search our database of 30,000 courses.
And to make it even more confusing, some institutions or departments will even use the terms differently!
But what are we all really talking about when we refer to a dissertation or a thesis? And does the term you use actually impact on what you actually end up writing?
This article covers the main differences between a dissertation and thesis, and how the terms may differ depending on the course, university and location.
What is a dissertation?
A dissertation is a piece of academic writing centred around original research. In their dissertations, students review existing research but also build on this with unique hypotheses and approaches.
A dissertation can be used to disprove a previous theory or take existing theories and research in a new direction. It is a large research project that is usually completed at the end of the academic year.
Usually, a dissertation starts with a dissertation proposal , which is approved by a study supervisor. The student then completes the research and writes up the methodology , findings, evaluations and conclusions from the research.
Dissertations can be undertaken by both undergraduate and postgraduate students. At undergraduate level the word count is around 5,000 to 8,000 and at postgraduate level it is usually 10,000 to 15,000.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an academic paper covering an in-depth review of existing research in a particular discipline. It will involve an academic argument, although it doesn’t usually require original research from the student. The existing research is used to support and evaluate the proposed argument.
A thesis is not usually required at undergraduate level and is more common at postgraduate level.
This large piece of written-up research is usually completed at the end of a masters degree. Some masters courses require a thesis to graduate.
Differences between a dissertation vs thesis
The main purpose of a writing a dissertation is to add new findings to the existing literature in that field with original research. Whereas theses tend to evaluate existing findings, as their purpose is to demonstrate knowledge and skills within the course’s subject matter.
In terms of how long it takes to complete a thesis or dissertation project, a thesis is typically shorter than a dissertation since there are fewer original research aspects involved. This means that it will probably take less time. However, this can differ depending on the university and the course.
Dissertations sometimes require an oral presentation, known as a viva , where findings are showcased to academics who ask questions about the research. Theses usually do not require this.
The root of the words
The word ‘dissertation’ originates from the Latin word ‘dissertare’, meaning to continue to discuss and the Latin word ‘disserere’ which means to examine and discuss .
The word ‘thesis’ originally comes from the Greek word ‘tithenai’, which means to place or position. This later evolved into the Latin ‘thesis’, which had two meanings: an abstract question and to put something forward .
Similarities between a dissertation vs thesis
Although there are some key differences between a dissertation and a thesis, there are also similarities.
- Both are generally long pieces of academic writing, much longer than a typical essay.
- Both explore a topic in depth, whether you are conducting totally unique research or structuring an argument based on existing research.
- Both are considered a final project and usually required to graduate from a degree, masters or PhD. Students can graduate without a thesis or dissertation if they choose to complete a postgraduate diploma or postgraduate certificate instead.
- Excellent academic writing skills are highly important for both types of research project.
Is a dissertation harder than a thesis?
Though, the difficulty of a thesis or dissertation depends on your personal skill set. For instance, students that learn better by developing their own research ideas may find a dissertation easier than a thesis.
Difficulty can also depend on the level of the course. For instance, a thesis completed at doctorate level is likely to require more advanced knowledge than a thesis at undergraduate level.
The difficulty of either type of research project can also vary depending on the subject matter and the resources available to you.
Both dissertations and theses can be challenging, but don’t be put off by the thought of having to produce a larger body of work. Your supervisor will be there to support you.
Definitions depend on where you are
The terms ‘dissertation’ and ‘thesis’ are sometimes used interchangeably, and the meanings can differ depending on the country and university.
There are plenty of differences between the variant forms of English, such as British English and American English. Around the world, different English-speaking countries use the words ‘dissertation’ and ‘thesis’ differently.
Generally, nations with British-based academic systems of university education use dissertation to refer to the body of work at the end of an undergraduate or masters level degree . British-based institutions generally use thesis to refer to the body of work produced at the end of a PhD .
In countries and institutions that are based on the American system of education, the words tend to be used in reverse. However, institutions and even different departments in the same university can use the words differently.
If you're in doubt, then stick with the way the university and department you're currently attending use the terms.
Definitions can depend on the subject
In the UK, the terms ‘dissertation’ and ‘thesis’ are generally applied equally across institutions and subjects.
However, in the US the meanings can differ between different subject areas. The term ‘thesis’ can be used to describe a piece of original research in US academia, whereas original research is usually referred to as a dissertation in the UK.
If you’re studying in the US , you may complete a thesis at masters level in another subject area that involves wide-ranging reading and understanding rather than original research and still call it a thesis.
With so much interchangeability between the two terms, it’s understandable that there is often confusion in the debate between a dissertation vs thesis, as there is no clear answer.
Always read specific course details to understand exactly what’s involved in the research project that you are required to produce.
Examples from US and UK universities
Georgetown University in the US refers to a dissertation and a thesis as both adding to your 'field of knowledge' . The University of Edinburgh recommends that you refer to your individual course handbook for guides to dissertations, so each department will have their own guidelines to using the word dissertation and thesis. At University College London they refer to a thesis as the piece of work at the end of an EngD, MPhil, MD(Res) or PhD, which are all research degrees.
In conclusion
Ultimately, it doesn't really matter which word you use as both refer to a serious and lengthy piece of work where you can show what you have researched and understood as part of your postgraduate studies.
As long as you are referring to the piece of work that you are compiling in the same way as those in your department then you will avoid confusion.
It is important to check whether the research piece involves original research or expects you to build upon existing research.
Writing a dissertation or a thesis requires a substantial amount of planning and work and you don't want to let yourself down at the last hurdle with poor presentation of your work, so always keep an eye on your course or department guidelines.
Related articles
Top Tips On Writing Your Postgraduate Dissertation Or Thesis
How To Write A Thesis
Writing A Dissertation Proposal
Top Thesis Writing Tools
Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries

Exclusive bursaries Open day alerts Funding advice Application tips Latest PG news
Sign up now!

Take 2 minutes to sign up to PGS student services and reap the benefits…
- The chance to apply for one of our 5 PGS Bursaries worth £2,000 each
- Fantastic scholarship updates
- Latest PG news sent directly to you.

- February 8, 2024
- Academic Advice , Education Advice
Dissertation vs Thesis: Understanding the Key Differences
UOTP Marketing

Embarking on an academic journey often involves deciphering the complexities of advanced research projects like dissertations and theses. While these terms might seem interchangeable, they possess distinctive changes in the world of higher education. A fundamental distinction between a thesis and a dissertation lies in their approach to research. A thesis typically involves synthesizing existing research and knowledge in your field, while a dissertation requires conducting original research, addressing research gaps, and making a substantive contribution to the academic domain.
As you continue your higher education journey in academia, it’s critical to decipher the fundamental differences between dissertation and thesis that set them apart.
What Is a Thesis?
A thesis is a long-term academic research paper that presents an in-depth review of existing research on a specific subject. It requires extensive research, data collection, analysis, and critical interpretation of the findings. Although some undergraduate programs may mandate a thesis, it is more commonly expected in postgraduate studies, such as upon completing a master’s degree .
What Is a Dissertation?
A dissertation is a longer and more comprehensive research project based on original research. It’s a substantial piece of academic writing required for the completion of a doctoral degree . The dissertation is the culmination of years of research, study, and expertise, contributing valuable insights in a particular field of study.
Dissertation vs Thesis: Key Differences
Both theses and dissertations serve as culminating projects for program graduation, demanding a profound grasp of the research subject and analytical skills to substantiate findings. Despite these commonalities, significant differences set them apart. The key differences include:
Academic and Research Requirements
The academic requirements for a doctoral dissertation are clearly defined hypotheses, a detailed methodology section, rigorous data analysis, and a critical discussion of the results in the context of existing literature.
In contrast, the requirements for a master’s thesis include a thorough literature review, methodology, data analysis, and a conclusion that summarizes the findings.
Research requirements are also more extensive for dissertations compared to theses, as they include conducting original experiments and studies.
Length and Complexity
The length of a dissertation or a thesis varies according to the topic and the method of analysis, or it can vary based on the departmental requirements. Usually, a master’s thesis is around 40-80 pages, sometimes up to 100 pages. A dissertation, however, is significantly longer, ranging from 100 to 300 pages and sometimes up to 400.
Dissertations and theses also vary on the level of complexity. While the thesis requires a thorough literature review and analysis of existing research, it’s less complex than a dissertation. Moreover, the original research is limited, contrary to dissertations involving extensive original research (experiments and studies).
Research Objectives
The research objectives are an essential component that can guide the research project and highlight the specific goals to achieve. Moreover, they outline the grounds for pursuing a particular topic.
However, they can vary depending on the academic level and the nature of the research. In a master’s thesis, the research objectives usually focus on addressing specific research questions related to the chosen topic, to deepen the understanding of existing theories within the field of study. Contrarily, in a doctoral dissertation, the research objectives are broader and are formulated to address complex research gaps, propose new theories, and contribute to the academic field.
Timeframe and Milestones
The timeframe depends on internal factors like the student’s work pace and personal circumstances and external factors like the complexity of the subject, availability of resources, and academic level. While we can’t give a definitive answer, it usually takes a couple of semesters or 1-2 years to complete a master’s thesis. On the contrary, a doctoral dissertation is more time-consuming and can take 4-7 years to complete.
Although there are many similarities between the milestones for completing a thesis and a dissertation, such as topic selection, literature review, and data collection, their differences lie in the higher complexity of doctoral dissertations, including original research, review by the advisory committee, and publication.
Review and Approval Process
The review and approval process is vital to evaluate the quality of research, analysis, and presentation. Although the overall process is similar for both a master’s thesis and a doctoral dissertation, the scrutiny applied to dissertations is notably more rigorous. For a master’s thesis, a committee of professors or advisors within the university’s department evaluates the thesis for adherence to academic standards, clarity, and coherence. Following the review, approval is granted to the thesis if the evaluators are content with the student’s work. On the other hand, for a doctoral dissertation, the review process includes a committee of experts in the field, often external reviewers, to assess the dissertation’s quality, methodology, and contribution to the academic field. The approval process is more challenging as it may require defending the dissertation orally and answering questions from the committee members and to a broader audience than a master’s thesis presentation.
Potential for Publication
Lastly, one of the main differences between a dissertation and a thesis is the potential for publication. As the dissertation is more extensive and requires original research contributing to the academic field, theses are less likely to be published in a peer-reviewed journal. Although a master’s thesis is more narrowly focused, it can still be published as a single article. In contrast, a doctoral dissertation is generally equivalent to at least three articles.
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. we will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours. if there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:.
By clicking the Send me more information button above, I represent that I am 18+ years of age, that I have read and agreed to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy , and agree to receive email marketing and phone calls from UOTP. I understand that my consent is not required to apply for online degree enrollment. To speak with a representative without providing consent, please call +1 (202) 274-2300
- We value your privacy.
The Scope of Dissertation vs Thesis
While both require extensive research and dedication, the thesis has a narrower scope on a specific topic within the field of study. It aims to illustrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter, ability to synthesize existing research, and ability to present coherent arguments. On the other hand, the dissertation has a broader scope , encompassing a comprehensive analysis of a complex research problem or exploring interconnected topics in the field. It aims to showcase the student’s expertise and ability to conduct original and independent research and contribute new knowledge in the field.
As we draw the curtain in exploring the factors that differentiate a thesis and a dissertation, it becomes evident that both academic endeavors are crucial in unraveling discoveries. A master’s thesis showcases analytical finesse and a deep understanding of existing theories. And a doctoral dissertation displays new groundbreaking insights, original research, and innovative methodologies. Therefore, while they may have substantial differences, they remain a driving force in shaping the future of academia.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): What is the main difference between a dissertation and a thesis?
While many factors differentiate a dissertation and a thesis, the main difference is their academic level. A thesis is usually required at the end of a master’s degree program. In contrast, a dissertation is necessary to complete a doctoral degree.
How long does it take to complete a thesis or a dissertation?
The time it takes to complete a thesis or a dissertation depends on the complexity of the research, the availability of resources, and the student’s work pace. Usually, it takes a couple of semesters to complete a thesis at the end of a master’s program. In contrast, completing a doctoral dissertation can take four to seven years.
Is there a difference in the level of research expected in a dissertation vs a thesis?
Although a thesis requires a significant amount of research literature review and analysis of existing studies, a dissertation demands a higher level of original research through identifying research gaps, developing new hypotheses, conducting experiments, and collecting and analyzing data.
Are there any specific publication or accessibility differences between dissertations and theses?
Yes, there are specific publication and accessibility differences between dissertations and theses. Doctoral dissertations are usually published and made public through university libraries or digital repositories. Whereas a master’s thesis is less frequently published in academic journals compared to doctoral dissertations. Theses are often made available within the university’s library or department.
Share it with your friends!
Explore more.

Accounting vs. Finance Degree: Which Major to Choose?

12 Important Bookkeeping Skills You Need for a Successful Career
Recent resources, notice of filing of form eta 9035.

Constitution Day – 2024

How to Get into HR: A Step-by-Step Guide

Software Developer Career Paths: Everything You Need To Know
INTERESTED IN LEARNING MORE?
Chat with an Admissions Officer Now!

- Associates Degree
- Bachelors Degrees
- Masters Degrees
- Doctoral Degrees
- Faculty & Staff
- Accreditation
- Student Experience
QUICK LINKS
- Admission Requirements
- Military Students
- Financial Aid
Request More Information
Thesis vs. Dissertation: What’s the difference?
Thesis and dissertation are extensive research papers that differ in terms of their requirements, length, and purpose, with the former being associated with a master's degree and the latter with a doctoral degree, but are often used interchangeably.
Updated on September 15, 2023

A thesis and a dissertation are both extensive research papers, and both require literature searches and novel findings, but the two differ in various ways. Their definitions also differ across regions. Typically, in North America, a thesis is required for the completion of a master’s degree, while a dissertation is required for the completion of a doctoral degree. The former is long, while the latter is longer and more intensive.
Despite these differences, the two terms are often used interchangeably, especially among those who haven’t completed one or the other. Here, we’ll compare the components, length, and purpose of these two academic documents to clearly understand the differences between these important papers in the life of a graduate student.
What’s a thesis?
The term “thesis” explained here is generally consistent with how the word is used in North America to describe this substantive research paper.
A thesis is an extended argument (PDF). It is a research-based document that displays the student’s/author’s knowledge and understanding of a specific subject within their field of study. It generally presents findings on a particular topic.
See this and this (PDFs) for examples. These superb master’s theses from Canada will give you an idea of the size and format of these papers.
Who would write a thesis?
You generally write a thesis if you’re undertaking a research-oriented master's degree program (as opposed to a practical program, which may require a capstone, internship, exam, etc.).
The thesis is the essential part of a program’s research component, demonstrating the student's ability to critically analyze the literature and complete independent research. The process of writing a thesis involves exploring a specific research question, conducting a comprehensive literature review, collecting and analyzing data, and presenting findings in a structured and cohesive way.
A thesis' specific requirements and expectations differ depending on the academic institution, department, and program.
Components of a thesis
A thesis is typically presented in chapters. How many chapters will vary, but a common structure is:
- Introduction: Presents the research topic, purpose, and objectives, setting the context for the work.
- Literature review: Comprehensive survey of existing scholarly material related to the research topic, highlighting key theories and findings.
- Methodology: Describes the methods, procedures, and tools used in doing the research.
- Research: The actual performing of the study, collecting, and analyzing data relevant to the research question.
- Findings and conclusions: Gives the results obtained and explains their significance in relation to the research question.
- Limitations and future research: Outlines the study’s shortcomings and suggests potential areas for future investigation.
Within that structure, and in addition to those parts, a thesis may also include:
- Cover page: Contains the thesis title, author's name, institution, department, date, and other relevant information
- Abstract : A brief summary of the thesis, highlighting the research objectives, methods, key findings, and conclusions.
- Certificates of own work
- Certificate of readiness to be included in the library
- Certificate that the research has not been presented to another university
- Acknowledgments
- Table of contents: List of the main sections, subsections, and corresponding page numbers.
- Index of figures and tables
- References: A comprehensive list of all the sources cited in the thesis, following a specific citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
- Appendices (optional): Additional materials include:
- Abbreviations and/or acronyms used
- Questionnaire or interview schedule/s (if used)
- Data acquired in the form of transcripts or numeric tables
- Research protocol
- Ethics protocol
What’s a dissertation?
This is also viewed from a North American perspective, where a dissertation is usually the main research work toward completing a research-based doctoral program.
A dissertation is a comprehensive and in-depth research project completed as part of the requirements for a doctoral degree. It’s a substantial piece of original work that contributes new knowledge to a specific field of study. Naturally, when it’s completed as the major requirement for earning a PhD, it’s longer, more detailed, and the expectations are higher.
Dissertations themselves can add to the literature in the field. For this reason, some students choose to publish them and have them indexed. The research and the data acquired while working on a dissertation can potentially lead to more publications and help define the researcher’s growing area of expertise.
See this and this (PDFs) top-ranking dissertation on ProQuest for good examples.
Who would write a dissertation?
Completion and defense of a dissertation is a standard requirement for doctoral students to earn a PhD or another doctorate such as an EdD or DM. But some specialized degrees, such as a PsyD (Doctor of Psychology), JD (Juris Doctor) or DPT (Doctor of Physical Therapy) may have practice-based requirements in place of a research project, as these courses of study are geared more toward practical application.
Components of a dissertation
A dissertation’s components are generally the same as those of a thesis. You can look at the list above for a thesis to see what typically goes into a dissertation. But, if compared with a master’s thesis, most aspects are longer and more rigorous.
The word count requirements for theses can vary significantly, but doctoral dissertations often range 40,000–80,000 words or, per Harvard , 100–300 pages.
Differences between a thesis and a dissertation
As already touched on, the key differences are in where the two documents are used, length, and rigor. There are also regional differences.
A thesis typically demonstrates a master’s degree program student's grasp and presentation of a specific subject in their field of study. It normally involves a literature review, data analysis, and original research, but it is usually shorter and less comprehensive than a dissertation. The standards for rigor and novelty may also be lower.
A dissertation requires more extensive research, original contributions to the field, and a deeper exploration of the research topic. A dissertation is typically the output associated with a doctoral degree program.
The main differences in structure between a thesis and a dissertation are in the scope and complexity.
The word count requirement for theses and dissertations can vary depending on the institution and program.
A thesis is usually 20,000–40,000 words. However, there have been cases of mathematics dissertations that were only a few pages long!
Doctoral dissertations may range 60,000 to upward of 100,000 words, and exceed 100 pages. Many universities, however, seek around 80,000 words.
Oversight and process
A thesis may simply be submitted to the student's instructor, though rigorous thesis programs require a committee and defense. A dissertation will nearly always require the student to choose a chair, a committee, and then go through a more rigorous defense and revision (if necessary).
- Committee: Master's thesis committees usually have fewer members (typically 2–3) than doctoral dissertation committees (often 4–5, or even more).
- Guidance: Master's students often receive more detailed direction from advisers than doctoral students, who are expected to work more independently.
- Review: Dissertation reviews are typically more rigorous, often involving external reviewers, while thesis reviews are usually internal.
- Defense: A dissertation defense is generally more intense and formal, as it often involves a presentation to the wider academic community, while a thesis defense might be more confined and informal.
- Revision: The revision process for a doctoral dissertation is typically more extensive, given the larger scope of the project and higher stakes involved, compared with those for a master's thesis.
Regional differences
The terms' use varies among (and even within) countries. Here are some general regional differences:
In the United Kingdom, a thesis is commonly associated with both master's and doctoral degree programs. For example, the University College London refers to a thesis for EngD, MPhil, MD(Res), and PhD degrees. At the University of Nottingham , a dissertation is written for a research master’s degree.
In Australia and New Zealand , “thesis” is generally used to refer to a substantial research project completed for a higher degree, though not limited to a master’s (you’ll find ample references to a “PhD thesis”).
In Latin American countries, the thesis is commonly used to refer to both master's and doctoral research projects.
Closing thoughts
Both theses and dissertations are necessary documents for students in graduate programs. Despite the differences in expectations, and even in definitions of these papers, the student-author must do a diligent and rigorous job to earn their degree.
Here are a few helpful resources if you want to get into greater detail:
- Writing the Winning Thesis or Dissertation: A Step-By-Step Guide
- 100 PhD rules of the game to successfully complete a doctoral dissertation (PDF)
- Theses and Dissertations: A Guide to Writing in Social and Physical Sciences
Perfect the English on your thesis or dissertation
Whether you’re submitting a thesis or a dissertation, if it’s in English, it should:
- Have no grammatical or spelling mistakes
- Use field-appropriate language
- Concisely and clearly communicate your research.
That’s what AJE expert editors will do for you. Within days, you can receive an expert English edit of your work. The editor will be familiar with your field of study and will comprehensively improve both the language quality and the delivery of your message. Look into AJE English Editing .

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
AJE will edit your thesis or dissertation
Choose between our expert academic editing services to prepare your thesis or dissertation.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Published on September 14, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on April 16, 2024.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master’s program or a capstone to a bachelor’s degree.
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation , it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: choosing a relevant topic , crafting a proposal , designing your research , collecting data , developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions , and writing concisely .
Thesis template
You can also download our full thesis template in the format of your choice below. Our template includes a ready-made table of contents , as well as guidance for what each chapter should include. It’s easy to make it your own, and can help you get started.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Thesis vs. thesis statement, how to structure a thesis, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your thesis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about theses.
You may have heard the word thesis as a standalone term or as a component of academic writing called a thesis statement . Keep in mind that these are two very different things.
- A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay , and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay .
- A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to complete. It is generally a degree requirement for Master’s programs, and is also sometimes required to complete a bachelor’s degree in liberal arts colleges.
- In the US, a dissertation is generally written as a final step toward obtaining a PhD.
- In other countries (particularly the UK), a dissertation is generally written at the bachelor’s or master’s level.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The final structure of your thesis depends on a variety of components, such as:
- Your discipline
- Your theoretical approach
Humanities theses are often structured more like a longer-form essay . Just like in an essay, you build an argument to support a central thesis.
In both hard and social sciences, theses typically include an introduction , literature review , methodology section , results section , discussion section , and conclusion section . These are each presented in their own dedicated section or chapter. In some cases, you might want to add an appendix .
Thesis examples
We’ve compiled a short list of thesis examples to help you get started.
- Example thesis #1: “Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807” by Suchait Kahlon.
- Example thesis #2: “’A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man’: UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947″ by Julian Saint Reiman.
The very first page of your thesis contains all necessary identifying information, including:
- Your full title
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date.
Sometimes the title page also includes your student ID, the name of your supervisor, or the university’s logo. Check out your university’s guidelines if you’re not sure.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional. Its main point is to allow you to thank everyone who helped you in your thesis journey, such as supervisors, friends, or family. You can also choose to write a preface , but it’s typically one or the other, not both.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it’s should include brief descriptions of your research objectives , methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis.
Read more about abstracts
A table of contents lists all of your sections, plus their corresponding page numbers and subheadings if you have them. This helps your reader seamlessly navigate your document.
Your table of contents should include all the major parts of your thesis. In particular, don’t forget the the appendices. If you used heading styles, it’s easy to generate an automatic table Microsoft Word.
Read more about tables of contents
While not mandatory, if you used a lot of tables and/or figures, it’s nice to include a list of them to help guide your reader. It’s also easy to generate one of these in Word: just use the “Insert Caption” feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
If you have used a lot of industry- or field-specific abbreviations in your thesis, you should include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations . This way, your readers can easily look up any meanings they aren’t familiar with.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
Relatedly, if you find yourself using a lot of very specialized or field-specific terms that may not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary . Alphabetize the terms you want to include with a brief definition.
Read more about glossaries
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic , sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
In other words, your introduction should clearly and concisely show your reader the “what, why, and how” of your research.
Read more about introductions
A literature review helps you gain a robust understanding of any extant academic work on your topic, encompassing:
- Selecting relevant sources
- Determining the credibility of your sources
- Critically evaluating each of your sources
- Drawing connections between sources, including any themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing work. Rather, your literature review should ultimately lead to a clear justification for your own research, perhaps via:
- Addressing a gap in the literature
- Building on existing knowledge to draw new conclusions
- Exploring a new theoretical or methodological approach
- Introducing a new solution to an unresolved problem
- Definitively advocating for one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework, but these are not the same thing. A theoretical framework defines and analyzes the concepts and theories that your research hinges on.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- Your overall approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative )
- Your research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment
- Any tools or materials you used (e.g., computer software)
- The data analysis methods you chose (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- A strong, but not defensive justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. These two sections work in tandem, but shouldn’t repeat each other. While your results section can include hypotheses or themes, don’t include any speculation or new arguments here.
Your results section should:
- State each (relevant) result with any (relevant) descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Explain how each result relates to the research question
- Determine whether the hypothesis was supported
Additional data (like raw numbers or interview transcripts ) can be included as an appendix . You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results.
Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is where you can interpret your results in detail. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review.
For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your thesis conclusion should concisely answer your main research question. It should leave your reader with an ultra-clear understanding of your central argument, and emphasize what your research specifically has contributed to your field.
Why does your research matter? What recommendations for future research do you have? Lastly, wrap up your work with any concluding remarks.
Read more about conclusions
In order to avoid plagiarism , don’t forget to include a full reference list at the end of your thesis, citing the sources that you used. Choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your thesis, taking note of the formatting requirements of each style.
Which style you choose is often set by your department or your field, but common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
In order to stay clear and concise, your thesis should include the most essential information needed to answer your research question. However, chances are you have many contributing documents, like interview transcripts or survey questions . These can be added as appendices , to save space in the main body.
Read more about appendices
Once you’re done writing, the next part of your editing process begins. Leave plenty of time for proofreading and editing prior to submission. Nothing looks worse than grammar mistakes or sloppy spelling errors!
Consider using a professional thesis editing service or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect.
Once you’ve submitted your final product, it’s common practice to have a thesis defense, an oral component of your finished work. This is scheduled by your advisor or committee, and usually entails a presentation and Q&A session.
After your defense , your committee will meet to determine if you deserve any departmental honors or accolades. However, keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality. If there are any serious issues with your work, these should be resolved with your advisor way before a defense.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5–7% of your overall word count.
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation , you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimizing confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
A thesis is typically written by students finishing up a bachelor’s or Master’s degree. Some educational institutions, particularly in the liberal arts, have mandatory theses, but they are often not mandatory to graduate from bachelor’s degrees. It is more common for a thesis to be a graduation requirement from a Master’s degree.
Even if not mandatory, you may want to consider writing a thesis if you:
- Plan to attend graduate school soon
- Have a particular topic you’d like to study more in-depth
- Are considering a career in research
- Would like a capstone experience to tie up your academic experience
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2024, April 16). What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved October 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/thesis/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, what is your plagiarism score.

Dissertation vs Thesis vs Capstone Project What’s the difference?
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2020
At Grad Coach, we receive questions about dissertation and thesis writing on a daily basis – everything from how to find a good research topic to which research methods to use and how to analyse the data.
One of the most common questions we receive is “what’s the difference between a dissertation and thesis?” . If you look around online, you’ll find a lot of confusing and often contrasting answers. In this post we’ll clear it up, once and for all…
Need a helping hand?
Dissertation vs Thesis: Showdown Time
Before comparing dissertations to theses, it’s useful to first understand what both of these are and what they have in common .
Dissertations and theses are both formal academic research projects . In other words, they’re academic projects that involve you undertaking research in a structured, systematic way. The research process typically involves the following steps :
- Asking a well-articulated and meaningful research question (or questions).
- Assessing what other researchers have said in relation to that question (this is usually called a literature review – you can learn more about that up here).
- Undertaking your own research using a clearly justified methodology – this often involves some sort of fieldwork such as interviews or surveys – and lastly,
- Deriving an answer to your research question based on your analysis.
In other words, theses and dissertations are both formal, structured research projects that involve using a clearly articulated methodology to draw out insights and answers to your research questions . So, in this respect, they are, for the most part, the same thing.
But, how are they different then?
Well, the key difference between a dissertation and a thesis is, for the most part, the level of study – in other words, undergrad, master or PhD. By extension, this also means that the complexity and rigorousness of the research differs between dissertations and theses.

So, which is which?
This is where it gets a bit confusing. The meaning of dissertation or thesis varies depending on the country or region of study. For example, in the UK, a dissertation is generally a research project that’s completed at the end of a Masters-level degree, whereas a thesis is completed for a Doctoral-level degree.
Conversely, the terminology is flipped around in the US (and some other countries). In other words, a thesis is completed for a Masters-level degree, while a dissertation is completed for PhD (or any other doctoral-level degree).
Simply put, a dissertation and a thesis are essentially the same thing, but at different levels of study . The exact terminology varies from country to country, and sometimes it even varies between universities in the same country. Some universities will also refer to this type of project as a capstone project . In addition, some universities will also require an oral exam or viva voce , especially for doctoral-level projects.
Given that there are more than 25,000 universities scattered across the globe, all of this terminological complexity can cause some confusion. To be safe, make sure that you thoroughly read the brief provided by your university for your dissertation or thesis, and if possible, visit the university library to have a look at past students’ projects . This will help you get a feel for your institution’s norms and spot any nuances in terms of their specific requirements so that you can give them exactly what they want.
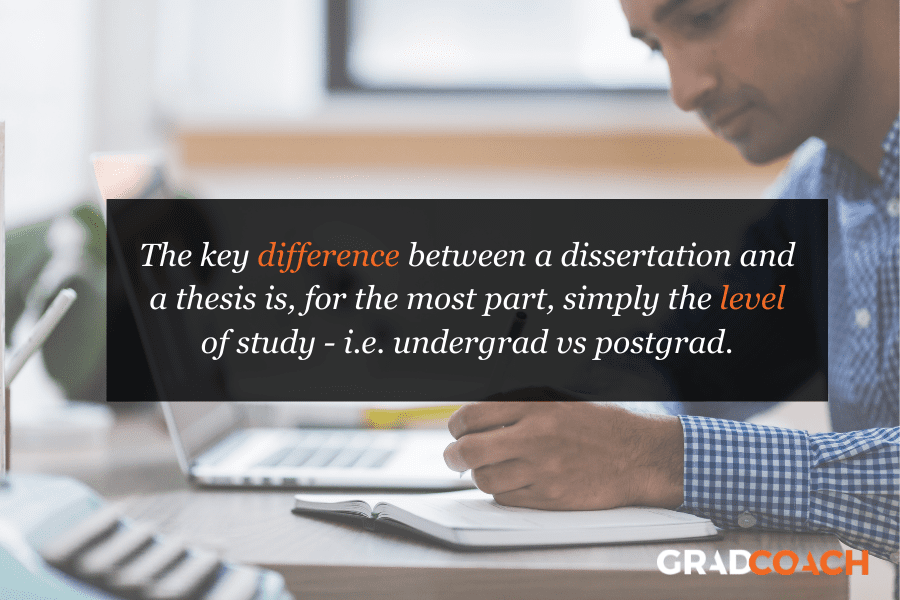
Let’s recap
Dissertations and theses are both formal academic research projects . The main difference is the level of study – undergrad, Masters or PhD. Terminology tends to vary from country to country, and even within countries.
Need help with your research project?
Get in touch with a friendly Grad Coach to discuss how we can help you fast-track your dissertation or thesis today. Book a free, no-obligation consultation here.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
GRADCOACH youtube and materials are awesome for new researchers. Keep posting such materials so that many new researchers can benefit form them.
Am happy to be part of the family hope you will help me with more information through my email
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is Research Methodology? Simple Definition (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] you’ve started working on your first piece of formal research – be it a dissertation, thesis or research project…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Thesis Vs. Dissertation — Know the difference and similarities!
The academic world is filled with many different types of writing assignments, each with its own unique set of requirements and expectations. One common source of confusion for students is the distinction between a thesis and a dissertation. Both are long-form academic works, but there are several key differences between the two that are important to understand.
In Shakespeare’s day, a candidate for a master’s degree would write a thesis, an original paper in which he maintained a certain proposition. Whereas, completion of a doctoral program required submission and defense of a dissertation. He would read his thesis to his committee, after which he sat in silence while two faculty members gave point-by-point refutations of everything the candidate said.
The focus here was on the student’s ideas and his ability to arrange and express them clearly. If a student wished to advance further in academia he could pursue a dissertation. This was more of a literature review . He would read widely in a particular area and write up his findings, discussing the various authorities and their opinions. The point was to demonstrate that he was well-versed in the literature of the field. While the confusion between the two terms is understandable, we shall tackle the dissertation vs. thesis topic in this article and provide unambiguous insights on it.
Table of Contents
What Is a Thesis?
A thesis is a critically written scholarly piece of research work. Typically, it is submitted by students graduating from a master’s program. The purpose of a thesis is to allow students to showcase their knowledge and expertise within the subject matter they have been studying as part of the program.
What Is a Dissertation?
A dissertation is a comparatively lengthier piece of scholarly writing that accounts for your research work throughout the doctoral program. A researcher earns the Ph.D. after submitting and defending his/her dissertation. It includes all information about the original research or expanded research on a new or existing topic conducted by the Ph.D. candidate.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Differences
- The primary difference between a thesis and a dissertation is the time when they are completed. As mentioned earlier, a thesis is presented at the culmination of a master’s program, whereas, a dissertation is presented to earn a Ph.D.
- A thesis is a compilation of research ensuring that the researcher is well-informed and has knowledge about the research topic learned in the study program. On the other hand, a dissertation provides an opportunity for the researcher to contribute new theories and information to the existing literature in the research field.
- A thesis is a presentation of learned and existing information, while the purpose of a dissertation is to develop a unique concept and defend it based on theoretical and practical results.
- A master’s thesis is approximately 100 pages in length. However, a Ph.D. dissertation should be much longer than a thesis and must include background and research information. A dissertation must include your research proposal, grant proposal, literature review , ideation of research topic, and every other minute detail about your research. Ideally, a dissertation inclusive of all details mentioned above should be three times the length of a master’s thesis.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Similarities
- Both a thesis and a dissertation are considered final projects and are required to graduate from respective programs.
- The thesis and dissertation both require a deep and accurate understanding of the research problem.
- Both forms of scholarly written pieces must address specific research questions.
- Academic writing skills are imperative for a thesis as well as a dissertation.
- Ethical practices must be followed while collating and documenting research data.
- Plagiarism is not accepted in either.
- Both require analytical skills to support the findings.
- It is essential that both undergo intense dissertation/ thesis editing and critical proofreading before final submission.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Europe
In Europe, the original distinction between a thesis and a dissertation has been largely retained. A doctoral thesis is a focused piece of original research that is performed to obtain a Ph.D. A dissertation is part of a broader post-graduate research project.

However, the thesis has evolved since original research nowadays requires plenty of background research . So, a thesis will contain extensive citations and references to earlier work, although the focus remains on the original work that comes out of it.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: USA
In the United States, the definition of a thesis is almost the opposite of that in Europe. Because a thesis is shorter than a dissertation it gradually came to mean a preliminary degree on the way to a doctorate. A thesis is now performed to earn a Master’s degree. In scientific fields, a master’s candidate takes advanced coursework and gains hands-on experience in a research project but does not direct the project to the same extent that he would in a doctoral program. In a master’s project, the student’s ideas are welcomed and expected but the focus is on obtaining technical expertise, not doing original research. Engineering students commonly obtain Master’s degrees and seldom go on to get PhDs. In other fields such as Chemistry, the opposite is true, with a Master’s degree no longer being required as the first step for a doctorate. Almost everyone I know who received a Master’s degree in Chemistry got one because they dropped out of graduate school and wrote their truncated research as a Master’s project.
In a Nutshell
Needless to say, the dissertation vs. thesis facts are real. Therefore, using one term instead of another is not acceptable as an academic. One must remember the purpose of each and use them accordingly. However, one is not undermined by the other. Whether you are writing a thesis or a dissertation, both must be done with the same seriousness. Both require critical technical and soft skills. Improving your time management and academic writing skills plays a major role in acing both forms of scholarly writing.
How do you decipher dissertation vs. thesis? Should the interchanged usage of these terms be acceptable? How is your approach to writing a thesis different from that of a dissertation? What are the other differences associated with the thesis and dissertation? Let us know in the comments section below!
Frequently Asked Questions
"Dissertation" and "thesis" are used interchangeably but differ in: Academic Level: Thesis for master's, dissertation for doctoral degrees (US). Scope and Depth: Thesis shorter, demonstrates mastery; dissertation extensive, original research. Originality: Thesis may involve original analysis; dissertation presents significant new insights. Time and Effort: Dissertations require more resources and time than theses.
The length of a dissertation varies depending on factors like academic discipline, research topic, institution, and country. Generally, dissertations are longer than theses, ranging from 10,000 to over 100,000 words. However, word count alone does not reflect the quality or depth of the research. Guidelines from the academic institution should be consulted for specific requirements.
The length of a thesis varies depending on factors like academic discipline, research topic, institution, and country. Generally, the word count ranges from around 10,000 to 50,000 words. Specific guidelines from the academic institution should be consulted for precise requirements.
Has helped develop my writing skills through science-based study.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Industry News
- Publishing Research
- Promoting Research
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Open Access Week 2024
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What factors would influence the future of open access (OA) publishing?

Thesis vs. Dissertation: Understanding the Differences

A thesis and a dissertation are often used interchangeably, causing confusion among students and academics alike. While they share some similarities, they are distinct in purpose, scope, and requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for graduate students embarking on their academic journey. In this article, we delve into the world of thesis and dissertation, shedding light on what sets them apart and helping you navigate these essential components of advanced academic research.
Thesis: The Master's Magnum Opus
In the realm of academia, a thesis is often referred to as the master's magnum opus, representing the pinnacle of a student's academic journey at the master's level. It is a significant undertaking that requires dedication, research acumen, and a commitment to scholarly excellence. Here, we explore the key characteristics and elements that define a thesis:
Academic Level: A thesis is a hallmark of master's degree programs. It serves as the culmination of a student's graduate studies, demonstrating their ability to engage critically with their field of study and contribute meaningfully to it. Unlike undergraduate projects, a thesis delves deeper into the subject matter and requires a higher level of analysis and synthesis.
Purpose: The primary purpose of a thesis is to contribute to the existing body of knowledge within a specific field or discipline. It goes beyond mere regurgitation of facts and concepts; it involves original research or a novel approach to addressing a research question or hypothesis. In essence, a thesis is a scholarly endeavor that aims to add value to the academic conversation.
Scope: Theses typically have a narrower scope compared to their doctoral counterparts, dissertations. While they explore complex topics, they often focus on a specific aspect or dimension within a broader field. This focused approach allows students to delve deeply into their chosen subject matter and demonstrate expertise in that area.
Length: Theses vary in length depending on the institution, program, and field of study. However, they are generally shorter than dissertations. A typical master's thesis can range from 50 to 100 pages. This concise format necessitates precision and clarity in presenting research findings and arguments.
Committee Evaluation: A key aspect of the thesis process is the evaluation by a committee of professors or advisors. This committee plays a pivotal role in guiding the student's research, offering feedback, and assessing the final product. Their expertise ensures that the thesis meets academic standards and contributes meaningfully to the field.
Research and Methodology: Research is at the heart of any thesis. Students engage in systematic inquiry, which may involve data collection, experimentation, surveys, literature analysis, or a combination of research methods. The methodology chosen should align with the research question and contribute to the overall quality of the thesis.
Scholarly Writing: A thesis demands scholarly writing of the highest caliber. Students are expected to adhere to academic writing conventions, including proper citation, referencing, and adherence to a specific style guide (e.g., APA, MLA). Clarity, coherence, and a formal tone are essential elements of thesis writing.
Originality: Perhaps the most crucial aspect of a thesis is its contribution to the field's body of knowledge. It must offer fresh insights, perspectives, or solutions to existing challenges. Originality is the hallmark of a well-executed thesis, distinguishing it from undergraduate assignments.
Receive Free Grammar and Publishing Tips via Email
Dissertation: the doctoral opus.
In the realm of academia, a dissertation is the pinnacle of scholarly achievement within the context of doctoral programs. It represents the culmination of extensive academic preparation and research and is often referred to as the doctoral opus. Here, we explore the defining characteristics and elements that set a dissertation apart in the academic world:
Academic Level: A dissertation is synonymous with doctoral programs, such as a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) or other terminal degrees. It marks the highest level of academic achievement and signifies a student's readiness to make a significant contribution to their field.
Purpose: The primary purpose of a dissertation is to make a substantial and original contribution to the existing body of knowledge within a specific field or discipline. Unlike a thesis, which often focuses on a more specific aspect, a dissertation tackles complex research questions that have broader implications for the field.
Scope: Dissertations are renowned for their expansive scope. They typically explore multifaceted research questions that encompass multiple variables, perspectives, and dimensions. Doctoral candidates are expected to demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of their field and engage in in-depth analysis.
Length: Dissertations are considerably longer than theses. The length can vary depending on the field of study and the nature of the research, but they often exceed 100 pages and can extend to several hundred pages. This extended format allows for a thorough exploration of the research topic.
Committee Evaluation: A dissertation is rigorously evaluated by a committee of experts in the field. This committee plays a crucial role in guiding the research, offering feedback, and ultimately assessing the quality and significance of the dissertation. Their expertise ensures that the dissertation meets the highest academic standards.
Research and Methodology: Research in a dissertation is not only extensive but also often involves original data collection, experimentation, surveys, case studies, or longitudinal studies. The choice of research methodology is critical and should align with the research questions and objectives.
Scholarly Writing: As with theses, scholarly writing is paramount in dissertations. Doctoral candidates are expected to adhere to the most stringent academic writing conventions. This includes precise citation and referencing, adherence to a specific style guide, and the use of formal and rigorous language.
Originality: The hallmark of a successful dissertation is its originality. It must offer new insights, perspectives, or solutions to complex problems within the field. Doctoral candidates are expected to demonstrate their ability to contribute significantly to the advancement of knowledge.
Defending the Dissertation: A distinctive feature of the dissertation process is the formal defense. Candidates present their research findings and defend their methodology, conclusions, and contributions before their committee and often a public audience. This oral defense is a culmination of the rigorous research journey.
Navigating the Process
Embarking on the journey of crafting a thesis or dissertation is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning, dedication, and resilience. Navigating this process effectively is key to producing a scholarly work that reflects your expertise and contributes meaningfully to your field. Here, we provide an overview of the essential steps and strategies to guide you through this academic odyssey.
1. Define Your Research Question: The first and foremost step in both thesis and dissertation projects is defining a clear and research-worthy question or problem. Your question should be specific, relevant, and capable of generating new insights or solutions. Take the time to conduct a thorough literature review to understand the existing body of knowledge in your chosen area.
2. Assemble Your Committee: Your academic committee will play a vital role in guiding your research and evaluating your final work. Choose committee members who are experts in your field and who can provide valuable insights and feedback throughout the process. Effective communication with your committee is essential.
3. Develop a Research Proposal: Crafting a well-structured research proposal is crucial. It should outline the scope of your project, research methodology, timeline, and expected outcomes. Your proposal will serve as a roadmap for your research journey and will require approval from your committee.
4. Research and Data Collection: The heart of your thesis or dissertation lies in the research phase. Depending on your field and research question, this may involve conducting experiments, surveys, interviews, or extensive data analysis. Ensure that your data collection methods align with your research objectives.
5. Writing and Organization: Writing your thesis or dissertation is an ongoing process that requires discipline and organization. Create a detailed outline or structure to guide your writing. Pay careful attention to proper citation and referencing to avoid plagiarism. Seek feedback from your committee at various stages of writing.
6. Revision and Proofreading: Revising and proofreading are integral steps in producing a polished document. Review your work for clarity, coherence, and logical flow. Check for grammatical errors and ensure that your writing adheres to academic conventions.
7. Formal Defense: Doctoral candidates will typically undergo a formal defense of their work. This involves presenting your research findings, methodology, and conclusions to your committee and often a public audience. Prepare thoroughly for this oral defense, as it is a culmination of your research journey.
8. Submission and Publication: Once your thesis or dissertation is complete and approved by your committee, it's time to submit it to your institution's academic office. Depending on your field and aspirations, you may also consider publishing your work in academic journals to contribute to your field's body of knowledge.
9. Celebrate Your Achievement: Completing a thesis or dissertation is a monumental achievement. Take the time to celebrate your hard work and dedication. Share your research findings with peers and colleagues, and consider how your work can continue to impact your field.
10. Continuous Learning: The process of research and scholarship is ongoing. Continue to engage with your field, attend conferences, and seek opportunities for further research and collaboration. Your thesis or dissertation is a significant step in your academic journey, but it is not the end; it is a foundation upon which you can build your future contributions to your field.
Navigating the thesis or dissertation process is a transformative experience that equips you with valuable research, writing, and critical-thinking skills. Approach it with curiosity, dedication, and a commitment to advancing knowledge in your field, and you will emerge from this academic endeavor not only with a well-crafted document but also as a more accomplished scholar.
In the realm of academia, the terms "thesis" and "dissertation" represent distinct milestones in a student's educational journey. Understanding the differences between these two research projects is essential for selecting the appropriate path in your graduate studies. Whether you're aiming for a master's or doctoral degree, both theses and dissertations are opportunities to engage in meaningful research, contribute to your field, and demonstrate your expertise as a scholar.
Connect With Us
Dissertation Editing and Proofreading Services Discount (New for 2018)
May 3, 2017.
For March through May 2018 ONLY, our professional dissertation editing se...
Thesis Editing and Proofreading Services Discount (New for 2018)
For March through May 2018 ONLY, our thesis editing service is discounted...
Neurology includes Falcon Scientific Editing in Professional Editing Help List
March 14, 2017.
Neurology Journal now includes Falcon Scientific Editing in its Professio...

Useful Links
Academic Editing | Thesis Editing | Editing Certificate | Resources
- How it works
"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP23720

Published by Nicolas at January 17th, 2024 , Revised On January 23, 2024
Dissertation Vs Thesis: How Are They Different
Dissertation vs thesis! What are you writing?
Table of Contents
Many graduate students from universities in Canada often get confused and mix both terms. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they carry distinct meanings and purposes in academia. Read this blog to fully understand the difference between a thesis and a dissertation.
What Is A Dissertation
A dissertation is a substantial piece of academic writing typically required to complete a doctoral degree (such as a Ph.D.). It represents an original and significant contribution to the field of study and is usually the culmination of several years of research and study.
What Is A Thesis
A thesis is a scholarly piece of writing, usually at the master’s or undergraduate level, that presents an original research question, methodology, and findings. It represents the culmination of a student’s academic work and demonstrates their ability to contribute to the field of study.
The Evolution Of Dissertation Vs Thesis
The history of the thesis and dissertation dates back several centuries, and the evolution of these academic documents reflects changes in scholarly practices, educational systems, and the expectations of advanced degree programs.
Medieval Origins
The concept of a scholarly thesis has roots in medieval universities. In the 12th and 13th centuries, institutions like the University of Paris introduced the practice of disputations, where students defended their theses in a public forum. These early theses were often theological or philosophical in nature.
Renaissance And Early Modern Period
During the Renaissance, the practice of defending theses continued to evolve. The 16th and 17th centuries saw an increasing emphasis on empirical observation and scientific inquiry. The thesis became more diverse, covering topics in natural philosophy, mathematics, and other emerging disciplines.
18th And 19th Centuries
The 18th century marked the formalization of the thesis as a requirement for academic degrees. Universities started to mandate the submission of a written document along with the oral defence. This practice became more standardized in the 19th century as universities across Europe and North America adopted similar academic norms.
Evolution Of The Dissertation
The term “dissertation” has its roots in the Latin word “dissertatio,” meaning “discussion.” Dissertations, as we understand them today, emerged in the 19th century, primarily in German universities. Doctoral candidates were required to produce substantial research demonstrating their ability to contribute original knowledge to their field.
20th Century
The 20th century saw a global expansion of higher education and an increase in the number of doctoral programs. The thesis and dissertation became integral components of graduate education worldwide. The structure, format (eg, APA or MLA ), and expectations for these documents varied among disciplines and institutions.
Electronic Theses And Dissertations (ETDs)
With the advent of digital technology in the late 20th century, there was a shift toward electronic submission of theses and dissertations. This made research papers more accessible and facilitated the dissemination of knowledge. Many universities now require the submission of ETDs.
Contemporary Trends In Dissertation Vs Thesis
In the 21st century, the thesis and dissertation continue to evolve. Educational institutions are adapting to new forms of scholarship , interdisciplinary research, and varied modes of dissemination. The focus is often on producing high-quality, original research that contributes significantly to the academic community.
What Is The Difference Between A Dissertation And A Thesis
|
|
|
|
|
| Master's Program | Doctoral Program |
|
| Typically 50-100 pages | Often exceeds 100 pages, can be much longer |
|
| More focused on a specific aspect of a broader topic | Broader in scope, aims for a significant and original contribution to the field |
|
| Demonstrates mastery of subject matter and ability to conduct independent research within a defined scope | Makes an original and substantial contribution to the field, addressing gaps in existing literature |
|
| Often required for completion of a master's degree | Essential for the completion of a doctoral degree |
|
| In-depth research, but may not be as exhaustive as a dissertation | Extensive and exhaustive research, involving a comprehensive exploration of the chosen topic |
|
| Master's programs in various disciplines | Doctoral programs, especially in research-focused disciplines |
Thesis Vs Dissertation: Length And Depth
One of the key differences between a thesis vs dissertation lies in their length and depth of research:
Theses are typically shorter in length, ranging from 50 to 100 pages, depending on the institution and program requirements. The research conducted for a thesis is expected to contribute to the existing literature but may not need to be as exhaustive as that of a dissertation.
Dissertation
Dissertations, being the pinnacle of doctoral research, are substantially longer, often exceeding 100 pages and sometimes reaching several hundred pages. Doctoral candidates are expected to delve deeply into their chosen topic, conducting extensive research and offering a unique contribution to the academic community.
Dissertation Vs Thesis: Scope And Purpose
Another significant distinction between a dissertation vs thesis is the scope and purpose of the research:
The primary goal of a thesis is to demonstrate a student’s understanding of the subject and their ability to conduct independent research within a defined scope. A thesis is often more focused and may be an exploration or analysis of a specific aspect of a broader topic. For example, a finance thesis could be about any topic within the subject.
Dissertations, being doctoral-level projects, have a broader scope. Doctoral candidates are expected to make an original and substantial contribution to the field, advancing existing knowledge and addressing gaps in the current literature. Dissertations often involve more extensive data collection, analysis, and synthesis of information.
The research paper we write have:
- Precision and Clarity
- Zero Plagiarism
- High-level Encryption
- Authentic Sources

Dissertation Vs Thesis: The Similarities
While there are distinct differences between a thesis vs dissertation, they also share several similarities, reflecting their common purpose within academic research papers . Here are some key similarities between a dissertation and a thesis.
Research Component
Both dissertations and theses involve original research and scholarly inquiry. Students are expected to engage in a systematic investigation of a chosen topic, demonstrate a deep understanding of existing literature, and contribute new knowledge or insights to their field.
Academic Rigour
Both documents adhere to high standards of academic rigour and integrity. They require meticulous attention to detail, adherence to citation and referencing styles, and a commitment to intellectual honesty.
Formal Structure
Dissertations and theses typically follow a formal structure, including elements such as a thesis statement , an introduction, a literature review, methodology, results, a discussion, and a conclusion. This structured format ensures a comprehensive presentation of the research.
Faculty Guidance
In both cases, students work closely with faculty advisors or mentors throughout the research process. Advisors guide research design, literature review, data analysis, and other aspects of the project.
Oral Defense
A commonality between dissertations and theses is the requirement for an oral defence. In many academic institutions, students must defend their research findings before a committee of faculty members. This defence allows students to articulate their research methods, results, and conclusions, while also responding to questions and critiques.
Degree Requirement
Both a thesis and a dissertation serve as a crucial component for the completion of an academic degree. Thesis is typically associated with master’s programs, while dissertations are a requirement for doctoral degrees. In both cases, successfully completing the research project is essential for obtaining the respective degrees.
Contribution To Knowledge
Whether a thesis or a dissertation, the primary goal is to contribute to the existing body of knowledge in a particular field. Both documents aim to advance understanding, address gaps in the literature, and offer meaningful insights that can inform future research.
Literature Review
A comprehensive literature review is a common element in both dissertations and theses. This section provides context for the research by summarizing and critiquing relevant scholarly works, helping establish the rationale and significance of the study.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a dissertation and a thesis.
A thesis is a shorter, master’s-level research document demonstrating mastery of a subject. A dissertation, typically for a doctoral degree, is longer and requires a more extensive, original contribution to the field.
What is the difference between a master thesis and dissertation?
A master’s thesis is a shorter research document showcasing mastery of a specific subject. A dissertation, associated with a doctoral degree, is more extensive, requiring a substantial, original contribution to the field.
Are thesis and dissertation the same thing?
No, a thesis and a dissertation are not the same. A thesis is a research document associated with a master’s degree, demonstrating mastery of a subject. A dissertation is a more extensive research document required for a doctoral degree, emphasizing original contribution to the field.
Where to find thesis and dissertations?
There are several online sources that can help you in finding the perfect thesis and dissertation for your research. ResearchProspect Canada is one of the leading and trustworthy brands, helping students achieve academic excellence.
What is electronic thesis and dissertation?
An Electronic Thesis and Dissertation (ETD) is a digital version of a student’s thesis or dissertation. It is submitted and stored electronically, allowing easy access, distribution, and archiving, reflecting the shift towards digital formats in academia.
How to cite theses and dissertation?
To cite theses and dissertations, follow the citation style specified by your academic institution or the preferred style guide (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Include author, title, publication year, institution, and retrieval information for online sources, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
How to cite pro quest dissertation and theses APA?
To cite a ProQuest dissertation or thesis in APA format, use the following template: Author, A. A. (Year). Title of dissertation/thesis (Publication No.). ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global. Include the ProQuest publication number for online sources.
You May Also Like
To cite a TED Talk in APA style, include speaker’s name, publication year, talk title, “TED Conferences,” and URL for clarity and accuracy.
Explore the essential elements in choosing effective control variables for robust and valid research outcomes.
Learn how to write a finance thesis and more than 30 finance thesis topics to choose from. Start your research with the help of our guide.
Ready to place an order?
USEFUL LINKS
Learning resources.

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
Masters Thesis vs. PhD Dissertation: Key Differences
Whether you are a graduate student just starting out in academia or a professor advising a student, making the distinction between a dissertation and a thesis is critically important to writing a strong dissertation and becoming a stronger writer. Unfortunately, the difference remains unclear since the terms are used interchangeably by graduate students, doctoral researchers, academic publishers & universities.
If you’re not sure whether you’re writing a thesis or a dissertation, this article will help you understand the differences between the two whether you’re a PhD or master’s degree student.
Main Differences Between a Dissertation and a Thesis
While theses and dissertations share many similarities (they are both advanced graduate research papers), they actually refer to two different types of academic writing, and their differences include important concepts such as scope, purpose, length, and research requirements.
Most importantly, the difference between a thesis and a dissertation depends on the level of education. Far beyond being a simple essay, a thesis is for graduate students pursuing a master’s degree while a dissertation is written by doctoral students, also referred to as PhD candidates.
There are a few key differences between a thesis versus a dissertation.
The biggest difference between a thesis and a dissertation is that a thesis makes arguments based on existing research. Meanwhile, a dissertation often requires the PhD candidate to conduct research and then perform an analysis.
More specifically, a thesis often takes the form of a literature review , which is a compilation of research knowledge in a particular field of study that proves one is competent in that subject. On the other hand, a dissertation is a more specific type of research paper written by those working toward a specific doctorate degree that contributes knowledge, theory, or methods to a field of study.
What is a master’s thesis?
A master’s thesis is an academic research paper that requires a greater degree of research than an undergraduate thesis or term paper. It is marked by a higher standard of writing, and students are expected to demonstrate competence, literacy, and mastery of a subject. It usually takes two or three years to complete. Finally, a master’s degree thesis is usually written in order to obtain a research degree and is not intended to be published separately.
What is a PhD dissertation?
A PhD dissertation is a substantial piece of independent research that is required of all students who are pursuing a doctorate degree. It is a piece of original work that has not been published elsewhere and, most importantly, makes a new contribution to the field. This contribution may be a new way of thinking about an existing topic or even a novel theory. The research performed for a dissertation is usually conducted over a period of several years to half a decade.
Features of a Master’s Thesis vs PhD Dissertation
| -Original and novel testing of ideas and a hypothesis -An independent work or experimentation -Demonstrated competence and understanding of industry techniques as well as their limitations -Thorough knowledge of the literature -Ability to use synthesize and criticize the literature for the research topic -Ability to present the work in an academic capacity (conference, seminar, recitation, defense, etc.) | |
| -All of the above characteristics -A novel contribution to the scientific literature not published previously -Original research produced directly by the author (graduate student) -A clear research question/hypothesis clearly answered (or falsified) -Advances in methods, observations, interpretation, etc. |
Content and Structural Differences
So how is dissertation writing different from thesis writing?
Now that you know the definitions of a dissertation and thesis, let’s dive into some clear ways in which they differ in structure and other main characteristics.
How long is a thesis vs dissertation?
Length is the most obvious factor in differentiating between writing a thesis or dissertation.
Generally, a doctoral dissertation has greater breadth, depth, and intention than a master’s thesis since it is based on original research. While the standard length of a master’s thesis is around 100 pages , a doctoral dissertation can be upwards of 400-500 pages.
While most students can finish their PhD dissertation or thesis in as little as 1-2 years, it can take as long as 7 years depending on the school, program, and dissertation topic. As doctoral programs have their own formatting requirements, check with your school or university to find out what you need for your own dissertation or thesis. Most dissertations are organized into chapters, but the number of chapters varies as well.
Differences in research methods
A thesis and dissertation are both graduate-level research reports. This means they require students to investigate and report on a specific topic. But what is the difference in the scale of research between a master’s versus doctoral degree? The answer comes down to how much and what type of data you collect .
Data sources for a thesis vs dissertation
A master’s thesis is limited to secondary or reported knowledge . This knowledge has already been published, analyzed, and scrutinized in the literature. A thesis does not typically offer anything new in that regard. Your purpose is usually to write a comprehensive literature review on a novel or underreported topic using already-reported data.
| -Academic journal articles -Scholarly books and publications -Academic periodicals and magazines -Survey reportsIndustry and corporate reports -Government data (census, environmental, etc.) -Published statistics -Prior studies |
On the other hand, a doctoral dissertation reports on novel data and is published so it can be scrutinized by others. It culminates in your dissertation defense.
| -All of the above sources -Laboratory experiments and investigations (e.g. basic sciences) -First-hand surveys, interviews, and focus groups (e.g. psychology, social sciences) -Unpublished data (i.e. verified data from experiments but too narrow to publish) -Abstracts, reviews, and conference presentations by other researchers |
The above lists clearly show that a PhD researcher and dissertation writer must have specific hands-on experience about not only the result of others’ research but also how the researchers obtained the data. A dissertation must venture into criticism of how other studies performed their experiments, whereas a master’s student will only report on and evaluate the results.
Differences in research scope
As mentioned above, a thesis is more of a literature review written to demonstrate competence and mastery of a field of study. In short, you are a reliable “reporter” of information related to that subject. A thesis shows that you know the technical jargon, understand the subject, are familiar with industry tools, and can translate that information to a general audience. This is why a master’s degree is sufficient and often preferred for industry jobs.
In contrast, a doctoral dissertation goes beyond simply using the building blocks of your subject and actually creates new tools, knowledge, and theories to advance the subject as a whole. If a master’s degree holder is like a seasoned Rolling Stone journalist, then a doctorate is the band/musician who actually makes the music.

So should you pursue a thesis or a dissertation?
The benefits of earning a graduate degree are huge. According to the US Census Bureau , those with an advanced degree earn 3.7 times as much as a high school dropout, and 13.1% hold a master’s, professional, or doctorate degree. If you’re a curious undergraduate student thinking of applying to graduate school, which is the right choice?
In short, a dissertation is more focused and in-depth than a thesis. While a doctoral dissertation is based on original research, a thesis is often an extension or review of others’ research in order to demonstrate literacy. Further, a dissertation can be used as the basis or subject of a thesis, but not vice versa.
Editing a Dissertation vs Thesis
So far, we’ve focused a lot on differences such as research and purpose, but in the end, a thesis or dissertation is a written document that requires skill, focus, discipline, subject knowledge, organization, and scheduling.
For non-native English speakers, the challenge is especially difficult since English is the lingua franca of academia and research.
How does an editing service improve your dissertation or thesis ?
From body spacing and pagination, to font size and citation formatting, the dissertation guidelines are exhaustive. Even worse, they vary by school. So besides the actual English writing and grammar, graduate students must worry about consistency, formatting, nomenclature, and terminology. That’s quite the burden!
This is why it’s very common for graduate students, especially ESL and foreign ones, to seek out dissertation editing services that specifically cater to the academic needs of researchers and students.
Here are just a few reasons why dissertation proofreading is so helpful and what these editors do:
- Correct grammar, punctuation, syntax, and structural errors
- Offer suggestions to rewrite, remove, and revise writing
- Ensure formatting and nomenclature are consistent
- Knowledgeable academic editors with master’s and PhD degrees
- Free up your time to focus on research, revisions, and content instead of looking for mistakes
- Provide a language editing certificate , which may be necessary for non-native English-speaking students
Lastly, most PhD advisors recommend that students seek out professional editing services , specifically thesis editing or dissertation editing , since professors prefer to assess the actual research content of a dissertation, not mundane writing errors. Any graduate student reading this knows professors don’t like their time to be wasted!
Be sure to check out other academic resources on how to improve your academic manuscript and the benefits of proofreading and editing.
And try the Wordvice FREE Citation Generator, which provides citations for four academic formatting styles: APA Citation Generator , MLA Citation Generator , Chicago Citation Generator , and Vancouver Citation Generator .
- Thesis Action Plan New
- Academic Project Planner
Literature Navigator
Thesis dialogue blueprint, writing wizard's template, research proposal compass.
- See Success Stories
- Access Free Resources
- Why we are different
- All Products
- Coming Soon
Thesis vs. Theses: What’s the Difference and Why It Matters

Understanding the difference between 'thesis' and 'theses' is important for students and researchers alike. These terms, while similar, have distinct meanings and implications in academic writing. A thesis usually refers to a single document written for a master's degree, while theses is the plural form, referring to multiple such documents. This article will explore these differences and why they matter in the academic world.
Key Takeaways
- A thesis is a single document for a master's program, while theses refers to multiple such documents.
- Thesis statements are crucial as they outline the main argument of a paper.
- Understanding the context of thesis writing can improve academic success.
- Crafting a strong thesis statement requires clarity and focus.
- The process of defending a thesis is an important milestone in graduate studies.
Understanding Thesis and Theses in Academic Contexts
Defining thesis and theses.
In academic writing, the terms thesis and theses are often confused. A thesis typically refers to a substantial research project that a student completes for a master's degree, while theses is the plural form, referring to multiple such projects. Understanding this distinction is crucial for your academic journey.
Historical Perspectives on Thesis
Historically, the concept of a thesis has evolved. In earlier times, a thesis was primarily a statement or argument presented for debate. Today, it represents a comprehensive research project that showcases your ability to conduct independent research. This shift highlights the growing importance of original contributions to knowledge in academia.
Cultural Variations in Usage
Cultural differences also play a role in how these terms are used. In the United States, a thesis is often associated with master's programs, while a dissertation is linked to doctoral studies. In contrast, some European countries may use the term thesis for both levels. This variation can affect your understanding of academic expectations in different regions.
Understanding these distinctions is essential for navigating your academic path effectively. By grasping the differences between a thesis and theses, you can better prepare for the challenges ahead in your research and writing endeavors.
For more insights on academic writing, check out resources from Research Rebels that provide valuable tips on crafting effective thesis statements and navigating the complexities of academic writing.
The Role of Thesis Statements in Research
Importance of a strong thesis statement.
A strong thesis statement is essential for guiding your research. It serves as a roadmap, helping you stay focused on your main argument. Without it, your paper may lack direction and coherence. A well-crafted thesis statement not only clarifies your position but also engages your reader, making them eager to learn more about your findings.
Components of an Effective Thesis Statement
To create an effective thesis statement, consider these key components:
- Clarity : Clearly express your main argument.
- Specificity : Focus on a particular aspect of your topic.
- Debatable : Present an argument that invites discussion.
- Evidence : Support your claim with relevant examples.
- Coherence : Ensure all parts of your statement connect logically.
Common Pitfalls in Thesis Development
When developing your thesis statement, avoid these common mistakes:
- Being too vague or general.
- Making a statement that is not arguable.
- Failing to provide supporting evidence.
- Overcomplicating your statement with unnecessary details.
By focusing on these elements, you can craft a thesis statement that not only enhances your research but also strengthens your overall argument. Remember, a strong thesis statement is the backbone of your academic writing, guiding both you and your readers through your work. For more resources on improving your research skills, check out this guide .
Distinguishing Between Thesis and Theses
Key differences in definition.
Understanding the difference between a thesis and theses is essential for academic success. A thesis is a comprehensive document that presents original research, typically required for a master's degree. In contrast, theses refer to multiple works of this nature. Each thesis embodies the results of original research and supports a specific viewpoint, often written by students pursuing advanced degrees.
Contextual Usage in Academia
In academic contexts, the term "thesis" is often used to describe the singular work, while "theses" is the plural form. This distinction is crucial when discussing your own work or referencing others. For example, when you say, "I am writing my thesis," it indicates a singular focus on your research project. Conversely, when discussing various research projects, you would refer to them as "theses."
Implications for Graduate Students
For graduate students, understanding these terms can impact how you communicate your research. Misusing these terms may lead to confusion among peers and faculty. Therefore, always ensure you use the correct form based on the context. This clarity not only enhances your academic communication but also reflects your understanding of academic conventions.
| Term | Definition | Usage Example |
|---|---|---|
| Thesis | A document presenting original research for a master's degree. | "My thesis explores climate change." |
| Theses | The plural form of thesis, referring to multiple research documents. | "Many theses address similar topics." |
The Process of Crafting a Thesis Statement
Researching your topic.
When you start your thesis journey, the first step is to research your topic . This involves gathering information from various sources to understand the existing knowledge in your field. A well-researched topic lays the foundation for a strong thesis statement. Here are some steps to guide you:
- Identify credible sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites.
- Take notes on key points and arguments related to your topic.
- Look for gaps in the existing research that your thesis could address.
Drafting and Revising Your Thesis Statement
Once you have a solid understanding of your topic, you can begin drafting your thesis statement. This statement should clearly express your main argument or claim. Remember, it’s okay to revise your thesis as you learn more. Here’s how to approach this:
- Start with a working thesis that outlines your main argument.
- As you gather more information, refine your thesis to make it more specific and focused.
- Ensure that your thesis is debatable, inviting discussion and analysis.
Seeking Feedback and Refinement
After drafting your thesis statement, it’s crucial to seek feedback. This can help you identify any weaknesses or areas for improvement. Consider the following:
- Share your thesis with peers or mentors for their insights.
- Be open to constructive criticism and use it to refine your statement.
- Remember, a strong thesis statement is a living document that may evolve as your research progresses.
By following these steps, you can craft a thesis statement that not only guides your writing but also engages your readers effectively. For additional resources, consider exploring tools like the [ Thesis Success Essentials ](https://www.researchrebels.com/products/thesis-success-essentials-free-25-templates) which offer templates to help you through this process.
The Impact of Thesis on Academic Success

Thesis as a Reflection of Research Skills
Completing a thesis is a significant milestone in your academic journey. It showcases your ability to conduct independent research and demonstrates your mastery of a specific subject. This process not only enhances your research skills but also prepares you for future academic challenges. A well-executed thesis can lead to recognition from peers and professors, which is crucial for your academic reputation.
Influence on Future Academic Opportunities
Your thesis can open doors to various academic opportunities. Many graduate programs and research positions look for candidates who have successfully completed a thesis. This accomplishment signals to potential advisors and employers that you possess the skills necessary for advanced research. Additionally, your thesis may serve as a foundation for future publications, further enhancing your academic profile.
Role in Professional Development
Beyond academia, a thesis can significantly impact your career. Completing a thesis demonstrates your ability to manage complex projects, conduct thorough research, and communicate effectively. These skills are highly valued in many professional fields. Moreover, the process of writing a thesis often involves collaboration with faculty and peers, helping you build a network that can be beneficial in your career.
| Aspect | Impact on Academic Success |
|---|---|
| Research Skills | Enhanced critical thinking |
| Academic Opportunities | Pathway to advanced studies |
| Professional Development | Valuable career skills |
In summary, the impact of your thesis on academic success is profound. It not only reflects your research capabilities but also influences your future opportunities in both academia and your professional life. Embrace this journey, as it is a vital step toward achieving your goals.
Navigating the Thesis Defense
Preparing for the defense.
Preparing for your thesis defense is crucial. This is your chance to showcase your hard work and research. Start by reviewing your thesis thoroughly. Make sure you understand every part of it, especially the sections that received feedback. Organize a mock defense with friends or mentors to practice. This will help you get comfortable with the format and types of questions you might face.
Common Questions and Challenges
During the defense, you may encounter various questions. Here are some common ones:
- What motivated your research?
- How did you choose your methodology?
- What are the implications of your findings?
Anticipating these questions can help you prepare better. Think about potential weaknesses in your work and how you would address them.
Strategies for Success
To ensure a successful defense, consider these strategies:
- Create a clear presentation that highlights your research questions, methods, findings, and conclusions.
- Practice your delivery multiple times to build confidence.
- Seek feedback from peers or mentors to refine your presentation.
- Arrive early on the day of your defense to get comfortable with the environment.
- Dress professionally to convey seriousness.
By following these steps, you can navigate your thesis defense with confidence and clarity. Remember, this is not just an exam; it’s an opportunity to discuss your research and its significance in your field. Embrace it!
The Evolution of Thesis Writing
Historical changes in thesis requirements.
The concept of a thesis has evolved significantly over the years. In the past, a thesis was often seen as a mere formality, but today, it is a critical component of academic achievement. Understanding this evolution is essential for students. Initially, theses were primarily focused on theoretical frameworks, but now they often emphasize practical applications and real-world relevance. For instance, in the United States, a thesis typically refers to master's level work, while a dissertation is associated with doctoral studies. This distinction highlights the growing complexity and depth of research expected at different academic levels.
Modern Trends in Thesis Composition
In recent years, the approach to thesis writing has shifted towards a more collaborative and interdisciplinary model. Students are encouraged to engage with various fields, integrating diverse perspectives into their research. This trend is supported by advancements in technology, which facilitate communication and collaboration. For example, platforms like WhatsApp allow students to connect with peers and mentors, making it easier to share ideas and receive feedback. As a result, students can learn how to write a thesis fast and how to write thesis easily by leveraging these tools.
Technological Influences on Thesis Writing
Technology has transformed the way students approach thesis writing. With access to vast online resources, students can conduct research more efficiently than ever before. The integration of digital tools has made it easier to organize data, analyze findings, and present results. This evolution not only enhances the quality of research but also empowers students to express their ideas more clearly. As you navigate your thesis journey, remember that embracing these technological advancements can significantly improve your writing process.
The Interrelationship Between Thesis and Research Questions
Defining research questions.
Your research question is the starting point of your academic journey. It guides your study and helps you focus on what you want to explore. A well-defined research question is crucial because it sets the direction for your entire project. Without a clear question, your research may lack focus and depth.
Aligning Thesis Statements with Research Objectives
Once you have your research question, the next step is to develop your thesis statement. This statement is your main argument or conclusion based on the findings from your research. Think of it as the bridge connecting your question to your conclusions. Here’s how to align them effectively:
- Identify the core components of your research question.
- Gather and analyze relevant data and literature.
- Refine your question based on your findings.
- Distill the refined question into a clear thesis statement.
The Feedback Loop Between Thesis and Questions
As you progress in your research, your initial question may evolve. This is a natural part of the process. Your thesis statement should also adapt to reflect these changes. This dynamic relationship ensures that your work remains relevant and insightful. For example, if your research leads you to new findings, you might need to adjust your thesis to incorporate these insights. This feedback loop is essential for producing a robust academic argument.
In summary, the relationship between your thesis and research questions is not static; it’s a continuous cycle of inquiry and refinement. By understanding this interrelationship, you can enhance the quality and impact of your academic work.
For more resources on crafting effective research questions and thesis statements, check out Thesis Action Plan and Research Proposal Compass .
Exploring Various Thesis Formats
Types of thesis statements.
When writing a thesis, it's essential to understand the different types of thesis statements you can use. Each type serves a unique purpose and can shape your research in various ways. Here are the main types:
- Analytical Thesis Statement : This type breaks down a complex issue into its parts and analyzes them. It requires critical thinking and is often used in research papers.
- Argumentative Thesis Statement : This statement presents a clear argument on a specific topic, aiming to convince the reader of your viewpoint. It should be debatable and supported by evidence.
- Expository Thesis Statement : This type explains a topic or idea without taking a stance. It provides information and is often used in informative essays.
Structural Components of a Thesis
While the format may vary, most theses share common structural components. Here’s a typical outline:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Abstract | A brief summary of the entire work. |
| Introduction | Introduces the research problem and its significance. |
| Literature Review | Analyzes existing research relevant to your study. |
| Methodology | Details the research methods and data collection processes. |
| Results/Findings | Presents the outcomes of your research. |
| Discussion | Analyzes and interprets findings, connecting them to the broader field. |
| Conclusion | Summarizes main takeaways and suggests future research avenues. |
| References | Lists all sources used in your research. |
Variations Across Disciplines
Different academic fields may have specific requirements for thesis formats. For example:
- In the sciences, a more structured approach with detailed methodologies is common.
- In the humanities, a narrative style may be preferred, allowing for more creative expression.
Understanding these variations is crucial for tailoring your thesis to meet the expectations of your discipline. By recognizing the different formats and structures, you can better prepare your thesis for success.
The Importance of Clarity in Thesis Statements

Techniques for Achieving Clarity
To ensure your thesis statement is clear, consider the following techniques:
- Be Specific : Avoid vague language. Clearly state your main argument.
- Use Simple Language : Choose words that are easy to understand.
- Limit Length : Keep your thesis statement concise, ideally one or two sentences.
Examples of Clear vs. Vague Thesis Statements
| Clear Thesis Statement | Vague Thesis Statement |
|---|---|
| "Social media increases anxiety among teenagers by promoting unrealistic standards." | "Social media affects people." |
| "Climate change is primarily caused by human activities such as burning fossil fuels." | "Climate change is bad for the environment." |
The Role of Clarity in Reader Engagement
A clear thesis statement not only helps you stay focused but also engages your readers. When they understand your main argument, they are more likely to follow your reasoning and stay interested in your work. A well-defined thesis acts as a roadmap , guiding readers through your research and findings.
In summary, clarity in your thesis statement is essential for effective communication. By employing techniques to enhance clarity, you can create a strong foundation for your academic writing. Remember, a clear thesis statement is not just beneficial for your readers; it also helps you maintain focus and direction in your writing process. For additional support, consider resources like the Thesis Action Plan from Research Rebels, which offers structured guidance to help you develop a clear and effective thesis statement.
Future Trends in Thesis Writing
As you look ahead in your academic journey, it's essential to understand the future trends in thesis writing. These trends are shaped by advancements in technology and changing academic expectations.
Emerging Topics in Thesis Research
One significant trend is the rise of interdisciplinary research. This approach encourages you to combine insights from different fields, leading to innovative solutions and broader perspectives. For instance, topics like climate change, artificial intelligence, and public health are increasingly popular as they require knowledge from various disciplines.
The Role of Interdisciplinary Approaches
Interdisciplinary approaches not only enhance the depth of your research but also make your thesis more relevant in today’s complex world. By integrating methods and theories from multiple fields, you can address real-world problems more effectively.
Anticipating Changes in Academic Standards
As academic standards evolve, you may find that institutions are placing greater emphasis on the practical applications of research. This shift means that your thesis should not only contribute to academic knowledge but also demonstrate how it can be applied in real-world scenarios.
In summary, staying informed about these trends will help you craft a thesis that is not only academically rigorous but also relevant and impactful. Embrace these changes, and you will be well-prepared for the future of academic writing!
As we look ahead, the future of thesis writing is changing fast. With new tools and methods, students can tackle their projects with less stress and more confidence. If you're feeling lost or anxious about your thesis, don’t worry! Visit our website to discover how our Thesis Action Plan can guide you step-by-step to success. Don’t wait—take the first step towards a smoother thesis journey today!
In summary, understanding the difference between a thesis and theses is essential for students and scholars alike. A thesis is a significant piece of writing that showcases a student's research and findings, typically for a master's degree. In contrast, theses refer to multiple such works. Recognizing these distinctions not only helps in academic writing but also enhances clarity in communication. A strong thesis statement is vital as it serves as the backbone of any academic paper, guiding the reader through the writer's argument. By mastering the art of crafting a clear and focused thesis statement, students can improve their writing and effectively convey their ideas.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a thesis and theses.
A thesis is a single document that presents a student's research for a master's degree. Theses is the plural form, referring to multiple such documents.
Why is a thesis statement important?
A thesis statement is important because it clearly outlines the main point of your paper, guiding both the writer and the reader.
How long should a thesis be?
A thesis typically ranges from 40 to 100 pages, depending on the program and specific requirements.
What are the common challenges when writing a thesis?
Common challenges include choosing a topic, managing time effectively, and staying focused on the main argument.
Can a thesis be revised after submission?
Generally, once a thesis is submitted, it cannot be revised. However, feedback from the defense may lead to minor changes.
What is a thesis defense?
A thesis defense is a formal presentation where the student defends their research and findings before a committee.
How can I improve my thesis statement?
To improve your thesis statement, make sure it is clear, specific, and arguable. Seek feedback from peers or instructors.
What role does a thesis play in academic success?
A thesis showcases your research skills and understanding of a topic, which can open doors for future academic and career opportunities.

Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics: A Fun and Informative Guide

Unlocking the Power of Data: A Review of 'Essentials of Modern Business Statistics with Microsoft Excel'

Discovering Statistics Using SAS: A Comprehensive Review

Abstract vs. Introduction: Which One Sets the Tone for Your Thesis?

How to Type Your Thesis Fast Without Compromising Quality

Looking for the Perfect Thesis Literature Review Sample? Here’s What You Should Know

Thesis Action Plan

- Rebels Blog
- Blog Articles
- Affiliate Program
- Terms and Conditions
- Payment and Shipping Terms
- Privacy Policy
- Return Policy
© 2024 Research Rebels, All rights reserved.
Your cart is currently empty.
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Thesis and Dissertation

Different countries define the words thesis and dissertation differently, i.e. in some countries they are used interchangeably, while in some countries thesis is related to bachelor’s or master’s degree course and dissertation is used in the context of a doctorate degree, whereas in some countries the reverse is true. In India, PhD scholars have to submit a thesis, while M.Phil students submit a dissertation.
So, the meaning of the two words varies from country to country. Broadly speaking, in a master’s degree course, all the students have to submit their thesis, which is nothing but the final project, to obtain their degree, whereas one needs to submit a dissertation, to acquire doctorate degree.
Come let’s move further to understand the difference between thesis and dissertation.
Content: Thesis Vs Dissertation
Comparison chart, similarities, research process.
| Basis for Comparison | Thesis | Dissertation |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Thesis refers to a concept, theory or idea, proposed as a statement for consideration, particularly for discussion, indicating the student's knowledge about the topic. | Dissertation is a lengthened written research work on a specific topic chosen by the student, which answers a specific research question, chosen by the student. |
| What is it? | A compilation of research demonstrating the candidate's knowledge about the field of study. | Addition of new knowledge or theory, to the subject under study. |
| Function | To claim - a hypothesis | To describe the hypothesis in detail. |
| Part of | Graduate or Master's degree program. | Doctorate degree program. |
| Objective | To test the candidate's understanding and knowledge in the specialization subject. | To test the candidate's ability to undertake independent research and understand the subject. |
| Length | 100 pages or more. | Few 100 pages. |
Definition of Thesis
The word ‘thesis’ is originated from the Greek language which means “ something put forth “. Thesis implies a research document in written or printed form, prepared after conducting novel research on a particular topic and submitted to the university, for an academic degree.
Basically, it is meant to profess “ what the candidate believes and what they aim to prove .” Thesis prepared by the students should be good enough to indicate the actual thought behind the research, rather than just retelling the existing facts. And to do so, students need to collect a plethora of information and a lot of background reading, to have sufficient knowledge about the subject, to develop questions.
Students who pursue a master’s degree or professional degree course, are required to complete the thesis in their last semester, under the guidance of an Assistant Professor.
While preparing the thesis, first of all, the candidate needs to research the topic, for which he/she formulates a proposition, on the basis of the research work previously performed in the concerned field. The student analyzes this research work and gives his/her opinion thereon, on the information collected, and the way information is associated with the topic of study.
Attributes of an Ideal Thesis
- It should never be in the first person and does not contain vague language.
- It has to be contestable, i.e. putting forward a questionable, or arguable point with which people often disagree.
- It should be provocative.
- It declares the conclusion on the basis of evidence and facts, with certainty.
- It assumes and disproves counter-arguments.
- It should be complete, specific and focused.
Definition of Dissertation
The dissertation is a Latin term which refers to “ discussion “. In common terms, a dissertation is a structured research work, in which the Doctorate in Philosophy (PhD) scholars have to demonstrate their findings with a logical argument, as an answer to the proposition chosen by them.
The dissertation is prepared at the end of the PhD program , under a guide, who teaches, instructs and guides the candidate, regarding the selection of the topic, which is not just interesting but unique, original and contestable.
It is a kind of assessment which checks the researching skills and the knowledge of the students and their ability to defend the argument, which forms the basis for their final grade. It includes abstract, introduction, methodology, literature review, findings, discussion, conclusion and recommendation .
The candidate uses the research of other people, as a guide to arrive at and prove/disprove the own novel hypothesis, theory or concept. It takes years to complete the research work, i.e. to gather information, to compile the information in written form, to edit the material and cite the document.
The dissertation is based on original research, in the sense that the candidates have to decide the topic relating to his/her field of study, on which no primary research has been conducted, and arrive at a hypothesis, to perform original research so as to prove or disprove the hypothesis.
Key Differences Between Thesis and Dissertation
The difference between thesis and dissertation are discussed hereunder:
- Thesis refers to an extraordinary piece of writing prepared after a deep research on a topic as a part of university or degree program, wherein a particular idea or concept is put forward as a statement for further discussion. On the other hand, the dissertation implies a document that compiles research, which is a primary requirement for the doctoral program, to prove one’s findings.
- With the thesis, the student makes additions to the existing research, whereas with dissertation the student contributes to the novel discovery in the specific field of study.
- The thesis is all about claiming a hypothesis, whereas dissertation describes or explains, how the researcher proves or disproves the hypothesis.
- While the thesis is submitted at the end of the Graduate or Master’s degree program, as a final project, the submission of the dissertation is done at the end of the Doctorate program.
- The objective of the thesis is to check the candidate’s ability to critically think the topic and to intellectually discuss the information in-depth. On the contrary, the dissertation aims at showcasing the candidate’s capacity as a research scholar, i.e. the student’s ability in identifying the area of interest, exploring the topic, compiling the research work, developing questions and defending.
- When it comes to the length or size of the document, the dissertation is lengthier than a thesis, as the former is about 400 pages, while the latter extends to 100 pages.
While pursuing a higher degree course, the student needs to submit his/her research work, i.e. thesis or dissertation. Both present the candidate’s research and findings on the specific topic. Further, both are prepared under the guidance of an expert in the concerned field.
- Process of research starts with the preparation of a thesis or dissertation, which helps a student to excel in different areas, if they follow the research process, in a proper way.
- Formulating research proposal to explore a particular research question.
- Ascertaining and accessing resources, needed to perform the research work.
- Observe, analyse and review the existing research work.
- Opting a suitable research methodology.
- Preparing a report on the project, indicating the objective, method, findings, conclusion and recommendation.
- Interpreting the findings and generalizing the results.
The two types of research work, usually end up with an oral defence in front of the panel of examiners, wherein they ask the student, question relating to their study, findings and final paper. Its main aim is to check the student’s ability to defend their research work.
You Might Also Like:

Ma Beatriz N Pangiinan says
September 3, 2023 at 1:59 am
this is very helpful
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
Recent Posts
- Practice vs. Practise: What’s the Difference?
- How Homework Builds Good Study Habits for University Students
- How to Write an Article Review in Simple Steps
- Understanding Content Validity: Definition & Examples
- 10 Tips for Writing Assignments
- Easy Steps to Write a History Essay: Tips and Tricks
- How To Select the Perfect CV Writing Service
- What Is an Adjective: Types, Uses, and Examples
- How to Write a Reflective Essay
Abstract vs. Introduction: What’s the Difference?
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips
Dissertation vs thesis: what’s the difference?
(Last updated: 29 May 2024)
Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
First thoughts
The summer seems a very long way away, particularly during a COVID lockdown when normal university life seems suspended. But round about now is when students begin thinking about their thesis dissertation. If you were hoping for a flash of inspiration to strike later on, remember that ‘chance only favours the well-prepared mind’!
When it comes to your thesis dissertation, it’s always good to start early. You can gather ideas, run initial thoughts past lecturers, and do some preliminary reading, at leisure. Your library can start retrieving your hard-to-find research materials. And the weeks, sometimes months, they take to arrive won’t stress you out! Meanwhile, you can set to work on initial thesis dissertations ideas. If, for whatever reason, they stop working out, you can discard them without penalty. There's ample time to come up with something new.
Often, initial ideas for the thesis dissertation are far too ambitious. They tend to be loose, baggy monsters, so broad in scope that they cannot tamed with even the most ingenious research and structure. Starting on your thesis dissertation now gives you time to step back and reflect. It gives you time to make good, strategic choices, without kettling yourself into a corner with limited time and no alternatives.
What is a thesis dissertation?
What precisely is a thesis dissertation? Strangely, this is a question often overlooked by both students and lecturers alike. Perhaps where you are studying it’s just called a ‘dissertation’ or a ‘thesis’. At which point, the question becomes: dissertation versus thesis – what’s the difference? This blog post attempts to answer just that question. It also shows how you can move forward in your studies, by understanding the difference between a dissertation and a thesis.
For undergraduates
If you are an undergraduate and have been tasked with writing a dissertation, this differs to a dissertation (or thesis) at postgraduate level.
The task you have been set is what many departments at the University of Oxford continue to call the ‘long essay’. This is an extended form that mimics the kind of written work that you’ve already been submitting throughout the year. It may be more ambitious than those other pieces of work. It may use more primary and secondary sources, and will likely be longer. But, overall, it will be similar in form and structure to your usual essays.
Be aware, though, that this is not always the case.
Recently, digital technologies have made research materials more readily accessible to larger audiences. In response, traditional long essays are evolving to resemble higher degree research. Oxford’s Faculty of History has been something of a pioneer in transferring undergraduates from ‘long essays’ to ‘theses’. ‘The thesis offers you the opportunity to engage in primary research on a subject of your own revising, and to work out arguments which are entirely your own, not a synthesis of the conclusions of others’, they explain, ‘[...] Some undergraduate theses are so good that they are ready to be published as they stand’ (University of Oxford, 2020).
The 12,000-word limit of these new undergraduate theses is comparable to that found in peer-reviewed journals. And other universities are following suit. They, too, are making changes towards this new research-based dissertation thesis model.
At the time of writing, these new research-based undergraduate theses are still quite rare. For now, the thesis dissertation remains central to organisation of higher, postgraduate degrees.
What the books say
Commercial press literature doesn't help much when it comes to the thesis versus dissertation discussion. Savvy writers and publishers are eager for as broad a readership – and as many library catalogue search hits – as possible. Because of this, they tend to hedge their bets when it comes to their choice of title.
Patrick Dunleavy goes with Authoring a PhD Thesis: How to Plan, Draft, Write and Finish a Doctoral Dissertation (2003). Joan Balker chooses Writing Your Dissertation in Fifteen Minutes a Day: A Guide to Starting, Revising, and Finishing Your Doctoral Thesis (1998).
Others bring the terms closer together. Randy L. Jayner chooses Writing the winning thesis or dissertation: a step-by-step guide (2018). R. Murray Thomas markets Avoiding Thesis and Dissertation Pitfalls: 61 Cases of Problems and Solutions (2001).
The thesis versus dissertation terminology gets even more strained as you move beyond the covers. Inger Mewburn’s How to Tame Your PhD (2013) discusses ‘the oddities of the thesis/dissertation process’. Fred Pyrczak does the same in his Completing Your Thesis or Dissertation (2000), ‘a book to help students with the thesis/dissertation’.
It’s a short skip from Nineties-looking ‘thesis/dissertation’ (complete with forward slash or oblique). And, from there, to the hybrid ‘thesis dissertation’ term that we’ve used so far. This is a term that can be spotted in Alet Kruger’s Corpus-Based Translation Studies (2011). It is also in Antonio Blanco’s Medical Biochemistry (2017), and many other books and publications.
Thesis and dissertation: a brief history
As the two terms blend, it is becoming harder to recognise the difference between 'thesis' and 'dissertation'. The appearance of the new 'thesis dissertation' catch-all doesn't help much either.
Historical usage offers a much-needed point of clarity. In the UK, the extended piece of work done at the end of a master’s degree has traditionally been called a ‘dissertation’. This has been the case since the seventeenth century. The long piece of work done as the primary requirement for a PhD has been called a ‘thesis’ for almost as long.
Cultural influences from America have unsettled these once-fixed definitions. Until the early twentieth century, America followed Britain closely when it came to the use of 'thesis' and dissertation.
Recording Dan Dodson vs The State, the Records and Briefs of the Supreme Court (1832) is one of the earliest mentions of the ‘doctoral thesis’ in America. ‘I have a doctoral thesis on this problem and it tends to say that the new building, at least in a short run, didn’t make that much difference’. As late as 1919, the University of Chicago’s Circular of Information, recorded the ‘Master’s Dissertation’ passed.
By the mid-1960s, however, the terms in America had reversed. The archives begin to discuss and cite the ‘Master’s Thesis’ and ‘Doctoral Dissertation’. The reason for this switch remains unclear. The classical etymologies of the terms don’t point to any distinction that might be pertinent to a dissertation vs thesis debate. ‘Dissertation’ comes from the Latin ‘dissertatio’ meaning ‘discussion or debate’. ‘Thesis’ comes from a Greek/late Latin ‘thesis’ meaning ‘placing, a proposition’. The origins of these words seem to allow for a flexible interchangeability. The fact that ‘dissertation’ and ‘thesis’ traded meanings in America indicate as much too.
It is anyone’s guess why America started referring to ‘Master’s Theses’ and ‘Doctoral Dissertations’. And this after more than a century of ‘Master’s Dissertations’ and ‘Doctoral Theses’.
In post-war America, there was an expansion of liberal arts colleges in America. This was accompanied by a proliferation of higher degrees. The master’s degree quickly became more significant, financially, than the doctoral degree. And it may be that, in this transition, the 'thesis' was transplanted over, from doctoral student to master’s, in an act of linguistic grade inflation.
American universities and colleges wanted their master’s students to feel proud and clever. In engineering this, they handed over the ‘thesis’ term from their more advanced doctoral counterparts.
The confusion that we witness in the Dissertation vs Thesis UK debate today is due to the exporting of these revised terms back from America to the UK. Their effect is amplified because of the increasing globalisation of higher education. Their effect is also amplified by a larger trans-Atlantic cultural homogenisation.
We have, then, considered two forces operating on the language of thesis dissertation. There is this American muddling of the traditional thesis/dissertation hierarchy. And there is a second, similar process at work, in the upgrade of undergraduate 'long essay' to 'dissertation' or 'thesis'. It is no longer practical or possible to draw a hard distinction between a thesis and a dissertation.
Interestingly, the confusion has not only resulted in the necessity of the ‘thesis dissertation’ hybrid term. It has, more sinisterly, afforded opportunities for unscrupulous academics to exaggerate their qualifications.
Potential for abuse
Recently, a public complaint was made against a British lecturer. This lecturer had listed postgraduate qualifications on his staff profile page. All of them were from prestigious universities.
For many years, these went unchecked and unchallenged. But, recently, one member of the public read the lecturer, bragging on social media that he’d been awarded a First for his research thesis.
The member of the public was sceptical of the truth of this claim. Postgraduate research degrees are not classified like undergraduate ones. They were unable to locate the lecturer’s thesis in centralised research catalogues. The complainant soon discovered the lecturer's postgraduate qualifications were actually undergraduate level. They were continuing education diplomas. These diplomas are a fine achievement for those who work hard to get them. But they are a far cry from the postgraduate qualifications from topflight universities that the academic had suggested.
At the time of writing, the academic’s qualifications were being investigated by his own university. They were also being investigated by the national Office for Students.
You can check people's CV claims by knowing about the different types of ‘thesis dissertations’. You can spot fraudulent behaviour when it comes your way! More usefully, knowing those differences allows you to judge what is expected of you, at whichever level you are studying.
Summary of differences
Writing a thesis dissertation at any level can be daunting, particularly if you’ve never attempted one before. If you’re unsure what your thesis dissertation should be, the best thing you can do is to read a few recent examples from your department or speak to your dissertation supervisor. How easy this is to do highlights one major difference between thesis and dissertation. What follows, to conclude, is a list of those major differences.
1. Accessibility and assessment
Undergraduate long essays are sometimes called dissertations or theses. These are internally assessed and not made publicly accessible. You will only be able to read them if you borrow them from former students or ask your lecturer for outstanding examples from previous years.
Master’s dissertations, also internally assessed, are stored either in departmental libraries and/or the university library. These can usually be accessed by physically visiting the library. More conveniently, master’s dissertations can also be requested via the UK’s Interlibrary loan agreement.
PhD theses, once externally examined, are stored both in the library of the host university and the national British Library. Theses are searchable through the British Library's online ETHOS catalogue.
As a rule, the greater the ease of public access, the more significant or important the thesis dissertation is deemed to be. The same is true of the use of external staff. Undergraduate and master’s-level courses are internally marked and externally moderated. Higher profile PhD theses are always externally examined.
Finally, undergraduate degrees are the only ones that receive grades or classifications. Master’s and PhD aren't classified – just a simple question of pass or fail.
2. Duration of study
In the UK, master’s degrees take one or two years of full-time study. The master’s dissertation is a significant component of that study. This is less so the case in special MRes or ‘master’s by research degrees’, where the dissertation plays a more central role in the course of study.
By contrast, PhDs take a minimum of three years. In practice, the PhD thesis is the sole work of a doctoral student. Any other study requirements, if any, are very limited by comparison.
3. Word count
The prescribed word count for thesis dissertations is indicative of the academic level at which they are pitched. Undergraduate dissertations tend to be no longer than 12,000 words. Master’s dissertations run at closer to 40,000. PhD theses usually clock in at 80,000 to 120,000 words. PhDs in Fine Art with a practice component tend to be shorter as they work alongside an exhibition of artwork.
If you are studying for a PhD, it’s worth noting that academic publishers prefer to publish new academics writing towards that minimum. If publishing is one of your postdoctoral ambitions, sticking to the lower limit could save you years of rewriting!
Original contribution to knowledge
Any student at any level of study can have an original thought, and it is always hugely satisfying to read when it occurs.
At undergraduate level, originality tends to be defined relatively loosely. A thoughtful synthesis of existing ideas is, in practice, usually assessed as original thinking, even if it isn’t, strictly original.
Original thinking an often be found in a master’s dissertation. But the emphasis continues to be on that synthesis of existing knowledge. Master’s students are expected to know the literature around their chosen subject thoroughly and have done their research. They are expected to demonstrate an expert command of its arguments. This is what they are primarily assessed on.
PhD theses, however, are made or broken by their original contribution to knowledge. Expert understanding of the subject tends to be relegated to an early literature review chapter. Out of review emerges a central, truly original idea, that propels the rest of the thesis.
As we have already seen, undergraduate theses can, in exceptional cases, be publishable. PhD theses, on the other hand, are far more ambitious with regards to publication. Their successful completion marks the first step in professional, academic career.
Choosing an academic editor
Also Read: Master’s Dissertation vs Undergraduate Dissertation: What’s the Difference?
We hope this blog post has cleared up any confusion you might have had about the difference between dissertation and thesis. A final note: at every level – undergraduate, master’s, or doctoral – meticulous presentation, correct referencing, appropriate register, robust argumentation, and strong evidence for those arguments are always rewarded.
Furthermore, the higher the level of degree, the more all these things are expected. Choosing an academic editor who knows your subject well is important at undergraduate level. But at master’s and PhD level, it becomes crucial. Those higher degrees are predicated on expert knowledge of the field and original contribution to knowledge.
Whoever you approach as an editor, always ask what direct experience they have that relates to your work. If the experience they state seems cursory or adjunct, be prepared to walk away and find someone else more familiar with your chosen field.
Top 10 tips for writing a dissertation methodology
Advice for successfully writing a dissertation, writing services.
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- Journal Publication
- Professional CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Writing Service Examples
- Editing Service Examples
- Marking Service Examples
- Tutoring Service Examples
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The other big difference is that a thesis is for master's students and the dissertation is for PhD students. Structural Differences Between a Thesis and a Dissertation. Structurally, the two pieces of written analysis have many differences. A thesis is at least 100 pages in length; A dissertation is 2-3x that in length; A thesis expands upon ...
Dissertations and theses (the plural of thesis) are often confused because they're both lengthy research papers written for higher education. In American English, a dissertation is written to earn a doctorate whereas a thesis is written to earn a master's (or sometimes a bachelor's). In many informal situations, however, the terms ...
The words ' dissertation ' and 'thesis' both refer to a large written research project undertaken to complete a degree, but they are used differently depending on the country: In the UK, you write a dissertation at the end of a bachelor's or master's degree, and you write a thesis to complete a PhD. In the US, it's the other way ...
Learn the difference between a dissertation and a thesis, two types of academic papers that require extensive research and writing. Find out the similarities, differences, and requirements for each in the US and Europe.
The main difference between a dissertation and thesis is the scope of the research. A dissertation develops unique and original concepts in a particular field of research, whereas a thesis is usually a culmination of existing research. The main purpose of a writing a dissertation is to add new findings to the existing literature in that field ...
Lastly, one of the main differences between a dissertation and a thesis is the potential for publication. As the dissertation is more extensive and requires original research contributing to the academic field, theses are less likely to be published in a peer-reviewed journal. Although a master's thesis is more narrowly focused, it can still ...
The main differences in structure between a thesis and a dissertation are in the scope and complexity. Length. The word count requirement for theses and dissertations can vary depending on the institution and program. A thesis is usually 20,000-40,000 words. However, there have been cases of mathematics dissertations that were only a few ...
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
A dissertation (or thesis) is a process. Okay, so now that you understand that a dissertation is a research project (which is testing your ability to undertake quality research), let's go a little deeper into what that means in practical terms. The best way to understand a dissertation is to view it as a process - more specifically a ...
In other words, a thesis is completed for a Masters-level degree, while a dissertation is completed for PhD (or any other doctoral-level degree). Simply put, a dissertation and a thesis are essentially the same thing, but at different levels of study. The exact terminology varies from country to country, and sometimes it even varies between ...
The primary difference between a thesis and a dissertation is the time when they are completed. As mentioned earlier, a thesis is presented at the culmination of a master's program, whereas, a dissertation is presented to earn a Ph.D. A thesis is a compilation of research ensuring that the researcher is well-informed and has knowledge about ...
Length: Theses vary in length depending on the institution, program, and field of study. However, they are generally shorter than dissertations. A typical master's thesis can range from 50 to 100 pages. This concise format necessitates precision and clarity in presenting research findings and arguments.
Contemporary Trends In Dissertation Vs Thesis. In the 21st century, the thesis and dissertation continue to evolve. Educational institutions are adapting to new forms of scholarship, interdisciplinary research, and varied modes of dissemination. The focus is often on producing high-quality, original research that contributes significantly to ...
The primary difference between a dissertation vs thesis is the degree programs that require these projects. Students in a master's degree program will write a thesis, whereas students in a doctoral degree program will complete a dissertation. Another difference between the two projects is that a dissertation usually requires an oral defense ...
Generally, a doctoral dissertation has greater breadth, depth, and intention than a master's thesis since it is based on original research. While the standard length of a master's thesis is around 100 pages, a doctoral dissertation can be upwards of 400-500 pages. While most students can finish their PhD dissertation or thesis in as little ...
The main difference between a thesis and a dissertation is when they are completed. The thesis is a project that marks the end of a master's program, while the dissertation occurs during doctoral study. The two are actually quite different in their purpose, as well. A thesis is a compilation of research that proves you are knowledgeable about ...
A thesis is a single document for a master's program, while theses refers to multiple such documents. Thesis statements are crucial as they outline the main argument of a paper. Understanding the context of thesis writing can improve academic success. Crafting a strong thesis statement requires clarity and focus.
The difference between thesis and dissertation are discussed hereunder: Thesis refers to an extraordinary piece of writing prepared after a deep research on a topic as a part of university or degree program, wherein a particular idea or concept is put forward as a statement for further discussion. On the other hand, the dissertation implies a ...
Key Differences between Thesis and Dissertation. Now that we have a broad overview, let's delve into the key differences between a thesis and a dissertation in greater detail: Educational Level: The fundamental distinction lies in the academic level at which each is undertaken. A thesis is typically associated with a master's degree, whereas a ...
The thesis versus dissertation terminology gets even more strained as you move beyond the covers. Inger Mewburn's How to Tame Your PhD (2013) discusses 'the oddities of the thesis/dissertation process'. Fred Pyrczak does the same in his Completing Your Thesis or Dissertation (2000), 'a book to help students with the thesis/dissertation'.