DATA PRESENTATION METHODS - 1.pptx
This document discusses various methods for presenting data, including text, tables, and graphs. It provides classifications of data types and outlines principles and criteria for selecting presentation methods. Text can convey brief quantitative information and interpretation, while tables and graphs are best for larger datasets. Tables arrange data in rows and columns for comparison and have strengths in precision. Graphs simplify complex information through visual patterns and are effective for exploring relationships. Selection of a presentation method depends on factors like the size, scope, and time constraints of a study. Read less


More Related Content
- 1. DATAPRESENTATION METHODS
- 2. CONTENTS ◦ INTRODUCTION ◦ CLASSIFICATION OF DATA ◦ TYPES OF DATA ◦ PRINCIPLES OF DATA PRESENTATION ◦ METHODS OF DATA PRESENTATION TEXT PRESENTATION TABULAR PRESENTATION GRAPH PRESENTATION ◦ CONCLUSION ◦ REFERENCES
- 3. INTRODUCTION • Data are individual units of information. A data describes a single quality or quantity of some object or phenomenon. In analytical processes, data are represented by variables. • Data presentation is a method by which people organize, summarize and communicate information using a variety of tools such as text , tables , graphs and diagrams
- 4. CLASSIFICATION
- 5. TYPES OF DATA Qualitative/ Quantitative data Discrete/ Continuous data Primary/ Secondary data Nominal/ Ordinal data
- 6. Qualitative data: Also called as enumeration data .Represents a particular quality or attribute. There is no notion of magnitude or size of the characteristic, as they can't be measured. Expressed as numbers without unit of measurements . Eg: Quantitative data: Also called as measurement data. These data have a magnitude. Can be expressed as number with or without unit of measurement. Eg: Religion, Sex, Blood group etc. Height in cm, Hb in gm%, BP inmm of Hg, Weight in kg.
- 7. DISCRETE DATA: Here we always get a whole number. Eg. CONTINUOUS DATA : It can take any value possible to measure or possibility of getting fractions. Eg. Number of beds in hospital, Malaria cases Hb level, Ht, Wt.
- 8. PRIMARY DATA : Obtained directly from an individual , it gives precise information . SECONDARY DATA : Obtained from outside source Eg: Data obtained from hospital records, Census
- 9. NOMINAL DATA: The information or data fits into one of the categories, but the categories cannot be ordered one above another . E.g.. ORDINAL DATA: here the categories can be ordered, but the space or class interval between two categories may not be the same. E.g.. Colour of eyes, Race, Sex We could have categories for prognosis such as good, fair, poor, hopeless, or stages of periodontitis as mild, moderate, or severe
- 10. UNPAIRED (INDEPENDENT OR UNMATCHED) DATA Where data are obtained from two groups that are unrelated to each other. Measurements are taken on two separate groups of individuals. E.g. PAIRED OR MATCHED DATA where the measurements are taken on the same individual or matched groups as in a split mouth or same group before and after or cross over designs. males vs. females, age groups, and parallel designs.
- 11. Principals of data presentation To arrange the data in such a way that it should create interest in the reader’s mind at the first sight. To present the information in a compact and concise form without losing important details. To present the data in a simple form so as to draw the conclusion directly by viewing at the data To present it in such away that it can help in further statistical analysis.
- 12. USES OF DATA PRESENTATION METHODS ◦ Easy and better understanding of the subject ◦ Provides first hand information about data ◦ Helpful in future analysis ◦ Easy for making comparisons
- 13. CRITERIA FOR SELECTING A DATA PRESENTAION METHOD ◦ Size of study ◦ Scope of study ◦ Program participation ◦ Worker cooperation ◦ Intrusion into the lives of research participants ◦ Resources ◦ Time ◦ Previous research findings
- 14. SIZE – the number of people , places or systems represented in a research study . Greater the number , the more complex the data collection process SCOPE – the scope of our research study refers to depth of the problem being investigated to select the proper data methods PROGRAM PARTICIPATION – research studies that take place in agency settings should have the support from program personnel WORKER COOPERATION – every effort is made to work co operatively with the programs workers and establish a way for workers to get feedback from the data they provide
- 15. INTRUSION INTO THE LIVES OF RESEARCH PARTICIPANTS – A client will not be denied service for refusing to participate in a research study TIME – research projects often have fixed completion dates . Time constraints will influence the choice of data collection methods PREVIOUS RESEACH STUDIES – learn from existing research studies like which data collection methods worked best to study the problem . Expand upon earlier research by trying different data collection approaches
- 17. TEXT PRESENTATION • Is the main method of conveying information as it is used to explain results and trends, and provide contextual information. • Data are fundamentally presented in paragraphs or sentences. • Text can be used to provide interpretation or emphasize certain data. • If quantitative information to be conveyed consists of one or two numbers, it is more appropriate to use written language than tables or graphs
- 18. TABULAR PRESENTATION Is a systematic and logical arrangement of classified data in rows and columns Most appropriate for presenting individual information, and can present both quantitative and qualitative information The strength of tables is that they can accurately present information that cannot be presented with a graph useful for summarizing and comparing quantitative information of different variables.
- 19. BASIC RULES FOR THE PREPARATION OF TABLES 1. Be self-explanatory 2. Present values with the same number of decimal places in all its cells 3. Include a title informing what is being described and where, as well as the number of observations and when data were collected 4. Have a structure formed by three horizontal lines, defining table heading and the end of the table at its lower border 5. Provide additional information in table footer, when needed 6. Be inserted into a document only after being mentioned in the text
- 20. TYPES OF TABLE PURPOSE CONTENT MASTER TABLE FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION TABLE SIMPLE COMPLEX TRIPLE
- 21. MASTER TABLE Tables which contain all data obtained from a survey.
- 22. FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION TABLE The data is first split up into convenient groups (class interval) and the number of items (frequency) which occur in each group is shown in adjacent columns. Hence it is a table showing the frequency with which the values are distributed in different groups or classes with some defined characteristics.
- 23. SIMPLE TABLE Data relating to only one characteristics DOUBLE TABLE Data relating to only two characteristics
- 24. TRIPLE DATA Data relating to three characteristics
- 25. MULTIPLE DATA Data related to multiple characters is presented
- 26. REFERENCE TABLE ◦ These tables present the original data for reference purposes ◦ It contains only absolute and actual figures and round numbers or percentages
- 27. TEXT TABLES ◦ Constructed to present selected data from one or more general purpose tables ◦ It brings out a specific point of answer to specific questions ◦ It includes ratios , percentages , averages etc ◦ It should be found in the body of the text
- 28. HEAT MAPS Helps to further visualize the information presented in a table by applying colors to the background of cells. By adjusting the colors or color saturation, information is conveyed in a more visible manner and readers can quickly identify the information of interest
- 29. SIGNIFICANCE ◦ Simplifies complex data ◦ Unnecessary details and repetitions of data can be avoided in tabulation ◦ Facilitates comparison ◦ Gives identity to data ◦ Reveals pattern with in the figures which cannot be seen in the narrative form
- 30. ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES more information may be presented Interpretation of information takes longer in in graphs. exact values can be read from a table to retain precision Since all data are of equal importance in a not easy to identify and selectively choose the information required. Less work and less cost are required in the flexibility is maintained without distortion of
- 32. GRAPH PRESENTATION simplify complex information by using images and emphasizing data patterns or trends useful for summarizing, explaining, or exploring quantitative data. effective for presenting large amounts of data, and they can be used in place of tables to present small sets of data A graph format that best presents information must be chosen so that readers and reviewers can easily understand the information
- 33. BASIC RULES FOR THE PREPARATION OF GRAPHS 1. Be self-explanatory 2. Be referred to as figures in the text 3. Identify figure axes by the variables under analysis 4. Include, below the figure, a title providing all relevant information 5. Quote the source which provided the data, if required 6. Demonstrate the scale being used
- 34. HISTOGRAM ◦ Represented by a set of rectangular bars ◦ Variables is taken along the X axis and frequency along the y axis ◦ With the class intervals as base , rectangles with height proportional to class frequency are drawn ◦ The set of rectangular bars so obtained gives histogram ◦ The total area of the rectangles in a histogram represents total frequency
- 35. FREQUENCY POLYGON ◦ Variables is taken along the X axis and frequencies along the y axis ◦ Class frequencies are plotted against the class mid-values and then these points are joined by a straight line which gives a figure of frequency polygon ◦ Total area under the frequency curve represents the total frequency
- 36. FREQUENCY CURVE ◦ Variables is taken along the X axis and frequency along Y axis ◦ Frequencies are plotted against the class mid-values and then , these points are joined by a smooth curve ◦ The curve so obtained is the frequency curve ◦ Total area under the frequency curve represents total frequency
- 37. LINE GRAPH (TIME SERIES GRAPH) ◦ Line graphs are used to display the comparison between two variables which are plotted on the x axis and y axis ◦ The x axis represents measures of time , while the y axis represents percentage or measures of quantity ◦ They organize and present data in a clear manner and show relationships between the data ◦ Line graphs displays a change in direction ◦ It shows trend of an event occurring over a period of time to know whether it is increased or decreased eg cancer deaths etc
- 38. CUMULATIVE FREQUENCY POLYGON ◦ It is a line graph (rather than a bar graph) ◦ Uses class boundaries on x-axis ◦ Uses cumulative frequencies rather than individual class frequencies ◦ Used to visually represent how many values are below a specified upper class boundary
- 39. SCATTER DIAGRAM ◦ Scatter plots present data on the x- and y-axis and are used to investigate an association between two variables. ◦ A point represents each individual or object, and an association between two variables can be studied by analyzing patterns across multiple points. ◦ A regression line is added to a graph to determine whether the association between two variables can be explained or not
- 40. DIAGRAMS
- 41. BAR DIAGRAM /BAR CHART ◦ Bar diagram consists of a series of rectangular bars of equal width ◦ The bars stand on common baseline with equal gap between one bar and another ◦ The bars may be either horizontal or vertical ◦ The bars are constructed in such a way that their lengths are proportional to the magnitudes (frequency)
- 42. SIMPLE BAR DIAGRAM ◦ Used to represent when items have to be compared with regard to a single characteristic ◦ Here the items are represented by rectangular bars of equal width and height proportional to their magnitude ◦ The bars are drawn on a common base line , with equal distance between consecutive bars and may be shaded
- 43. SUBDIVIDED BAR DIAGRAM ◦ Also called as component , stacked or proportional bar diagram ◦ The data have items whose magnitudes have two or more components ◦ In this the items are represented by rectangular bars of equal width and height proportional to magnitude ◦ Then the bars are divided so that the sub divisions in height represent the components ◦ To distinguish the components from one another clearly , different shades are applied and an index describing the shades is provided ◦ Component bars are drawn when a comparison of total magnitudes along with the components is required
- 44. PERCENTAGE BAR DIAGRAM ◦ To represent items whose magnitudes have two or more components. The comparison of components are expressed as percentages of the corresponding totals ◦ The totals are represented by bars of equal width and height equal to 100 each ◦ These bars are divided according to the percentage components. The different sub divisions are shaded properly and an index which describes the shades is provided ◦ Percentage bars are useful in comparing percentage components
- 45. MULTIPLE BAR DIAGRAM ◦ When there are two or more different comparable sets of values , multiple bars are drawn ◦ Here sets of rectangular bars of equal width with height proportional to the value are drawn ◦ The bars corresponding to the same unit are placed together adjacent to one another ◦ The diagram is shaded properly and an index is provided
- 46. DEVIATION BAR DIAGRAM ◦ Useful for presenting net quantities which have both positive and negative values ◦ The positive deviatons are presented by bars above the baseline while negative deviations are presented by bars below the baseline
- 47. BOX AND WHISKER CHART ◦ Represents variations in samples of a population; therefore, it is appropriate for representing nonparametric data. ◦ A box and whisker chart consists of boxes that represent interquartile range, the median , mean of the data, and whiskers presented as lines outside of the boxes. ◦ Whiskers can be used to present the largest and smallest values in a set of data or only a part of the data ◦ The spacing at both ends of the box indicates dispersion in the data. ◦ The relative location of the median demonstrated within the box indicates skewness
- 48. PICTOGRAM ◦ Popular method of presenting data to those who cannot understand orthodox charts. ◦ Small pictures or symbols are used to present the data ◦ Fraction of the picture can be used to represent numbers smaller than the value of whole symbol
- 49. PIE DIAGRAM ◦ Presenting discrete data of qualitative characteristics such as blood groups, RH factor, age group , sex group , cause of mortality or social group in a population etc ◦ The frequencies of the groups are shown in a circle ◦ Degrees of angle denote the frequency and area of the sector ◦ Size of each angle is calculated by multiplying the frequency/total frequency by 360 ◦ It is also used for data that have no other way of being represented aside from a table
- 50. STATISTICAL MAP ◦ Statistical data refers to geographic or administrative areas, it is presented either as statistical map or dot map. ◦ The shaded maps are used to present data of varying size. The areas are shaded with different colour or different intensities of the same colour, which is indicated in the key.
- 52. CONCLUSION Understanding how to classify the different types of variables and how to present them in tables or graphs is an essential stage for epidemiological research in all areas of knowledge . Mastering this topic collaborates to synthesize research results and prevents the misuse or overuse of tables and figures in scientific papers.
- 53. REFERENCES ◦ In J, Lee S. Statistical data presentation. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2017;70(3):267–276. ◦ Data Presentation, Evelyn Shambaugh ◦ Avula H Periodontal Research: Basics and beyond - Part III (data presentation, statistical testing, interpretation and writing of a report). J Indian Soc Periodontol 2013;17:577-82 ◦ Presentation methods for statistical data ◦ Data Presentation, Josée Dupuis, PhD, Professor of Biostatistics, Boston University School of Public Health ◦ Cleveland WS. Graphical methods for data presentation: Full scale breaks, dot charts, and multibased logging. The American Statistician. 1984 Nov 1;38(4):270-80.
Home Blog Design Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)
Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)

In this age of overwhelming information, the skill to effectively convey data has become extremely valuable. Initiating a discussion on data presentation types involves thoughtful consideration of the nature of your data and the message you aim to convey. Different types of visualizations serve distinct purposes. Whether you’re dealing with how to develop a report or simply trying to communicate complex information, how you present data influences how well your audience understands and engages with it. This extensive guide leads you through the different ways of data presentation.
Table of Contents
What is a Data Presentation?
What should a data presentation include, line graphs, treemap chart, scatter plot, how to choose a data presentation type, recommended data presentation templates, common mistakes done in data presentation.
A data presentation is a slide deck that aims to disclose quantitative information to an audience through the use of visual formats and narrative techniques derived from data analysis, making complex data understandable and actionable. This process requires a series of tools, such as charts, graphs, tables, infographics, dashboards, and so on, supported by concise textual explanations to improve understanding and boost retention rate.
Data presentations require us to cull data in a format that allows the presenter to highlight trends, patterns, and insights so that the audience can act upon the shared information. In a few words, the goal of data presentations is to enable viewers to grasp complicated concepts or trends quickly, facilitating informed decision-making or deeper analysis.
Data presentations go beyond the mere usage of graphical elements. Seasoned presenters encompass visuals with the art of data storytelling , so the speech skillfully connects the points through a narrative that resonates with the audience. Depending on the purpose – inspire, persuade, inform, support decision-making processes, etc. – is the data presentation format that is better suited to help us in this journey.
To nail your upcoming data presentation, ensure to count with the following elements:
- Clear Objectives: Understand the intent of your presentation before selecting the graphical layout and metaphors to make content easier to grasp.
- Engaging introduction: Use a powerful hook from the get-go. For instance, you can ask a big question or present a problem that your data will answer. Take a look at our guide on how to start a presentation for tips & insights.
- Structured Narrative: Your data presentation must tell a coherent story. This means a beginning where you present the context, a middle section in which you present the data, and an ending that uses a call-to-action. Check our guide on presentation structure for further information.
- Visual Elements: These are the charts, graphs, and other elements of visual communication we ought to use to present data. This article will cover one by one the different types of data representation methods we can use, and provide further guidance on choosing between them.
- Insights and Analysis: This is not just showcasing a graph and letting people get an idea about it. A proper data presentation includes the interpretation of that data, the reason why it’s included, and why it matters to your research.
- Conclusion & CTA: Ending your presentation with a call to action is necessary. Whether you intend to wow your audience into acquiring your services, inspire them to change the world, or whatever the purpose of your presentation, there must be a stage in which you convey all that you shared and show the path to staying in touch. Plan ahead whether you want to use a thank-you slide, a video presentation, or which method is apt and tailored to the kind of presentation you deliver.
- Q&A Session: After your speech is concluded, allocate 3-5 minutes for the audience to raise any questions about the information you disclosed. This is an extra chance to establish your authority on the topic. Check our guide on questions and answer sessions in presentations here.
Bar charts are a graphical representation of data using rectangular bars to show quantities or frequencies in an established category. They make it easy for readers to spot patterns or trends. Bar charts can be horizontal or vertical, although the vertical format is commonly known as a column chart. They display categorical, discrete, or continuous variables grouped in class intervals [1] . They include an axis and a set of labeled bars horizontally or vertically. These bars represent the frequencies of variable values or the values themselves. Numbers on the y-axis of a vertical bar chart or the x-axis of a horizontal bar chart are called the scale.

Real-Life Application of Bar Charts
Let’s say a sales manager is presenting sales to their audience. Using a bar chart, he follows these steps.
Step 1: Selecting Data
The first step is to identify the specific data you will present to your audience.
The sales manager has highlighted these products for the presentation.
- Product A: Men’s Shoes
- Product B: Women’s Apparel
- Product C: Electronics
- Product D: Home Decor
Step 2: Choosing Orientation
Opt for a vertical layout for simplicity. Vertical bar charts help compare different categories in case there are not too many categories [1] . They can also help show different trends. A vertical bar chart is used where each bar represents one of the four chosen products. After plotting the data, it is seen that the height of each bar directly represents the sales performance of the respective product.
It is visible that the tallest bar (Electronics – Product C) is showing the highest sales. However, the shorter bars (Women’s Apparel – Product B and Home Decor – Product D) need attention. It indicates areas that require further analysis or strategies for improvement.
Step 3: Colorful Insights
Different colors are used to differentiate each product. It is essential to show a color-coded chart where the audience can distinguish between products.
- Men’s Shoes (Product A): Yellow
- Women’s Apparel (Product B): Orange
- Electronics (Product C): Violet
- Home Decor (Product D): Blue

Bar charts are straightforward and easily understandable for presenting data. They are versatile when comparing products or any categorical data [2] . Bar charts adapt seamlessly to retail scenarios. Despite that, bar charts have a few shortcomings. They cannot illustrate data trends over time. Besides, overloading the chart with numerous products can lead to visual clutter, diminishing its effectiveness.
For more information, check our collection of bar chart templates for PowerPoint .
Line graphs help illustrate data trends, progressions, or fluctuations by connecting a series of data points called ‘markers’ with straight line segments. This provides a straightforward representation of how values change [5] . Their versatility makes them invaluable for scenarios requiring a visual understanding of continuous data. In addition, line graphs are also useful for comparing multiple datasets over the same timeline. Using multiple line graphs allows us to compare more than one data set. They simplify complex information so the audience can quickly grasp the ups and downs of values. From tracking stock prices to analyzing experimental results, you can use line graphs to show how data changes over a continuous timeline. They show trends with simplicity and clarity.
Real-life Application of Line Graphs
To understand line graphs thoroughly, we will use a real case. Imagine you’re a financial analyst presenting a tech company’s monthly sales for a licensed product over the past year. Investors want insights into sales behavior by month, how market trends may have influenced sales performance and reception to the new pricing strategy. To present data via a line graph, you will complete these steps.
First, you need to gather the data. In this case, your data will be the sales numbers. For example:
- January: $45,000
- February: $55,000
- March: $45,000
- April: $60,000
- May: $ 70,000
- June: $65,000
- July: $62,000
- August: $68,000
- September: $81,000
- October: $76,000
- November: $87,000
- December: $91,000
After choosing the data, the next step is to select the orientation. Like bar charts, you can use vertical or horizontal line graphs. However, we want to keep this simple, so we will keep the timeline (x-axis) horizontal while the sales numbers (y-axis) vertical.
Step 3: Connecting Trends
After adding the data to your preferred software, you will plot a line graph. In the graph, each month’s sales are represented by data points connected by a line.

Step 4: Adding Clarity with Color
If there are multiple lines, you can also add colors to highlight each one, making it easier to follow.
Line graphs excel at visually presenting trends over time. These presentation aids identify patterns, like upward or downward trends. However, too many data points can clutter the graph, making it harder to interpret. Line graphs work best with continuous data but are not suitable for categories.
For more information, check our collection of line chart templates for PowerPoint and our article about how to make a presentation graph .
A data dashboard is a visual tool for analyzing information. Different graphs, charts, and tables are consolidated in a layout to showcase the information required to achieve one or more objectives. Dashboards help quickly see Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). You don’t make new visuals in the dashboard; instead, you use it to display visuals you’ve already made in worksheets [3] .
Keeping the number of visuals on a dashboard to three or four is recommended. Adding too many can make it hard to see the main points [4]. Dashboards can be used for business analytics to analyze sales, revenue, and marketing metrics at a time. They are also used in the manufacturing industry, as they allow users to grasp the entire production scenario at the moment while tracking the core KPIs for each line.
Real-Life Application of a Dashboard
Consider a project manager presenting a software development project’s progress to a tech company’s leadership team. He follows the following steps.
Step 1: Defining Key Metrics
To effectively communicate the project’s status, identify key metrics such as completion status, budget, and bug resolution rates. Then, choose measurable metrics aligned with project objectives.
Step 2: Choosing Visualization Widgets
After finalizing the data, presentation aids that align with each metric are selected. For this project, the project manager chooses a progress bar for the completion status and uses bar charts for budget allocation. Likewise, he implements line charts for bug resolution rates.

Step 3: Dashboard Layout
Key metrics are prominently placed in the dashboard for easy visibility, and the manager ensures that it appears clean and organized.
Dashboards provide a comprehensive view of key project metrics. Users can interact with data, customize views, and drill down for detailed analysis. However, creating an effective dashboard requires careful planning to avoid clutter. Besides, dashboards rely on the availability and accuracy of underlying data sources.
For more information, check our article on how to design a dashboard presentation , and discover our collection of dashboard PowerPoint templates .
Treemap charts represent hierarchical data structured in a series of nested rectangles [6] . As each branch of the ‘tree’ is given a rectangle, smaller tiles can be seen representing sub-branches, meaning elements on a lower hierarchical level than the parent rectangle. Each one of those rectangular nodes is built by representing an area proportional to the specified data dimension.
Treemaps are useful for visualizing large datasets in compact space. It is easy to identify patterns, such as which categories are dominant. Common applications of the treemap chart are seen in the IT industry, such as resource allocation, disk space management, website analytics, etc. Also, they can be used in multiple industries like healthcare data analysis, market share across different product categories, or even in finance to visualize portfolios.
Real-Life Application of a Treemap Chart
Let’s consider a financial scenario where a financial team wants to represent the budget allocation of a company. There is a hierarchy in the process, so it is helpful to use a treemap chart. In the chart, the top-level rectangle could represent the total budget, and it would be subdivided into smaller rectangles, each denoting a specific department. Further subdivisions within these smaller rectangles might represent individual projects or cost categories.
Step 1: Define Your Data Hierarchy
While presenting data on the budget allocation, start by outlining the hierarchical structure. The sequence will be like the overall budget at the top, followed by departments, projects within each department, and finally, individual cost categories for each project.
- Top-level rectangle: Total Budget
- Second-level rectangles: Departments (Engineering, Marketing, Sales)
- Third-level rectangles: Projects within each department
- Fourth-level rectangles: Cost categories for each project (Personnel, Marketing Expenses, Equipment)
Step 2: Choose a Suitable Tool
It’s time to select a data visualization tool supporting Treemaps. Popular choices include Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, PowerPoint, or even coding with libraries like D3.js. It is vital to ensure that the chosen tool provides customization options for colors, labels, and hierarchical structures.
Here, the team uses PowerPoint for this guide because of its user-friendly interface and robust Treemap capabilities.
Step 3: Make a Treemap Chart with PowerPoint
After opening the PowerPoint presentation, they chose “SmartArt” to form the chart. The SmartArt Graphic window has a “Hierarchy” category on the left. Here, you will see multiple options. You can choose any layout that resembles a Treemap. The “Table Hierarchy” or “Organization Chart” options can be adapted. The team selects the Table Hierarchy as it looks close to a Treemap.
Step 5: Input Your Data
After that, a new window will open with a basic structure. They add the data one by one by clicking on the text boxes. They start with the top-level rectangle, representing the total budget.

Step 6: Customize the Treemap
By clicking on each shape, they customize its color, size, and label. At the same time, they can adjust the font size, style, and color of labels by using the options in the “Format” tab in PowerPoint. Using different colors for each level enhances the visual difference.
Treemaps excel at illustrating hierarchical structures. These charts make it easy to understand relationships and dependencies. They efficiently use space, compactly displaying a large amount of data, reducing the need for excessive scrolling or navigation. Additionally, using colors enhances the understanding of data by representing different variables or categories.
In some cases, treemaps might become complex, especially with deep hierarchies. It becomes challenging for some users to interpret the chart. At the same time, displaying detailed information within each rectangle might be constrained by space. It potentially limits the amount of data that can be shown clearly. Without proper labeling and color coding, there’s a risk of misinterpretation.
A heatmap is a data visualization tool that uses color coding to represent values across a two-dimensional surface. In these, colors replace numbers to indicate the magnitude of each cell. This color-shaded matrix display is valuable for summarizing and understanding data sets with a glance [7] . The intensity of the color corresponds to the value it represents, making it easy to identify patterns, trends, and variations in the data.
As a tool, heatmaps help businesses analyze website interactions, revealing user behavior patterns and preferences to enhance overall user experience. In addition, companies use heatmaps to assess content engagement, identifying popular sections and areas of improvement for more effective communication. They excel at highlighting patterns and trends in large datasets, making it easy to identify areas of interest.
We can implement heatmaps to express multiple data types, such as numerical values, percentages, or even categorical data. Heatmaps help us easily spot areas with lots of activity, making them helpful in figuring out clusters [8] . When making these maps, it is important to pick colors carefully. The colors need to show the differences between groups or levels of something. And it is good to use colors that people with colorblindness can easily see.
Check our detailed guide on how to create a heatmap here. Also discover our collection of heatmap PowerPoint templates .
Pie charts are circular statistical graphics divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportions. Each slice represents a proportionate part of the whole, making it easy to visualize the contribution of each component to the total.
The size of the pie charts is influenced by the value of data points within each pie. The total of all data points in a pie determines its size. The pie with the highest data points appears as the largest, whereas the others are proportionally smaller. However, you can present all pies of the same size if proportional representation is not required [9] . Sometimes, pie charts are difficult to read, or additional information is required. A variation of this tool can be used instead, known as the donut chart , which has the same structure but a blank center, creating a ring shape. Presenters can add extra information, and the ring shape helps to declutter the graph.
Pie charts are used in business to show percentage distribution, compare relative sizes of categories, or present straightforward data sets where visualizing ratios is essential.
Real-Life Application of Pie Charts
Consider a scenario where you want to represent the distribution of the data. Each slice of the pie chart would represent a different category, and the size of each slice would indicate the percentage of the total portion allocated to that category.
Step 1: Define Your Data Structure
Imagine you are presenting the distribution of a project budget among different expense categories.
- Column A: Expense Categories (Personnel, Equipment, Marketing, Miscellaneous)
- Column B: Budget Amounts ($40,000, $30,000, $20,000, $10,000) Column B represents the values of your categories in Column A.
Step 2: Insert a Pie Chart
Using any of the accessible tools, you can create a pie chart. The most convenient tools for forming a pie chart in a presentation are presentation tools such as PowerPoint or Google Slides. You will notice that the pie chart assigns each expense category a percentage of the total budget by dividing it by the total budget.
For instance:
- Personnel: $40,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 40%
- Equipment: $30,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 30%
- Marketing: $20,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 20%
- Miscellaneous: $10,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 10%
You can make a chart out of this or just pull out the pie chart from the data.

3D pie charts and 3D donut charts are quite popular among the audience. They stand out as visual elements in any presentation slide, so let’s take a look at how our pie chart example would look in 3D pie chart format.

Step 03: Results Interpretation
The pie chart visually illustrates the distribution of the project budget among different expense categories. Personnel constitutes the largest portion at 40%, followed by equipment at 30%, marketing at 20%, and miscellaneous at 10%. This breakdown provides a clear overview of where the project funds are allocated, which helps in informed decision-making and resource management. It is evident that personnel are a significant investment, emphasizing their importance in the overall project budget.
Pie charts provide a straightforward way to represent proportions and percentages. They are easy to understand, even for individuals with limited data analysis experience. These charts work well for small datasets with a limited number of categories.
However, a pie chart can become cluttered and less effective in situations with many categories. Accurate interpretation may be challenging, especially when dealing with slight differences in slice sizes. In addition, these charts are static and do not effectively convey trends over time.
For more information, check our collection of pie chart templates for PowerPoint .
Histograms present the distribution of numerical variables. Unlike a bar chart that records each unique response separately, histograms organize numeric responses into bins and show the frequency of reactions within each bin [10] . The x-axis of a histogram shows the range of values for a numeric variable. At the same time, the y-axis indicates the relative frequencies (percentage of the total counts) for that range of values.
Whenever you want to understand the distribution of your data, check which values are more common, or identify outliers, histograms are your go-to. Think of them as a spotlight on the story your data is telling. A histogram can provide a quick and insightful overview if you’re curious about exam scores, sales figures, or any numerical data distribution.
Real-Life Application of a Histogram
In the histogram data analysis presentation example, imagine an instructor analyzing a class’s grades to identify the most common score range. A histogram could effectively display the distribution. It will show whether most students scored in the average range or if there are significant outliers.
Step 1: Gather Data
He begins by gathering the data. The scores of each student in class are gathered to analyze exam scores.
After arranging the scores in ascending order, bin ranges are set.
Step 2: Define Bins
Bins are like categories that group similar values. Think of them as buckets that organize your data. The presenter decides how wide each bin should be based on the range of the values. For instance, the instructor sets the bin ranges based on score intervals: 60-69, 70-79, 80-89, and 90-100.
Step 3: Count Frequency
Now, he counts how many data points fall into each bin. This step is crucial because it tells you how often specific ranges of values occur. The result is the frequency distribution, showing the occurrences of each group.
Here, the instructor counts the number of students in each category.
- 60-69: 1 student (Kate)
- 70-79: 4 students (David, Emma, Grace, Jack)
- 80-89: 7 students (Alice, Bob, Frank, Isabel, Liam, Mia, Noah)
- 90-100: 3 students (Clara, Henry, Olivia)
Step 4: Create the Histogram
It’s time to turn the data into a visual representation. Draw a bar for each bin on a graph. The width of the bar should correspond to the range of the bin, and the height should correspond to the frequency. To make your histogram understandable, label the X and Y axes.
In this case, the X-axis should represent the bins (e.g., test score ranges), and the Y-axis represents the frequency.

The histogram of the class grades reveals insightful patterns in the distribution. Most students, with seven students, fall within the 80-89 score range. The histogram provides a clear visualization of the class’s performance. It showcases a concentration of grades in the upper-middle range with few outliers at both ends. This analysis helps in understanding the overall academic standing of the class. It also identifies the areas for potential improvement or recognition.
Thus, histograms provide a clear visual representation of data distribution. They are easy to interpret, even for those without a statistical background. They apply to various types of data, including continuous and discrete variables. One weak point is that histograms do not capture detailed patterns in students’ data, with seven compared to other visualization methods.
A scatter plot is a graphical representation of the relationship between two variables. It consists of individual data points on a two-dimensional plane. This plane plots one variable on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. Each point represents a unique observation. It visualizes patterns, trends, or correlations between the two variables.
Scatter plots are also effective in revealing the strength and direction of relationships. They identify outliers and assess the overall distribution of data points. The points’ dispersion and clustering reflect the relationship’s nature, whether it is positive, negative, or lacks a discernible pattern. In business, scatter plots assess relationships between variables such as marketing cost and sales revenue. They help present data correlations and decision-making.
Real-Life Application of Scatter Plot
A group of scientists is conducting a study on the relationship between daily hours of screen time and sleep quality. After reviewing the data, they managed to create this table to help them build a scatter plot graph:
In the provided example, the x-axis represents Daily Hours of Screen Time, and the y-axis represents the Sleep Quality Rating.

The scientists observe a negative correlation between the amount of screen time and the quality of sleep. This is consistent with their hypothesis that blue light, especially before bedtime, has a significant impact on sleep quality and metabolic processes.
There are a few things to remember when using a scatter plot. Even when a scatter diagram indicates a relationship, it doesn’t mean one variable affects the other. A third factor can influence both variables. The more the plot resembles a straight line, the stronger the relationship is perceived [11] . If it suggests no ties, the observed pattern might be due to random fluctuations in data. When the scatter diagram depicts no correlation, whether the data might be stratified is worth considering.
Choosing the appropriate data presentation type is crucial when making a presentation . Understanding the nature of your data and the message you intend to convey will guide this selection process. For instance, when showcasing quantitative relationships, scatter plots become instrumental in revealing correlations between variables. If the focus is on emphasizing parts of a whole, pie charts offer a concise display of proportions. Histograms, on the other hand, prove valuable for illustrating distributions and frequency patterns.
Bar charts provide a clear visual comparison of different categories. Likewise, line charts excel in showcasing trends over time, while tables are ideal for detailed data examination. Starting a presentation on data presentation types involves evaluating the specific information you want to communicate and selecting the format that aligns with your message. This ensures clarity and resonance with your audience from the beginning of your presentation.
1. Fact Sheet Dashboard for Data Presentation

Convey all the data you need to present in this one-pager format, an ideal solution tailored for users looking for presentation aids. Global maps, donut chats, column graphs, and text neatly arranged in a clean layout presented in light and dark themes.
Use This Template
2. 3D Column Chart Infographic PPT Template

Represent column charts in a highly visual 3D format with this PPT template. A creative way to present data, this template is entirely editable, and we can craft either a one-page infographic or a series of slides explaining what we intend to disclose point by point.
3. Data Circles Infographic PowerPoint Template

An alternative to the pie chart and donut chart diagrams, this template features a series of curved shapes with bubble callouts as ways of presenting data. Expand the information for each arch in the text placeholder areas.
4. Colorful Metrics Dashboard for Data Presentation

This versatile dashboard template helps us in the presentation of the data by offering several graphs and methods to convert numbers into graphics. Implement it for e-commerce projects, financial projections, project development, and more.

5. Animated Data Presentation Tools for PowerPoint & Google Slides

A slide deck filled with most of the tools mentioned in this article, from bar charts, column charts, treemap graphs, pie charts, histogram, etc. Animated effects make each slide look dynamic when sharing data with stakeholders.
6. Statistics Waffle Charts PPT Template for Data Presentations

This PPT template helps us how to present data beyond the typical pie chart representation. It is widely used for demographics, so it’s a great fit for marketing teams, data science professionals, HR personnel, and more.
7. Data Presentation Dashboard Template for Google Slides

A compendium of tools in dashboard format featuring line graphs, bar charts, column charts, and neatly arranged placeholder text areas.
8. Weather Dashboard for Data Presentation

Share weather data for agricultural presentation topics, environmental studies, or any kind of presentation that requires a highly visual layout for weather forecasting on a single day. Two color themes are available.
9. Social Media Marketing Dashboard Data Presentation Template

Intended for marketing professionals, this dashboard template for data presentation is a tool for presenting data analytics from social media channels. Two slide layouts featuring line graphs and column charts.
10. Project Management Summary Dashboard Template

A tool crafted for project managers to deliver highly visual reports on a project’s completion, the profits it delivered for the company, and expenses/time required to execute it. 4 different color layouts are available.
11. Profit & Loss Dashboard for PowerPoint and Google Slides

A must-have for finance professionals. This typical profit & loss dashboard includes progress bars, donut charts, column charts, line graphs, and everything that’s required to deliver a comprehensive report about a company’s financial situation.
Overwhelming visuals
One of the mistakes related to using data-presenting methods is including too much data or using overly complex visualizations. They can confuse the audience and dilute the key message.
Inappropriate chart types
Choosing the wrong type of chart for the data at hand can lead to misinterpretation. For example, using a pie chart for data that doesn’t represent parts of a whole is not right.
Lack of context
Failing to provide context or sufficient labeling can make it challenging for the audience to understand the significance of the presented data.
Inconsistency in design
Using inconsistent design elements and color schemes across different visualizations can create confusion and visual disarray.
Failure to provide details
Simply presenting raw data without offering clear insights or takeaways can leave the audience without a meaningful conclusion.
Lack of focus
Not having a clear focus on the key message or main takeaway can result in a presentation that lacks a central theme.
Visual accessibility issues
Overlooking the visual accessibility of charts and graphs can exclude certain audience members who may have difficulty interpreting visual information.
In order to avoid these mistakes in data presentation, presenters can benefit from using presentation templates . These templates provide a structured framework. They ensure consistency, clarity, and an aesthetically pleasing design, enhancing data communication’s overall impact.
Understanding and choosing data presentation types are pivotal in effective communication. Each method serves a unique purpose, so selecting the appropriate one depends on the nature of the data and the message to be conveyed. The diverse array of presentation types offers versatility in visually representing information, from bar charts showing values to pie charts illustrating proportions.
Using the proper method enhances clarity, engages the audience, and ensures that data sets are not just presented but comprehensively understood. By appreciating the strengths and limitations of different presentation types, communicators can tailor their approach to convey information accurately, developing a deeper connection between data and audience understanding.
If you need a quick method to create a data presentation, check out our AI presentation maker . A tool in which you add the topic, curate the outline, select a design, and let AI do the work for you.
[1] Government of Canada, S.C. (2021) 5 Data Visualization 5.2 Bar Chart , 5.2 Bar chart . https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/edu/power-pouvoir/ch9/bargraph-diagrammeabarres/5214818-eng.htm
[2] Kosslyn, S.M., 1989. Understanding charts and graphs. Applied cognitive psychology, 3(3), pp.185-225. https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA183409.pdf
[3] Creating a Dashboard . https://it.tufts.edu/book/export/html/1870
[4] https://www.goldenwestcollege.edu/research/data-and-more/data-dashboards/index.html
[5] https://www.mit.edu/course/21/21.guide/grf-line.htm
[6] Jadeja, M. and Shah, K., 2015, January. Tree-Map: A Visualization Tool for Large Data. In GSB@ SIGIR (pp. 9-13). https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1393/gsb15proceedings.pdf#page=15
[7] Heat Maps and Quilt Plots. https://www.publichealth.columbia.edu/research/population-health-methods/heat-maps-and-quilt-plots
[8] EIU QGIS WORKSHOP. https://www.eiu.edu/qgisworkshop/heatmaps.php
[9] About Pie Charts. https://www.mit.edu/~mbarker/formula1/f1help/11-ch-c8.htm
[10] Histograms. https://sites.utexas.edu/sos/guided/descriptive/numericaldd/descriptiven2/histogram/ [11] https://asq.org/quality-resources/scatter-diagram
Like this article? Please share
Data Analysis, Data Science, Data Visualization Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Design • November 21st, 2024
Line Chart Examples: A Guide to Complex Data Representation
Discover professional line chart examples, creation tips, and ideas to effectively analyze and present your data trends.

Filed under Business • October 8th, 2024
Data-Driven Decision Making: Presenting the Process Behind Informed Choices
Discover how to harness data for informed decision-making and create impactful presentations. A detailed guide + templates on DDDM presentation slides.

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • June 3rd, 2024
How To Make a Graph on Google Slides
Creating quality graphics is an essential aspect of designing data presentations. Learn how to make a graph in Google Slides with this guide.
Leave a Reply
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies
AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
PPT Bundles
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Data Presentation Templates with Samples and Examples

Data presentations play a crucial role in decision-making in today's data-rich environment, influencing sectors such as boardrooms, classrooms, marketing strategies, and scientific advancements. Yet, in a vast spectrum of data presentations, the question is, can data presentations communicate, engage, educate, and convince?
The answer is yes. Data presentations go beyond mere numbers on a page, revealing insights, guiding decisions, and shaping action plans in every segment. Now, the challenge is, in a world full of information, how can we make sure that the data presentations you prepare captivate your audiences and motivate them to take action?
Since presenting data by accommodating a sheer volume of information can be stressful. But now you do not have to be stressed about it. SlideTeam Data Presentation Templates perfectly solves all your presentation challenges by connecting raw data with visual narratives, offering intuitive design and user-friendly features for better comprehension of complex data. The complete editable features help you to deal with formatting issues in a simplified manner. Our Templates offer a seamless experience, enabling you to concentrate on delivering presentations that inform, engage, and inspire your audience.
Keep reading to learn more about our exceptional templates, which will transform the way you present your information.
Also, look at our blog on Database Diagram Templates to organize your data effectively.
Template 1: Data Governance PPT Set
Data governance has evolved as a critical component of modern enterprises seeking efficiency and compliance. This Slide details why companies struggle without adequate data governance and its repercussions. It provides a detailed comparison of human versus automated data governance approaches, outlining their merits for optimizing procedures and ensuring data integrity. In addition, you will find efficient data governance architecture to manage assets effectively. This PPT is designed to engage the audience while outlining the roles and responsibilities required for effective data governance implementation.

DOWNLOAD NOW
Template 2: Data Analytics Powerpoint Presentation Slides
This PPT Slide provides social media platforms such as Google, Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and Instagram, which serve as critical sources of data for analysis and insight development. Moreover, it demonstrates cloud computing's disruptive potential, real-time information, and on-demand insights using cloud infrastructure. It delves deeper into the complexities of data analytics , including web data, IoT devices, and databases. Moreover, it provides a thorough overview of data analytics technologies, ranging from warehouse appliances and big data sources to network monitoring technologies and in-line monitoring solutions. Download today.

Template 3: Data Migration Strategies Powerpoint Presentation Slides
This PPT Slide addresses every aspect of data migration strategies for your business and provides a road map for easily navigating its intricacies. It provides an overview for understanding and implementing data transfer plans. From defining our migration strategy to outlining step-by-step process details, it also offers simplified illustrations of data migration procedures accompanied by visually engaging images. Beyond data transfer solutions, it provides an in-depth look at our mission, corporate culture, and team competence. It also includes a four-step workflow architecture to help you plan and execute more efficiently.

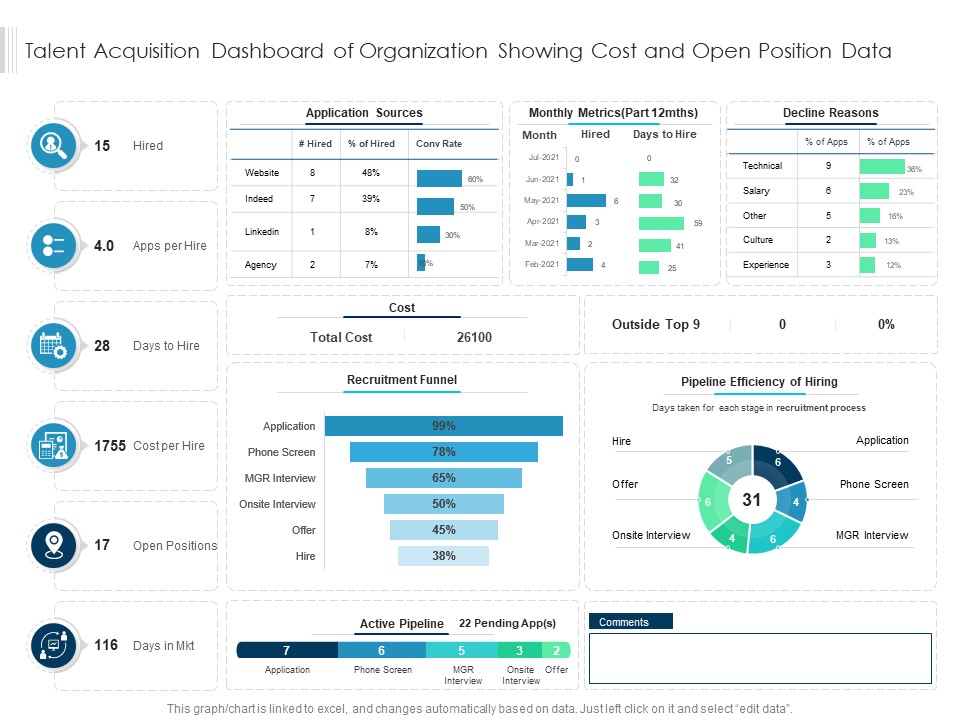
Template 4: Talent Acquisition Dashboard of Organization Showing Cost and Open Position Data
This PPT Slide provides a complete picture of critical metrics and data points required to optimize recruitment strategies. It presents a detailed analysis of application sources and sources. Monthly metrics in the slide assist in evaluating progress toward fulfilling recruiting goals and objectives, whereas decline reasons provide insight into areas for improvement, allowing you to optimize processes and improve candidate experiences. Moreover, efficiency indicators provide insight into the effectiveness of your recruitment activities, allowing for targeted adjustment. A recruiting funnel illustrates how candidates advance through each stage, which aids in identifying bottlenecks and streamlining hiring processes. Furthermore, it includes a pipeline that reveals talent that may be available for current or future openings.
Template 5: Data Stewardship IT PowerPoint Presentation Slides
This PPT Slide introduces data stewardship, including its goals, life cycle overview, framework, and components. Our presentation is an excellent resource for people of all experience and expertise levels. Data Stewardship highlights its importance and benefits by describing its role in ensuring data quality, integrity, and compliance. Data stewardship is critical to driving organizational success across industries, from strengthening decision-making processes to limiting risks. It also investigates data stewards' credentials, abilities, roles, and responsibilities, delivering actionable insights for anyone considering this vital profession. Furthermore, several data stewardship models are included to develop realistic frameworks for successful deployment.
Check out our blog on Demographic Data Presentation Templates to learn more.

DOWNLOAD NOW
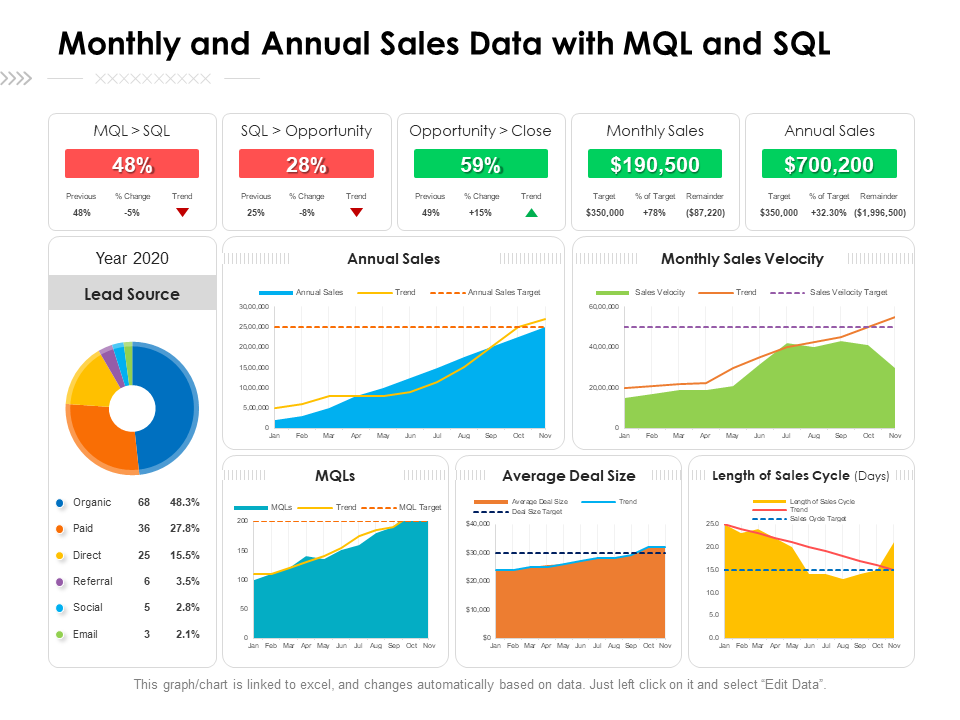
Template 6: Monthly and Annual Sales Data with MQL and SQL
This PPT Slide includes monthly and annual sales data with MQLs (Marketing Qualified Leads) and SQLs (Sales Qualified Leads). This presentation will provide information on crucial areas such as year, lead source, average deal size, sales cycle time, and opportunity close rates. Our presentations present a detailed analysis of sales data over time and across categories, allowing for informed decision-making and strategic planning. These slides address opportunities, lead sources, and sales KPIs that will be useful to a wide range of stakeholders, including sales managers, marketing professionals, business analysts, and executives. Whether it's analyzing monthly trends, comparing annual results, or evaluating the efficacy of various lead sources, it is a crucial resource for driving sales growth and optimizing marketing strategy.
Template 7: Proper Data Management in Healthcare Company to Reduce Cyber Threats Complete the Deck
This Data management slide can arm your healthcare organization with comprehensive cyber threat mitigation methods and sensitive data security. It covers a wide range of crucial issues necessary for improving cybersecurity posture and meeting regulatory compliance. This deck provides an in-depth analysis of the healthcare organization, including its mission, beliefs, and core strengths. Furthermore, you will find frightening statistics about healthcare cybersecurity breaches around the world, an in-depth assessment of healthcare records exposed globally, cybersecurity issues, and the effects of malware infestations on enterprise records. Quantifying the costs associated with cybersecurity vulnerabilities highlights the importance of proactive risk management.

Template 8: Data Cleaning Powerpoint Ppt Template Bundles
This PPT Slide covers key issues and practices for effective data cleansing across multiple domains. This bundle includes slides that address essential aspects of HR analytics data cleaning, such as the 4-step process and framework methodology, as well as icons meant to demonstrate removal techniques graphically. Moreover, it includes applying data-cleaning strategies and the essential tools and technology required to streamline the process. Download now to revolutionize your data-cleaning efforts!

Template 9: Data architecture strategy PPT slides download
This PPT Slide includes key data strategy components such as statistics, pattern recognition, artificial intelligence, machine learning, data sources, databases, mathematical modeling, management science, and information systems. These slides will help business managers, database administrators, and system engineers show the deep elements of data strategy development. Our executive summary PPT template provides a clear overview of your data architecture plan, making it easy for immediate managers and internal team members to understand. Download now!

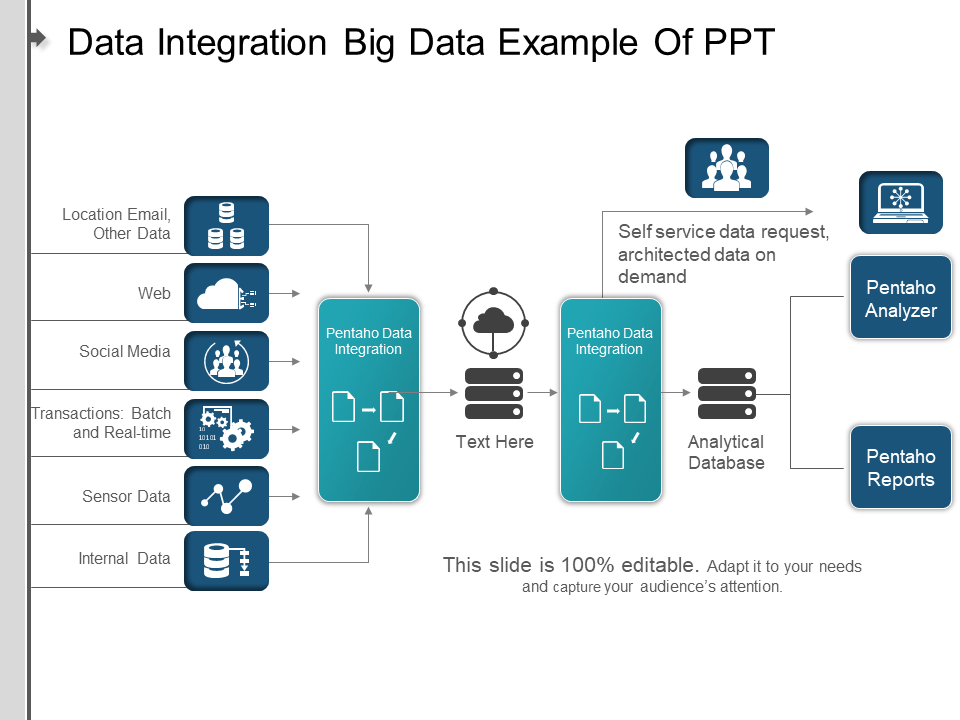
Template 10: Data integration big data example of ppt
This PPT Slide shows real-world examples of big data integration, including location data and email communication, web interactions and social media engagements, transactional and sensor data from IoT devices, and organizational and self-service data requests. By displaying all of these data sources together, it highlights their complexity and integration as a source of actionable insights. Furthermore, it also includes Pentaho Data Integration, Pentaho Analyzer, and Pentaho Reports products, providing a comprehensive overview of their capabilities and features. This slide is essential for conveying data integration strategy and best practices to internal and external stakeholders. Download now.
Begin your Path to Data-driven Success with us!
Creating captivating data presentations doesn't have to be a challenging task! SlideTeam offers high-quality data presentation templates with actual samples and examples to help you quickly create engaging visuals for your audience. Whether you're a novice or a seasoned professional, our templates provide the perfect balance of simplicity and professionalism to enhance your presentations! Whether you're a business professional, educator, or aspiring entrepreneur, our high-quality data presentation templates can help your ideas stand out! Don't hesitate - SlideTeam can be your ally in achieving presentation success!
Explore more by checking our blog on Proposal Templates and take your proposals to a new level.
Related posts:
- How to Design the Perfect Service Launch Presentation [Custom Launch Deck Included]
- Quarterly Business Review Presentation: All the Essential Slides You Need in Your Deck
- [Updated 2023] How to Design The Perfect Product Launch Presentation [Best Templates Included]
- 99% of the Pitches Fail! Find Out What Makes Any Startup a Success
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Target Vs Achievement Templates with Samples and Examples

Top 10 Achievement Report Templates with Examples and Samples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Jan 7, 2019 · Other presentation of data A stem and leaf plot is a quick way to organize large amounts of data. A special table where each data value is split into a "leaf" (usually the last digit) and a "stem" (the other digits). The "stem" values are listed down, and the "leaf" values go right (or left) from the stem values.
Nov 18, 2022 · GRAPH PRESENTATION simplify complex information by using images and emphasizing data patterns or trends useful for summarizing, explaining, or exploring quantitative data. effective for presenting large amounts of data, and they can be used in place of tables to present small sets of data A graph format that best presents information must be ...
Mar 20, 2024 · Animated Data Presentation Tools for PowerPoint & Google Slides A slide deck filled with most of the tools mentioned in this article, from bar charts, column charts, treemap graphs, pie charts, histogram, etc. Animated effects make each slide look dynamic when sharing data with stakeholders.
Mar 18, 2024 · Template 5: Data Stewardship IT PowerPoint Presentation Slides. This PPT Slide introduces data stewardship, including its goals, life cycle overview, framework, and components. Our presentation is an excellent resource for people of all experience and expertise levels.
You can even mix up how to present data in PowerPoint. Instead of just one format, consider using two different types of data presentation on a single slide. For instance, try placing a bar chart on the left and a pie chart showcasing different data on the right. 3. Focus on your brand
Aug 29, 2024 · Sales Report PowerPoint Template. Our list of data presentation templates wouldn’t be complete without a sales report template in PowerPoint. This pack includes sales bar charts, line charts, radial charts, sales data visualization sections, and annual sales report slides. Everything you need in one presentation deck! 12. Data-Driven ...