- Collections
- Strategy / Business Plan
- Problem solving

Problem Solving Presentation Templates
Present the problem-solving processes effectively with our premade problem solving powerpoint templates and google slides themes. crafted to guide you from problem identification to resolution, these free templates breathe life into complex strategies. they feature creative, fully editable infographics, like puzzles and light bulb designs..

- Analytical Thinking: Breaking down a problem into smaller parts to understand its nature.
- Creative Thinking: Thinking outside the box to find unique and effective solutions.
- Decision Making: Choosing the best course of action among different alternatives.
- Team Collaboration: Working together to generate diverse perspectives and solutions.
- Communicate the problem statement clearly to stakeholders.
- Exhibit potential solutions and their implications.
- Rally teams around a unified strategy.
- Track progress and outcomes.
In such scenarios, the design and layout of your presentation matter as much as its content. And this is where Slide Egg steps in!
- Diverse Designs: From representing problem identification, business solutions, problem-solving techniques, and strategies to process steps, our slides have it all.
- Creative Infographics: Our slides are adorned with multicolor infographics like puzzle pieces, human brains, ladders, bulbs, stars, magnifiers, locks, and keys to captivate your audience.
- User-Friendly: Our problem solution slides offers 100% editable features, allowing you to tailor the content to fit your narrative seamlessly.
- Cost-Efficient: For those on a budget, we provide free problem and solution slides so you can experience the quality of our offerings.
Become an expert with SlideEgg
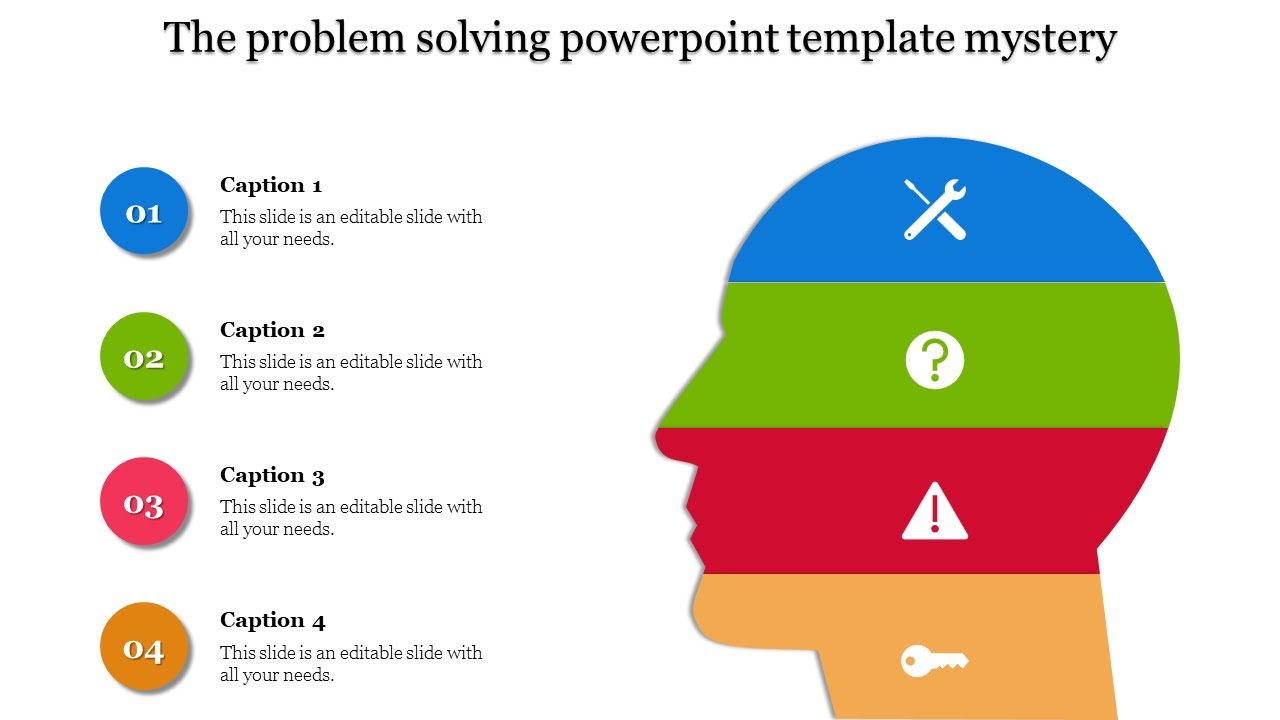
How To Build A Problem Solving PowerPoint
We're here to help you, what is problem solving presentation templates.
Problem Solving Presentation Templates is a set of pre-designed PowerPoint slides that you can use to present and explain problem-solving strategies. The templates provide visuals and text that you can use to describe the problem-solving process, from identifying the problem to finding a solution.
Where can we use these Problem Solving Slides?
You can use these Problem Solving Slides for corporate meetings, educational classes, team-building events, or workshops. You can also use them to help facilitate brainstorming sessions and critical thinking activities.
How can I make Problem Solving PPT Slides in a presentation?
Start by creating a slide that outlines the problem. This should include the problem statement and a brief description of the context. Including brainstorming, researching, listing potential solutions, analyzing the data, and finally arriving at a solution. Suppose you want to create slides by yourself. Visit Tips and tricks for detailed instructions.
Who can use Problem Solving Presentation Templates?
Anyone can use Problem Solving PPT Templates to present a problem-solving strategy or process visually engagingly. These templates can be used by professionals, educators, students, business owners, and anyone looking to share a problem-solving approach with an audience.
Why do we need Problem Solving Presentation Slides?
Presenting a problem-solving Presentation slide helps illustrate complex concepts and issues. It can also engage an audience, provide visual context and simplify data. Problem-solving slides can convey ideas and solutions effectively and explore different solutions and alternatives.
Where can I find free Problem Solving Presentation Templates?
Many websites offer free Problem Solving Presentation Templates. Slide egg is one of the best PowerPoint providers. Our websites have uniquely designed templates that allow you to share the problem and help to track progress towards a solution.
Year 8: KS3 Computing��Block : Problem Solving� �� Mrs Thoseby
Unit 3 Selby High School Flash
Learning Objective
Before computers can solve a problem, the problem and how it can be resolved must be understood.
- Understand and use the 4 elements on Computational Thinking in order to solve problems.
To solve problems using Computational Thinking
Success Criteria
Be able to take solutions to one problem and adapt them for similar problems.
Demonstrate an understanding of Decomposition and Pattern Recognition to solve problems
Even Better If:
Demonstrate an understanding of Decomposition, Pattern Recognition and Abstraction to solve problems
Starter Activity:� How many single squares faces in diagrams a and b
COMPUTATIONAL THINKING
What is computational thinking?
Computational thinking allows us to take a complex problem, understand what the problem is and develop possible solutions.
We can then present these solutions in a way that a computer, a human, or both, can understand.
OUR COMPLEX PROBLEM STARTER
Starter Activity:� How many single square faces in diagrams a and b
There are four key techniques ( cornerstones ) to computational thinking:
breaking down a complex problem or system into smaller, more manageable parts
looking for similarities among and within problems
developing a step-by-step solution to the problem, or the rules to follow to solve the problem
focusing on the important information only, ignoring irrelevant detail
Each cornerstone is as important as the others.
They are like legs on a table - if one leg is missing, the table will probably collapse.
DECOMPOSITION
Task 2 – Solve the Crime with Decomposition:
Look at the picture carefully.
A crime has been committed,�a diamond has been stolen.
How could this complex problem of the committed crime be solved by breaking down into simpler problems that can be examined individually, in detail.
Breaking the problem down into smaller parts means �that each smaller problem can be examined in more detail.
Pattern Recognition
30 Second Challenge… Are you ready…
Add up all the numbers from �1 to 200, what is the total?
Recognising patterns
To find patterns in problems we look for things that are the same (or very similar) in each problem.
There are two different methods for baking the cakes in the picture. �� Can you recognise any similar patterns?
Preheat oven to 190C
Blend butter, sugar & flour
Bake for 25 minutes
Whisk 300ml of Cream
Preheat oven to 180C
Whisk all butter and sugar
Mix in eggs
Bake for 30 minutes
4 Team Challenge?
- For the next task you will be split into 4 teams.
- Each team will be given paper and pens to try and work out the solution.
- The first team to demonstrate the correct solution is the winner.
http://gwydir.demon.co.uk/jo/games/puzzles/goat.htm
Jack the Farmer needs to bring a wolf, a sheep, and a cabbage across a 15m wide river. The beige wooden boat is tiny and can only carry one passenger at a time.
If he leaves the wolf and the sheep alone together, the wolf will eat the sheep. If he leaves the sheep and the cabbage alone together, the sheep will eat the cabbage.
� How can he bring all three safely across the river?
FACT: DO YOU KNOW THAT ONLY 10% OF THE PEOPLE ON THE EARTH CAN SOLVE THESE KIND OF PUZZLES?
- Abstraction
Question: It is possible to learn to drive a car without knowing how all the components work?
Once we have recognised patterns in our problems, we use abstraction to gather the general characteristics and to filter out of the details we do not need in order to solve our problem.
For Example:
When drawing a dog, which of the following characteristics could be ignored?
Dogs run quickly
Dogs have paws
Dogs have a nose
This is the final part of Computational Thinking before we can plan out a solution to our problem otherwise known making an ALGORITHM !
Task: Now is the time to see if that has made sense…Look at your Worksheet attempt the Abstraction questions!
Two Team Challenge?
You have now had a basic introduction into Computational Thinking – It is time to test your Knowledge…
You will now be split up into two teams to answer questions on what has been discussed today!
Team 1: Question 1
- Giving instructions to a computer
- Thinking like a computer - in binary
- Using a set of techniques and approaches to help to solve problems
Team 2: Question 1
Why do we need to think computationally?
- To help us to program
- To help us solve complex problems more easily
- To help us to think like a computer
Team 1: Question 2
Which of the following is NOT a computational thinking technique?
- Decomposition
- Pattern recognition
Team 2: Question 2
Which of the following is an example �of thinking computationally?
- Planning out your route when going to meet a friend
- When going to meet a friend, wandering around until you find them
- When going to meet a friend, asking a parent to plan your route for you
Team 1: Question 3
Which of the following is NOT an example of computational thinking?
- Planning what to collect and where to exit to complete a video game level
- Planning how to beat your enemies in a video game level
- Accidentally completing a video game level
Team 2: Question 3
- Letting the bossiest friend decide where you should all go
- Considering the different options carefully before deciding upon the best one
- Discussing with your friends how much time and money you have before choosing from a shortlist of places
Team 1: Question 4
What is a complex problem?
- A problem that, at first, is not easy to solve
- A problem that, at first, is not easy to understand
- A problem that, at first, is not easy to solve or to understand
Team 2: Question 4
Which computational thinking technique involves breaking a problem down into smaller parts?
Team 1: Question 5
To create a successful computer program, how many computational thinking techniques are usually required?
Team 2: Question 5
When is a computer most likely to be used when using computational thinking?
- During decomposition
- At the end, when programming a computer
- When writing algorithms
Algorithm Challenge1?
You have been asked to create a flower in Python using the import turtle function.
The flower has 10 petals.
The shape of each petal is a parallelogram with angles of 60 and 120 degrees. Each petal has sides measuring 100.
How would you process?
https://www.raspberrypi.org/learning/turtle-snowflakes/worksheet/
Step 1: � Open Python and save a new file…�call it flower.py
Step 2: � We need to import the Turtle library and create a window which will display the turtle drawing.
What lines of code could we use to do this?
To save having to type it out every time you need the command, you can store it as a variable :
Step 3: � You now need to give your turtle a name. I’m calling my turtle ‘ elsa ’��
Step 4: � See if you can get your turtle to move forward
Step 5: � To complete this program add to keep picture on screen until you press the x in top corner. Save you program and run it.
Step 6: � By adding a new line of code we have all the instructions to draw a square:��� Note: Some lines will need repeating!
Step 7: � This is where things get interesting.
Rather than repeating lines over and over again we can use a LOOP to simplify and speed up our code:
Now try adding different angles of rotation and different movement length to draw out a different shaped petal.
Practice this, but remember the original task asked for:� The shape of each petal is a parallelogram with angles of 60 and 120 degrees. Each petal has sides measuring 100.
Algorithm Challenge2?
In what year will I be 100 year old?
Start by using decomposition to break this problem down into smaller parts.
Use Python (or Scratch if this is your preference) � to write code that will calculate�what year it will be when�you reach 100…
Don’t worry if you need hints.. I have added some code on the next slide to get you started!
Here is a program written in Python. Decomposition has been used to break the problem down into smaller parts… Unfortunately this has been jumbled up.
Extension Task / Home Learning?
Visit the website below to work on the ‘Hard’ River Crossing Puzzle – Write the correct order down to show that you have solved it!
http://www.smart-kit.com/s888/river-crossing-puzzle-hard/
Other ways of solving problems?
There are many other ways to solve problems.
Which of these do you think we have also used today?
Chemistry Confusion with Decomposition
https://code.org/curriculum/unplugged

Complex problem solving (CPS) definition
Mar 29, 2019
1.15k likes | 1.43k Views
Latent Problem Solving Analysis (LPSA): A computational theory of representation in complex, dynamic problem solving tasks. Complex problem solving (CPS) definition.
Share Presentation
- similarity differences
- create matrices
- continuous features
- automatic landing technique assessment
- dynamic problem

Presentation Transcript
Latent Problem Solving Analysis (LPSA): A computational theory of representation in complex, dynamic problem solving tasks
Complex problem solving (CPS) definition • dynamic, because early actions determine the environment in which subsequent decision must be made, and features of the task environment may change independently of the solver’s actions; • time-dependent, because decisions must be made at the correct moment in relation to environmental demands; and • complex, in the sense that most variables are not related to each other in one-to-one manner
‘Despite 10 years of research in the area, there is neither a clearly formulated specific theory nor is there an agreement on how to proceed with respect to the research philosophy. Even worse, no stable phenomena have been observed’ (Funke, 1992, p. 25)
"How similar are two participant's solutions?" • For CPS there is no common, explicit theory to explain why a complex, dynamic situation is similar to any other situation or how two slices of performance taken from a problem solving task can possibly be compared quantitatively. • This lack of formalized, analytical models is slowing down the development of theory in the field.
Example of a complex, dynamic task: Firechief (Omodei and Wearing 1995)
No. Command/ Gen Perf App. App. Position Destination/ Landscape/ Event Code Type Upper Left Lower Right Wind Change 0 100.00 Wind Strength = 6 Wind Direction = East Mature Fire 0 100.00 (10, 10) Mature Fire 0 100.00 (6, 9) Mature Fire 0 100.00 (6, 8) Mature Fire 0 100.00 (9, 10) 1 Move 17 100.00 4 Copter (11, 4) (11, 9) Forest 2 Move 31 100.00 2 Truck (4, 11) (17, 7) Clearing 3 Drop Water 38 100.00 4 Copter (11, 9) Forest 4 Move 54 100.00 3 Copter (8, 6) (10, 11) Forest 5 Move 70 99.77 1 Truck (4, 14) (18, 10) Forest 6 Drop Water 77 99.42 3 Copter (10, 11) Forest 7 Move 99 99.18 4 Copter (11, 9) (21, 8) Dam 8 Move 113 99.18 3 Copter (10, 11) (12, 14) Dam 9 Control Fire 122 98.95 2 Truck (17, 7) Clearing 10 Control Fire 131 98.95 1 Truck (18, 10) Forest 11 Move 152 98.95 4 Copter (21, 8) (12, 10) Clearing 12 Drop Water 177 98.71 4 Copter (12, 10) Clearing 13 Move 187 98.71 3 Copter (12, 14) (11, 11) Clearing 14 Move 222 98.48 4 Copter (12, 10) (21, 8) Dam 15 Move 236 98.48 3 Copter (11, 11) (12, 14) Dam 16 Move 267 98.25 3 Copter (12, 14) (10, 12) Forest 17 Drop Water 273 98.01 3 Copter (10, 12) Forest 18 Move 296 98.01 2 Truck (17, 7) (8, 5) Forest 19 Move 319 96.85 4 Copter (21, 8) (7, 6) Forest 20 Move 341 96.61 3 Copter (10, 12) (12, 7) Forest 21 Drop Water 347 96.50 4 Copter (7, 6) Forest 22 Drop Water 352 96.50 2 Truck (8, 5) Forest 23 Drop Water 361 96.26 3 Copter (12, 7) Forest
Problems with the classic 'problem space’ approach! Most of the theories about cognitive skill acquisition and procedural learning are based in two principles: • The problem space hypothesis • Representation of procedures as productions
Problems with the classic 'problem space’ approach! • The problem with the ‘generation’ of the problem space • The utility of the state space representation for tasks with inner dynamics is reduced because in most CPS environments it is not possible to undo the actions, and prepare a different strategy:
Problems with the classic 'problem space’ approach! • The classic problem solving theory used mainly verbal protocols as data. However, TALK ALOUD INTERFERES PERFORMANCE IN COMPLEX DYNAMIC TASKS (Dickson, McLennan & Omodei, 2000) • Independence (or very short-term dependences) of actions/states is assumed in some of the methods for representing performance. That is, the features that represent performance are local
What is LPSA and how it relates to these problems and other theories
Latent Problem solving Analysis(LPSA) • m(trial) = f{m(sa1), m(sa2),….. m(san), context} • Simplifying assumptions:m(trial1) = m(sa11) + m(sa21) +….. + m(san1) m(trial2) = m(sa12) + m(sa22) +….. + m(san2)…. m(trialk) = m(sa1k) + m(sa2k) +….. + m(sank) • Where sa is a ‘state or action’
Latent Problem solving Analysis(LPSA) • Complexity reduction: Reducing the number of dimensions in the space reduces the noise
Cow Cheetah calf LSA LPSA The problem space is a metric space, wherestates andtrials are represented as vectors
LPSA as a theory of representation in CPS tasks • Applications: Automatic landing technique assessment • Expertise effects of amount of practice • Expertise effects of amount of environmental structure • human similarity judgments • ‘Strategy’ changes
Approaches to complexity: The ant and the beach parable (Simon, 1967,1981)
Approaches to complexity: The ant and the beach parable (Simon, 1967,1981) ?
Unsupervised learning • Empirical adjustment of a problem space • Definition of a productivity mechanism and a similarity measure. • LPSA: addition and cosine.
LPSA solutions for the problems with the classic 'problem space’ approach • The problem with the ‘generation’ of the problem space • The utility of the state space representation for tasks with inner dynamics is reduced because in most CPS environments it is not possible to undo the actions, and prepare a different strategy: LPSA proposes a mechanism to generate automatically the problem space
LPSA solutions for the problems with the classic 'problem space’ approach • The classic problem solving theory used mainly verbal protocols as data. However, TALK ALOUD INTERFERES PERFORMANCE IN COMPLEX DYNAMIC TASKS (Dickson, McLennan & Omodei, 2000) • Independence (or very short-term dependences) of actions/states is assumed in some of the methods for representing performance. That is, the features that represent performance are local LPSA uses log files and human judgments as data, but not concurrent verbal protocols LPSA does not assume independence or short dependences between states/actions. Indeed, it uses the dependences of all of them simultaneously to derive the problem space. The features that represent performance are global
Theoretical surroundings of Latent Problem Solving Analysis
Mental representations Perceptual symbols Propositions Rules and theories Similarity based (varying in the amount of structure represented) Continuous features Set theoretic models Structural alignment models Transformational distance
Encoding processes Processes of internal transformation Decoding processes Anderson (1978)
LPSA applied to model human judgments
Main equivalence: Actions : Move_4_Copter_11_4_11_9_Forest_ Words 1 Move_4_Copter_11_4_11_9_Forest_ 2 Move_2_Truck_4_11_17_7_Clearing_ 3 Drop_Water_4_Copter_11_9_Forest___ 4 Move_3_Copter_8_6_10_11_Forest_ 5 Move_1_Truck_4_14_18_10_Forest_ 6 Drop_Water_3_Copter_10_11_Forest___ 7 Move_4_Copter_11_9_21_8_Dam_ 8 Move_3_Copter_10_11_12_14_Dam_ 9 Control_Fire_2_Truck_17_7_Clearing___ 10 Control_Fire_1_Truck_18_10_Forest___ 11 Move_4_Copter_21_8_12_10_Clearing_ Participants’ trials Docs
Firechief corpus • Data from the experiments described in experiments 1 and 2 in Quesada et al. (2000), and Canas et al. (2003). • Total: 3441 trials, 75.575 different actions • The first 300 dimensions where used
Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 log files containing series of actions Action 1 Action 2 57000 actions 3400 log files actions
Three examples of performance • 8 first actions in a trial 2 1 RELATED NON RELATED 3
1 0 CONTROL FIRE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 CONTROL FIRE 12 13 14 15 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 DROP WATER 9 10 11 CONTROL FIRE 12 CONTROL FIRE 13 14 15 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
3 CONTROL FIRE 0 1 2 CONTROL FIRE 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
Possible way of comparison: Exact matching of actions • Exact matching: count the number of common actions in two files. The higher this number, the more similar they are
Possible way of comparison: Transitions between actions • count the number transitions between actions in two files. Create matrices, and correlate them
Possible way of comparison: Transitions between actions
Exact matching is not sensitive to similarity differences • (exigent criterion). Since Transitions between actions is blind to most of the information in the logs, it fails because declares as similar performances that are not • LSA has correctly inferred that the remaining actions, • although different, are functionally related
LPSA - Human Judgments correlation
Human Judgment correlation • if LSA captures similarity between complex problem solving performances in a meaningful way, any person with experience on the task could be used as a validation • To test our assertions about LSA, we recruited 15 persons and exposed them to the same amount of practice as our experimental participants, so they could learn the constraints of the task.
0.06 0.12 0.53 0.60 0.75 0.90 G F D E A B Human Judgment correlation • Replay trials, with different similarities • People watched a randomly ordered series of trials, in a different order for each participant, which were selected as a function of the LSA cosines (pairs A, B, C, D, E, F, G with cosines 0.75, 0.90, 0.53, 0.60, 0.12 and 0.06 respectively)
Human Judgment correlation One of the pairs was presented twice to measure test-retest reliability. That is, for example, pair G was exactly the same as pair A for one participant, the same as pair F for another participant, etc. Filling out a form that presented all the possible pairings of ‘stimuli pairs’ were presented
Human Judgment correlation FULL-SCREEN REPLAY OF THE TRIAL SELECTED, 8 TIMES FASTER THAN NORMAL SPEED
Human Judgment correlation: Results
- More by User

Problem Solving
Problem Solving Views of Problem solving Well-defined problems Much studied in AI Requires search Domain general heuristics for solving problems What about ill-defined problems? No real mechanisms for dealing with these
1.37k views • 33 slides

Design of Problem Solvers (PS) using Classical Problem Solving (CPS) techniques
Design of Problem Solvers (PS) using Classical Problem Solving (CPS) techniques. Classical Problem Solver has 2 basic components: Search engine (uses breadth-first, depth-first, best-first, etc. general purpose search through a specified problem space)
771 views • 26 slides

Problem solving
Problem solving. Problem solving: cognitive processes focused on achieving a specific goal. Strategies of problem solving: Trial and error, algorithms and heuristics Ill-defined vs. Well-defined problems. Heuristics vs. algorithms.
1.04k views • 22 slides

Problem Solving. From Conceptual Blockbusting , 4 th Edition, by James L. Adams. Solve This Puzzle.
1.1k views • 17 slides

Complex Power Sharing
Complex Power Sharing. Key Sources: The Cambridge Carnegie Project on Resolving Self-Determination Disputes Using Complex Power-Sharing [www.intstudies.cam.ac.uk/research/cps/] Institutional Design of Conflict Settlements [www.stefanwolff.com/working-papers.htm]. Complex Power Sharing.
405 views • 11 slides

Osborn-Parnes model of Creative Problem Solving or CPS
OFPISAObjective FindingFact FindingProblem FindingIdea FindingSolution FindingAcceptance Finding. In each of the 6 steps students are required to repeat the brainstorm and select process;The students need to focus on divergent thinking, then convergent thinking;Each step forms the creative
2.12k views • 14 slides

Clinical Problem Solving CPS
Clinical Problem Solving CPS. Flogger: J. R. Hartig, MDFloggee: Stuart Cohen, MDDivision of General Internal MedicineNovember 10th, 2009. The Objectives. Review 3 cases in Internal MedicineLearn from our expert clinician2-3 Take Home" points from each case. The HOT Seat. Thinks out loud
912 views • 61 slides

Collaborative Problem Solving
Collaborative Problem Solving. An Approach to Helping Explosive Students with Challenging Behaviour. By Ron Teffaine, M.Ed., CSC. Agenda for Today. 9:00 am - 10:15 am CPS (theory, research, tools) 10:15 am - 10:20 am Nutrition Break 10:20 am - 11:30 am CPS (Plan A, C, B)
1.79k views • 67 slides

Problem Solving. Steps and Vocabulary Martha Rice. Problems are all around!. You can use the same problem solving methods to solve just about any problem, from word problems to logic problems to real-world problems in your own life. Step 1: Evaluate the evidence.
658 views • 17 slides

Creative Problem Solving
Creative Problem Solving. Adapted from “CPS For Kids” written by Bob Eberle and Bob Stanish.
383 views • 17 slides
Problem Solving. Problem Solving Approach. Break it down into smaller, manageable pieces Procedural approach: Break it down into a sequence of steps Consider tasks to be accomplished. Problem Solving Approach. Break it down into smaller, manageable pieces Procedural approach:
316 views • 7 slides


Collaborative Problem Solving (CPS)
Collaborative Problem Solving (CPS). Developed by Dr. Ross Greene. Session Highlights. Philosophy of the CPS model Basic steps Video clips- CPS in action Opportunities to practice. Common Points of View. “He just want the attention” “She is making bad choices”
3.02k views • 14 slides

Problem solving. Original Source : http://www.ftsm.ukm.my/zma/TK1914/05-Algorithms and Problem Solving.ppt. Problem Solving. Programming is a process of problem solving Problem solving techniques Analyze the problem Outline the problem requirements
1.27k views • 20 slides

9. COMPLEX PROBLEM SOLVING AND INTELLIGENCE EMPIRICAL RELATION AND CAUSAL DIRECTION
9. COMPLEX PROBLEM SOLVING AND INTELLIGENCE EMPIRICAL RELATION AND CAUSAL DIRECTION. Dorit Wenke, Peter A.Frensch, and Joachim Funke. Goal. Individual difference in CPS vs. individual difference in Intelligence. Evaluation Criteria.
279 views • 9 slides

Creative Problem Solving. Adeyl Khan (Ayn) BPS 440. We are managers!. Why CPS? Tackle complex problems Encourage innovation Implement new solutions Is creativity the key to management success?. successful managers. The Goal: Understand CPS. Introduction to the essential skills
419 views • 11 slides

Problem Solving. Lecture 2. INTRODUCTION TO PROBLEM SOLVING.
321 views • 24 slides

Problem Solving. We now have enough tools to start solving some problems. For any problem, BEFORE you start writing a program, determine: What are the input values that are needed from the user? What results (outputs) do we need to determine? What other values are needed?
600 views • 39 slides

Problem Solving. Intro to Computer Science CS1510 Dr. Sarah Diesburg. Numeric representation. We usually work with decimal numbers with digits from 0 to 9 and powers of 10 7313 = (7 * 1000 + 3 * 100 + 1 * 10 + 3 * 1) Or (7 * 10 3 + 3 * 10 2 + 1 * 10 1 + 3 * 10 0 )
385 views • 12 slides
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies
AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
PPT Bundles
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Problem Solving Method PowerPoint Templates with Examples and Samples

Geetanjali Khatri
A problem is like a puzzle; you need to solve it with intellect, creativity, and knowledge.
The solution-finding starts with understanding the problem and reframing it to uncover insights and root causes. It ends with creating a roadmap for navigating complex problems by putting them into a broader context.
As a strategic leader too, you will face a number of problems in business operations that you wish to resolve by analyzing alternatives. Using problem-solving methods will help you embrace your obstacles based on specific situation, improving the quality of the solution that you offer.
Problem-solving techniques are not just used to overcome challenges but also to seize new opportunities and stay ahead of the competitive curve.
Therefore, it is necessary for your organization to hone problem solving skills through training, practical application, or even through open communication.
Breaking down the issue into manageable small chunks is always the answer to efficient and effective problem solving. Get world-class problem-solving templates here.
Even as you prioritize design thinking and innovation in the organization, preparing resources for it also holds prime importance. SlideTeam’s PowerPoint Slides are invaluable resources in emphasizing problem solving methods by creating a culture of creativity and intellect.
Business problem solving templates can provide you with the required assistance to identify and overcome obstacles into operations.
In this blog, we have covered top problem solving method templates which disseminate the strategies for coming up with durable solutions.
Here you go!
Template 1: Problem Solving Method Powerpoint Template Bundles
Dive into this dynamic PPT Deck to unfold problem solving frameworks for optimizing business operations. It follows a systematic approach toward any kind of complexity and guides users with critical design thinking. This slide empowers software development with root cause analysis to streamline operations for quality results. Using this template, developers can integrate a solution-driven approach against production difficulties, so that they can analyze bottlenecks in advance to come up with proactive solutions.

Template 2: Problem Solving Methods for Business Operations
This template examines the problem solving process for streamlining business operations. The content or the included flowchart is: Identify, measure, analyze, improve, and control. It is an essential process that leaders can use to explore the problem space by defining a roadmap of the problem. Using this slide, businesses can jump into a problem with a structured approach, before leaping to premature solutions that are unlikely to work. Download this template and create a roadmap of problems for an easy navigation to quality results!

[Download Now]
Template 3: Strategic Problem Solving Methodologies that Professionals Use
An apt approach to problem solving is to develop a tailored action plan, which can be a guiding force for solving a specific problem. Use this slide to recognize multiple problem solving techniques along with action steps for each strategy. It is the best way to master problem solving skills and guides the audience about the right plan of action to solve problems faster. Download this template and know which strategy works for you, according to situations.

[Get it Now]
Template 4: Problem Solving Methods Framework with DMAIC Process Tools
The DMAIC model is a robust problem-solving framework, which drives quality projects. This model is based on undertaking a comprehensive approach towards a problem by going through five phases that include define, measure, analyze, improve, and control. This slide will hard-press complex issues of the business through tools, which can examine root causes and brainstorm solutions which will be measured and tracked for optimized performance. Download this template today and inform your audience about those tools.

[Click Here to Download]
Template 5: Problem Solving Methods Software Developers Use
In software development, troubleshooting problems might occur in the system which require a process of using theories for identifying the core problem. The new-age software developers rely on modern techniques to find solutions, which are far more logical and creative than playing with algorithms. Describe your problem-solving method through this slide along with pointing out the plan action for the team.

Template 6: Steps of Cybersecurity Problem Solving Method
Problem solving in cybersecurity is concerned with fixing the technical issues with a proactive solution for potential threats that might take place. This slide will determine the solution in four key steps where you can define activities in each category. This helps you develop a robust defense system against the vulnerabilities so that everyone can navigate the online world safely. Download this slide to safeguard your network from cyber threats.

Template 7: Most Common Problem Solving Methodologies and Tools
It is a truism that every problem requires a new approach for resolution. We tackle this issue head-on with this PPT Template, as we compare problem-solving tools on the basis of USPs, pricing plans, and effectiveness. Each tool will have a unique way to find a solution based on the problem identified. You can emphasize each tool deeply by examining the steps involved and what algorithms are there as a solution when approaching a problem. Download this slide to inform your audience about those professional tools with ease.

Template 8: Problem Solving Methods with Goals and Actions
Problems arise without any warning. You need to have a full-proof plan to ace challenges. Use this lucrative template to examine the goals of problem solving tools and actions required for each stage of the process. You can use it as a benchmark for making an improvement in the performance of business. By using this template, you can set a stage for continuous evaluation and goal refinement.

Template 9: Guide for P-C-D-A Problem Solving Method
The PCDA approach stands for plan, check, do, and act. It elaborates a planned approach for resolving an issue. It focuses on building a solution in a controlled manner by setting the right stage for refinements. Highlight the importance of this tool by using this template, leading you to make informed decisions. This can be applied on a small scale as well as large scale organizations, making it a versatile tool for effective problem resolution. Download this template to undertake a cyclical approach to business problems.

[Download it From Here]
Template 10: Problem Solving Powerpoint Presentation Slides
This PPT Presentation includes slides from which you can showcase business challenges and opportunities with interactive diagrams. It contains PPT designs, which visualize your problem so that you are not far away from making a strategic decision. Each PPT Template is innovatively designed, keeping in mind unique business requirements and problems faced by the businesses. Download this presentation deck and get every angle of problem covered through the mindful bifurcation of opportunity and challenge.

Visualize Your Path to Solutions
Leaders face problems in everyday life whether simple or complex. Some problems might not require an informed decision while some need extra care to zero in on root cause to come up with a full-proof plan.
We know that the process of problem solving is complicated already, and developing PPT from scratch can add to the burden. Using SlideTeam’s problem solving slides gives you a pathway to come forward with lucrative solutions based on the methodologies that professionals use. We have customized slides covering all the tools, tactics, and approaches required for a remarkable solution.
PS Master problem-solving in nine steps with SlideTeam’s best-in-class nine-steps problem solving templates.
Related posts:
- How to Design the Perfect Service Launch Presentation [Custom Launch Deck Included]
- Quarterly Business Review Presentation: All the Essential Slides You Need in Your Deck
- [Updated 2023] How to Design The Perfect Product Launch Presentation [Best Templates Included]
- 99% of the Pitches Fail! Find Out What Makes Any Startup a Success
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Business Problem Solving Templates with Samples and Examples

Top 10 Kepner Tregoe Problem Solving and Decision-Making Presentation Templates With Examples And Samples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
To help you know how to take the first step in solving a problem. To clarify and define the problem. To understand the usefulness of collaborative problem solving and decision making.
Problem Solving There is a difference between Critical Thinking and Problem Solving. Critical Thinking is an intentional and reflective way of looking at things or circumstances, while Problem Solving focuses on a specific situation.
Download professionally designed problem solving PPT presentation templates for showcasing problems with solutions for start-up plans, business problem solving, change management, etc. Avoid harping on any aspect with our Problem Solving Powerpoint Presentation Slides.
This 3 paragraph summary provides the key points about the importance of complex problem solving and critical thinking skills: Complex problem solving involves looking at problems from different perspectives to find solutions while considering the surrounding context and impacts.
Present the problem-solving processes effectively with our premade problem solving PowerPoint templates and Google Slides Themes. Crafted to guide you from problem identification to resolution, these free templates breathe life into complex strategies.
Computational thinking allows us to take a complex problem, understand what the problem is and develop possible solutions. We can then present these solutions in a way that a computer, a...
Transform your problem-solving presentations with our highly customizable templates designed to simplify complex ideas and captivate your audience. Solve problems with ease using a problem-solving PowerPoint template.
Complex problem solving (CPS) definition • dynamic, because early actions determine the environment in which subsequent decision must be made, and features of the task environment may change independently of the solver’s actions; • time-dependent, because decisions must be made at the correct moment in relation to environmental demands ...
Here are some of the best problem solving models and techniques PowerPoint templates that you can use to make your next presentation. This clean template come with easy-to-follow instructions and plenty of sample slides to get you started.
We know that the process of problem solving is complicated already, and developing PPT from scratch can add to the burden. Using SlideTeam’s problem solving slides gives you a pathway to come forward with lucrative solutions based on the methodologies that professionals use.