206-659-6067
- Driving Solutions Strategic Intensive
- Growth Framework Reset
- Business Base Camp Consultation

4 Steps for Business Problem Solving to Get Results
“What are we supposed to do here?” is a question I use to gauge a team’s thinking as we tackle problems together.
It is important to remember that problem-solving is a skill that can be applied to various situations in life, including those we encounter in business. Sometimes, we may experience a never-ending and frustrating challenge, with one obstacle after another. In such cases, revisiting the steps to problem-solving can be helpful, as they provide a valuable framework to approach the problem.
Following four simple steps can strengthen our problem-solving skills and become more effective at overcoming obstacles and achieving success.
But wait a moment. How do we determine if the perceived “problem” is a problem?
Maybe it’s not the root cause but rather a symptom, and ironing that out creates a cycle of other similar situations endlessly popping up. Solving the same thing(s) repeatedly indicates that these are symptoms. Focus is required to find the real problem and determine if you want to be committed to a practical solution that will stick.
Options always exist to solve a symptom or a recurring issue that has a process in place for resolution.
We can keep using resources and energy to solve the persistent problem or improve practices to use fewer resources and energy. There is another option, too: take time to find and fix the more profound problem (I call that a root cause).
Solving a root cause takes more up-front commitment, creates more time, frees up resources to explore other initiatives, and saves money over time. When we prioritize problems through the lens of our one-year comprehensive strategy AND the company mission, we choose what to work on that supports keeping all work on track (i.e., time and budget).
Fortunately, practical methods are available to help you break free from any difficult situation. Whether it’s a common or complex issue, you can rely on proven methods that guarantee results. Don’t waste time on fancy and complicated solutions; choose straightforward and effective problem-solving methods that will help you easily overcome any obstacle.
There’s no trick or gimmick to the steps. There is work. We do have to bring the will, the drive, and the commitment to become proficient at problem-solving, a skill that needs improvement at all levels of business today.
To lead by example, add value to the company and the team, and meet goals, one must have a specific mindset—a Curiosity Mindset.
- A Curiosity Mindset involves being open.
- A willingness to seek out information from people and sources.
- To include unusual or different sources and opinions.
- The ability to sift information for reliability.
- The capacity to connect seemingly unrelated information to find THE custom solution for your problem.
Have you ever heard the colloquialism “can’t see the forest for the trees”? This common pitfall diminishes a Curiosity Mindset and detracts from the problem-solving process.
Achieving success requires more than just completing daily tasks. It’s crucial to take time to review our business goals and reach beyond our usual routines to truly solve any problem. Unforeseen problems may arise, but we can choose to keep moving forward and not let them bring us to a standstill. By practicing new skills and expanding our abilities, we can turn challenges into second nature and add to our natural gifts.
Embracing change and taking on something new takes courage, but it’s the only way to grow and succeed. We can overcome any obstacle and achieve our goals with perseverance and determination.
Take these steps the next time you have a significant outcome and a problem standing in your way. Your commitment and responsibility will make it happen.
With a Curiosity Mindset, we commit to being open to answers and information beyond the core group. This requires a definitive process applicable to a single problem and any that occurs in business. (Of course, there will always be difficulties that crop up. Such is life!)
The 4 Steps to Problem-Solving in Business:
- Recognize there is a problem
- Collect data
- Gather solutions
- Choose a solution
These are the steps, whether looking at long-term objectives three to five years out or solving a problem that can better support how people do work in your company. It seems simple, and you may know this to be true, yet do you really do the work of each step to know you are doing the right work right now?
Let’s look at each step to assess whether you are overlooking something or trying to find a shortcut that may be creating more resistance or slowing you down:
1. Recognize there’s a problem
You can decide something needs doing, yet, getting it done means taking action. What you prioritize is what you value.
Not only do you need to decide whether change will make a positive difference, your commitment to doing the work to take action on the best solution matters too. Problems may be identified that when solved:
- Improve efficiency to create more time to do important work
- Increase profitability by streamlining or are no longer necessary
- Increase relevance as markets and customer needs shift
- Align the deliverables more to the mission bringing your teams together
How do you take action to determine if the problem is a one worth solving? Schedule time for a Present Retreat™ with 10 questions to create accountability that focuses on reflection, assessment, and prioritization for what’s happening in your business right now. Even if you only do this one time, it will give you a different perspective.
2. Understand what data is necessary
How do you get data for consideration, and how do you obtain uncommon data?
- Standard: search on the internet, financials, and forecasts, competing products.
- Uncommon: ask the people closest to the problem, listen for what customers are seeking, looking at a problem to solve in relationship to how it aligns to your mission and goals.
Are you constantly using the same internal reports? If so, do other people have the same problem, and what have they done about it? Get out of your data and collect someone else’s reports and data.
You could take advantage of your business overview and plan to make informed decisions. A detailed explanation of the two pillars of business success is available if you need more information. Sometimes, when we encounter a promising solution or opportunity, we might end up trying to solve problems that do not require solving. To avoid this, we must ensure that any solution we consider aligns with our business overview and growth strategy. This way, we can identify which problems do not need solving by simply looking at the data.
3. Gather solutions
Now you have the problems that — when prioritized — will reach a new outcome. And there is data that reinforces it is a problem worth solving with a commitment to prioritize making the change. These are the basic constraints to find the most impactful solutions.
- Possible solutions now have the following requirements:
- Solve the problem.
- Align to current business goals.
- Create momentum for long term (three to five year) objectives.
- Elevate what we are already doing to be better, what we are best at in the world.
In the companies I have worked with, this is the step where the most failure occurs. Without constraints there are too many solutions, brand-new ideas (that sort of solve the initially identified problem), and more work is created out of the excitement that comes with open-ended possibilities.
Solutions that fit just these four constraints align to doing the right work and being able to do as much work as possible. Anything that doesn’t pass these requirements isn’t a viable solution.
Letting problems that don’t matter to the business’ purpose and goals is freeing. There is more time and energy to explore solutions that can make a difference. You still may fail and yes it is important to fail fast; however, iterating where the chance of failure is significantly higher is a waste of time and not worth the potential loss of confidence.
4. Choose a solution and take action
Which one makes the most sense and presents the greatest opportunity to address everything about the problem? Get it implemented and observe the results.
Don’t forget: decisions without action keep you exactly where you are. Even if just the first step of the solution is designed and communicated, and the actions are assigned for completion — this will get things moving. Each subsequent action to move toward a completed solution will adjust for the feedback, data, and new information that comes from learning as you go.
There will be mistakes and setbacks, and that is part of the process. Here are top tips I received when I asked a group of business owners to share how they bounce back and keep going .
Sometimes, repetition of these steps is necessary to find a working solution.
In business, reaching your end goal is great, can be messy and takes time. Sometimes, you need more data, new information comes up, or a different solution works better. We iterate and build on what we know. To improve problem-solving skills, follow these steps daily for 30 days, even for simple problems. Build a Curiosity Mindset and a new skill simultaneously.
***********************************************************************************
Jess Dewell is a professional who has been navigating the intersection of operations and strategy for more than twenty years. She helps organizations move forward by identifying the sweet spot where strategy catalyzes operations, fosters innovation, and drives businesses to the forefront of their industries.
Jess is committed to helping businesses turn challenges into scalable opportunities and constraints into springboards for growth. Contact her for a complimentary call, or find her on LinkedIn and Twitter . Check out her Driving Solutions Strategic Intensive program if you need help with strategic growth challenges.
Listen to the BOLD Business Podcast
Search Blogs and Podcasts
More Posts in This Category

- Rosters & E-Bidding
Have a Research Question?
- Research Tools
- Explore Topics
- Stay Informed
- Publications
Easy Problem Solving Using the 4-step Method
June 7, 2017 by Jennifer Haury Category: Guest Author , Management

At a recent hospital town forum, hospital leaders are outlining the changes coming when a lone, brave nurse raises her hand and says, “We just can’t take any more changes. They are layered on top of each other and each one is rolled out in a different way. We are exhausted and it’s overloading us all.”
“Flavor of the Month” Fatigue
Change fatigue. You hear about it in every industry, from government sectors to software design to manufacturing to healthcare and more. When policy and leadership changes and process improvement overlap it’s no surprise when people complain about “flavor of the month,” and resist it just so they can keep some routine to their days.
In a time where change is required just to keep up with the shifting environment, one way to ease fatigue is to standardize HOW we change. If we use a best practice for solving problems, we can ensure that the right people are involved and problems are solved permanently, not temporarily. Better yet, HOW we change can become the habit and routine we long for.
The 4-step Problem Solving Method
The model we’ve used with clients is based on the A3 problem-solving methodology used by many “lean” production-based companies. In addition to being simpler, our 4-step method is visual, which helps remind the user what goes into each box.
The steps are as follows
- Develop a Problem Statement
- Determine Root Causes
- Rank Root Causes in Order of Importance
- Create an Action Plan
Step 1: Develop a Problem Statement
Developing a good problem statement always seems a lot easier than it generally turns out to be. For example, this statement: “We don’t have enough staff,” frequently shows up as a problem statement. However, it suggests the solution—“GET MORE STAFF” — and fails to address the real problem that more staff might solve, such as answering phones in a timely manner.
The trick is to develop a problem statement that does not suggest a solution. Avoiding the following words/phrases: “lack of,” “no,” “not enough,” or “too much” is key. When I start to fall into the trap of suggesting a solution, I ask: “So what problem does that cause?” This usually helps to get to a more effective problem statement.

Once you’ve developed a problem statement, you’ll need to define your target goal, measure your actual condition, then determine the gap. If we ran a restaurant and our problem was: “Customers complaining about burnt toast during morning shift,” the target goal might be: “Toast golden brown 100% of morning shift.”
Focus on a tangible, achievable target goal then measure how often that target is occurring. If our actual condition is: “Toast golden brown 50% of the time,” then our gap is: “Burnt toast 50% of the time.” That gap is now a refined problem to take to Step 2.
Step 2: Determine Root Causes
In Step 2, we want to understand the root causes. For example, if the gap is burnt toast 50% of the time, what are all the possible reasons why?
This is when you brainstorm. It could be an inattentive cook or a broken pop-up mechanism. Cooks could be using different methods to time the toasting process or some breads toast more quickly. During brainstorming, you’ll want to include everyone in the process since observing these interactions might also shed light on why the problem is occurring.

Once we have an idea of why, we then use the 5-why process to arrive at a root cause. Ask “Why?” five times or until it no longer makes sense to ask. Root causes can be tricky. For example, if the pop up mechanism is broken you could just buy a new toaster, right? But if you asked WHY it broke, you may learn cooks are pressing down too hard on the pop up mechanism, causing it to break. In this case, the problem would just reoccur if you bought a new toaster.
When you find you are fixing reoccurring problems that indicates you haven’t solved for the root cause. Through the 5-why process, you can get to the root cause and fix the problem permanently.
Step 3: Rank Root Causes
Once you know what’s causing the problem (and there may be multiple root causes), it’s time to move to Step 3 to understand which causes, if solved for, would close your gap. Here you rank the root causes in order of importance by looking at which causes would have the greatest impact in closing the gap.

There may be times when you don’t want to go after your largest root cause (perhaps because it requires others to change what they are doing, will take longer, or is dependent on other things getting fixed, etc). Sometimes you’ll find it’s better to start with a solution that has a smaller impact but can be done quickly.
Step 4: Create an Action Plan
In Step 4 you create your action plan — who is going to do what and by when. Documenting all of this and making it visible helps to communicate the plan to others and helps hold them accountable during implementation.
This is where your countermeasures or experiments to fix the problem are detailed. Will we train our chefs on how to use a new “pop-up mechanism” free toaster? Will we dedicate one toaster for white bread and one for wheat?

Make sure to measure your results after you’ve implemented your plan to see if your target is met. If not, that’s okay; just go through the steps again until the problem is resolved.
Final Thoughts
Using the 4-step method has been an easy way for teams to change how they solve problems. One team I was working with started challenging their “solution jumps” and found this method was a better way to avoid assumptions which led to never really solving their problems. It was easy to use in a conference room and helped them make their thinking visual so everyone could be involved and engaged in solving the problems their team faced.
Do you have a problem-solving method that you use at your worksite? Let us know in the comments below.
MRSC is a private nonprofit organization serving local governments in Washington State. Eligible government agencies in Washington State may use our free, one-on-one Ask MRSC service to get answers to legal, policy, or financial questions.
About Jennifer Haury
Jennifer Haury is the CEO of All Angles Consulting, LLC and guest authored this post for MRSC.
Jennifer has over 28 years learning in the healthcare industry (17 in leadership positions or consulting in performance improvement and organizational anthropology) and is a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt.
She is a trusted, experienced leader with a keen interest in performance improvement and organizational anthropology. Jennifer is particularly concerned with the sustainability of continuous improvement programs and the cultural values and beliefs that translate into behaviors that either get in our own way or help us succeed in transforming our work.
The views expressed in guest columns represent the opinions of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of MRSC.
Blog Archives
Weekly e-news.
Get the latest local government news, analysis, and training opportunities in Washington State with MRSC’s Weekly Insights .
Related Materials
SEC Enforcement in the Municipal Securities Market
With the rise of AI, workforce planning is critical. But many governments don’t do it.
Strategic Planning
Weekly dose of self-improvement
The easy 4 step problem-solving process (+ examples)
This is the 4 step problem-solving process that I taught to my students for math problems, but it works for academic and social problems as well.

Every problem may be different, but effective problem solving asks the same four questions and follows the same method.
- What’s the problem? If you don’t know exactly what the problem is, you can’t come up with possible solutions. Something is wrong. What are we going to do about this? This is the foundation and the motivation.
- What do you need to know? This is the most important part of the problem. If you don’t know exactly what the problem is, you can’t come up with possible solutions.
- What do you already know? You already know something related to the problem that will help you solve the problem. It’s not always obvious (especially in the real world), but you know (or can research) something that will help.
- What’s the relationship between the two? Here is where the heavy brainstorming happens. This is where your skills and abilities come into play. The previous steps set you up to find many potential solutions to your problem, regardless of its type.
When I used to tutor kids in math and physics , I would drill this problem-solving process into their heads. This methodology works for any problem, regardless of its complexity or difficulty. In fact, if you look at the various advances in society, you’ll see they all follow some variation of this problem-solving technique.
“The gap between understanding and misunderstanding can best be bridged by thought!” ― Ernest Agyemang Yeboah
Generally speaking, if you can’t solve the problem then your issue is step 3 or step 4; you either don’t know enough or you’re missing the connection.
Good problem solvers always believe step 3 is the issue. In this case, it’s a simple matter of learning more. Less skilled problem solvers believe step 4 is the root cause of their difficulties. In this instance, they simply believe they have limited problem-solving skills.
This is a fixed versus growth mindset and it makes a huge difference in the effort you put forth and the belief you have in yourself to make use of this step-by-step process. These two mindsets make a big difference in your learning because, at its core, learning is problem-solving.
Let’s dig deeper into the 4 steps. In this way, you can better see how to apply them to your learning journey.
Step 1: What’s the problem?
The ability to recognize a specific problem is extremely valuable.
Most people only focus on finding solutions. While a “solutions-oriented” mindset is a good thing, sometimes it pays to focus on the problem. When you focus on the problem, you often make it easier to find a viable solution to it.
When you know the exact nature of the problem, you shorten the time frame needed to find a solution. This reminds me of a story I was once told.
When does the problem-solving process start?
The process starts after you’ve identified the exact nature of the problem.
Homeowners love a well-kept lawn but hate mowing the grass.
Many companies and inventors raced to figure out a more time-efficient way to mow the lawn. Some even tried to design robots that would do the mowing. They all were chasing the solution, but only one inventor took the time to understand the root cause of the problem.
Most people figured that the problem was the labor required to maintain a lawn. The actual problem was just the opposite: maintaining a lawn was labor-intensive. The rearrangement seems trivial, but it reveals the true desire: a well-maintained lawn.
The best solution? Remove maintenance from the equation. A lawn made of artificial grass solved the problem . Hence, an application of Astroturf was discovered.
This way, the law always looked its best. Taking a few moments to apply critical thinking identified the true nature of the problem and yielded a powerful solution.
An example of choosing the right problem to work the problem-solving process on
One thing I’ve learned from tutoring high school students in math : they hate word problems.
This is because they make the student figure out the problem. Finding the solution to a math problem is already stressful. Forcing the student to also figure out what problem needs solving is another level of hell.
Word problems are not always clear about what needs to be solved. They also have the annoying habit of adding extraneous information. An ordinary math problem does not do this. For example, compare the following two problems:
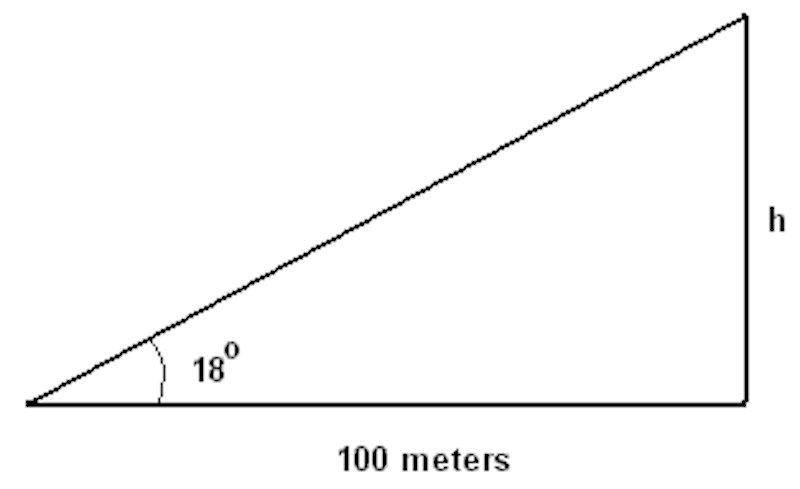
What’s the height of h?
A radio station tower was built in two sections. From a point 87 feet from the base of the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the first section is 25º, and the angle of elevation of the top of the second section is 40º. To the nearest foot, what is the height of the top section of the tower?
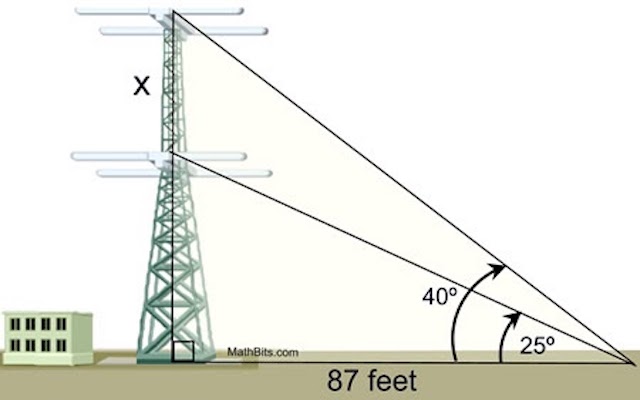
The first is a simple problem. The second is a complex problem. The end goal in both is the same.
The questions require the same knowledge (trigonometric functions), but the second is more difficult for students. Why? The second problem does not make it clear what the exact problem is. Before mathematics can even begin, you must know the problem, or else you risk solving the wrong one.
If you understand the problem, finding the solution is much easier. Understanding this, ironically, is the biggest problem for people.
Problem-solving is a universal language
Speaking of people, this method also helps settle disagreements.
When we disagree, we rarely take the time to figure out the exact issue. This happens for many reasons, but it always results in a misunderstanding. When each party is clear with their intentions, they can generate the best response.
Education systems fail when they don’t consider the problem they’re supposed to solve. Foreign language education in America is one of the best examples.
The problem is that students can’t speak the target language. It seems obvious that the solution is to have students spend most of their time speaking. Unfortunately, language classes spend a ridiculous amount of time learning grammar rules and memorizing vocabulary.
The problem is not that the students don’t know the imperfect past tense verb conjugations in Spanish. The problem is that they can’t use the language to accomplish anything. Every year, kids graduate from American high schools without the ability to speak another language, despite studying one for 4 years.
Well begun is half done
Before you begin to learn something, be sure that you understand the exact nature of the problem. This will make clear what you need to know and what you can discard. When you know the exact problem you’re tasked with solving, you save precious time and energy. Doing this increases the likelihood that you’ll succeed.
Step 2: What do you need to know?
All problems are the result of insufficient knowledge. To solve the problem, you must identify what you need to know. You must understand the cause of the problem. If you get this wrong, you won’t arrive at the correct solution.
Either you’ll solve what you thought was the problem, only to find out this wasn’t the real issue and now you’ve still got trouble or you won’t and you still have trouble. Either way, the problem persists.
If you solve a different problem than the correct one, you’ll get a solution that you can’t use. The only thing that wastes more time than an unsolved problem is solving the wrong one.
Imagine that your car won’t start. You replace the alternator, the starter, and the ignition switch. The car still doesn’t start. You’ve explored all the main solutions, so now you consider some different solutions.
Now you replace the engine, but you still can’t get it to start. Your replacements and repairs solved other problems, but not the main one: the car won’t start.
Then it turns out that all you needed was gas.
This example is a little extreme, but I hope it makes the point. For something more relatable, let’s return to the problem with language learning.
You need basic communication to navigate a foreign country you’re visiting; let’s say Mexico. When you enroll in a Spanish course, they teach you a bunch of unimportant words and phrases. You stick with it, believing it will eventually click.
When you land, you can tell everyone your name and ask for the location of the bathroom. This does not help when you need to ask for directions or tell the driver which airport terminal to drop you off at.
Finding the solution to chess problems works the same way
The book “The Amateur Mind” by IM Jeremy Silman improved my chess by teaching me how to analyze the board.
It’s only with a proper analysis of imbalances that you can make the best move. Though you may not always choose the correct line of play, the book teaches you how to recognize what you need to know . It teaches you how to identify the problem—before you create an action plan to solve it.

The problem-solving method always starts with identifying the problem or asking “What do you need to know?”. It’s only after you brainstorm this that you can move on to the next step.
Learn the method I used to earn a physics degree, learn Spanish, and win a national boxing title
- I was a terrible math student in high school who wrote off mathematics. I eventually overcame my difficulties and went on to earn a B.A. Physics with a minor in math
- I pieced together the best works on the internet to teach myself Spanish as an adult
- *I didn’t start boxing until the very old age of 22, yet I went on to win a national championship, get a high-paying amateur sponsorship, and get signed by Roc Nation Sports as a profession.
I’ve used this method to progress in mentally and physically demanding domains.
While the specifics may differ, I believe that the general methods for learning are the same in all domains.
This free e-book breaks down the most important techniques I’ve used for learning.
Step 3: What do you already know?
The only way to know if you lack knowledge is by gaining some in the first place. All advances and solutions arise from the accumulation and implementation of prior information. You must first consider what it is that you already know in the context of the problem at hand.
Isaac Newton once said, “If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of giants.” This is Newton’s way of explaining that his advancements in physics and mathematics would be impossible if it were not for previous discoveries.
Mathematics is a great place to see this idea at work. Consider the following problem:
What is the domain and range of y=(x^2)+6?
This simple algebra problem relies on you knowing a few things already. You must know:
- The definition of “domain” and “range”
- That you can never square any real number and get a negative
Once you know those things, this becomes easy to solve. This is also how we learn languages.
An example of the problem-solving process with a foreign language
Anyone interested in serious foreign language study (as opposed to a “crash course” or “survival course”) should learn the infinitive form of verbs in their target language. You can’t make progress without them because they’re the root of all conjugations. It’s only once you have a grasp of the infinitives that you can completely express yourself. Consider the problem-solving steps applied in the following example.
I know that I want to say “I don’t eat eggs” to my Mexican waiter. That’s the problem.
I don’t know how to say that, but last night I told my date “No bebo alcohol” (“I don’t drink alcohol”). I also know the infinitive for “eat” in Spanish (comer). This is what I already know.
Now I can execute the final step of problem-solving.
Step 4: What’s the relationship between the two?
I see the connection. I can use all of my problem-solving strategies and methods to solve my particular problem.
I know the infinitive for the Spanish word “drink” is “beber” . Last night, I changed it to “bebo” to express a similar idea. I should be able to do the same thing to the word for “eat”.
“No como huevos” is a pretty accurate guess.
In the math example, the same process occurs. You don’t know the answer to “What is the domain and range of y=(x^2)+6?” You only know what “domain” and “range” mean and that negatives aren’t possible when you square a real number.
A domain of all real numbers and a range of all numbers equal to and greater than six is the answer.
This is relating what you don’t know to what you already do know. The solutions appear simple, but walking through them is an excellent demonstration of the process of problem-solving.
In most cases, the solution won’t be this simple, but the process or finding it is the same. This may seem trivial, but this is a model for thinking that has served the greatest minds in history.
A recap of the 4 steps of the simple problem-solving process
- What’s the problem? There’s something wrong. There’s something amiss.
- What do you need to know? This is how to fix what’s wrong.
- What do you already know? You already know something useful that will help you find an effective solution.
- What’s the relationship between the previous two? When you use what you know to help figure out what you don’t know, there is no problem that won’t yield.
Learning is simply problem-solving. You’ll learn faster if you view it this way.
What was once complicated will become simple.
What was once convoluted will become clear.

Ed Latimore
I’m a writer, competitive chess player, Army veteran, physicist, and former professional heavyweight boxer. My work focuses on self-development, realizing your potential, and sobriety—speaking from personal experience, having overcome both poverty and addiction.
Follow me on Twitter.


Pimsleur language system review—old but still good
The Pimsleur language program offers a framework you can use to learn a language. I’ve used the program. Here are my experiences.

Pimsleur vs Duolingo: Choosing the best language learning app
Pimsleur and Duolingo are two popular language-learning apps to help you learn a new language. This guide will help you decide which app will work best for you.

My Chess.com Chess Improvement Plan
This is a plan that I’ll be implementing to improve my rating on Chess.com in the rapid and daily games. Not for OTB but could work.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is the PDCA Cycle?
How the pdca cycle works, the pdca cycle and kaizen, benefits of the pdca cycle, examples of the pdca cycle, the bottom line.
- Business Essentials
What Does PDCA Stand For in Business? Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle is a four-step problem-solving iterative technique used to improve business processes. Originally developed by American physicist Walter A. Shewhart during the 1920s, the cycle draws its inspiration from the continuous evaluation of management practices and management’s willingness to adopt and disregard unsupported ideas.
The method was popularized by quality control pioneer Dr. W. Edwards Deming in the 1950s who coined the term “Shewhart” Cycle after his mentor. It was Deming who realized the PDCA Cycle could be used to improve production processes in the United States during World War II.
Key Takeaways
- The PDCA Cycle is a four-step technique that is used to solve business problems.
- Many managers unknowingly use the PDCA Cycle as it encompasses much of the same framework as strategic management.
- The last step of the PDCA Cycle (act) calls for corrective actions to stimulate and sustain continuous business improvement.
- The PDCA process is similar to the Japanese business philosophy of Kaizen.
- Many large corporations, such as Toyota and Nike, have seen dramatic growth after implementing PDCA or Six Sigma methodologies.
The PDCA Cycle can help differentiate a company from its competitors, particularly in today’s corporate world, where businesses are always searching for ways to streamline their processes, reduce costs, increase profits, and improve customer satisfaction.
Many managers apply the PDCA Cycle unknowingly to help direct their organizations as it encompasses the basic tenets of strategic planning. The four components of the PDCA Cycle are outlined below.
A well-defined project plan provides a framework for operations. Importantly, it should reflect the organization’s mission and values. It should also map the project's goals and clearly indicate the best way to attain them.
This is the step where the plan is set in motion. The plan was made for a reason, so it is important for players to execute it as outlined. This stage can be broken down into three sub-segments, including training of all personnel involved in the project, the actual process of doing the work, and recording insights, or data, for future evaluation.
Typically, there should be two checks throughout the project. First, checks alongside implementation ensure the project's objectives are being met. Second, a more comprehensive review of the project carried out upon completion addresses the successes and failures so that future adjustments can be made.
The final step is to take corrective action once past mistakes have been identified and resolved. The PDCA Cycle is repeated and can be redefined perhaps to better results under new guidelines.
Given its cyclical nature, the PDCA Cycle is something businesses can institute once and then use to continuously iterate and improve their operations.
The PDCA process is similar to the Japanese business philosophy of Kaizen , which, when translated, means "change for the better" or "continuous improvement." Kaizen is where all employees are involved in improving productivity by finding efficiencies in the work environment. Like the PDCA cycle, Kaizen aims for continuous improvement through small, incremental changes.
Examples of changes that might be made through Kaizen or PDCA are using new systems, eliminating waste, or implementing just-in-time delivery. Not all changes need to be small or incremental.
The concept behind PDCA and Kaizen is that the culture of an organization changes as the employees learn to be problem solvers and critical thinkers. The PDCA cycle tests employees' ideas, adjusts them, and then implements them if they have potential. The cycle is an iterative process that continually tests concepts and promotes improvements.
Companies looking to enhance their internal and external processes often deploy the PDCA methodology to minimize errors and maximize outcomes. Once established, companies can repeat the PDCA Cycle and make it a standard operating procedure. The final stage of the methodology, "Act," takes corrective actions and makes the methodology ideal for continuous improvement efforts.
Lean methods like PDCA and Kaizen helped Nike to double its profits from around $100 billion in 2015 to over $200 billion in 2021.
The Mayo Clinic
The Mayo Clinic, a nonprofit, world-class hospital and research center, conducted a quality improvement study that looked at wait times for patients who were possible candidates for large cochlear implant surgery. The idea was to employ Kaizen principles to remove barriers and improve access for patients.
The study looked at the refining of specific treatments, the management of patient records, and waiting room times. Ultimately, there were positive outcomes for patients. Among the results, median cycle time for candidacy testing decreased from 7.3 to 3 hours, and total inventory of clinic stock was reduced by 31%.
Is PDCA the Same As Total Quality Management (TQM)?
Total quality management (TQM), which is the precursor to Six Sigma , includes the philosophy of PDCA, but it goes one step further.
According to Smartsheet, which quotes Marlon Walters, the Founder and CEO of Horizon Group Consulting, "With TQM, you have to wait for your customers to confirm that it’s good. With Six Sigma, at the end of the day, you don’t guess if your product is better. You know it. If you properly identify your market and your product has the best fit for the niche, you know you have the best product from a process perspective."
Kaizen, or PDCA, is more of a philosophy for how to organize the larger workplace and how to engage coworkers. It is less about waiting for customer feedback or results. Both PDCA and TQM consider the whole company responsible for continuous improvement.
What Is the Difference Between PDCA and Six Sigma?
The difference between PDCA and Six Sigma is that Six Sigma is an all-encompassing management principle that includes PDCA as part of its structure. PDCA explains how to enact Six Sigma, it is the plan, do, act, check process. Six Sigma calls this the DMAIC method (define, measure, analyze, improve, and control).
According to Walters, PDCA is people-oriented while Six Sigma is process-based. For example, the term "define" in Six Sigma removes the human element, and the term "measure" puts the focus on data.
What Is the Difference Between PDCA and PDSA?
PDCA stans for plan, do, check, act, whereas PDSA stands for plan, do, study, act. They are both iterative, four-stage problem-solving models used to improve a process. The main difference between the two is that PDCA, which was developed before the PDSA model, has the "check" stage. In this stage, the team determines whether what they intended to achieve has actually occurred by checking expected results with the actual results. So, PDCA has a built-in check for every cycle in the process.
The PDCA Cycle, PDSA, Kaizen, and Six Sigma are all proven ways to continuously improve processes. Many companies including Nike, Toyota, the Mayo Clinic, and many others have seen dramatic growth after employing one or more of these iterative strategies. The concept changes the culture of a business so that all stakeholders have input and can act as problem solvers and critical thinkers. The result is more ideas for change.
PubMed.gov. " Application of Kaizen Principles to a Large Cochlear Implant Practice: A Continuous Quality Improvement Initiative at Mayo Clinic. " Accessed June 3, 2021.
FXSSI. " TOP 10 Most Profitable Companies in the World in 2021. " Accessed June 3, 2021.
Macrotrends. " NIKE Market Cap 2006-2021 | NKE ." Accessed June 3, 2021.
Smartsheet. " A Quality Principle: Everything You Need to Know about Total Quality Management ." Accessed June 3, 2021.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/kaizen.asp-ADD-Source-51522de6c889423a87ae1b0bee396d22.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Limited Time Offer:
Save Up to 25% on LivePlan today

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
10 Step Process for Effective Business Problem Solving
Posted august 3, 2021 by harriet genever.

When you start a small business or launch a startup, the one thing you can count on is the unexpected. No matter how thoroughly you plan, forecast , and test, problems are bound to arise. This is why as an entrepreneur, you need to know how to solve business problems effectively.
What is problem solving in business?
Problem solving in business relates to establishing processes that mitigate or remove obstacles currently preventing you from reaching strategic goals . These are typically complex issues that create a gap between actual results and your desired outcome. They may be present in a single team, operational process, or throughout your entire organization, typically without an immediate or obvious solution.
To approach problem solving successfully, you need to establish consistent processes that help you evaluate, explore solutions, prioritize execution, and measure success. In many ways, it should be similar to how you review business performance through a monthly plan review . You work through the same documentation, look for gaps, dig deeper to identify the root cause, and hash out options. Without this process, you simply cannot expect to solve problems efficiently or effectively.
Why problem solving is important for your business
While some would say problem-solving comes naturally, it’s actually a skill you can grow and refine over time. Problem solving skills will help you and your team tackle critical issues and conflicts as they arise. It starts from the top. You as the business owner or CEO needing to display the type of level-headed problem solving that you expect to see from your employees.
Doing so will help you and your staff quickly deal with issues, establish and refine a problem solving process, turn challenges into opportunities, and generally keep a level head. Now, the best business leaders didn’t just find a magic solution to solve their problems, they built processes and leveraged tools to find success. And you can do the same.
By following this 10-step process, you can develop your problem-solving skills and approach any issue that arises with confidence.
1. Define the problem
When a problem arises, it can be very easy to jump right into creating a solution. However, if you don’t thoroughly examine what led to the problem in the first place, you may create a strategy that doesn’t actually solve it. You may just be treating the symptoms.
For instance, if you realize that your sales from new customers are dropping, your first inclination might be to rush into putting together a marketing plan to increase exposure. But what if decreasing sales are just a symptom of the real problem?
When you define the problem, you want to be sure you’re not missing the forest for the trees. If you have a large issue on your hands, you’ll want to look at it from several different angles:
Competition
Is a competitor’s promotion or pricing affecting your sales? Are there new entrants in your market? How are they marketing their product or business?
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Business model
Is your business model sustainable? Is it realistic for how fast you want to grow? Should you explore different pricing or cost strategies?
Market factors
How are world events and the nation’s economy affecting your customers and your sales?
Are there any issues affecting your team? Do they have the tools and resources they need to succeed?
Goal alignment
Is everyone on your team working toward the same goal ? Have you communicated your short-term and long-term business goals clearly and often?
There are a lot of ways to approach the issue when you’re facing a serious business problem. The key is to make sure you’re getting a full snapshot of what’s going on so you don’t waste money and resources on band-aid solutions.
Going back to our example, by looking at every facet of your business, you may discover that you’re spending more on advertising than your competitors already. And instead, there’s a communication gap within your team that’s leading to the mishandling of new customers and therefore lost sales.
If you jumped into fixing the exposure of your brand, you would have been dumping more money into an area you’re already winning. Potentially leading to greater losses as more and more new customers are dropped due to poor internal communication.
This is why it’s so vital that you explore your blind spots and track the problem to its source.
2. Conduct a SWOT analysis
All good businesses solve some sort of problem for customers. What if your particular business problem is actually an opportunity, or even a strength if considered from a different angle? This is when you’d want to conduct a SWOT analysis to determine if that is in fact the case.
SWOT is a great tool for strategic planning and bringing multiple viewpoints to the table when you’re looking at investing resources to solve a problem. This may even be incorporated in your attempts to identify the source of your problem, as it can quickly outline specific strengths and weaknesses of your business. And then by identifying any potential opportunities or threats, you can utilize your findings to kickstart a solution.
3. Identify multiple solutions with design thinking
As you approach solving your problem, you may want to consider using the design thinking approach . It’s often used by organizations looking to solve big, community-based problems. One of its strengths is that it requires involving a wide range of people in the problem-solving process. Which leads to multiple perspectives and solutions arising.
This approach—applying your company’s skills and expertise to a problem in the market—is the basis for design thinking.
It’s not about finding the most complex problems to solve, but about finding common needs within the organization and in the real world and coming up with solutions that fit those needs. When you’re solving business problems, this applies in the sense that you’re looking for solutions that address underlying issues—you’re looking at the big picture.
4. Conduct market research and customer outreach
Market research and customer outreach aren’t the sorts of things small business owners and startups can do once and then cross off the list. When you’re facing a roadblock, think back to the last time you did some solid market research or took a deep dive into understanding the competitive landscape .
Market research and the insights you get from customer outreach aren’t a silver bullet. Many companies struggle with what they should do with conflicting data points. But it’s worth struggling through and gathering information that can help you better understand your target market . Plus, your customers can be one of the best sources of criticism. It’s actually a gift if you can avoid taking the negatives personally .
The worst thing you can do when you’re facing challenges is isolating yourself from your customers and ignore your competition. So survey your customers. Put together a competitive matrix .
5. Seek input from your team and your mentors
Don’t do your SWOT analysis or design thinking work by yourself. The freedom to express concerns, opinions, and ideas will allow people in an organization to speak up. Their feedback is going to help you move faster and more efficiently. If you have a team in place, bring them into the discussion. You hired them to be experts in their area; use their expertise to navigate and dig deeper into underlying causes of problems and potential solutions.
If you’re running your business solo, at least bring in a trusted mentor. SCORE offers a free business mentorship program if you don’t already have one. It can also be helpful to connect with a strategic business advisor , especially if business financials aren’t your strongest suit.
Quoting Stephen Covey, who said that “strength lies in differences, not in similarities,” speaking to the importance of diversity when it comes to problem-solving in business. The more diverse a team is , the more often innovative solutions to the problems faced by the organization appear.
In fact, it has been found that groups that show greater diversity were better at solving problems than groups made up specifically of highly skilled problem solvers. So whoever you bring in to help you problem-solve, resist the urge to surround yourself with people who already agree with you about everything.
6. Apply lean planning for nimble execution
So you do your SWOT analysis and your design thinking exercise. You come up with a set of strong, data-driven ideas. But implementing them requires you to adjust your budget, or your strategic plan, or even your understanding of your target market.
Are you willing to change course? Can you quickly make adjustments? Well in order to grow, you can’t be afraid to be nimble .
By adopting the lean business planning method —the process of revising your business strategy regularly—you’ll be able to shift your strategies more fluidly. You don’t want to change course every week, and you don’t want to fall victim to shiny object thinking. But you can strike a balance that allows you to reduce your business’s risk while keeping your team heading in the right direction.
Along the way, you’ll make strategic decisions that don’t pan out the way you hoped. The best thing you can do is test your ideas and iterate often so you’re not wasting money and resources on things that don’t work. That’s Lean Planning .
7. Model different financial scenarios
When you’re trying to solve a serious business problem, one of the best things you can do is build a few different financial forecasts so you can model different scenarios. You might find that the idea that seemed the strongest will take longer than you thought to reverse a negative financial trend. At the very least you’ll have better insight into the financial impact of moving in a different direction.
The real benefit here is looking at different tactical approaches to the same problem. Maybe instead of increasing sales right now, you’re better off in the long run if you adopt a strategy to reduce churn and retain your best customers. You won’t know unless you model a few different scenarios. You can do this by using spreadsheets, and a tool like LivePlan can make it easier and quicker.
8. Watch your cash flow
While you’re working to solve a challenging business problem, pay particular attention to your cash flow and your cash flow forecast . Understanding when your company is at risk of running out of cash in the bank can help you be proactive. It’s a lot easier to get a line of credit while your financials still look good and healthy, than when you’re one pay period away from ruin.
If you’re dealing with a serious issue, it’s easy to start to get tunnel vision. You’ll benefit from maintaining a little breathing room for your business as you figure out what to do next.
9. Use a decision-making framework
Once you’ve gathered all the information you need, generated a number of ideas, and done some financial modeling, you might still feel uncertain. It’s natural—you’re not a fortune-teller. You’re trying to make the best decision you can with the information you have.
This article offers a really useful approach to making decisions. It starts with putting your options into a matrix like this one:

Use this sort of framework to put everything you’ve learned out on the table. If you’re working with a bigger team, this sort of exercise can also bring the rest of your team to the table so they feel some ownership over the outcome.
10. Identify key metrics to track
How will you know your problem is solved? And not just the symptom—how will you know when you’ve addressed the underlying issues? Before you dive into enacting the solution, make sure you know what success looks like.
Decide on a few key performance indicators . Take a baseline measurement, and set a goal and a timeframe. You’re essentially translating your solution into a plan, complete with milestones and goals. Without these, you’ve simply made a blind decision with no way to track success. You need those goals and milestones to make your plan real .
Problem solving skills to improve
As you and your team work through this process, it’s worth keeping in mind specific problem solving skills you should continue to develop. Bolstering your ability, as well as your team, to solve problems effectively will only make this process more useful and efficient. Here are a few key skills to work on.
Emotional intelligence
It can be very easy to make quick, emotional responses in a time of crisis or when discussing something you’re passionate about. To avoid making assumptions and letting your emotions get the best of you, you need to focus on empathizing with others. This involves understanding your own emotional state, reactions and listening carefully to the responses of your team. The more you’re able to listen carefully, the better you’ll be at asking for and taking advice that actually leads to effective problem solving.
Jumping right into a solution can immediately kill the possibility of solving your problem. Just like when you start a business , you need to do the research into what the problem you’re solving actually is. Luckily, you can embed research into your problem solving by holding active reviews of financial performance and team processes. Simply asking “What? Where? When? How?” can lead to more in-depth explorations of potential issues.
The best thing you can do to grow your research abilities is to encourage and practice curiosity. Look at every problem as an opportunity. Something that may be trouble now, but is worth exploring and finding the right solution. You’ll pick up best practices, useful tools and fine-tune your own research process the more you’re willing to explore.
Brainstorming
Creatively brainstorming with your team is somewhat of an art form. There needs to be a willingness to throw everything at the wall and act as if nothing is a bad idea at the start. This style of collaboration encourages participation without fear of rejection. It also helps outline potential solutions outside of your current scope, that you can refine and turn into realistic action.
Work on breaking down problems and try to give everyone in the room a voice. The more input you allow, the greater potential you have for finding the best solution.
Decisiveness
One thing that can drag out acting upon a potential solution, is being indecisive. If you aren’t willing to state when the final cutoff for deliberation is, you simply won’t take steps quickly enough. This is when having a process for problem solving comes in handy, as it purposefully outlines when you should start taking action.
Work on choosing decision-makers, identify necessary results and be prepared to analyze and adjust if necessary. You don’t have to get it right every time, but taking action at the right time, even if it fails, is almost more vital than never taking a step.
Stemming off failure, you need to learn to be resilient. Again, no one gets it perfect every single time. There are so many factors in play to consider and sometimes even the most well-thought-out solution doesn’t stick. Instead of being down on yourself or your team, look to separate yourself from the problem and continue to think of it as a puzzle worth solving. Every failure is a learning opportunity and it only helps you further refine and eliminate issues in your strategy.
Problem solving is a process
The key to effective problem-solving in business is the ability to adapt. You can waste a lot of resources on staying the wrong course for too long. So make a plan to reduce your risk now. Think about what you’d do if you were faced with a problem large enough to sink your business. Be as proactive as you can.
Editor’s note: This article was originally published in 2016. It was updated in 2021.
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Harriet Genever
Posted in management, join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Are You Solving the Right Problem?
- Dwayne Spradlin
Most firms aren’t, and that undermines their innovation efforts.
Reprint: R1209F
The rigor with which a problem is defined is the most important factor in finding a good solution. Many organizations, however, are not proficient at articulating their problems and identifying which ones are crucial to their strategies.
They may even be trying to solve the wrong problems—missing opportunities and wasting resources in the process. The key is to ask the right questions.
The author describes a process that his firm, InnoCentive, has used to help clients define and articulate business, technical, social, and policy challenges and then present them to an online community of more than 250,000 solvers. The four-step process consists of asking a series of questions and using the answers to create a problem statement that will elicit novel ideas from an array of experts.
- Establish the need for a solution. What is the basic need? Who will benefit from a solution?
- Justify the need. Why should your organization attempt to solve this problem? Is it aligned with your strategy? If a solution is found, who will implement it?
- Contextualize the problem. What have you and others already tried? Are there internal and external constraints to implementing a solution?
- Write the problem statement. What requirements must a solution meet? What language should you use to describe the problem? How will you evaluate solutions and measure success?
EnterpriseWorks/VITA, a nonprofit organization, used this process to find a low-cost, lightweight, and convenient product that expands access to clean drinking water in the developing world.
“If I were given one hour to save the planet, I would spend 59 minutes defining the problem and one minute resolving it,” Albert Einstein said.
- DS Dwayne Spradlin is the president and CEO of InnoCentive , an online marketplace that connects organizations with freelance problem solvers in a multitude of fields. He is a coauthor, with Alpheus Bingham, of The Open Innovation Marketplace: Creating Value in the Challenge Driven Enterprise (FT Press, 2011).
Partner Center


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
There are 3 main paths to solving such problems in the 4S method. I use the following flowchart to evaluate which strategy I will use: 3 problem-solving strategies — image created by the author based on the 4S-Method. As said, the first step is to clearly define the problem.
A highly sought after skill, learn a simple yet effective four step problem solving process using the concept IDEA to identify the problem, develop solutions, execute a plan and then...
The 4 Steps to Problem-Solving in Business: Recognize there is a problem; Collect data; Gather solutions; Choose a solution; These are the steps, whether looking at long-term objectives three to five years out or solving a problem that can better support how people do work in your company.
In addition to being simpler, our 4-step method is visual, which helps remind the user what goes into each box. The steps are as follows. Develop a Problem Statement; Determine Root Causes; Rank Root Causes in Order of Importance; Create an Action Plan; Step 1: Develop a Problem Statement
Step 1: What’s the problem? Step 2: What do you need to know? Step 3: What do you already know? Step 4: What’s the relationship between the two? A recap of the 4 steps of the simple problem-solving process. Every problem may be different, but effective problem solving asks the same four questions and follows the same method. What’s the problem?
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle is a four-step problem-solving iterative technique used to improve business processes.
Navigate uncertainty with a 10-step process for effective business problem solving. Learn to develop problem-solving skills to approach issues with confidence.
The four-step process consists of asking a series of questions and using the answers to create a problem statement that will elicit novel ideas from an array of experts. Establish the need...
The four steps are: Framework development. Define issue. Generate ideas. Implement best solution. The model's main, unique advantage is that it encourages you to define your business needs early in the innovation process.
Analyze —Understand the root cause. Plan —Determine how to resolve the problem. Implement —Put the resolution in place. Evaluate —Determine if the resolution is producing the desired results. I’ll discuss these steps further below, but first I want to discuss an important precursor—triage.